What is included in the biochemical blood test deployed. Full blood test
W. healthy man The composition of the blood has been unchanged over life. Therefore, any deviations in the structure of its cells speak of certain diseases. The structure of human blood cells is studied different species Laboratory testing of blood. It is they who serve as a reliable factor in establishing a patient's diagnosis and its further treatment.
As is known, the blood consists of plasma, leukocytes, erythrocytes and thrombocytees. Also in the composition of blood visible chemical and biological processes are visible. According to their violations, medical specialists establish a diagnosis.
Most often, a common blood test is used to study the blood structure, less often - full biochemical analysis blood and special (on sugar, hormones, markers of oncological diseases, cholesterol and so on).
Among clinical studies The blood is isolated expanded (that is, a complete blood test) and a reduced (determination of only the amount of hemoglobin, leukocytes and the rate of sedimentation of erythrocytes) blood tests.
Complete blood test and decoding its results
To diagnose many diseases, a complete blood test is widely applied. It includes all the main indicators of the general clinical analysis of blood (hemoglobin, erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, color indicators, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocyte formula), as well as the establishment of hematocrit values \u200b\u200band erythrocyte indexes.
It should be remembered, with full analysis of blood decoding the results and the establishment of a diagnosis should be carried out only by a specialist in the field of medicine.
 Biochemical blood test involves the study of certain human organs (for example, the functioning of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder and other internal organs). In addition, it evaluates the equilibrium of vitamins and trace elements. Biochemical research of blood is used in gynecology, cardiology, therapy, urology, as well as other industries of medicine.
Biochemical blood test involves the study of certain human organs (for example, the functioning of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder and other internal organs). In addition, it evaluates the equilibrium of vitamins and trace elements. Biochemical research of blood is used in gynecology, cardiology, therapy, urology, as well as other industries of medicine.
Along with conventional biochemical diagnostics, a complete biochemical blood test is used, which includes a study of such indicators:
- protein (study of general protein, albumin, ferritin, c-jet protein, rheumatoid factor, anti-superstolized);
- various types of enzymes (study of aspartataminotransferase (AST), Alaninotransferase (ALT), amylase, gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), creatineinase, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), alkaline phosphatases);
- lipids (a study of total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol (high density lipoprotein), LDL cholesterol (low density lipoprotein), as well as triglyceride);
- glucose (carbohydrates);
- nitrogenous low molecular weight (examination of creatinine, uric acid and urea);
- inorganic substance and vitamins (calcium, potassium, sodium, chlorine, iron, magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin B12).
Full biochemical blood test is considered the most effective method diagnostics, especially when setting early stages Diseases. Therefore, one should not refuse to hold it.
Complete blood test with leukocyte formula
Often, in modern laboratories, a complete blood test is carried out with leukocyte formula (leukogram). Leukocyte formula Blood is calculated based on the morphological characteristics of cells, taking into account their size, form, structure of the kernel, painting and cytoplasmic inclusions. Complete analysis Blood with leukocyte formula includes a microscopic study of five types of leukocytes (neutrophils, monocytes, basophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes).
In other words, a leukogram is a study. various shapes leukocytes, which is expressed in their percentage ratio.
A complete blood test is of great value, since when diagnosing various diseases, the attending physician can observe undergoing negative processes. This method Studies are used in identifying inflammatory and infectious diseases, pathologies of hematological processes, and also establishes the effectiveness of treatment.
Biochemical blood test is important for the diagnosis of almost all diseases, therefore it is prescribed first.
What are the indicators included in a standard biochemical blood test?
Glucose (in blood)
The main test in diagnosis of diabetes. This analysis is very important in selection of therapy and evaluation of the effectiveness of diabetes treatment. Reducing the level of glucose is observed in some endocrine diseases and liver function disorders.
Normal blood glucose indicators:
Bilirubin common
Yellow blood pigment, which is as a result of the decay of hemoglobin, myoglobin and cytochromes. The main reasons for increasing the number of total bilirubin in the blood: damage to liver cells (hepatitis, cirrhosis), enhanced decay of erythrocytes (hemolytic anemia), violation of bile outflow (for example, gall-eyed disease).
Normal values \u200b\u200bof general bilirubin: 3.4 - 17.1 μmol / l.
Bilirubin direct (bilirubin conjugated)
The fraction of the general bilirubin of blood. Straight bilirubin rises with a jaundice developed due to the violation of the outflow of bile from the liver.
Normal values \u200b\u200bof direct bilirubin: 0 - 7.9 μmol / l.
Bilirubin indirect (bilirubin unconjugated, free)
The difference between the indicators of the overall and direct bilirubin. This indicator increases when the decay of erythrocytes is increased - when hemolytic anemia, malaria, massive hemorrhages in fabrics, etc.
Normal values \u200b\u200bof indirect bilirubin:< 19 мкмоль/л.
Asat (AST, AspartataminTransferase)
One of the main enzymes synthesized in the liver. Normally, the content of this serum enzyme is small, since most of it is in hepatocytes (hepatic cells). The increase is observed in diseases of the liver and heart, as well as with long-term admission of aspirin and hormonal contraceptives.
Normal asat values:
- Women - up to 31 units / l;
- Men - up to 37 units / l.
Alat (Alt, Alaninotransferase)
Enzyme synthesized in the liver. Most of it is located and works in liver cells, therefore, in the normal, the concentration of Alt in the blood is small. The increase is observed in the mass death of hepatic cells (for example, with hepatitis, cirrhosis), severe heart failure and blood diseases.
Normal values \u200b\u200bof amalats:
- Women - up to 34 units;
- Men - up to 45 ed / l.
Gamma GT (Gamma-GlutamilTransferase)
Normal values \u200b\u200bof Gamma GT:
- Women - up to 38 units;
- Men - up to 55 units / l.
Alkaline phosphatase
Enzyme, widespread in human tissues. The largest clinical significance has a hepatic and bone-shaped alkaline phosphatase, the activity of which is determined in the serum.
Normal alkaline phosphatase values: 30-120 units / l.
Cholesterol (cholesterol shared)
The main lipid of blood, which enters the body with food, and also synthesized by the liver cells.
Normal cholesterol indicators: 3.2-5.6 mmol / l.
Lipoproteins of low density (LDL)
One of the most atherogenic, "harmful" fractions of lipids. LDL is very rich in cholesterol and, transporting it to vessel cells, delay in them, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
Normal indicators of LDL: 1.71-3.5 mmol / l.
Triglycerides
Neutral fats located in the blood plasma, an important lipid metabolism.
Normal triglyceride indicators: 0.41-1.8 mmol / l.
Common protein
An indicator reflecting the total amount of proteins in the blood. Its reduction is observed in some diseases of the liver and kidneys, accompanied by an increased elusion of protein with urine. Increase - with blood diseases and infectious-inflammatory processes.
Normal values \u200b\u200bof the total protein: 66-83 g / l.
Albumen
The most important protein of blood, which is approximately half of all serum proteins. Reducing the content of albumin may also be a manifestation of some kidney diseases, liver, intestines. An increase in albumin is usually associated with dehydration.
Normal values \u200b\u200bof albumin: 35-52 g / l
Potassium (K +)
The electrolyte contained mainly inside the cells. Raising The level of potassium in the blood is most often observed in acute and chronic renal failure, a sharp decrease in the amount of urine allocated or its complete absence, most often associated with severe kidney diseases.
Normal potassium values: 3.5-5.5 mmol / l.
Sodium (Na +)
The electrolyte contained mainly in the extracellular fluid, and in smaller quantities - inside the cells. He is responsible for the work of nervous and muscle tissue, digestive enzymes, blood pressure, water exchange.
Normal sodium values: 136-145 mmol / l.
Chlorine (SL-)
One of the main electrolytes, which is in the blood in an ionized state and plays an important role in maintaining water and electrolyte and acid-base balances in the body.
Normal chlorine values: 98-107 mmol / l.
Creatinine
A substance that plays an important role in the energy exchange of muscle and other tissues. Creatinine is fully excreted by the kidneys, so the determination of its blood concentration has the greatest clinical significance for the diagnosis of kidney disease.
Normal creatinine values:
- Women - 53 - 97 μmol / l;
- Men - 62 - 115 μmol / l.
Urea
The substance that is the end product of the metabolism of proteins in the body. The urea is excreted by the kidneys, so the determination of its blood concentration gives an idea of \u200b\u200bthe functional abilities of the kidneys and is most widely used to diagnose renal pathology.
Normal urea values: 2.8-7.2 mmol / l.
Uric acid
One of the finite products of protein metabolism in the body. Uric acid is completely excreted by the kidneys. P vegetted The concentrations of uric acid occurs with renal disease, other kidney diseases flowing with renal failure.
Normal uric acid values:
- Men - 210 - 420 μmol / l;
- Women - 150 - 350 μmol / l.
C-jet protein (CRB)
Normal values \u200b\u200bof C-reactive protein: 0 - 5 mg / l.
Iron (serum iron)
A vital trace element, which is part of hemoglobin, is involved in the transport and deposition of oxygen and plays an important role in blood formation processes.
Normal wires of serum iron:
- Women - 8.95 - 30.43 μmol / l;
- Men - 11.64 - 30.43 μmol / l.
How to prepare for research?
During the day before taking blood on the biochemistry, it is necessary to exclude alcohol, in 1 hour - smoking. Blood takes preferably to produce an empty stomach in the morning. Between the last meal and blood taking should pass at least 12 hours. Juice, tea, coffee, chewing gum not allowed. You can drink water. It is necessary to exclude elevated psycho-emotional and physical exercise.
What are the timing of the analysis?
How do the results of biochemical blood test evaluate?
Using various methods Diagnostics with different clinics leads to unequal results, may also differ units of measurement. Therefore, to properly decipher the result of biochemical blood test requires the consultation of the attending physician.
For information on the correctness of the functioning of human organs, successfully apply laboratory method Diagnostics - biochemical blood test. The study has high informativeness and reliability of the results obtained. The diagnostic value of the analysis is not only that it makes it possible to evaluate violations in the functioning of organs and systems of the body, but whether the patient has a lack of vitamins or trace elements. Any deviation in the results obtained testifies to the unfavorable situation and requires medical intervention.
Biochemical blood test - laboratory diagnostic method used in medicine to assess the correctness of the functioning of organs and organism systems. The study makes it possible to determine the level of hormones, which has an indirect attitude towards the functions of the work. Hardware, kidney, progressive inflammatory processes, rheumatism and many other diseases. Biochemical analysis is a standard diagnostic method that helps to make a diagnosis to determine the course of the disease, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy used.
Blood research on a biochemistry doctor prescribes patients on outpatient and inpatient treatment. The list of indicators under study is determined based on each specific case. The doctor may appoint a detailed study of blood, which will determine violations in all organs and systems, as well as assess their dependence among themselves. A biochemical study, along with the clinical list, is included in the list of mandatory analyzes in passing the population's clinicalization, which is effective for diagnosing pathologies in the early stages of development. Actually conduct analysis in diseases of the following organs:
- abdominal cavity;
- kidney;
- endocrine system;
- digestive tract;
- of cardio-vascular system;
- musculoskeletal system;
- blood I. blood system generally;
- gynecological system.
Newborn baby biochemical blood tests are carried out with order to exclude hereditary pathologies. In young children, blood is taken with difficulties in mental and physical development, as well as for preventive health control. The study makes it possible to identify pathological disorders of genetic origin. If there are deviations from the norm in the results of the analysis, the doctor most often appoints a more advanced examination, subsequently, pathology is either confirmed, or vice versa is excluded.
Norm of indicators
Biochemical blood test analysis has a high value due to the fact that it makes it possible to simultaneously explore a large number of important indicators. Sometimes it takes only one indicator to confirm the diagnosis, and in some cases, to coordinate further actions, the doctor needs to evaluate several values \u200b\u200bat once. The norms of biochemical blood test may differ depending on the laboratory, but slightly. It is also worth noting that the norms of values \u200b\u200bchange relative to the age of the patient and its sexuality, in the table you can see the average generally accepted values.
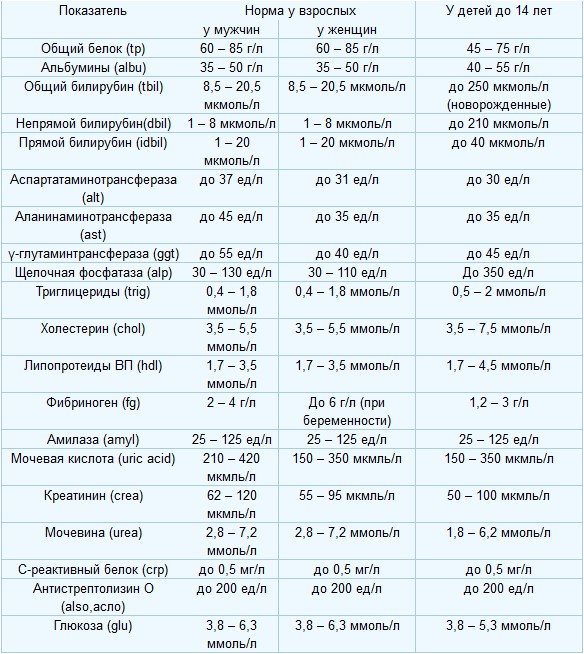
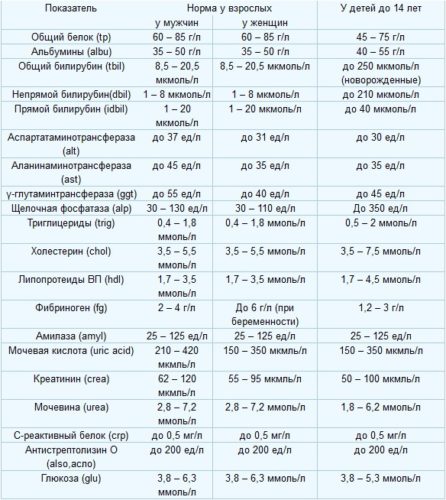
The process of collection of biological material for research is a standard procedure requiring simple preliminary training. But it is due to the observance of simple rules and recommendations, the results of the analysis will be as reliable as possible. It is necessary to donate blood to a strictly on an empty stomach, from the last meal must pass at least 8 hours. A few days before the passage of biological material, you need to abandon alcohol, sharp, oily and fried food. It is also desirable to temporarily stop therapy with medicines.
Before passing to a laboratory assistant to put blood, you need to sit down and relax 10-15 minutes. During the day before the intake of the material, it is necessary to protect themselves from physical and emotional loads.
2-3 hours before visiting the laboratory, it is not recommended to smoke. Also, a day before the analysis, you cannot visit the bath, sauna and take a hot bath. In compliance with all recommendations, the material under study will have a high clinical and diagnostic value, will allow you to get the most reliable results.
Decoding indicators
Under the deciphering of the results of the biochemical study, a comparative analysis of the indicators of the norm with the results obtained is implied. In some cases, the deviation of only one or more indicators is enough to put the accurate diagnosis, but in most cases there are additional surveys to get full clinical picture Diseases. Next, consider the main indicators and the reasons for their deviation it is the norm in the study biological material with biochemistry.
- Total concentration of all proteins present in blood plasma. In proteins, large quantities contain nitrogen. After removal of protein compounds, residual nitrogen is formed. The value of the total protein indicator is that it makes it possible to determine the diseases of many organs and the circulatory system. The growth of concentration is noted during dehydration, infection of the body, oncology. Reduced overall protein during starvation, liver pathologies, extensive bleeding, thyrotoxicosis.
Bilirubin is a bile pigment, the main component of the bile of the human body. It is formed by splitting proteins: hemoglobin, myoglobin and cytochrome. The process of formation of bilirubin and its excretion occurs due to the correct operation of the liver. Therefore, it is necessary to donate blood on a bile pigment when suspected of the pathology of the liver, biliary tract and anemia. In the human body, the pigment is represented in two forms: free and related. The growth of free is noted in hepatitis, infection of the liver bacteria, cirrhosis, alertrovia. Bilirubin in the bound form increases with violations of the process of bile outflow.
Data on enzyme activity make it possible to conclude the functioning of the internal organs. Enzymes are one of the main diagnostic indicators. The concentration growth indicates the defeat of cells of internal organs and tissues. The increase in the content of aminotracerase is noted in hepatitis, leafing tissues, myocardial infarction, significant traumatic lesions of the skeleton and muscle tissue, cholestasis, hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of fabrics. The growth of lactate dehydrogenase occurs when myocardial and kidney hearterts, myocarditis, hemolysis, pulmonary pathologies, hepatitis in the acute stage.
Deciphering nitrogen exchange rates
IN human organism The processes in which protein compounds, various acids, lipids containing nitrogen, hormones and other substances are involved. Under the indicators of nitrogen exchange means the difference between entered the body with nitrogen food and allocated with called masses, urine and through the sweating system. Nitrogen formed in the process of exchanging proteins is a component of the residual nitrogen component. Among the indicators of this exchange are allocated: urea and creatinine, as well as residual nitrogen, creatine, uric acid, ammonia and others.

Urea - product formed as a result of protein decay. In humans, the norm of this indicator changes with age. The urea content increases with the progression of pathological disorders in the kidneys, such as glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, polycystic and tuberculosis of the kidneys, renal failure other. Reducing the blood concentration may be caused by physiological processes (pregnancy, insufficient nutrition, strong physical exertion) or as a result of such pathologies as a cirrhosis lesion of the liver, poisoning, celiac disease.
Creatine is a product of the exchange process that occurs in muscles and to a small degree in the brain. The substance is derived from the body through the kidneys. His deviation from the norm is caused by violations in the work of the kidneys or muscles. Enhance creatinine can be caused by such diseases as renal failure, diabetes, intestinal obstruction, dystrophy, extensive burn damage, and after some therapy medicinal preparations. A low deviation from the norm is found in athletes.
Residual nitrogen - a product formed after blood purification from protein compounds. In the largest amount of nitrogen in proteins, as well as in urea, amino acids, creatine and ammonia. An increase in the level of residual nitrogen content in the blood is called azotemia. Pathological deviations in the work of the kidneys lead to an increase in the concentration of residual nitrogen. Among the diseases are distinguished: kidney disease in chronic stage, Polycystrosis, Tuberculosis Kidney, urolithiasis disease, hydronephrosis.
Biochemical study has high informativeness and allows you to detect pathology as separate organsAnd the system as a whole is already in the early stages of development. The analysis includes a large number of indicators, each of which or several in the aggregate enable the doctor to determine the cause of the violation in operation. The norms applied in the study may differ depending on the laboratory and techniques. It is important to know the standards of the values \u200b\u200bused at the site of diagnostics.



















