Sugar in the morning in the morning 7.4 what to do. Independent measurement of sugar. What is dangerous low blood sugar
Sugar in blood 5.8 - is it normal or pathology? Normal glucose indicators in human organism indicate the quality of his work. If there is a deviation to a larger or smaller direction, this signals a pathological state.
The human body is the most difficult mechanism that is known to humanity. And all the processes in it have a close relationship between themselves. When one process is disturbed, it inevitably leads to the fact that pathological failures in other areas are observed.
However, if an increase in glucose concentration in the body is a consequence of pathological processes - endocrine disorders, disorder of the functionality of the pancreas, the independent decrease in sugar to the required level will not happen.
Glucose 5.8 units - norm or pathology?
To know, whether the norm is 5.8 units, or still pathology, it is necessary to clearly know which indicators indicate that everything is fine, which values \u200b\u200bare talking about the border, that is, prediabetic state, and when diabetes is diagnosed.
The sugar rate in the body regulates the hormone of insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. If there are failures in its operation, the glucose concentration may increase or decrease.
As mentioned above, the increase in sugar can be observed under the influence of certain physiological reasons. For example, a man experienced the strongest stress, was renumbered, overlooked with physical activity.
In all these cases, with a 100% probability, the blood sugar content will increase, and significantly "leap" the permissible upper boundary of the norm. Ideal when the glucose content in the body varies from 3.3 to 5.5 units.
Children and adults will have their own. Consider the data on the example of the table of indicators depending on the age of a person:
- A newborn baby has blood sugar from 2.8 to 4.4 units.
- Starting from one month and up to 11 years, glucose is 2.9-5.1 units.
Starting from about 11 years of age and up to 60 years, the normally indicators of sugar consider variability from 3.3 to 5.5 units. After 60 years of age, the norm will be a bit different, and the upper boundary of the permissible limits increases to 6.4 units.
Thus, it can be concluded that blood sugar is 5.8 units - this is the excess of the upper boundary normal indicators. In this case, we can talk about the prediabetic state (border state between the norm and diabetes).
To refute or confirm a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional research.
High glucose symptoms
Sugar level
 Practice shows that in the overwhelming majority, sugar in the blood at a mark of 5.8 units will not indicate its increase in symptoms. However, this value gives a reason to worry, and it is not excluded that the sugar content will grow steadily.
Practice shows that in the overwhelming majority, sugar in the blood at a mark of 5.8 units will not indicate its increase in symptoms. However, this value gives a reason to worry, and it is not excluded that the sugar content will grow steadily.
The high concentration of glucose can be determined in a patient according to certain features and symptoms. It should be noted that a certain category of patients with symptoms will be more pronounced, in others, on the contrary, is characterized by a small severity or a complete lack of signs.
In addition, there is a concept as "sensitivity" to improving sugar. In medical practice it is noted that some people have high susceptibility to exceeding indicators, and an increase of 0.1-0.3 units can lead to a variety of symptoms.
It should be alert if the patient has the following alarming signs:
- Constant weakness, chronic fatigue, lethargy, apathy, general ailment.
- An increase in appetite, while there is a decrease in body weight.
- Permanent dryness B. oral cavity, thirst.
- Abundant I. frequent urination, Increased urine specific weight in 24 hours, night visits toilet.
- Skin diseases arising from a periodic frequency.
- Itching in the field of genitals.
- Reduced immune systemfrequent infectious diseasesAllergic reactions.
- Violation spectatic perception.
If the patient has such symptoms, it signals that there is a pathological increase in blood sugar. It should be noted that the patient will not have all the signs listed above, clinical paintings differ.
Therefore, if even a few signs in an adult person or child manifests itself, it is necessary to undergo a blood study on sugar.
What, after you need to do, tells your doctor when decipheres the results obtained.
Glucose tolerance, what does this mean?
 When, according to the results of the first blood test, the doctor suspected its prediabetic state or diabetes, it recommends to make a tolerance test to sugar. Due to this study, you can early stage Remove diabetes mellitus, determine glucose suction disorders.
When, according to the results of the first blood test, the doctor suspected its prediabetic state or diabetes, it recommends to make a tolerance test to sugar. Due to this study, you can early stage Remove diabetes mellitus, determine glucose suction disorders.
This study makes it possible to determine the degree of violation of carbohydrate metabolism. When the results of the study do not exceed the figure of 7.8 units, then the patient is not worried about, he is all right with health.
If after sugar load is detected from 7.8 units and up to 11.1 mmol / l, then it is already a reason for concern. It is not excluded that it was possible to reveal the prediatric state at an early stage, or a hidden form of chronic pathology.
In a situation where the test showed the result over 11.1 units, the conclusion may be alone - it is diabetes, as a result, it is recommended to immediately begin adequate therapy.
The test for susceptibility to glucose is especially important in such situations:
- When the patient, sugar indicators are in acceptable limits, but it is periodically observed glucose in Urin. Norma U. healthy man Sugar in the urine should be missing.
- In a situation where there are no signs sugar diseaseBut at the same time there is an increase in the proportion of urine per day. Against the background of this symptom, blood sugar on an empty stomach within the established norm.
- High sugar content during pregnancy testifies to the likely development of gestational diabetes.
- When signs of chronic disease are observed, but there are no glucose in urine, and in the blood sugar does not exceed the upper border.
- Negative hereditary factor when a patient has sugar diabetes in independence from its type (symptoms increased glucose may be absent). There are information that.
Women who during pregnancy scored more seventeen kilograms during pregnancy, and the weight of the child had a 4.5 kilogram during her time.
The test is carried out simply: the patient take blood, after they give a drink dissolved glucose, then a biological fluid is taken again at certain intervals.
Determination of glycated hemoglobin
 Glycated hemoglobin is a diagnostic study that allows you to determine the presence of sugar pathology in patients. The glycated hemoglobin is called the substance with which sugar in the blood is associated.
Glycated hemoglobin is a diagnostic study that allows you to determine the presence of sugar pathology in patients. The glycated hemoglobin is called the substance with which sugar in the blood is associated.
The level of this indicator is determined as a percentage. The norm is accepted for all. That is, a newborn baby, children before school age, adults and people of an elderly age group will be the same values.
This study has a lot of advantages, it is convenient not only for the doctor, but also for the patient. Since blood fence can be carried out at any time of the day, and the results will not depend on meals.
The patient does not need to drink glucose dissolved in water, and then wait a few hours. In addition, the study does not affect physical activity, nervous stress, stress, drug intake and other circumstances.
A feature of this study is that the test allows you to determine the blood sugar content over the past three months.
Despite the effectiveness of the test, its significant advantages and dignity, it has certain disadvantages:
- Expensive procedure, if compared with the usual blood test.
- If the patient has a small amount of hormones thyroid glandYou can get an incorrect result, and the indicators will be higher.
- With low hemoglobin and anemia in history, distortion of results.
- Not in each polyclinic you can go through such a test.
If the results of the study show the level of glycated hemoglobin less than 5.7% - this indicates the minimum risk of development sugar diabetes. When indicators vary from 5.7 to 6.0%, it can be said that diabetes is, but the likelihood of its development is quite high.
With rates 6.1-6.4%, it is possible to talk about the prediabetic state, and the patient urgently recommended to change your lifestyle. If the result of the study is above 6.5%, then diabetes is pre-diagnosed, you will need additional diagnostic events.
Activities to help reduce sugar
 So, it is now known that the rate of sugar content in the human body varies from 3.3 to 5.5 units, and these are ideal indicators. If sugar stopped at a mark of 5.8 units, it is a reason to revise your lifestyle.
So, it is now known that the rate of sugar content in the human body varies from 3.3 to 5.5 units, and these are ideal indicators. If sugar stopped at a mark of 5.8 units, it is a reason to revise your lifestyle.
It should be immediately noted that such a minor excess is easily controlled, and non-good preventive measures will allow not only normalize sugar at the required level, but also will not allow him to rise over the permissible border.
Nevertheless, if the patient has an increase in glucose concentration, it is recommended to control the sugar independently, measure it in the home atmosphere. This will help the device called a glucometer. Glucose control will prevent numerous probabilities to increase sugar.
So, what should I do to normalize your indicators? It is necessary to pay attention to the following preventive measures:
- Body mass control. If there is an overweight or obesity, you need to do everything to lose weight. Change nutrition, in particular calorie dishes, play sports or addicted to hiking.
- Balance your menu, giving preference to seasonal vegetables and fruits, refuse potatoes, bananas, grapes (there is a lot of glucose). Eliminate oily and fried food, alcoholic and caffean-containing drinks, gas.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day, refuse to exhaust graphics. In addition, it is recommended to go to rest and get up at the same time.
- Make an optimal physical activity in your life - to do the morning exercise, run in the morning, go to the gym. Either just walk through fresh air to a quick step.
Many patients are afraid of diabetes, completely refuse to have a full nutrition, preferring to starve. And this is not correct.
The hunger strike will only exacerbate the situation, exchange processes are even more violated, which in turn will lead to complications and negative consequences.
Independent measurement of sugar
You can find out the level of glucose in the clinic by handling blood, and as mentioned above, you can use the glucometr - a device for measuring the content of sugar in the body. It is best to use
Sugar 6.7 - is it diabetes? The lower boundary of the blood glucose concentration rate for an adult healthy person is 3.3 units, and the upper limit border should not exceed 5.5 units.
If sugar is on an empty stomach, that is, before meals, it varies from 6.0 to 7.0 units, then we can talk about the prediabetic state. It is prediabet - it is not a full diabetes, and it is quite possible to draw, if you take certain actions.
However, if we start the situation on samonek, ignore the pathological excess of blood sugar, the probability of the development of diabetes mellitus with all the resulting negative consequences, increases many times.
So, you need to consider, how is the prediatric state of sugar diabetes, and for what criteria is diagnosed prediabet? What to do with the increase in glucose content, and what to do to reduce it?
Prediabetic condition and diabetes: difference
Medical practice shows that in 92% of cases of disorders of glucose digestibility in the human body - this is sugar chronic illness second type. This pathology develops far from quickly.
Sugar diabetes of the second type is characterized by slow progression, after the prediatric state is manifested, and only the pathology itself is gradually developing.
Unfortunately, it is rare to determine the likelihood of diabetes mellitus, that is, to diagnose the prediabetic state in time. However, if it succeeds, then there is a great chance to keep your health, and avoid full-fledged incurable diabetes.
In which cases is the prediabetic state is diagnosed? It is prediabet to be patient if he has at least one criterion from the items below:
- On the hungry stomach, the glucose concentration varies from 6.0 to 7.0 units.
- The study of glycated hemoglobin from 5.7 to 6.4 percent.
- Sugar performance after glucose loads make up variability from 7.8 to 11.1 units.
Prediatric condition is a serious disorder exchange processes in the human body. And this pathology indicates a high probability of the development of a sugar disease of the second type.
Along with this, on the background of prediabet, numerous diabetic complications, increases the load on the visual apparatus, lower limbs, kidneys, liver, brain. If the situation is ignored, not to take any action in changing your nutrition, physical activity, then sugar diabetes is waiting in the future. It's unavoidable.
Criteria for which the second type of sugar disease is diagnosed:
- When glucose concentration in the human body on an empty stomach is 7 units. At the same time, a minimum of two studies were carried out at a certain interval in days.
- At some point, the sugar content indicators reroxed the mark of 11 units, and this did not depend on the use of food.
- Research on glycated hemoglobin showed a result of 6.5% inclusive and higher.
- The study for susceptibility to glucose showed the result of more than 11.1 units.
As with prediabetic state, one confirmed criterion is enough to diagnose sugar disease.
With a detected hyperglycemic state on time, it is necessary to immediately begin the measures that reduce blood sugar.
Timely therapy will reduce the likelihood of diabetic complications.
Clinical picture of prediabeta
Sugar level
As mentioned above, the sugar diabetes of the second type is preceded by a prediatric state. In some cases, the patient may not have negative changes in its body, in other situations, no deterioration is observed.
Speaking frankly, even if people notice negative symptoms, few people hurry to go for qualified medical care. After all, everything can be written off on fatigue and other reasons.
In medical practice, there are not rarely cases when patients are asked for help with a launched form of sugar disease (this condition is called). At the same time, they have long noticed their symptoms, but did not take any action. Unfortunately, there is a lot of time missed, and there are already complications.
The prediabetic state can be characterized by the following symptomatics:
- Dream is disturbed. Since glucose exchange is frustrated during the prediabetic state, it leads to a violation of the nervous system, which in turn leads to a breakdown of sleep.
- Peeling and sebus itching, violation of visual perception. Since due to the high concentration of sugar in the body, the blood becomes thicker, it is heavier to move on the blood vessels, in turn, it negatively affects the skin and vision.
- The constant desire to drink, which in turn leads to frequent hikes to the toilet, an increase in the share of urine per day. Such a symptom is leveled only in the case when the patient normalizes the sugar content indicators.
The following symptoms are both the following symptoms: headaches in the field of temples, dizziness, frequent mood swings, decreased appetite, lowering body weight.
The symptoms listed above should alert any person, even if only a few of them are observed - there is already a reason to consult a doctor.
How to avoid diabetes?
Sugar in blood 6.7 units, what to do? As mentioned above, the sugar rate at 6.7 units is not yet complete diabetes, it is a prediabetic state, which, unlike pathology, is treated.
The main way of avoiding numerous problems in the near future is a balanced and rational nutrition. What should be done? It is necessary to fully revise the menu, eliminate the products resulting in improving sugar after meals.
From the menu, eliminate the following:
- Food containing fructose and sugar sand.
- Roasted and alcoholic beverages.
- Baking, cakes, cakes, etc. If you want to pamper yourself something, then it is better to use.
- Potatoes, bananas, grapes.
Cooking also has its own characteristics, it is necessary to abandon such a way like frying, as well as limit consumption of fats. Practice shows that along with the prediabetic state, an increased mass of the body is often observed in patients.
Therefore, it is necessary not only to revise the names of food, but also reduce the calorie content of their diet. This does not mean that you need to starve and refuse food, it is enough to consume 1800-2000 calories per day.
In addition to strengthen the sensitivity of soft tissues to insulin, you must not forget about physical activity. What kind of sport choose, will help to decide the doctor.
However, it is not forbidden to go swimming, ride a bike, walk a quick step, slowly run, carry out charging in the morning.
Treatment of diabetes by folk remedies - myth?
Unfortunately, many in the head firmly "sits" a stereotype that if our ancestors could overcome many diseases with various braveractions and infusions based on medicinal plantsThis is an effective effective way.
No one argues, some funds really help, but no one knows how one or another home "drug" works, and never knows how our ancestors were treated.
Nevertheless, adherents of non-traditional medicine "are disappeared" from drug treatment, if there is already a need for a preference to folk therapy. But is it justified?
In fact, it is not excluded that there are certain recipes that help reduce blood sugar, but the most common, found on the Internet is just a myth:
- It is believed that an earthling pear effectively reduces sugar performance. However, it has a significant amount of carbohydrate plus fructose, so it will not help with diabetics.
- It is the opinion that cinnamon not only lowers sugar a few mmol / l, but also holds it stable in acceptable limits. Practice shows that the spice of action reduces glycemia, but literally at 0.1-0.2 units.
If the blood sugar reached the value of 7.7, what does this mean? Is there a danger to diabetics? After all, with diabetes, it is important to constantly check the testimony. Patients periodically pass the blood test on an empty stomach in a laboratory or self-measured sugar several times a day with a glucometter. It can be applied at home. Therefore, each diabetics should know which indicator is considered overestimated and is a pretext for immediate visits to the doctor.
Normal values
Sugar diabetes is considered a serious disease in which the patients must be monitored by the amount of blood sugar. Under this meaning is meant glucose. There are special standards for which diabetics should be relying. These values \u200b\u200baffect the age and diet, but sugar in the blood should not increase above 7 mmol / liter. Its composition is constantly changing throughout the day.
If you take the analysis immediately after eating food, the indicator will be high. Therefore, blood should be handed over in the morning on an empty stomach.
The amount of blood sugar in adults is considered the norm from 3.6-5.2 mmol / liter. If the patient consumed carbohydrates, then the value may increase to 6.8 mmol / liter. As a rule, after a few hours, the indicator will return to normal. These parameters refer to a person aged 14 to 59 years. In people over the sixty years, the normal glucose parameter in the blood varies within 4.6-6.5 mmol / liter.
Other readings:
- Pregnant women are allowed about 3.4-6.7 mmol / liter.
- In kids up to two years - 2.6-4.4 mmol / liter.
- From two to seven age - 3.2-5.0 mmol / liter.
- From seven to fourteen years, 3.2-5.6 mmol / liter is allowed.
During the expectation of the baby, you need to follow the size of sugar in the blood, because the increased indicator may affect the development of the fetus. Therefore, a woman should periodically donate blood, so doctors watch her health.
If the accumulation of glucose in the blood shows 7 mmol / liter and more, then you need to immediately consult a doctor and go through the relevant course of therapy.
Causes of increased parameter
It is known that with an increase in blood sugar in a patient with diabetes deteriorates well-being, and complications may manifest. And if you do not undertake all measures, then death may come.
There are symptoms for which you can see an increased indicator:
- dry mouth and constant thirst;
- dizziness;
- itching burning sensation;
- student urination, especially at night;
- worsening visibility;
- a tendency to frequent infectious diseases;
- bad healing of cuts on the skin;
- tablets received, do not apply.
In these cases, you need to refer to the doctor and pass the blood test. When confirming the increase in glucose, it is necessary to start therapy that will help reduce blood sugar. It will also be necessary to strictly observe, exclude carbohydrates from the diet.
The deviation of sugar in the blood is called hyperglycemia. During it, sugar accumulates, as a result of which the metabolism failure occurs. A person appears drowsiness, fatigue, nausea, in some cases - fainting.
If, when surrender analysis, blood sugar is from 5.8 to 7.8 mmol / liter, then the reasons for such a phenomenon should be found. Various factors can cause hyperglycemia.
These include:
- diabetes;
- overeating, inclusion in the diet large amount of carbohydrates;
- strong stress;
- different infectious diseases;
- reception of medicinal and hormonal drugs;
- incorrect preparation for blood.
 If blood sugar is 7.7 mmol / l, what does this mean? Usually after such conclusions, it is proposed to pass a test for the reaction to glucose and on the glycated hemoglobin. Only after that the diagnosis is diagnosed with diabetes. Patients must constantly visit the endocrinologist, take medicines and comply with the appropriate diet.
If blood sugar is 7.7 mmol / l, what does this mean? Usually after such conclusions, it is proposed to pass a test for the reaction to glucose and on the glycated hemoglobin. Only after that the diagnosis is diagnosed with diabetes. Patients must constantly visit the endocrinologist, take medicines and comply with the appropriate diet.
A high blood sugar parameter must be reduced. If this is not done, there may be sharp and chronic manifestations of diabetes. They are expressed by the loss of consciousness, fainting, damage to the nervous system and internal organs. Therefore, medical care is necessary. Often the absence of proper treatment can lead to death with diabetes mellitus.
Test results
To get reliable results, diabetics are recommended to donate blood in the morning and necessarily on an empty stomach. Evening meal must be 10 hours before the laboratory visit. On the eve, it is recommended to refrain from rich food carbohydrates, you can not drink alcohol and drinks containing caffeine.
This type of survey helps to recognize the metabolic states in the body, the magnitude of deviation from normal values, diagnose prediabetic syndrome and diabetes mellitus 1 or 2.
In conventional people, the glycemic index during the surrender of blood in the morning is about 3.2-5.5 mmol / l. If the parameter is enhanced, then secondary analysis and additional examination are carried out for reliable diagnosis. The sensitivity test of glucose allows you to identify the degree of development of glycemia.
The test is carried out in this way:
- Make blood fence on an empty stomach.
- After that, the patient has a mixture of glucose.
- Then take blood every half hour, to two hours (4 times).
Following the test, the diagnosis is made. The degree of glucose in the blood reaches up to 7.5 mmol / l - this means normal; If the value varies from 7.6 to 11.0 mmol / l - it is prediable; Values \u200b\u200babove 11.1 are considered a symptom of illness.
However, this test is not enough - it is necessary to determine the level of the glycated hemoglobin, since diabetes can manifest itself in a hidden form and when the blood is delivered, not to show signs. To check whether sugar in the blood rose, they make an analysis to the concentration of glycated hemoglobin. The results reveal the percentage of the hemoglobin contained in the chemical reaction with glucose.
No further preparation in this analysis is not necessary, a person can use food, drink, engaged in physical exertion. Reception medicines And nerve experiences on the indicators do not affect. In a normal person, this substance should be within 4.5-5.8%. Increased value indicates the development of diabetes. If this parameter reaches the indicator above 6.5%, this means one thing - in the blood there is a large amount of hemoglobin combined with glucose.
If the testimony of sugar remains increased (over 7.8-11.1 mmol / l), then the diabetes is predicted. After all, the content of glucose, the metabolic process is disturbed. These data often develops second-type diabetes.
Methods for reducing glucose
When risking the disease, when the blood sugar reaches the value of 8-11 mmol / l, it is necessary to go to the endocrinologist and get advice on subsequent actions. These parameters indicate the metabolic disorders. If you do not take all measures, then a person can develop such serious diseaselike diabetes mellitus.
The blood sugar standards are not always constant and may vary, depending on the age, time of day, diet, physical exertion, the presence of stressful situations.
The glucose parameters in the blood can increase or decrease on the basis of a particular need for the body. This complex system is controlled by the pancreas insulin and, to some extent, adrenaline.
If the insulin is lacking in the body, the regulation fails, which causes a disruption of metabolism. After a certain time, irreversible pathology of internal organs is formed.
To assess the patient's health and prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to constantly explore the content of glucose in the blood.
Sugar 5.0 - 6.0
Indicators of blood sugar ranks in the range of 5.0-6.0 units are considered permissible. Meanwhile, the doctor may be alert if the tests vary from 5.6 to 6.0 mmol / liter, as this can symbolize the development of the so-called prediabet
- Permissible indicators in adult healthy people can be between 3.89 to 5.83 mmol / liter.
- For children, the norm is considered to be the gap from 3.33 to 5.55 mmol / liter.
- The age of children is also important to consider: in newborns up to a month, the indicators may be between 2.8 to 4.4 mmol / liter, up to 14 years of age, data range from 3.3 to 5.6 mmol / liter.
- It is important to take into account that with age, these data becomes higher, so for the elderly from 60 years, the level of sugar levels in the blood can be higher than 5.0-6.0 mmol / liter, which is considered the norm.
- During pregnancy, women due to hormonal changes may increase data. For pregnant women are considered the norm of analysis of 3.33 to 6.6 mmol / liter.
When studying glucose venous blood The norm automatically increases by 12 percent. Thus, if you analyze from veins, the data may vary from 3.5 to 6.1 mmol / liter.
Also indicators can be varied if you take whole blood from the finger, vein or blood plasma. In healthy people, the plasma glucose level is 6.1 mmol / liter.
If a pregnant woman takes blood from a finger on an empty stomach, the average data may vary from 3.3 to 5.8 mmol / liter. In the study of venous blood, the indicators can be from 4.0 to 6.1 mmol / liter.
It is important to take into account that in some cases, under the influence of certain factors, sugar can temporarily increase.
Thus, increase glucose data can:
- Physical work or training;
- Long mental work;
- Fear, fear or acute stress situation.
Also to enhance sugar, in addition to diabetes, causes such diseases as:
- The presence of pain syndrome and pain;
- Acute myocardial infarction;
- Brain stroke;
- The presence of burn diseases;
- Injury brain;
- Carrying out a surgical operation;
- Epilepsy attack;
- The presence of liver pathology;
- Fractures and injury.
Some time after the impact of the provoking factor will be discontinued, the patient's condition is normalized.
An increase in glucose in the body is often connected not only with the fact that the patient consumed a lot of fast carbohydrates, but also with a sharp physical activity. When the muscles are loaded, they need energy.
Glycogen in the muscles is converted into glucose and is released into blood, which is why there is an increase in blood sugar. Next, glucose is used for its intended purpose, and sugar after a while comes to normal.
Sugar 6.1 - 7.0
It is important to understand that in healthy people, glucose indicators in capillary blood never increase above 6.6 mmol / liter. Since in the blood of a finger, glucose concentration is higher than from vein, venous blood has other indicators - from 4.0 to 6.1 mmol / liter with any form of research.
If blood sugar data on an empty stomach above 6.6 mmol / liter, a doctor, as a rule, diagnoses prediabet, which is a serious metabolic failure. If you don't undertake all efforts to normalize the state of health, a diabetes of second type can develop a patient.
With predominant, the blood glucose level on the hungry stomach is from 5.5 to 7.0 mmol / liter, the glycated hemoglobin indicators are from 5.7 to 6.4 percent. One or two hours after meals, these blood tests on sugar are from 7.8 to 11.1 mmol / liter. Quite at least one of the signs to diagnose the disease.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient will have:
- give a re-analyzing blood on sugar;
- pass the test for glucose tolerance;
- explore the blood to the indicators of glycosylated hemoglobin, since this method is considered the most accurate to detect diabetes.
Also necessarily takes into account the age of the patient, since data from 4.6 to 6.4 mmol / liter is considered in the elderly the norm.
In general, the increase in blood sugar in pregnant women does not indicate explicit violations, but also sakes the reason to worry about their own health and health of the future child.
If during pregnancy, the sugar concentration increases sharply, it can talk about the development of hidden latent diabetes. If you get into the risk group, the pregnant woman is registered, after which it is prescribed to take blood test on glucose and the test with the load on glucose tolerance.
If the glucose concentration in the blood of pregnant women is above 6.7 mmol / liter, most likely in a woman diabetes. For this reason, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor if a woman has such symptoms as:
- Feeling dryness in the mouth;
- Permanent thirst;
- Frequent urination;
- Constant feeling of hunger;
- Appearance unpleasant odor from mouth;
- Education in the oral cavity of the oxygen metallic lifting;
- Appearance general weakness and frequent fatigue;
- Arterial pressure rises.
To prevent the appearance of gestational diabetes, you need to regularly observe the doctor, pass all the necessary analyzes. It is also important not to forget about a healthy lifestyle, if possible, refuse frequent use of dishes with elevated glycemic index, high content of simple carbohydrates, starch.
If you take a timely manner necessary measuresThe pregnancy will pass without problems, healthy and strong kid will be born.
Sugar 7.1 - 8.0
If the performance in the morning clock on an empty stomach in an adult is 7.0 mmol / liter and above, the doctor may argue about the development of diabetes mellitus.
In this case, blood sugar data does not depend on meals and time can reach 11.0 mmol / liter and above.
In the case when the data is in the interval from 7.0 to 8.0 mmol / liter, while there are no obvious signs of the disease, and the doctor doubts the diagnosis, the patient is assigned to the passage of the test with the load on glucose tolerance.
- For this, the patient takes a blood test on an empty stomach.
- 75 grams of pure glucose is diluted with water in a glass, and the resulting solution must be patient to drink.
- Two hours the patient must be alone, you can not eat, drink, smoke and actively move. After that, he takes a repeated blood test on sugar.
A similar test for glucose tolerance is mandatory for pregnant women in the middle of the term. If, according to the results of the analysis, the indicators will be from 7.8 to 11.1 mmol / liter, it is believed that tolerance is broken, that is, the sensitivity to sugar is increased.
When the analysis shows the result above 11.1 mmol / liter, diabetes is pre-diagnosed.
The risk group for the development of diabetes mellitus of the second type includes:
- People having overweight;
- Patients with constant arterial pressure 140/90 mm Mercury post and above;
- People who have cholesterol indicators in the blood above the norm;
- Women who during pregnancy were diagnosed between gestational diabetes, as well as those whose child had a weight of 4.5 kg and above;
- Patients with ovarian polycystic;
- Ludi, having a hereditary predisposition to the development of diabetes.
With any risk factor, it is necessary to take blood test for sugar at least once every three years, starting from 45 years of age.
Children with overweight over 10 years old also need to be regularly checked for sugar.
Sugar 8.1 - 9.0
If three times in a row, the analysis of sugar has shown overestimated results, the doctor diagnoses diabetes mellitus of the first or second type. If the disease is running, high level Glucose will be found in the urine.
In addition to the saccharincing drugs, the patient is assigned strict medical diet. If it turns out that the sugar rises sharply after dinner and these results are saved up to sleep, it is necessary to reconsider their diet. Most likely, highly carbon dishes are used in food, which are contraindicated with diabetes mellitus.
A similar situation may be observed if, throughout the day, a person did not eat fully, and coming home in the evening, pounced on the food and ate an excessive portion.
In this case, to prevent sugar jumps, doctors recommend that there is evenly throughout the day in small portions. It is impossible to allow starvation, and from the evening menu it is necessary to eliminate dishes rich in carbohydrates.
Sugar 9.1 - 10
Blood glucose indicators of 9.0 to 10.0 units are considered a threshold value. With an increase in the data above 10 mmol / liter of kidney diabetics are not able to perceive such a large concentration of glucose. As a result, sugar begins to accumulate in the urine, which causes the development of glucose.
Due to the disadvantage of carbohydrates or insulin, the diabetic organism does not supplies the required amount of energy from glucose, and therefore fat reserves are used instead of the required "fuel". As is known, ketone bodies perform substances that are formed as a result of the collapse of fat cells. When blood glucose indicators reaches 10 units, the kidneys are trying to remove excess sugar from the body as slag waste along with urine.
Thus, diabetics, sugar indicators of which with several blood measurements above 10 mmol / liter, it is necessary to undergo urine analysis for the presence of ketone substances in it. For this purpose, special test strips are used, with which the presence in the urine of acetone is determined.
Also, such a study is carried out if a person, in addition to high data, more than 10 mmol / liter, sharply felt badly, the body temperature rose, while the patient feels nauseous, vomiting is observed. Such symptoms make it possible to reveal the decompensation of diabetes in a timely manner and prevent the diabetic coma.
With a decrease in blood sugar with the help of sugar-based drugs, physical exercises or insulin, the amount of acetone in the urine decreases, the patient has improved performance and overall well-being.
Sugar 10.1 - 20
If, with blood sugar indicators from 8 to 10 mmol / liter, the easy degree of hyperglycemia is diagnosed, then with increasing data from 10.1 to 16 mmol / liter is determined middle degree, above 16-20 mmol / liter - a severe degree of the disease.
This relative classification exists in order to navigate the doctors in suspected hyperglycemia. The average and severe degree reports the decompensation of diabetes, as a result of which all sorts of complications of chronic character are observed.
Allocate the main symptoms that indicate the overestimated content of blood sugar from 10 to 20 mmol / liter:
- The patient experiences frequent urination, sugar is found in the urine. Due to the increased concentration of glucose in the urine of underwear in the field of genital organs, it becomes shocked.
- At the same time, due to the large loss of fluid through the urine, diabetics feels strong and constant thirst.
- In the mouth there is constant dryness, especially at night.
- The patient is often sluggish, weak and quickly tires.
- Diabetic dramatically loses body weight.
- Sometimes a person feels nausea, vomiting, headache, the temperature rises.
The reason for this condition is associated in an acute lack of insulin in the body or the inability of cells to influence insulin in order to dispose of sugar.
At this point, the renal threshold above 10 mmol / liter is exceeded, can reach 20 mmol / liter, glucose is released with urine, which causes frequent urge from urination.
Such a state leads to loss of moisture and dehydration, this is exactly the cause of the neatoly thirst for diabetics. Along with the liquid from the body, not only sugar, but also all sorts of vital elements, such as potassium, sodium, chlorides, as a result, a person feels strong weakness and loses weight.
The higher the blood sugar level, the faster the processes described above occur.
Blood sugar above 20
With such indicators, the patient feels strong signs of hypoglycemia, which often leads to loss of consciousness. The presence of acetone with data 20 mmol / liter and is higher than the easiest to detect the smell. This is a clear sign that sugar diabetes is not compensated and the person is on the verge of a diabetic coma.
You can identify dangerous violations in the body using the following symptoms:
- The result of blood test is above 20 mmol / liter;
- The patient's company felt an unpleasant sharp smell of acetone;
- The person is quickly tired and feels constant weakness;
- There are frequent headaches;
- The patient dramatically loses appetite and he appears aversion to the food offered;
- In the abdomen area there is pain;
- Diabetics can feel nauseous, vomiting and liquid chair is possible;
- The patient has a noisy deep frequent breathing.
If at least three last features are found, it is necessary to immediately seek medical help to the doctor.
If the results of blood analysis above 20 mmol / liter, it is necessary to eliminate all physical exertion. In a similar condition, the load on the cardiovascular system may increase, which in combination with hypoglycemia is doubly dangerous for health. In this case, exercise can lead to a sharp increase in blood sugar.
With an increase in glucose concentration above 20 mmol / liter, the first thing is eliminated by the cause of a sharp increase in the indicators and the necessary dose of insulin is introduced. Reduce blood sugar rates from 20 mmol / liter to the norm by means of a low-carbid diet, which will bring closer to 5.3-6.0 mmol / liter.
diabethelp.org.
Prediabetic condition and diabetes: difference
Medical practice shows that in 92% of cases of violation of glucose digestibility in the human body - this is a sugar chronic disease of the second type. This pathology develops far from quickly.
Sugar diabetes of the second type is characterized by slow progression, after the prediatric state is manifested, and only the pathology itself is gradually developing.
Unfortunately, it is rare to determine the likelihood of diabetes mellitus, that is, to diagnose the prediabetic state in time. However, if it succeeds, then there is a great chance to keep your health, and avoid full-fledged incurable diabetes.
In which cases is the prediabetic state is diagnosed? It is prediabet to be patient if he has at least one criterion from the items below:
- On the hungry stomach, the glucose concentration varies from 6.0 to 7.0 units.
- The study of glycated hemoglobin from 5.7 to 6.4 percent.
- Sugar performance after glucose loads make up variability from 7.8 to 11.1 units.
The prediabetic state is a serious disorder of exchange processes in the human body. And this pathology indicates a high probability of the development of a sugar disease of the second type.
Along with this, on the background of prediabet, numerous diabetic complications are developing, the load on the visual apparatus, the lower limbs, kidneys, the liver, and the brain increase. If the situation is ignored, not to take any action in changing your nutrition, physical activity, then sugar diabetes is waiting in the future. It's unavoidable.
Criteria for which the second type of sugar disease is diagnosed:
- When glucose concentration in the human body on an empty stomach is 7 units. At the same time, a minimum of two studies were carried out at a certain interval in days.
- At some point, the sugar content indicators reroxed the mark of 11 units, and this did not depend on the use of food.
- A study on the glycated hemoglobin showed the result of 6.5% inclusive and higher.
- The study for susceptibility to glucose showed the result of more than 11.1 units.
As with prediabetic state, one confirmed criterion is enough to diagnose sugar disease.
With a detected hyperglycemic state on time, it is necessary to immediately begin the measures that reduce blood sugar.
Timely therapy will reduce the likelihood of diabetic complications.
Clinical picture of prediabeta
As mentioned above, the sugar diabetes of the second type is preceded by a prediatric state. In some cases, the patient may not have negative changes in its body, in other situations, no deterioration is observed.
Speaking frankly, even if people notice negative symptoms, few people hurry to go for qualified medical care. After all, everything can be written off on fatigue and other reasons.
In medical practice, there are not rarely cases when patients are asked for help with a launched form of sugar disease (this condition is called decompensated diabetes mellitus). At the same time, they have long noticed their symptoms, but did not take any action. Unfortunately, there is a lot of time missed, and there are already complications.
The prediabetic state can be characterized by the following symptomatics:
- Dream is disturbed. Since glucose exchange is frustrated during the prediabetic state, it leads to a violation of the nervous system, which in turn leads to a breakdown of sleep.
- Peeling and sebus itching, violation of visual perception. Since due to the high concentration of sugar in the body, the blood becomes thicker, it is heavier to move on the blood vessels, in turn, it negatively affects the skin and vision.
- The constant desire to drink, which in turn leads to frequent hikes to the toilet, an increase in the share of urine per day. Such a symptom is leveled only in the case when the patient normalizes the sugar content indicators.
The following symptoms are both the following symptoms: headaches in the field of temples, dizziness, frequent mood swings, decreased appetite, lowering body weight.
The symptoms listed above should alert any person, even if only a few of them are observed - there is already a reason to consult a doctor.
How to avoid diabetes?
Sugar in blood 6.7 units, what to do? As mentioned above, the sugar rate at 6.7 units is not yet complete diabetes, it is a prediabetic state, which, unlike pathology, is treated.
The main way of avoiding numerous problems in the near future is a balanced and rational nutrition. What should be done? It is necessary to fully revise the menu, eliminate the products resulting in improving sugar after meals.
From the menu, eliminate the following:
- Food containing fructose and sugar sand.
- Roasted and alcoholic beverages.
- Baking, cakes, cakes, etc. If you want to pamper yourself something, it is better to use desserts without sugar.
- Potatoes, bananas, grapes.
Cooking also has its own characteristics, it is necessary to abandon such a way like frying, as well as limit consumption of fats. Practice shows that along with the prediabetic state, an increased mass of the body is often observed in patients.
Therefore, it is necessary not only to revise the names of food, but also reduce the calorie content of their diet. This does not mean that you need to starve and refuse food, it is enough to consume 1800-2000 calories per day.
In addition to strengthen the sensitivity of soft tissues to insulin, you must not forget about physical activity. What kind of sport choose, will help to decide the doctor.
However, it is not forbidden to go swimming, ride a bike, walk a quick step, slowly run, carry out charging in the morning.
diabetik.Guru.
What is blood sugar level?
First of all, it should be noted that it would be more correct to say "the level of glucose in the blood", since the concept of "sugar" includes a whole group of substances, but determined in the blood glucose. However, the term "blood sugar levels" was so accustomed that it is used both in colloquial speech and in the medical literature.
Blood sugar level (blood glucose level) is one of the most important biological constants indicating the constancy of the inner environment of the body.
This indicator, in the first place, reflects the state carbohydrate exchange. Glucose is a kind of fuel (energy material) for cells of all organs and tissues.
It enters the human body mainly in the composition of complex carbohydrates, which subsequently split in the digestive tract, and enter blood. Thus, the blood sugar level may be violated with various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, under which the absorption of glucose is reduced into blood.
The glucose came from the gastrointestinal tract only partially used by the cells of the body, the larger part is postponed in the form of RIR »Rurєrѕrμrѕr ° in the liver.
Then, if necessary (elevated physical or emotional loads, lack of glucose intake from the gastrointestinal tract), glycogen is split, and glucose enters blood.
Thus, the liver is a glucose depot in the body, so that during its severe diseases, disturbances of blood sugar are also possible.
It should be noted that the admission of glucose from the capillary bed inside the cell is enough difficult processwhich in certain diseases may violate. This is another reason for the pathological change in blood sugar levels.
The yield of glucose from the depot in the liver (glycogenolysis), the glucose synthesis in the body (gluconeogenesis) and the absorption of its cells is controlled by a complex neuroendocrine regulation system, in which the hypothalamic-pituitary system (the main center of neuroendocrine regulation), pancreas and adrenal glands take directly participation. The pathology of these bodies is often the cause of blood sugar levels.
How is the allowable blood sugar level regulated?
 The main hormone regulating permissible level Sugar in the blood is the hormone of the pancreas - insulin. With an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, the secretion of this hormone increases. This occurs both directly as a result of the stimulating effect of glucose on the receptors of the pancreas cells, and is indirectly, by activating the parasympathetic nervous system through glucose-sensitive receptors in the hypothalamus.
The main hormone regulating permissible level Sugar in the blood is the hormone of the pancreas - insulin. With an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, the secretion of this hormone increases. This occurs both directly as a result of the stimulating effect of glucose on the receptors of the pancreas cells, and is indirectly, by activating the parasympathetic nervous system through glucose-sensitive receptors in the hypothalamus.
Insulin contributes to the consumption of glucose by cells of the body, and stimulates the synthesis of the glycogen in the liver - thus the blood sugar level is reduced.
The main insulin antagonist is another hormone of the pancreas - glucagon. With a decrease in blood sugar levels, its increased secretion occurs. Glucagon enhances the decay of glycogen in the liver, contributing to the exit of glucose from the depot. The same action has a hormone of brainstabs of adrenal glands - adrenaline.
Hormones stimulating glucoseogenesis are also promoted to increase blood glucose levels - the formation of glucose in the body from simpler substances. In addition to glucagon, such an action is made of cerebral hormones (adrenaline, norepinephrine) and cortical (glucocorticoid) adrenal substances.
To substances that increase blood sugar levels also relate to the hypophism of growth hormone and thyroid hormone - thyroxin.
The sympathetic nervous system, activating when requiring increased consumption of stress energy, increases blood glucose levels, and parasympathetic - reduces. Therefore, deep at night and early in the morning, when the predominance of the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system is observed, the blood glucose level is the lowest.
What tests are carried out to determine blood sugar levels?
There are two most popular in clinical medicine Method of measuring blood sugar levels: in the morning on an empty stomach (while the break in the meal and fluid should be at least 8 hours), and after the load of glucose (the so-called oral glucose-olerant test, OGTT).
The oral glucose-bearing test is that the patient takes inside 75 grams of glucose dissolved in 250-300 ml of water, and after two hours, the blood sugar level is determined.
The most accurate results can be obtained with a combined conduct of two tests: after three days, a conventional diet in the morning on an empty stomach determines the blood sugar level, and after five minutes, the glucose solution is taken to measure this indicator in two hours.
In some cases (diabetes, violation of glucose tolerance) is needed by constant monitoring of blood sugar levels, so as not to miss serious pathological changes, fragile threat to life and health.
Is it possible to measure the blood sugar level at home?
 The blood sugar level can be measured at home. To do this, you should purchase a special device in a pharmacy - a glucometer, for example, OneTouch Select - it is compact, it is easy to take with you and check the level of glucose where it is necessary. Facilitates checking the interface in Russian, the marks before and after eating. The device is extremely easy to use, while it is distinguished by the measurement accuracy. With the help of a portable glucometer can be held a poor under control.
The blood sugar level can be measured at home. To do this, you should purchase a special device in a pharmacy - a glucometer, for example, OneTouch Select - it is compact, it is easy to take with you and check the level of glucose where it is necessary. Facilitates checking the interface in Russian, the marks before and after eating. The device is extremely easy to use, while it is distinguished by the measurement accuracy. With the help of a portable glucometer can be held a poor under control.
The traditional glucometer is a device with a set of sterile lanceters for blood and special tail strips. In sterile conditions, Lanzet is punctured by the skin on the tip of the finger, the blood droplet is transferred to the trees strip, which is subsequently placed in the device to determine blood sugar levels.
There are glucometters processing capillary bloodderived from other places (shoulder, forearm, foundation thumb, thigh). But it should be remembered that blood circulation in the tips of the fingers is much higher, therefore, using the traditional method, you can get more accurate results on the level of blood sugar at the moment. This can be very important, since this indicator in some cases is changing rapidly (physical or emotional load, food, developing a concomitant disease).
How to properly measure blood sugar levels at home?
To properly measure the level of blood sugar at home, you should carefully read the instructions for the acquired device, and in doubtful cases, seek explanations to a specialist.
When measuring blood sugar levels at home, some general rules must be observed:
1.
Before the blood fence should be thoroughly wash his hands with warm water. It must be done not only to ensure purity, but also to improve blood circulation. Otherwise, the puncture on the finger will have to do deeper, and take blood for the analysis will be more difficult.
2.
The point of puncture should be well dried, otherwise the blood obtained will dilute with water, and the results of the analysis will be distorted.
3.
For blood collection, the inner surface of the three-finger pads of both hands is used (large and index finger traditionally do not touch the workers).
4.
So that the manipulation brings as few painful sensations as possible, it is best to make a puncture not in the center of the pads, but a slightly side. The depth of the puncture should not be too large (2-3 mm for an adult - optimal).
5.
With a regular measurement of the level of sugar in the blood, it is necessary to constantly change the place of blood intake, otherwise there will be inflammation or / and thickening of the skin, so in the subsequent bonding the blood from the usual place will be impossible.
6.
The first drop of blood obtained after the puncture is not used - it should be carefully removed with a dry robe.
7.
It should not be too squeezing a finger, otherwise the blood is mixed with the tissue fluid, and the result will be released inadequate.
8.
It is necessary to remove the blood droplet until it was smeared, because the lubricated drop is not absorbed into the test strip.
What is the level of blood sugar level?
The level of blood sugar level in the morning on an empty stomach is 3.3-5.5 mmol / l. The deviation from the norm in the range of 5.6 - 6.6 mmol / l indicates a disturbed tolerance to glucose (condition, border between the norm and pathology). The increase in the level of blood sugar is an empty stomach to 6.7 mmol / l and above gives grounds to suspect the presence of diabetes.
In doubtful cases, it is additionally carried out to measure the level of blood sugar in two hours after the load of glucose (oral glucose-bearing test). The rate indicator with this study increases to 7.7 mmol / l, indicators within 7.8 - 11.1 mmol / l are indicated for violation of glucose tolerance. In diabetes mellitus, the sugar level two hours after the load of glucose reaches 11.2 mmol / l and above.
What is the normal blood sugar level in a child?
In children early age A physiological propensity is noted to reduce blood sugar levels. The norms of this indicator in babies and preschoolers are somewhat lower than in adults.
So, in breast-age children, the level of glucose on an empty stomach is normal 2.78 - 4.4 mmol / l, preschoolers - 3.3 - 5.0 mmol / l, in school children - 3.3 - 5.5 mmol / l.
If the level of blood sugar in an empty stomach exceeds 6.1 mmol / l, then they speak of hyperglycemia (increasing blood sugar). Indicators below 2.5 mmol / l indicate hypoglycemia (reduced blood sugar levels).
In the case when the sugar level of an empty stomach is within 5.5 - 6.1 mmol / l, an additional oral glucose-bearing test is shown. Glucose tolerance in children is significantly higher than adults. Therefore, normal indicators of blood sugar levels in two hours after standard glucose load are slightly lower.
If a child has a blood sugar level on an empty stomach exceeds 5.5 mmol / l, and two hours after a load of glucose reaches 7.7 mmol / l or higher, then sugar diabetes mellitus.
How does blood sugar level change during pregnancy?
![]() During pregnancy in the body of a woman there is a complex restructuring, leading to physiological insulin resistance. The development of such a state naturally contributes to a high level of ovarian and placental steroids (cross-rival hormones secreted by the ovaries and the rye "R ° C † RμRѕС,РѕР№), as well as the increased secretion of cortisol hormone adrenal cortex.
During pregnancy in the body of a woman there is a complex restructuring, leading to physiological insulin resistance. The development of such a state naturally contributes to a high level of ovarian and placental steroids (cross-rival hormones secreted by the ovaries and the rye "R ° C † RμRѕС,РѕР№), as well as the increased secretion of cortisol hormone adrenal cortex.
In some cases, physiological insulin resistance exceeds the possibilities of the pancreas in insulin production. This develops so-called gestational diabetes mellitus, or diabetes of pregnant women. In most cases, after childbirth, women with diabetes are pregnant, all indicators of blood sugar are returned to normal. However, caution should be taken, since approximately 50% of women who have undergone gestational diabetes, for 15 years after pregnancy develops sugar diabetes of the second type.
In gestational diabetes, as a rule, there are no clinical manifestations of hyperglycemia. However, this condition is a danger to the development of the child, since in the absence of compensatory therapy, an increased level of glucose in the blood of the mother in 30% of cases leads to the pathology of the fetus.
Gestational diabetes usually develops in the middle of pregnancy (between 4 and 8 months), and women from the risk group should be especially attentive to the blood sugar levels at this time.
The risk group includes women with an increased body weight, unfavorable heredity (diabetes of pregnant women or second type near the nearest relatives), burdened by the obstetric R ° RѕR ° RјRѕrμr · Rѕrј (large fruit or stilling during previous pregnancies), as well as suspected large Fetrus with current pregnancy.
The diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is made with an increase in blood sugar levels taken on an empty stomach, to 6.1 mmol / l and higher, if two hours after the load is load, this indicator is 7.8 mmol / l and above.
Increased blood sugar level
When is the elevated blood sugar level?
There are physiological and pathological increase in blood sugar levels.
The physiological increase in blood glucose concentration occurs after meals, especially easily digestible carbohydrates, with intensive physical and mental load.
A short-term increase in this indicator is characteristic of such pathological conditions as:
- strong pain syndrome;
- burns;
- epileptic seizure;
- acute myocardial infarction;
- heavy attack of angina.
Reduced glucose tolerance is observed under states caused by stomach operations and duodenalisticianleading to accelerated absorption glucose from the intestine to blood.
In the cranial and brain injury with the lesion of the hypothalamus (there is a reduced ability of tissues to dispose of glucose).
With severe liver lesions (reduced synthesis of glycogen from glucose).
A long-term increase in blood sugar levels leading to the appearance of glucose (glucose removal with urine) is called diabetes diabetes (sugar diabetes).
Due to the occurrence, the primary and secondary diabetes are distinguished. Primary diabetes mellitus is called two separate nosological units (first and second diabetes) having internal reasons Development, while the reasons of secondary diabetes serve various diseases, leading to pronounced violations of carbohydrate metabolism.
First of all, it is severe pancreatic lesions, characterized by absolute insulin insulsion (pancreatic cancer, severe flow of pancreatitis, damage to the organ when cycidosis, removal of the pancreas, etc.).
Secondary diabetes mellitus also develops with diseases accompanied by an increase in the secretion of conjunral hormones - glucagon (hormonally active tumor - glucagonomoma), growth hormone (giantism, acromegaly), thyroid hormones (thyrotoxicosis), adrenaline (brainstorm tumor of adrenal glands - feuhromocytoma), cortical hormones adrenal glands (Isenko-Cushing syndrome).
Quite often occurs, reduced tolerance for glucose, up to the development of diabetes mellitus caused by a long-term intake of drugs, such as:
- glucocorticoids;
- tiazide diuretics;
- some hypotensive and psychotropic drugs;
- estrogen-containing drugs (including oral contraceptives);
- РєР ° С,РμС ... РѕР »Р ° РјРёРѕС \u003c.
According to the classification of VOZ, as a separate nosological unit allocated gestational diabetes (pregnant women). It does not apply to any primary, nor to secondary types of sugar diabetes.
What is the mechanism for increasing blood sugar levels in diabetes type?
 Increased blood sugar levels with type-type diabetes mellitus associated with absolute insulin deficiency. it an autoimmune diseaseIn which the cells of the pancreas, producing insulin, are subjected to autoimmune aggression and destruction.
Increased blood sugar levels with type-type diabetes mellitus associated with absolute insulin deficiency. it an autoimmune diseaseIn which the cells of the pancreas, producing insulin, are subjected to autoimmune aggression and destruction.
The reasons for the occurrence of this pathology have not yet been fully understood. Sugar diabetes of type is considered a disease with a hereditary predisposition, but the effect of hereditary factor is insignificant.
In many cases, there is a connection with the transferred viral diseases that launched an autoimmune process (the peak of morbidity falls on the autumn-winter period), but a significant part of the disease diabetes mellitus is idiopathic, that is, the cause of pathology remains unknown.
Most likely, the disease is based on a genetic defect that is implemented under certain conditions ( viral disease, physical or mental injury). Sugar diabetes of the type is developing in a children's or youthful, less often in adulthood (up to 40 years).
Pancreas compensatory capabilities are large enough, and symptoms Sugar diabetes of type is manifested only if more than 80% of insulin production cells are destroyed. However, when the critical limit of compensatory capabilities is achieved, the disease develops very quickly.
The fact is that insulin is necessary for the consumption of glucose cells of liver, muscles and adipose tissues. Therefore, if it is drawn, on the one hand, the level of blood sugar increases, because in the part of the body of the body of glucose does not come, on the other, the cells of the liver, as well as muscle and adipose tissue, are experiencing energy hunger.
Energy hunger cells launches glycogenolysis mechanisms (glycogen decay with glucose formation) and glucose genesis (glucose formation of simple substances), as a result, the blood sugar level increases at times.
The situation complicates the fact that reinforced glukegenesis passes with the collapse of fats and proteins necessary for glucose synthesis. Disintegration products - toxic substancesTherefore, against the background of hyperglycemia there is a general poisoning of the body. Thus, type-type diabetes can lead to the development of critical states (coma) in the first weeks of the development of the disease.
Due to the rapid development of symptoms in the preinsulin era, the diabetes mellitus I was called malignant diabetes. Today, when there is the possibility of compensatory treatment (the introduction of insulin), this type of disease is called insululin-dependent diabetes (ECD).
Energy hunger of muscular and adipose tissue causes quite characteristic appearance Patients: as a rule, these are thin people of asthenic physique.
The type-type diabetes is about 1-2% of all cases of disease, however, the risk of complications, as well as the young age of the majority of patients (the peak of morbidity is 10-13 years old) attract special attention both doctors and public figures.
What is the mechanism for increasing blood sugar levels in diabetes type?
The mechanism of increasing blood sugar levels in type-type diabetes is associated with the development of the resistance of target cells to insulin.
This disease relate to pathologies with a pronounced hereditary predisposition, the implementation of which contributes by many factors:
- obesity;
- hypodynamine;
- stress;
- incorrect nutrition (fast food, consumption of a large amount of sweet carbonated water);
- smoking;
- alcoholism;
Some associated pathologies ( hypertonic disease, atherosclerosis).
The disease develops at the age after 40 years, and with age, the risk of pathology is increasing.
In diabetes mellitus of the type of insulin levels, it remains normal, but the blood glucose level is increased, since glucose into cells does not flow as a result of a decrease in the cell reaction to the impact of the hormone.
The disease develops slowly, since long-term pathology is compensated by increasing the level of insulin in the blood. However, further continues to reduce the sensitivity of target cells to insulin, and the exhaustion of the organism's compensatory capabilities occurs.
Pancreatic cells can no longer generate insulin in the quantity required for this state. In addition, due to the increased load in cells producing hormone, degenerative changes occur, and hyperinsulamia is naturally replaced by a reduced hormone concentration in the blood.
Early detection of diabetes mellitus allows you to protect the cells secreting insulin, from damage. Therefore, people from a risk group need to regularly undergo an oral glucose-bearing test.
The fact is that due to compensatory reactions, the level of sugar in the blood is on an empty stomach for a long time remains normal, but at this stage there is a reduced tolerance for glucose, and the OGTT allows it to identify it.
What are the signs of high blood sugar?
Classic diabetes is manifested by triad clinical symptoms:
1.
Polyuria (increased urine release).
2.
Polydipsia (thirst).
3.
Polyphagia (increased food intake).
The high level of blood sugar leads to the appearance of glucose in the urine (glucosuria). To remove the surplus glucose, the kidneys need to use a greater amount of liquid for urine formation. As a result, urine volume increases, and with it the frequency of urination. Hence the old name of diabetes mellitus - sugar diabetes.
Polyuria naturally leads to increased loss of water, which is clinically manifested by thirst.
The target cells do not receive a sufficient amount of glucose, so the patient constantly feels hunger, and absorbs more food (polyphagia). However, in pronounced insulin insulsion, patients are not corrected, since the fatty tissue does not receive a sufficient amount of glucose.
In addition to the triad characteristic sacrificial diabetes, the clinically elevated level of blood sugar is manifested by a number of nonspecific (characteristic of many diseases) symptoms:
- increased fatigue, reduction of working capacity, drowsiness;
- headache, irritability, sleep disorders, dizziness;
- itching the skin and mucous membranes;
- bright blush cheeks and chin, appearance yellow spots on the face, and flat yellow formations on centuries (symptoms of concomitant violations of lipid metabolism);
- pain in the limbs (most often alone or at night), night cramps of the calf muscles, numbness of the limbs, paresthesia (tingling, feeling of crawling goosebumps);
- nausea, vomiting, pain in the opposite region;
- increased tendency to infectious inflammatory diseases that are poorly treatable and transferred to chronic form (kidneys and urinary Ways, leather, mucous membrane of the oral cavity).
Acute complications of high blood sugar levels
 The high level of blood sugar inevitably causes complications that are divided into:
The high level of blood sugar inevitably causes complications that are divided into:
1.
Acute (arising from raising sugar levels to critical numbers).
2.
Late (characteristic of long-term flow of diabetes).
The sharp complication of the high level of blood sugar is the development of a comatose state, which is the defeat of the central nervous system, clinically manifested by the progressive violation of the nervous activity, up to the loss of consciousness and the extinction of elementary reflexes.
The sharp complications of the high level of blood sugar are especially characteristic of the type of diabetes mellitus, which often manifests heavy manifestations close to the terminal states of the body. However, comatose states are complicated by other types of diabetes, especially with a combination of several factors that predispose to the development of a sharp increase in this indicator.
The most commonly predisposing factors for the development of sharp complications in diabetes are:
- acute infectious diseases;
- other sharp stress for the body factors (burns, frostbite, injury, operations, etc.);
- exacerbations of severe chronic diseases;
- errors in the treatment and mode (skipping insulin injection or drugs corrective blood sugar levels, rough diet disorders, alcohol use, increased physical activity);
- reception of some medicines (glucocorticoids, diuretic, estrogenic preparations, etc.).
All types of comatous states at an elevated level of blood sugar are developing gradually, but are characterized high degree mortality. Therefore, it is especially important to know the early signs of their manifestation in order to ask for help.
The most common general precursors for the development of comatose states at an elevated blood sugar level:
1.
An increase in the amount of urine allocated to 3-4, and in some cases up to 8-10 liters per day.
2.
Permanent dryness in the mouth, thirst, contributing to the consumption of a large amount of fluid.
3.
Fatigue, weakness, headache.
If, with the appearance of early signs of increasing blood sugar levels, adequate measures were not taken, then in the future gross neurological symptoms increase.
First, the stupidity of consciousness occurs, manifested by a sharp reaction inhibition. Then the copor (hibernation) is developing when the patient has a dream close to the loss of consciousness. However, it can still be derived from such a state with superphic effects (tweaks, shaking by shoulders, etc.). Finally, in the absence of therapy, comatose and death occurs naturally.
Different types of comatous states at an elevated blood sugar level have its own development mechanisms, and, therefore, distinctive clinical signs.
Thus, the development of the ketoacidotic coma is based on the disintegration of proteins and lipids caused by hyperglycemia to form a large number of ketone bodies. Therefore, in the clinic of this complication, specific symptoms of intoxication by ketone bodies are expressed.
First of all, it is the smell of acetone from the mouth, which, as a rule, is still felt from the patient's distance before the development of the comatose state. In the future, the so-called breathing of Kussmaulyuly appears - deep, rare and noisy.
To the late precursors of the ketoacidotic coma include the violations of the gastrointestinal tract - nausea, vomiting, pain in the opposite region (sometimes so pronounced, which causes a suspicion of "acute stomach").
The mechanism of development of the hyperosmolar coma is completely different. The elevated level of blood glucose causes blood thickening. As a result, according to the laws of osmosis, the liquid from the outside and intracellular medium rushes into the blood. Thus, the dehydration of the extracellular medium and the cells of the body occurs. Therefore, with hyperosmolar coma, there are clinical symptoms associated with dehydration (dry skin and mucous membranes), and no signs of intoxication is observed.
Most often, such a complication occurs with the accompanying dehydration of the body (burn, massive blood loss, pancreatitis, vomiting or / and diarrhea, diuretic reception).
Lacacidotic coma is the most rare complication, the development mechanism of which is associated with the accumulation of lactic acid. As a rule, it is developing in the presence of concomitant diseases occurring with severe hypoxia (disadvantage of oxygen). Most often it is respiratory and heart failure, anemia. We provoke the development of a lactacidotic coma can be taken alcohol and increased physical activity in old age.
The specific harbinger of the lactacidotic coma is pain in the ion muscles. Sometimes there is nausea and vomiting, but other symptoms of intoxication characteristic of the ketoacenedical coma - no; There are no signs of dehydration.
Late complications of high blood sugar
 If you do not correlate the blood sugar level, complications in diabetes are inevitable, since under hyperglycemia, all organs and tissues of the human body suffer. However, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy and syndrome are the most common and dangerous complications. diabetic foot.
If you do not correlate the blood sugar level, complications in diabetes are inevitable, since under hyperglycemia, all organs and tissues of the human body suffer. However, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy and syndrome are the most common and dangerous complications. diabetic foot.
Diabetic retinopathy is a degenerative damage to the retina, in severe cases, leading to irreplaceable blindness. The retina of the eye consists of photoreceptor cells that provide visual perception that linse the inner surface of the eye.
The high level of blood sugar leads to the defeat of small blood vesselslocated under the retina. Stages Diseases often pass without clinical manifestationsBut in the future there is a so-called proliferative phase when the reactive formation of new vessels occurs. Newly formed vessels - thin and brittle, so in adverse conditions increased level Sugar in the blood often occur hemorrhages, leading to complications, up to complete loss of vision (retinal detachment).
Diabetic РѕРμС "СђРѕРїР ° С. С,РОСџ - the lesion of the renal filter, leading ultimately to the development of chronic renal failurewhich is the cause of the death of many patients with diabetes. The mechanism for the development of diabetic nephropathy is that at a high level of blood sugar in blood, degenerative changes occur in the vessels of renal glomers, providing blood filtering. An important role is played by an increased load, caused by the need to bring surplus sugar with urine.
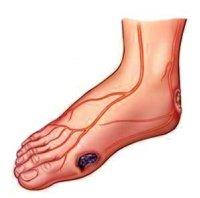
The diabetic foot syndrome is a complex symptom complex caused by several mechanisms of influence of increased blood sugar levels:
1.
Diabetic neuropathy (damage to the peripheral nervous system);
2.
Diabetic angiopathy (vessel damage);
3.
The addition of infectious processes, which under hyperglycemia, tend to chronic recurrent flow.
The diabetic foot syndrome in many cases is heavily, and leads to the forced amputation of the limb due to the development of gangrene.
How to achieve an increase in blood sugar levels?
The main rule when assisting in the case of hypoglycemic states: raising blood sugar levels should be achieved as soon as possible. It should be noted that some symptoms of hypoglycemia are similar to those with hyperglycemia (drowsiness, fatigue, headache, confusion of consciousness).
Therefore, it is necessary, if possible, measure the blood sugar level to properly assist. If for one or another reasons it is impossible to urgently conduct a test for the definition of this indicator, then the state is treated as hypoglycemic.
The fact is that a small dose of glucose is not able to apply tangible harm in hyperglycemic states when the blood sugar level is raised at times. And in the case of hypoglycemia, the reception of accessible carbohydrates will give a quick positive effect.
If the patient is conscious, and his behavior is adequately, it is best to cook tea with two-three tablespoons of sugar. You can use the same amount of honey or jam.
As a rule, the condition is improving after ten to fifteen minutes. It should be remembered that the careless carbohydrates, going into the blood, quickly disappear, since the effect of insulin continues. Therefore, to prevent the "second wave of hypoglycemia", the patient needs to eat products containing more complex carbohydrates (black bread, apple).
If the patient is in a state without consciousness, or his behavior is inadequate, it is necessary to cause an emergency medical care. In anticipation of the arrival of the doctor, you should try to persuade the patient with inadequate behavior to take a sweet syrup. The behavior of people in the state of hypoglycemia is often aggressive and unpredictable, so it is necessary to show a maximum of patience.
Reduced blood sugar level
How to reduce blood sugar levels?
In order to effectively reduce blood sugar levels, it is necessary to know the reason for its increase.
In many cases, secondary diabetes can eliminate the cause that caused pathology:
1.
Cancellation of drugs that caused the level of blood sugar;
2.
Removal of a tumor producing conjunral hormones (glucagonoma, feochromocytoma);
3.
Treatment of thyrotoxicosis, etc.
In cases where it is impossible to eliminate the reason for increasing blood sugar levels, as well as at primary diabetes mellitus І and ІІ type, compensatory treatment are prescribed. It may be insulin or medicationsreduced blood sugar levels. In gestational diabetes, it is possible to achieve a decline in this indicator, as a rule, with the help of one diet and therapy.
Treatment is selected strictly individually (not only the type of diabetes is taken into account, but also general state Specific patient), and is carried out under constant medical control.
The general principles of treatment of all types of diabetes are:
- constant control of blood sugar levels;
- fulfillment of all recommendations for compensatory treatment;
- strict adherence to the diet, labor and recreation;
- invalidation of alcohol and smoking.
In the case of a diabetic coma (ketoacidotic, hyperosmolar or lactacidotic) at any stage of its development, emergency medical care is necessary.
When is the reduced blood sugar level?
The reduced level of blood sugar is observed:
1.
In case of diseases that impede glucose absorption in blood (Malabsorption syndrome).
2.
With severe lesions of the liver parenchyma, when glucose output from the depot (lightning hepatic necrosis during infectious and toxic lesions) is impossible.
3.
In endocrine pathologies, when the synthesis of conjunral hormones is reduced:
- hypocituitarism (pituitary hypofunction);
- addison disease (lack of hormones of adrenal cortex);
- hypothyroidism);
- increased insulin synthesis (Rurѕsѓsѓr »Rurzrѕrјr °).
However B. clinical practice The doctor most often encounters hypoglycemia attacks caused by poorly corrected diabetes therapy.
The most common cause of hypoglycemia in such cases becomes:
- overdose of prescribed drugs, or improper administration (intramuscular injection insulin instead of subcutaneous);
- errors in the diet (long starvation);
- vomiting or diarrhea;
- increased physical exertion;
- acceptance of alcohol (especially no snacks);
- using some medical preparations: acetylsalicylic acid, sulfonamides (ethasol, bispetol), some antibiotics (levomycetin, tetracycline), antidepressant amitriptyline, antihistamines, etc.
What are the signs of low blood sugar?
 With a low level of blood sugar, the cells undergo energy hunger, since glucose is the main energy material for all intracellular metabolic processes. The most sensitive to glucose starvation of the cerebral cell, therefore the preferential majority of signs of low blood sugar levels are the symptoms of the lesion of the central nervous system.
With a low level of blood sugar, the cells undergo energy hunger, since glucose is the main energy material for all intracellular metabolic processes. The most sensitive to glucose starvation of the cerebral cell, therefore the preferential majority of signs of low blood sugar levels are the symptoms of the lesion of the central nervous system.
Early signs of low blood sugar levels:
- increased sweating;
- hunger;
- shiver;
- increased heartbeat;
- paresthesia leather around lips;
- nausea;
- unmotivated alarm.
Late signs of low blood sugar:
- difficulty in concentration of attention, difficulties in communication, confusion;
- headache, weakness, drowsiness;
- vision impairment;
- violation of adequate perception of the surrounding, disorientation in space.
When the first signs of lowering the level of sugar in the blood, the patient can and should help himself. In the case of late signs, he remains to hope for helping others. In the future, in the absence of adequate therapy, a hypoglycemic coma is developing.
What is dangerous low blood sugar?
Low blood sugar levels may cause serious irreversible brain damage.
In addition, heavy hypoglycemia oppressively acts on the central nervous systemAnd violates the orientation of the patient in the surrounding world, so that his behavior becomes inadequate. This can lead to sad consequences for both the patient and the surrounding (road traffic accidents, household injuries, etc.).
www.tiensmed.ru.
Normal blood glucose level
It is known that the blood sugar level is regulated by the pancreatic hormone - insulin, if it is not enough or tissue the body inadequately react to insulin, then the glucose indicator in the blood increases. The growth of this indicator affects smoking, stress, improper nutrition. According to the World Health Organization, the norms of blood glucose in humans were approved, on empty shop In capillary or solid venous blood, they must be within the following limits specified in the table in mmol / l:
With age, a person falls the sensitivity of tissues to insulin, as part of the receptors dies and, as a rule, the weight increases. As a result of insulin, even produced normally, with age, it is worse than tissues and sugar in the blood grows. It is also believed that when taking blood from a finger or from a vein, the result fluctuates a little, therefore the norm of glucose in venous blood is slightly overestimated, by about 12%.
The average norm of venous blood is 3.5-6.1, and from the finger - capillary 3.5-5.5. To determine the diagnosis of diabetes - a one-time blood test on sugar, it is possible to pass the analysis several times and compare them with possible symptoms Patient and other examination.
- In any case, if the level of glucose in the blood from a finger from 5.6 to 6.1 mmol / l (from vein 6.1-7) is predominant or violation of glucose tolerance
- If from veins - more than 7.0 mmol / l, from the finger more than 6.1 - therefore, it is diabetes.
- If the sugar level is below 3.5, they talk about hypoglycemia, the reasons for which can be both physiological and pathological.
Blood analysis on sugar is used and as a diagnosis of the disease, and as an assessment of the effectiveness of therapy and compensation for diabetes. At the level of glucose in the blood of an empty stomach or even during the day not more than 10 mmol / l - type 1 diabetes mellitus is considered compensated. For diabetes mellitus 2, the criteria for assessing compensation is strictly glucose in the blood in the norm of an empty stomach should not be more than 6 mmol / l, and during the day not over 8.25 mmol / l.
To translate mmol / l in mg / dl \u003d mmol / l * 18.02 \u003d mg / dl.
Signs of increased blood sugar
If the patient has the following symptoms, such as:
- Increased fatigue, weakness, headaches
- Weight loss with elevated appetite
- Dry mouth, constant thirst
- Frequent and abundant urination, especially characteristic - night urination at urination
- The appearance of mine lesions on the skin, employed ulcers, furunculus, long non-healing wounds and scratches
- General decrease in immunity, frequent colds, reduced performance
- The appearance of itching in groin, in the field of genital organs
- Reducing vision, especially in persons over 50 years old.
It may be signs increased sugar in blood. Even if a person has only some of the listed symptoms, the blood test on glucose should be passed. In case the patient is in the risk group by diabetes - hereditary location, age, obesity, pancreatic disease, etc., then, a single analysis of blood glucose when normal meaning Does not exclude the possibility of the disease, because often sugar diabetes occurs unnoticed, asymptomatic, wave-like.
When estimating the level of glucose in the blood, the norms of which are considered taking into account age, it is necessary to take into account that there are false-positive results. To confirm or refute the diagnosis of diabetes in a patient who has no signs of the disease, it is desirable to carry out additional tests on glucose tolerance, for example, when the blood sample is triggered.
The glucose tolerance test is carried out or to determine the hidden process of diabetes, or to diagnose the impaired suction syndrome and hypoglycemia. If the patient determines the violation of glucose tolerance, then in 50% of cases it leads to diabetes for 10 years, the state remains unchanged by 25%, in 25% disappears at all.
Test for determination of violation of glucose tolerance
To determine the tolerance for glucose, doctors conduct a test. This is enough effective method definitions of hidden and explicit violations of carbohydrate exchanges, various shapes Sugar diabetes. And also it allows you to clarify the diagnosis of dubious results of the usual blood test on sugar. It is especially necessary to carry out such diagnostics for the following categories of patients:
- People without signs of increased blood sugar, but with the episodic detection of sugar in the urine.
- For individuals without clinical symptoms of diabetes, but with signs of polyuria - an increase in the amount of urine per day, with the norm of an empty stomach of blood glucose.
- Increased sugar level in the urine in women during pregnancy, in patients with thyrotoxicosis, with liver diseases.
- People with signs of diabetes, but with normal content Glucose in the blood and lack of sugar in the urine.
- Persons with genetic predisposition, but without signs of increased blood sugar.
- Women and their children born with a lot of weight, more than 4 kg.
- As well as patients with retinopathy, neuropathy of not clarified origin.
To carry out a test for glucose tolerance in the examined first taking on an empty stomach capillary blood on sugar, then the patient orally drinks 75 grams of glucose, divorced in warm tea. Children dose are calculated based on the weight of 1.75 g / kg of the child's mass. The determination of glucose tolerance is carried out after 1 and 2 hours, many doctors consider the level of glycemia in the most reliable result after 1 hour of glucose intake.
The assessment of glucose tolerance in healthy people and patients with diabetes is presented in the table, in mmol / l.
Then, to determine the condition of carbohydrate exchange, calculate 2 coefficients:
- Hyperglycemic The indicator is the ratio of the level of glucose hour after the sugar load on the blood glucose on an empty stomach. The norm should not be more than 1.7.
- Hyogolcemic The indicator is the relationship of glucose in the blood two hours after glucose load on the blood test on the sugar on an empty stomach, the norm should be less than less than 1, 3.
These coefficients should be calculated necessarily, since there are cases when the patient in absolute indicators after the test on the tolerance of glucose disorders are not detected, and the value of one of these coefficients above the norm. In this case, the result is estimated as doubtful, and the person is in the risk group for the further development of diabetes.
What is glycated hemoglobin?
Since 2010, the American Diabetic Association officially recommends applying a test-glycated hemoglobin for reliable diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. This is hemoglobin, with which blood glucose is connected. It is measured in% of the total hemoglobin, the analysis is the hemoglobin level of the HBA1C. The norm is the same for adults and children.
This blood test is considered the most reliable and convenient for the patient and doctors:
- blood surrenders at any time - not necessarily an empty stomach
- more accurate and convenient way
- no use of glucose and waiting for 2 hours
- the result of this analysis does not affect the reception of drugs, the presence of a cold, viral infectionAs well as stress in the patient (stress and the presence of infection in the body can affect the usual blood test for sugar)
- it helps to determine whether diabetes has been able to clearly monitor blood sugar over the past 3 months.
The disadvantages of HBA1C analysis are:
- more expensive analysis
- with a low thyroid hormone levels - the result may be overestimated
- in patients with low hemoglobin, with anemia - the result is distorted
- not in all polyclinics there is a similar test
- it is assumed, but it has not been proven that when taking high doses of vitamin E or with an indicator of this analysis decreases
Norms of glycated hemoglobin
Many people wonder if sugar in blood 7, what does this mean? In fact, glucose indicators in normal limits indicate that the body works fully, all internal organs and systems are functioning correctly.
At the moment, a prerequisite for people over a 40-year-old is a blood test on sugar. Analyzes make it possible to judge how the exchange of carbohydrates in the human body is functioning.
If sugar is observed 7.1-7.3 units, the doctor may recommend to undergo additional diagnostic measures. This is necessary in order to confirm or disprove sugar diabetes.
It is necessary to consider what the blood sugar is 7 units, as well as glucose to 7 mmol / l? What are the indicators to consider the norm depending on the age of a person? And what to do if blood sugar level 7?
What is the norm?
Before you know that you mean the results of the analysis on sugar, which show blood glucose levels 7.2-7.8 units, you need to find out which indicators in medical practice are called normal.
It should be noted that the norm is not called a single magnitude that could come up with an adult and a child, while independence on their age. The norm varies, and its variability depends on the age group of the person, as well as, slightly, on the floor.
Nevertheless, it is assumed that blood sugar in the morning (on an empty stomach), men and women should not exceed the upper border, which is determined at a mark of 5.5 units. The lower limit is 3.3 units.
If a person is fully healthy, all internal organs and systems work fully, that is, there are no failures in the work of the body and other pathological conditions, then in the overwhelming majority, the level of sugar can be 4.5-4.6 units.
After meals, glucose has a property to rise, and there may be 8 units, both in men and women, as well as young children. And this is also normal.
Consider the blood sugar rate depending on the age:
- A child from birth to 3 months - 2.8-4.5 units.
- Until 14 years of age, blood sugar should be 3.3-5.5 units.
- From 60 to 90 years of variability of indicators 4.6-6.4 units.
Relying on such information can be concluded that about one year and up to 12 years of age, normal indicators in children regardless of gender, slightly lower adult values.
And if the child has an upper border of sugar, there will be 5.3 units, it is quite normal, corresponds to age. Along with this, for example, at a 62-year-old person, the sugar rate will be slightly exceeded.
If sugar from the vein shows 6.2 units at the age of 40 - this is a reason to think, since such a disease is not excluded as diabetes. But if the same indicators are observed after 60 years of age, then all within the normal range.
In this regard, we can conclude that if the sugar is an empty stomach 7 - it can be diabetes.
To refute or confirm a preliminary diagnosis, you must pass additional surveys.
Sugar 7, what does this mean?
Sugar level
How to find out your blood sugar? There are several options. You can use a special glucose measurement device at home - glucometer. This device allows you to identify exact indicators, and if they are high, you need to contact the doctor.
In addition, you can immediately contact medical institution, And there to pass the blood on the content of glucose in it. Before research, it is recommended not to eat at least ten o'clock, while you cannot eat alcoholic and caffean-containing drinks to the analysis.
The study provides not only accurate glucose magnitudes in the human body, but also makes it possible to learn about the state of exchange processes, see the level of deviation from normal indicators, to diagnose prediabet or diabetes first or second type.
As mentioned above, the variability of normal indicators is from 3.3 to 5.5 units per hungry stomach. If the study shows that the patient has a deviation to a larger or smaller side, then an additional analysis is assigned.
When the sugar concentration varies from 5.5 and to 6.9 units, the prediabetic state is diagnosed. Thus, it can be concluded that if the sugar is above 5.5 units, but it does not exceed 7 mmol / l, this is not yet diabetes.
If several studies of blood sugar concentrations in different days have shown that the indicators are more than 7 units, then you can safely talk about diabetes mellitus.
Etiology of high sugar
It should be noted immediately noted that one analysis on sugar does not say anything. Since the increase in blood sugar can be physiological or pathological.
In addition, a number stands out pathological reasonswhich can lead to an increase in blood sugar content. Diseases of diabetes mellitus is not the only pathology that can lead to hyperglycemic state.
The following diseases and circumstances may cause hyperglycemic condition:
- Reception of some drugs (contraceptive pills, diuretics, corticosteroids).
- Oncological education in the pancreas.
- Inflammatory processes in the body.
- Status after surgery.
- Chronic liver pathologies.
- Endocrine disorders in the body.
The results of the analysis may affect the incorrect preparation of the patient to research. For example, the patient has neglected the advice of the doctor, and attempted before analyzing. Either the eve of overreed with alcoholic beverages.
If the patient takes any drug drugs on a regular basis in connection with the accompanying diseases, he must inform the Doctor. Doctor This circumstance will definitely take into account when deciphering the results.
When the doctor suspects a patient diabetes, it proposes to make a test for glucose tolerance, as well as take an analysis of the glycated hemoglobin.
Glucose sensitivity determination
If the patient has a sugar level on an empty stomach from 6.2 to 7.5 units, then the determination of glucose sensitivity is assigned. Analysis uses sugar load that allows you to confirm or refute a preliminary conclusion.
This analysis, that is, a test for susceptibility to glucose, gives the doctor to see how much sugar is rising after the use of carbohydrates, and how fast sugar returns to the permissible limits.
As mentioned above, sugar after meals rises from any, even an absolutely healthy person, and this is normal. However, in a healthy person, the glucose concentration is gradually decreasing within 2 hours, and after it is fixed at the required level.
In turn, the diabetic was broken by the functionality of the pancreas, respectively, the process described above will be observed with failures, and the glucose after meals will decrease slightly, thereby observing a hyperglycemic state.
Test for susceptibility to glucose looks like this:
- At first, the patient takes a fence of biological fluid (blood) on an empty stomach.
- Then it is provided with a glucose load (75 grams of glucose dissolved in a warm liquid, give a sick).
- After the blood is taken after half an hour, an hour and two hours.
If a patient is two hours after such a sugar load, the blood sugar concentration is less than 7.8 units, then this suggests that everything is fine.
If the study showed that the level of sugar is above 11.1 units, the diagnosis of diabetes is made.
Sugar 6.1-7.0 units: symptoms
When the indicators of the sugar content in the human body range from 6.1 to 7.0 units, we can talk about the prediabetic state. No, it is not short diabetes, but it is already a pathological condition that requires immediate correction.
If the situation is ignored, and not to take any therapeutic actions, then a full-fledged diabetes is waiting for a patient soon with all the consequences that arise.
Many people are wondering if there are symptoms of the prediabetic state, and is it possible to detect them? In fact, every person, in particular his body, responds to a hyperglycemic state in different ways.
People who have high sensitivity to pathological changes may notice the increase in glucose in their body, even if it rises into several units. However, there are cases when sugar in the blood is increased long period of time, but the patient does not feel changes, and there is no symptomatic.
The clinical picture of the prediabetic state:
- Sleep disorder: or drowsiness. This symptom indicates a failure in the development of insulin, as a result of which the protective functions of the body are disturbed.
- Violation of visual perception. Signs that indicate a violation of vision, most often arise due to blood lungs, as it becomes a tight.
- Permanent desire to drink, abundant and frequent urination.
- Unfinished decrease or increase in body weight.
- Increased body temperature regime can be a consequence of short-term sugar drops in the human body.
The symptoms listed above most often characterize the prediabetic state. Nevertheless, medical practice shows that in the overwhelming majority of cases, patients are not at all observed negative symptoms.
It often happens that the increase in blood sugar is found quite by chance, during a preventive examination.
What if the blood sugar is above 7 units?
If blood sugar stopped at 7 units, this circumstance testifies to diabetes mellitus. When sugar from 6.5 to 7.0 units, then we can talk about the prediabetic state.
Despite the fact that two different diagnoses are put, medication therapy at the beginning of the treatment process will not differ significantly. In the other case, it is necessary to immediately begin correction of lifestyle.
Sugar diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by violation of the digestibility of glucose in the body. Most often occurs the first and second type of diabetes, but the patient may have its specific varieties (modes, Lada).
The pathology itself is not a dangerous person. However, a high level of sugar over a long period of time, negatively affects the work of internal organs and systems, which in turn leads to numerous negative consequences, including irreversible.
If blood sugar is 6.5-7.0 units, you need to take the following actions:
- Eradicate the harmful habits, it is recommended to reduce or abandon the use of alcoholic products, smoking.
- Adjust your food, add products to your diet that contain a small amount of carbohydrates.
- If the patient has overweight, then you need to lose weight. First of all, food should be not only low-carb, but also a small-calorie.
- Optimal physical exertion.
- Treatment of related pathologies.
When the patient strictly adheres to these recommendations, then with more probability, he does not have to face the negative effects of the disease.
Sugar concentration at a mark of 7 units is not a sentence, it just means that it is necessary to take "yourself in hand" and lead the right way of life.
Reduced sugar by nutrition
The main therapy of diabetes is powered, and food should include small amounts of carbohydrates in its composition. Practice shows that if you exclude harmful products, you can not only normalize your blood sugar, but also stabilize it in the required level.
First Tip: From the diet, it is necessary to exclude all products that contain easily digestible carbohydrates. In addition, it is necessary to refuse foods that have starch in their composition.
Second Council: You need to eat often and small portions. The portion should be placed in the palm. If saturation is felt, but the food remained on the plate, it is better to abandon further use.