What is high blood insulin. High levels of insulin in the blood: the consequences of a violation
Elevated insulin is no less dangerous than its lack: it can provoke the development of hypoglycemia, which is characterized by a decrease in blood glucose levels, which leads to headaches, lethargy, confusion, seizures and coma.
Insulin does this by converting glucose into glycogen, which accumulates in the liver and muscles, so that when there is a shortage of sugar in the body, it is again transformed into glucose.
Insulin also ensures the delivery of glucose and other nutrients to all cells of the body, saturating them and giving them the opportunity to develop and renew themselves. It affects the increase in the synthesis of proteins and fats, inhibits enzymes that break down glycogen and fats. With a lack of this hormone, diabetes develops, when cells begin to experience hunger, stop updating and die, the metabolism slows down, if left untreated, a person falls into a coma and dies.
Above normal
Elevated insulin levels are no less dangerous. Cells cease to receive glucose in the amount necessary for them, which leads, as with a lack of insulin, to their starvation. An excess of the hormone in the body enhances the work of the sebaceous glands, a symptom of which is the appearance of acne, dandruff, excessive sweating. If a woman is obese (this is the most common cause excess of the hormone of the norm), this can provoke an ovarian cyst, a violation menstrual cycle and infertility.
Since insulin is characterized by a vasoconstrictor effect, an excess of the hormone causes an increase blood pressure, reduces the elasticity of the arteries, which leads to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. The walls of the carotid artery gradually thicken, which reduces the ability of a person to think clearly in old age.
If the amount of the hormone is not reduced, due to circulatory disorders, gangrene of the extremities, kidney failure may develop, and disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system are observed. The disease is also negatively displayed on the reproductive function: any problems in endocrine system a person can cause infertility.

Also, high insulin levels inhibit the enzymes that affect the transition of glycogen to glucose, as well as gluconeogenesis, when glucose is formed from non-carbohydrate compounds. Because of this, the body is unable to compensate for low blood sugar, which leads to hypoglycemia, which is characterized by insufficient supply of blood flow, glucose and other nutrients to the brain (it is glucose that is the main source of energy for brain cells).
This leads to symptoms such as headaches, blurred vision, lethargy, obesity, confusion, amnesia, and even coma.
After some time, the cells of the pancreas, "realizing" that there is an excess of the hormone in the body, reduce, which causes the development of diabetes and its accompanying symptoms. The level of insulin drops, it ceases to perform its functions in the right amount, which leads to metabolic disorders, starvation and cell death, if the disease is not treated, the person dies.
Causes of excess hormone
Among the main factors of elevated insulin levels, experts call obesity, which leads to slow absorption of fats, poor blood flow, kidney failure, polycystic ovaries, infertility. In diabetic patients, an overdose of insulin preparations can provoke an increase.

Also, the following reasons can affect the excess of the hormone:
- tumors of the pancreas, which cause increased synthesis of the hormone. These are usually benign growths known as insulinomas;
- overgrowth of beta cells or their stimulation;
- decreased secretion of glucagon (a hormone that stimulates the breakdown of glycogen in the liver to convert it into glucose);
- violation of carbohydrate metabolism;
- liver disease;
- polycystic ovaries, which leads to infertility;
- malignant tumors abdominal cavity;
- diseases of the pituitary or adrenal cortex;
- excessive physical activity;
- stressful situations.
Also elevated insulin can provoke problems with the central nervous system, reduced production of other hormones (glucocorticoids, growth hormone, corticotropin). The content of the hormone in the blood also increases with increased sensitivity of insulin receptors, which are located on each cell and interact with the hormone.
High can be the result of malnutrition, when a person consumes too many sweets and carbohydrates. It can provoke a violation of the level of the hormone hunger strike, lack of vitamin E or chromium.
Therapy and diet
To bring excess insulin back to normal, it is necessary to eliminate the cause that provoked the disease. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor prescribes a treatment regimen, diet and physical exercise that need to be executed. If it is a tumor (for example, polycystic ovaries that caused infertility), doctors first try to apply conservative treatment with the help of drugs or diet, if they do not help, they resort to surgical intervention.

You need to eat small meals with excess insulin about five times a day. A diet with increased insulin excludes the use of sugar and sweets based on it. They must be replaced with products specially designed for diabetics, sweeteners, low-calorie marshmallows, marmalade.
It is also necessary to monitor the amount of carbohydrates consumed and properly distribute their use. The amount of salt during meals should be reduced to the minimum doses. You can not eat canned food, sausages, crackers, salted nuts.
Every day you need to drink 2 to 2.5 liters of water per day. Unsweetened compotes are allowed, green tea, rosehip broth, drinking water. Alcoholic drinks are not allowed. Dairy products are allowed, but with low percentage fat content.
Nutrition with increased insulin includes dishes from buckwheat, oatmeal, brown rice(but don't abuse it). Low-fat varieties of meat, fish, poultry are allowed. Eggs can be eaten, but no more than two eggs three times a week. Useful raw or boiled vegetables, pears, apples, watermelon, grapefruits, oranges. Without fear, you can eat strawberries, raspberries, strawberries, cherries.
If you follow all the doctor's recommendations and start therapy on time, you can achieve positive results and lower insulin levels. There have been numerous cases in women when, after normalizing body weight, the level of insulin returned to normal, all the symptoms of polycystic ovaries disappeared, which led to the establishment of a regular monthly cycle and a cure for infertility.
Increased insulin in the blood of women should be alarming, although for some time such a pathology will not cause concern and visible diseases. Excess insulin can adversely affect the health of any person, lead to the development serious illnesses and negative consequences.
This hormone is produced by the pancreas, and it is one of the most important substances. The main role of insulin is to lower the amount of sugar in the blood. This process occurs when glucose moves from the blood to the cells of the internal organs. In addition, the hormone is involved in ensuring the normal course of metabolic processes in the body of both women and men.
Another important role of insulin is participation in the metabolism and synthesis of proteins. Actively works in the creation of new compounds that are responsible for the normal functioning of our body.
Indicators of the normal state
At healthy person the level of this hormone should not be more than 20 mcU / ml. A higher or lower level of this hormone leads to the development of a disease such as diabetes. That's not all. This pathology provokes the appearance of problems with internal organs, and all this negatively affects the state of human health.
An increase in insulin levels can also occur if a person does not take tests correctly. When carbohydrates in the form of sweets enter the body, the content of this hormone will be increased, and this is a natural process. To correctly determine what level of insulin you have in the body, the analysis must be taken only on an empty stomach.

If a person is healthy and has no prerequisites for the development of diabetes, the amount of sugar in the blood will be in the range of 3.5-5.5 mmol / l. When cells begin to block such a function as the absorption and absorption of glucose, this leads to the development of an irreversible process that causes an increase in blood sugar.
The fact that the cells stop absorbing glucose disrupts their nutrition. The latter does not get into the tissues and begins to accumulate in the blood. If you do not start to fix this problem in time, then usually such a malfunction in the body leads to the development of type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms of elevated insulin in women will manifest themselves in the form of weakness, a significant decrease in performance, and more frequent urination. The features of the latter are defensive reaction to an increase in blood sugar, and the kidneys actively begin to produce urine.
An increase in sugar leads to a decrease in insulin levels, and an accumulation of glucose causes blood to thicken.
All this leads to the fact that the latter does not penetrate well into the blood vessels and therefore the nutrition of the internal organs worsens, as a result of which the normal functioning of the whole organism is disrupted.
In the first stage of diabetes, high blood sugar levels can be corrected by constant monitoring and a special diet. If such treatment is not started on time, the disease will progress and then the patient will be prescribed insulin.

Determination of sugar in the blood
To determine what a person's blood glucose level is, 2 methods can be used:
- conducting a blood test;
- doing research on glycated hemoglobin.
Although fasting analysis behavior is popular and common, this method has its drawbacks. This method allows you to determine what level of glucose in the blood, only at the time of the analysis. If you begin to carry out this study every day, then the indicators will be different, while the sugar level can be both low and high.
For example, in the morning a person elevated level glucose, but by the time the patient walks to the hospital, as a result of physical activity, the sugar will already be low. It should also be taken into account that a large amount of water drunk in the morning leads to the fact that the blood thins and the glucose content in it decreases.
An analysis of glycated hemoglobin allows you to accurately determine what the patient's sugar level is. In this case, factors such as the time of day, how much water or food you drank, the emotional state of the patient, the level of physical activity do not matter. During the analysis, the number of candied erythrocytes is determined.

Causes of hypoglycemia
When the level of insulin in the body rises significantly, a pathology such as hypoglycemia develops. Symptoms that a person has insulin levels above normal will be as follows:
- depressed and depressed state;
- decreased concentration;
- memory impairment;
- weight increases;
- increased sweating;
- over time, fatigue becomes chronic;
- pressure rises;
- insomnia appears;
- kidney failure develops;
- due to the deterioration of blood circulation, gangrene of the legs may begin;
- start working hard sebaceous glands, so dandruff appears, seborrhea develops.
If we talk about the dangers of increased insulin in the blood in women, then it is worth noting that this condition worsens the patency of blood vessels, and this leads to an increase in blood pressure. Poor blood flow leads to malnutrition internal organs which can cause gangrene lower extremities, sleep disturbance, the skin becomes oily, kidney failure develops.

If a person has a high level of insulin, then this will indicate that some kind of disease is developing in his body. Depending on what caused the increase in insulin, there are primary and secondary hyperinsulinism.
Low or high glucose levels will be a signal of the onset of the development of the first form of this disease. Such hyperinsulinism is also called pancreatic hyperinsulinism, in which case the cause of high insulin levels will be a violation of glucagon production.
The reasons for high insulin levels when a person has normal glucose levels may be the development of a pancreatic tumor or a decrease in glucagon production.
If glucose levels are normal, secondary hyperinsulinism may begin to develop. In this case, this is characterized by an excess of hormones such as somatotropin and corticotropin, the glucocorticoid group of substances, as well as the appearance of a disturbance in the functioning of the nervous system.
The development of secondary hyperinsulinism is caused by failures in carbohydrate metabolism that occur with the development of liver pathology. If tumors begin to develop in the abdominal cavity, there are malignant formations in the adrenal glands and disturbances occur in the work of the anterior part of the brain.

How is the treatment carried out?
Excessive is considered when the level of the hormone exceeds 3.5 mmol / l. If increased insulin in the blood in women, treatment is aimed at eliminating the causes of this phenomenon. To determine the consequences of an excess of a substance in the body, it is necessary to conduct a complete clinical examination.
Most often, the causes of increased insulin in women are associated with the development of a tumor, in which case the only treatment is surgery.
If there is an increased level of insulin in the body, this will lead to a decrease in glucose and then there is a high probability that hypoglycemia attacks will appear.
In such cases, the patient is intravenously injected with a glucose solution, this procedure should be performed in a hospital. If the patient has an acute form of hyperinsulinism, then glucagon is administered to him or it may be adrenaline.
You need to know how to lower your insulin levels yourself, because you can do it at home. To achieve this, doctors recommend sticking to a special diet and giving the body physical activity, this will not allow you to gain excess weight. It is necessary to constantly control your weight and not allow it to increase.
Nutrition should be fractional, you should eat at least 5 times a day, you should not consume more than 150 g of carbohydrates per day. It is necessary to abandon foods that contain a large amount of carbohydrates. In the diet of such a patient, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge must be present, it is necessary to eat sour-milk low-fat products, more vegetables and fruits, eggs, low-fat fish.
With elevated insulin, salt intake should be minimized and foods that are high in sodium should not be eaten: canned food, sausages, various snacks, nuts, crackers, etc.
It is necessary to stop drinking alcohol, and it is recommended to drink a lot of liquids, at least 2.5 liters per day, it is better that it be an unsweetened rosehip broth, green tea, compote and plain water.
We must try to avoid nervous tension, stressful situations, and be sure to remember that no medicines and folk remedies they will not help you if you do not adjust your diet and diet.
Available to the cells of the body, as a result of which they receive the energy necessary for the functioning. The importance of insulin in the body is best known to diabetics who are deficient in this hormone. The level of the hormone in the blood must be monitored by people without diabetes as a preventive measure.
Insulin is vital, without which metabolism is disturbed, cells and tissues cannot function normally. It is being developed. In the gland there are areas with beta cells that synthesize insulin. Such areas are called islets of Langerhans. First, an inactive form of insulin is formed, which passes through several stages and turns into an active form.
It is necessary to control the level of insulin in the blood, the norm of which can vary depending not only on age, but also on food intake and other factors.
Insulin acts as a kind of conductor. Sugar enters the body with food, in the intestines it is absorbed from food into the blood, and glucose is released from it, which is important source energy for the body. However, glucose by itself does not enter cells, with the exception of insulin-dependent tissues, which include brain cells, blood vessels, blood cells, retina, kidneys, and. The rest of the cells need insulin, which makes their membrane permeable to glucose.
If the level of glucose in the blood rises, insulin-independent tissues begin to absorb it in large quantities, therefore, when blood sugar is greatly exceeded, brain cells, eyesight, and kidneys are the first to suffer. They experience a huge load, absorbing excess glucose.
Several important functions of insulin:
- It allows glucose to enter the cells, where it is broken down into water, carbon dioxide and energy. Energy is used by the cell, and carbon dioxide is excreted and enters the lungs.
- Glucose is synthesized by cells. Insulin blocks the formation of new glucose molecules in the liver, reducing the load on the organ.
- Insulin allows you to store glucose for the future in the form of glycogen. In the case of starvation and sugar deficiency, glycogen breaks down and is converted into glucose.
- Insulin makes the cells of the body permeable not only to glucose, but also to some amino acids.
- Insulin is produced in the body throughout the day, but its production increases with an increase in blood glucose levels (in a healthy body), during meals. Disruption of insulin production affects the entire metabolism in the body, but mainly - the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Diagnosis and norm depending on age
Diagnosis of insulin is usually prescribed by a doctor, but it is possible to check the level of insulin in the blood, as well as the level of glucose, without indications, for prevention. As a rule, fluctuations in the level of this hormone are noticeable and sensitive. A person notices various unpleasant symptoms and signs of disruption of the internal organs.
Insulin rate:
- The norm of the hormone in the blood of women and children ranges from 3 to 20-25 mcU / ml.
- In men - up to 25 mcU / ml.
- During pregnancy, the tissues and cells of the body need more energy, the body receives more glucose which means that insulin levels rise. The norm in pregnant women is the level of insulin 6-27 mcU / ml.
- In older people, this figure is also often elevated. Pathology is considered an indicator below 3 and above 35 mcU / ml.
The level of the hormone fluctuates in the blood during the day, and also has wide reference values in diabetics, since the level of the hormone depends on the stage of the disease, treatment, type of diabetes.
As a rule, in diabetes, a blood test for sugar is taken, the determination of insulin in the blood is required for more serious cases of diabetes with complications and for various hormonal disorders.
The rules for taking blood for insulin in serum do not differ from the standard rules for preparation:
- The analysis is given on an empty stomach. Before blood sampling, it is not recommended to eat, drink, smoke, brush your teeth, use mouth rinses. You can drink pure water without gas an hour before the examination, but the last meal should be no later than 8 hours before blood donation.
- During the examination, the patient should not take any medication. It is recommended to conduct an analysis a couple of weeks after the end of taking all the drugs. If it is impossible to cancel the drugs for health reasons, the entire list of medications and dosages taken is included in the analysis.
- A day or two before visiting the laboratory, it is recommended to give up “harmful” food (deep-fried, too spicy, fatty meat, heavily salted food), spices, alcohol, fast food, carbonated sugary drinks.
- It is advisable to avoid physical and emotional stress on the eve of the examination. Before donating blood, you need to rest for 10 minutes.
 Excess insulin can be observed after a meal, but even in this case, the hormone level should be within the reference values. A pathologically high level of insulin leads to irreversible consequences, disrupts the functioning of all vital body systems.
Excess insulin can be observed after a meal, but even in this case, the hormone level should be within the reference values. A pathologically high level of insulin leads to irreversible consequences, disrupts the functioning of all vital body systems.
Symptoms of elevated insulin typically include nausea when hungry, increased appetite, fainting, trembling, sweating, tachycardia.
Physiological conditions (pregnancy, eating, physical activity) lead to a slight increase in the level of the hormone. The causes of a pathological increase in the level of this indicator are most often various serious diseases:
- insulinoma. Insulinoma is most often a benign tumor of the islets of Langerhans. The tumor stimulates the production of insulin and leads to hypoglycemia. The prognosis is usually favorable. The tumor is removed surgically, after which almost 80% of patients recover completely.
- Type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is accompanied by high levels of insulin in the blood, but it is useless for the absorption of glucose. This type of diabetes is called non-insulin dependent. It occurs due to heredity or overweight.
- . This disease is also called gigantism. The pituitary gland begins to produce an excess amount of growth hormone. For the same reason, the production of other hormones, such as insulin, is enhanced.
- Cushing's syndrome. With this syndrome, the level of glucocorticoids in the blood increases. People with Cushing's syndrome have problems with excess weight, fat in the goiter, various skin diseases, muscle weakness.
- Polycystic ovaries. Women with polycystic ovaries experience various hormonal disorders, including an increase in insulin levels in the blood.
A large amount of insulin leads to the destruction of blood vessels, excess weight, hypertension, an increase, in some cases to oncological diseases, since insulin stimulates the growth of cells, including tumor cells.
Insulin in the blood is low
Lack of insulin leads to an increase in blood sugar levels and a decrease in its penetration into cells. As a result, the tissues of the body begin to starve from lack. In people with low level increased thirst, sharp bouts of hunger, irritability, frequent urges to urination.
The lack of insulin in the body is observed in the following conditions and diseases:
- Type 1 diabetes. Often, type 1 diabetes occurs due to a hereditary predisposition, as a result of which the pancreas cannot cope with the production of the hormone. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is acute and leads to a rapid deterioration of the patient's condition. Most often, diabetics experience severe hunger and thirst, do not tolerate fasting, but do not gain weight. They are lethargic, tired, bad smell from mouth. This form of diabetes is not age-related and often manifests itself in childhood.
- Binge eating. Insulin deficiency can be observed in people who abuse flour products and sweets. The wrong diet can also lead to diabetes.
- Infectious diseases. Some chronic and acute infectious diseases lead to the destruction of the tissues of the islets of Langerhans and the death of beta cells responsible for the production of insulin. The body is deficient in the hormone, which leads to various complications.
- Nervous and physical exhaustion. With constant stress and excessive physical exertion, a large amount of glucose is consumed, and insulin levels can drop.
More information about insulin can be found in the video:
In the vast majority of cases, it is the first type that leads to a lack of a hormone. It often leads to various complications that are life-threatening. The consequences of this form of diabetes include hypoglycemia (a dangerous and sharp drop in blood glucose levels), which can lead to hypoglycemic coma and death, ketoacidosis ( increased content in the blood of metabolic products and ketone bodies), leading to disruption of the work of all vital organs of the body.
With a long course of the disease, other consequences may occur over time, such as diseases of the retina, ulcers and boils on the legs, trophic ulcers, limb weakness and chronic pain.
Noticed an error? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Insulin is one of the most important hormones produced in human body. It is responsible for the normal functioning of many systems and organs, but its main task is to control the level of glucose in human blood. If this level is higher or lower than normal, then metabolic processes in the body, and if you do not pay attention to the violation of this ratio in time, serious diseases can develop.
The need and norms of insulin
All processes occurring in the human body are somehow "tied" to insulin. Without this hormone produced by the pancreas, the nutrients that enter the body with food cannot be broken down. In case of malfunctions of the pancreas or other problems, energy metabolism is disturbed, which has the most detrimental effect on health.
In a healthy person, the level of insulin normally ranges from 3 to 25 units, in children the upper limit is slightly lower - 20 units. In elderly people, the upper limit is considered to be no higher than 35 units, such indicators can be after 60 years. All this is the norm. And everything that is above normal levels is a reason for immediately contacting doctors, since elevated insulin levels in the blood are an alarming bell, announcing that the coordinated work of all human systems and organs has given a serious failure.
The greatest concern should be caused by high insulin levels during normal, normal sugar in blood. By the way, doctors strongly recommend keeping a glucometer at home, with which you can always measure the level of both sugar and insulin without going to a medical institution.
The most objective picture of blood sugar can be obtained by measuring the level every 2-2.5 hours, but in such a way that at least five measurements per day are obtained. But not everyone has such an opportunity, so it is advisable to check your blood for sugar, at least immediately after waking up, in morning time, and before going to bed.
Symptoms
A significant increase in the level of insulin in the blood is called hypoglycemia. Symptoms of this pathological condition:
- depression,
- oppression,
- deterioration of memory and memory abilities,
- extremely difficult to concentrate.

With progressive hypoglycemia, the main symptoms develop very quickly:
- chronic fatigue,
- rapid weight gain.
In addition, elevated insulin levels directly affect the condition blood vessels, provoking the occurrence of hypertension, and if you do not pay attention to all this set of symptoms, then non-intervention in the situation can lead to more serious circulatory disorders, in which a person can be overtaken:
- disruption of normal sleep
- increased secretion of sebum,
- kidney failure,
- gangrene of the lower extremities.
Women usually notice these changes more often, as they begin to worry about the transformations taking place with them: firstly, being overweight, which is perceived as an undesirable phenomenon at any age, and secondly, increased oiliness of the skin. The latter phenomenon directly changes the appearance: the skin not only acquires a characteristic oily sheen, but also multiple acne appears, and the hair quickly becomes “greasy”.
Causes
Let's make a reservation from the very beginning: always, under any circumstances, high insulin is not normal. But only a doctor of the appropriate profile can, with a high degree of probability, determine what kind of pathology we are talking about, and how it can and should be dealt with.

Based on the root cause of this phenomenon, we can talk about:
- primary hyperinsulinism,
- secondary hyperinsulinism.
Primary hyperinsulinism is an elevated level of insulin reduced level blood sugar, that is, it is the primary form of the development of pathology. Such hyperinsulinism is also called pancreatic, as it develops against the background of a violation of the production of an insulin antagonist hormone, which is called glucagon (glucagon hyposecretion). Both of these hormones are produced in the pancreas, in the so-called islets of Langerhans. When there is a malfunction in the production of glucagon, an excess of insulin occurs in the body.
Elevated or high levels of insulin in the blood normal level sugar may indicate the following disorders:
- the occurrence of neoplasms (benign or malignant tumors) in the body of the pancreas,
- decreased production of glucagon.
Secondary hyperinsulinism is also an increase in insulin levels with normal sugar levels. With this type of hyperinsulinism, the work of the central nervous system is disrupted, and in addition, excessive production is observed:
- adenocorticotropic hormone (corticotropin),
- somatotropin, or growth hormone (both of these hormones are produced by the pituitary gland),
- hormones produced by the adrenal cortex (glucocorticoids).

The reason for this phenomenon can be multiple factors, both external and internal, including:
- liver failure or impaired liver function,
- violation of carbohydrate metabolism,
- pathological changes in the anterior part of the brain,
- the occurrence of tumors in the abdominal region,
- development of malignant neoplasms in the adrenal glands.
What do we have to do
First of all, for proper treatment you need to find out the cause of this pathology. Without finding out the cause, treatment should not be started, since it cannot be effective. And independent symptomatic treatment, especially long-term (taking antihypertensive drugs to lower blood pressure, analgesics for headaches, and so on), can “lubricate” clinical picture and postpone your visit to the doctor. And in such a situation, the sooner you apply, the greater the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
Only a thorough and comprehensive examination can reveal the cause of hyperinsulinism. But often patients end up in a hospital with hyperinsulinism already in acute form when the patient needs to be injected to normalize the state of glucagon and adrenaline. But even if a person was hospitalized before an exacerbation of the disease, very often one cannot do without a dropper with glucose, since high insulin will sooner or later lead to a decrease in blood sugar, this phenomenon is called hypoglycemia. Symptoms of this condition:
- increased sweating,
- tachycardia,
- increased fatigue and weakness,
- pallor of the skin.
In this case, the patient constantly experiences a feeling of hunger. With a sharp decrease in sugar, loss of consciousness is possible, if sugar is not brought back to normal - hypoglycemic coma.

Often the question arises: is it possible to lower the level of insulin at home?
Yes, of course you can. But reducing insulin levels at home is not synonymous with self-treatment without resorting to specialists. It is possible to be treated for hyperinsulinism not in a hospital, but at home, but only after the doctor with whom the person visited fully writes out and explains the treatment regimen to him and prescribes all the medications necessary for this. But since the treatment is prescribed as a complex one, the list of therapeutic measures may include those for which it is necessary to visit medical institutions: for example, when prescribing physiotherapy or manual therapy, acupuncture, acupuncture, etc. Droppers, too, not every patient can put himself at home, so in no case can you ignore either clinics or even hospitals.
If we talk about home treatment, then doctors emphasize: the main thing is self-control. And this applies not only to the mandatory five-time measurement of insulin levels, but also to some other points. Sometimes, in order to maintain health, it is necessary to step on the throat of your “I” and your desires (but it’s more honest to call them human weaknesses). It is difficult to force yourself to do what you are not used to doing, and to refuse what you really want. But it is precisely this that boils down to two points of home treatment:
- physical exercise,
- preventive diet.
Body weight should never increase. To do this, you need to follow a diet, which can be very strict. If a person does not feel enough willpower in himself, it is better that one of his relatives monitors his nutrition.
A diet with elevated insulin should be based on fractional nutrition - the patient should eat at least five times a day, while food portions should be small. Carbohydrates should be reduced to 150 g per day. If a person experiences moral discomfort from some food restrictions, you need to pay attention to the readings of blood tests: as soon as the doctor's prescriptions are scrupulously followed, the insulin readings in the blood will return to normal. And when the patient sees with his own eyes that he is getting healthier, this will have a positive effect on his condition.

But in addition to psychological moments, there will also be an undoubted objective improvement in the state. But in any case, you will need to periodically visit a doctor for a preventive examination and do a blood test several times a year.
In addition, you need to continue to follow a diet and try to keep healthy lifestyle life. What is included in this concept? The list is not that big:
- watch your weight, don't overeat,
- do morning exercises
- before going to bed, take at least a short walk in the fresh air,
- try to give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
By detecting the disease in time and coping with it, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of relapses.
The hormonal system in a healthy person is completely balanced. If the synthesis of hormones has deteriorated or they are produced much more than the permissible amount, then various pathological processes begin. These include diabetes mellitus (DM) type 1-2, which can be diagnosed even in a newborn child.
You can find out if a healthy woman or man has diabetes by measuring insulin, because when it is normal, sugar will not be high, otherwise the concentration of glucose in the blood is most often increased. People with diabetes often have trouble detecting it, as their cells may be less able to perceive the hormone. This process is characterized by increased insulin in the blood with normal or high sugar levels, and diabetics need to understand what this means and whether it is possible to undergo treatment using special medications.
The norm of insulin in the blood in healthy men and women indicates that the pancreas is coping with its functions, but at the same time, it is necessary to take an analysis for sugar levels. Only according to the results of 2 tests, the doctor will be able to tell whether a person has diabetes or not, and usually these examinations are performed when high glucose levels are suspected.
Insulin is a protein molecule that is produced in the pancreas. Its synthesis occurs in beta cells accumulated on the islets of Langerhans. Insulin is mainly responsible for transporting glucose to the cells of the body, where it, after splitting, gives energy to a person. Without sugar, nerve tissues will begin to starve, while a person will become less able to think and his appetite will increase, so it is important to notice any changes in your body in time.
Acceptable limits in analyzes
In order for a woman's blood sugar level to remain normal, insulin should not be low or high at the same time, and you can find out which hormone level is normal based on these data:
- In people after 60-65 years, the results should be from 3 to 26 mcU / ml;
- In a child, insulin should normally not be lower than 3 and higher than 19 mcU / ml;
- In a pregnant woman, the norm, taken on an empty stomach, should be in the range from 6 to 25 mcU / ml;
- In healthy people, its rate is from 3 to 24 mcU / ml.
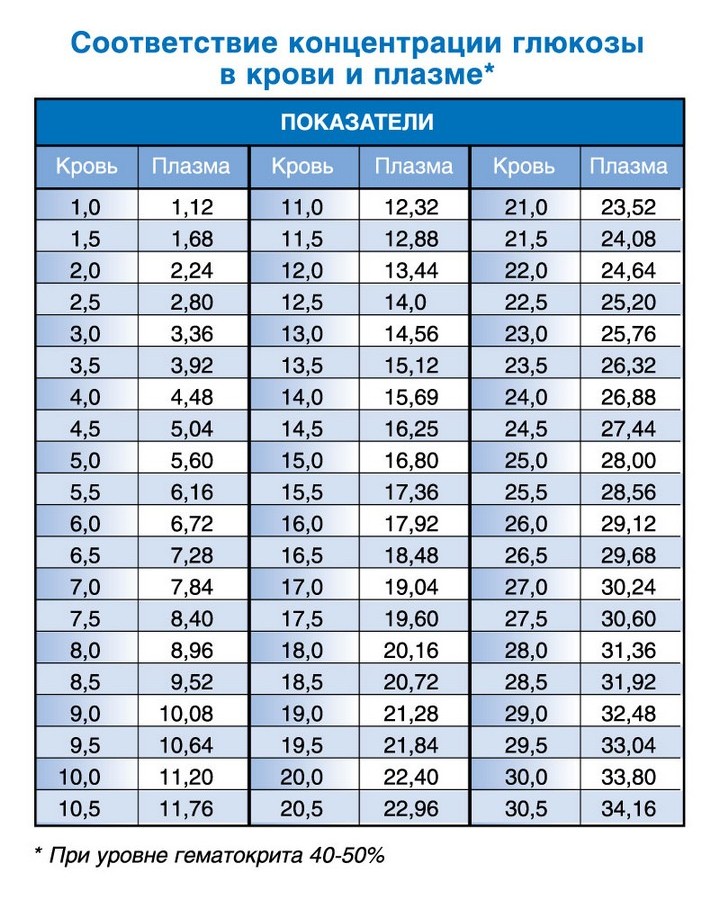
If insulin levels in a healthy person are normal, then sugar should not be increased and is no more than 5.9 mmol / l, which means that the pancreas produces the hormone in a normal amount. The process of processing glucose itself looks like this:
- In all cells of the body there are receptors that perceive insulin and after the hormone is produced, it connects to them;
- Cells become more receptive to glucose, so sugar, with the help of insulin, easily penetrates and oxidizes them, producing energy.
The function of this hormone also includes the creation of glycogen stores in the liver. The need for it arises when the level of glucose in the body decreases during physical exertion or with malnutrition. Sometimes hypoglycemia occurs after drugs to lower blood sugar, and these reserves will contribute to the normalization of the condition.
Reasons for a decrease or increase
Decreased levels of insulin in the blood with normal or high sugar, especially in a child, speaks of problems in the pancreas, and you can understand what this means by finding out their cause. When the production of this hormone is reduced, the activity of its antagonist called glucagon increases. It is also produced in the pancreas, but by alpha cells located on the islets of Langerhans.
Glucagon serves to increase the amount of glucose in a person's blood. That is why its increase can lead to irreversible consequences, including diabetes.
Doctors advise in order to prevent a child or an adult low insulin take blood tests at least 1-2 times a year.
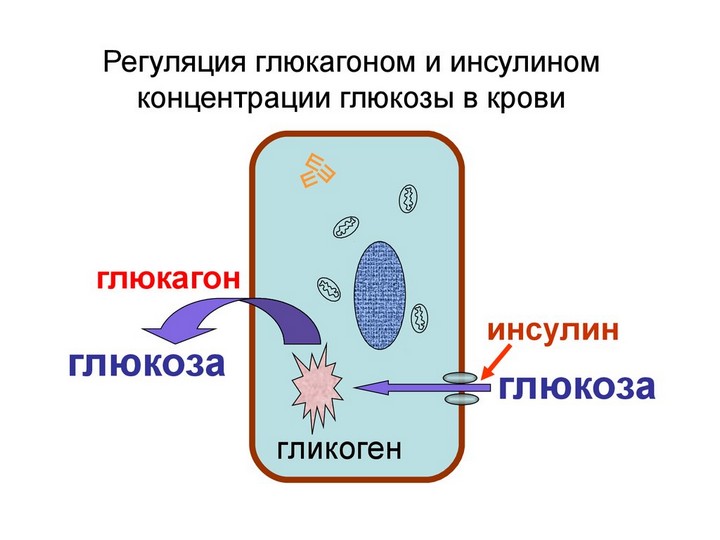
It is equally important to find out why a woman has elevated insulin in her blood with normal or high sugar levels and find out what this means by reading the following reasons:
- severe mental and exercise stress. In this situation, there is elevated insulin with normal or low blood glucose levels. This phenomenon occurs due to the fact that the body needs more sugar to cope with the difficulties that have arisen, so the production of the hormone increases significantly;
- Tumor in the pancreas. If insulin is above normal in such a situation, then this means that the oncological disease has touched the beta cells. Because of this reason, the symptoms only become brighter and a person can fall into a hypoglycemic coma if treatment is not started on time.
Symptoms for such a phenomenon as an increased amount of insulin in a woman's blood are as follows:
- Extreme activity (before the depletion of glucose reserves);
- excessive sweating;
- A little fever(up to 38);
- Groundless anxiety.
You can understand what the elevated insulin level in combination with the norm of blood sugar means by passing a glucose test, because diabetes is often the cause of the problem.
Increased hormone due to diabetes

With diabetes, insulin in the blood can be increased, decreased, or even normal, since it all depends on the type of disease and its course:
- type of insulin. This variety belongs to the first type of pathology and it is typical for people under 30-35 years old. The disease develops due to the fact that an acute lack of insulin occurs in the body, as they were damaged by their own immune system beta cells. Experts associate this process with past viral or infectious diseases, due to which there was a failure in the body's defense system. Treatment of type 1 diabetes is carried out only with the help of injections of the missing hormone;
- Insulin-independent type. It is type 1 diabetes and develops in older people after 40 years of age due to metabolic failures, obesity, etc. function or there is resistance to their own hormone. The course of treatment for type 2 diabetes includes taking drugs to improve the absorption of glucose, and with severe course disease and insulin. To compensate, you will also need drugs that increase insulin production and medications to improve its perception by body cells.
Sometimes sugar can be normal, and insulin in the blood is increased or decreased for other reasons, and this may mean that a woman leads a sedentary lifestyle or she is overweight. Among the factors causing this problem, there is also prolonged fasting, disorders in the central nervous system and chronic diseases.
Testing procedure
Before looking for what to do if you suspect a high level of insulin, you need to take blood tests, which will contain all the necessary data to confirm or refute the diagnosis. First you need to know the concentration of sugar in the body. A fasting test is performed and normal considered to be 5.9 mmol/l and below. This result means that insulin in the blood is not lower than normal and performs the functions assigned to it.
If glucose, according to the test results, is at a level of 6 to 12 mmol / l, then doctors call this condition prediabetes with a clear violation of the perception of the hormone produced by the pancreas. This analysis means that it is impossible to say for sure whether there is an excess of insulin in the blood due to diabetes or it is simply not enough. Formally, it exists, but does not fully fulfill its functions due to weak production or resistance. In such a situation, it is necessary to do additional tests, after which it will be known what pathological process has begun in the body.
When the final figures show 12 mmol / l and above, the doctor will make a preliminary diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, but will do a few more tests. After them, it will be known whether insulin is to blame or if there is another reason.
Examining the pancreas is a rather difficult process. To do this, you will have to do tests early in the morning and on an empty stomach.
To get accurate information about whether there is a lot of insulin in the blood or not, you need to perform the following preparation:
- You can’t eat anything for 8-12 hours so that the final indicators of glucose and insulin are not overestimated after that;
- The day before the test, it is better to have a good rest and not to be physically or mentally loaded;
- For 2-3 days, alcohol and fatty foods should be excluded from the diet, as well as the use of various drugs especially hormonal ones. If this cannot be done, then you need to consult a doctor.
It is possible to determine the level of insulin in the blood, but it will take a lot of time, since first a biomaterial is taken from a vein, and then it is placed in a special apparatus for research. The results are usually taken in the evening or the next day, and after receiving them, you should immediately go to the doctor.
Insulin stabilization
Can insulin, or rather, its insufficient amount, increase blood sugar, or is it all the fault of the cells that perceive it poorly, it is quite important to know to determine the cause of the problem. After all, a person who has experienced an endocrine failure must put his hormonal system in order and, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the culprit of the pathological process.
A high level of insulin is usually determined by its characteristic symptoms or after examination. Most people have problems with obesity due to poor nutrition. You can fix this problem by properly adjusting your diet. The foods consumed should not contain a large amount of fast carbohydrates, as they greatly increase blood sugar. You need to choose food based on its glycemic index and the lower it is, the better.
In the treatment of diabetes, patients are often prescribed special drugs that increase insulin levels. The effect of them is also fixed by other medicines created to improve the perception of cells to their own hormone.
The rate of insulin in children in the blood, as in adults, must be observed so that you do not have to deal with the treatment of endocrine disruptions. Avoiding them is quite simple, because for this you need to take blood sugar tests once a year and lead a healthy lifestyle.