What is a glycated hemoglobin HBA1C. What does glycated hemoglobin show? Why give diabetics to take this analysis? When should you think and pass the analysis?
Diabetes - severe disease that has become the scourge of humanity in our time. In order to prevent early complications that are inevitably developing in the course of the disease, there are ways to control blood glucose levels. One of them is the analysis on the level of glycated hemoglobin.
Glycated hemoglobin - what is it?
Glycated hemoglobin HB A1 (Alfa-1 hemoglobin) is an intention of hemoglobin associated with glucose.
What does the analysis need
Metabolic imbalance. In the case of metabolic dermatitis. If the blood glucose level is fully elevated: nausea and pain in the stomach, disturbances of consciousness often with the smell of acetone smell of breathing. After sugar, anxiety, cold sweat and fast heart rhythm. . The following days with the specified complaints.
Immediately drowsiness, drowsiness or other signs of metabolic dermatitis. Glucose and glucose. Glucose is our main source of energy and is mainly obtained by digesting carbohydrates from food. This is the smallest carbohydrate unit, that is, glucose molecules that are transported by blood and, for example, for metabolic processes are required, blood sugar says.
Glucose is always present in the blood, in a larger or smaller quantity. Hemoglobin molecules gradually and irreversibly connect with it.
The life of the erythrocytes (they are "capacity" for hemoglobin) is about 120-125 days, so blood test glycated hemoglobin Demonstrates blood sugar levels over the past four months. The higher this indicator, the greater the likelihood of the development of diabetes or its decompensation.
HBA1C Glikated HB Norm in Blood
Glucose in the form of glucose in the blood is transported in all cells of the body through blood to ensure their necessary energy. If available more glucose In the blood than the cells are required, the excess glucose in the blood is stored as glucose, especially in the liver and adipose tissue, as energy reserves. If necessary, the margin is then distributed evenly into the blood.
Insulin. In order for glucose in blood penetrated the cells, the "lock" is required. This is an insulin of a metabolic hormone, which allows blood glucose to pass from the blood flow to the inside of the cell. At the same time, insulin inhibits the destruction of glucose reserves in the liver. Both effects reduce blood sugar levels.
This analysis is considered to be the most reliable. Periodic control of glucose in the blood does not show the overall picture of the patient's state. By the level of glycated hemoglobin You can judge the threat of complications or, on the contrary, about careful control of the disease by the patient himself.
Insulin is formed by beta cells, cell groups on the Islands of the Langerhans of the pancreas. If the feedback between the release of insulin and the flow of glucose in the blood functions smoothly, the amount of glucose in the blood fluctuate very little. If beta cells no longer produce sufficient insulin or not, or if the released insulin is insufficient, the blood glucose level increases. At the same time, however, glucose is absent as an energy supplier in the cells of the body.
Analysis value for people with diabetes mellitus
Stripes for urine analysis. Restrictions on blood glucose: below the value of 60 - hypoglycemia, above 140 - hypersgmentation. From the concentration of glucose in the blood of 180 people exceeds the renal threshold, i.e. The kidneys can no longer be absorbed by sugar, released in the urine, and return it to blood. Consequently, glucose is contained in the urine. Glucosuria is detected by a simple dough with stripes for urine analysis.
Why and who needs control of hemoglobin levels?
It is needed not only to diabetics. From time to time its level needs to be checked and healthy people, especially those who have a tendency to elevated arterial pressure and completeness. Both may be a harbinger of diabetes.
The analysis will show a threat or the presence of diabetes on the very early stages. Recommended regular control:
Impact of excessively sugars. If the blood glucose level increases significantly, the kidneys can no longer return sugar from the primary urine back into the blood. The result is the removal of glucose with urine, which also leads to an increase in the amount of urine. Despite the fact that patients drink a lot to compensate for the loss of liquid, typical drying phenomena appear, such as wrinkled, cold, dry skin and coarse dry tongue. In addition, violations are observed due to fluid loss in the eye lens and eyeball.
In some cases, the brain also limits its ministry - and the result of life, threatening life, reaches a diabetic coma. However, the long-term effects of increased blood glucose levels are much more dramatic than short-term: diabetes, as a turbocharger, accelerates all the processes of arteriosclerosis with serious consequences, such as turbidity, blindness, renal failure. These damage threatens to all diabetics - especially diabetic vulnerable, which are subjected to ill-treatment with blood glucose levels, which suffer or suffer from other metabolic disorders.
- for all people over 45 years old - 1 time in 3 years, if the first analysis showed a level of 5-6% (norm);
- those who have a genetic predisposition to diabetes (patients relatives);
- with a sedentary lifestyle;
- with glucose tolerance;
- women who during pregnancy transferred gestational diabetes;
- women who gave birth to a child with a weight of more than 4 kg;
- in the syndrome of polycystic ovary (SEC);
- patients with diabetes minimum 1 time in 6 months.
What is the optimal norm in women?
The norm of glycohemoglobin is the same for all healthy people - Women, men and children. It must be in the range of 4.5-6%, which corresponds to the blood glucose level of 5.7-7 mmol. If the indicator is above 6%, it means that the risk of developing diabetes is great. The doctor conducts additional research and prescribes a corrective low-carbon diet.
Glicked hemoglobin in children
In addition, it was shown that the disease increases the risk of multiple species of cancer - first of all, the risk of developing cancer of the pancreas and hepatocellular cancer increases. Absolute insulin deficiency with type 1 diabetes. With type 1 diabetes, the beta cells producing insulin occurs, which leads to absolute insulin insufficiency. The reason is an autoimmune reaction in which the immune system forms antibodies against falsely recognized as " foreign bodies" Why the immune system is directed against body structures, has not yet been clarified.
The indicator of the glycated hemoglobin can be reduced due to:
- frequent or recent bleeding;
- anemia;
- frequent hypoglycemia.
Does the analysis need for pregnancy? The feasibility of holding a test on glycohemoglobin during pregnancy defines a doctor.
 Sugar diabetes develops, as a rule, in the third trimester.
Sugar diabetes develops, as a rule, in the third trimester.
Advantages and disadvantages of laboratory research
It is very likely that environmental factors and, presumably, viral infectionsFounded on hereditary predisposition cause disease. How quickly, the destruction of beta cells attracts complete cessation of insulin production in itself, differs from the patient to the patient: in general, there is an initially residual function, but all beta cells die sooner or later, and insulin in the body is necessary for life supplied from the outside insulin replacement . Reducing the insulin value in the stimulation test may already be indicated on the prediable of the 1st type before the start of type 1 diabetes.
Usually, other tests and analyzes are used to identify it - measurement of the level of sugar on an empty stomach, blood test after eating and at ridual time, a test for glucose tolerance.
High sugar adversely affects the development of the fetus and can cause complications and difficulties in childbirth. In such a woman, the fruit has large sizes - up to 4-4.5 kg.
In the meantime, risk groups can also be identified using newborn genetic surveys. Relative insulin deficiency with type 2 diabetes. Unlike type 1 diabetes is type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, muscle, adipose tissue and liver, starting point - all these body structures are not suspicious to insulin and, therefore, no longer can use sugar supply of blood sugar. As a result, sugar is no longer transferred from blood into the cells and, therefore, the blood glucose level increases.
The risk factor may be the presence of a SEC, similar diagnosis (diabetes) during previous pregnancy, age over 35 years old, obesity.
The rate of the substance in the body in children
In a healthy child normal indicator Glicated hemoglobin such as in adults - 4.5-6%. If the child is diagnosed diabetes, regular dimensions are required, have this in mind.
In addition to insulin resistance, insulin is a violation of insulin secretion - this is done especially after eating with a delay - which further increases the concentration of glucose in the blood. First, the body manages to maintain blood glucose level as normal, increasing insulin production. If the insulin levels, but constantly high and the cell is constantly offered too much glucose, "weaken" insulin receptors, causing insulin resistance strengthened; Beta cells are also "paralyzed", as a result of which the production of insulin is reduced.
 For children, a rigid minimum rate indicator is installed in the presence of a disease: without the risk of severe complications - 6.5%, which corresponds to the blood glucose level of 7.2 mmol; In the presence of complications and risk of the development of hypoglemia - 7% - 8.2 mmol. With this level, diabetes is considered compensated.
For children, a rigid minimum rate indicator is installed in the presence of a disease: without the risk of severe complications - 6.5%, which corresponds to the blood glucose level of 7.2 mmol; In the presence of complications and risk of the development of hypoglemia - 7% - 8.2 mmol. With this level, diabetes is considered compensated.
Effect on indicators of fatal hemoglobin tests
There is a relative insulin deficiency, and the blood glucose level is currently constantly increasing - type 2 diabetes is noticeable. From this relative deficiency of insulin over time, absolute insulinant failure is developing. This process crawls for many years, and people do not know about anything. Thus, it was found that the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is most often found within a medical examination or blood test.
In order to clarify the diabetes a matter of a doctor in the morning of glucose in the blood of an empty stomach, obtained from the blood of a finger or vein hands is used in addition to the physical examination. While diabetes type 1 type is often significantly increased, and the diagnosis can be made quickly, the patient of the second type can still be close to the normal range, and the dough repetition is not clear.
Teenagers, suffering from diabetes, can somewhat "fake" the overall picture of the course of the disease, showing good results of the Touchscreen sugar (on an empty stomach morning sugar), refusing some products on the eve of the analysis. In this case, parents must necessarily insist that the child makes the analysis on the glycated hemoglobin.
Causes of overestimated and understated indicators
Further tests are then carried out: the hospital is preparing a profile of a day-level glucose in the blood, for which the level of glucose in the blood is determined by sober, shortly before and two hours after each meal intake. Measured after the food of the postprandial value of glucose in the blood always almost increased in explicit diabetes of type 2 as a result of insulin secretion violated.
The oral test for glucose tolerance can also be carried out in an outpatient practice. For this purpose, the sober level of blood sugar is first determined in the morning after 12 hours of nutrition, and then drink a sugar solution of glucose and water. Two hours later, the doctor again determines the blood glucose concentration.
As for small children, suffering from this severe ailment, they must be constantly under such control. With good sugar compensation, life expectancy may be no less than a healthy person.
Type 1 diabetes is also called young diabetes, that is, those who fell ill under the age of 30. Therefore, these norms fully relate to young people suffering from this ailment.
In the case of type 1 diabetes, the autoantibodies can often be detected in the blood as a sign of an autoimmune process both against the components of islet cells and against insulin. In case of success, a nationwide screening program is planned. The usual measurement of the sugar content in the urine is no longer recommended as part of the initial diagnosis, it is too inacciable.
Lab diagnostics for long-term diabetes care. This value is a change in metabolism over the past 8-10 weeks and is therefore called "blood glucose memory." It is measured how many percent of the hemoglobin of red blood is associated with glucose in the blood - the higher the level of glucose in the blood, the higher the "saccharification" of hemoglobin. That is, with a value exceeding 6, 5%, type 2 diabetes is present at a value below 5, 7 of type 1. Diabetes with a value from 5, 7 to 6, 5 percent experts continue to appear for the definition of sugar in sobriety.
Indicators in patients with diabetes mellitus 2
Indicators of blood sugar levels have a very thin line between the norm and abnormal. For diabetics of type 2, especially in old age and, when applying substitution therapy (insulin), with a decrease in blood sugar levels, it would seem normal numbers - 6.5-7 mmol - very high risk of hypoglycemia.
In the fructosamine test, the protein content is determined, in particular albumin, on which glucose molecules in the blood are stored. This allows us to talk about control of blood glucose in the last two weeks. The purpose of treating diabetes is normal control of blood glucose levels for restoring well-being and performance, as well as preventing long-term damage. While type 1 diabetes, in addition to the corresponding diet, means lifelong injection of insulin, this is only necessary when type 2 diabetes, if the beta cells themselves do not produce sufficient insulin.
 This reduction can cause severe consequences. Especially it is dangerous for older people. Therefore, it is simply impossible to reduce sugar to the indicators of a healthy person. It should be a little higher.
This reduction can cause severe consequences. Especially it is dangerous for older people. Therefore, it is simply impossible to reduce sugar to the indicators of a healthy person. It should be a little higher.
For patients with diabetes 2 type, the rate of indicators is determined depending on the age, the tendency to hypoglycemia and the availability of complications.
Thus, the basis of each type 2 diabetic therapy is a diet favorable for diabetes, regular exercise and reduction of excess weight. Basic building blocks of diabetic therapy. Both diabetic and diabetic diets play a decisive role both with type 1 diabetes and in type 2.
Treatment of type 1 diabetes. For diabetes type 1, insulin therapy is always required. If possible, intensive insulin therapy is used: on the one hand, it provides high degree Flexibility in terms of deadlines, the number of dishes and determining carbohydrate levels.
Type 2 diabetes develops in people of middle and older people. The norm for people in old age: without the risk of severe complications - 7.5% is the level of sugar 9.4 mmol, if there are complications of 8% - 10.2 mmol.
For middle-aged people, these indicators are 7% (8.6 mmol) and 7.5% (9.4 mmol), respectively.
Diagnostics of type 2 diabetes using analysis on glycated hemoglobin. The blood test on the glycated hemoglobin is very effective for the early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially its hidden form - prediabet.
Secondary prophylaxis. A new one is an opportunity to slow down the decline in insulin in the body at an early stage of the disease with immunotherapy. Currently, three approaches are being studied. Anti-inflammatory approach to stop inflammation in the pancreas, so the destruction of beta cells producing insulin in the pancreas ceases. Antigen-specific approach: vaccination in order to reduce immune tolerance to antigen antigen.
- Immuno-target approach to the attack of destructive immune cells.
- Currently, vaccines are being developed.
It reveals tolerance to glucose. This means that the body ceases to fully react to insulin And part of glucose is not utilized by cells, but remains in the blood. Such. early diagnosis allows you to adjust the condition using a diet and physical Loadswithout resorting to sugar preparations.
Analysis value for people with diabetes mellitus
Diabetics with experience, carefully controlling and regulating sugar levels with a glucometter asks: "Why do I need it?".
 Indicators may be excellent, diabetes seem to be compensated. The fact is that it can not know this.
Indicators may be excellent, diabetes seem to be compensated. The fact is that it can not know this.
An emission indicator on an empty stomach may be within the normal range - 6.5-7 mmol. And after eating, it will rise to 8.5-9 mmol, and this is already a lot.
It is such a hesitation of sugar within a day and shows the level of the glycated hemoglobin. This is the average. Perhaps, according to the results of the analysis, the doctor will decide to change the dose of insulin or the sugar.
There are sick, especially this applies to those who have type 2 diabetes, which believe that 2-3 measurements of the level of sugar level on an empty stomach per month.
Some do not even use a glucometer. For them, the regular dimension of the glycated hemoglobin is necessary to avoid the development of complications. And they are no less severe than with type 1 diabetes.
Where and how do you need to donate blood?
 Today, the analysis on glycated hemoglobin can be made in private clinics and municipal medical institutions.
Today, the analysis on glycated hemoglobin can be made in private clinics and municipal medical institutions.
Within oMS programs And for the disabled, this analysis is free. If the coupons for free analysis do not give or miss them, in private clinic You will make it even without direction. Approximate cost from 500 rubles.
You can donate analysis on glycohemoglobin at any time, even after meals. Does not affect the result of the analysis and condition of a person - stress, colds , sports, alcohol intake. Blood fence is produced at any time of the day from Vienna. Prepared analysis for 3-4 days.
They say who is warned, he is armed. Take care to avoid such a serious disease, like diabetes or keep it under constant control.
Glycated hemoglobin plays an important role in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Thanks to him, detect the disease in the early stages of its development. This makes it possible to start treatment in a timely manner.
The level of this indicator is monitored to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. But few know what it is.
Get acquainted with glycated hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a component of erythrocytes - blood taurus responsible for the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide. When sugar penetrates over the erythrocyte membrane, the reaction occurs. Amino acids and sugar interact. The result of this reaction is the glycated hemoglobin.
Inside erythrocytes, hemoglobin is stable, so the level of this indicator is constant for quite a long time (up to 120 days). For 4 months, red blood cells perform their work. After this period, they are destroyed in the red spleen pulp. Together with them, the decay process undergo glycohemoglobin and its free form. After that, bilirubin (the final product of the decay of hemoglobin) and glucose are not associated.
The glycosylated form is an important indicator in patients with diabetes, and in healthy people. Difference only in concentration.
What role plays in the diagnosis
There are several forms of glycated hemoglobin:
- HBA1A;
- HBA1B;
- HBA1C.
In medical practice, the last type appears most often. The correctness of the proceedings carbohydrate exchange - That's what the glycated hemoglobin shows. Its concentration will be high if the sugar level is greater than the norm.
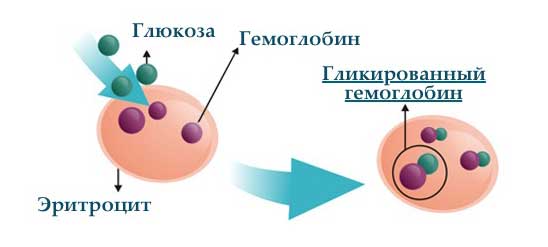
The HBA1C value is measured as a percentage. An indicator is calculated as a percentage of the total hemoglobin volume.
The blood test on the glycated hemoglobin is needed in suspected of the presence of diabetes and tracking the body's reaction for treatment from this disease. It is very accurate. In a percentage, you can judge the blood sugar over the past 3 months.
Endocrinologists successfully use this indicator when diagnosing hidden forms of diabetes, when there are no obvious symptoms of the disease.
This indicator is used as a marker that determines people entering the risk area for the development of complications in diabetes. The table shows the indicators for age categories that specialists are focused.
Standard analyzes are significantly losing on its background. Analysis on HBA1C is more informative and convenient.
Norm for women
Each woman should pay attention to the level of glycated hemoglobin in the body. Significant deviations from accepted norms (table below) - indicates the following failures:
- Diabetes of various shapes.
- Lack of iron.
- Renal failure.
- Weak vessel walls.
- The consequences of surgical intervention.
The norm in women should be within these values:
If the inconsistency was found to the specified indicators, it is necessary to undergo a survey, which will help identify the reasons for changing the level of glucose.
Regulations for men
In men, this indicator is higher than women. The rate of age is indicated in the table:
Unlike women, strong sex representatives, this study must be held regularly. This is especially true of men older than 40 years.
A quick weight gain may mean that a sugar diabetes has started to develop. Appeal to a specialist at the first symptoms helps to diagnose the disease in the early stages, which means timely and successful treatment.
Children's norms
In a healthy child, the level of "sugar compound" is equal to the indicators of an adult: 4.5-6%. If B. childhood Diabetes was diagnosed, it contains strict control of compliance with standard indicators. So, the norm in children suffering from this disease without the risk of complications is 6.5% (7.2 mmol / l glucose). The indicator at the level of 7% indicates the possibility of the development of hypoglycemia.
In teenage-diabetics, the overall picture of the disease may be hidden. This option is possible if the analysis they passed on an empty stomach.
Norms for pregnant women
During pregnancy female organism He undergives many changes. This affects both glucose levels. Therefore, the norm during pregnancy a woman is somewhat different than in its usual condition:
- At the old age, it is 6.5%.
- The average corresponds to the indicator of 7%.
- "Elderly" pregnant women should be at least 7.5%.
Glycated hemoglobin, the norm during pregnancy should be checked every 1.5 months. Since on this analysis determine how the future kid develops and feels. Deviations from standards are negatively reflected in the state of not only "pupportier", but also his moms:
- The indicator below indicates an insufficient level of iron and can lead to braking the development of the fetus. It is necessary to revise the lifestyle, there are more seasonal fruits and vegetables.
- The high level of "sugar" hemoglobin suggests that the kid is likely to be large (from 4 kg). So, childbirth will be heavy.
In any case, to properly enter adjustments, you must consult with your doctor.
Standards for patients with diabetes
Analysis on glycated hemoglobin is given in diagnosis when the patient already knows about his disease. Purpose of the study:
- Best control of blood glucose levels.
- Correction of dosage of sugar drugs.
Norma with diabetes mellitus is approximately 8%. Maintaining such high level due to addiction of the body. If the indicator decreases sharply, it can provoke the development of the hypoglycemic state. This is especially true of people aged. The younger generation needs to strive for a level of 6.5%, this will warn the appearance of complications.
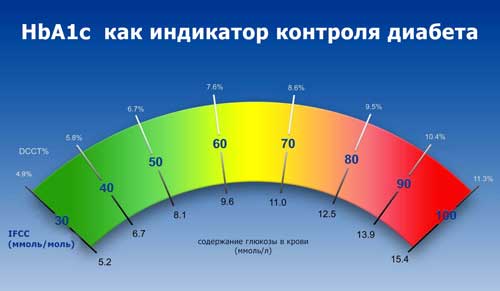
If the level is more than 8%, it means that the assigned therapy is ineffective and requires changes. A person with an indicator from 12% requires urgent hospitalization.
But at the same time, it is necessary to remember that a sharp decrease in the level of glycated hemoglobin is dangerous. It can provoke the development of complications in small eye and kidney vessels. The right is considered to be a decline of 1-1.5% per year.
Factors contributing to increasing
Increasing the level of this hemoglobin is possible not only when the risk of sugar diabetes occurs. It also contributes to other states of the human body:
- High content of fetal hemoglobin in infants. After HBF displays the baby, the HBA1C is equal with a norm of a healthy person.
- Iron deficiency in the body contributes to an increase in the concentration of HBA1.
- After removing the spleen (the organ where red blood cells break).
These processes provoke an increase in the level of glycated hemoglobin, but over time it comes to normal.
Factors contributing to a decrease
If the level of "sugar" hemoglobin is lowered, this means that a person is:
- The blood loss, as a result of which the level of hemoglobin decreased.
- It was blood transfusion, and with it there was a dilution of the HBA1C concentration.
- Malokroviya, that is, the duration of the existence of erythrocytes is reduced.
- Reducing glucose content.
There are defective forms of hemoglobin, and they can distort the results of the tests. At level below, 4% may manifest symptoms of hypoglycemia. One of the reasons for this phenomenon may be insulin (pancreatic tumor), at which the level of insulin is elevated.
Low HBA1C concentration can be called:

- Overdose of saccharifying tablets.
- Low carb diet.
- Insufficiency of adrenal glands.
- Genetic diseases.
Simple ways to stabilize the indicator
The target level of glycated hemoglobin can be achieved by performing standard recommendations:
- Proper nutrition.
- Stress management.
- Regular sports.
Right ration
Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants contribute to stabilization of sugar concentration. Therefore, it is necessary to use them more into food. Special attention should be paid to bananas and bean.
Low-calorie milk and yogurt will help not only lose weight, but also enrich the body by calcium and vitamins of the group D. These products are especially necessary for diabetics of the second type. They also need to increase the consumption of fatty fish (tuna, mackerel, salmon) and nuts. This measure will help reduce body resistance to insulin..
As a refueling for products it is worth using cinnamon. The required rate of its consumption is 1/2 teaspoon. It can be added to tea, sprinkle fruits, meat and vegetables with it.
It is necessary to reduce the consumption of fatty and high-calorie food to a minimum. Sweets and snacks lead to an increase in sugar levels.
Regular physical exertion
Daily exercise should take at least 30 minutes a day, as it is possible to lower the level of the glycated indicator by improving the work of the heart and reduce weight.

It is necessary to combine aerobic (walking, swimming) and anaerobic (strength training) exercise. It is important to try to move more during the day, giving preference to stairs and walks on foot.
The more active man, the level of hemoglobin A1C is closer to normal.
Caring for the nervous system
Specialists argue that stress and concern have a negative impact on the heart, and this, in turn, leads to an increase in the level of glycated hemoglobin. Therefore, it is advisable to perform respiratory gymnastics, engage in yoga and meditation.
If possible, it is necessary to gradually get rid of habits causing stress. Take all prescribed medicines in a timely manner.
How to prepare for the surrender
The blood test on the glycated hemoglobin is recommended in the morning. He does not require special preparation. The only condition: before visiting the laboratory, do not perform any physical exertion.
The accuracy of the results does not affect:
- How tightly patient was on the day before.
- Whether man has alcoholic beverages.
- Transferred stress.
- The presence of viral and colds.
But there are temporary limitations. Here is a small list of recommendations, how to take the analysis:
- If a person has no symptoms of diabetes, then you need to visit the laboratory once every 3 years (the norm for a healthy person).
- If earlier the result was 5.7-6.4%, then it is necessary to donate blood annually.
- If the indicator above is 7%, it means that the test passes 1 time in 6 months.
- People with poorly controlled sugar levels are examined every 3 months.
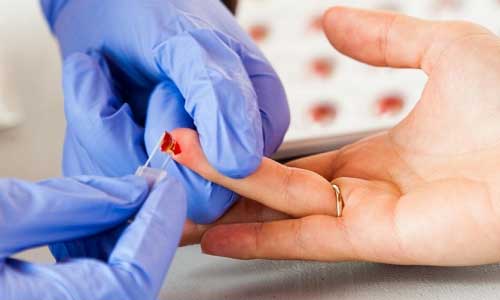
Blood fence is made from vein or finger. It all depends on the choice of the analyzer. The results will be ready the next day. The following factors can distort data:
- The patient suffers to anemia.
- The presence of thyroid disease.
- Reception of vitamins C and E.
Causes of overestimated and understated indicators
To accurately determine the cause of the overestimated level, which showed the analysis, only after a comprehensive examination. Increased blood sugar, which shows glycated hemoglobin, is not always the only reason. Other prerequisites are possible for obtaining such a result:
- Splenectomy - removal of the spleen.
- Renal failure.
- Elevated level Fetal hemoglobin.
- Reduced content Iron in the body.
The low level of "sugar hemoglobin" is also dangerous as its elevated concentration. Although it rarely happens, the reasons for this phenomenon still should be known.

If the analysis showed 4% below, it is a bad sign. Strong fatigue, vision disorder, drowsiness, fainting, irritability - all this symptoms show that the glycated hemoglobin fell. Factors that provoked it may be:
- Recent blood loss in large volumes.
- Pathologies that caused the premature destruction of red blood cells.
- Hepatic and renal failure.
- Failure to work the pancreas.
- Hypoglycemia.
HBA1C analysis makes it possible to detect diabetes in the early stages, control its development and even determine the correctness of the development has not yet born.
Another advantage of this technique is the stability of the indicators: it is possible to donate blood in the presence of colds and viral diseases, After eating food and an empty stomach. The data obtained as a result of this study is accurate and informative (a period of 3 months is traced). The only negative is that not in each laboratory is carried out on the glycated hemoglobin.



















