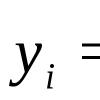Qualification test in obstetrics and gynecology. Clinical Tests: Obstetrics and Gynecology
51. To make a diagnosis of pyelonephritis of pregnant women, all studies are carried out, except:
A. general analysis urine, blood;
B. urinalysis according to Nechiporenko;
C. urine culture to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to the antibiotic;
D. angiography; +
E. Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract.
52. Intrauterine infection of the fetus can lead to:
A. SARS during pregnancy;
B. exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis during pregnancy;
C. threatened miscarriage;
D. colpitis during pregnancy;
E. all of the above. +
53. Excessive vomiting during pregnancy is characterized by:
A. vomiting up to 20 times a day;
B. progressive weight loss;
C. severe symptoms of intoxication;
D. ptyalism;
E. all of the above;
F. points A, B, C. +
54. The lack of effect from the therapy of preeclampsia is manifested:
A. decreased diuresis;
B. persistent arterial hypertension;
C. progressive proteinuria;
D. violations of the central and cerebral hemodynamics;
E. all of the above. +
55. Severe complications of gestosis are:
A. premature detachment of the placenta;
B. antenatal fetal death;
C. cerebral hemorrhage;
D. renal failure;
E. all of the above. +
56. The issue of obstetric tactics in intensive care for severe forms of preeclampsia is decided by:
A. within a few hours; +
B. within 1 day;
C. within 3 days;
D. within 7 days;
E. all answers are wrong.
57. At what stage of childbirth is it most appropriate to relieve pain with narcotic analgesics:
A. in the latent phase;
B. in the active phase; +
C. in the deceleration phase;
D. with the appearance of the first contractions;
E. from the beginning of the exertion.
58. The most characteristic clinical symptom of placenta previa is:
A. chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
B. decrease in hemoglobin levels and the number of red blood cells in the blood;
C. repeated spotting from the genital tract; +
D. arterial hypotension;
E. threatened miscarriage.
59. Premature detachment of a normally located placenta is complicated by:
A. the appearance of the Kuveler's uterus;
B. ante- or intrapartum fetal death;
C. development of DIC;
D. hemorrhagic shock;
E. all of the above. +
60. Tactics of the doctor in the event of bleeding in the third stage of labor in the absence of signs of separation of the placenta:
A. introduce means that cause uterine contractions;
B. apply the Krede-Lazarevich method;
C. apply the Abuladze technique;
D. to perform manual separation of the placenta and the allocation of the placenta; +
E. introduce antispasmodics.
61. Coagulopathic bleeding in early postpartum period may be due to:
A. massive blood loss and hemorrhagic shock;
B. the presence of an initial pathology of the hemostasis system;
C. premature detachment of the placenta in childbirth;
D. prolonged retention of a dead fetus in the uterine cavity;
E. all of the above. +
62. Principles of dealing with hemorrhagic shock in obstetrics:
A. local hemostasis;
B. prevention of violations of the hemostasis system;
C. restoration of BCC and microcirculation;
D. prevention of respiratory failure;
E. all of the above. +
63. Absolute indications for caesarean section, except:
A. central placenta previa;
B. prolapse of the umbilical cord;
C. narrowing of the pelvis III degree;
D. running transverse position of the fetus; +
E. extragenital and genital cancer.
64. After the operation, a caesarean section is performed:
A. pain therapy;
B. infusion-transfusion therapy;
C. uterotonic therapy;
D. stimulation of intestinal activity;
E. all of the above. +
65. Conditions for the operation of applying obstetric forceps, except:
A. full dilatation of the cervix;
B. absence of a fetal bladder;
C. fetal head in the outlet of the small pelvis;
D. dead fetus; +
E. fetal head in the narrow part of the small pelvis.
66. To the risk factors for the occurrence of purulent-septic complications caesarean section should include:
A. urinary tract infection;
B. premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
C. large blood loss during surgery;
D. bacterial vaginosis;
E. all of the above factors. +
67. Subinvolution of the uterus after childbirth is due to:
A. Development inflammatory process;
B. lack of breastfeeding;
C. retention of parts of the placenta in the uterus;
D. weakness of the contractile activity of the uterus;
E. All of the above are correct. +
68. Substances taken orally, which are excreted in mother's milk:
A. antibiotics;
B. salicylates;
C. alcohol;
D. hormonal contraceptives (COC);
E. all of the above. +
69. The perinatal period is the period:
A. from conception to birth;
B. from 22 weeks of pregnancy, childbirth and the first 7 days of a child's life; +
C. from 22 weeks of pregnancy to childbirth;
D. from conception to 28 weeks of gestation.
70. The postpartum period is:
A. lactation period;
B. the first 2 hours after childbirth;
C. the first 6-8 weeks after childbirth; +
D. the first 2 weeks after childbirth.
71. Which of the following is not a symptom of preeclampsia:
A. epigastric pain;
B. hyperreflexia;
C. hypotension; +
D. headache.
72. The borderline conditions of the newborn do not include:
A. physiological weight loss;
B. transient hyperbilirubinemia;
C. hormonal crisis;
D. cephalohematoma. +
73. Postpartum purulent-septic diseases do not include:
A. endometritis;
B. postpartum ulcer;
C. mastitis;
D. peritonitis;
E. chorioamnionitis. +
74. In what cases can we talk about the primary weakness of labor activity:
A. labor activity is weak from the beginning of contractions; +
B. duration of the first stage of labor 12 hours;
C. contractions became weaker when the cervix was dilated by 6 cm;
D. points B, C.
75. What extragenital diseases are indications for termination of pregnancy in terms of up to 12 weeks:
A. combined heart defects with circulatory disorders;
B. endemic goiter I degree;
C. hypertension stage I;
D. chronic gastritis;
E. glomerulonephritis with hypertensive syndrome;
F. points A, E; +
G. points A, C.
76. Doctor's tactics in case of clinical discrepancy between the fetal head and the mother's pelvis:
A. expectant management of labor;
B. rodoactivation;
C. caesarean section; +
D. obstetric forceps.
77. What is characteristic of a clinically narrow pelvis:
A. Vasten's sign is negative;
B. good advancement of the fetal head;
C. swelling of the cervix and vagina;
D. urinary retention;
E. Zangenmeister size is smaller than the outer conjugate;
F. points C, D. +
78. The most consistent early symptom of uterine rupture in childbirth is:
C. termination of labor;
D. vaginal bleeding.
E. points A, B, C; +
F. points A, C, D.
79. Benefits of a caesarean section in the lower uterine segment:
A. reduction of blood loss;
B. reduction in the frequency of postoperative complications;
C. reducing the likelihood of uterine rupture in subsequent pregnancies;
D. all of the above. +
80. Treatment acute appendicitis during pregnancy:
A. operational at any stage of pregnancy; +
B. conservative and expectant tactics;
C. surgery after 12 weeks of pregnancy.
81. Symptoms of a threatened uterine rupture:
A. contraction ring at the level of the navel;
B. profuse bleeding from the uterus;
C. hourglass shaped uterus;
D. pain on palpation of the lower segment;
E. swelling of the cervix;
F. items C, D, E; +
G. points B, C, E.
82. What complications of pregnancy can be treated in a antenatal clinic:
A. mild form toxicosis;
B. bleeding in the first half of pregnancy;
C. late preeclampsia, mild course;
D. trichomonas colpitis;
E. started miscarriage;
F. Iron-deficiency anemia, hemoglobin 100 g/l;
G. items B, E, F;
H. points A, D, F. +
83. Permissible methods of conducting childbirth with a threatening rupture of the uterus:
A. turning the fetus on the leg;
B. craniotomy;
C. caesarean section; +
D. obstetric forceps;
E. conservative management of childbirth.
84. Causes of bleeding in the early postpartum period:
A. hypotension of the uterus;
B. violation of the blood coagulation process;
C. retention of remnants of placental tissue in the uterine cavity;
D. anomalies of attachment and separation of the placenta.
E. soft tissue injury of the birth canal;
F. all of the above; +
G. points B, D, E.
85. In which of the following cases, uterine trauma should be sutured:
A. rupture of the uterus in childbirth along the rib with the transition to the cervix;
B. the vascular bundle is involved in the gap;
C. perforation during criminal abortion;
D. curette perforation of the uterine fundus during a medical abortion;
E. rupture along the anterior wall of the uterus without damage to the vascular bundle;
F. rupture along the anterior wall of the uterus without damage to the vascular bundle, endometritis;
G. items D, E; +
H. points A, B.
86. Belated birth confirms the following signs, Besides:
A. amniotic fluid stained with meconium;
B. wide sutures and fontanelles of the fetal head;
C. dense bones of the fetal skull;
D. a small amount of lubrication, maceration of the skin of the fetus;
E. multiple calcifications on the placenta;
F. low location of the umbilical ring in the fetus;
G. items D, F, E;
H. points B, F. +
87. Which of the following is not characteristic of a progressive detachment of a normally located placenta:
A. abdominal pain;
B. local tenderness of the uterus on palpation;
C. change in fetal heart rate;
D. during vaginal examination, the edge of the placenta is determined; +
E. bleeding from the uterus.
88. Rare forms of early toxicosis are:
A. tetany;
B. dermatosis;
C. bronchial asthma;
D. acute yellow dystrophy of the liver;
E. all of the above. +
89. Differential diagnosis of vomiting of pregnant women is most often carried out with:
A. diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
B. food toxic infection;
C. diseases of the biliary tract and pancreatitis;
D. hepatitis;
E. appendicitis;
F. points A, B, C, D; +
G. all of the above.
90. For an abortion that has begun, it is characteristic:
A. spotting from the genital tract;
B. cramping pain in the lower abdomen;
C. shortening of the cervix;
D. the body of the uterus is dense and less than the gestational age;
E. all of the above. +
91. Medical tactics during abortion in progress:
A. use of tocolytic therapy;
B. hospitalization;
C. antibiotic therapy;
D. instrumental removal of the ovum. +
92. Treatment with antibiotics in the postpartum period is carried out taking into account:
A. pathogen sensitivity;
B. effects on the child during breastfeeding;
C. maternal toxicity;
D. achieving the required concentration in the focus of inflammation;
E. all of the above. +
93. Postpartum endometritis manifests itself:
A. fever on the 3rd-5th day of the postpartum period;
B. soreness and subinvolution of the uterus;
C. pathological lochia;
D. slowing down the formation of the cervix;
E. all of the above. +
94. Tactics in the development of peritonitis after cesarean section:
A. hysterectomy with tubes; +
B. conducting detoxification therapy;
C. prescription of antibacterial agents;
D. drainage and dynamic debridement abdominal cavity.
95. Name the most characteristic clinical manifestations of infectious-toxic shock:
A. hyperthermia over 38 0С;
B. arterial hypotension;
C. oliguria;
D. shortness of breath;
E. all of the above. +
96. Indications for lactation suppression are:
A. severe extragenital diseases of the mother;
B. cicatricial changes in the mammary glands;
C. serious condition of the newborn;
D. purulent mastitis;
E. points A, D; +
F. points A, C, D.
97. What is the first method to stop bleeding in the early postpartum period:
A. compression of the aorta, the imposition of clamps on the cervix according to Baksheev;
B. introduction of reducing agents, manual examination of the walls of the postpartum uterus;
C. examination of soft tissues and the birth canal, the introduction of reducing agents;
D. cold on the lower abdomen, catheterization Bladder, the introduction of funds that reduce the uterus. +
98. Mendelssohn's syndrome is:
A. aorto-caval compression syndrome;
B. amniotic fluid embolism;
C. hypotension of the uterus;
D. aspiration syndrome; +
E. All of the above are correct.
99. The most formidable complication in women with a scar on the uterus is:
B. threatened miscarriage;
C. uterine rupture; +
D. prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid;
E. anemia.
100. Before a planned caesarean section, the following is performed:
A. clinical analysis of blood and urine;
B. biochemical study of blood, hemostasis system;
C. ECG, consultation of a therapist;
D. examination for RW, HIV, determination of blood group, Rh factor;
E. all of the above. +
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
Choose ONE correct answer.
1. The second degree of narrowing of the pelvis is characterized by conjugata vera:
A. Less than 7.5cm
B. 7.5-6 cm
H. 9-7.5 cm
G. 10-9 cm
2. The most significant factor in the development of postpartum endometritis:
A. History of chronic infections
B. Cesarean section
B. Duration of labor more than 24 hours
D. More than 5 vaginal examinations
D. All of the above
3. Is it possible to continue pregnancy in a patient with stage 3 mitral stenosis:
A. Under the condition of observation in the hospital
B. No
B. Yes
4. The most common cause of detachment of a normally located placenta is:
A. Excessively strong contractions
B. Trauma
B. Premature rupture of amniotic fluid
D. Absolute shortness of the umbilical cord
D. Long-term preeclampsia
5. The beginning of the first stage of labor is characterized by:
A. Outflow of amniotic fluid
B. Development of regular labor activity
B. Increased fetal heart rate
D. Change in the shape of the uterus
D. Increased tone of the myometrium
Choose two or more correct answers. Use the chart below to select answers to questions:
A. If 1, 2, 3 is correct
B. If 1, 3 is correct
B. If 2, 4 is correct
D. If 2, 3, 4 is correct
D. If everything is correct
6. The main clinical symptoms of threatened miscarriage:
1. Pain in the lower abdomen and in the sacrum
2. The size of the uterus corresponds to the gestational age
3. The tone of the uterus is increased
4. In the cervical canal, the tissues of the fetal egg are determined
7. Rh-negative woman can be sensitized:
1. By introducing Rh-positive blood
2. When Rh-positive fetal erythrocytes enter the bloodstream
3. By injecting Rh-positive blood IM
4. With autohemotherapy
8. A woman gave birth to a child weighing 1000 g. The child died on the 2nd day after birth. What kind of death is this case?
1. Perinatal
2. Intranatal
3. Early neonatal
4. Antenatal
9. What is an indication for removal of the uterus in case of premature detachment of a normally located placenta?
1. The presence of an additional uterine horn
2. Imbibition of the uterine wall with blood
3. Coagulopathy disorders
4. Hypotension of the uterus
10. What research methods are used to diagnose pelvic diseases:
1. Ultrasound
2. External measurement of the pelvis
3. Vaginal examination
4. X-ray pelviometry
Tasks
1. A primigravida has had spotting twice in the last month. Hemodynamics remained stable. The uterus is painless. In the period of 35 weeks. with the development of labor, profuse bleeding from the genital tract began. The cervix is sharply shortened, the cervical canal is passable for one finger. The head of the fetus over the entrance to the small pelvis. The fetal heartbeat is clear, 140 beats/min., rhythmic. The presenting part of the vaginal examination is not clearly defined.
11. Your diagnosis during the examination of the woman in labor:
A. Premature birth
B. Detachment of a normally located placenta
B. Uterine rupture
D. Placenta previa
D. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
12. What to do?
A. Amniotomy
B. Cesarean section
B. In / in the drip of oxytocin
D. Hemostatic therapy
2. A primipara was admitted to the maternity ward. Pregnancy 39 weeks. The dimensions of the pelvis are 24-26-29-18 cm. Contractions after 2-3 minutes. 40 s. The waters poured out 8 hours ago. The head of the fetus is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. Vasten's sign is positive. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, up to 140 bpm. Does not urinate on its own. Urine is brought out by a catheter, saturated.
On vaginal examination: the opening of the cervix is 8 cm, its edges are swollen, the head of the fetus is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis, a large birth tumor is determined on the head, the cape is reached, the diagonal conjugate is 10.5 cm.
13. Name the shape of the pelvis:
A. Flat rachitic pelvis
B. Simple flat pelvis
B. General uniformly narrowed pelvis
G. General flat
D. Normal size of the pelvis
14. Name the complication of the birth process:
A. Weak labor activity
B. Clinically narrow pelvis
B. Discoordinated labor activity
15. Determine the tactics of labor management:
A. Stimulation of labor
B. Cesarean section
B. Medical sleep-rest
3. A multi-pregnant woman was admitted to the maternity ward. The first pregnancy 3 years ago ended in premature birth at 34 weeks, a girl weighing 2350 g, 50 cm tall was born.
Contractions began 6 hours ago, amniotic fluid poured out 4 hours ago. Attempts after 2-4 minutes. 40 s. The circumference of the abdomen is 102 cm, the height of the bottom of the uterus is 38 cm. The dimensions of the pelvis are 26-28-32-22 cm. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, up to 140 beats / min. Vasten's sign is positive. The head is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. On vaginal examination: the opening of the uterine os is 8 cm, the head is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis, the sagittal suture is in the right oblique size, the large fontanel is facing anteriorly, is located close to the wire axis of the pelvis, the configuration of the skull bones is pronounced.
16. Name the shape of the woman's pelvis:
A. Flat rachitic
B. Normal pelvis
B. Common flat
G. Simple flat
17. Name the complications of the birth process:
A. Threatened uterine rupture
B. Discoordination of labor activity
B. Clinically narrow pelvis
D. Weak labor activity
18. Signs of clinical non-compliance are all, except:
A. Vasten's sign is positive
B. Contractions of an agonizing nature with the head pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis
G. The head is pressed to the entrance to the small pelvis with the full opening of the uterine os
19. Causes of a clinically narrow pelvis are all, except:
A. Large fruit
B. Anterior head presentation
B. Early rupture of amniotic fluid
20. What is the tactics of conducting childbirth:
A. Expectant, within 2 hours
B. Cesarean section
B. Stimulation of labor
4. During vaginal examination, it is determined: the cervix is smoothed, the opening is complete, there is no fetal bladder. The head of the fetus is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. Arrow-shaped seam in the right oblique size, small fontanel on the left front. The cape is not reached, there are no exostoses.
21. Determine head insertion:
A. Posterior view of the occipital presentation
B. Anterior-parietal
B. Anterior occipital presentation
G. Asynclitic
22. Is spontaneous childbirth possible:
A. Possible with intravenous administration of oxytocin
B. Possible when applying obstetric forceps
B. Possible
D. Impossible
23. Tactics of conducting:
A. Cesarean section
B. Expectant tactics
B. Obstetric forceps
D. Use a vacuum extractor
D. Fruit-destroying operation - perforation of the head
5. A 25-year-old woman in labor had the 2nd timely delivery with a fetus of 3650 g, 52 cm. The first stage of labor was 6 hours, the second period was 30 minutes. In 10 minutes. the placenta separated on its own, the placenta stood out. When examining the placenta, there are doubts about its integrity.
24. Probable diagnosis:
A. Remnants of the placenta
B. Hypotension of the uterus
B. Uterine rupture
G. DIC
D. Cervical rupture
25. Tactics of conducting:
A. Tamponade of the uterus
B. Curettage of the uterus
B. Manual examination of the uterine cavity
D. Introduction of blood substitutes
D. External massage of the uterus
Gynecology
Choose ONE correct answer.
26. Uterine fibroids have to be differentiated:
A. With ovarian tumors
B. Endometrial cancer
B. Adenomyosis
G. Pregnancy
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
27. Which of the research methods is the most reliable in the diagnosis of endometrial hyperplastic processes:
A. Echography
B. Hysteroscopy
B. Cytological examination of aspirate from the uterine cavity
G. Hysterography
D. Separate diagnostic curettage with histological examination.
28. Which tumor is most often exposed to malignancy:
A. Teratoma
B. Serous cystoadenoma
B. Endometrial cyst
D. Papillary cystoadenoma
D. Mucinous cystoadenoma
29. Hormonal treatment delays in sexual development of central genesis, it is advisable to produce using:
A. Gestagenov
B. Cyclic hormone therapy
B. clomiphene
G. Combined estrogen-gestagenic drugs.
30. How does the level of hormones in postmenopause change:
A. Does not change
B. Increased FSH and LH
B. Decreased prolactin levels
D. Decreased levels of FSH and LH
D. Increased progesterone levels
Choose two or more correct answers.
Use the chart below to select answers to questions:
A. If 1, 2, 3 is correct
B. If 1, 3 is correct
B. If 2, 4 is correct
D. If 2, 3, 4 is correct
D. If everything is correct
31. What anatomical structures should be crossed during adnexectomy:
1. Own ligament of the ovary
2. Round ligament of uterus
3. Funnel-pelvic ligament
4. Broad ligament of uterus
32. The contraceptive effect of combined estrogen-gestagen preparations is:
1. In inhibition of the ovulation process
2. In reducing the viscosity of cervical mucus
3. In the suppression of secretory changes in the endometrium
4. Immobilization of spermatozoa
5. In the normalization of the ratio of FSH and LH
33. Genital tuberculosis is characterized by:
1. Slow development of the disease
2. The manifestation is associated with the onset of sexual activity
3. In the anamnesis there are indications of extragenital tuberculosis
4. Primary chronic course
34. Most common causes prolapse and prolapse of the uterus:
1. Failure of the pelvic floor muscles
2. Elongation of the cervix
3. Hard physical labor after childbirth
4. Rectocele
35. For amenorrhea ovarian origin characteristic:
1. Thickening of the ovarian capsule on ultrasound
2. Increased FSH and LH levels
3. Positive test with GnRH agonists
4. Negative test with progesterone
36. To confirm the diagnosis of the uterine form of amenorrhea, it is necessary:
1. Determination of the level of gonadotropins
2. Tests with progesterone
3. Laparoscopy
4. Hysterosalpingography
Tasks
1. A 28-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of sudden onset pain in the lower abdomen. The menstrual cycle is not disturbed. History of one pregnancy, which ended in normal delivery 3 years ago. Upon admission, the condition is satisfactory, the pulse is 102 bpm, the abdomen is somewhat swollen on palpation, sharply painful in the lower sections, more on the left, Shchetkin's symptom is positive. On vaginal examination, the cervix is cylindrical, not eroded. The body of the uterus is of normal size, painless. To the left of the uterus, the formation of a tight-elastic consistency is palpable, movable 7x8 cm, painful during examination. Discharges are light, mucous.
37. Most likely diagnosis:
A. Ectopic pregnancy
B. Torsion of the legs of the ovarian cyst
B. Malnutrition of the myomatous node
38. Medical tactics:
A. Observation of the patient
B. Surgical treatment
B. Antispasmodic and analgesic therapy
2. A 47-year-old patient was delivered to a gynecological hospital with profuse blood secretions from the genital tract. Hb 112 g/l. The last menstruation came with a delay of 5 weeks, lasts for 9 days, accompanied by weakness, dizziness. History of 2 births, 1 abortion, complicated by endometritis. Menses irregular throughout the year. On vaginal examination, the cervix is without features, the uterus is of normal size, dense, mobile, painless. Appendages are not defined.
39. What is the most likely diagnosis:
A. Ectopic pregnancy
B. Spontaneous abortion
B. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
D. Exacerbation of chronic endometritis
40. Medical tactics:
A. Prescribe contracting and hemostatic agents
B. Hormonal hemostasis
B. Anti-inflammatory therapy
D. Hysteroscopy and curettage of the endocervix and endometrium
D. Take an aspirate from the uterine cavity
41. What diagnostic method will confirm the diagnosis:
A. Hysterography
B. Echography
B. Hysteroscopy
D. Cytological examination of aspirate
42. What treatment should be prescribed:
A. Anti-inflammatory therapy
B. Hormone therapy
B. Androgens
D. Surgical treatment
D. Gestagens
Answers to test tasks:
1. V 12. B 23. B 34. B
2. L 13. V 24. A 35. V
3. B 14. B 25. C 36. C
4. D 15. B 26. D 37. B
5. B 16. B 27. D 38. B
6. A 17. C 28. D 39. C
7. A, D 18. C 29. B 40. D
8. B 19. C 30. B 41. C, D
9. D 20. B 31. B 42. B, D
10. D 21. V 32. A
11. G 22. V 33. D
1. False amenorrhea may be due to:
A. atresia of the cervical canal;+
B. aplasia of the body of the uterus;
C. gonadal dysgenesis;
D. all of the above diseases;
E. none of the above diseases.
2. Puberty is characterized by:
A. growth spurt;
B. breast enlargement;
C. the appearance of the first menstruation;
D. appearance of pubic and axillary hair growth;
E. all of the above. +
3. characteristic clinical manifestations nonspecific vulvovaginitis should be considered all except:
B. itching of the perineum;
C. vaginal itching;
D. acyclic spotting; +
E. dyspareunia.
4. Tactics of managing a patient with DMC in the juvenile period:
A. limited to symptomatic hemostatic and antianemic therapy;
B. to carry out hormonal hemostasis with progesterone;
C. therapeutic and diagnostic curettage of the endometrium and endocervix;
D. complex therapy, including hemostatic, antianemic, uterotonic therapy, with inefficiency - hormonal hemostasis; +
E. hysteroscopy.
5. The main method of stopping dysfunctional bleeding in the premenopausal period is:
A. the use of synthetic estrogen-progestin preparations;
B. administration of hemostatic and uterine contracting agents;
C. androgen use;
D. continuous use of 17-hydroxyprogesterone capronate (17-OPK);
E. separate diagnostic curettage of the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity and cervical canal, followed by hormone therapy, according to the response of the histological examination. +
6. Polycystic ovary syndrome is characterized by:
A. hirsutism;
B. oligomenorrhea;
C. infertility;
D. bilateral increase in the size of the ovaries;
E. all of the above. +
7. To verify the diagnosis of peritoneal endometriosis, it is enough:
A. clinical data;
B. clinical data and transvaginal sonography;
C. clinical data and laparoscopy subject to the detection of typical endometrioid heterotopias;
D. clinical data and cytological examination punctate from the abdominal cavity;
E. clinical data and laparoscopy followed by histological examination of biopsy specimens. +
8. What symptoms may indicate endometriosis of the uterus?
A. hyperpolymenorrhea;
B. scanty bleeding from the genital tract before and after menstruation;
C. algomenorrhea;
D. decrease in hemoglobin;
E. all of the above. +
9. When choosing a method of treatment for endometriosis, it is necessary to take into account:
A. patient's age, individual drug tolerance;
B. localization of endometriosis;
C. the extent of the process;
D. the presence of concomitant diseases;
E. all of the above. +
10. Specify the main symptoms of acute salpingitis:
A. pain in the lower abdomen;
B. increase and soreness of the uterine appendages;
C. fever;
D. all of the above; +
E. points A, B.
11. Specify possible complications acute inflammation of the uterine appendages:
A. transition to a chronic form;
B. peritonitis;
C. abscess formation;
D. formation of chronic pelvic pain syndrome;
E. all of the above. +
12. Violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes may be the result of:
A. genital chlamydia;
B. genital endometriosis;
C. hyperandrogenism;
D. gonorrheal salpingitis;
E. points A, B, D; +
13. What are the main clinical symptoms of a progressive ectopic pregnancy?
A. paroxysmal pain in the lower abdomen; delay of menstruation;
B. "smearing" bloody discharge from the genital tract;
C. dry mouth, feeling of pressure on the rectum;
D. points A, B, C; +
E. points A, C.
14. Basic clinical symptom submucosal uterine fibroids:
A. chronic pelvic pain;
B. algomenorrhea;
C. menorrhagia; +
E. secondary infertility.
15. Indications for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids:
A. uterine fibroids, exceeding the size of a 12-week pregnancy; fast growth tumors;
B. submucosal arrangement of nodes; interstitial nodes with centripetal growth;
C. combination of uterine fibroids with ovarian tumors and adenomyosis;
D. menorrhagia leading to anemia in patients;
E. points A, C;
F. all of the above. +
16. Treatment of an ovarian tumor during pregnancy:
A. pre-term follow-up;
B. conservative treatment;
C. surgery after 12 weeks of pregnancy; +
D. surgery at any stage of pregnancy;
E. surgery for torsion of the tumor stem.
17. The most common symptoms of cervical cancer are:
A. crater-shaped ulcer, bleeding when touched;
B. contact bleeding;
C. menometrorrhagia;
D. points A, B; +
E. all of the above.
18. List the most serious complications when taking combined drugs. oral contraceptives:
A. thromboembolic complications; +
B. cardiovascular diseases;
C. disorders of carbohydrate, fat, vitamin metabolism;
D. points A, B;
E. points A - C;
19. Place of production of gonadotropic hormones:
A. adrenal glands;
B. hypothalamus;
C. pituitary gland; +
D. ovaries.
20. Signs of physiological menstrual cycle:
A. acyclicity;
B. two-phase;
C. dysmenorrhea;
D. Duration 21-35 days;
E. points B, D. +
21. The external genital organs of a woman include:
A. vagina, cervix;
B. uterus, tubes, ovaries;
C. bartholin glands;
D. labia, pubis, clitoris, vestibule;
E. points C, D. +
22. The pelvic floor is:
A. hymen;
B. vagina;
C. muscles and fascia of the perineum; +
D. vestibule of the vagina.
23. For the production of artificial abortion before 12 weeks of pregnancy, tools are needed, except for:
A. bullet tongs;
B. uterine probe;
C. perforator; +
D. curette;
E. Hegar's dilators.
24. The acidic environment of the vagina is provided by the presence of:
A. vaginal epithelium;
B. leukocytes;
C. Doderlein sticks; +
D. gonococci.
25. If pathological changes are detected on the cervix, it is necessary:
A. take a smear from the altered area for a cytological examination; +
B. treat the neck with a disinfectant solution;
C. observation with periodic inspections.
26. For clinical picture ascending gonorrhea is characterized by:
A. acute onset;
B. pronounced pain syndrome;
C. hyperthermia;
D. all of the above; +
E. none of the above.
27. Tactics in the clinic of "acute abdomen" at the prehospital stage:
A. pain relief;
B. cold on the stomach;
C. cleansing enema;
D. urgent hospitalization; +
E. all of the above.
28. Basal body temperature is measured:
A. in the morning; +
B. in the evening;
C. 2 times a day;
D. after 3 hours.
29. Special gynecological examination includes:
A. examination of the external genital organs;
B. bimanual examination;
C. inspection with mirrors;
D. all of the above. +
30. Endoscopic research methods in gynecology do not include:
A. hysteroscopy;
B. colposcopy;
C. culdocentesis; +
D. laparoscopy;
E. culdoscopy.
31. Barrier methods of contraception have the following advantages except:
A. reversibility of action;
B. security;
C. protection against sexually transmitted diseases;
D. prevent cervical cancer. +
32. All of the following are functional tests except:
A. changes in the nature of cervical mucus;
B. measuring basal temperature;
C. hormonal tests; +
D. definition of KPI.
33. What corrective hormonal therapy is performed for juvenile DMK:
A. cyclic estrogen-progestogen preparations;
B. gestagens in the II phase of the cycle;
C. gestagens in contraceptive mode;
D. gonadotropins;
E. points A, B. +
34. Sterilization is carried out by:
A. pipe crushing;
B. hysterosalpingography;
C. tubal ligation;
D. pipe crossings;
E. points C and D. +
35. Which drug belongs to ovulation stimulants:
A. dexamethasone;
B. clomiphene; +
C. organometry;
D. logest.
36. Bacterial vaginosis is:
A. inflammation of the vagina;
B. vaginal dysbiosis; +
C. malformation of the vagina;
D. malignant lesion of the vagina.
37. An infertile marriage is the absence of pregnancy:
A. due to the use of contraceptives;
B. within 6 months of unprotected sexual intercourse;
C. within 12 months of sexual activity; +
D. within 2 years of sexual activity.
38. The most common pathology in postmenopausal women, except for:
A. cardiovascular diseases;
B. osteoporosis;
C. depression;
D. endometrial cancer;
E. premenstrual syndrome. +
39. Choriocarcinoma most often develops:
A. not related to pregnancy.
B. after a miscarriage;
C. after childbirth;
D. after hydatidiform mole. +
40. The most common localization of genital tuberculosis:
b. pipes; +
C. ovaries;
D. vagina.
41. Hormonal contraceptives do not include:
A. postcoital;
B. estrogen-gestagenic;
C. spermicides; +
D. microdoses of gestagens.
42. Examination of a married couple with infertility begins with:
A. hysterosalpingography;
B. postcoital test;
C. determination of sperm fertility; +
D. functional diagnostic tests.
43. Clinical signs of an infected miscarriage, except:
A. cessation of fetal movement; +
B. temperature increase;
C. soreness of the uterus on palpation;
D. purulent bloody discharge from the uterus.
44. Can galactorrhea / amenorrhea occur in women who have long-term use of psychotropic, antihypertensive drugs or hormonal contraceptives:
45. What drugs are used for hormonal hemostasis in juvenile bleeding:
A. androgens;
B. gestagens;
C. choriogonin;
D. estrogens;
E. estrogen-gestagenic.
F. points D, E. +
46. What corrective hormonal therapy is performed for DMC of the reproductive period:
A. gestagens in phase II;
B. estrogen-gestagenic drugs in contraceptive mode;
C. estrogen-gestagenic drugs in the II phase of the cycle;
D. points A, B. +
47. For the treatment of endometrial hyperplastic processes are used:
A. estrogens;
B. gestagens;
C. androgens;
D. estrogen-progestin preparations;
E. glucocorticoids;
F. thyroid-stimulating hormones;
G. points B, C, D. +
48. Clinic of endometrial hyperplastic processes:
A. menorrhagia;
B. metrorrhagia;
C. menometrorrhagia;
D. asymptomatic course;
E. all of the above. +
49. Indications for surgical treatment in inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages:
A. frequent exacerbations chronic course illness;
B. the threat of perforation of a purulent tubo-ovarian formation;
C. tubo-ovarian formations that are not amenable to treatment;
D. perforation of the pyosalpinx, pyovarium;
E. points B, C, D. +
50. With dysfunctional uterine bleeding of the premenopausal period, hemostasis is performed:
A. prescribing estrogen-progestin preparations;
B. blood transfusion;
C. uterotonics;
D. diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity. +
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
In contact with
1.
According to the principles of Safe Motherhood, the first attachment of healthy newborns to the mother's breast is carried out:
Answer: immediately after birth
2.
What test is the most appropriate for fetal monitoring during pregnancy?
Answer: Measurement of the standing height of the uterine fundus
3.
Specify the initial level of hemoglobin in a pregnant woman, which requires medical intervention:
Answer: <100 г>
4.
What criterion is used to diagnose severe preeclampsia:
Answer: Diastolic blood pressure >100mmHg, Systolic blood pressure >160mmHg with proteinuria 300mg or more
5.
How often is it necessary to conduct a vaginal examination in the first stage of physiologically proceeding labor?
Answer: Every 4 hours
6.
How often should you listen to the fetal heartbeat during labor?
Answer: Every 30 minutes
7.
What position would you advise a woman to take in the first stage of physiological labor?
Answer: Position at the request of a woman
8.
When should I start completing the partogram?
Answer: On admission to the delivery room with regular contractions
9.
Crossing the line of action on the partogram means:
Answer: Quickly assess the situation in order to make a decision
10.
The minimum allowable progress of cervical dilatation in the active period of labor is
Answer: 1cm/h
11.
When can a puerperal push in the second stage of labor?
Answer: When there is a desire
12.
At what position of a woman in the second stage of labor is a large blood loss possible during childbirth?
Answer: standing
13.
What temperature should be maintained in the maternity ward?
Answer: 25 degrees
14.
What dose of dexamethasone should be prescribed in preterm labor to prevent fetal RDS:
Answer: 6 mg x 2 times a day for 2 days
15.
Until what gestational age in preterm birth should fetal RDS be prevented:
Answer: up to 34 weeks
16.
The concentration of hCG, as a marker of pregnancy, increases to:
Answer: 11-12 weeks
17.
According to the principles of Safe Motherhood, active management of the 3rd stage of labor involves the administration of oxytocin:
Answer: immediately after the birth of the fetus
18.
Define the perinatal period:
Answer: from the period of fetal viability and 28 days after delivery
19.
When prolonging pregnancy up to 36 weeks with the outflow of amniotic fluid antibiotic therapy should start with:
Answer: immediately upon admission to the hospital
20.
With active management of the 3rd stage of labor, oxytocin is administered at a dose of:
Answer: 10 IU intramuscularly once
21.
What formula should be used to calculate the maternal mortality rate:
Answer: (number of dead pregnant women, women in childbirth and puerperas within 42 days after termination of pregnancy) / (number of live births) x 100,000.
22.
Answer:
23.
When conducting a double biochemical test during prenatal screening for a genetic pathology of the fetus in terms of 16-21 weeks of pregnancy, the following are examined:
Answer: AFP and HCG
24.
Prenatal biochemical screening in the 1st trimester of pregnancy is carried out at the following times:
Answer: 10-14 weeks
25.
Prenatal biochemical screening in the second trimester of pregnancy is carried out at the following times:
Answer: 20-22 weeks
26.
Primary prevention of cervical cancer is:
Answer: vaccination
27.
The second period of timely birth of twins. After the birth of the first fetus, a vaginal examination was performed, which revealed that the second fetus was in a transverse position, the fetal head was on the right. What is the tactics of further conducting childbirth?
Answer: after amniotomy, perform a classic rotation of the fetus, followed by its extraction by the leg.
28.
Breech presentation of the fetus was detected in a multiparous woman at 32 weeks of gestation. Tactics of the doctor of female consultation?
Answer: recommend corrective therapy
29.
A 29-year-old pregnant woman came to the antenatal clinic with complaints of aching pain lower abdomen and lower back. The gestation period is 15-16 weeks. History of 1 childbirth and 3 honey. abortion. On vaginal examination: the cervix is 2.5 cm long, the external os gapes, the cervical canal is closed, the uterus is enlarged according to the gestational age, the discharge from the genital tract is mucous, moderate. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: threatened spontaneous miscarriage
30.
A 30-year-old pregnant woman came for a consultation with complaints of aching pains in the lower abdomen and lower back. The gestation period is 16-17 weeks. History of 1 childbirth and 2 spontaneous miscarriages in the period of 14-15 weeks. On vaginal examination: the cervix is 2.5 cm long, the external os gapes, the cervical canal is closed, the uterus is enlarged according to the gestational age, the discharge from the genital tract is mucous, moderate. Tactics of the doctor of female consultation?
Answer: hospitalize a pregnant woman
31.
On the 3rd day after delivery, a 35-year-old woman in labor complains of pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, chills, headache, an increase in body temperature to 39 C. In childbirth, due to the partial dense attachment of the placenta, manual separation and separation of the placenta was performed. In history - chronic pyelonephritis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: endometritis
32.
On the 4th day after childbirth, a 30-year-old woman in labor complains of pain in the lower abdomen, chills, headache, fever up to 38.9 C. The mammary glands are moderately engorged.
In the 3rd stage of labor, due to a defect in the placenta, a manual examination of the uterine cavity and the isolation of the delayed parts of the placenta were performed. In the anamnesis - two honey. abortion, chronic cystitis, chronic pyelonephritis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: mastitis
33.
On the 4th day after childbirth, a 30-year-old woman in labor complains of pain in the lower abdomen, chills, headache, fever up to 38.9 C. In childbirth, due to partial dense attachment of the placenta, manual separation and separation of the placenta was performed. What studies are indicated to clarify the diagnosis?
Answer: all of the above
34.
A 25-year-old patient complained of soreness and engorgement of the mammary glands, swelling of the face and legs, bloating, sweating, which stopped after the next menstruation. Gynecological examination revealed no pathology. What form of premenstrual syndrome is most likely in this observation?
Answer: edematous
35.
A 25-year-old pregnant woman came to the antenatal clinic with complaints of aching pains in the lower abdomen and lower back. The gestation period is 11-13 weeks. History of 1 childbirth, complicated by rupture of the cervix of the 1st degree and 1 spontaneous miscarriage in the early period with curettage of the uterine cavity. On vaginal examination: the cervix is 3.0 cm long, the external os is gaping, the cervical canal is passable for 1 transverse finger behind the internal os, the uterus is enlarged according to the gestational age, the discharge from the genital tract is mucous. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Answer: isthmic-cervical insufficiency
36.
30 minutes after the start of the second stage of labor, the multiparous woman developed bloody discharge from the genital tract. BP 120/70 mmHg Contractions in 2-3 minutes for 50 seconds, good strength. The uterus does not relax well out of contraction, is painful on palpation in the lower segment, the size of the pelvis is 26-27-30-18 cm. The fetal heartbeat is muffled. Bladder catheterization fails due to mechanical obstruction. At vaginal examination: the opening of the uterine os is complete, the head is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis, there is a large birth tumor on the head. The sagittal suture is deflected anteriorly, large and small fontanelles are reached, located at the same level. Most likely diagnosis?
Answer: clinical narrow pelvis, incipient uterine rupture
37.
30 minutes after the start of the second stage of labor diagnosed: clinical narrow pelvis, uterine rupture. doctor's tactics?
Answer: emergency abdominal surgery, lower median laparotomy, caesarean section, hysterectomy
38.
A woman in labor was delivered to the maternity hospital, in which a neglected transverse position and prolapse of the fetal handle were established. The fetal heartbeat is not heard. What method of delivery is possible in this situation?
Answer: perform fetal decapitation
39.
An ambulance delivered a pregnant woman unconscious after three bouts of eclampsia to the maternity hospital. The gestational age is 32 weeks. The condition is extremely difficult. BP 180120 mmHg The fetal heartbeat is deaf, 142 beats. per minute. Vaginal examination: the cervix is preserved, the canal is closed. Tactics of conducting a pregnant woman?
Answer: emergency delivery by caesarean section
40.
In a multiparous child, labor continues for 12 hours. The amniotic fluid is intact. Suddenly there were severe arching pains in the abdomen, a sharp pallor of the skin. Fetal heartbeat - bradycardia. On vaginal examination: the opening of the uterine os is complete, the fetal bladder is tense, the head is in the pelvic cavity. What is your tactic?
Answer: open the fetal bladder and apply obstetric forceps
41.
In a primipara in the first stage of labor, 30 minutes after the vaginal examination, light amniotic fluid poured out in a moderate amount. What is your tactic?
Answer: auscultate the fetal heart
42.
The third stage of labor lasts 30 minutes. There are no signs of placental separation. Blood loss - 200 ml. and the bleeding continues. What is your tactic?
Answer: perform manual separation and separation of the placenta
43.
Primiparous 20 years old, delivered to serious condition in the emergency room of a maternity hospital by relatives after an attack of eclampsia that occurred at home. The gestation period is 39-40 weeks. Consciousness is retarded. Pale skin, anasarca, blood pressure 150100 mm Hg. What set of therapeutic measures should be carried out upon admission to the hospital?
Answer: all of the above
44.
Primiparous 26 years old, delivered to the maternity hospital by an ambulance medical care after an attack of eclampsia that occurred at home. The gestation period is 36-37 weeks. Consciousness is retarded. Pale skin, anasarca, blood pressure 150100 mm Hg. Lead tactics?
Answer: caesarean section after intensive care for 2-3 hours.
45.
Repeatedly pregnant, 36 years old with a full-term pregnancy, was admitted to the hospital with amniotic fluid. History of caesarean section, performed 2 years ago due to acute fetal hypoxia, postpartum period was complicated by endometritis. medical tactics?
Answer: perform an emergency caesarean section
46.
A multiparous woman, 26 years old, has a mixed breech presentation of the fetus. In the second stage of labor, prolapse of the umbilical cord loop was noted, and the fetal heart rate slowed down to 100 beats. In a minute and deafness of heart tones. A vaginal examination revealed: the buttocks and feet of the fetus are in the pelvic cavity, a prolapsed loop of the umbilical cord is determined in the vagina. What is your tactic?
Answer: perform an emergency caesarean section
47.
A woman in labor, aged 21, was admitted in the second stage of labor. The fetal head is located in the narrow part of the pelvic cavity. During the attempts, an attack of eclampsia occurred. What is the next tactic?
Answer: conduct complex intensive therapy and continue conservative treatment
48.
A 31-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of spotting spotting from the genital tract and pulling pains in the lower abdomen. Delay of menstruation - 2 months. She has a history of three spontaneous miscarriages. On vaginal examination: the cervix is preserved, cyanotic, the external os passes the tip of the finger, the uterus has a doughy consistency, it is enlarged up to 8 weeks of pregnancy, the appendages are without pathology, the arches are deep. The pupil sign is negative. What is your preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: incipient miscarriage
49.
A 29-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of spotting spotting from the genital tract and pain in the lower abdomen. Last period 2 months ago. She has a history of two spontaneous miscarriages. On vaginal examination: the cervix is preserved, cyanotic, the external os passes the tip of the finger, the uterus has a doughy consistency, it is enlarged up to 8 weeks of pregnancy, the appendages are without pathology, the arches are deep. Preliminary diagnosis: incipient miscarriage. What should be done to clarify the diagnosis?
Answer: all of the above
50.
A 31-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of spotting spotting from the genital tract and pulling pains in the lower abdomen. Delay of menstruation - 2 months. She has a history of three spontaneous miscarriages. On vaginal examination: the cervix is preserved, cyanotic, the external os inserts the tip of the finger, the uterus has a doughy consistency, it is enlarged up to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, the appendages are without pathology, the vaults are deep. Further tactics?
Answer: start hormonal and antispasmodic therapy aimed at maintaining pregnancy
51.
A 50-year-old patient consulted a gynecologist with cervical erosion. A biopsy of the cervix was performed. The histological picture is squamous nonkeratinizing cancer. Depth of invasion 5 mm. Determine the stage of the disease.
Answer: II B
52.
After coloscopy in a 38-year-old woman, the results of a biopsy of the cervical mucosa were found to be normal (negative biopsy), while at the same time, atypical cells were detected in a scraping from the cervical canal (positive). What action should be taken?
Answer: conize the cervix
53.
A 50-year-old woman diagnosed with uterine fibroids presented with complaints of irregular menstrual bleeding. From the anamnesis: profuse menstruation every 5-6 weeks, in the last three cycles intermenstrual spotting appeared lasting 5-7 days. Patient management?
Answer: diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity
54.
A 38-year-old woman diagnosed with uterine fibroids presented with moderate pain in the lower abdomen. From the anamnesis: 3 years ago she underwent surgical sterilization. On examination: the uterus is enlarged corresponding to 14 weeks of pregnancy, on the left in the bottom area, a myomatous node 4 cm in size is clearly defined. The most correct tactic for managing this patient?
Answer: hysterectomy
55.
A 28-year-old woman with one child was diagnosed with uterine fibroids corresponding to 13-14 weeks of pregnancy. Complaints of hypermenorrhea, pain in the lower abdomen. What is your tactic?
Answer: conservative myomectomy
56.
A 30-year-old patient was taken to the hospital with complaints of acute pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and frequent urination. On examination: the abdomen is moderately swollen, a positive symptom of Shchetkin-Blumberg. Pulse 90 beats per minute, body temperature -37C. Vaginal examination: the uterus is not enlarged, dense, mobile, painless on palpation. In front and to the right of the uterus, a formation measuring 5x6 cm is palpable, of a tight-elastic consistency, sharply painful when displaced, the appendages are not determined to the left, the arches are free, the discharge is mucous. Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian tumor
57.
A 28-year-old patient was taken to the hospital with complaints of acute pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and frequent urination. Vaginal examination: the uterus is not enlarged, dense, mobile, painless on palpation. In front and to the right of the uterus, a formation measuring 5x6 cm is palpable, of a tight-elastic consistency, sharply painful when displaced, the appendages are not determined to the left, the arches are free, the discharge is mucous.
A preliminary diagnosis was made — torsion of the pedicle of the ovarian tumor.
What is the most rational tactic for treating the patient?
Answer: emergency abdominal surgery, removal of the right uterine appendages
58.
A 25-year-old patient underwent perforation of the uterus with a curette during an abortion. What is your tactic?
Answer: emergency abdominal surgery, suturing of the perforation, revision of the abdominal organs
59.
A 45-year-old patient was admitted to the hospital with submucosal uterine fibroids. Vaginal examination: the cervix is hypertrophied, deformed, the body of the uterus is enlarged up to 9-10 weeks of pregnancy, dense, painless. Appendices are not changed. Optimal volume of operation?
Answer: extirpation of the uterus without appendages
60.
A 43-year-old patient was admitted to a gynecological hospital for surgical treatment for submucosal uterine fibroids. Vaginal examination: the cervix is hypertrophied, deformed, the body of the uterus is enlarged up to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, dense, painless. The appendages are not changed, the discharge is mucous. What factor influences the choice of the volume of operation in this case?
Answer: condition of the cervix
61.
A 23-year-old patient underwent hysterosalpingography for primary infertility. In the picture: the uterine cavity is T-shaped, the fallopian tubes are shortened, rigid, with club-shaped extensions in the ampullae, there is no release of a contrast agent into the abdominal cavity. For what disease such changes are most typical?
Answer: genital tuberculosis
62.
A 58-year-old patient complained of bloody discharge from the genital tract. Postmenopause - 10 years. Vaginal examination: external genitalia and vagina with signs of age-related involution, the vaginal mucosa is easily vulnerable, the cervix is clean, the pupil symptom is “negative”, there is scant bloody discharge from the cervical canal. The uterus is of normal size, the appendages are not defined, the parameters are free. Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: uterine body cancer
63.
In a 54-year-old patient, after a biopsy of the cervix, a histological examination result was obtained: squamous cell nonkeratinizing cancer. The depth of invasion is 5 mm. Determine the volume and tactics of treatment of the patient?
Answer: Wertheim operation followed by radiotherapy
64.
Complaints about the delay of the next menstruation for 10 days. Sexual life is regular, not protected. The condition is satisfactory. Transvaginal echography showed a suspected progressive tubal pregnancy. Tactics of the doctor of female consultation?
Answer: emergency hospitalization to clarify the diagnosis
65.
In connection with metastatic gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, the woman underwent chemotherapy for 1 year. After the examination three months ago, the test for HCG was negative, X-ray examination of the lungs revealed no pathology. After that, monthly tests for HCG were negative. What is shown to this patient in the first place?
Answer:
66.
The patient underwent curettage of the uterine cavity due to hydatidiform mole. During the three weeks of the postoperative period, the HCG titer gradually decreased to 6500 mIU ml and has remained at this level since then. What should be done first for this patient?
Answer: chest x-ray
67.
A woman in labor enters the maternity ward with complaints of painful contractions that occur every 2 minutes. The dilatation of the cervix is 2 cm. After 2 hours, she continues to complain of painful frequent contractions, the dilatation of the cervix is still 2 cm. Diagnosis?
Answer: uncoordinated labor activity
68.
A woman in labor enters the maternity ward with regular contractions every 5 minutes, cervical dilatation 3 cm. After 2 hours, contractions every 2-3 minutes, light waters poured out, opening of the pharynx - 6 cm. Diagnosis?
Answer: active phase of labor
69.
A 56-year-old patient complained of nagging pains in the lower abdomen. She has a history of two deliveries with a large fetus. Somatic pathology was not revealed. On examination: when straining outside the vulvar ring, the body of the uterus is determined, the cervix is elongated, hypertrophied, hyperemic, the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina are lowered, there is a divergence of the muscles that lift anus. Diagnosis?
Answer: complete prolapse of the cervix, failure of the pelvic floor muscles, elongation of the cervix
70.
A 51-year-old patient (postmenopausal 2 years) was admitted to the hospital with complaints of general malaise and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. On examination, it was noted: an increase in the size of the abdomen, dullness of percussion sound in the lateral sections. Vaginal examination determines the uterus of normal size, shifted to the left. To the right of the uterus, a lumpy, inactive, painless formation of a dense consistency 10x10 cm in size is determined. Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: ovarian cancer
71.
In a patient in menopause, a vaginal examination determines the uterus of normal size, displaced to the right. To the left and posterior to the uterus, a lumpy, inactive, painless formation of a dense consistency 10x10 cm in size is determined. Preliminary diagnosis: ovarian cancer. What kind additional methods researches it is expedient to use for specification of the diagnosis?
Answer: all of the above
72.
A 50-year-old patient complained of drawing pains in the lower abdomen, difficulty urinating. In the anamnesis - childbirth with a large fetus, perineal rupture of the 2nd degree. On examination: when straining outside the vulvar ring, the body of the uterus is determined, the cervix is elongated, hypertrophied, the anterior and posterior walls of the vagina are lowered, there is a divergence of the muscles that lift the anus. What complications are possible with this pathology?
Answer: all of the above
73.
A 55-year-old patient with an uncomplicated somatic history and an established diagnosis: Complete prolapse of the cervix, incompetence of the pelvic floor muscles, elongation of the cervix. Cysto- and rectocele. What is the treatment strategy for the patient?
Answer: vaginal hysterectomy, anterior and posterior colporrhaphy, levatoroplasty
74.
In a 54-year-old patient, after a biopsy of the cervix, a histological examination result was obtained: squamous cell nonkeratinizing cancer. The depth of invasion is 5 mm. What is the first stage of lymphogenous metastasis in cervical cancer?
Answer: external and internal iliac and obturator lymph nodes
75.
A 58-year-old patient complained of bloody discharge from the genital tract. Postmenopause - 10 years. Vaginal examination: external genitalia and vagina with signs of age-related involution, the vaginal mucosa is easily vulnerable, the cervix is clean, the pupil symptom is “negative”, there is scant bloody discharge from the cervical canal. The uterus is of normal size, the appendages are not defined, the parameters are free. What additional research methods will help you clarify the diagnosis?
Answer: separate diagnostic curettage followed by histological examination of scrapings
76.
A 19-year-old patient complained of pain in the lower abdomen, fever up to 37.5 C, purulent discharge from the genital tract, and painful urination. On examination: the urethra is infiltrated, in the mirrors - the cervix is hyperemic, eroded, the discharge is abundant mucopurulent. Vaginal examination: the uterus is not enlarged, painful on palpation, the appendages on both sides are thickened, painful. When bacterioscopy of smears - gonococci, located outside and intracellularly. Diagnosis?
Answer: fresh acute ascending gonorrhea
77.
Pregnant L., 23 years old. The gestation period is 28 weeks. She was admitted to the hospital with complaints of weakness, dizziness, dry mouth, increased thirst, pain in the region
heart, shortness of breath, feeling of heaviness and pain in the epigastrium, nausea and vomiting with blood, bleeding gums, weight loss within 6 weeks, pruritus, chills. Objectively: The skin is icteric in color. HELL 9060 mm.R.st., PS 100 beats. in min. In the analyzes - moderate hypochromic anemia, pronounced leukocytosis, neutrophilic shift to the left. Severe hypoproteemia. A sharp increase in blood urea, creatinine. Cholesterol is within normal limits. Laboratory signs of DIC syndrome.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
78.
Woman L., 22 years old, was urgently delivered to the gynecological department by an ambulance. with complaints of cramping pains in the lower abdomen and spotting from the genital tract. From the anamnesis: the last menstruation was two months ago.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pale pink in color, Ps 84 per minute. Body temperature 37°C. BP 110/70 and 110/70 mm Hg. Art.
Per speculum: the cervical canal is open, the lower pole of the fetal egg protruding into the vagina is visible.
Per vaginam: the body of the uterus is enlarged to 6 weeks of gestation, soft consistency. Appendages are not defined. The vaults of the vagina do not hang. The discharge is bloody, bright, profuse. The cervical canal passes a finger, it is determined fertilized egg, freely around the circumference. Blood loss is about 500 ml.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 6 weeks. Spontaneous abortion in progress
79.
Pregnant M., 20 years old, was taken to the gynecological department by ambulance on October 20, on an emergency basis. Complaints of cramping pain in the lower abdomen, bloody discharge from the genital tract. From history. Sexual life since 20 years. Last period August 2-6. Pregnancy first, married, desired.
Condition of moderate severity. The skin and mucous membranes are pale, acrocyanosis. Body temperature 36.6°C, Ps 120 per minute, BP 90/40 and 90/50 mm Hg. Art. The abdomen is soft, painful in the lower abdomen. Diuresis is reduced. Blood loss is about 1500 ml.
Per vaginam: large number of blood clots in the vagina. The cervix is shortened, the cervical canal is passable for two fingers. The body of the uterus is soft in consistency, enlarged about the 6-week gestation period. The appendages are not palpable.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 10 weeks. Spontaneous incomplete abortion. Hemorrhagic shock II degree.
80.
Woman N., 26 years old, on May 5, went to the antenatal clinic about the delay in the next menstruation. Complaints of nausea, vomiting in the morning, aversion to meat food, fatigue, irritability. Last menstruation March 25-28. Does not use contraceptives. Over the past 2 years - three medical abortions.
The condition is satisfactory. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pale pink in color, clean. Body temperature 36.7°C. BP 120/80 mm Hg. Art. Ps 72 per min. The abdomen is soft, slightly painful in the lower sections.
Per speculum: the cervix is sharply cyanotic, hypertrophied, barrel-shaped, the external os is closed, decentrically located, displaced to the right and upwards. Discharges are spotting, bloody.
Per vaginam: the body of the uterus is soft, slightly enlarged. The appendages are not palpable. The vaults do not hang. Neck movements are painless.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Neck pregnancy. OAA.
81.
Pregnant O., 35 years old, was taken to the maternity hospital on June 30 at 19 o'clock by ambulance, on an emergency basis with complaints of bloody discharge from the genital tract, minor pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, last menstruation on September 27-30, this is the fifth pregnancy. The obstetric anamnesis is aggravated - 3 medical abortions. According to the woman, in the second half of pregnancy, at 27 weeks, spotting bloody discharge from the genital tract appeared. Didn't go to the doctor. On June 30 at 17 o'clock there were slight pains in the lower abdomen and lower back, and at 18 o'clock moderate bloody discharge from the genital tract. Delivered to the hospital.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pale pink. BP 120/80 and 120/80 mm Hg. Art., Ps 80 min. There are no edema. The uterus is soft, painless. The position of the fetus is longitudinal. The presenting part of the fetus is not clearly defined, the heartbeat is clear, rhythmic 140 beats / min. There is a stain of scarlet blood on the lining.
Per speculum: the cervix is cyanotic, with red blood coming out of the external os.
Per vaginam: the cervix is softened, up to 1.5 cm long, the cervical canal is freely passable for one finger. The fetal bladder is intact. The presenting part of the fetus is dense, rounded. Roughness is determined behind the internal pharynx. Allocations are bloody, moderate.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 39 weeks. Preparation period. Marginal placenta previa. OAA.
82.
Pregnant P., 18 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on March 15 at 8:10 am by ambulance, on an emergency basis with complaints of sharp pains in the lower abdomen and weakness during the last hour. The last menstruation was on July 12-17, the first pregnancy, out of wedlock, from the 30-week period she received inpatient treatment in the pregnancy pathology department for preeclampsia.
Condition of moderate severity. The skin and mucous membranes are pale, swelling of the legs. BP 90/50 and 90/50 mmHg Art., Ps 120 min. The uterus is ovoid in shape, dense, does not relax. The position of the fetus is longitudinal. The presenting part of the fetus is not determined due to uterine hypertonicity, the heartbeat is muffled, rhythmic, 170 beats / min.
Per speculum: the cervix is tilted backwards, clean, bloody discharge.
Per vaginam: the cervix is formed, 3 cm long, the cervical canal passes one finger, the presenting part of the fetus is dense, rounded above the entrance to the small pelvis. The fetal bladder is intact. Discharge from the genital tract is bloody, scanty.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 35 weeks. PONRP. Hemorrhagic shock II degree. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
83.
Woman in labor R., 28 years old, is in the delivery room. The last menstruation was on August 23-26, the third pregnancy, the two previous ones ended in community-acquired abortions, followed by curettage of the uterine cavity. Labor activity from 4 o'clock in the morning on May 27, delivered to the maternity hospital. Childbirth was complicated by primary and secondary weakness of labor activity, labor intensification was carried out, drug sleep was used. On May 28 at 6 o'clock in the morning she was delivered through the birth canal by a live full-term female baby. Independently separated and stood out afterbirth. On examination - intact, shells all. Inspection of the cervix in the mirrors: intact. There are no ruptures of the vagina and perineum.
The condition is satisfactory. Body weight 80 kg. The skin is pale. BP 110/60 and 110/60 mm Hg. Art., Ps 100 per minute, rhythmic, weak filling. The uterus is soft on palpation, the bottom is at the level of the navel. Abundant bloody discharge from the genital tract. Blood loss 500 ml.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Prolonged term labor 1, early postpartum period. Primary and secondary weakness of labor. Hypotonic bleeding. OAA.
84.
A woman in labor S., 33 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on June 1 about the onset of labor, the outflow of amniotic fluid. The last menstruation was on August 22-25, the third pregnancy, one premature birth, the second birth was protracted, the child died on the second day. Real pregnancy without complications. After 12 hours, there were complaints of frequent, painful contractions, difficulty urinating, the woman was screaming, tossing about in bed.
The general condition is satisfactory. There are no edema. Ps 100 per minute, BP 130/80 and 130/80 mmHg. Art. Uterus in the shape of an "hourglass", a contraction ring during attempts at the level of the navel. The uterus is in constant hypertonicity, sharply painful on palpation. The position of the fetus is longitudinal. The presenting part of the fetus is not determined due to tension and soreness of the uterus, palpation of the lower segment is very painful. Pelvic dimensions: 25-26-29-18 cm. Solovyov's index 15 cm. Signs of Vasten and Zangemeyster are positive. Fetal heart rate 110 beats / min.
Additional examination methods Cardiotachogram according to Fisher 4 points.
Tokogram: uterine tone 20 mm Hg. Art., contractions for 90-100 seconds, after 20 seconds, with a force of 50 mm Hg. Art., for 10 minutes - 4.5 contractions.
Per vaginam: the opening of the cervix is complete, its edges are swollen. The head of the fetus is pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. There is a large birth tumor on the head. The cape is not reachable. Urine is catheterized and stained with blood. Diagnosis?
Answer: Term delivery III, P period of childbirth. Threatened uterine rupture. Clinically narrow pelvis. Acute severe fetal hypoxia. OAA.
85.
Woman in labor T., 32 years old, was delivered on December 5 at 10.30 am to the Central District Hospital by air ambulance. Complaints of cramping abdominal pain, pain in the area of the postoperative scar that appeared 1 hour ago, the absence of fetal movements. Last menstruation March 27-30. The third pregnancy, the first pregnancy ended in an urgent birth through the natural birth canal with a live baby. Second, six years ago, premature birth by corporal caesarean section for placenta previa, postoperative period complicated by metroendometritis, received treatment in a hospital.
Severe condition. Consciousness is confused. The skin is pale. Ps 130 per min. BP 70/0 and 70/10 mm Hg. Art. The abdomen has an irregular shape, painful on palpation. Small parts of the fetus are palpated through the anterior abdominal wall. The fetal heartbeat is not heard. The contours of the uterus are absent. There are no fights. From the genital tract moderate bleeding.
Complete blood count: erythrocytes 1.5x1012/l, Hb 62 g/l, Ht 23%.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Preterm labor III at 35 weeks. Complete uterine rupture. Intrauterine fetal death. Hemorrhagic shock III degree. OAA. Scar on the uterus.
86.
Woman in labor F., 30 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on April 10 due to regular labor activity for 5 hours. On admission, about 2 liters of clear amniotic fluid was shed. Last period July 1-4. Pregnancy 4 is real.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin is clean. The tongue is wet. BP 110/70 and 115/70 mm Hg. Art., Ps 80 min. Internal organs without pathology. The bottom of the uterus is 3 cm below the xiphoid process. In the bottom of the uterus, the soft volumetric part of the fetus is determined. Back left. A dense rounded part of the fetus is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. OB 100 cm, VDM 40 cm, pelvic dimensions: 25-27-31-22 cm. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 130 beats / min. Palpation contractions after 2-3 minutes for 30-35 seconds of medium strength.
Per vaginam: The vagina is loose. The cervix is smoothed, the opening is 2 cm. The fetal bladder is intact. A dense, rounded part of the fetus is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. The pelvis is capacious. The cape is not reachable.
Additional examination methods
Tokogram: contractions with a force of 50 mm Hg. Art., for 60 seconds, after 60 seconds, in 10 minutes - 4 contractions. The basal tone of the uterus is 10 mm Hg. Art.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Term labor II, I stage of labor. Head presentation. First position. Polyhydramnios. Early rupture of amniotic fluid. Large fruit. OAA.
87.
Primigravida X., 20 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on June 30 due to the development of labor activity 2 hours ago with complaints of cramping abdominal pain. Last menstruation 15-19 September. First pregnancy.
The general condition is satisfactory. Excited. Ps 85 per min. BP 120/80 and 120/80 mm Hg. Art. Pathologies from the side internal organs no. The abdomen is enlarged due to the pregnant uterus. Urination is not disturbed, the stool is irregular, after 2-3 days. The uterus is ovoid, the bottom of the uterus is 2 cm below the xiphoid process. Palpation: contractions for 60-70 seconds, after 30-40 seconds, painful. In the bottom of the uterus, a volumetric softish part of the fetus is determined, palpation through the lateral surfaces of the uterus and determining the position of the fetus is difficult. In the lower segment of the uterus, the dense presenting part of the fetus is determined, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. OB 98 cm, VDM 37 cm. Pelvic dimensions: 25-28-31-21 cm.
Per vaginam: the vagina is narrow, the cervix is smoothed, the edges are thin, easily extensible, the opening is 6 cm. The fetal bladder is intact. The head is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. The pelvis is capacious. The sacral cavity is well expressed. The cape is not reachable. Sagittal suture in the right oblique size of the plane of the entrance to the small pelvis, small fontanel on the left front.
Cardiotachogram: Fisher score 7 points.
Tokogram: contractions with a force of 70-80 mm Hg. Art., for 80-90 seconds, after 20-25 seconds, the basal tone of the uterus is 15 mm Hg. Art.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Term delivery I, I stage of childbirth. Premature discharge of amniotic fluid. Discoordinated labor activity. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia of moderate degree. OAA. Age primipara.
88.
Pregnant E., 36 years old, at 22-23 weeks gestation, went to the antenatal clinic for pregnancy with complaints of irritability, fatigue, insomnia, palpitations, excessive sweating, hand tremors. Pregnancy is the second. The first ended a year ago with a medical abortion at 8 weeks due to medical reasons. The second, real pregnancy was complicated by early gestosis (mild vomiting of pregnant women), threatening miscarriage. She treated herself. She took cerucal, no-shpu, multivitamins. Suffering from diffuse toxic goiter from 22 years old. Heredity, allergic anamnesis are not burdened.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin is hyperemic, high humidity. Thyroid increased on palpation. Heart sounds are clear, rhythmic. Systolic murmur at the apex of the heart. BP 120/80 and 130/90 mm Hg. Art., Ps 104 in min. NPV 22 min. Pelvic dimensions: 26-28-20-19 cm. The uterus is in increased tone, relaxes. The position of the fetus is longitudinal. The head is provided. Back right, back. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 140 beats/min.
Per uaginam: the neck is up to 2.5 cm long, of medium density, deviated posteriorly from the wire axis of the pelvis. The external os passes the tip of the finger. The cape is not reachable. Bone pelvis without pathology.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 28 weeks. Head presentation. Longitudinal position, second position, rear view. Threatening premature birth. thyrotoxicosis. OAA. Primiparous older.
89.
Pregnant I., 33 years old, was observed in the antenatal clinic regularly, from 8 weeks of pregnancy. Complaints. At 24-25 weeks of gestation, complaints of weakness, thirst, dry mouth, itching of the external genitalia appeared. Pregnancy fifth. The first 7 years ago ended in term delivery of a live full-term baby, weighing 4850 g, height 51 cm. The next two pregnancies ended in medical abortions, without complications. The fourth pregnancy a year ago ended in a spontaneous miscarriage at 9-10 weeks of gestation, the cause was a burdened obstetric and somatic history. The fifth, real pregnancy was complicated by early preeclampsia (vomiting of a pregnant woman of mild severity), threatening miscarriage at 10-11 weeks. She was treated permanently, the effect is positive. Heredity is burdened with diabetes in my grandmother.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin is pale pink, dry. Woman increased nutrition. Weight 104 kg, height 167 cm. BP 120/80 mm Hg. Art., Ps 84 in min. Pelvic dimensions: 26-28-31-20 cm. The position of the fetus is unstable. The fetal heartbeat is muffled, rhythmic, 152 beats/min, on the right below the navel.
Per speculum: the cervix is clean, cyanotic, the external os is closed. Discharge milky, moderate.
Per vaginam: The vagina is loose. The cervix is formed, up to 3 cm, dense, deflected backwards. The external os is closed. The cape is not reachable. The presenting part is high above the entrance to the small pelvis, it is easily repelled.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 24-25 weeks. Threatening premature birth. Large fruit. Polyhydramnios. OAA. Diabetes. Obesity III degree.
90.
Pregnant Sh., 30 years old, was taken to the maternity hospital on July 17 on an emergency basis by an ambulance on a stretcher because of preeclampsia with complaints of headache, tinnitus, weakness, and vomiting. First pregnancy. Last period January 20th. In the period of 13-14 weeks, there was an increase in blood pressure to 160/90 mm Hg. Art., headaches, nosebleeds. On this occasion, she was treated in the therapeutic department for 3 weeks. In the period of 20-22 weeks, headaches reappeared. On July 17, the condition worsened, headaches intensified, more in the temporal areas, weakness, there was a single vomiting. Heredity is burdened - both parents have GB.
Severe condition. Edema of the legs, anterior abdominal wall. Heart sounds are clear, rhythmic, accent 2 tones on the aorta. BP 150/90 and 160/100 mm Hg. Art., Ps 98 in min. The uterus is in high tonus. In the bottom of the uterus is a dense rounded part of the fetus. VDM 35 cm, coolant 100 cm. The position of the fetus is longitudinal. The soft, voluminous part of the fetus is supposed to be mobile above the entrance to the small pelvis. Back left, front. The fetal heartbeat is muffled, rhythmic, 156 beats/min, on the left above the navel.
Per vaginam: the cervix is shortened to 2 cm, of medium density, located along the wire axis of the pelvis. The cervical canal is passable for the finger. The soft presenting part of the fetus is palpated, pressed at the entrance to the small pelvis. The cape is not reachable. The fetal bladder is intact.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 34 weeks. Breech presentation, longitudinal position, first position, anterior view. Moderate Preeclampsia Hypertonic disease III degree. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia. Threatened preterm birth
91.
The primigravida S., 20 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on November 3 in the direction of the antenatal clinic in a planned manner for antenatal hospitalization. Makes no complaints. Last period February 10th. Pregnancy was complicated by anemia of a mild degree at 24 weeks of pregnancy, she was treated on an outpatient basis. From the age of 14, she suffers from rheumatism, is registered at the dispensary. Notes frequent colds.
The general condition is satisfactory. The skin and visible mucous membranes are pink. There are no edema. NPV 20 per minute. Heart sounds are clear, rhythmic. A systolic murmur is heard at the apex of the heart. BP 110/70 and 110/70 mm Hg. Art., Ps 78 per minute. The uterus is in high tone, relaxes. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, the head is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. Back right, front. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 140 beats/min, on the right below the navel.
Per speculum: the cervix is clean, mucous is cyanotic, loose. The external os is gaping. Discharge milky, moderate.
Per vaginam: the cervix is shortened to 2 cm, soft, located along the wire axis of the pelvis. The cervical canal is passable for 1 finger. The cape is not reachable. Bone pelvis without pathology.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 38 weeks. Head presentation. Rheumatism Ao. Failure mitral valve NK o.
92.
Pregnant R., 25 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on May 5 in the direction of the antenatal clinic with complaints of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and lower back. Menstruation from the age of 16, established after two years, 3-5 days, after 25-28 days, scanty, moderately painless. Last menstruation from 4 to 8 November. In the antenatal clinic, it is observed regularly from a 6-week period. The pregnancy was complicated by a threatened miscarriage at 8-9 weeks, received treatment: dexamethasone, duphaston, antispasmodics, vitamins, the effect of the treatment is positive. Ultrasound examination of the uterus showed that the internal os was expanded to 1 cm. At the gestational age of 16 weeks, a purse-string suture with lavsan was applied to the cervix according to Macdonald in the pregnancy pathology department of the perinatal center. At 22 weeks, she was examined for HSV (herpes simplex virus), CMV (cytomegalovirus), toxoplasmosis, chlamydia. The titer of IgG antibodies for HSV was 1:800, for CMV 1:800, for chlamydia IgG 1:400, toxoplasmosis was negative. Pregnancy - 2, 1 pregnancy ended in intrauterine fetal death at 9 weeks, conducted abrasio cavi uteri.
The condition is satisfactory. Integuments of physiological color, pronounced hirsutism. Ps 76 per minute, BP 110/70 and 110/70 mm Hg. Art. The uterus is palpated in increased tone. The presenting part is dense, rounded. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 140 beats/min.
Per vaginam: the cervix is formed, 3 cm long, dense, tilted backwards. The cape is not reachable. The external os is closed, there is no discharge.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 26 weeks. Head presentation. Threatening premature birth. Organic and functional ICI. Seam on the cervix according to McDonald. Infection with HSV, CMV. Chlamydia.
93.
On May 5, a 26-year-old primigravida K. was admitted to the hospital with complaints of pulling pains in the lower abdomen. Not registered. Menstruation from the age of 17, established after 2 years, scanty, painful. According to her, she has been married since the age of 22, she did not use protection P / m - November 4. When examining the hormonal status outside of pregnancy, a decrease in the level of estradiol, progesterone, an increase in testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone were found.
Satisfactory condition, reduced nutrition, asthenic constitution. Height 172 cm, weight 65 kg. Integuments of physiological color, pronounced hirsutism. The mammary glands are hypoplastic. Ps 76 per minute, BP 110/70 and 110/70 mm Hg. Art. The uterus is palpated in increased tone. The presenting part is dense, rounded. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 140 beats/min.
On examination: the external genital organs are formed incorrectly, there is hypoplasia of the labia majora, increased hair growth on the inner surface of the thighs, along the midline from the womb to the navel (male-type hair).
Per speculum: Vagina narrow, long. The cervix is clean, conical in shape, the pharynx is rounded. Allocations mucous, moderate.
Per vaginam: the cervix is preserved, 3 cm long, dense, posteriorly rejected. The cape is not reachable. The external os is closed, there is no discharge.
Preliminary diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 26 weeks. Head presentation, longitudinal position. Threatening premature birth. adrenogenital syndrome. OAA.
94.
On November 10, a woman in labor D., 25 years old, was delivered by ambulance to the perinatal center due to the onset of labor with complaints of cramping pains in the lower abdomen, mucous discharge from the genital tract. Last menstruation March 18-22. Pregnancy third, observed regularly.
The condition is satisfactory. T 36.8°C, Ps 92 per minute, BP 110/70 mm Hg. st on both hands. There are no edema. Coolant 80 cm. VDM 30 cm. Pelvis dimensions: 26-28-30-20 cm. Palpation: contractions are regular, intense, 30 seconds each, every 5-6 minutes The presenting part is dense, rounded, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. The back is turned to the left. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 138 beats/min.
Per speculum: the cervix is cyanotic, the external os is open, the fetal bladder prolapses, the discharge is mucous.
Per vaginam: the cervix is soft, shortened to 1 cm, along the wire axis of the pelvis, opening 4 cm. The cape is not achievable. The head is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. The bones of the skull are soft, the sutures and fontanelles are pronounced. Arrow-shaped seam in the right oblique size, small fontanel on the left front. The fetal bladder is intact.
Cardiotachogram: Fisher score 6 points.
Tokogram: basal tone 10 mm Hg. Art., contractions with a force of 30 mm Hg. Art., for 60 seconds, after 60 seconds, in 10 minutes - 4 contractions.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Premature birth at 34-35 weeks. Head presentation, longitudinal position, 1 position. Mild fetal hypoxia. OAA.
95.
On May 5, a woman in labor V., 26 years old, was delivered to the perinatal center by ambulance due to the outflow of amniotic fluid at 6.00. Pregnancy first, desired, in marriage. Last menstruation on October 3 last year.
The condition is satisfactory. Skin and mucous membranes of physiological color. Ps 78 per minute, BP 110/70 mm Hg. Art. on both hands. There are no edema. OJ 80 cm. VDM 28 cm. Pelvis dimensions: 27-29-30-20 cm. Palpation of the uterus in normal tone. The presenting part is dense, rounded, above the entrance to the small pelvis. The back is turned to the left. The fetal heartbeat is muffled, rhythmic 162 beats/min.
Per speculum: the cervix is clean, the external os is ajar, amniotic fluid is leaking with an admixture of meconium.
Per vaginam: the cervix is soft, shortened to 1 cm, deflected backwards, opening 1 cm. There is no membranes. The cape is not reachable. The head is located above the entrance to the small pelvis.
Cardiotachogram: Fisher score 5 points.
Tokogram: basal tone of the uterus 5-10 mm Hg. Art., no labor pains.
A smear for microflora: 30-40 leukocytes in the field of view, epithelium - single cells in the field of view. Gonococci and Trichomonas were not found, abundant gr(+), gr(-) coccal flora.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Pregnancy 31-32 weeks. Head presentation, longitudinal position, 1 position. Premature discharge of amniotic fluid. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia of moderate severity. Nonspecific colpitis.
96.
On July 22, a pregnant R., 30 years old, was delivered to the maternity hospital from the antenatal clinic by ambulance due to the outflow of amniotic fluid. Complaints about leakage of amniotic fluid within an hour, increased fetal movements in the last 2-3 days. Menses from 16, irregular, scanty, painful. Last menstruation 25-29 September last year. I felt the first movement of the fetus on February 14th. From 16 weeks of chronic primary compensated placental insufficiency, received inpatient treatment, the effect is positive.
The condition is satisfactory, the skin and mucous membranes are clean, pink. Body temperature 36.6°C, Ps 76 per minute, BP 110/70 mm Hg. Art. on both hands. There are no edema. OJ 112 cm. VDM 38 cm. Pelvis dimensions: 25-27-30-20 cm. The uterus is soft on palpation. The length of the fetus in the uterus when measured by a pelvis meter is 30 cm. The head is located above the entrance to the small pelvis, the fronto-occipital size of the head is 12 cm. The fetal heartbeat on the right below the navel is muffled, rhythmic, 125 beats / min.
On examination: the labia majora are hypoplastic. Hair on the pubis is expressed poorly.
Per speculum: Vagina narrow, loose. The cervix is conical, clean. The throat is rounded. Turbid, thick green waters leak in small quantities. In the waters, vellus hair, cheese-like lubricant.
Per vaginam: the cervix is shortened to 2 cm, soft, tilted backwards, the external os passes the tip of the finger. Through the vaults, the dense presenting part is highly defined. The cape is not reachable.
Cardiotachogram: Fisher score 4-5 points.
Type III smear (term of delivery).
Diagnosis?
Answer: Post-term pregnancy. Chronic PN, primary, subcompensated. Intrauterine fetal hypoxia of moderate severity. Premature discharge of water. Large fruit. Primiparous older. Infantilism.
97.
Pregnant V., aged 26, was admitted to the maternity hospital at 13.00, at 43 weeks' gestation, due to the onset of labor. The condition is satisfactory. Body temperature 36.6°C, Ps 76 per minute, BP 110/70 - 120/70 mm Hg. Art. OB 108 cm. WDM 37 cm. Pelvic dimensions: 25-27-30-21 cm. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, the head is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. The back is turned to the right. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic 136 beats/min.
Per vaginam: the cervix is smoothed, the edges are soft, thin, easily extensible, along the wire axis of the pelvis, the opening is 3 cm. The head is placed, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. On examination, light amniotic fluid was poured out in the amount of 100 ml. The cape is not reachable.
Cardiotachogram: Fisher score 8 points.
At 23.00, she gave birth to a live male child, weighing 3900 g, 50 cm long. A large fontanel with a facet of 2 cm is determined on the head, a birth tumor is in the area of the small fontanel. Vellus hair on shoulders. The skin is not macerated. The nail plates extend to the edge of the nail bed. The afterbirth is examined - intact, without pathology.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Late delivery at 42-43 weeks. Head presentation, 2 position. Premature discharge of water.
98.
Woman in labor U., 28 years old, was admitted to the maternity hospital on an emergency basis, delivered by an ambulance team about the onset of labor and bloody discharge from the genital tract. Pregnancy 8th. The first - 7 years ago, proceeded without complications, delivered a live full-term male baby, weighing 3400 g. The second - 6 years ago, transcervical amniocentesis in a period of 25 weeks, according to social indications. Medaboards - 5. The last menstruation was on August 8-14, the first fetal movement on December 12, was not observed in the antenatal clinic.
The condition is satisfactory. Integuments of physiological coloring. BP 105/65 and 100/60 mm Hg. Art., Ps 88 in min. OB 84 cm, VDM 31 cm. Pelvic dimensions: 26-28-30-20 cm. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, the head is high above the entrance to the small pelvis, the back is front and right, the fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic 128 beats / min. Palpation contractions for 60 seconds, after 2-3 minutes. Bloody discharge from the genital tract, profuse. Blood loss 500 ml.
Per speculum: the cervix is clean, from the cervical canal profuse, scarlet spotting.
Per uaginam: the cervix is tilted backwards, shortened to 1.5 cm, of medium density, the external os is closed, rough, soft, spongy tissue is determined through the arches.
Diagnosis?
Answer: Premature birth at 32-33 weeks, cephalic presentation, anterior view, 1st position. Central placenta previa. OAA.
99.
A team consisting of an obstetrician-gynecologist and an anesthetist was called to the settlement for a woman in labor L., 25 years old, for sanitation in the village. Complaints of fatigue, frequent painful contractions.
The real pregnancy was the first, desired, registered at the feldsher-obstetric station from 7-8 weeks, visited regularly. Pregnancy was complicated by mild anemia from 20 weeks.
The condition is satisfactory. Integuments of physiological coloring. BP 120/90 and 120/85 mm Hg. Art., Ps 80 min. There are no edema. The dimensions of the pelvis: 23-24-28-18, Solovyov's index 15.5 cm, OB 110 cm, VDM 40 cm. The uterus is ovoid in shape, the position of the fetus is longitudinal. The head is presented, pressed against the plane of the entrance to the small pelvis, the back is in front and on the right. Contractions by palpation for 30-40 seconds, after 1.5-2 minutes. Labor activity for 19 hours, water was not poured out, within 2 hours the fetal heartbeat is not heard. Signs of Zangemeister and Vasten are positive. Urination rare, painful.
Per speculum: vaginal and cervix mucosa cyanotic, edematous. Discharges are mucosal.
Per vaginam: the cervix is smoothed, the edges are soft thin, the opening is 12 cm, the fetal bladder is intact, opened instrumentally, about 200 ml of green turbid amniotic fluid poured out, the sagittal suture in the right oblique size of the plane of entry into the small pelvis, the cape is achievable, p. diagonalis 9 cm. The sacral cavity is well expressed.
Estimated diagnosis?
Answer: Prolonged term labor I, cephalic presentation, anterior view. Large fruit. Clinically narrow pelvis. Intranatal fetal death. General uniformly narrowed pelvis II degree. Amniotomy.
100.
In severe preeclampsia, the initial dose of magnesia therapy:
Answer: 4-5 grams intravenously over 20 minutes
101.
How much blood loss during childbirth is considered physiological:
Answer: up to 400 ml
102.
At what insertion does the fetal head pass through the pelvic cavity with its large oblique size:
Answer: in frontal presentation
103.
What indicators of hematocrit should be followed during infusion therapy for preeclampsia.
Answer: 29-30%
104.
Peritonitis, against the background of chorionamnionitis, usually begins on:
Answer: start 1-2 days after surgery,
105.
The indication for a targeted biopsy of the cervix is:
Answer: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
106.
To confirm the diagnosis of HIV, the following laboratory tests are performed:
Answer: two positive ELISA results + immunoblot
107.
Antibodies to HIV are most likely to be detected after infection:
Answer: in 6 months
108.
Doctor's tactics in cervical pregnancy:
Answer: ablation, extirpation of the uterus
109.
Patient L., 28 years old, was admitted to the gynecological department with acute inflammation of the uterine appendages. The examination revealed a positive reaction to HIV. When should an HIV infection be considered laboratory-confirmed?
Answer: double positive ELISA reaction + immunoblot
110.
A primigravida P., 24 years old, 10 weeks pregnant, with a known HIV-positive status, was registered at the antenatal clinic. At what gestational age should prophylactic treatment be started to reduce the risk of HIV transmission to the mother?
Answer: from 14 weeks
111.
The female child was born at term. The structure of the external genitalia according to the intersex type: enlarged clitoris, urogenital sinus.
Diagnosis:
Answer: adrenogenital syndrome
112.
In a 3-year-old girl, her mother noticed an increase in the mammary glands, which manifested themselves against the background of a child's cold and disappeared during recovery. This episode of breast enlargement is the third.
Diagnosis:
Answer: isolated transient thelarche
113.
A 5-year-old girl at the time of surgery for bilateral inguinal hernias the testicles were found in the hernial sac and were inserted into the abdominal cavity.
Diagnosis:
Answer: testicular feminization syndrome
114.
A 16-year-old girl with well-developed secondary sexual characteristics turned to a gynecologist due to the primary absence of menstruation.
Diagnosis:
Answer: uterine form of amenorrhea
115.
In a 15-year-old girl, after 1 year of regular menstruation, menstruation stopped, i.e. secondary amenorrhea occurs. A girl with a cosmetic goal lost 6 kg in two months and continues to lose weight.
Diagnosis:
Answer: amenorrhea due to weight loss.
116.
Girl 18 years old notes irregular menstruation with a delay of 3-4 months. Objectively: increased nutrition, dry skin, thickened tongue, constipation.
Most likely diagnosis:
Answer: hypothyroidism
117.
A 13-year-old girl consulted a pediatrician due to an enlarged abdomen and periodic, regular abdominal pain. The degree of sexual development corresponds to age, menstruation was not. On palpation, the abdomen is asymmetric, the formation of a tight-elastic consistency is determined, protruding 3 transverse fingers above the bosom. On rectal examination, the formation deforms the capsule of the rectum.
Diagnosis:
Answer: malformation of the vagina with a delay in the outflow of menstrual blood
118.
A mother with a 14-year-old girl turned to a gynecologist due to the absence of secondary sexual characteristics and menstruation. Examination revealed a sharp elevated levels pituitary hormones responsible for ovarian function.
Diagnosis:
Answer: ovarian form
119.
, 34 years old, was delivered by ambulance to the gynecological department with complaints of a rise in body temperature up to 38.40C, pain in the lower abdomen. He considers himself ill for 1 day, when for the first time, on the 7th day of the menstrual cycle, the above complaints appeared. Objectively: a state of moderate severity. Pulse 104 beats per 1 minute, t - 38.40С. The abdomen is soft on palpation, painful in the lower sections. The symptom of peritoneal irritation on the left is positive. Gynecological examination: on the mirrors - the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix is hyperemic, the discharge is purulent. PV: The cervix is cylindrical, the os is closed. The uterus is in the correct position, normal size. In the area of the uterine appendages on both sides, painful formations, oblong in shape, are determined. Make a diagnosis:
Answer: acute bilateral adnexitis
120.
A 26-year-old patient consulted a gynecologist with complaints of pain in the area of the left labia. Notes the rise in body temperature to 37.80C. Examination of the external genitalia revealed swelling and hyperemia of the left labia. On palpation, a formation in the thickness of the left labia is determined with a size of 5x4 cm with a softening area in the center. Choose the correct diagnosis:
Answer: barolin gland abscess
121.
Patient A., aged 24, was admitted with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen and bloody discharge from the genital tract with a delay in menstruation for 2 weeks. BP 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 90 beats/min. On the mirrors: cyanosis of the mucous membrane of the cervix, bloody discharge, dark. PV: the uterus is slightly enlarged, mobile, on the right in the area of the appendages there is a formation, painful, doughy consistency. The posterior fornix is flattened, painful. Your diagnosis:
Answer: ectopic pregnancy
122.
A 36-year-old patient was delivered to the gynecological department with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, vomiting, and a rise in body temperature up to 380C. Consists of a dispensary for uterine fibroids, primary infertility for 3 years. Objectively: the state of moderate severity, body temperature 380C. Positive symptom of peritoneal irritation. When viewed on the mirrors: the cervix is clean, discharge of leucorrhoea. PV: the uterus is enlarged up to 5-6 weeks, at the right corner of the uterus there is a painful dense formation 5x6 cm in size. The area of the appendages is without features. Your diagnosis:
Answer: torsion of the ovarian cyst
123.
Patient O., 34 years old, was hospitalized on an emergency basis in the gynecological department due to torsion of the leg of the myomatous subserous node. During the operation to open the abdominal cavity, it was found: The uterus is tuberous, turned into a multiple myomatous tumor, up to 13 weeks of pregnancy. On the front wall - the leg of the subserous myomatous node is twisted, the node is 4x4 cm in size, purple. Appendages on both sides without visible pathology. What volume of operation is shown in this case:
Answer: supravaginal amputation of the uterus without appendages
124.
A 34-year-old patient came to the antenatal clinic. Married 1 year. Delay of menstruation for 12 weeks, during the day pains in the lower abdomen on the right side, scanty spotting. On palpation of the abdomen in the lower sections, the formation is determined, the upper border is 4 p / p above the womb, the lower pole goes into the small pelvis. On the mirrors: the neck is clean, the discharge is bloody. PV: the cervix is cylindrical, the cervical canal is passable for 1 p / p finger. The uterus turned into a tuberous tumor, the total value of 17-18 weeks. Appendages are not defined. Choose the correct diagnosis:
Answer: pregnancy and uterine fibroids, abortion that has begun
125.
A 42-year-old patient was admitted with complaints of cramping pains in the lower abdomen, heavy menstruation. On the mirrors: the cervix is shortened, in the cervical canal - the formation of a purple color. The bleeding is profuse. PV: the cervix is shortened, in the pharynx there is a formation 5x5 cm in size of a softish consistency. The uterus is enlarged up to 8-9 weeks of pregnancy, with a smooth surface. The area of appendages without features. Your diagnosis:
Answer: uterine fibroids, nascent submucosal node
126.
Patient V., 30 years old, was brought to the gynecological department with complaints of a rise in temperature up to 380C, pain in the lower abdomen, purulent-sanitary discharge from the genital tract, general weakness, malaise. I fell ill 2 days ago after a medical abortion in the period of 8-9 weeks. Objectively: the pulse is 96 beats. in 1 minute. BP 120/70 mm Hg, no peritoneal symptoms. On the mirrors: the cervix is clean, the discharge is purulent-sanitary. PV: the cervix is cylindrical, the external os is closed, the uterus is slightly larger than normal, painful on palpation, the appendages are not defined, their area is painless. Make a diagnosis:
Answer: metroendometritis
127.
Patient V., aged 25, was admitted with complaints of bloody discharge from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen, a rise in body temperature up to 38.5°C. She fell ill on the 2nd day after the introduction of the catheter into the uterine cavity in order to terminate the pregnancy in the period of 13-14 weeks. On the mirrors: the cervix is clean, the discharge is bloody, moderate, the cervical canal is passable for 2 p / n fingers, the uterus is enlarged up to 12-13 weeks of pregnancy, soft consistency, sensitive to palpation. The area of appendages on both sides without features. Choose the correct diagnosis:
Answer: uncomplicated infected abortion
128.
Patient R., 28 years old, was delivered by an ambulance doctor to a hospital with complaints of a rise in body temperature up to 400C, chills, vomiting, muscle pain, jaundice with a bronze tint, decreased diuresis, urine the color of meat slops, bloody-purulent discharge. She went to the doctor 7 days after the introduction of a solution of soap into the uterine cavity through the catheter in order to terminate the pregnancy in the period of 17-18 weeks. On the mirrors: necrotic plaque on the cervix, ichorous discharge. PV: the cervix is smoothed, the opening of the uterine os is 4 cm, the body of the uterus is not clearly contoured, enlarged up to 12-13 weeks, sharply painful, heterogeneous consistency. Hourly diuresis - 25 ml / hour. Laboratory data: Hb-52 g/l erythrocytes-2.4x1012/l, leukocytes-3.4x109/l, ESR-60 mm/hour, bilirubin-230 mmol/l. Your diagnosis:
Answer: anaerobic sepsis
129.
, 32 years old, was in a gynecological hospital due to exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the uterine appendages. Before discharge, the patient asked the gynecologist to advise on the method of contraception. The woman is married and has 2 children. Over the past 3 years, she was twice treated by a gynecologist for an exacerbation of the inflammatory process of the uterine appendages. Which method of contraception should be advised to the patient:
Answer: COOK
130.
, 26 years old after a medical abortion with subsequent transformation, no menstruation for 4 months. On the days of the expected menstruation, there are pains in the lower abdomen. PV: the uterus is enlarged up to 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, soft consistency. The area of appendages without features. Choose the correct diagnosis:
Answer: uterine form of amenorrhea, atresia of the cervical canal
131.
, 25 years old, turned to a gynecologist with complaints about the absence of menstruation, general weakness. A year ago she gave birth to a child, in the postpartum period there was massive bleeding, she received intensive treatment, blood transfusion was performed. After childbirth, she noted a meager amount of milk, soon, despite medical measures, lactation completely stopped. Objectively: the woman is underweight, mammary glands are flabby, hairiness in armpits and scanty on the forehead. The external genitalia are atrophic, depigmented. PV: the vagina is capacious, the cervix is shortened, the body of the uterus is smaller than normal, the area of the appendages is without features. Choose the correct diagnosis:
Answer: sheehan syndrome
132.
Patient G., 28 years old, complains of rare menstruation and lack of pregnancy. From the anamnesis: in childhood she suffered - measles, parotitis, frequent sore throats. Menarche from the age of 13, has not yet been established, occurs irregularly - after 30-45-65 days, duration 1-2 days, scanty, painless. Married for 4 years, regular sex life. The husband has been examined and is healthy. Objectively - 160 cm, body weight - 70 kg, there is hair growth on the chin, around the nipples, along the white line of the abdomen. The external genitalia are formed correctly. On the mirrors: the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix are clean. PV: the cervix is conical, the external os is closed. The body of the uterus is in the correct position, small. In the region of the appendages, dense formations 5.0x3.5x3.5 and 4.5x2.0x2.0 cm in size are determined on both sides. Make a diagnosis:
Answer: polycystic ovaries
133.
, 34 years old, complains of rapidly progressing hirsutism, cessation of menstruation. He considers himself ill for 6 months, when menstruation delays first began to be noted, facial hair growth appeared (beard, mustache). Last period 3 months ago. On examination: height - 152 cm, weight 57 kg. Marked hirsutism. The mammary glands are atrophic. There is no discharge from the nipples. PV: the cervix is cylindrical, the pharynx is closed. The uterus is not enlarged. The area of the left appendages without features. On the right, in the region of the appendages, a dense formation 5.5x4.5x5.0 cm in size is palpated. Make the correct diagnosis:
Answer: hormone-producing ovarian tumor
134.
, 25 years old, complains of bloating, pain in the mammary glands, swelling of the arms and legs. All symptoms begin a week before menstruation and disappear after they stop. The patient suffers from frequent colds. Gynecological examination revealed no pathology, mammary glands without pathology. Make a diagnosis:
Answer: premenstrual syndrome, edematous form
135.
, 48 years old, complains of hot flashes to the head up to 8-10 times a day, sweating. These symptoms are observed during last year. Menstruation in 2-3 months, scanty - 1-2 days. In history - operated on for calculous cholecystitis. Childbirth - 3, abortion -2. Gynecological examination revealed no pathology. Your diagnosis:
Answer: climacteric syndrome
136.
A 36-year-old patient consulted a gynecologist with complaints of hot flashes, sweating, frequent urination. Symptoms appeared after surgery for rapidly growing uterine fibroids and endometriosis in both ovaries. On examination somatic diseases not found. Mammary glands without pathology. On the mirrors: the vaginal mucosa is clean. PV: vaginal stump without pathology. There are no infiltrates in the small pelvis.
Answer: condition after hysterectomy. post-castration syndrome
137.
A 46-year-old patient was admitted with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urination, profuse bleeding during menstruation. For 3 years she has been registered for uterine fibroids. 3 months ago, curettage of the uterine cavity was performed. The result of histological examination is glandular cystic hyperplasia of the endometrium. On the mirrors: the cervix is hypertrophied, eroded. The discharge is bloody and profuse. PV: the cervix is hypertrophied, of normal consistency. The uterus is turned into a tumor up to 14-15 weeks, bumpy, immobile, painless. The area of appendages without pathology. Your diagnosis:
Answer: multiple symptomatic uterine fibroids large sizes, cervical erosion
138.
A 50-year-old patient was delivered to the gynecological department with complaints of pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, fever in the evenings, and a tendency to constipation. A year ago, she refused the proposed operation for an ovarian cyst. When viewed in the abdominal cavity, the presence of free fluid is determined. Vaginal examination: in the small pelvis, the formation of an uneven consistency is determined, motionless, 15x12x14 cm in size, painful, in the posterior fornix "spur". Diagnosis:
Answer: ovarian cyst
139.
Therapeutic effect combined oral contraceptives in hyperandrogenism is associated with:
Answer: inhibition of FSH and LH production by the pituitary gland
140.
What formula should be used to calculate the maternal mortality rate from obstetric bleeding:
Answer: (number of women who died from obstetric bleeding) / (number of live births) x 100,000.
141.
The morphological picture in atypical endometrial hyperplasia is most similar to:
Answer: with highly differentiated cancer
142.
What injury to the fetus can be caused by artificial rotation of the head with a fixed shoulder girdle:
Answer: injury spinal cord and/or spine
143.
Which of the following insertions of the fetal head is indicated for operative delivery:
Answer: posterior asynclitism
144.
You can talk about the onset of menopause after the last menstruation:
Answer: After 12 months
145.
A decrease in ovarian function in premenopause can be judged by such an early symptom as:
Answer: Changes in the length of the menstrual cycle
146.
What hormone is considered a marker of menopause
Answer: FSH
147.
What reserve of follicles remains in the ovaries during the initial manifestations of menopause:
Answer: 10 000
148.
Which sign contradicts hyperandrogenism:
Answer: High growth
149.
Under what diagnosis is pregnancy impossible under any circumstances:
Answer: testicular feminization syndrome
150.
The use of COCs for therapeutic and contraceptive purposes should be limited in patients with:
Answer: Hyperprolactinemia
151.
With isolated thelarche, as one of the forms of PPR in girls, best method therapy is:
Answer: No need for special drug therapy
152.
What formula should be used to calculate the Body Mass Index:
Answer: Weight (kg) / height (sq.m)
153.
What is meant by "insulin resistance"?
Answer: Insensitivity to own insulin
154.
high levels FSH in women is a consequence of:
Answer: Decreased ovarian function
155.
Among the following drugs, identify the insulin sensitizer:
Answer: Metformin
156.
Gestagens as part of combined HRT preparations are necessary for:
Answer: Endometrial protection
157.
What indicators of CTG should be paid attention to when diagnosing fetal hypoxia:
Answer: all of the above
158.
Volume surgical treatment with perforation of the uterus during an abortion depends mainly on:
Answer: on the nature of the damage
159.
The absence of estrogenic influence during puberty is characterized by:
Answer: amenorrhea / lack of breast growth
160.
Chronic endometritis is characterized by:
Answer: all of the above are correct
161.
In the treatment of chlamydial infection, antibiotics are effective, except for: A. doxycycline
Answer: ampicillin
162.
Which of the diseases does not correspond to the third stage of the spread of infection according to the Sazonov-Bartels classification:
Answer: metrotroendometritis
163.
Detection of antibodies to HIV is most likely:
Answer: in 6 months
164.
The therapeutic effect of COCs on elevated androgen levels is due to:
Answer: inhibition of FSH and LH production by the pituitary gland
165.
When HIV enters the body, it affects:
Answer: Lymphocytes
166.
Preventive treatment HIV-infected women should start:
Answer: from 28-32 weeks
167.
With hypofunction of the thyroid gland, laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis is:
Answer: increase in TSH
168.
When are we talking about "recurrent miscarriage"?
Answer: 2 or more spontaneous miscarriages
169.
The initial dose of magnesium sulfate in the treatment of eclampsia is:
Answer: 6 g intravenously for 15-20 minutes, then 2 g per hour during the day
170.
To replenish the BCC, control is necessary:
Answer: CVP
171.
The gold standard for diagnosing chlamydial infection is:
Answer: cultural method
172.
To clarify the discoordination of labor, all should be excluded, except:
Answer: weakness in labor
173.
For adrenal hyperandrogenism during a test with dexamethasone, the following change in the level of 17-ketosteroids in the daily amount of urine is characteristic:
Answer: reduction of 50% or more
174.
The readiness of the fetoplacental system for childbirth is
Answer: in increased fetal adrenal production of cortisol
175.
The action of the preventive vaccine against cervical cancer is based on:
Answer: development of immunity against types 16 and 18 of the human papillomavirus
176.
Pathogenetic drug in the treatment of herpetic infection is:
Answer: acyclovir
177.
The amplitude of instantaneous oscillations on CTG may indicate severe intrauterine suffering of the fetus when:
Answer: less than 5
178.
The severity of the menopausal syndrome can be objectively assessed by:
Answer: Kupperman index
179.
The pH of the vaginal environment in bacterial vaginosis in young women:
Answer: 5,0- 5,2
180.
How does the pH of the vaginal environment change in estrogen deficient conditions:
Answer: Decreases
181.
For ovulation you need:
Answer: LH Peak
182.
According to ultrasound, PCOS is characterized by an increase in ovarian volume more than:
Answer: 9 cc
183.
In modern conditions, PCOS therapy should begin with:
Answer: Weight loss and smoking cessation
184.
In PCOS, insulin resistance is a cardinal feature and is associated with:
Answer: Hyperandrogenism
185.
The "empty Turkish saddle" syndrome is most often accompanied by:
Answer: Hyperprolactinemia
186.
Patient T., aged 29, first applied to the antenatal clinic at a gestational age of 29-30 weeks. Complains of thirst, itching, increased urination. This pregnancy is the second, the first - ended in premature birth with a dead fetus at a period of 29-30 weeks 2 years ago. Objectively: height 159 cm, weight 71 kg, blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Art., coolant - 96 cm, VDM - 29 cm. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, the head is presented, above the entrance to the small pelvis. The fetal heartbeat is clear, rhythmic, 136 beats per minute.
Make a diagnosis:
a) Pregnancy 29-30 weeks. OAA
b) Pregnancy 29-30 weeks. Obesity. Large fruit. OAA
c) Pregnancy 29-30 weeks. Diabetes. Obesity. OAA
d) Pregnancy 29-30 weeks. Obesity. OAA
e) Pregnancy 29-30 weeks. OAA
Answer: in
187.
Pregnant N., 24 years old, went to the antenatal clinic at a gestational age of 6-7 weeks. This pregnancy - the 3rd, the first two - ended in spontaneous miscarriages at 12-13 and 15-16 weeks with curettage of the uterine cavity. From the anamnesis it was found out that in childhood she often had a sore throat, menarche from the age of 15, irregular periods, every 40-45 days, 3-4 days each. Last menses 2.5 months ago. Objectively: height - 168 cm, weight - 60 kg, hair growth on the upper lip, in the nipple area, along the white line of the abdomen.
Your diagnosis:
a) Pregnancy 6-7 weeks. Threatened spontaneous miscarriage
b) Pregnancy 6-7 weeks. Habitual miscarriage. Hirsutism.
c) Pregnancy 6-7 weeks. Abortion is on the way. OAA
d) Pregnancy 6-7 weeks. Threatened spontaneous miscarriage
e) Pregnancy 6-7 weeks. Started spontaneous miscarriage
Answer: b
188.
Primiparous A., aged 22, was admitted with a full-term pregnancy and regular labor activity for 4 hours. The dimensions of the pelvis are 25-28-31-21. The position of the fetus is longitudinal, the back is on the left, the head is present, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. Fetal heartbeat 136 beats per minute, clear, rhythmic. Contractions after 5-6 minutes to 40-45 seconds, good strength.
R.V. The cervix is smoothed, the opening of the uterine os is 4 cm, the fetal bladder is intact. The head is presented, pressed against the entrance to the small pelvis. Arrow-shaped seam in the left oblique size, small fontanel on the right front. The cape is not reachable.
Make a diagnosis and determine the type, position, presentation of the fetus:
a) Pregnancy at full term. Longitudinal position, I position, front view, cephalic presentation. Preliminary period
b) Pregnancy full-term. I stage of labor, I position, anterior view, cephalic presentation
c) full-term pregnancy. I period of childbirth. Weak labor activity
d) full-term pregnancy. Longitudinal position, I position, anterior view, cephalic presentation
e) Pregnancy at full term. Longitudinal position, I position, anterior view, cephalic presentation, harbingers of labor
Answer: b