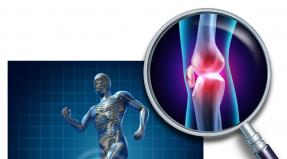
Lateral epicondylitis code according to ICB 10. Epicondylitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment. Best Natural Pharmacy Recipes
What is shoulder epicondylitis?
Video about epicondylitis of the elbow joint from the program "Health": The solution to the first problem in the treatment of epicondylitis is carried out by using traditional and surgical methods.
Construction workers (plasterers, painters, bricklayers);
Since the disease itself refers to chronic pathology, the treatment process will be long. First of all, it is required to create rest for the sore hand, to limit movements that cause acute pain. You can purchase special elbow pads or fix the joint with an eight-band bandage. At chronic course it is recommended to apply an elastic bandage during the day and remove it in the evening. You should not lift weights, otherwise all therapeutic measures will be useless.
Do not ignore the warm-up before the power load;
Types of shoulder epicondylitis
Treatment of the disease is carried out on an outpatient basis, for this you need to contact a traumatologist or orthopedist. The main objectives of therapy are:
Sudden movement that could result in injury.
When the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately contact an experienced specialist, and not try to treat the damaged forearm on your own. This is very important because epicondylitis has symptoms similar to those of other diseases. It can be easily confused with shoulder arthritis, arthritis and osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, and bursitis of the bursa supracondylar.
The prognosis is generally favorable, with the observance of the correct regime of work, physical activity and rest, you can achieve a stable remission.
Causes of shoulder epicondylitis
With mild pain in the shoulder, it is recommended to exclude the movements that cause them to appear, temporarily providing peace to the elbow joint (take sick leave at work or take a break from sports training). Doing certain sports; Epicondylitis of the shoulder
Treatment of lateral epicondylitis in the acute stage occurs by such a method as immobilization of the upper limb for a period of 7-8 days with the forearm bent at the joint (80 degrees), and the wrist joint - with small dorsal extension.
Athletes (kettlebell lifters, weightlifters, wrestlers, boxers) and others.
Great success can be achieved with the help of physiotherapy exercises, only all exercises must be performed for a long time - several weeks, or even months. Also used hirudotherapy, massage of the affected area, mud therapy.
It is better to conduct classes in the gym under the supervision of a trainer;
Pain relief:
The basis for the development of inflammation is small tears of the tendons and muscles at the site of their attachment to the epicondyle. These injuries lead to the appearance of a limited traumatic periostitis. Epicondylitis can be accompanied by calcifications and inflammation of the joint capsule (bursitis).
The disease can be diagnosed using dynamometry or thermography methods. X-ray studies are also used, but on early stages it is not always possible to identify signs of pathology. Finding foci of compaction in the epicondyle is possible only with a long-standing disease.
Symptoms of shoulder epicondylitis

After the end of the acute stage of the disease, it helps to restore the functionality of the joint physiotherapy, which aims to stretch and relax muscles and tendons. Exercises of exercise therapy include flexion and extension of the hand and elbow joint, pronation-supination of the forearm. At first, they are performed as passive movements, i.e. with the help of a healthy hand, then they move on to active movements carried out by the muscles of the developed hand.
In case of severe pain syndrome in the exacerbation phase, short-term immobilization of the joint is carried out using a plaster of Paris or a splint. You can also wear a special orthopedic orthosis, but it long-term use ineffective.
The presence of concomitant diseases.
- This is a degenerative-inflammatory tissue damage in the area of the shoulder joint: the epicondyles and the tendons attached to them.
By themselves, such activities do not cause epicondylitis. This disease occurs with constant monotonous flexion and extension of the elbow joint, when there is a load on the arm. Accordingly, the dominant hand suffers the most. In other words, the main version of the reasons for the development of epicondylitis is tendon overload, as well as some tissue microtrauma that provoke the development of inflammation processes.
Other methods of physiotherapy are also effective. Your doctor will advise you on how to treat elbow epicondylitis without surgery. Electrophoresis with acetylcholine, potassium iodide is prescribed. Often, the patient is relieved by phonophoresis with hydrocortisone.
Diagnostics
With regular sports, daily massage sessions are required;
Treatment of shoulder epicondylitis
Depending on the cause that caused the development of the disease, the following forms can be distinguished:
Treatment of shoulder epicondylitis involves the use of conservative and surgical methods.
Medical treatment includes:
Epicondylitis of the shoulder is often diagnosed in people whose main activity is associated with repetitive hand movements: in drivers of various Vehicle, from surgeons, masseurs, plasterers, painters, milkmaids, hairdressers, typists, musicians, etc.
The humerus bones have at their ends the so-called condyles - bony thickenings, on the surface of which there are other protrusions - epicondyles, which serve for the attachment of muscles.
Ultrasound has a good analgesic effect in the treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint, but it is even better to use phonophoresis (the so-called ultrasound with hydrocortisone).
Epicondylitis is of two types.
Epicondylitis
Take complex vitamins regularly;
When contacting a doctor immediately after an injury, cold must be applied to the damaged area;
Traumatic - occurs due to the presence of microtraumas of tendons and muscles in athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor. A factor that can provoke the development of traumatic epicondylitis is the presence of deforming arthrosis.
Epicondylitis of the shoulder is a disease resulting from overstrain and microdamage of the muscles that attach to the epicondyle of the humerus.
Use of NSAIDs for external use (ointments and gels): Diclofenac, Voltaren, Indomethacin, Nurofen;
Among athletes, tennis and golfers are most prone to this disease. No wonder lateral epicondylitis is also called "tennis elbow", and medial - "golfer's elbow".
The main cause of epicondylitis is chronic overstrain of the muscles of the forearm, in most cases - in the course of professional activity.
ayzdorov.ru
Symptoms and treatment of shoulder epicondylitis
 Bernard currents, ozokerite and paraffin applications are also widely used.
Bernard currents, ozokerite and paraffin applications are also widely used.
Lateral epicondylitis
- degenerative-dystrophic process in the places of muscle attachment to the epicondyle of the humerus.
Cure all chronic foci of infection.
Signs of the disease
Locally, the use of ointments and gels is prescribed, which include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; Post-traumatic - can occur after dislocations, sprains or other damage to the joint. The likelihood of developing post-traumatic epicondylitis increases significantly if the doctor's recommendations are not followed during the rehabilitation period after injury.
You can also fix the affected arm with an elastic neoprene bandage, which also performs a warming function and performs micromassage.
Epicondylitis is very frequent illness working hand. The general decrease in the load, which is observed due to high level production mechanization, and at the same time increasing specific gravity small movements carried out by the muscles of the forearms leads to the onset of the development of muscle overstrain.
Blockade with corticosteroid drugs (hydrocortisone or methylprednisolone), which are injected directly into the area of inflammation;
Among other diseases, epicondylitis is often accompanied by cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis, periarthritis of the shoulder scapula, osteoporosis.
Shoulder epicondylitis accounts for 21% occupational diseases hands.
Diagnostics and treatment
 In order to anesthetize the area and improve local trophism, blockades are carried out at the attachment point of the extensors of the fingers and hand with novocaine or lidocaine, which are very often combined with hydrocortisone.
In order to anesthetize the area and improve local trophism, blockades are carried out at the attachment point of the extensors of the fingers and hand with novocaine or lidocaine, which are very often combined with hydrocortisone.
Is a disease in which there is inflammation of the muscle attachment site to the lateral epicondyle of the bone. Often this disease is called "tennis elbow", as this problem is quite typical for those people who practice this sport. Nevertheless, lateral epicondylitis sometimes occurs not only in athletes. The cause of lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint is muscle overstrain at the site of their attachment to the epicondyle of the shoulder bone. Such overvoltage occurs when playing tennis, but it can also appear during other monotonous work (sawing wood, painting a wall, etc.). The disease usually appears between the ages of 30 and 50.
What is the difference between external and medial elbow epicondylitis? The prognosis of the disease is always favorable, it does not threaten the patient's life, and with the appointment of adequate treatment, remission can be achieved, which will last for a long time if the rules of prevention are followed.
With prolonged intractable pain, a blockade with glucocorticosteroids can be used;
The severity of symptoms and signs of epicondylitis depends on the stage of development of the inflammatory process and destructive changes in the joint. Experts point out:
After the acute pains disappear, the patient will need to switch to physiotherapy: diadynamic therapy and paraffin applications. Massage is contraindicated in this case, as it can exacerbate inflammation.
VashaSpina.ru
Epicondylitis of the knee: causes, symptoms, treatment
Epicondylitis can be external and internal. The first occurs many times more often.
B vitamins injections.
The reasons for the development of the disease

The peak incidence is in the 40-60 age range. External epicondylitis occurs 10 times more often than internal epicondylitis. Also, this type of epicondylitis affects mainly men, while medial epicondylitis is diagnosed mainly in women.
There are two main types of epicondylitis:
- Over the entire period of treatment for epicondylitis of the elbow joint, 4 blocks are performed (an interval of a couple of days). When the plaster splint is removed, use warming compresses with petroleum jelly, camphor alcohol, or ordinary vodka compresses.
- Medial epicondylitis
- Medical treatment for epicondylitis is aimed at relieving pain and inflammation. Ointments containing ibuprofen or diclofenac are recommended; nanoplasts are also used.
- The answer to the question: "How to treat epicondylitis of the elbow joint?" can be obtained from an orthopedic surgeon or surgeon. Pain localized to the elbow can also be a sign of arthritis, myositis, or arthrosis. Therefore, it is better to go for a consultation and determine what kind of pathology you have. Often, patients themselves postpone the treatment process until the process turns into chronic form when recovery is taking place with great effort.
- Restoration of blood supply to the affected area;
The acute stage of the disease, characterized by the presence of acute or burning pain, which has a different duration and duration, painful sensations intensified when moving in the joint and can radiate (spread) along the muscle fibers, while the focus of pain is clearly defined;
If conservative methods do not work, a surgical operation is indicated - fasciomyotomy.
- The most susceptible to the development of this disease are people who constantly rotate their forearm and at the same time often bend and unbend the elbow. These are workers in such professions as: blacksmith, bricklayer, ironer, painter-plasterer, locksmith, hand-milking milkmaid, cutter and so on. Among the patients there are also seamstresses, draftsmen, typists.
- A wide range of physiotherapy procedures can also be used:
Epicondylitis symptoms
Common symptoms of the disease:
- External (lateral), in which the tendons extending from the external epicondyle of the humerus are affected;
- To improve regional blood circulation in the affected area, UHF therapy, electrophoresis with acetylcholine, novocaine or potassium iodide is used.
- Known as golfer's elbow. However, this does not mean that only golfers can suffer from this ailment. Nevertheless, golf is common reason medial epicondylitis. In addition, other repetitive movements lead to epicondylitis. These include throws, sports, use different types hand tools, the consequences of trauma.

In a severe form of the disease, local injections of glucocorticoids in combination with anesthetics, for example, betamethasone or hydrocortisone, together with novocaine, are indicated. These injections are made at the most painful point in cases where other medical measures do not help.
Elbow epicondylitis is an inflammatory-degenerative disorder associated with inflammation of those muscles that attach to the epicondyles of the humerus and forearm bones. Distinguish between external, or lateral epicondylitis, and internal (medial) epicondylitis.
- Prevention of the development of muscle atrophy and restoration of the functional characteristics of the joint and the full range of motion in it:
- Painful sensations in the subacute stage appear during the load on the joint or shortly after it;
- Epicondylitis knee joint is called a degenerative inflammatory process that develops in the epicondyle, to which the muscles that provide the joint work are attached, and is characterized by the gradual destruction of these attachments. Late treatment leads to the development of inflammation in the structures and tissues surrounding the joints. The disease is more common in men over the age of 40.
How the doctor makes this diagnosis
Epicondylitis usually develops on the right limb, since most have it in a working limb.
Epicondylitis treatment
Shock wave therapy;
- Spontaneous pain in the elbow joint, intense and burning during exacerbations, dull and aching in the chronic course of the disease;
- Internal (medial), when the site of attachment of muscle tendons to the internal epicondyle of the humerus is affected.
- In addition, medications such as nikoshpan and aspirin are prescribed to treat medial epicondylitis of the elbow.
- In other words, any activity in which the muscles of the forearm are actively used can cause medial epicondylitis.
- If these methods are ineffective, shock wave therapy is used. This is a relatively new technique, when high power ultrasound is applied to the affected joint.
- External develops with inflammation of the muscles on the outside of the elbow, most often this pathology is present in professional tennis players.
- Massage;
- Chronic epicondylitis of the knee is characterized by an undulating course with periodic remissions and exacerbations.
- The prevalence of this disease has not been fully understood, since people suffering from epicondylitis often try to be treated with traditional medicine, contacting a doctor only if the condition worsens or there is no improvement. And even when contacting a traumatologist, the correct diagnosis is not always made, since the clinical manifestations of epicondylitis are similar to many joint diseases.
- The first symptoms of the disease are pain in the area of the epicondyle of the humerus, aching, pulling or stabbing. At the initial stage, pain can occur only directly during work. Over time, they become permanent, and with rotation and flexion / extension of the forearm, they become stronger. At the slightest touch of the epicondyle, the pain becomes so pronounced that patients have to limit the movements of the injured limb, wrap elbow joint bandages, thus trying to protect him.

Magnetotherapy;
Strengthening of pain syndrome during loading on the elbow joint and muscles of the forearm;
Prevention and prognosis
The muscles extending from the external epicondyle extend the elbow, hand and fingers, and are responsible for supination (outward rotation) of the hand and forearm. The tendons of the flexor muscles of the elbow, wrist and fingers are attached to the internal epicondyle. These muscles provide pronation of the forearm and hand.
- To change the trophism of tissues at the site of tendon attachment, blockade with bidistilled water is used. Although such blockages have a good effect, it should be said that the very process of drug administration is quite painful. In the case of a chronic course of the disease, injections of vitamins such as B1, B2, B12 are prescribed.
- Treatment of epicondylitis is complex, based on the duration of the disease, the level of dysfunction of the joint, as well as changes in the tendons and muscles in the area of the hand and forearm.
- It should be noted that epicondylitis is a rather insidious disease. Medical measures are able to stop pain in a short time, but when returning to previous physical activity, all symptoms can resume. It will take a long time for the affected areas to fully recover.
- Internal epicondylitis occurs with inflammation of the muscle tendons located on the medial side of the elbow joint.
- Gymnastics;
ArtrozamNet.ru
How to treat elbow epicondylitis
Then weakness appears in the hand, which makes it impossible for the patient to hold even light objects. He constantly drops tools, dishes and other things. If the hand is left alone and slightly bent at the elbow, then the pain stops.
What is epicondylitis?
Phonophoresis and electrophoresis;
- Gradual loss of muscle strength in the arm.
- The main cause of epicondylitis
To prevent and treat muscle atrophy and restore joint function, massage of the muscles of the forearm and shoulder, mud therapy, exercise therapy and dry air baths are used. In addition, special exercises for elbow epicondylitis help well.
Symptoms
The main objectives of the treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint can be formulated in a certain way:
Elbow epicondylitis is an inflammatory condition in the elbow area (where muscles attach to the forearm bone). The disease, depending on the place where the inflammation occurred, is external and internal. In this case, external epicondylitis of the elbow joint can develop during inflammation of the tendons that are located on the outside of the elbow joint.
What is the treatment for lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint?
Physiotherapy: phonophoresis, cryotherapy, shock wave therapy, diadynamic therapy, pulse magnetotherapy.
How is shoulder epicondylitis treated?
Since the main reason for the development of knee epicondylitis is professional sports, experts distinguish several types of development of the process, which are somewhat different from each other:
Experts consider professional sports to be the main reason for the development of knee joint lesions, in addition to this, the following factors can contribute to the development of the disease:
During examination of the patient's elbow joint, the doctor may find slight swelling at the site of the epicondyle, accompanied by pain at the moment of touching the elbow. The doctor can fully extend the patient's elbow joint slowly and smoothly. If the patient himself unbends the elbow, then severe pains will occur in the epicondyle. There is no discomfort when flexing.
Bernard's currents; With epicondylitis of the shoulder, joint pain appears only with independent active movements and muscle tension. Passive movements (extension and flexion), when the doctor himself performs them with the patient's hand, are painless. This is the difference between this disease and arthritis or arthrosis.
Shoulder joint
Surgical methods for the treatment of medial epicondylitis of the elbow joint are used with unsuccessful conservative treatment for 3-4 months.
Eliminate pain at the site of the lesion;
Internal epicondylitis is an inflammation of those muscles that provide extension and flexion of the hand (in other words, the inner part).
The main complaint that patients present is a sharp pain in the elbow joint. Pain sensations can spread up and down the outer or inner side of the arm, reaching the middle of the forearm.
tvoisustavi.ru
Elbow epicondylitis: treating inflammation
With the so-called "swimmer's knee" microtraumas develop during repulsion from the water, while the medially located ligament of the joint is constantly overstrained, which contributes to the development of the disease;
Stereotypical repetitive movements in the joint, which are performed by people engaged in some work or visiting the fitness room;
Causes of epicondylitis of the elbow joint
Rotational movements with a bent forearm are easy and painless for the patient, but when the arm is fully extended, they are difficult because of the severe pain that occurs.
- Paraffin applications;
- With lateral epicondylitis, the pain increases with wrist extension and supination (turning the forearm outward, palm up). With medial epicondylitis, the pain increases with flexion and pronation of the forearm (turning the hand palm down).
- Is the regular trauma of the tendons with light, but systematic stress. The constant continuous work of muscles and tendons causes ruptures of individual tendon fibers, in the place of which scar tissue is subsequently formed. This gradually leads to degenerative changes in the joint area, against which the inflammatory process begins to develop.
The so-called Hohmann operation is widely used. In 1926, he proposed excising some of the tendon at the extensors of the fingers and hand. Today, such an excision is not performed at the point of transition into the muscle, as was proposed in the original version, but near the area of attachment of the tendon to the bone itself.
Types of epicondylitis
To restore or improve regional blood circulation;
It should be noted that the development of external epicondylitis occurs most often. This disease is considered one of the most common in the area of the musculoskeletal system.As a rule, pain occurs when the forearm is extended and rotated outward. A characteristic feature of epicondylitis is the absence of pain during passive hand movements (without the participation of the patient's muscular apparatus). This allows you to distinguish epicondylitis from other diseases of the elbow joint - arthritis and arthrosis.
If epicondylitis cannot be cured by conservative methods, surgical intervention can be prescribed.with the "jumper's knee", the inflammatory process is localized in the patella, pain is felt at the place of attachment of the ligaments at the bottom of the patella; basketball and volleyball players are susceptible to the development of such a pathology;
Joint injuries - shock, sprain, fall, tearing of ligaments when trying to lift or move a heavy load;
Elbow epicondylitis treatment
Epicondylitis is characterized by symptoms of Thomsen and Welsh. In the first case, an attempt to hold the hand, clenched into a fist, in the dorsiflexion position in the epicondyle of the affected limb is accompanied by acute pain, while the hand immediately drops. Identification of Thomsen's symptom involves conducting a test simultaneously on two hands.
Cryotherapy, etc.
- The diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints and external examination. Radiography in epicondylitis is informative only in the case of a long chronic course, when structural changes become noticeable in the affected joint: a decrease in bone density (osteoporosis), pathological outgrowths (osteophytes).
- The risk factors that trigger the disease include:
- After such an operation, it takes some time to recover, carry out the appropriate procedures and perform special exercises for epicondylitis of the elbow joint.
- Restore full range of motion in the elbow joint;
This inflammation doesn't just happen because epicondylitis is a secondary condition. The exact causes of elbow epicondylitis are not known to doctors. Experts were able to find out which groups of people are most susceptible to this disease. These include:
The projection of pain does not fall on the joint itself, but on the lower portions of the ulna. Often the patient can point with his finger the most painful place. The process of shaking hands, lifting small weights, for example, a tea cup, causes great difficulties.
It is possible to prevent the development of epicondylitis by following some simple recommendations:
The most common (practically in one third of all professional athletes-runners) the development of "runner's knee" pain is the result of compression of the nerves that innervate the patella.
Chronic increased stress on the knees;
Welsh's symptom is the appearance of severe pain in the epicondyle zone with simultaneous extension of the forearms, which are in a bent position at the level of the chin.
Experts have different opinions about massage. Some of them believe that massage for epicondylitis is useless and even harmful.
MRI and biochemical analysis blood tests are carried out when it is necessary to differentiate epicondylitis from other diseases or injuries (fracture, tunnel syndrome or SGS).
The specifics of professional activity;
In the case of a chronic course of this disease with frequent exacerbations and unsuccessful treatment, patients must change the nature of their work.
Prevent forearm muscle atrophy.
Agricultural workers (milkmaids, tractor drivers, handymen);
Causes and symptoms of elbow epicondylitis
Follow the rules for performing physical exercises;
In order to prescribe adequate treatment, it is necessary to carefully collect data about the patient and carry out a qualified examination. In rare cases, an X-ray examination is additionally prescribed (in order to exclude the presence of a fracture) or MRI (to confirm the diagnosis if tunnel syndrome is suspected).
Inconsistent functioning of the muscles that ensure the work of the knee joint;
sustavy-svyazki.ru
Epicondylitis is treated on an outpatient basis by a traumatologist or orthopedist. The scheme and methods of treatment of epicondylitis are determined taking into account the severity functional disorders, the duration of the disease, as well as changes in the muscles and tendons. The main goals of treatment:
Elimination of pain syndrome.
Restoration of blood circulation in the affected area (to ensure favorable conditions for the restoration of damaged areas).
Restoration of full range of motion.
Restoration of strength of the muscles of the forearm, prevention of their atrophy.
If the pain syndrome in epicondylitis is not very pronounced, and the patient goes to the doctor mainly in order to find out the reason for the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the elbow joint, it will be enough to recommend the patient to observe a protective regime - that is, to carefully monitor their own feelings and exclude movements in which pain appears.
If a patient with epicondylitis plays sports or his work is associated with large physical activity on the muscles of the forearm, it is necessary to temporarily ensure the rest of the affected area. The patient is given a sick leave or is advised to temporarily stop exercising. After the pain disappears, the load can be resumed, starting with a minimum and gradually increasing. In addition, the patient is advised to find out and eliminate the cause of the overload: revise the sports regimen, use more convenient tools, change the technique for performing certain movements.
With severe pain in the acute stage of epicondylitis, short-term immobilization is required. A light plaster or plastic splint is applied on the elbow joint for a period of 7-10 days, fixing the bent elbow joint at an angle of 80 degrees and hanging the hand on a kerchief bandage. In the chronic course of epicondylitis, the patient is recommended to fix the elbow joint and forearm area with an elastic bandage in the daytime. The bandage must be removed at night.
If symptoms of epicondylitis appear after an injury, cold should be applied to the affected area (an ice pack wrapped in a towel) during the first days. In the acute period, patients suffering from epicondylitis are prescribed physiotherapy: ultrasound, phonophoresis (ultrasound with hydrocortisone), paraffin, ozokerite and Bernard's currents.
Pain syndrome with epicondylitis is due to inflammatory process v soft tissues, therefore, in this disease, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a certain effect. NSAIDs are used topically, in the form of ointments and gels, since inflammation in epicondylitis is local in nature. The appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs orally or intramuscularly in modern traumatology for epicondylitis is not practiced due to their insufficient effectiveness and an unjustified risk of development side effects.
With persistent pain that does not subside for 1-2 weeks, therapeutic blockade with glucocorticosteroids is performed: betamethasone, methylprednisolone or hydrocortisone. It should be borne in mind that when using methylprendizolone and hydrocortisone during the first day, there will be an increase in pain due to the tissue reaction to these drugs.
A glucocorticosteroid is mixed with an anesthetic (usually lidocaine) and injected into the area of maximum pain. With external epicondylitis, the choice of the injection site is not difficult, the blockade can be performed in the patient's position, both sitting and lying. In case of internal epicondylitis, to carry out the blockade, the patient is placed on a couch face down with arms extended along the body. This position provides access to the area of the internal epicondyle and, unlike the sitting position, excludes accidental damage to the ulnar nerve during the procedure.
At the end of the acute phase of epicondylitis, the patient is prescribed electrophoresis with potassium iodide, novocaine or acetylcholine, UHF and warming compresses on the affected area. In addition, starting from this moment, the patient with epicondylitis is shown therapeutic exercises - repeated short-term overextension of the hand. Such movements help to increase the elasticity of the connective tissue structures and reduce the likelihood of subsequent microtraumas. In the recovery period, massage and mud therapy are prescribed to restore range of motion and prevent muscle atrophy.
At conservative therapy without the use of glucocorticosteroids, the pain syndrome in epicondylitis is usually completely eliminated within 2-3 weeks, with blockades - within 1-3 days. In rare cases, persistent pain is observed that does not disappear even after injections of glucocorticosteroid drugs. The likelihood of such a course increases with chronic epicondylitis with frequent relapses, joint hypermobility syndrome and bilateral epicondylitis.
In the chronic course of epicondylitis with frequent exacerbations, patients are advised to stop playing sports or switch to another job, limiting the load on the muscles of the forearm. If the pain syndrome persists for 3-4 months, it is indicated surgery- excision of the affected areas of the tendon in the area of its attachment to the bone.
The operation is carried out in a planned manner under general anesthesia or conduction anesthesia. V postoperative period a splint is applied, the stitches are removed after 10 days. Subsequently, restorative therapy is prescribed, which includes physiotherapy exercises, massage and physiotherapy procedures.
Therapeutic tactics depend on the duration of the disease, the severity of clinical symptoms and the causes of tendon overload. With fresh epicondylitis with a mild pain syndrome, it is sometimes sufficient to prescribe a protective mode, in which certain movements of the limb are excluded. If epicondylitis occurs as a result of occupational overload, the patient is issued a sick leave. If sports are the reason for the development of the disease, it is recommended to temporarily stop training. After the pain disappears, the load is gradually increased.
To prevent relapse, it is necessary to establish what caused the muscle overload. Patients are advised to pay attention to the technique of performing stereotyped movements, use other tools, regularly pause during work, review the training regimen. Sometimes the above measures are enough to eliminate the symptoms of the disease and prevent relapses. With inefficiency this method, as well as with an intense pain syndrome and a protracted course of epicondylitis, more active treatment is needed.
The arm is provided with complete rest by applying a splint and hanging the limb on a kerchief. After pain relief, the plaster cast is removed, patients are advised to use NSAIDs local action... NSAIDs in tablets are usually not prescribed because the risk of side effects (irritation of the stomach wall) outweighs the potential of anti-inflammatory therapy. With persistent sharp pains, blockade of the affected area is carried out with solutions of glucocorticosteroids.
The best option for epicondylitis is blockade with betamethasone, since this drug does not cause an increase in pain immediately after blockade and does not provoke degenerative changes in tissues at the injection site. Betamethasone can be replaced with methylprednisolone or hydrocortisone, however, in this case, the patient must be warned that the pain will intensify on the first day after the blockade, and only then relief will come. The use of triamcinolone for epicondylitis is contraindicated, since this drug, when administered subcutaneously, can cause a violation of skin pigmentation and the formation of adhesions between the skin and underlying tissues (in this case, the surface of the condyle of the humerus).
The prognosis for epicondylitis of the elbow joint is favorable. Rest and the use of local NSAIDs can completely eliminate the pain syndrome in 2-3 weeks. With the introduction of glucocorticosteroid drugs, pain disappears within 2-3 days. In some cases, there is a persistent course with frequent exacerbations and low effectiveness of therapy. Usually the cause is congenital failure connective tissue... In such patients, joint hypermobility is revealed, and epicondylitis is often bilateral in nature. The best option in such cases is a constant gentle mode and an individual selection of tolerable loads (possibly with a change in specialty or refusal to go in for sports).
Epicondylitis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the elbow joint. It can be internal and external, depending on the pathology of the place of muscle attachment to the epicondyle of the shoulder bone.
Epicondylitis the elbow joint is characterized by regular pain syndromes of the forearm and elbow area in the absence of any noticeable functional abnormalities.
Only fourth part of all identified cases of the disease affect left limb, the rest are fixed on the elbow of the right hand. This unpleasant ailment, although it does not deprive a person of it labor activity, does not affect the quality of life in the best way.
With a belated appeal to medical care significant destruction of tendons and cartilaginous tissue occurs, and nearby parts of the body also become inflamed.
Causes of occurrence
Epicondylitis mainly affects people who, by virtue of their profession, regularly overload the shoulder girdle. Because of this, the tissues of the tendons and muscles receive microtrauma, the ligaments become inflamed, and functional cells are replaced by connective tissues. As a result, the tendon grows and, losing its previous elasticity, responds to normal loads in an inadequately painful way.
Factors leading to inflammation of the elbow joint:
- hereditary tendon dysplasia;
- repeated monotonous dynamic loads on the forearm and elbow joint, typical for musicians, tennis players, builders and other handicraft specialists;
- mechanical damage in the elbow area;
- arthrosis of the elbow joint;
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic and cervical spine;
- osteoporosis - fragility of bones due to leaching of calcium from bone tissue, as a result of certain diseases or age-related climacteric changes;
- violation of blood circulation in the articular tissues;
- extreme muscle strain.

Disease classification
Depending on the location and nature of the occurrence, epicondylitis is divided into:
- Lateral, or external epicondylitis of the elbow joint is manifested by an inflammatory process at the site of attachment to the external epicondyle. This type of disease is characteristic of activities associated with constant tension of the extensor muscles ("tennis elbow").
- Medial, or internal, epicondylitis of the elbow joint, as the name suggests, is characterized by inflammation of the attachment site of the tendons to the internal epicondyle with the inclusion of the ulnar nerve. This syndrome is caused by multiple repetitive strains of the flexor muscles of the wrist ("golfer's elbow").
- Epicondylitis, traumatic- the consequence of regular traumatic effects on the tendons of the same type of movement. Often this disease is accompanied by arthrosis and damage to the nerve of the elbow joint, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, which is typical for the age group of 40 years and older due to a decrease in the activity of tissue regeneration processes in the body.
- Post-traumatic develops in connection with incorrect or insufficient treatment measures during the rehabilitation period for dislocations, sprains and other mechanical damage to the joint area.

ICD-10 code epicondylitis of the elbow joint in the list of diseases musculoskeletal system, referred to as "other enthesopathies". M code 77.1 it is used in case of damage to the external epicondyle, and M 77.0- with the involvement of the medial tubercle.
Epicondylitis symptoms
V initial stage diseases for epicondylitis of the elbow characteristic symptoms there are occasional minor pains radiating to the hand, as well as a slight burning sensation in the forearm and elbow area. Over time, the painful sensations intensify, the gaps between them are reduced, until the pain merges into a continuous exhausting torture.
Despite significant difficulties in everyday life and professional activities, the radiograph does not show any anatomical changes in the internal structures of the elbow, as well as no edema and hyperemia of the skin in the painful area.
Due to increased pain during physical exertion of the limb, over time, a person reflexively reduces the activity of the affected arm, while flexion or extension of the elbow joint by external force does not lead to pain. Epicondylitis is also manifested by a feeling of tingling and numbness in the elbow zone.

- Lateral Epicondylitis is diagnosed by the simple shaking of the hand, which causes severe pain. Pain is localized on the upper surface of the elbow. The most intense pain occurs when the arm is extended independently. Palpation of the affected area, identified with the help of movement, gives only a slight pain response, and the nearby tissues do not react at all to palpation.
- Medial epicondylitis can be identified by pressing the internal epicondyle. In this case, there is severe pain, which is aggravated by turning the forearm inward. Pain syndrome persists with passive flexion of the arm and is localized on the inner side of the elbow bend. The imitation of the milkmaid's movements increases the pain several times.
Internal and external epicondylitis are usually chronic.

Forms of epicondylitis
Disorders in the elbow joint with epicondylitis are divided into three conditions:
- Acute form- severe persistent pain weaken the forearm. When the patient tries to clench his fingers into a fist on an outstretched arm, unbearable pain occurs.
- Subacute form precedes the acute stage. The latent period for the development of the disease is about 30 days, after which, during physical activity, the first pains appear and the muscles weaken.
- Chronic form develops in the complete absence or improper treatment of the acute phase of the disease. It is characterized by regular aching meteorological pains, which are especially aggravated at night and lead to constant muscle weakness.

Diagnostics
If you do not know which doctor to go to, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately contact your local therapist, and he will refer you to the right specialist. The main methods for establishing an accurate diagnosis in this case are:
- detailed patient survey;
- examination in the clinic.
The main distinguishing feature external epicondylitis- no pain during passive movement of the arm in the elbow joint. Painful sensations appear only during active tension of muscles and tendons.
X-ray in the diagnosis of epicondylitis is practically not used, due to its low rate. External epicondylitis is not accompanied by anatomical changes, only a deviation from the norm in bone density with concomitant diseases or bone fractures in the examined area is diagnosed.
The examination includes two main tests:
- Mobility test. With the patient's elbow stationary, the doctor begins to twist his hand to the side. When the patient, countering, tries to return the hand to its original position, pain occurs.
- Welt's test... The patient tries to simultaneously turn his arms outstretched in front of him up or down with his palms. In this case, the diseased hand will noticeably lag behind the healthy one.

If there is a suspicion of other complications, for example, a fracture, which is manifested by swelling of the soft tissues in the elbow area, additional examinations are carried out to identify hidden diseases:
- Arthrosis and arthritis also manifested by swelling of the elbow joint and pain during passive movement, are diagnosed using X-rays and blood tests for an inflammatory process. In addition, these diseases are indicated by pain in the joint itself, and not in the epicondyle.
- Neuritis, or nerve entrapment, is defined through a change in sensitivity in the affected area and a decrease in muscle strength.
- Joint hypermobility, caused by congenital degeneration of connective tissues, is confirmed by the presence of longitudinal or transverse flat feet, pathological mobility of bone joints, back pain and frequent sprains.
- Tunnel Syndrome, leading to prolonged pain with simultaneous numbness of the fingers, is established using magnetic resonance imaging.

Epicondylitis treatment
How to treat epicondylitis is decided by a specialist based on:
- the degree of dysfunction of the limb;
- the duration of the disease;
- anatomical changes in tendons and muscles.
The goals of therapy are:
- restoration of movement in the elbow joint in full;
- relief of pain in the affected area;
- restoration of healthy blood circulation in the elbow joint area;
- prevention of complete atrophy of the muscles of the forearm.
In this case, the symptoms and treatment are closely related:
- Weak pains initial stage diseases are relieved by temporary provision of complete rest of the affected limb. Then it is necessary to clarify at what moments of activity there are overloads that provoke the development of the disease and try to exclude these manipulations or change the technique of their implementation. After the relief of the pain syndrome, the implementation of new movements should be started, minimizing and gradually increasing the load to the working level. When this is not possible, it is necessary to change the field of activity.
- Acute stage suggests short-term (about a week), but rigid immobilization of the elbow joint using a plastic splint or plaster cast. After 7-10 days, you can remove the fixation and carry out various warming procedures, for example, compresses with camphor alcohol and other components.
- V chronic stage it is recommended to use an elastic bandage to fix the joint during the day, removing the bandage before going to bed. In case of frequent exacerbations, try to choose another type of activity where you will not have to expose your health to such tests.

Use of NSAIDs
- Depending on the stage of the disease and the severity of the changes, either local treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments is prescribed, such as Ketonal, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Nurofen, Nimesil Nise, or injection therapy.
- Injection blockade zones of inflammation are indicated for unrelenting unbearable pain. The affected area is injected with corticosteroids: metiprednisolone or hydrocortisone. The unpleasant moment of this procedure is the increase in pain on the first day after the injections.
- Also applies Glucocorticosteroid which is bred for pain relief Lidocaine or Novocain... Typically, the course of treatment includes 2-4 injections with an interval of 3 to 7 days.
- Blockades drugs type of glucocorticosteroids allows you to eliminate the pain syndrome within three days, while less radical drugs give a result only after 2-3 weeks of therapy.
- Based on the patient's condition, in addition, the doctor may prescribe Aspirin, Nikoshpan or Butadion... To improve the trophism of tissues, blockades with bidistilled water are used, which are quite painful, but very effective. Chronic pain is relieved by injections Milgamma.

Physiotherapy
For the treatment of epicondylitis, a full range of physiotherapy procedures are used.
The acute form is removed:
- course high-intensity magnetotherapy making up 5-8 sessions;
- taping;
- diadynamic therapy a course of 6-7 sessions;
- course laser infrared 5-8 minutes 10-15 procedures;
After stopping the acute stage, the following are prescribed:
- phonophoresis from a mixture of hydrocortisone and anesthetic;
- extracorporeal shock wave therapy;
- electrophoresis with novocaine, acetylcholine or potassium iodide;
- paraffin-ozokerite and naphtholone applications;
- Bernard currents;
- cryotherapy dry air.
After 20-30 days after novocaine blockade and joint immobilization, paraffin applications are applied.
Shock wave method provides for the exact direction of the acoustic wave to the joint area so as not to have a negative effect on the blood vessels, as well as on the median, ulnar and radial nerves.
Massage, dry and wet air baths, mud therapy and Exercise therapy prevent muscle atrophy and restore the function of the elbow joints. Acupuncture also has a good effect.
In some cases, when the chronic bilateral course of the disease with regular exacerbations and increasing muscle atrophy and compression of nerve endings is not corrected even by injections of glucocorticosteroid drugs, a more radical intervention is provided.
Surgical methods
If conservative treatment does not give positive results after 3-4 months - this is a sufficient basis for the appointment of surgery. Surgery involves removing calcifications and scar tissue and suturing the remaining tendon to the fascia.

Gohman's operation
This is a planned surgery with general anesthesia or local anesthesia.
In the recent past, the altered tendons were simply excised at the sites where they passed into the extensor muscles. Today, surgical intervention takes place directly in the area of attachment of the tendon to the bone.
The operation is performed through a small, about three centimeters, horseshoe-shaped incision over the external epicondyle. An incision is made in front of the opened epicondyle tendon fibers 1-2 centimeters in size. Only a small portion of the extensor attachments is cut, leaving the bone intact.
The corrected muscle traction ceases to provoke pain at the attachment site, and the nerve and blood channels are not damaged. At the end of the surgical procedures, superficial sutures and a plaster cast are applied. The stitches are removed after about half a month.

Exercise therapy for epicondylitis
Therapeutic gymnastics is not an independent sufficient therapy, but is prescribed in conjunction with complex treatment for more quick recovery joint functions.
A set of exercises aimed at stretching and relaxing the tendons and muscles should be discussed with your doctor. It is strictly forbidden to start exercise therapy in the acute period of the disease.
Gymnastics also requires compliance with some rules:
- compulsory performance of the complex 1 or 2 times every day;
- a gradual increase in loads and duration of classes;
- immediate termination of the exercise in the event of acute pain and resumption only after consultation with the attending physician.
Physiotherapy exercises are designed to improve blood flow, stimulate the secretion of synovial fluid and lymphatic flow, increase muscle tone and elasticity of the ligaments, which helps the elbow joint more easily withstand significant loads.
Epicondylitis is one of the few diseases for which not only active, but also passive movements in exercise are prescribed.
Exercises with passive elements
- Exercise 1. Relax your good arm completely by placing it on a flat surface just below your chest. Grab a hand lying on the table with the other hand and slowly pull it up, unbending it to 90 degrees. It is important not to force the movement, but to reach the desired position of the hand gradually, increasing the angle by a couple of degrees, every few days. At the extreme point, fix the brush for 10-15 seconds and also gently lower it back. Perform 2-3 approaches, 8-10 times.
- Exercise 2... It is performed similarly to the first, only the sore arm should lie, hanging the hand over the edge of the support, and it should be bent down to the wrist.
- Exercise 3. Standing in front of a table or any other suitable surface for this, put your palms on it and tilt the body so that a right angle is formed between the forearms and the plane on which the palms lie. You should not force the movement, but reach the desired angle gradually, adding a couple of degrees every few days. At the extreme point, linger for 10-15 seconds and also smoothly return to the starting position. Perform 2-3 sets of 8-10 times.
- Exercise 4. Similar to the third, but the hands lie on the surface with the back side (palms up) with the fingers facing you, the arms are slightly bent at the elbows. The desired angle is obtained by deflection in the opposite direction.
After achieving maximum comfort while performing the passive part of exercise therapy, you can add exercises to strengthen muscles and ligaments.
Active movement exercises
- Exercise 1. Bend and unbend the wrist alternately to the maximum possible angle without feeling discomfort.
- Exercise 2. In a standing position with arms hanging freely along the body, raise and lower the forearms, trying to keep the shoulders motionless.
- Exercise 3. With your arm bent at the elbow, squeeze and unclench your fist.
- Exercise 4. Weave the fingers into the lock in front of the chest, straighten and bend the elbows. The exercise can be performed with palms turned towards you and away from you.
- Exercise 5. Rotation back and forth with the shoulders, repeat the same circular motion with the forearms.
- Exercise 6. Stretch straight arms in front of you, make a "scissors" movement with palms turned to the bottom, and then to the top.
- Exercise 7. Fasten one end of the rubber band in any convenient place, make a loop at the other end and grab it with the hand of a sore hand. Stretch the tourniquet, bending the hand at the wrist, first with the palm to the surface, then vice versa.
- Exercise 8. Standing position with a gymnastic stick in an outstretched hand in front of you. Turn the stick, like a propeller, all the way to the left, then to the original vertical position and then all the way to the right. Linger in this position for 10-15 seconds. Perform 2-3 sets of 15-20 times.
After mastering the entire complex of the active part of exercise therapy, it is permissible to start strength exercises with a small load, for example, with an expander for the hand, avoiding excessive tension of the sore arm.
Epicondylitis - treatment with folk remedies

In addition to the injections prescribed by the doctor, ointments, antibacterial therapy and exercise therapy, treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint at home can be carried out using a variety of folk remedies:
- compresses
- rubbing
- trays
- tinctures
- massages and other things.
Together with a fixing elastic bandage, all of the above methods are aimed at restoring the normal functioning of the limb, eliminating pain and restoring the person's ability to work and lead a comfortable lifestyle.
Best Natural Pharmacy Recipes
It is impossible in one article to describe all the methods of treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint folk remedies... Their list would take at least a page. Therefore, here are the best practices.
Rubbing
These ointments can be combined with massage:
- Propolis ointment... A small amount of propolis and linseed oil mix in a steam bath, cool and rub thoroughly into the skin of the elbow joint overnight. Secure with foil and insulate with woolen cloth. Remove in the morning, repeat until cured.
- Honey rub... If you are not allergic to honey, apply a little honey to the area of pain, massage it gently for 10-15 minutes, wrap it with foil and woolen cloth.
Compresses
- Laurel oil compress warms and relieves pain. It can be rubbed into the forearm or applied as a compress for up to half an hour. If it is not possible to buy ready-made laurel oil, it is easy to prepare it at home by mixing 150 g of vegetable oil with four tablespoons of chopped bay leaves and infusing for 7-14 days.
- Blue clay compress... Diluted with warm water to the consistency of an ointment, apply it in a thick layer on the fabric and wrap the painful area, insulating it on top in any way possible. Healing effect from the compress is achieved when applied for 60 minutes, 3 times a day, for 1-2 weeks.
- If we are talking about lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint, then treatment with folk remedies offers an effective compress of black radish, honey and vinegar... Grate the radish, add one teaspoon of honey and 3-5 drops of vinegar essence to 100 g of the mass. The skin must first be lubricated with oil so as not to burn, and apply a compress for 1-2 hours. In case of severe burning, remove the bandage, rinse the skin and lubricate with a remedy for burns.
Baths
Since the baths have a steaming effect, their use should be discussed with your doctor.
- Saline... Dissolve 3 tablespoons of salt in 1 liter of warm water, lower the elbow into the solution for half an hour before bedtime. After that, you can simply insulate the elbow joint or leave the saline solution on the arm in the form of a night compress.
- From oat straw... Boil the straw over low heat for about ten minutes, cool to a safe temperature and keep the elbow in a warm broth.
- Coniferous baths... They relieve inflammation well. Boil the needles and cones for 10-15 minutes over low heat, leave for 2-3 hours, wrapped in a towel, warm up and keep the elbow in a warm broth.
Disease prevention

In order to prevent the development of epicondylitis of the elbow joint, it is necessary to comply with certain conditions in professional activities and everyday activities:
- Athletes should carefully select the appropriate sports equipment, be sure to use special elastic elbow pads, and do a full-fledged high-quality warm-up before each workout.
- If there is a danger of acquiring this disease as a result of any activity, daily preventive massage of the forearms with the inclusion of the elbow joint is necessary.
- Correctly measure the load on the elbow and forearm, do not lift the load with one hand, if it can be done with two, etc .; to introduce rest breaks and industrial gymnastics into the work schedule.
- Timely identify and treat all types of osteochondrosis, especially cervical.
- Follow the rules healthy eating strengthening the body with vitamins and collagens, which have a positive effect on tissue elasticity. If it is not possible to diversify the daily diet, use it periodically in courses edible gelatin, at the rate of 10 gr. per day for 2-3 weeks in a row.
- Exclude from the diet foods that interfere with the absorption of calcium and its incorporation into tendons and bone tissues.
- Personal Area
- neurotechno.ru
- home
- What is this site?
- What is neurotechnology?
- Site news
- Glossary of terms
- Command
- Contacts and communication
- All articles
Neurotechno.ru
Elbow epicondylitis: symptoms and treatment
Epicondylitis of the elbow joint is a very common disease among athletes and representatives of some other professions. The disease is accompanied by inflammatory and degenerative tissue changes in the elbow joint. If untreated, pathology can lead to very dangerous and serious complications.
Many people are interested in any additional information about the disease. Why does epicondylitis of the elbow joint develop? Symptoms and treatment, causes and possible complications, preventive measures are very useful information not to be ignored.
Brief information about the disease
Many people are faced with a problem such as epicondylitis of the elbow joint. ICD-10 classifies this disease into the "Other enthesopathies" group (code M77).
This is a very common disease of the musculoskeletal system, which is accompanied by damage to the tendons, periosteum, epicondyle and its vagina. The main reason for the development of the disease is chronic overstrain of the muscles of the forearm.
According to statistics, in most cases, the disease is diagnosed in patients aged 40 to 60 years. On the other hand, if we are talking about professional athletes, then degenerative processes can begin much earlier.
The main reasons for the development of the disease

As already mentioned, the inflammatory process is preceded by degenerative changes in the elbow joint. The reasons for the development of epicondylitis can be different.
- Such a disease often develops as a result of the peculiarities of the profession, especially if the work is associated with the same type of movements, chronic overload of the joint, and regular microtraumas. The risk group includes builders (plasterers, bricklayers, painters), agricultural workers (milkmaids, tractor drivers), athletes (golfers, weightlifters, tennis players, boxers), musicians, doctors (surgeons), etc.
- Causes include direct injury to the elbow.
- Inflammation can develop against the background of local circulatory disorders and, accordingly, tissue trophism.
- Such a pathology is often associated with some other diseases, in particular, cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, periarthritis of the shoulder scapula.
- The list of reasons includes congenital weakness of the ligamentous apparatus.
Elbow epicondylitis: symptoms and signs

Of course clinical picture largely depends on the form of the disease and the stage of its development. However, there are several common symptoms of elbow epicondylitis.
- The ailment is accompanied by intense pain in the elbow area. Unpleasant sensations arise spontaneously, for no apparent reason. The pain during the attack is very strong, burning. Gradually, it takes on an aching character, but it becomes constant.
- The pain syndrome intensifies during physical exertion, prolonged tension of the muscles of the forearm.
- As the disease progresses, the muscles lose strength. Even the usual daily movements cause severe and rapid fatigue.
- In the initial stages, soreness disappears at rest. But as the disease develops, unpleasant sensations are present almost constantly.
External epicondylitis
Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint is a common form of the disease, in which tissues in the area of attachment of muscle tendons to the lateral epicondyle become inflamed.
Painful attacks in this case appear against the background of overstrain of the extensor muscles, which are located on the outside of the forearm. This form of the disease is called "tennis elbow", since it is people who are actively involved in this sport who suffer from pain in the elbow. Soreness can appear when the hand is turned up, as well as during a handshake.
Internal (medial) epicondylitis
Medial epicondylitis of the elbow joint is accompanied by tissue damage in the place where the muscle tendons are attached to the medial epicondyle. By the way, this form of the disease also has a special name - "golfer's elbow". Monotonous movements, which are performed due to the tension of the flexor muscles of the wrist, lead to the development of the disease.
Of course, golfers are not the only victims of this disease. Tailors and machinists often face this problem. Sports such as throwing the nucleus or throwing are also predisposing to the development of the disease.
Typically, an attack of pain is associated with pressure on the epicondyle. The unpleasant sensations intensify during flexion of the forearm. The disease often becomes chronic. The ulnar nerve is often involved in the pathological process.
Other forms of the disease
You already know how and why medial and lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint develops (treatment will be described below). But there are other forms of the disease.
- They talk about traumatic epicondylitis if the disease develops as a result of constant microtraumas. This is observed, for example, with the constant performance of monotonous movements. In most cases, patients over 40 years old face a similar problem. In addition, the disease is often associated with cervical osteochondrosis, ulnar nerve damage, deforming arthrosis.
- The post-traumatic form of the disease develops in patients who have previously suffered a dislocation or sprain of the joint. In most cases, the disease is associated with non-compliance with the rules of rehabilitation.
- Chronic epicondylitis of the elbow joint, as a rule, is the result of improper treatment of an acute form of the disease or no therapy at all. In this case, episodes of exacerbations are replaced by relatively long periods of relative well-being.
Diagnostic procedures

Diagnosis in this case is rarely difficult. Anamnesis and general examination are sufficient to suspect the presence of epicondylitis in a patient. For example, during the consultation, you may notice that pain occurs only against the background of muscle tension - if the doctor moves the patient's arm, bending it at the elbow, then there are no unpleasant sensations.
Of course, in the future, some additional procedures are carried out. For example, a blood test can help detect inflammation. An x-ray is taken in order to confirm the presence / absence of a fracture, foci of osteoporosis. If there is a suspicion of the presence of tunnel syndrome, then the patient may be sent for magnetic resonance imaging.
Drug therapy
The treatment regimen directly depends on the stage of development of the disease and the intensity of the symptoms. If the pain is not too severe, then patients are recommended rest and bed rest. In the event that the pain syndrome is severe, the arm is temporarily immobilized with a plaster cast.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are available in the form of tablets and ointments (they are used to treat skin tissues in the elbow joint), help to cope with pain. Means such as "Nimesil", "Nurofen", "Ketonal", "Diclofenac", "Ibuprofen", "Nise" are considered effective.
With severe symptoms, a blockade with the use of corticosteroids is performed. Methyprednisolone, hydrocortisone is considered effective (they are mixed with anesthetics and injected only later). Such drugs help to quickly relieve pain and improve the patient's condition. Sometimes drugs are introduced into the therapy regimen that improve tissue trophism and normalize blood circulation.
Physiotherapy for lesions of the elbow joint
This disease requires an integrated approach. In addition to drugs, various physiotherapy procedures are used. For example, during an exacerbation, high-intensity magnetotherapy is effective (the course of treatment consists of 5–8 sessions). Infrared laser radiation is also effective (the full course of treatment includes 10-15 procedures).
After the inflammatory process has subsided, other techniques are used. During rehabilitation, shock wave therapy, electrophoresis (using potassium iodide, acetylcholine, novocaine), phonophoresis (anesthetics and hydrocortisone are used during the procedure). Cryotherapy using dry air is indicated for patients. Good results can be achieved with regular naphtholone and paraffin-ozokerite applications.
Epicondylitis of the elbow joint: treatment with folk remedies

Drug therapy lasts several weeks, followed by a long period of rehabilitation. Patients are constantly engaged with a physiotherapist - exercise therapy is extremely important, as it helps to prevent muscle wasting.
What else can be done with a disease such as epicondylitis of the elbow joint? Folk remedies, of course, exist, but they can be used only with the permission of a doctor.
- Compresses from horse sorrel are considered effective. A liter jar is filled with fresh plant leaves, poured with a bottle of vodka, closed and insisted in a dark place for ten days. In the resulting liquid, a cloth or gauze bandage is moistened, which is then applied to the skin over the affected joint. The compress is fixed and left overnight.
- There are other recipes that are used for epicondylitis of the elbow joint. Treatment with folk remedies includes the use of laurel oil. You can buy it at the pharmacy or you can prepare it yourself. Four tablespoons of chopped bay leaves are poured into a glass of sunflower (or olive) oil. The mixture is infused in a dark place for a week. The resulting oil tincture is rubbed into the skin in the elbow area daily.
- Blue clay wraps are considered effective. Clay powder is poured with hot water and mixed so that a homogeneous mass is obtained. The warm mixture is spread on cheesecloth, which is then wrapped around the affected elbow. From above, the compress is covered with cling film and a woolen shawl or towel. The clay is kept on the skin until the mixture has completely cooled. Since the procedure involves the use of heat, it should not be performed in case of acute inflammation.
When is surgery needed?

In the event that conservative therapy does not work and the pain persists for 3-4 months, the doctor may decide to perform a surgical intervention.
The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia. The epicondyle is exposed by making a small incision. In front of it, the doctor makes a small incision in the tendon fibers. At the same time, the integrity of the bone, extensor attachments is not violated. Also, the procedure is not associated with damage to nerve fibers and blood vessels... After the operation, the patient is stitched, and the arm is fixed with a plaster cast. The stitches are removed after two weeks. This is followed by a period of rehabilitation.
Patient predictions
The prognosis for patients with epicondylitis of the elbow joint is in most cases favorable, especially if the disease was diagnosed on time. On the other hand, if untreated, degenerative processes can spread to the tissues of the joint itself. Complications include bursitis, which is much more difficult to treat and often requires surgical intervention.
Preventive actions

Elbow epicondylitis is a very unpleasant disease that requires immediate treatment. But even after successful therapy, patients need to take some precautions in order to avoid complications and relapses. Preventive measures come down to a simple list of rules.
- If you are involved in sports, it is important to follow the correct technique for performing all exercises.
- Before any kind of physical activity, you need to do a warm-up in order to warm up the muscles and other structures.
- If intense physical activity is coming, then you need to use special pads on the elbow or fix the joint with an elastic bandage.
- If the work is associated with constant monotonous movements, then it is important to take periodic breaks.
- Doctors recommend taking vitamin complexes periodically (1-2 times a year, as a prophylaxis).
- All inflammatory diseases should respond to appropriate therapy in time.
Of course, when the first signs appear, you should not hesitate - immediately contact a specialist.
fb.ru
Epicondylitis is a pathology that affects only the area of the elbow joint and leads to a violation of its functions. The main reason for the formation of such a disease is physical overstrain in conjunction with the addition of an inflammatory process. However, clinicians identify several more rare predisposing factors.
The first and main symptom of the disease is intense pain, against the background of which other clinical manifestations are formed.
Establishing the correct diagnosis requires an integrated approach, and treatment is most often carried out in conservative ways.
V international classification diseases ailment can be found under several codes that differ in the form of the disease. Thus, the ICD-10 code is M77.0 and M77.1.
Etiology
The fundamental factor in the formation of pathology is overstrain of the elbow joint of a physical nature, however, degenerative changes precede inflammation.
This type of ailment can be provoked by:
- difficult working conditions, in which a person is forced to constantly strain the muscles of the shoulder and forearm;
- persistent microtrauma in this area;
- chronic sports overload;
- violation of local blood circulation;
- direct injuries to the shoulder or elbow;
- osteochondrosis;
- humerus periarthritis or osteoporosis.
Such a disease is very common in individuals whose field of activity is directly related to the same type of hand movements, in particular, with the turn of the forearm inward and palm down or turn the elbow outward, and the palm is directed upward.
It follows from this that the main risk group is:
- agricultural workers;
- builders and doctors;
- athletes, namely boxers, tennis players, weightlifters, golfers, as well as people involved in kettlebell lifting and weightlifting;
- musicians and service workers such as hairdressers.
It should be borne in mind that the above working conditions themselves are not a factor in the formation of elbow epicondylitis. The disease develops against the background of the strongest overload of the muscles of the forearm, provided that microtrauma of the tissues of the joint appears. As a result, inflammation begins to form, small scars - they even more affect the decrease in the resistance of the tendons to physical exertion.
Less often, the disease develops against the background of:
- weakness of the ligamentous apparatus of the elbow joint - but subject to its congenital form;
- one-time strongest muscular excessive tension.
Classification

Lateral and medial epicondylitis
It is customary for clinicians to distinguish several forms of the course of the disease:
- external or lateral epicondylitis of the elbow joint - is formed much more often of the opposite type of pathology. It is characterized by slower progression and severe course. Often observed in males and leads to damage to the short radial extensor of the hand;
- internal or medial epicondylitis of the elbow joint is the rarest type of disease that is often diagnosed in women. In this case, the lesion of the radial flexor of the hand occurs.
In addition, there are three stages of the disease:
- subacute - characterized by the appearance of minor pain and muscle weakness;
- acute - differs in the expression of a strong pain syndrome;
- chronic - the main clinical sign has an aching but constant manifestation. This nature of the course of the disease is said when the alternation of symptoms of exacerbation and remission is observed for more than three months.
Symptoms
External epicondylitis is expressed following signs:
- localization of pain is on the outer surface of the elbow joint. Increased pain occurs during extension or rotation of the hand;
- muscle weakness of the affected upper limb;
- the appearance of soreness when trying to take a full cup from the table;
- discomfort arising in cases of pressure on the lateral condyle.
Internal epicondylitis is determined by the following symptoms:
- the focus of pain is located on the inside of the elbow joint;
- muscle weakness on the affected side during grasping;
- increased pain while holding the affected arm at a right angle, as well as when bending the forearm;
- the presence of seals during palpation in the area of the medial epicondyle.
In addition, quite rarely with such a disease, the presence of such clinical manifestations is noted:
- spasm of capillaries;
- the acquisition of a red tint by the skin in the affected area;
- an increase in temperature in the area from the elbow to the forearm.
Diagnostics
When one or more of the above signs appear, you need to seek advice from such specialists as a traumatologist or orthopedist, they are the ones who know how to treat epicondylitis of the elbow joint.
A distinctive feature of the disease from other pathologies is that with such a disease, the basis of diagnosis is played by an initial examination, consisting of:
- clarification of patient complaints;
- studying the anamnesis of the disease and the patient's life;
- objective examination of the patient, which is based on conducting several specific tests, for example, for Thomson's and Welt's symptoms, but only if the patient himself performs physical exercises... If the clinician makes movements with the affected limb, then soreness and other symptoms of epicondylitis of the elbow joint will not be expressed.
It is worth noting that Thomson's test is for the patient to clench his hand into a fist, while it should be in the back position. It will unfold quickly enough so that the palm is pointing up.
To identify the Velta symptom, the patient needs to keep both forearms at the level of the chin, as well as bend and extend at the same time. Such actions performed by the affected hand will noticeably lag behind similar processes performed by the healthy one.
Laboratory examinations are meaningful only if the doctor suspects the presence of acute inflammation in the body.
As for instrumental examinations of the patient, then for differential diagnosis CT, MRI or X-ray are used.

MRI of the elbow
Treatment
Therapy consists in the appointment conservative methods therapy and is carried out on an outpatient basis. Therapy includes:
- splint overlay;
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy procedures;
- gymnastic exercises - are compiled by the attending physician individually for each patient, depending on the form of the course of such a disorder;
- the use of alternative medicine recipes.
Treatment of epicondylitis with drugs involves the use of:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - it is worth noting that doctors often prescribe ointments, and not substances in the form of tablets;
- glucocorticosteroids - used as an intramuscular injection into the affected area. If ineffective, it is possible re-introduction medicinal product, but only after a few days;
- anesthetics - to neutralize pain.
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, it is worth highlighting:
- magnetotherapy;
- the influence of infrared radiation;
- medicinal applications;
- phonophoresis;
- drug electrophoresis.
Also in the treatment of the disease are widely used:
- hirudotherapy;
- mud therapy;
- massage;
- acupuncture.
In addition, the elimination of the disease at home involves the preparation of potions from medicinal herbs and plants used as compresses and for rubbing. The most effective natural substances for the treatment of epicondylitis of the elbow joint by folk remedies are:
- horse sorrel;
- Bay leaf;
- nettle;
- olive oil;
- green tea;
- blue clay;
- beeswax;
- Salo;
- garlic juice;
- wine alcohol;
- birch leaves;
- chamomile and black elderberry.
In those situations where conservative treatment of epicondylitis was unsuccessful, the patient needs surgery. This method of therapy is extremely rare, since there is a high likelihood of a relapse of the disease, increased pain and formation adhesive processes... Nevertheless surgical treatment provides for:
- myofasciotomy;
- tenotomy;
- neurotomy;
- lengthening or excision of the radial extensor or wrist flexor tendons.
Prevention and prognosis
Preventive measures for a similar disease of the elbow joint are based on the following rules:
- exclusion of exercises of the same type that overload the joint;
- wearing a retainer - but only with an exacerbation of the disease;
- regular admission vitamin complexes;
- timely elimination of any inflammatory processes.
Subject to an early complex therapy and in cases of adherence to preventive recommendations, a favorable prognosis can be achieved, namely, stable remission.
If you think that you have Epicondylitis and symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: an orthopedic traumatologist, an orthopedist.
We also suggest using our online disease diagnostics service, which, based on the entered symptoms, selects probable diseases.
Diseases with similar symptoms:
Synovitis is an inflammatory process localized on the inner shell of the joint capsule. The danger of the disease lies in the fact that it often proceeds almost painlessly. Because of this, people postpone a visit to the doctor and do not start a full-fledged treatment of synovitis on time.
...Tendinitis is an acute inflammatory lesion of a tendon or muscle structure. The pathological process can affect any tendon or muscle. But most often the disease is diagnosed in the area of large joints. According to statistics, men are more susceptible to illness. Most often, the ailment is the result of regular excessive physical activity or sports injury. There are no age restrictions. Tendinitis can trigger other, more complex ailments.
...Streptococcal infection- a group of diseases that causes pathological processes in the area respiratory tract and skin. This type of infection is present in the body healthy person... The development of the disease is possible only if there is a favorable environment for this. Children and pregnant women are most susceptible to the disease.
...Phlegmon is an ailment characterized by the formation of diffuse inflammation of a purulent nature. It mainly affects the fiber. Pathology has one, characteristic only of it, feature - the process of inflammation has no clearly defined boundaries. It can easily and quickly spread through soft tissues, posing a threat not only to health, but also to the patient's life.
...Carbuncle is an inflammatory disease that affects hair follicles, sebaceous glands as well as skin and subcutaneous tissue. As a rule, the inflammatory process can spread to the deep layers of the dermis. Most often, purulent formations are localized in the neck, but their appearance on the buttocks or shoulder blades is also possible.
...simptomer.ru
causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Epicondylitis is a degenerative-dystrophic process in the area of attachment of the tendons of the muscles of the forearm to the epicondyle of the humerus and the tissues surrounding these tendons. Depending on the localization, it manifests itself as local pain along the outer or inner surface of the elbow joint. It develops as a result of chronic overload of the muscles of the forearm. The diagnosis of epicondylitis is made on the basis of characteristic clinical findings. Treatment is conservative, the prognosis is favorable.
Epicondylitis of the elbow joint is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system. At the same time, it is not possible to accurately assess the incidence of morbidity, since a large number of patients do not go to doctors due to mild symptoms. The disease usually develops at the age of 40-60, while right-handers are more often affected by the right, and in left-handers - left hand.
The reasons for the development of epicondylitis
External (lateral) epicondylitis is called tennis elbow because this disease is often seen in tennis players. However, much more often the disease develops in connection with professional activities... Epicondylitis is caused by stereotypical, constantly repetitive movements - extension of the forearm and its rotation outward. External epicondylitis often affects massage therapists, construction workers (painters, carpenters, bricklayers), tractor drivers, milkmaids, and laborers. The disease develops more often in men.
Internal (medial) epicondylitis, which is also called the golfer's elbow, occurs with repetitive movements of low intensity and develops mainly in people doing light physical labor - seamstresses, typists, etc. The disease is more common in women.
The cause of epicondylitis in both cases is chronic overload. As a result of repeated microtraumas in the tendon tissue, a degenerative process develops, accompanied by inflammation of the surrounding tissues. Small scars are formed, which further weaken the resistance of the tendon to stress, which, in turn, contributes to an increase in the number of microdamages.
In some cases, symptoms of epicondylitis occur after direct trauma. Congenital weakness of the ligamentous apparatus increases the risk of developing this disease and causes it more heavy course.
Epicondylitis symptoms
With lateral epicondylitis, there is clearly localized pain along outer surface the elbow joint, which occurs when the hand is extended and rotated outward. In the study of muscle strength, the weakening of the muscles on the diseased side is determined when the hand is rotated outward and the resistance to grasping. Coffee cup text (pain when trying to lift a liquid-filled cup off the table) is usually positive. When pressing on the lateral condyle, obvious, but not acute pain is determined.
With medial epicondylitis, pain is localized along the inner surface of the elbow joint. In the study of muscle strength, a weakening of the muscles on the sore side during grasping is noted. There is an increase in pain with pronation at a right angle and flexion of the forearm with resistance. On palpation, pain and induration in the lower part of the medial epicondyle is determined. Milking test (increased pain when simulating milking) is positive.
Diagnostics and differential diagnosis of epicondylitis
The diagnosis of epicondylitis is made on the basis of the patient's complaints and external examination data. Additional research is usually not required. Differential diagnosis of epicondylitis is carried out with diseases of the elbow joint itself (aseptic necrosis of the articular surfaces, arthritis) and tunnel syndromes: (cubital canal syndrome - infringement of the ulnar nerve and pronator round syndrome - infringement of the median nerve). Diagnosis is usually straightforward.
With arthritis, pain occurs in the area of the elbow joint itself, and not in the area of the epicondyle, while it is more "blurred" rather than localized in a well-defined area. Flexion contracture of the elbow joint may develop. When nerves are pinched, neuritis is observed and neurological symptoms characteristic of it - there are violations of sensitivity in the zone of innervation and a decrease in the strength of the innervated muscles.
If epicondylitis develops in young people, joint hypermobility syndrome (HMS), due to congenital connective tissue weakness, should be ruled out. To do this, the doctor examines the life history, paying attention to the frequency of sprains, tendinitis, acute and chronic arthralgias and back pain. In addition, the presence of HMS may be indicated by longitudinal and transverse flat feet, as well as an increase in joint mobility.
Additional methods studies to diagnose epicondylitis are not usually used. In some cases, radiography is performed to exclude traumatic injury (epicondyle fracture). If it is difficult to differentiate between epicondylitis and tunnel syndrome, MRI can be prescribed. If inflammatory joint disease is suspected, a blood test is performed to rule out signs of acute inflammation.
Epicondylitis treatment
Epicondylitis is treated on an outpatient basis by a traumatologist or orthopedist. The scheme and methods of epicondylitis therapy are determined taking into account the severity of functional disorders, the duration of the disease, as well as changes in the muscles and tendons. The main goals of treatment:
- Elimination of pain syndrome.
- Restoration of blood circulation in the affected area (to ensure favorable conditions for the restoration of damaged areas).
- Restoration of full range of motion.
- Restoration of strength of the muscles of the forearm, prevention of their atrophy.
If the pain syndrome in epicondylitis is not very pronounced, and the patient goes to the doctor mainly in order to find out the reason for the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the elbow joint, it will be enough to recommend the patient to observe a protective regime - that is, to carefully monitor their own feelings and exclude movements in which pain appears.
If a patient with epicondylitis is involved in sports or his work is associated with great physical exertion on the muscles of the forearm, it is necessary to temporarily ensure the rest of the affected area. The patient is given a sick leave or is advised to temporarily stop exercising. After the pain disappears, the load can be resumed, starting with a minimum and gradually increasing. In addition, the patient is advised to find out and eliminate the cause of the overload: review the sports regimen, use more comfortable tools, change the technique for performing certain movements, etc.
With severe pain in the acute stage of epicondylitis, short-term immobilization is required. A light plaster or plastic splint is applied on the elbow joint for a period of 7-10 days, fixing the bent elbow joint at an angle of 80 degrees and hanging the hand on a kerchief bandage. In the chronic course of epicondylitis, the patient is recommended to fix the elbow joint and forearm area with an elastic bandage in the daytime. The bandage must be removed at night.
If symptoms of epicondylitis appear after an injury, cold should be applied to the affected area (an ice pack wrapped in a towel) during the first days. In the acute period, patients suffering from epicondylitis are prescribed physiotherapy: ultrasound, phonophoresis (ultrasound with hydrocortisone), paraffin, ozokerite and Bernard's currents.
The pain syndrome in epicondylitis is caused by the inflammatory process in the soft tissues, therefore, in this disease, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have a certain effect. NSAIDs are used topically, in the form of ointments and gels, since inflammation in epicondylitis is local in nature. The appointment of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs orally or intramuscularly in modern traumatology for epicondylitis is not practiced due to their insufficient effectiveness and an unjustified risk of side effects.
With persistent pain that does not subside for 1-2 weeks, therapeutic blockade with glucocorticosteroids is performed: betamethasone, methylprednisolone or hydrocortisone. It should be borne in mind that when using methylprendizolone and hydrocortisone during the first day, there will be an increase in pain due to the tissue reaction to these drugs.
A glucocorticosteroid is mixed with an anesthetic (usually lidocaine) and injected into the area of maximum pain. With external epicondylitis, the choice of the injection site is not difficult, the blockade can be performed in the patient's position, both sitting and lying. In case of internal epicondylitis, to carry out the blockade, the patient is placed on a couch face down with arms extended along the body. This position provides access to the area of the internal epicondyle and, unlike the sitting position, excludes accidental damage to the ulnar nerve during the procedure.
At the end of the acute phase of epicondylitis, the patient is prescribed electrophoresis with potassium iodide, novocaine or acetylcholine, UHF and warming compresses on the affected area. In addition, starting from this moment, the patient with epicondylitis is shown therapeutic exercises - repeated short-term overextension of the hand. Such movements help to increase the elasticity of the connective tissue structures and reduce the likelihood of subsequent microtraumas. In the recovery period, massage and mud therapy are prescribed to restore range of motion and prevent muscle atrophy.
With conservative therapy without the use of glucocorticosteroids, the pain syndrome with epicondylitis is usually completely eliminated within 2-3 weeks, with blockades - within 1-3 days. In rare cases, persistent pain is observed that does not disappear even after injections of glucocorticosteroid drugs. The likelihood of such a course increases with chronic epicondylitis with frequent relapses, joint hypermobility syndrome and bilateral epicondylitis.
In the chronic course of epicondylitis with frequent exacerbations, patients are advised to stop playing sports or switch to another job, limiting the load on the muscles of the forearm. If the pain syndrome persists for 3-4 months, surgical treatment is indicated - excision of the affected areas of the tendon in the area of its attachment to the bone.
The operation is performed routinely under general anesthesia or local anesthesia. In the postoperative period, a splint is applied, the sutures are removed after 10 days. Subsequently, restorative therapy is prescribed, which includes physiotherapy exercises, massage and physiotherapy procedures.
www.krasotaimedicina.ru