Rules for administering insulin with a syringe. What is insulin? Technique for administering insulin using a pen-syringe.
The good news is that insulin shots can be given absolutely painlessly. You just need to master the correct technique. subcutaneous injection... You may have been treating diabetes with insulin for years, and each time you get the shots hurt you. So, this is only due to the fact that you are injecting the wrong way. Study what is written below, then practice - and you will never again worry about insulin injections.
What is it and why should you pay attention to this topic when it comes to diabetes control? - Hypoglycemia literally means low level blood glucose. Hypoglycemia usually develops too quickly and is very often associated with terrible experiences on the part of patients. In fact, hypoglycemia is a life-threatening condition and, if not responded appropriately, can lead to a number of side effects. Many people with diabetes who have experienced hypoglycemia do not want it to happen again, so they practice the so-called Preventive Nutrition, which leads to poor diabetes control and a tendency to high blood glucose levels.

Patients with type 2 diabetes who are not yet receiving insulin injections spend many years in fear of becoming insulin dependent and experiencing pain from the injections. Many diabetics literally stay awake at night because of this. Master the technique of painless insulin delivery and make sure there is really nothing to worry about.
The fear of new hypoglycemia is one of the main obstacles to achieving good diabetes control, especially in patients on insulin therapy. Approximately 30% of young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus have had at least one hypoglycemic coma in their lifetime, with the incidence of severe hypoglycemia being about 10% per year. Hyperglycemia or high level blood glucose causes dry mouth, thirst, water intake and frequent urination but occur slowly and gradually, especially in the elderly, and are not associated with horrible experiences.
Learning to inject insulin is very important for anyone with type 2 diabetes. This should be done even if you are good at controlling your blood sugar without insulin, exercise, and pills. Nevertheless, it will be useful for you to study this article and practice in advance by giving yourself injections of sterile saline with an insulin syringe.
Both extreme conditions are equally unfavorable for the body, so a person with diabetes should strive to maintain the recommended blood sugar levels within certain limits. Due to the recommendations of treatment in recent years, these limits are individual and depend on the age of the patient, the duration diabetic complications and comorbidities, life expectancy, and last but not least the patient's motivation and desire for adherence to treatment. To achieve these goals, it is important to educate people with diabetes about daily exercise and drug therapy, and, just as important, to use modern medications that have a significantly reduced risk of hypoglycemia. - What could be the cause of hypoglycemia?
What is it for? Because when you have an infectious disease - a cold, dental caries, inflammation in the kidneys or joints - then blood sugar rises sharply, and insulin cannot be avoided. Infectious diseases greatly enhance, that is, reduce the sensitivity of cells to insulin. Normally, a person with type 2 diabetes may have enough insulin from their pancreas to maintain normal sugar in blood. But during infectious disease own insulin may not be sufficient for this purpose.
Additional comorbidities that cause renal failure lead to a delay in the clearance of antidiabetic drugs, resulting in relatively high doses leading to hypoglycemia. Alcohol can also cause hypoglycemia because its toxic effect on the liver leads to suppression of liver blood glucose uptake. Paradoxically, the most severe and prolonged hypoglycemia does not result from insulin therapy, but from sulfonylurea treatment in patients with impaired renal and hepatic function.

As you know, insulin is produced by beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes starts when most of the beta cells die for various reasons. With type 2 diabetes, we try to reduce the stress on them and thus keep as many of them alive as possible. Two common reasons death of beta cells - excessive stress, as well as glucose toxicity, that is, they are killed elevated level blood glucose.
Physical activity - sports, dancing, farming, house cleaning, etc. leads to increased use of glucose from the muscles and can provoke hypoglycemia. Anomaly in function thyroid gland and the pituitary gland can also occur with hypoglycemia. It is always very important to investigate the causes of hypoglycemia in order to counteract and therefore avoid future incidents. There are times when hypoglycemia may remain unrecognized by the patient. In practice, we use patient-filled questionnaires that tell us if we should look for episodes of hypoglycemia.
During an infectious disease, insulin resistance increases. As a result, beta cells are required to synthesize even more insulin. We remember that in type 2 diabetes, they are already initially weakened and even in a normal situation they work to the limit of their capabilities. Against the background of the fight against infection, the load on beta cells becomes prohibitive. Also, blood sugar rises, and glucose toxicity has a toxic effect on them. An infectious disease can kill a significant proportion of beta cells and worsen the course of type 2 diabetes. At its worst, type 2 diabetes will turn into type 1 diabetes.
Therefore, our recommendation, when patients have hypoglycemia, measure their blood sugar and consult their doctor! - How does hypoglycemia occur? How does the patient feel about hypoglycemia? - In most cases, hypoglycemia occurs like a "storm" for the patient. When the blood sugar level drops, the so-called adrenergic phase, and the person with diabetes feels palpitations, sweating, trembling, severe hunger. If sugar continues to fall, the neuroglycotic phase develops with symptoms of dizziness, decreased concentration, fatigue, headache, irritability, blurred vision, and if not taken, impaired consciousness occurs, convulsions and delirium may occur.
What is described in the previous paragraph happens quite often. If type 2 diabetes turns into type 1 diabetes, you will have to take at least 5 shots of insulin per day for life. Not to mention, the risk of disability as a result of complications from diabetes is increasing and life expectancy is decreasing. To insure against troubles, during infectious diseases it is very desirable to temporarily inject insulin. To do this, you need to master the technique of painless injections in advance, practice and be ready to apply it when needed.
In the final phase, the patient falls into a coma due to energy starvation of the brain structures. It is not necessary for all people with diabetes to consistently adhere to all the symptoms described, and this depends on the rate of decrease in blood sugar levels and the body's ability to adapt. With long-term diabetes and associated complications, diabetic neuropathy with the involvement of autonomic nervous system may lose the feeling of hypoglycemia, and the onset of coma and coma develops within a few minutes. - What do we do with hypoglycemia? - All patients with diabetes and, if possible, their relatives should be trained to cope with hypoglycemia.
How to give injections painlessly
You need to train in the technique of painless insulin injection by making yourself injections of sterile saline with an insulin syringe. If the doctor knows the technique of painless subcutaneous injections, he will be able to show it to you. If not, then you can learn on your own. Insulin is usually injected subcutaneously, that is, into the layer of fatty tissue under the skin. Areas of the human body that contain the most fatty tissue are shown in the figure below.
Due to the life-threatening nature of hypoglycemia, immediate action must be taken to act very quickly. We train our patients with mild to moderate hypoglycemia IMMEDIATELY to take 15 g of sugar contained in: - 1 tablespoon of sugar, 3 sachets of 5 g of sugar or 5 sachets for 3 years.
Chocolate is not suitable for controlling hypoglycemia because the fat it contains slows down the absorption of sugar and raises blood glucose levels. If, 15 minutes after taking 15 grams of sugar, the signs of hypoglycemia have not died out, you should take another 15 grams of sugar. If the next 1 hour after hypoglycemia is not the main meal, the person with diabetes should take additional carbohydrates - for example, a slice of bread, 1 apple, 1 banana, etc. we advise our patients to inform their relatives, relatives, friends and colleagues about diabetes and with a diabetes card with brief information.
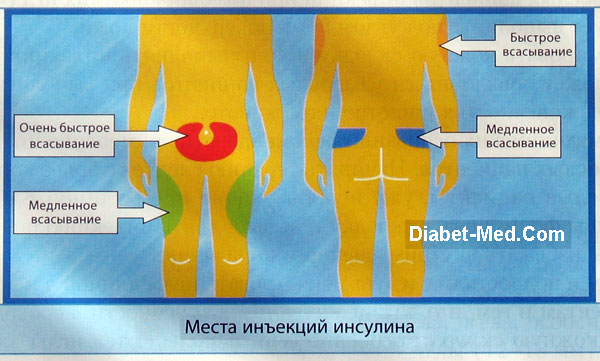
Now practice in these areas to take the skin in a fold with the thumb and forefinger of both hands.
People usually do not have enough subcutaneous fat on their hands and feet. If you give insulin injections there, then they are obtained not subcutaneously, but intramuscularly. As a result, insulin acts much faster and more unpredictably. Also, intramuscular injections are really painful. Therefore, it is not advisable to give insulin injections to the arms and legs.
If there is a person who is sick with hypoglycemia, the surrounding area must burn the honey on the inside of the cheek, resulting in an increase in blood sugar. After recovering consciousness, the patient needs to receive carbohydrate food.
What should be the behavioral and lifestyle changes for people with diabetes to achieve good blood sugar control? - Achieving good blood sugar control ensures that diabetes does not damage target organs and does not develop micro- and macrovascular complications diabetes mellitus... The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in humans leads to a complete change in his lifestyle if he wants to control his disease. Depending on the type of diabetes, the recommendations have some peculiarities, but are mostly similar.
If a healthcare professional teaches you the technique of painless administration of insulin, then first he will show himself how easy it is to make such injections, and that no pain arises at the same time. Then he asks you to practice. To do this, you can use an empty insulin syringe or about 5 U filled with saline.
Adherence to proper medication and regular self-monitoring of blood sugar will reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. In type 1 diabetes mellitus, in which treatment is usually in boosted insulin preparations, self-monitoring of blood glucose is recommended, instructions to change the dose, suit the food and daily life.
Doctor Bakalov is receiving at the endocrinology clinic at the Aleksandrovsk University Hospital. An insulin pump is a small electronic device, about the size of a mobile phone, that can be easily fitted on the waistband of your trousers, put in your pocket, or even attached to your bra.
You will inject with one hand. And now you need to take the skin into a fold in the area where you will inject with the other hand. With your fingers, grab only the subcutaneous tissue, as shown in the figure.
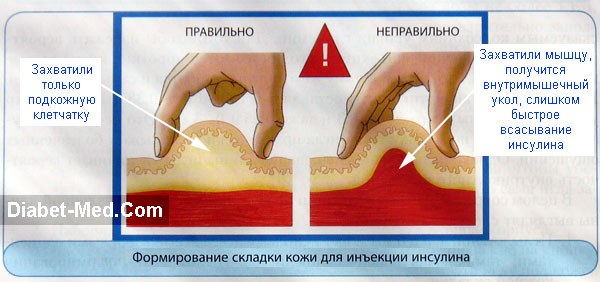
In this case, you do not need to press too much and bruise yourself. You should be comfortable holding the fold of the skin. If you have a solid layer of fat around your waist, go in there. If not, then use a different area from those shown in the picture above.
An insulin pump can help to mimic insulin secretion from a healthy pancreas much more accurately: with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion, it is necessary to replace the introduction of frequent injections of insulin. An insulin pump day and night gives your body the exact amount of fast-acting insulin that meets your body's needs.
Basal rate: Setting the basal rate of a small amount of insulin that the body, thus, continuous dosing of basal insulin secretion mimics a healthy pancreas. The basal insulin rate is determined by your healthcare provider based on your personal needs. The Pill Calculator helps you calculate your bolus dose using parameters that have been previously determined by your doctor and based on your specific needs. What are the benefits of insulin pump therapy and how can these treatments help you achieve better blood glucose control. Insulin pumps offer a bolus calculator function. ... From a clinical point of view, provides an insulin pump compared to a booster regimen of the following benefits.
Almost everyone has enough subcutaneous fat on their buttocks to inject insulin there without the need to form a fold of skin. Just feel for the fat under your skin and inject into it.
Hold the syringe like a dart dart thumb, and two or three other fingers. Now comes the most important thing. For the injection of insulin to be painless, it must be very quick. Learn to thrust like throwing a dart while playing darts. This is the painless injection technique. Once you master it, you will not feel at all how the needle of the insulin syringe penetrates the skin.
Insulin pump system: how is insulin injected into the body?
In this way, the need for dosage adjustments can be more effectively managed, especially after meals and at night, and thus contribute to better blood glucose control. The pump also provides a temporary basal rate function, with which it proportionally decreases or increases the basal rate, for example, during physical exercise or illness. The measured glucose values from the Concentration Meter are automatically sent to the pump, making the Master® Bolus Calculator easier to use. This data, as well as information about dosing of the insulin pump, is stored in a digital diary. Insulin is dosed from the reservoir via an infusion.
Touching the skin with the tip of the needle and then pressing it in is a mistaken technique that causes unnecessary pain. You don't need to inject insulin this way, even if you were taught it in diabetes school. Form a skin fold and inject, depending on how long the syringe needle is, as shown in the figure. Obviously the newer short needle syringes are the most convenient.
A small and flexible cannula of an infusion set, which delivers insulin into the subcutaneous tissue, is inserted using a stylet. The infusion set is connected to the reservoir by tubing that can be disconnected at any time and reconnected at the puncture point.
Insulin pump accessories
This can be useful if you want to swim, shower or exercise.
This is for me to pump up the right solution
Many people with type diabetes do not understand what benefits they should bring from insulin pump therapy. Talk to your healthcare provider about your insulin pump and if it's right for you.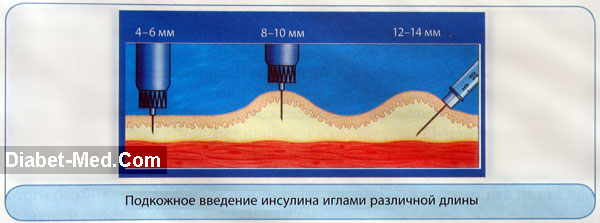
You need to start accelerating the syringe about 10 cm before the target, so that it has time to pick up speed and the needle instantly penetrates the skin. The correct injection of insulin is like throwing a dart while playing darts, but just do not let the syringe out of your fingers, do not let it fly away. You accelerate the syringe by moving your entire arm, including your forearm. And only at the very end, the wrist also moves, directing the tip of the syringe exactly to the specified area of the skin. When the needle has penetrated the skin, push the plunger all the way down to inject fluid. Do not remove the needle immediately. Wait 5 seconds and then remove it with a quick motion.
Insulin treatment is the oldest hypoglycemic treatment for patients with diabetes mellitus. While type 1 diabetes is the only possible replacement treatment, patients with type 2 diabetes have recently expanded their use of insulin therapy to varying degrees of disease progression.
Insulin therapy in diabetic patients is no longer considered the last treatment option for patients with poor compensation, but to treat B cell function. Insulin therapy of the type of diabetes mellitus uses all known and available regimens of insulin from insulin once a day using a combination therapy with insulin with an oral antidiabetic after classical intensified insulin therapy.
There is no need to practice injecting oranges or other fruits. You can first practice on yourself "throwing" the syringe to the injection site, like a dart at a target, with a cap on the needle. After all, the key is to inject yourself with insulin for the first time using the correct technique. You will feel that the injection was completely painless, and your speed made it so. Subsequent injections can be done very simply. To do this, you just need to master the technique, and courage has absolutely nothing to do with it.
How to fill a syringe
We will describe several unusual method to fill the syringe. Its advantage is that air bubbles do not form in the syringe. If, with the injection of insulin, air bubbles get under the skin, then this is not a big deal. However, they can skew accuracy if insulin is injected in low doses.
The step-by-step instructions below are suitable for all pure, clear insulin. If you are using turbid insulin (with Hagedorn's neutral protamine - NPH, aka protaphan), then follow the procedure described below in the section “How to fill a syringe with NPH insulin from a vial”. Apart from NPH, any other insulin must be perfectly clear. If the liquid in the vial suddenly becomes cloudy, it means that your insulin has deteriorated, has lost its ability to lower blood sugar, and must be thrown away.
Remove the cap from the syringe needle. If there is another cap on the piston, remove that too. Draw as much air into the syringe as you plan to inject. The end of the seal on the piston closest to the needle should move from zero on the scale to the mark that corresponds to your insulin dosage. If the seal is tapered, then the dose should be viewed along its wider part, and not along the sharp tip.
Pierce the rubber airtight cap on the vial with a syringe approximately in the middle. Release the air from the syringe into the vial. This is necessary so that a vacuum does not form in the vial, and so that next time it is just as easy to draw a dose of insulin. Then turn the syringe and bottle over and hold them as shown in the figure below.

Press the syringe to the palm of your hand with your little finger so that the needle does not pop out of the rubber cap of the bottle, and then pull the plunger down sharply. Draw about 10 U more insulin into the syringe than the dose you plan to inject. Continuing to hold the syringe and bottle upright, gently press the plunger until the syringe contains as much liquid as needed. While removing the syringe from the vial, continue to hold the entire assembly upright.
How to fill a syringe with NPH insulin Protafan
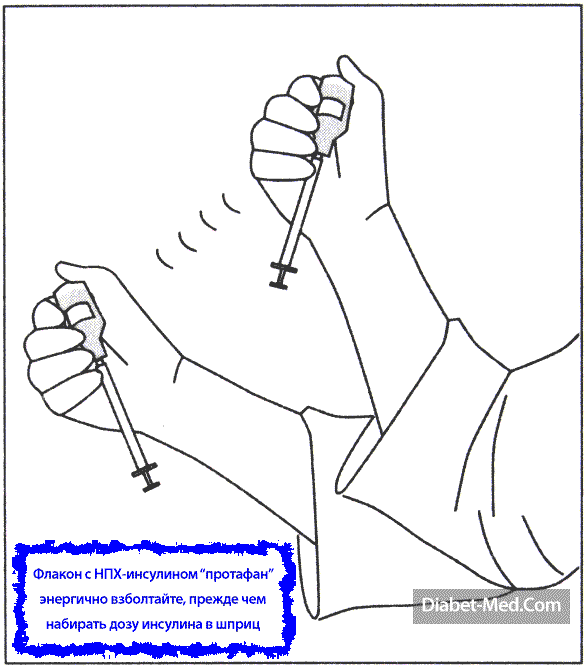
Medium-acting insulin (NPH insulin, also called protaphan) comes in vials that contain a clear liquid and a gray precipitate. Gray particles quickly settle to the bottom when you leave the bottle and do not shake it. Before each set of a dose of NPH insulin, the vial must be shaken so that the liquid and particles form a uniform suspension, that is, so that the particles float in the liquid in a uniform concentration. Otherwise, the action of insulin will not be stable.
To shake insulin "protafan", you need to shake the bottle well several times. You can safely shake the bottle with NPH insulin, there will be nothing terrible, you do not need to roll it between your palms. The main thing is to ensure that the particles float evenly in the liquid. After that, remove the cap from the syringe and pump air into the vial, as described above.
When the syringe is already in the bottle and you hold it all upright, shake the entire structure a few more times. Make 6-10 movements so that a real storm occurs inside, as shown in the picture below.
Now briskly pull the plunger toward you to fill it with excess insulin. The main thing here is to fill the syringe quickly, after having made a storm in the bottle, so that the gray particles do not have time to settle on the walls again. After that, while continuing to hold the entire structure upright, gradually release the excess insulin from the syringe until the dose you need remains in it. Remove the syringe carefully from the vial as described in the previous section.
The annual cost of disposable insulin syringes can be quite significant, especially if you are giving multiple shots of insulin per day. Therefore, it is tempting to use each syringe several times. It is unlikely that in this way you will pick up some kind of infectious disease. But it is very likely that this will cause insulin to polymerize. The penny saving on syringes will result in significant losses from the fact that you have to throw out insulin, which will go bad.
Dr. Bernstein describes the following typical scenario in his book. The patient calls him and complains that his blood sugar remains high and cannot be repaid. In response, the doctor asks if the insulin in the vial remains crystal clear and transparent. The patient replies that the insulin has become slightly cloudy. This means that polymerization has occurred, due to which insulin has lost its ability to lower blood sugar. To regain control over diabetes, it is urgent to replace the bottle with a new one.

Dr. Bernstein emphasizes that insulin polymerization sooner or later happens to all of his patients who try to reuse disposable syringes. This is because insulin is converted into crystals when exposed to air. These crystals remain inside the needle. If they fall into the vial or cartridge during the next injection, this causes a chain reaction of polymerization. This happens with both prolonged and rapid insulin.
How to give injections of several different types of insulin at the same time
There are often situations when you need to inject several different types of insulin at the same time. For example, in the morning on an empty stomach, you need to inject a daily dose of extended insulin, plus ultrashort insulin to extinguish high sugar as well as short to cover a low-carb breakfast. Such situations do not only happen in the morning.
First of all, inject the most fast insulin, i.e., ultrashort. Behind it is a short one, and behind it is already extended. If your extended insulin is Lantus (glargine), then his injection must be done with a separate syringe. If even a microscopic dose of any other insulin gets into the bottle with Lantus, the acidity will change, because of which Lantus will lose some of its activity and will act unpredictably.
Never mix different types insulin in one vial or in one syringe, and do not inject ready-made mixtures. Because they are unpredictable. The only extremely rare exception is to use insulin containing Hagedorn's neutral protamine (protaphan) to slow down the action of short insulin before meals. This method is intended for patients with. They have delayed gastric emptying after eating, a serious complication that makes diabetes control even more difficult.
What to do if some of the insulin has leaked from the injection site
After the injection, place your finger on the injection site and then smell it. If some of the insulin has leaked from the puncture, you will smell a preservative called metacrestol. In such a situation, you do not need to inject an additional dose of insulin! In your self-control diary, make a note that there were losses. This will explain why you have high blood sugar. Normalize it later, when the effect of that dose of insulin is over.

In this article, you learned how to painlessly give insulin shots using the quick injection technique. The method of injecting insulin painlessly is useful not only for type 1 diabetics, but also for all type 2 diabetics. During an infectious disease with type 2 diabetes, your own insulin may not be enough, and your blood sugar will jump very much. As a result, a significant proportion of beta cells can die and the course of diabetes worsens. At its worst, type 2 diabetes will turn into type 1 diabetes. To insure yourself against trouble, you need to master the correct technique for administering insulin in advance and, until the infection is cured, temporarily maintain your pancreas.
As a rule, one milliliter of the drug in the form of a solution or suspension contains 40 IU of the active substance.
Part antidiabetic drugs may include insulin extracted from pancreas animals (pigs or large cattle), human insulin, or a biosynthetic substance obtained by genetic engineering.
The composition of the auxiliary components differs for each specific drug.
Release form
Insulin preparations are available in the form of solutions and in the form of suspensions in vials and special cartridge systems (cartridges, sleeves and systems designed for use with a syringe pen).
The injection solution is produced in sterile glass vials with a volume of 5 and 10 ml, with an activity, as a rule, from 20 to 100 IU in 1 ml of solution.
Designed for medical use the substance is a water-soluble, hygroscopic white powder, which contains 3.1% sulfur.
The solutions look like a clear, colorless or slightly yellowish liquid with an acidity (pH) of 2.0 to 3.5). To prepare the solution, the crystalline powder is diluted in water for injection (Aqua pro injectionibus), acidified hydrochloric acid(Acidum hydrochloricum) with the addition of glycerin (Glycerinum) and 0.25–0.3% solution (Phenolum) or tricresol (Tricresolum) for canning.
Sustained-release suspensions are supplied to pharmacies in sterile 5 and 10 ml vials. Each bottle is hermetically sealed with a rubber stopper with a rolling aluminum cap.
The most physiological control profile hypoglycemia characterized by a two-phase drug Novomix, which is a two-phase suspension, which consists of 30% of ultra-short-acting insulin aspart and 70% of protamine-crystallized insulin aspart.
To date, scientists have managed to solve the problem of the passage of insulin through the stomach (since the substance is protein , it undergoes destruction under the influence of digestive juices) and create also effective remedy for diabetics in tablets.
pharmachologic effect
Insulin preparations belong to a group of agents that affect digestion and metabolic processes in the body .
Endogenous insulin is essential regulator of carbohydrate metabolism in the body, exogenous is a specific sugar reducing agent .
The main functions of insulin:
- regulation of carbohydrate metabolism ;
- stimulation of glucose uptake by tissues and the processes of its conversion into glycogen ;
- facilitating the penetration of glucose into tissue cells ;
- increased glycogen stores in muscle tissue ;
- stimulation of synthesis ;
- reduced protein consumption ;
- stimulation of glucosyltransferase, polyenzyme complex of pyruvate dehydrogenase, hexokinase ;
- lipase inhibition , the action of which is aimed at activating fatty acids adipose tissue;
- inhibition of lipoprotein lipase which reduces the "haze" after meals with high content fat.
Insulin affects metabolism of carbohydrates ... This is due to the fact that the substance stimulates transport glucose across cell membranes , enhances its utilization by tissues, and also promotes its biotransformation to glycogen in the liver .
At the expense of inhibition of glycogenolysis (the process by which glycogen is broken down into glucose) and gluconeogenesis (education process glucose from non-carbohydrate sources : from amino acids , fatty acids etc.) insulin suppresses production endogenous glucose .
The effect of the substance on lipid metabolism manifests itself in suppression lipolysis (breakdown of fats). As a result, income decreases free fatty acids v systemic blood flow .
Insulin prevents formation acetone (ketone) bodies in the body, stimulates fatty acid synthesis and subsequent education esters ... He also takes part in proteins : enhances transport amino acids across cell membranes , stimulates peptide synthesis , reduces tissue consumption proteins , slows down the transformation process amino acids to oxocarboxylic acids .
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The mechanism of action of insulin is associated with its ability to interact with specific receptor which is localized to plasma cell membrane , and form insulin receptor complex .
In complex with insulin receptor it enters the cell, where it affects the processes phospholation of cellular proteins ; To date, there are no exact data on further reactions inside the cell.
Insulin affects almost all organs and tissues in the human body, while its main targets are liver , muscle and adipose tissue .
How complete the absorption of insulin will be and how quickly the effect of its use will come depends on the injection site (more precisely, on the degree of blood supply to the subcutaneous fat at the injection site), the dose administered (more than 12-16 units of solution should not be injected into one place / suspension), the concentration of the active substance in the drug, such as insulin, the rate of local blood flow, muscle activity at the injection site.
The profile of the drug's action is subject to significant fluctuations both in different people and in the same person.
In addition, they are often prescribed as anabolic agent (mass gainers) for malnourished and malnourished patients.
The agent can also be used as one of the components of “polarizing” solutions that are used to treat acute coronary insufficiency (condition caused by spasm of the coronary vessels ).
Insulin in bodybuilding
There is an opinion that the use of insulin in sports is a real find. In this case, the necessary effect is provided by the use of short-acting drugs, and, in particular, in combination with some anabolic or androgenic agent .
What happens if a healthy person is injected with insulin? Under the influence of the hormone, it increases permeability of muscle tissue cell membranes and, therefore, the penetration of these substances to the cell is accelerated and facilitated. As a result - even in the smallest dose steroids have a much more pronounced result than in the case when they are used independently.
So how do you take insulin in bodybuilding? First, do not overeat (the body stores an excess of nutrients entering it in the form fat ). Second, cut down on your intake as much as possible. simple carbohydrates ... And, thirdly, to be guided not by weight, but by the reflection in the mirror and the measuring tape (it is necessary to be guided by the volume of the lower leg, biceps, thigh). The appearance of folds of fat in the abdomen is evidence of an incorrect dose.
Contraindications
Insulin should not be prescribed for diseases that occur with hypoglycemia : at hemolytic jaundice , acute hepatitis , jade , amyloid dystrophy , decompensated heart disease ; peptic ulcer , affecting the stomach and duodenum .
Insulin preparations are prescribed with caution:
- diabetic patients who have coronary insufficiency or impaired blood circulation in the brain ;
- patients with diseases of the thyroid gland ;
- at Addison's disease (adrenocortical insufficiency, which occurs when more than 90% of the tissue is affected adrenal glands );
- at .
Side effects
With subcutaneous administration of insulin preparations, lipodystrophy (pathology characterized by atrophy or hypertrophy of adipose tissue ) at the injection site.
Modern insulins undergo thorough cleaning, therefore, against the background of their use, they develop extremely rarely, but the likelihood of such side effects is not excluded.
In case of development allergic reactions of an immediate type, the patient requires immediate specific hyposensitization and replacement of the drug.
Instructions for the use of Insulin
Features of the introduction of Insulin
According to the instructions for use, Insulin can be injected under the skin, into a muscle or into a vein. It follows that only short-acting drugs can be administered intravenously and only if the patient has symptoms precomatose state or he fell into.
The introduction into a vein of drugs that are produced in the form of a suspension is contraindicated. Before injection, the medicine should warm up to room temperature... This is because cold insulin is absorbed much more slowly.
It is preferable to use a plastic injection syringe (not glass). The reason for this is that there is more so-called "dead" space in a glass syringe than in their plastic syringes. This, in turn, reduces the dosing accuracy of the drug and leads to insulin losses.
Insulin syringe pens with special, filled with solution, cartridges installed in them are considered convenient to use. They are used for the introduction of solutions of short, medium and mixed (combined) action. When using such systems, before injecting the drug, you do not need to draw it or mix it every time.
The needles used in modern insulin syringes and pens are so thin and short that they cause little painful sensations when injected. The thickness of the needle is usually from 0.3 to 0.4 mm), the length does not exceed 12 mm (usually from 8 to 12 mm).
Where to inject the drug?
The question "Where is insulin injected?" occurs quite often.
Fastest absorption in blood flow celebrated after subcutaneous injection v anterior abdominal wall , more slowly the substance is absorbed into blood from the area of the shoulder and the front of the thigh, the slowest absorption is noted after the introduction of the drug into the subcutaneous fatty tissue under the scapula or on the buttock.
Therefore, in clinical practice the optimal route of administration for continuous therapy is subcutaneous injection.
Considering the fact that the drug is absorbed into the blood from different parts of the body at different rates, doctors recommend injecting short-acting drugs (look like a clear solution) into the abdomen, avoiding the navel, and prolonged-acting drugs (cloudy solution) into the area thighs or buttocks.
Another important rule is that the areas of drug administration are alternated, following a strict order in accordance with the time of day (for example, in the morning a short-acting solution is injected into the abdomen, in the afternoon - into the thigh area, in the evening hours - under the skin of the buttocks.
This is due to the fact that for different areas, the calculation of the drug for the amount of XE will be different (as well as at different times of the day).
Algorithm for the introduction of insulin subcutaneously
The main rules for administering insulin: before you make an injection, you must check the suitability of the medication, its type, duration and dosage, wash your hands and ensure the cleanliness of the injection site;
The technique for administering insulin is as follows:
- Before administration, the drug is warmed in the hands to room temperature. Do not shake the bottle, as this is fraught with the formation of bubbles.
- The bottle cap is wiped with 70º alcohol.
- Air is drawn into the syringe for the required number of units of insulin, after which it is injected into the vial, the required dose of the drug is taken + up to 10 IU more.
- The dose of the solution is adjusted by holding the syringe at eye level (if you change the angle, a vision error of 1-5 units is possible)
- By shaking the bottle, the bubbles are removed.
- Do not treat the skin at the injection site with alcohol, as alcohol destroys insulin and, as a result, the patient may form lipodystrophy ... If necessary, simply wash the skin and wipe dry. It is allowed to administer the drug through clothing.
- The injection is made in the recommended areas of drug administration: 2.5 cm from the navel, 3 cm from the shoulder, thigh, upper part buttocks. A fold of skin is formed with the thumb and forefinger so as not to capture the muscle layer (if it enters the muscle, the drug is absorbed into the blood faster than from the subcutaneous layer). How to properly grab the skin is shown in the following illustration:
- The solution should be injected half an hour before meals (insulin is absorbed within an hour, so food intake should be approximately 15-30 minutes after injection).
How to put the syringe during injection
The needle is inserted into the skin at an angle of 45º, if the injection is made into a skin fold, at an angle of 90º - if the injection is made without a skin fold.
A fold is formed if medication is to be injected into the shoulder or thigh, the fold is not made if medication is to be injected into the abdomen or buttocks (because there is a thick layer of subcutaneous tissue).
How to inject the drug correctly?
Video instruction on how to inject Insulin with a pen
What's the best Insulin?
There is no definite answer to this question. The primary selection of insulin (as well as the set of the dose and the administration of the drug) is carried out in a hospital setting, depending on the severity of the course of the disease and the characteristics of the clinical situation, general condition the patient, the rate of onset antihyperglycemic effect and the duration of its action.
Calculation of the dose and administration of insulin
The dose of the drug is selected individually in each case.
Short-acting drugs are intended for administration under the skin or into a muscle (in some cases, it is allowed intravenous administration). These solutions act quickly, the effect of their use is relatively short-lived.
Short-acting insulins are administered 15-20 minutes before a meal from one to several times (depending on the characteristics of the disease) during the day. Sugar reducing effect develops after 15-20 minutes and reaches its maximum after 2 hours (while the total duration of action does not exceed 6 hours).
Medicines of this type are used mainly in a hospital in order to establish the dose necessary for the patient, as well as when diabetic and precom (conditions that require a rapid change in insulin activity in the body).
In addition, short-acting solutions are used as anabolic agent ... For this purpose, they are usually used in small doses (from 4 to 8 IU once or twice a day).
Long-term (prolonged) action drugs have several dosage forms and are characterized by different duration of the effect (for example, insulins semilong, long, ultralong are secreted).
As a rule, the effect is noted within 10-36 hours. Using this type of drug can reduce the number of daily injections.
Most often, long-acting insulins are a suspension. They are injected under the skin or into the muscle; intravenous administration is unacceptable. It is also forbidden to use drugs from this group when coma and precoma.
When choosing a drug, you need to ensure that the period during which sugar-reducing effect expressed most strongly, coincided in time with the reception of writing.
If necessary, it is allowed to mix two drugs in one syringe at the same time. long acting.
In some cases, patients need not only long-term maintenance of the required level glucose but also in its rapid normalization. To do this, they are prescribed the introduction of drugs, both short and long-acting.
As a rule, the injection of a suspension of prolonged action is done in the morning hours, before the first meal, however, administration is allowed at other times of the day.
Patients are recommended to combine injections in compliance with the special one for diabetics. Energy value food in each case should be determined by the patient's body weight during the treatment period and the degree of his physical activity.
With a lack of nutrition and increased physical activity, the patient is shown to consume at least 3000 kilocalories per day, with excess nutrition and hypodynamia the number of calories should not exceed 2000 (optimal - about 1700).
How to draw the medication into the insulin syringe correctly?
If it is required to inject one type of insulin, the syringe plunger is pulled back to the mark corresponding to the required number of units, after which the cork of the drug bottle is pierced and, pressing the plunger, air is admitted into it.
It is better to puncture the stopper with the medicine in its very center, using a thick needle for ordinary syringes. To introduce air and draw up the medicine, an insulin syringe is already used - its needle is inserted into the puncture site.
If air bubbles are visible in the drawn syringe, you need to lightly flick your fingers on the syringe and gently move the plunger until the required dose is marked.
Insulin dose calculation
The calculation and administration of the dose of the drug is made based on the fact that the highest daily dose medicines should not exceed 1 IU per kilogram of the patient's body weight.
For grade I diabetes, the dose is:
- 0.5 U / kg - for patients who have recently been diagnosed with the disease;
- 0.6 U / kg - if compensation lasts for a year or more;
- 0.7 U / kg - in case of unstable compensation;
- 0.8 U / kg - in case of decompensation;
- 0.9 U / kg - if the disease is complicated ketoacidosis ;
- 1.0 U / kg - for women in the last 3 months.
Calculation for prolonged-release drugs at a dose of 0.6 U / kg and a patient's weight of 75 kg: 0.6 * 75 = 45. It is necessary to take 50% of the resulting value and round down (up to 20). Thus, 12 units should be introduced before the morning meal, and the remaining 8 before the evening meal.
The correct calculation for short-acting drugs at a dose of 0.6 U / kg and a patient's weight of 75 kg is made according to the formula: 0.6 * 75 = 45; 45-20 = 25. Therefore, from 9 to 11 units must be entered before the morning meal, from 6 to 8 units - before lunch, the remainder - from 4 to 6 units - before dinner.
Overdose
Exceeding the dose of the drug prescribed by the doctor inevitably provokes the development hypoglycemic syndrome accompanied by low blood sugar and can be fatal for the patient.
paresis , mental abilities are greatly reduced.It should also be remembered that high doses are harmful to blood vessels. Against the background of their application reduced elasticity of arteries and the blood supply to the brain deteriorates .
On initial stages hypoglycemia Sweet tea, honey or fruit juice can help normalize sugar levels.
At coma requires immediate introduction into a vein of 10-20 ml of a concentrated solution glucose (20-40%). If it is not possible to inject the solution into a vein, it is allowed to do:
- intramuscular injection of 1-2 mg (glucagon is a physiological insulin antagonist);
- subcutaneous injection of 0.5 ml hydrochloride solution 0.1%;
- an enema using 150 ml of a 10% solution
Temperatures above 30-35 degrees Celsius are destructive for the medicine.
For people with an active lifestyle, the best solution is an insulin thermal bag.
When is a drug considered tainted?
If at least one storage condition is violated, the drug should be thrown away. Also, a solution that, for one reason or another, has changed its color, and a solution in which lumps, suspensions, fibers have appeared, are not subject to use.
A suspension is considered spoiled if, upon stirring, it does not form a uniform white or whitish suspension.
It is important to remember that only ultrashort, short and fast acting insulins should remain transparent and, in addition, also insulin glargine extended action.
Shelf life
The drug is suitable for use within 24 months from the date of release.
If the storage conditions are observed, the opened insulin bottle is fit for use within a month.
special instructions
What is insulin?
Wikipedia indicates that the hormone insulin is a substance that has a multifaceted effect on the course metabolic processes in almost all tissues.
Immunoreactive insulin makes the plasma membranes more permeable to glucose, which ensures a faster and easier transition of the latter from the blood to the intracellular space.
Lack of insulin synthesis causes metabolic disturbances, which as a result leads to the development of diabetes mellitus.
Immunoreactive insulin - what is it? Which organ makes insulin?
To the questions "which gland produces insulin?" or "where is insulin produced?" Wikipedia replies that the hormone insulin is produced by β-cells of the islets of Langerhans (localized mainly in the tail pancreas (PZH) endocrine cell clusters).
The hormone synthesized by the body is called insulin or immunoreactive insulin (abbreviated as IRI).
The initial source for the production of insulin preparations, which provide the ability to lead a normal life for people whose body does not produce the hormone on its own in the quantities it needs, are pancreas pigs and cattle.
A little over 30 years ago, human insulin began to be used to treat patients. To obtain it, they resort to one of two methods:
- the method of transformation of porcine insulin, which involves the replacement of the amino acid it contains alanine on ;
- method genetic engineering, which involves a change in a specific section of DNA.
Insulin drug classification
Currently used drugs are usually divided according to a number of characteristics:
- by the duration of the action;
- by source of origin;
- depending on the pH of the solution (can be neutral or acidic);
- by the presence of preservatives in the preparation (phenol, methylparaben, cresol, phenol-cresol);
- depending on the concentration of insulin (40, 80, 100, 200, 500 units per ml).
Classification according to the duration of action:
- ultra-short-acting drugs;
- short-acting drugs;
- prolonged-acting drugs (including intermediate-acting (intermediate) and long-acting);
- long-acting drugs;
- drugs combined action(biphasic remedies).
Ultrashort action is characterized by Lispro , aspart , and glulisine .
Short-acting insulin, names:
- insulin soluble human genetic engineering;
- soluble human semi-synthetic;
- soluble pork monocomponent.
Intermediate insulins are insulin isophane (human genetic engineering); insulin isophane (human semi-synthetic); insulin zinc compound suspension.
What are the types of long-acting insulin? This category includes glargine and detemir.
Biphasic drugs - biphasic human semi-synthetic; biphasic human genetic engineering; aspart two-phase.
In accordance with the classification, depending on the degree of purification, preparations obtained from animal tissues are divided into:
- monopic (MP);
- monocomponent (MC).
Insulin types depending on origin:
- pork (denoted by the letter C; monopic - SMP, mono-component - SMK);
- cattle (beef, denoted by the letter G; monopic - GMF, monocomponent - GMC);
- human (denoted by the letter H).
Insulin level in the blood - the norm and options for deviating from it
An indicator that displays the level of the hormone in blood healthy person, is in the range of values from 3 to 20 μU / ml.
Reducing it is a prerequisite for development diabetes mellitus ... In this case, the cause of serious consequences can be an excess of hubbub in the blood.
Increased insulin in the blood - what does it mean?
Insulin inhibits the process synthesis of glucose from proteins and lipids ... Thus, with an increase in the concentration of the hormone of more than 20 μU / ml (hyperinsulinism), in a person, as with insulin deficiency, symptoms begin to appear hypoglycemia - irritability increases, memory worsens and concentration of attention decreases, general fatigue increases (over time, it turns into chronic form), increases, etc.
Causes of high insulin
If insulin is elevated blood , the reason may lie in the fact that the person has eaten too much food rich in carbohydrates (that is, glucose).
Since carbohydrate-containing foods contribute to a sharp increase in the level of the hormone, you should not eat before donating blood for analysis for an insulin test (analysis blood do on an empty stomach).
Functional dysfunctions can also provoke an increase in the level of the hormone. β-cells of pancreas (in this case, they speak of primary, pancreatic, hyperinsulinism), as well as disturbances in the secretion of some other hormones (for example catecholamines or corticotropin ), nervous system damage , hypersensitivity insulin receptors (in all these cases, the diagnosis is "secondary, or extra-pancreatic, hyperinsulinism").
Cause functional impairments PJJ thus becoming the reason high insulin, can:
- tumors on PJJ that contribute to the production of the hormone;
- decrease in the concentration produced in the body glucagon ;
- hyperplasia of the islets of Langerhans .
It is also often noted increased insulin with excess weight. An increase in the concentration of the hormone indicates that PJJ works with additional load.
How to lower blood insulin levels
Before treating elevated insulin, it is necessary to establish the cause that provoked it. As a rule, after its elimination, the patient's condition is normalized.
To avoid an attack hypoglycemia , you should eat something sweet or introduce a solution glucose ... In severe cases, it may be necessary to administer glucagon or .
How to lower hormone levels at home? To normalize insulin levels, you should first adjust your diet. Meals should be fractional (it is optimal to eat in small portions at least five times a day), and the daily amount of carbohydrate foods should not exceed 150 g.
At the same time, oatmeal, buckwheat porridge, low-fat kefir and milk, unsweetened cottage cheese, bran, eggs, vegetables, fish, and individual fruits should prevail in the diet.
The normalization of indicators is also facilitated by physical exercise and weight loss.
What sugar is insulin prescribed for?
An analysis to determine the concentration of the hormone for differentiating the form of the disease is done to people who have not previously received insulin preparations. This is due to the fact that the body reacts to the introduction of an exogenous hormone by producing antibodies.
High level at normal sugar is one of the symptoms metabolic syndrome ... The condition is regarded as prediabetes .
If insulin is elevated, and sugar is normal, they talk about insulin-resistant glucose intolerance and diabetes ... It may also indicate a number of others. insulin resistant conditions .
A high level with low sugar is often an indicator pathological hyperinsulinemia ... In some cases high concentrations circulating in blood hormone associated with hypertension ,diseases of the heart and blood vessels .
A low level with normal sugar also requires contacting an endocrinologist to determine the cause of this condition and conduct the necessary tests (HLI typing, performing a test for antibodies to insulin, determining the level of antibodies to GAD, performing a glycated test).
The decision on the need to prescribe injections is made not based on the sugar level indicators, but taking into account the reasons that provoked such an increase.
As a rule, the administration of the drug becomes inevitable if the blood sugar concentration values are kept for a long time within the range of 12 mmol / L, and the pills and a strict diet do not lead to their decrease.
Deciphering the blood test for insulin allows the doctor to obtain the data necessary for it.
The rate for women and men is the same. Indicators of 3.3-7.8 mmol / l indicate noormoglycemia. The norm of blood sugar on an empty stomach is from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol / l. After a meal, a normal indicator is considered that does not exceed 7.8 mmol / l.
The rate of insulin after glucose load is up to 7.7 mmol / l. If the indicator is in the range of 7.8-11.1 mmol / l, they speak of impaired glucose tolerance.
Insulin and alcohol
The drug reduces alcohol tolerance. When used simultaneously with alcoholic beverages the risk of developing hypoglycemia also increases.
Insulin during pregnancy
Treatment restrictions diabetes mellitus with the use of insulin when and not.