From what can be high sugar. The reasons for increasing blood sugar: why the glucose rises.
Increased blood sugar is a disputed process. On the one hand, it can be explained by quite natural causes, on the other - signals the presence of serious endocrine disorders.
The reasons for which blood sugar is rising
Human blood sugar increases for various reasons. Natural:
- incorrect metabolism when the reception and absorption of food is disturbed;
- lack of physical exertion with abundant nutrition;
- stress, nervous breakdownsdepressed;
- bad habits, such as excessive alcohol, smoking, etc.;
- Premenstrual syndrome in women, etc.
Of course, most often the reason causing an increase blood sugar is such endocrine diseaselike diabetes mellitus. In this case, there will be a number of characteristic symptoms.
Symptoms of blood sugar increase
Increased blood sugar can be felt. So you can feel the following signs Increase blood glucose:
- feeling of hunger and weight gain;
- irritability and drowsiness appear;
- Non the feet and brushes;
- There are various vaginal infections and impotence.
That sugar already exceeds the norm indicate:
- frequent urinationnot caused by frequent fluid intake;
- nausea and vomiting;
- unexpected weight loss;
- a sharp loss or excessive weight gain;
- Weakness and fatigue.
Why are those or other symptoms appear
The mechanism of appearance characteristic to increase sugar symptoms is due to a number of factors. So, for example, the thirst appears due to the fact that glucose is pulling the water. An increase in fluid consumed leads to the fact that the kidneys begin to work more active - from here and more frequent urination.
The weight loss is manifested because the cells do not take glucose and begin to suffer from energy starvation. This phenomenon is most often found at diabetes of the first type.
Weakness, headacheThe increased fatigue is a consequence of the brain's starvation. If glucose is in insufficient quantity goes to the brain (and this may happen in the event that it is produced in excessive amounts), the brain stops receiving power in the desired quantity, and switches to the energy conservation mode.
Increased blood sugar leads to the development of a number of symptoms, it is simply impossible to confuse with others. Doctors easily manage to make a diagnosis and send a patient for analyzes to assign it correct treatment.
An increase in glucose levels in the blood is also called hyperglycemia. The phenomenon is often observed when disorders carbohydrate exchange Due to various physiological changes. Sugar enters the human body together with food, then transported by blood for all organs. There are certain norms for the presence of glucose in the blood. W. healthy man The norm is considered to be 3.3-5 mmol / l. This norm is established for the analysis taken from the patient's finger, venous blood, often has a higher concentration.
The level of glycemia is an important indicator of the right work. human organism. Changes in the direction of decrease in / increasing may be an indicator of any disease. For maintaining the level of glycemia within the allowable hormones are followed. The main hormone responsible for the sugar content is insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. If the body has an increase in the concentration of sugar, the pancreas enhances the production of the right hormone. Insulin contributes to the penetration of sugar into human cells, thereby reducing its content.
When hyperglycemia, the source of this phenomenon should be installed. Causes are natural or pathological. The presence of pathology is not judged by one analysis. When the high level is detected, it is desirable to repeat the analysis. If repeated results do not fit into normal, then the doctor must find out why the glucose indicator increases.
Natural causes of glucose level increase
Sometimes sugar concentration in healthy people naturally rises. If there is an insufficient amount of time after eating food, then the analysis will be unreliable. From the last meal before passing the analysis must pass, at least 10 hours. The level of glycemia is also naturally rising in stress, strong fatigue, anxiety. Women naturally considered an increased indicator before menstruation. Also, the indicator affects smoking, abundant physical exertion.
Collection of analysis should occur taking into account the natural reasons for increasing the concentration. The analysis should be taken early in the morning, on an empty stomach. From smoking before analyzing it is necessary to refuse.
Pathological causes of hyperglycemia
The most common pathological cause Increases sugar content is diabetes. Diabetes is different types. Each type is characterized by a mechanism for improving sugar.
With a disease 1 type, an increase in glucose concentration is determined by the fact that the pancreas does not cope with the development of insulin. In the presence of diabetes of this type the immune system destroys cells synthesizing insulin.
In case of disease, the type of iron produces the desired amount of insulin, but the hormone is not able to interact with the cells of the body. In this case, the content of glucose in the blood increases, and the cells feel a flaw.
Separate category feature pregnant diabetes. During pregnancy, insulted insulin, and, consequently, high Sugar. In the blood, after childbirth, the state is usually normalized. The development of this disease in the early deadlines may cause complications of the child's developmentalities. During the manifestation of signs increased sugar In the blood of women during pregnancy, contact a specialist.

There are other reasons for increasing blood sugar except diabetes. These include:
- pathology of the endocrine gland;
- disorders of the pancreas;
- various liver diseases;
- the emergence of infections;
- reception of certain drugs.
Temporary increase in the indicator may be observed in burns various degrees, during an epileptic seizure, with strong pains.
Symptoms of hyperglycemia
Basic symptoms high Sahara In the blood of an adult:
- student urination;
- regular desire to drink, there is dry mouth;
- regular feeling of hunger;
- feeling of severe weakness, fast fatigue;
- numbness of the limbs;
- the appearance of itching;
- slowing down wound healing;
- nausea;
- the increase in headaches;
- rapid loss of body weight;
- rapid impairment.
When identifying the above symptoms, you should contact a specialist and immediately pass the blood test for glycemia. Strong levels of levels from the norm can lead to the appearance of convulsion, to the deterioration of respiration and the work of the heart. The signs of high blood sugar detected on time will help to provide the necessary timely assistance.
Sometimes an increased concentration is not expressed by certain symptoms, a person feels relatively normal, but diabetes develops in a hidden form. This type of diabetes is often diagnosed by chance with a prophylactic inspection.
Consequences of increased glucose concentration
Critically high indicator It may be the reason for the emergence of strong complications. A person can go into a state that is characterized by the defeat of the central nervous system. This state is manifested in the developing violation of the nervous system activity, may be accompanied by the loss of consciousness, the simplest reflexes.
A sharp increase in blood sugar content may cause violations of metabolic processes, thereby causing anyone. The states of the coma are characterized by a high probability of death, so it is very important to seek medical help already when identifying the first signs.
Long increase in glucose indicator causes late complications, such as:
- damage retina eye;
- diabetic stop (the development of gangrene);
- renal failure.
Ways to lower glucose concentrations
If the cause of increasing blood sugar is the development of diabetes, then the first actions for the normalization of glycemia should be: development of the diet of the right nutrition and the purpose of the necessary drugs.
When diabetes mellitus 1, the patient is necessary daily in the form of injections to introduce insulin. Treatment of type 2 diabetes meant the regular reception of drugs aimed at stimulating insulin production and restoring cell ability to take a mining hormone.
If necessary, normalize the glucose indicator from the diet completely eliminate sweet, confectionery, white bread, alcoholic beverages, fruits.
To achieve a stable level of blood glucose in the blood, uncomplicated rules should be performed:
- maintaining the right nutrition plan;
- implementation of permanent control of the concentration using a glucometter;
- performing exercise;
- regular reception of prescribed drugs.
IN preventive purposes, in order to avoid the growth of blood sugar level, it is recommended to track the diet and an increase in physical activity. Daily execution of simple physical exercises will contribute to a decrease in the indicator. Genetic predisposition to diabetes is already indicated to proper nutrition and healthy lifestyle.
At first and even minor signs of hyperglycemia should immediately consult a doctor. Do not try to diagnose yourself, and even more so you do not need to deal with self-medication.
First of all, it should be noted that it would be more correct to say "blood glucose level", since the concept of "sugar" includes a whole group of substances, and determined in the blood glucose. However, the term "blood sugar level" was so accustomed that it is used both in colloquial speech and in the medical literature.Then, if necessary (elevated physical or emotional loads, lack of glucose intake from gastrointestinal tract), Glycogen is split, and glucose enters blood.
Thus, the liver is a glucose depot in the body, so that during its severe diseases, disturbances of blood sugar are also possible.
It should be noted that the admission of glucose from the capillary bed inside the cell is enough difficult processwhich in certain diseases may violate. This is another reason for the pathological change in blood sugar levels.
The yield of glucose from the depot in the liver (glycogenolysis), the glucose synthesis in the body (gluconeogenesis) and the absorption of its cells is controlled by a complex neuroendocrine regulation system, in which the hypothalamic-pituitary system (the main center of neuroendocrine regulation), pancreas and adrenal glands take directly participation. The pathology of these bodies is often the cause of blood sugar levels.
How is the allowable blood sugar level regulated?
 The main hormone regulating permissible level Sugar in the blood is the hormone of the pancreas - insulin. With an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, the secretion of this hormone increases. This occurs both directly as a result of the stimulating effect of glucose on the receptors of the pancreas cells, and is indirectly, by activating the parasympathetic nervous system through glucose-sensitive receptors in the hypothalamus.
The main hormone regulating permissible level Sugar in the blood is the hormone of the pancreas - insulin. With an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood, the secretion of this hormone increases. This occurs both directly as a result of the stimulating effect of glucose on the receptors of the pancreas cells, and is indirectly, by activating the parasympathetic nervous system through glucose-sensitive receptors in the hypothalamus. Insulin contributes to the consumption of glucose by cells of the body, and stimulates the synthesis of the glycogen in the liver - thus the blood sugar level is reduced.
The main insulin antagonist is another hormone of the pancreas - glucagon. With a decrease in blood sugar levels, its increased secretion occurs. Glucagon enhances the decay of glycogen in the liver, contributing to the exit of glucose from the depot. The same action has a hormone of brainstabs of adrenal glands - adrenaline.
Hormones stimulating glucoseogenesis are also promoted to increase blood glucose levels - the formation of glucose in the body from simpler substances. In addition to glucagon, such an action is made of cerebral hormones (adrenaline, norepinephrine) and cortical (glucocorticoid) adrenal substances.
The sympathetic nervous system, activating when requiring increased energy consumption, increases blood glucose levels, and parasympathetic - reduces. Therefore, deep at night and early in the morning, when the predominance of the influence of the parasympathetic nervous system is observed, the blood glucose level is the lowest.
What tests are carried out to determine blood sugar levels?
There are two most popular in clinical medicine Method of measuring blood sugar levels: in the morning on an empty stomach (while the break in the meal and fluid should be at least 8 hours), and after the load of glucose (the so-called oral glucose-olerant test, OGTT).The oral glucose-bearing test is that the patient takes inside 75 grams of glucose dissolved in 250-300 ml of water, and after two hours, the blood sugar level is determined.
The most accurate results can be obtained with a combined conduct of two tests: after three days by the usual morning on an empty stomach, the level of sugar in the blood is determined, and after five minutes, the glucose solution is taken to measure this indicator in two hours.
In some cases (diabetes, violation of glucose tolerance) is needed by constant monitoring of blood sugar levels, so as not to miss serious pathological changes, fragile threat to life and health.
Is it possible to measure the blood sugar level at home?
 The blood sugar level can be measured at home. To do this, you should purchase a special device in a pharmacy - a glucometer, for example, OneTouch Select - it is compact, it is easy to take with you and check the level of glucose where it is necessary. Facilitates checking the interface in Russian, the marks before and after eating. The device is extremely easy to use, while it is distinguished by the measurement accuracy. With the help of a portable glucometer can be held a poor under control.
The blood sugar level can be measured at home. To do this, you should purchase a special device in a pharmacy - a glucometer, for example, OneTouch Select - it is compact, it is easy to take with you and check the level of glucose where it is necessary. Facilitates checking the interface in Russian, the marks before and after eating. The device is extremely easy to use, while it is distinguished by the measurement accuracy. With the help of a portable glucometer can be held a poor under control. The traditional glucometer is a device with a set of sterile lanceters for blood and special tail strips. In sterile conditions, Lanzet is punctured by the skin on the tip of the finger, the blood droplet is transferred to the trees strip, which is subsequently placed in the device to determine blood sugar levels.
There are glucometters processing capillary bloodderived from other places (shoulder, forearm, foundation thumb, thigh). But it should be remembered that blood circulation in the tips of the fingers is much higher, therefore, using the traditional method, you can get more accurate results on the level of blood sugar at the moment. This can be very important, since this indicator in some cases is changing rapidly (physical or emotional load, food, developing a concomitant disease).
How to properly measure blood sugar levels at home?
To properly measure the level of blood sugar at home, you should carefully read the instructions for the acquired device, and in doubtful cases, seek explanations to a specialist.
When measuring blood sugar levels at home, some general rules must be observed:
1.
Before the blood fence should be thoroughly wash his hands with warm water. It must be done not only to ensure purity, but also to improve blood circulation. Otherwise, the puncture on the finger will have to do deeper, and take blood for the analysis will be more difficult.
2.
The point of puncture should be well dried, otherwise the blood obtained will dilute with water, and the results of the analysis will be distorted.
3.
For blood collection, the inner surface of the three-finger pads of both hands is used (large and index finger traditionally do not touch the workers).
4.
So that the manipulation brings as little as possible painful sensationsIt is best to make a puncture not in the center of the pads, but a slightly side. The depth of the puncture should not be too large (2-3 mm for an adult - optimal).
5.
With a regular measurement of the level of sugar in the blood, it is necessary to constantly change the place of blood intake, otherwise there will be inflammation or / and thickening of the skin, so in the subsequent bonding the blood from the usual place will be impossible.
6.
The first drop of blood obtained after the puncture is not used - it should be carefully removed with a dry robe.
7.
It should not be too squeezing a finger, otherwise the blood is mixed with the tissue fluid, and the result will be released inadequate.
8.
It is necessary to remove the blood droplet until it was smeared, because the lubricated drop is not absorbed into the test strip.
What is the level of blood sugar level?
The level of blood sugar level in the morning on an empty stomach is 3.3-5.5 mmol / l. The deviation from the norm in the range of 5.6 - 6.6 mmol / l indicates a disturbed tolerance to glucose (condition, border between the norm and pathology). The increase in the level of blood sugar is an empty stomach to 6.7 mmol / l and above gives grounds to suspect the presence of diabetes.In doubtful cases, it is additionally carried out to measure the level of blood sugar in two hours after the load of glucose (oral glucose-bearing test). The rate indicator with this study increases to 7.7 mmol / l, indicators within 7.8 - 11.1 mmol / l are indicated for violation of glucose tolerance. In diabetes mellitus, the sugar level two hours after the load of glucose reaches 11.2 mmol / l and above.
What is the normal blood sugar level in a child?
In young children, there is a physiological propensity to reduce blood sugar levels. The norms of this indicator in babies and preschoolers are somewhat lower than in adults.So, in breast-age children, the glucose level of an empty stomach is 2.78 - 4.4 mmol / l, preschoolers - 3.3 - 5.0 mmol / l, in children school age - 3.3 - 5.5 mmol / l.
If the level of blood sugar in an empty stomach exceeds 6.1 mmol / l, then they speak of hyperglycemia (increasing blood sugar). Indicators below 2.5 mmol / l indicate hypoglycemia (reduced blood sugar levels).
In the case when the sugar level of an empty stomach is within 5.5 - 6.1 mmol / l, an additional oral glucose-bearing test is shown. Glucose tolerance in children is significantly higher than adults. therefore normal indicators blood sugar levels in two hours after standard glucose load are somewhat lower.
If a child has a blood sugar level on an empty stomach exceeds 5.5 mmol / l, and two hours after a load of glucose reaches 7.7 mmol / l or higher, then sugar diabetes mellitus.
How does blood sugar level change during pregnancy?
In some cases, physiological insulin resistance exceeds the possibilities of the pancreas in insulin production. This develops so-called gestational diabetes mellitus, or diabetes of pregnant women. In most cases, after childbirth, women with diabetes are pregnant, all indicators of blood sugar are returned to normal. However, caution should be taken, since approximately 50% of women who have undergone gestational diabetes, for 15 years after pregnancy develops sugar diabetes of the second type.
In gestational diabetes, as a rule, there are no any clinical manifestations hyperglycemia. However, this condition is a danger to the development of the child, since in the absence of compensatory therapy, an increased level of glucose in the blood of the mother in 30% of cases leads to the pathology of the fetus.
Gestational diabetes usually develops in the middle of pregnancy (between 4 and 8 months), and women from the risk group should be especially attentive to the blood sugar levels at this time.
The risk group includes women with increased body weight, unfavorable heredity (diabetes of pregnant or second type for the nearest relatives), burdened by obstetric history (large fruit or stilling during previous pregnancies), as well as suspicion of large fruit at current pregnancy.
The diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus is made with an increase in blood sugar levels taken on an empty stomach, to 6.1 mmol / l and higher, if two hours after the load is load, this indicator is 7.8 mmol / l and above.
Increased blood sugar level
When is the elevated blood sugar level?
There are physiological and pathological increase in blood sugar levels.The physiological increase in blood glucose concentration occurs after meals, especially easily digestible carbohydrates, with intensive physical and mental load.
A short-term increase in this indicator is characteristic of such pathological conditions as:
- strong pain syndrome;
- epileptic seizure;
- acute;
- heavy attack.
In the cranial and brain injury with the lesion of the hypothalamus (there is a reduced ability of tissues to dispose of glucose).
With severe liver lesions (reduced synthesis of glycogen from glucose).
A long-term increase in blood sugar levels leading to the appearance of glucose (glucose removal with urine) is called diabetes diabetes (sugar diabetes).
Due to the occurrence, the primary and secondary diabetes are distinguished. Primary diabetes mellitus is called two separate nosological units (first and second diabetes) having internal reasons Development, while the reasons of secondary diabetes serve various diseases, leading to pronounced violations of carbohydrate metabolism.
First of all, these are severe pancreatic lesions, characterized by absolute insulin insulsion (pancreas, severe flow, damage to the organ with fiberglass, the removal of the pancreas, etc.).
Secondary diabetes mellitus is also developing in diseases accompanied by an increase in the secretion of conjunral hormones - glucagon (hormonally active tumor - glucagonomoma), growth hormone (giantism, acromegaly), hormones (thyrotoxicosis), adrenaline (brainstorm tumor of adrenal adrenal glands - adrenal cortex hormones ( Incenko-Cushing syndrome).
Quite often occurs, reduced tolerance for glucose, up to the development of diabetes mellitus caused by a long-term intake of drugs, such as:
- glucocorticoids;
- tiazide diuretics;
- some hypotensive and psychotropic drugs;
- estrogen-containing drugs (including oral contraceptives);
What is the mechanism for increasing blood sugar levels in diabetes type?
 Increased blood sugar levels with type-type diabetes mellitus associated with absolute insulin deficiency. This is an autoimmune disease in which the cells of the pancreas, producing insulin, are exposed to autoimmune aggression and destruction.
Increased blood sugar levels with type-type diabetes mellitus associated with absolute insulin deficiency. This is an autoimmune disease in which the cells of the pancreas, producing insulin, are exposed to autoimmune aggression and destruction. The reasons for the occurrence of this pathology have not yet been fully understood. Sugar diabetes of type is considered a disease with a hereditary predisposition, but the effect of hereditary factor is insignificant.
In many cases, there is a connection with the transferred viral diseases that launched an autoimmune process (the peak of morbidity falls on the autumn-winter period), but a significant part of the disease diabetes mellitus is idiopathic, that is, the cause of pathology remains unknown.
Most likely, the disease is based on a genetic defect, which is implemented under certain conditions (viral disease, physical or mental injury). Sugar diabetes of the type is developing in a children's or youthful, less often in adulthood (up to 40 years).
Pancreas compensatory capabilities are large enough, and symptoms Sugar diabetes of type is manifested only if more than 80% of insulin production cells are destroyed. However, when the critical limit of compensatory capabilities is achieved, the disease develops very quickly.
The fact is that insulin is necessary for the consumption of glucose cells of liver, muscles and adipose tissues. Therefore, if it is drawn, on the one hand, the level of blood sugar increases, because in the part of the body of the body of glucose does not come, on the other, the cells of the liver, as well as muscle and adipose tissue, are experiencing energy hunger.
Energy hunger cells launches glycogenolysis mechanisms (glycogen decay with glucose formation) and glucose genesis (glucose formation of simple substances), as a result, the blood sugar level increases at times.
The situation complicates the fact that reinforced glukegenesis passes with the collapse of fats and proteins necessary for glucose synthesis. Disintegration products - toxic substancesTherefore, against the background of hyperglycemia there is a general poisoning of the body. Thus, type-type diabetes can lead to the development of critical states (coma) in the first weeks of the development of the disease.
Due to the rapid development of symptoms in the preinsulin era, the diabetes mellitus I was called malignant diabetes. Today, when there is the possibility of compensatory treatment (the introduction of insulin), this type of disease is called insululin-dependent diabetes (ECD).
Energy hunger of muscular and adipose tissue causes quite characteristic appearance Patients: as a rule, these are thin people of asthenic physique.
The type-type diabetes is about 1-2% of all cases of disease, however, the risk of complications, as well as the young age of the majority of patients (the peak of morbidity is 10-13 years old) attract special attention both doctors and public figures.
In diabetes mellitus of the type of insulin levels, it remains normal, but the blood glucose level is increased, since glucose into cells does not flow as a result of a decrease in the cell reaction to the impact of the hormone.
The disease develops slowly, since long-term pathology is compensated by increasing the level of insulin in the blood. However, further continues to reduce the sensitivity of target cells to insulin, and the exhaustion of the organism's compensatory capabilities occurs.
Pancreatic cells can no longer generate insulin in the quantity required for this state. In addition, due to the increased load in cells producing hormone, degenerative changes occur, and hyperinsulamia is naturally replaced by a reduced hormone concentration in the blood.
Early detection of diabetes mellitus allows you to protect the cells secreting insulin, from damage. Therefore, people from a risk group need to regularly undergo an oral glucose-bearing test.
The fact is that due to compensatory reactions, the level of sugar in the blood is on an empty stomach for a long time remains normal, but at this stage there is a reduced tolerance for glucose, and the OGTT allows it to identify it.
What are the signs of high blood sugar?
Classic diabetes is manifested by triad clinical symptoms:
1.
Polyuria (increased urine release).
2.
Polydipsia (thirst).
3.
Polyphagia (increased food intake).
The high level of blood sugar leads to the appearance of glucose in the urine (glucosuria). To remove the excess glucose, it is necessary to use a greater amount of liquid for urine formation. As a result, urine volume increases, and with it the frequency of urination. Hence the old name of diabetes mellitus - sugar diabetes.
itching the skin and mucous membranes;
Acute complications of high blood sugar levels
 The high level of blood sugar inevitably causes complications that are divided into:
The high level of blood sugar inevitably causes complications that are divided into:
1. Acute (arising from raising sugar levels to critical numbers).
2. Late (characteristic of long-term flow of diabetes).
The sharp complication of the high level of blood sugar is the development of a comatose state, which is the defeat of the central nervous system, clinically manifested by the progressive violation of the nervous activity, up to the loss of consciousness and the extinction of elementary reflexes.
The sharp complications of the high level of blood sugar are especially characteristic of type-type diabetes, which often manifests heavy manifestations close to terminal states organism. However, comatose states are complicated by other types of diabetes, especially with a combination of several factors that predispose to the development of a sharp increase in this indicator.
The most commonly predisposing factors for the development of sharp complications in diabetes are:
- sharp infectious diseases;
- other sharp stress for the body factors (burns, frostbite, injury, operations, etc.);
- exacerbations of severe chronic diseases;
- errors in the treatment and mode (skipping insulin injection or drugs corrective blood sugar levels, rough diet disorders, alcohol use, increased physical activity);
- reception some medicines (glucocorticoids, diuretic, estrogenic preparations, etc.).
The most common general precursors for the development of comatose states at an elevated blood sugar level:
1.
An increase in the amount of urine allocated to 3-4, and in some cases up to 8-10 liters per day.
2.
Permanent dryness in the mouth, thirst, contributing to the consumption of a large amount of fluid.
3.
Fatigue, weakness, headache.
If, with the appearance of early signs of increasing blood sugar levels, adequate measures were not taken, then in the future gross neurological symptoms increase.
First, the stupidity of consciousness occurs, manifested by a sharp reaction inhibition. Then the copor (hibernation) is developing when the patient has a dream close to the loss of consciousness. However, it can still be derived from such a state with superphic effects (tweaks, shaking by shoulders, etc.). Finally, in the absence of therapy, comatose and death occurs naturally.
Different types of comatous states at an elevated blood sugar level have its own development mechanisms, and, therefore, distinctive clinical signs.
Thus, the development of the ketoacidotic coma is based on the disintegration of proteins and lipids caused by hyperglycemia to form a large number of ketone bodies. Therefore, in the clinic of this complication, specific symptoms of intoxication by ketone bodies are expressed.
First of all, it is the smell of acetone from the mouth, which, as a rule, is still felt from the patient's distance before the development of the comatose state. In the future, the so-called breathing of Kussmaulyuly appears - deep, rare and noisy.
To the late precursors of the ketoacidotic coma are caused by the general intoxication by the ketone bodies of the disorder from the gastrointestinal tract - nausea, vomiting, pain in the opposite region (sometimes so pronounced, which causes suspicion of "acute belly").
The mechanism of development of the hyperosmolar coma is completely different. Elevated level Glucose in the blood causes blood thickening. As a result, according to the laws of osmosis, the liquid from the outside and intracellular medium rushes into the blood. Thus, the dehydration of the extracellular medium and the cells of the body occurs. Therefore, with hyperosmolar coma there clinical symptomsassociated with dehydration (dry skin and mucous membranes), and no signs of intoxication is observed.
Most often, such a complication occurs with the accompanying dehydration of the body (burn, massive blood loss, pancreatitis, vomiting or / and diarrhea, diuretic reception).
Lacacidotic coma is the most rare complication, the development mechanism of which is associated with the accumulation of lactic acid. As a rule, it is developing in the presence of concomitant diseases occurring with severe hypoxia (disadvantage of oxygen). Most often it is respiratory and, anemia. We provoke the development of a lactacidotic coma can be taken alcohol and increased physical activity in old age.
The specific harbinger of the lactacidotic coma is pain in the ion muscles. Sometimes there is nausea and vomiting, but other symptoms of intoxication characteristic of the ketoacenedical coma - no; There are no signs of dehydration.
Late complications of high blood sugar
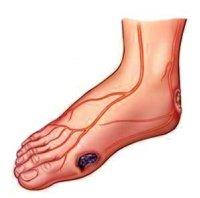 If you do not correlate the blood sugar level, complications in diabetes are inevitable, since under hyperglycemia, all organs and tissues of the human body suffer. However, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic foot syndrome are the most common and hazardous complications.
If you do not correlate the blood sugar level, complications in diabetes are inevitable, since under hyperglycemia, all organs and tissues of the human body suffer. However, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic foot syndrome are the most common and hazardous complications. If the patient is in a state without consciousness, or his behavior is inadequate, it is necessary to cause an emergency medical care. In anticipation of the arrival of the doctor, you should try to persuade the patient with inadequate behavior to take a sweet syrup. The behavior of people in the state of hypoglycemia is often aggressive and unpredictable, so it is necessary to show a maximum of patience.
Reduced blood sugar level
How to reduce blood sugar levels?
In order to effectively reduce blood sugar levels, it is necessary to know the reason for its increase.In many cases, secondary diabetes can eliminate the cause that caused pathology:
1.
Cancellation of drugs that caused the level of blood sugar;
2.
Removal of a tumor producing conjunral hormones (glucagonoma, feochromocytoma);
3.
Treatment of thyrotoxicosis, etc.
In cases where it is impossible to eliminate the reason for increasing blood sugar levels, as well as at primary diabetes mellitus І and ІІ type, compensatory treatment are prescribed. It may be insulin or medicationsreduced blood sugar levels. In gestational diabetes, it is possible to achieve a decline in this indicator, as a rule, with the help of one diet and therapy.
Treatment is selected strictly individually (not only the type of diabetes is taken into account, but also general state Specific patient), and is carried out under constant medical control.
The general principles of treatment of all types of diabetes are:
- constant control of blood sugar levels;
- fulfillment of all recommendations for compensatory treatment;
- strict adherence to the diet, labor and recreation;
- invalidation of alcohol and smoking.
When is the reduced blood sugar level?
The reduced level of blood sugar is observed:1. In case of diseases that impede glucose absorption in blood (Malabsorption syndrome).
2. With severe lesions of the liver parenchyma, when glucose output from the depot (lightning hepatic necrosis during infectious and toxic lesions) is impossible.
3. In endocrine pathologies, when the synthesis of conjunral hormones is reduced:
- hypocituitarism (pituitary hypofunction);
- addison disease (lack of hormones of adrenal cortex);
- increased insulin synthesis (insulinoma).
The most common cause of hypoglycemia in such cases becomes:
- overdose of prescribed drugs, or improper administration (intramuscular injection insulin instead of subcutaneous); Early signs of low blood sugar levels:
- increased sweating;
- hunger;
- shiver;
- increased heartbeat;
- leather paresthesia around the lips;
- nausea;
- unmotivated alarm.
- difficulty in concentration of attention, difficulties in communication, confusion;
- headache, weakness, drowsiness;
- vision impairment;
- violation of adequate perception of the surrounding, disorientation in space.
What is dangerous low blood sugar?
Low blood sugar levels may cause serious irreversible brain damage.In addition, heavy hypoglycemia oppressively acts on the central nervous systemAnd violates the orientation of the patient in the surrounding world, so that his behavior becomes inadequate. This can lead to sad consequences for both the patient and the surrounding (road traffic accidents, household injuries, etc.).
With any handling of a person to the hospital, it takes tests to determine the level of blood sugar. It is these indicators that are main to determine the patient's health. Thanks to glucose cell cells are saturated and obtained all the necessary energy.
But it is worth remembering that the body is independently not able to process the resulting sugar without such a hormone, as insulin, which is produced by the pancreas. There is a group of products that helps maintain blood sugar levels in both adults and children. Signs of high blood sugar may not appear immediatelySo, with any discomfort in the body, you should consult a doctor and pass the survey.
Blood glucose rate
Sugar performance in the body should not exceed the level of permissible and, if we talk about numbers, then the maximum allowable glucose level is 100 ml / 1 decylitr. With minor increases, the patient may not feel any changes. But if the level significantly exceeds the necessary norm, the symptoms will be visible "is obvious". Unfortunately, few people know what provisions of sugar are considered permissible.
Both men and women have the same blood sugar. But the exception can be attributed a pregnancy period. For 9 months of to wear in the body of weak gender, there are many changes, and the level of sugar is not an exception, which respectively affects the development of the child.
It is worth considering that before surrendering blood on sugar, it is necessary to refuse food, as it affects the end result. Otherwise, you need to warn your doctor's doctor, it will help correctly calculate the indicators. A healthy person is considered a level within 3.9-5 mmol / 1 liter. In the case when a person used food, either drinks shortly before delivery, the indicators may increase to 5.5 mmol. It is worth remembering that the indicators of capillary and venous blood A little different.
The testimony of the level of sugar in the blood in men and women is significantly different from the indicators of the child, but the symptoms and causes of changes are the same.
Signs of improving sugar levels
Both the increase and the decrease in blood sugar levels will not be ignored, and the body instantly starts responding to such changes. A sharp change in the level of glucose can be revealed independently. This can be done according to the following symptoms:
- For high level Human sugar is actively starting to work kidneys, and desire arises frequently visiting toilet. The body begins to actively get rid of excess fluid, and this is dangerous to the health of the child.
- Against the background of the first sign, there is a constant feeling of thirst. A person constantly drinks water, but the sense of saturation still does not occur. Already in the manifestation of these symptoms it is worth visiting the doctor.
- It occurs its item on the skin. In children, such a phenomenon can lead to the formation of wounds in the skin.
- An increase in blood sugar can lead to inflammatory processes of the urogenital system. There are pains in the field of groin in men, the inflammation of the extreme flesh. Women may have itching, burning in the field of sex.
- The high level of sugar leads to the fact that a person has a bad sense of various damage on the skin.
- In the body there are such changes as violation electrolyte balance. Such changes occur due to the fact that a person withdraws a large amount of fluid with which all useful trace elements leave, this is especially dangerous for the child and its development. It is manifested in the form of muscle and icy convulsions and violations of the cardiovascular system.
- In parallel, a person can feel the overall constant fatigue, lethargy. In children, this is manifested in a constant desire to sleep and inattention.
- Another symptom of high blood sugar is a constant feeling of hunger. If a person begins to eat a lot, and as a result, picks up a mass.
If adults have a clearer, then children in the first signs are difficult to designate it in order to identify a high level of sugar, it is necessary to pass on glucose tests.
Causes of glucose increase

The reasons why the blood sugar level can increase is very much, but the following can be attributed:
- The factor of heredity. Genetic predisposition can manifest itself in early age in children. Most often it is worth revising the diseases of the nearest relatives to determine the level of risk.
- For autoimmune diseases. In this case, the body begins to reject its own authorities, damaging them.
- Excess body weight.
- Physical and psychological injuries. Often, strongly experienced stresses become impaired sugar. A child can manifest itself in constant irritability and nervousness.
- Changes in the blood supply to the pancreas.
All of the above symptoms occur in the case of a disease, but there are also concomitant moments that can change glucose indicators in a healthy person. To the main reasons for changing sugar can be attributed:
- eating containing a large amount of carbohydrates;
- if low physical activity;
- harmful habits (smoking, alcohol), very often it is this reason to become the main thing in men.
Also in the risk group I can get patients who have such complications as:
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- liver disease;
- pancreatic disorders.
It is worth noting that elevated sugar In the blood of children whose symptoms are the same as in an adult manifests itself slightly and to identify it costs more carefully to pay attention to the well-being of the baby.
Restoration of blood glucose level
Before proceeding with the treatment and normalization of blood sugar levels, it is necessary to identify the causes of its violation. This can only be done after surrendering and consulting a specialist.
Usually, the violation of the sugar rate is the consequence of any disease and only when it is detected and appropriate treatment, it is possible to bring sugar to normal. It is possible to restore the level of glucose not only with the help of medicines, but also use a certain diet, but only with the coordination of the doctor.
If the patient has a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, the doctor prescribes a certain course of treatment is the same for both men and women. In parallel, it is necessary to observe a certain diet, which implies a decrease in sugar consumption.
It is also necessary to add products that help reduce glucose content in the body. You need to discuss with your doctor what dishes can be used in diabetes. For children, such a diet is much more complicated, but if it is difficult for them to abandon sweet, then such products can be replaced with sugar substitutes.
In any case, with the slightest deviations in health, or changing the well-being of a child or an adult is worth visiting the doctor and pass a full survey. After all, this can help the timely definition of the disease and the beginning of treatment, which in essential cases can even save from the most departing effects.
Sugar, or rather, glucose, we need our body in order to obtain the energy necessary for its existence after its processing. However, if you have symptoms of increased blood sugar, it can be a very disturbing sign of the disease that is called - diabetes mellitus. How not to miss these symptoms and how to understand what you need to urgently go to the laboratory and pass the blood to define the level of sugar?
What features can be guessed to increase blood sugar levels
Normally, as soon as carbohydrates contain glucose containing glucose, the pancreas begins to produce a special hormone that promotes its neutralization and recycling. This hormone is called insulin. Therefore, the increase in blood sugar after meals is short-term - all excess glucose is used by its direct purpose. However, in some diseases, this process may violate and then the blood sugar level rises and continues to hold at a high level for a long time. The main signs for which you can guess that sugar in your blood is raised, are:
- feeling of constant dryness in the mouth and constant thirst;
- itching in the field of genital organs;
- an increased amount of urine allocated and frequent urination;
- total weakness;
- dizziness and headaches;
- nausea, vomiting;
- significant and not caused by any cause of weight loss.
If blood sugar levels significantly exceed permissible normThe person can develop cramps, arrhythmia or respiratory disruption appear. In particularly severe cases, the patient may lose consciousness, to go to whom and even die.
Why there is an increase in blood sugar
Increasing blood glucose levels can be short-lived and cause, for example, increased exercise or stress when the cells of the body required increased quantity Energy to cope with this condition. ILO blood sugar rose and simply from the fact that you used to eat too much sweet or products containing a significant number of fast carbohydrates. But a healthy and well-established organism himself quickly copes with such an increase, so it is not something pathological or life-threatening.
The following pathological conditions can also be brought to a short-term increase in blood sugar.
- increased temperature bodies caused by infectious disease;
- long and persistent pain;
- burns;
- epileptic seizure.
The long-term increase in blood sugar levels often occurs when:
- diseases of the stomach or intestines;
- liver diseases;
- inflammatory processesdeveloping in thyroid gland, hypophysies, pancreas, adrenal glands;
- violations of hormonal balance in the body caused by, for example, pregnancy;
- diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms of elevated blood sugar
Increased content Sugar is the pathological condition of the body, accompanied by certain symptoms that can not develop immediately, and gradually, and the patient himself can not notice them for a long time. The main symptoms of sugar disease include:
- drowsiness;
- unjustified irritability, wrath flashes, sullen state;
- furunculese I. skin itch;
- poor healing of even small damage on the skin and mucous membranes;
- violation of potency;
- often repeated infectious diseases of the female genital sphere. For example, thrush or vulvoginitis;
- feeling numbness in feet and hands.
Separately, each of these symptoms may not mean anything or talk about a completely different disease. But if you have noticed or close to your loved ones, some similar symptoms in the complex, it is necessary to take blood to determine blood sugar levels.
It should be remembered that in a timely manner, an endocrinologist will allow not only to determine the increase in blood sugar in time, but also to establish the reason for which this happened is, if possible, eliminate it and reduce sugar performance to normal sizes. And this means to prevent the development of such a severe disease, like diabetes mellitus.
Hidden flow of diabetes
But diabetes is a very insidious disease that can flow almost asymptomatic or implicit symptoms for a long time or with implicit symptoms. Such diabetes is called latent or hidden. A person may feel absolutely normal, it does not bother him, but some drowsiness or fatigue can be easily recorded at the expense of overwork. Most often, elevated blood sugar is determined by the results of the tests when the patient appeals to the doctor about a completely different disease. For example, it may be disturbed periodically manifested furunculese. Or, since constantly increased sugar leads to a significant weakening of immunity, a person becomes a victim of some infectious or viral disease, for example - influenza. And only after the blood test is carried out, it turns out that the patient's sugar level is unreasonably high.
There are people who relate to the so-called risk group diabetes. This is primarily:
- patients suffering from excess weight or obesity;
- women who suffered with polycystic ovarian;
- women who have diabetes develop during pregnancy;
- patients with genetic predisposition to diabetes.



















