For subcutaneous injection, needle needs a length. Needle Medical Disposable Injection. Characteristics
Injection insulin, in contrast to injections of other medicines, have its own characteristics. First of all, it is 1) the mode of performing injections and 2) the technique of performing injections, including the depth of administration, the possible use of the skin folds and alternation of the injection places.

Given the multiple regime of insulin administration during the day, the introduction with minimal pain and discomfort becomes relevant. In addition, insulin preparations must be administered strictly subcutaneously (into subcutaneous fiber cells), not allowing intramuscular injection, which is dangerous to the rapid development of hypoglycemia, since under intramuscular injection, insulin acts much faster than when injected into subcutaneous fat tissue. Making these conditions is achieved by selecting the needle of a suitable length.
The selection of the needle length is individual and taking into account physical, pharmacological and psychological factors. Studies have shown that, depending on the body weight index, the thickness of the skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue have some differences ranged from the loflization - the body area (shoulder, thigh, belly, buttocks), as well as on the floor and age of the patient. For example, a man has a pronounced layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue in the field of anterior abdominal wall can be combined with the minimum layer of subcutaneous fat fiber in the hips area. Because of this, it is considered incorrect to recommend shorter needles with thin patients, and long needles - overweight patients. Each patient should be recommended to use needles of different lengths.
Classification of insulin needles
- short needles - 4-5 mm
- medium-length needles - 6-8 mm
- long needles - more than 8 mm
Used earlier needles 12.7 mm long at present are not recommended for use in adults, because Increase the risk of administration of the drug intramuscularly. For most children, the length of the needle is 8 mm.
According to the conducted studies, it was established that in patients suffering from obesity, short (5, 6 mm) and long (8, 12.7 mm) needles are comparable in efficiency and safety. At the same time, shorter needles (5, 6 mm) are safer and, as a rule, their use is less painful. At the same time, a sufficient number of research has shown the danger of using patients with long needles due to an increase in the risk of intramuscular injection with the possible development of hypoglycemia. Data on the meaning of insulin flowing, a decrease in control over the course of diabetes, an increase in the severity of lipogeneity or other complications when using short needles today is not presented. In addition, a number of studies are already conducted with a 4 mm length needles to give recommendations for their application.
| Table 1. Recommendations for choosing needles of optimal length for individual groups of patients | |||
| Group of patients | Needle length | Injection at an angle ** | |
| Children and teenagers | 5 and 6 mm 8 mm (syringe) * | Yes | 90 ° for needles 5 mm 45 ° for needles 6 and 8 mm |
| Adults | 5 and 6 mm (including obesity) 8 mm (syringe) * | Yes - thin Yes, at the length of the needle more than 8 mm |
90 ° for needles 5 and 6 mm 45 ° at the length of the needle more than 8 mm |
| * Currently, the shortest needle for syringes present on sale has a length of 8 mm. ** Children, thin patients and patients performing injections in the thigh or shoulder, in order to minimize the risk of random intramuscular injection, should form a skin fold and injection at an angle of 45 °. |
|||
| Comments on the choice of needles | |||
| Needle length | Children and adolescents should be used with needles long 5 or 6 mm. No medical grounds for the use of needles longer than 6 mm. The needles are 5 and 6 mm long and 6 mm can be used in any adult patients, including patients suffering from obesity. There is no medical grounds for use in adult needles longer than 8 mm. |
||
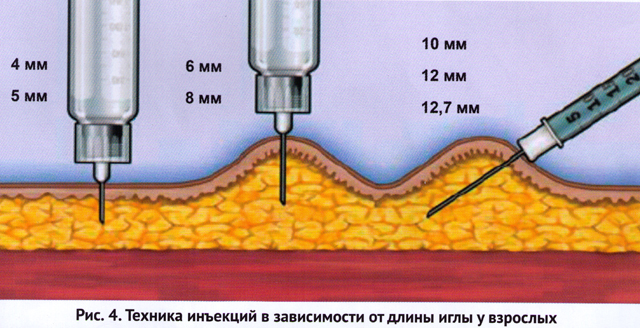



When prescribing preparations for subcutaneous administration to patients with diabetes It is recommended to start therapy with the use of shorter needles 4 and 5 mm long. They are less traumatic and make it focus on the simpler technique of administration of the drug, which allows for the minimum time to teach the patient to perform injections (at an angle of 90 °) and reduce the risk of insulin intramuscular administration (or injuric). However, the patient, due to some difference in the price of insulin needles (long needles cheaper), can acquire needles long, absolutely not corresponding to its physique and the places of administration of the drug. Therefore, it is very important to teach the patient how to safely and safely perform insulin injections (or incremental) into any anatomical area using needles of various lengths.
Injection techniques needles of different lengths
- Short needle (4-5 mm) Injection is performed at an angle of 90 ° to the surface of the skin;
- The needles of the middle length (6-8 mm) injections are performed in the skin fold at an angle of 90 °.
- Long needles (more than 8 mm) are recommended to be administered to a skin fold at an angle of 45 °.
The technique of forming a skin fold is shown in Fig. 5. The skin taken into the fold is not allowed until the end of the insulin administration. It is necessary to avoid compression and displacement of the skin during injection, since the injection may be deeper and get into the muscular layer. Proper formation of the skin fold and hold it until the end of the drug administration reliably reduces the risk of intramuscular injections.
Using these 3 main variants of injection techniques can be effectively and safely performed by the subcutaneous injection of a needle of any length into any anatomical area.
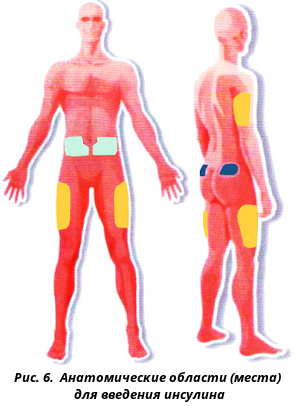
Anatomical areas for insulin administration
For self-administration, insulin is better to use the stomach and thigh, less often a buttock (Fig. 6.).
In addition, insulin cannot be introduced into the sections where there are scars, seals or signs of inflammation.
- Analogs of man insulin as long action (Lantus, Leewemir) and short action (Humalog, Apidra, Novorad) can be administered to any commonly used for injection areas, as there are no differences between the absorption rate of the drug.
- Human insulins of short-acting (anktrapid, instant rapid, humulin regular) should be administered to the abdomen; This increases the speed of their suction.
- Human insulins of extended - basal insulins (NPH, Insubs Basal, Protofan) should be administered to the thighs and buttocks to slow down their suction. It is necessary to avoid accidental intramuscular administration of durable analogues, since otherwise there is a high risk of severe hypoglycemia.
Daily self-examination of insulin administration
The patient should independently examine and palpation of insulin injection places to identify signs of inflammation and sealing sites - lipoogypertrophy (Fig. 7). To do this, it is used for the method of palp and simultaneous "prototing" of symmetric sections of the digestive tissue with the right and left sides. The difference in tissue density is a sign of the presence of changes in subcutaneous fat tissue. In case of detection of cones and seals, you should seek help to your doctor during the next scheduled visiting.
Alternation of anatomical areas for insulin administration
Each patient who receives insulin should be aware of the need to change injection places in the anatomical regions.
Multiple studies have shown that in order to protect normal tissues, it is necessary to correctly and consistently alternate injection areas. According to one of the schemes with proven effectiveness, the injection area is divided into four quadrants (or parts when it comes to hips or buttocks), while only one quadrant is used every week, and then the next with alternation clockwise, as shown in rice . eight.
To change the injection places you need to know simple rules:
- Use one quadrant per week.
- Monday - day for changing the quadrant.
- Rotation clockwise.
In addition, with each injection in one quadrant, it is necessary to retreat from the previous injection site 1-2 cm in order to avoid repeated injury. At the same time, it is advisable to perform the condition: the injection is performed in the same area at the same time. This allows you to make the insulin suction process more predictable.
Drug administration technique
Preparation for injection
- Before performing the injection, it is necessary to inspect the appropriate area of \u200b\u200bthe skin.
- Change the injection site if the current has signs of lipoogypertrophy, inflammation or infection.
- Injections must be performed in a clean skin with clean hands.
- Outside the hospital, as a rule, there is no need to disinfect the injection site.
- Disinfection may be needed if the skin area is contaminated, or if you are in conditions conducive to the drift of infection with the hands of the injection (for example, in the hospital).
- When using alcohol for disinfection, follow the injection only after it evaporates.
- Injections through clothes are not accompanied by an unfavorable outcome, but the fact that when performing an injection cannot be collected by the skin fold or consider the plot of administration, makes such a non-optimal technique.
Method of performing an injection
- Perform an injection slowly and make sure that the piston (syringe) or key (syringe knobs) are completely squeezed.
- If you use a syringe knob after administration of a dose, wait 10 seconds before removing the needle in order to avoid the return current of the solution; This guarantees the full admission of the administered dose.
- Massage of the injection site before the procedure and after the procedure is fulfilled, the suction can accelerate and is not recommended as a whole.
Proper use of syringe-handles
- The syringe knobs and cartridges should be used individually for each patient, and should never be transmitted from one patient to another, as there is a risk of suction biological material In the cartridge.
- Needles from syringe-handles are desirable to use only once.
- Immediately after use, the needle should be disconnected, and not to leave attached to the syringe knob. This will prevent air from entering or other pollutants in the cartridge, as well as leakage medicinal preparation.
- After a complete pressure of the key, the patient must slowly count to 10 before removing the needle so that the entire dose reaches the destination, and the drug leakage occurred.
- With the introduction of higher doses, it may be necessary to count more than 10.
Proper use of syringes
- The world has many regions where a significant number of people still use syringes as a fixed assessment to perform injections. Currently no syringes with a needle length< 8 мм, что продиктовано необходимостью соответствия пробкам некоторых ампул с инсулином.
- Unlike syringe-handles, there is no reason to believe that the needle of the syringe should hold in the skin for 10 seconds after the pressure of the piston of the syringe.
- Medical Justification of the use of syringes with interchangeable needles for injection insulin is not.
- The syringes with a non-removable needle allow you to more accurately dispense the drug and reduce the dead space, which allows you to mix insulins if necessary.
- In those regions of the world, where there are still insulin preparations U40 and U100 (for example, in Asia, Africa), special attention should be paid to use for each concentration of the corresponding syringe.
- When filling the syringe, first need to aspirate the equivalent dose amount of air and enter into the ampoule to facilitate insulin intake.
- If the air bubbles are visible in the syringe slightly shake the syringe cylinder so that they move to the surface, and then release them by pressing the piston.
- As in the case of needles from syringe-handles, syringes are desirable to use only once.
Reducing the pain of injection
- Keep used insulin when room temperature Or thirty minutes before use, remove it from the refrigerator so that it acquires room temperature, as the cold insulin can cause more painful feelings injecting;
- do not perform injections in the roots of the hair;
- with each injection, use a new needle.
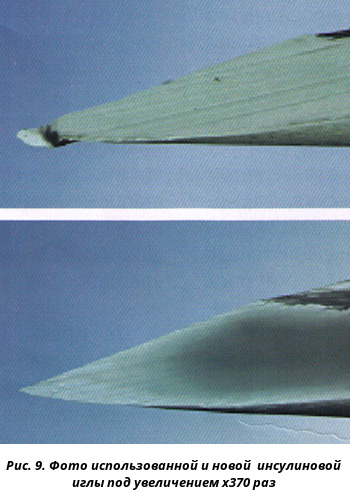
Danger of reuse of insulin needle
The main argument against the multiple use of the needle is microtraumatization of injections. The fact is that when the needle is reused, it is bent, acquired the shape of the hook, which is clearly visible under the microscope (Fig. 9). Repeated injections of such a needle as a result of microtraumamization of tissues can lead to development. inflammatory processes In the field of injection with the formation of lipodystrophs.
Complications with incorrect techniques Injection insulin and their prevention
With incorrect technique of insulin administration, the following complications are possible:

Disposal means of introducing insulin
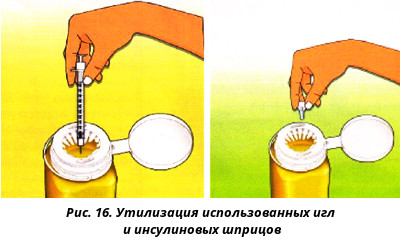
Used needles and insulin syringes are a socially dangerous subject and cannot be disposed of as household garbage. Throw the needles used only with the protective caps on them. Do not expose other people at risk of injury. It is better to fold the needles used into a special container to be disposed of tightly closed (Fig.).
A source: Compiled by publications Chernikova N.A., Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Endocrinology and Diabecolism Goudpo RMAPO Roszdrava in the journal Diabetes. Lifestyle, 2010, 2011
- Name: B. Brown Slerikan (Bibraon is the name of the company-producer, Sterican is a brand under which Bibraon produces injection / punitive disposable medical needles)
- Disposable: It is necessary to dispose after use (re-use, besides, the needle sharpening is spoiled during re-injection and subsequent injections will be painful)
- Purpose: Injection needles (hollow needle, intended for the introduction of solution, blood take, puncture)
- Sterile: The needle is sterilized and packed in an individual packaging - blister, also has a protective cap (plastic)
- 21g.coding on the Gage scale, denotes the outer diameter of the needle (correspondence in millimeters indicative, can be slightly different from different manufacturers, such as a needle 30G may have an outer diameter of 0.3mm or 0.29mm - is not a violation). Below (in this material) provides a table with the size of the correspondence code on the GAUGE scale (G) to the external diameter of the needle in millimeters.
- 0,8 - The outer diameter of the needle 0.8 mm (the inner diameter depends on the type of wall: normal or thin)
- 120 - needle length 120mm (i.e. 12cm)
1) Metal part
(title options: rod, cannula, needle tube)
Material: It is made of steel, one of its end (distal, or remote) has a cut at a certain angle, and the other end (proximal, or near) ends in the plastic part of the needle (Vpanyan, is inserted).
Dimensions: It has a different diameter and length (in Figure - L).
Outer needle diameter:
There are two indicators:
- NEEDLE GAUGE, reduction G) is usually used to measure the outer diameter of tubular (injectable, biopsy) needles. Smaller sizes on the Gage scale correspond to larger exterior diameters.
- Digital value in millimeters.
Thus, you can navigate the following table:
| Calibration code on the Gauge scale (G) | Nominal external needle diameter (in millimeters) |
| 33 | 0.20 |
| 32 | 0.23 |
| 31 | 0.25 |
| 30 | 0.30 |
| 29 | 0.33 |
| 28 | 0.36 |
| 27 | 0.40 |
| 26 | 0.45 |
| 25 | 0.50 |
| 24 | 0.55 |
| 23 | 0.60 |
| 22 | 0.70 |
| 21 | 0.80 |
| 20 | 0.90 |
| 19 | 1.10 |
| 18 | 1.25 |
| 17 | 1.50 |
| 16 | 1.65 |
| 15 | 1.80 |
| 14 | 2.10 |
| 13 | 2.45 |
Additionally, read the material color encoding needles of medical injection disposable
The inner diameter of the cannula needles of the same external diameter (and the code on the Gage scale) may vary.
- normal
- thin
- ultrathine (ultra-thin).
The difference in bandwidth can be tangible. For example:
This means that with the same external diameter (0.30mm) using a needle with a thin or super-thin wall, you can enter a more viscous substance or introduce a larger amount of substance during the same time (i.e., increase the current of the infusion solution during injection or increase the speed of the current during blood intake).
Needle surface: The needle is ground and lubricated (typically - silicone composition) for light, safe and painless injection injection. The grinding of the needle is governed by the relevant standards (for example, ISO 7864).
Sharpening: As a rule, trothed.
Sing: It is of great importance for selecting the needle in accordance with the estimated use. May be "ordinary" or "short". A regulatory document has been developed, GOST R ISO 7864-2009. Excerpt from this Regulation:
(Click on the drawing to enlarge)

The longer the cut, the more painless it will be puncture. Long cut will provide a slight hit in Vienna, but in some cases, for example, for the puncture of difficult veins, a needle with a short cut is required.
A number of manufacturers reflect the type of slice in the needle articula. For example, the needle of Terumo Neolus needle a disposable sterile 19G (1.1 x 50 mm) was supplied in two versions: art.nn-1950r - a slice ordinary and art.nn-1950s - short.
In this case, the needles of Terumo:
- letter " R."In the article means normal slice (12 °)
- letter " S."In Article (Short) means short slice (18.5 °)
Injecting needles B. Brown Sleric There are options for performing needles with a short and long cut, for example:
On the packaging, the designation BL / LB - a slice long

Parenteral(bypassing the digestive tract) drugs are injected in an injection method.
There are two brands of syringes for injection: "record" and "lone" (disposable and reusable, Fig. 9.20, a). The syringe device and the differences in two grades are presented in Figure 9.20, b.
The capacity of the syringes for injection is 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20 ml.
To gain the necessary dose of the drug in the syringe, you need to know the "price" of the division of the syringe, i.e. What amount of solution can be between the two closest divisions of the cylinder (division and figures indicate the spaciousness of the syringe in milliliters and millilita shares). In order to determine the "price" of division, it should be found on the cylinder the syringe close to the digital cone (the number of milliliters) and divided by the number of divisions on the cylinder (between this number and the playback cone). It will be the "price" of the division of the syringe (Fig. 9.20, c).
Most often, the dose of medicines for parenteral administration is expressed in milliliters and millilita shares. Other dose symbols are found. For example, insulin appointed in units (ed) is introduced to patients suffering from diabetes mellitus. Therefore, for the introduction of insulin, special syringes are produced, on the cylinder of which are not the shares of millilitra, but "actions units" (Fig. 9.20, d). At home, as well as for the convenience of their permanent transportation, for example, in a bag, pocket, for the introduction of insulin there are syringes resembling appearance handle.
The needles for the syringes "Record" and "Looker" differ in the form of cannula (Fig. 9.21, a). In addition, the needles for intradermal, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intravenous injections differ significantly in length, cross section and sharpening shape (Fig. 9.21, B, B). Patriotic industry for reusable use needles for injection different sizes: 0415, 0420, 0520, 0840, 1060. The first two digits mean the diameter of the internal lumen of the needle in millimeters, increased 10 times; The following two digits are the needle length in millimeters.
Fig. 9.20. Syringes "Record" and "Looker" (a); Fig. 9.21. Injection needles:
device of a reusable syringe (b): 1- Qi- A: for the syringe "Record" (1), for a syringe
lindre, 2 - high-power cone, 3-piston, 4- "LUER" (2); B: Needles for intramuscular (1),
piston lock, 5 - piston handle; the price of intravenous (2), subcutaneous (3) injections;
dividing syringes of various capacity (B, D) in: needles for various injections
Needles should be applied strictly by appointment. For example, for intramuscular injection into the upper-storey quadrant, the buttocks are used a needle with a length of 40, 60 mm and a cross section of 0.8-1, 0 mm, for intravenous - 40 mm long and a cross section of 0.8 mm, for subcutaneous - 20 mm long and cross section 0.4-0.6 mm, for intradermal - 15 mm long and a cross section of 0.4 mm.
Together with a syringe of one-time application is often packaged and a needle for injection. When choosing such an injection syringe, make sure that the needle lying there is intended for this injection.
Build a syringe.
Technique assembly syringe reusabledepends on the type of packaging in which it was sterilized.
Assembling a syringe packed in the package:
1. Wash hands.
2. Check the sterilization date indicated on the package and its tightness.
3. Open (break) the package and use its inner (sterile) surface when assembling a syringe.
4. Take the piston behind the handle and enter it into the cylinder.
5. Take a needle for a set drug For the cannula (this needle is usually a larger diameter than the needle for injection) and put it on the playback cone, without touching the needle isle. You can use one needle and for dialing, and for injection.
6. Secure the cannula needles with his fingers, having squeezing it to the playback cone.
7. Check the needle's passability by releasing the air from the syringe.
8. Put the collected syringe on the inner surface of the package.
Syringe single applicationavailable in assembled form (Fig. 9.22). To prepare a syringe to injection, you should open the package from the other side where
If the syringes sterilized in open capacity(with decentralized sterilization), then after sterilization they are laid out on a sterile table, standing in the procedural office.
The surface of this table is washed daily in the morning using disinfectants. Owing sterile gloves, the table is covered with a sterile sheet, having previously folded it into four layers: it should hang from all sides of the table for 15 - 20 cm. The bottom of the sheet (two layers) covers the table, the upper part (two layers) will cover the syringes, needles , trays laid out on the table from the sterilizer: the syringes of different tanks must lie separately, the needles in the container in which they sterilized, trays - upside down, stack.
![]()

Fig. 9.22. Opening a package with disposable rice. 9.23. Sterile and desktops
In order for the sheet to not slide on the table, it is fixed from 4 sides by an arm for linen. The thrusts are fixed to the corners of the part of the sheet, which covers the tools and hangs down (Fig. 9.23).
Sheder should be changed every 6 hours. The time to preserve the sterility of the tools on the table - 6h. If they are not used during this time, then sterilization is subject to.
It should be noted that this method of storing sterile instruments in the procedural office does not provide the necessary infectious safety.
Next to sterile should be the so-called "desktop", on which:
Tweezers in the sterile package (the package can stand in high capacity) or in a 1-percent aqueous solution of bigluconata chlorhexidine;
Bix or packets with sterile balls (it is better to use Damispet napkins);
Scissors, sawmills for autopsy ampoules, non-sterile tweezers.
Assembling a syringe from a sterile table (Fig. 9.24).
1. Wash hands.
2. Open the sterile table for the tap for linen, which are attached to the free ends of the sterile sheet.
3. Sterile tweezers (removed from the aqueous solution of chlorhexidine or from the package) from the sterile table one of the silent tray and put it at the bottom of the hand.
4. The same tweezers put a piston in the tray, cylinder and 2 needles (for a set of solution and for injection). Locate them in the tray as shown in Figure 9.24, in.
5. Put a tray with a syringe on the desktop, and tweezers put in a container with a solution of chlorhexidine (package).
6. Close the sterile table (for the ass).
7. A tweezers re-taken from a chlorhexidine solution or from a package, take a cylinder, "intercept" his other hand (Fig. 9.24, d).
8. Take piston tweezers and introduce it into the cylinder (Fig. 9.24, e). Secure a removable lid.
9. Take on the needle for a set of medicinal to the playback cone, taking it to a tweezers for the cannula (you can immediately wear a needle for injection).
10. Secure the needle on the playback cone.
11. Put tweezers in the container with aqueous solution chlorhexidine (or package), and a syringe with a needle put in the tray (Fig. 9.24, g).



















