Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. The flow, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods. Pancreatic pancreatitis
It is about 2% of all tumors. Distinguish BSD cancer, head cancer, body, pancreatic tail.
Malignant tumors of the pancreas - carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, sarcoma, carcinosarkom - develop from immature epithelial tissue. Primary pancreatic cancer is observed in 0.1% of all patients sent for inpatient treatment. The most often pancreatic cancer is observed aged 50 - 60 years, although in some cases it also happens in early childhood and youthful age. Pancreatic cancer more often sick men. The ratio of men and women is 2: 1. More often occurs cancer head (70%), less often - body cancer and tail (30%).
Macroscopically pancreas cancer has the form of a bug-in node, which can spread diffusely, on a different outlet or infiltrate the gland, hitting the vessels and causing necrosis of parenchyma. Uncrolized areas can dilute, forming a similar pseudocyst. Often even during difficult to differentiate such a form of pancreatic cancer from chronic pseudotumorous pancreatitis. The latter has a longer anamnesis of the disease. Only biopsy, and it does not always, it allows you to detect tumor cells that determine the correct diagnosis. Microscopically distinguishes cancers from the epithelium of the ducts, parenchyma glands and islet epithelium. Skirrs are most often found, less often - adenocarcinoma, mucous, flat-belling cancers.
Depend on a specific estimate, the types of tumor propagation beyond the limits of the gland and the nature of metastasis are detected. There are direct distribution and germination of the tumor of the entire pancreas and neighboring organs with the compression of the latter (common bull duct, duodenum); Hematogenic metastasis, in particular on a portal vein, followed by her thrombosis; The distribution of the tumor elements is perioreural (with the development of pain syndrome) and metastasis for lymphatic paths with damage and an increase in lymph nodes at the gate of the liver, pararaortyl and other nodes.
The first place to metastasize the pancreatic cancer occupies the liver, then lymphatic nodes abdominal cavity Various localization.
Cancer and tail cancer usually does not give jaundice, less often is diagnosed, not accompanied by violations by the liver function, proceeds relatively more well, although it is prognostically unfavorable.
Symptoms
In the pancreatic cancer there are no pathognomonic signs, it is most often about the correctness. clinical Evaluation combinations of these signs. Pancreatic cancer is determined by a number of reasons. The most important of them is the magnitude and localization of the tumor, the degree of compression by the tumor of nearby organs and the anatomical formations preceding the patient's state.
Other parameters in the formation of the disease are the nature of tumor growth, the presence or absence of jaundice, the degree of development of intoxication, the nature of the change in external and internal secretion, the features of metastasis. In 80% of cases, pancreatic cancer is accompanied by a jaundice. A rudeness of the disease is much less common, which usually takes place when localizing the tumor in the body and the tail of the gland.
Early signs of pancreatic cancer who do not have specificity should be called the decline of strength, fast fatigue, reduced performance, weight loss (a month to 10 kg), disgust for food, lack of appetite, "unpretentious" liquid stools, stupid discomforts all over the abdomen , Irradias B. lumbar region, gastric discomfort. The appearance of a jaundice often causes the thought of Botkin's disease, in connection with which the patient may be on the bay of the infectious branch. Consultation often identifies the second, unfortunately, the late sign of the disease is increased, sometimes to large sizes, a gallbubble, which, in combination with the jaundice (Curvoisier syndrome), makes you think about the pancreatic cancer.
When localizing cancer in body and tail gland, clinical symptoms of the disease are even less pronounced. Assess the symptom of the pulsation of the abdominal aorta, similar to the symptom of the Resurrection in acute pancreatitis (the transfer of the aorta pulsation through the tumor of the pancreatic body), isolated the shape of the Shoffara - Lerish, when the body and tail tumor and the gland is manifested by weakness, cachexia and slouching pain.
There are forms of the disease that are diagnosed already in running stages. In these cases, the clinical picture forms a tumor of glands, and its metastases in various organs, for example, in the pleura (chest pain), in the liver (jaundice), in the lymph nodes of the peritoneum (peritonitis, abscess), in the zone of the portal vein (ascites), In the stomach (bleeding), in the spine (lumbar-sacral pains simulating radiculitis).
Pancreas Cancer may be accompanied by the development of multiple peripheral thrombophlebitis, and then the diagnosis of the disease is difficult.
Diagnostics
Evaluating the possible clinical signs of the disease, the clinician can use some laboratory data, as well as the data of modern diagnostic techniques.
Increasing the body temperature to subfebrile digits can be observed together with the first symptoms of the disease, but the fever may be due to the decay of the tumor.
In the study of blood, an increase in ESP is noted, in later stages anemia is detected, not achieving, however, high numbers, as with. For BSD cancer, it is characteristic, on the contrary, rapid development, frequent appearance in feces hidden blood and the appearance of blood in duodenal content. The detected leukocytosis during pancreatic cancer is usually associated not only with the tumor itself, but also with the advent of metastases, jaundice and secondary infection in the bile duct system due to cholestasis.
In case of duodenal sensing of patients, it is possible to detect two essential features of the disease: the obtuctive type of pancreatic secretion with a decrease in volume or even the absence of pancreatic enzymes and the presence of atypical, cancer cells with cytological examination Duodenal content.
If, due to the compression of the main pancreatic duch, the secretion of the secret, the pancreatic enzymes is found in the blood, in the urine, in feces. A sufficiently resistant biochemical feature is normal indicators of the content of aminotransferase, in contrast to hepatitis, in which they are significantly increased.
Radiological studies in pancreatic cancer detect, as a rule, indirect signs of changes in neighboring organs. Proper diagnosis is about 40%.
When the stomach radiography detects the displacement of the last kiver and left, the presence of malignant restructuring of the relief of the mucous membrane, sometimes defect filling, especially when compression and in the horizontal position of the patient. When cancer, the pancreatic head can observe the deformation of the stomach with the stenosis of the anthral department. At duodenography, the extension of the horseshoe is detected in some cases. duodenal gut, shifting it up and right, in others - the narrowing of the lumen and deformation of the duodenum. When irrigoscopy, you can reveal the displacement of the transverse colon book. Cholangiography reveals a narrowing (compression, deformation) distal department General bile duct and even change in the direction of hepatic choles, due to the pressure on it from the outside.
Signs of pancreatic cancer, according to ultrasound echoscaning, are the detection of dense homogeneous formation with an uneven contour and a small amount of internal echo signals, elevated level Echosognals, expansion of the main pancreatic duct, the attenuation of echo signals behind some tumors, an even iron circuit.
Computer tomography reveals a modified density of pancreatic tissue. At the same time, the maximum density is indistinguishable from the density of unchanged tissue, and the minimum is below it. The most important is the deformation of the gland, uneven, fuzzy contours of the pathological focus, the loss of differentiation of parapancreative fatty fiber. Indirect signs is the expansion of bile ducts.
In the angiography of the branches of the ventricular trunk, it is possible to identify a malignant type of vascularization of the tumor area with the presence of amputation of small vessels and the sections of the evolving zone.
The pancreatic scanning makes it possible to detect the presence of a major defect of the accumulation of radioactive substance in the tumor zone.
The radiographic signs of body cancer and the tail of the glands are reduced to the appearance of the accumulation defect at the small curvature of the stomach and the detection of the rounded shape defect on the rear wall of the stomach during profile radiography. In antitegrand endoscopic pancreatography, you can identify the amputation of the output duct at a particular level.
Summarizing the data obtained in the study of the clinical picture and as a result of the use of various diagnostic techniques, it is possible to make a list of clinical and diagnostic signs of pancreatic cancer, which can help a practical surgeon.
- Stupid pain in the depth of the belly of unclear localization mainly in men over 45 years.
- Progressive body weight loss.
- Dyspeptic disorders (liquid chair, nausea, meteorism).
- Jaundice.
- fast fatigue, loss of appetite.
- Palpation of an enlarged painless gallbladder.
- Palpation of a tumor in the epipment region, an increase in the liver, dark skin color on the background of jaundice, reinforced pulsation of the abdominal aorta, systolic noise when listening to the abdominal aorta.
- Skin itch.
- Subfebrile body temperature, anemia, an increase in ESP, leukocytosis, hyperbilirubinemia.
- Increased content of ether soluble bilirubin.
- Detection in the duodenal content of blood and atypical cells.
- Improving the activity of amylase in the blood and urine normal indicators Aminotransferase activity.
- Steatery, Creator, positive Reaction of Gregersen.
- Detection of signs of epigastric formation, changing the contour of the stomach or duodenum with radiological gastroduodenography.
- The deformation of the total bile duct at the chopper.
- Detection of thick homogeneous formation with an uneven contour and a small amount of echo signals at ultrasound exam.
- Deformation of the gland with uneven, fuzzy contours and changing the tissue density according to computer tomography.
- X-ray change in the contour of the transverse colon.
- The presence of symptoms of the "swelling of the tumor" contrasted vessels of the basin of the ventricular barrel.
- Identification of the "accumulation defect" of radionuclide when scanning the pancreas.
Do not be afraid, having heard the term "hypo echogenicity" from the doctor. This word is not a diagnosis, but describes a structure with a smaller density than all neighboring tissues. This formation can be both normal phenomenon and pathologies. It all depends on the authority in question.
The methodology of the examination with the help of an ultrasound is that with the help of special equipment, sound oscillations of a certain frequency are generated, sent to the organs, and then the answer is taken, that is, the reflected sound, echo. On acoustic density (echogenicity), one can judge the structure of the organs.
Some formation in the body can show reduced acoustic density, looks on the screen darker than the adjacent fabrics. This phenomenon is called hypo echogenicity, that is, a reduced density. In this area, the progress of ultrasound is slower. Most often, such a phenomenon has a liquid structure: it may be, for example, cyst. The doctor will not be able to immediately say the exact diagnosis.
The structure with uneven outlines can be not only a pile, but also adenosis, fibroadenoma or tumor. However, only biopsy, as well as cystoscopy, laparoscopy or bronchoscopy, is capable of identifying such a phenomenon.
What is hypo echogenic education (node) in various organs?
If the survey concerns the thyroid gland, then it is not necessary to immediately fall into a panic and run to the oncologist. As a rule, only 5% of patients find out that the formation (hypo echogenic assembly) is oncological pathology. Most often, the discovery is a cyan, vascular formation or liquid structure.
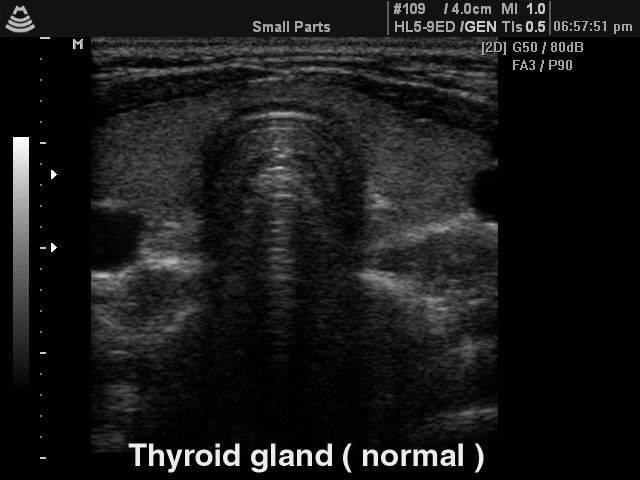
Normal thyroid on ultrasound
It is necessary, first of all, to consult an endocrinologist and pass tests for hormones (Read more about which the doctor will tell, prescribing the direction). If nothing terrible is clear, it is advisable to repeat all the analyzes in half a year. Growing or non-changing dimensions The hypooehogenic node will have to be examined using biopsy.
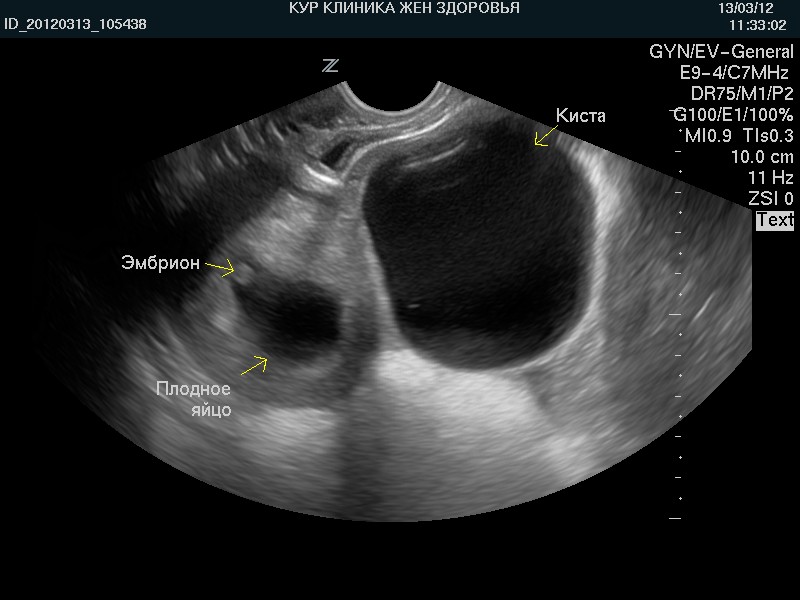
In the case when the node is detected in the uterus, most likely it is a tumor. It is only necessary to find out whether it is benign or malignant. If the education also has an echo-echo inside, then it is about inflammation of the uterus.
The phenomenon of reduced echogenicity is very important in the case of pregnancy:
- if such a plot is localized near the embryo, it says about the threatening miscarriage.
The hypo echogenic node can be detected in the breast in the process of carrying out a mammography. As a rule, such sites can be:
- carcinoma glands. She has fuzzy, uneven outlines, there is a shadow, an inhomogeneous structure.
- adenosis.
- typical cyst. The contours in this case will be clear, and the form is rounded.
- atypical cyst, capable of being malignant.
- fibroadenoma. She has smooth, clear contours, there is a similarity with malignant tumors.
In the event of identifying such formations, it is necessary to repeat the study in a month and, depending on the results, go to the biopsy.
If the hypooehogenic node is detected in the ovaries, then you should not worry too much: it is extremely rare it can be oncological pathology. Most often, the phenomenon is a cyst, follicle, lutein body or vascular education.
But in the case of the kidney, such a node can be either a pile (then it has a clear contour, a homogeneous structure), or a tumor (malignant, if the increase in retroperitoneal lymph nodes is revealed). As a rule, the patient immediately sends additional surveys to accurately set the nature of the find.
Nodes in other organs
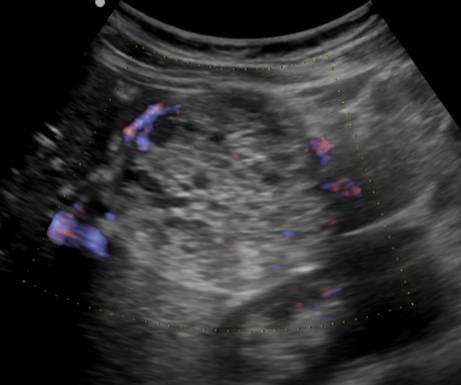
The presence of nodes in the pancreas suggests that the doctor may deal with the following phenomena:
- Cysts (especially if they have smooth outlines, a homogeneous structure).
- Pancreatitis or fibrolipomatous processes.
- Metastases (borders will be blurred).
- Oncology.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to pass not only the ultrasound of the body, but also dopplerography.
If a violation of the structure in the liver, pathologies can be the following:
- The consequence of the cirrhosis when the nodes have a rounded or barride form.
- Cyst.
- Thrombose.
- Abscess.
- The consequence of liver fluid infiltration when the hypooehogenic node is a particle of normal tissue.
- Hyperplasia or adenoma.
- Oncology and metastases.
Again, additional research is needed for accurate diagnosis. 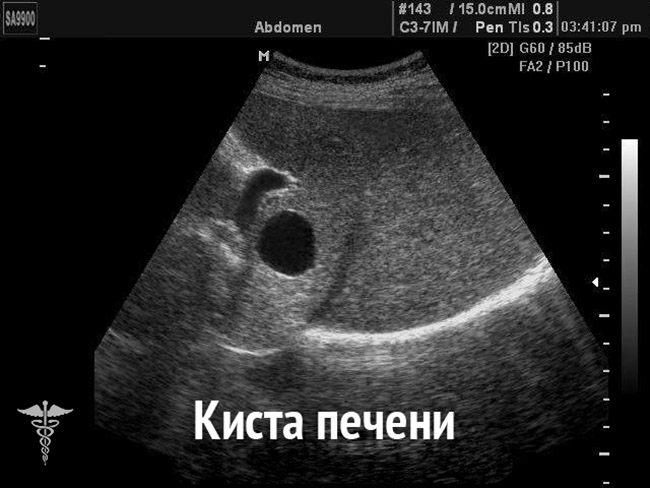
Conclusion
Such a hypo echogenic education, depending on the authorized body, may be both almost any pathology and natural phenomenon. Most often, cysts or tumors are detected, but sometimes it can be the phenomena that need to urgently operate or heal with medicines. Only an ultrasound is not able to give an accurate diagnosis, therefore, for all recommendations and the preparation of the treatment plan, the doctor will have to send a patient to a number of additional surveys.
The flow of chronic pancreatitis
Four stages clinical picture HP:Stage I. Preclinical stage characterized by lack clinical signs diseases and random identification of changes characteristic of CP during examination using radiation diagnostics techniques (CT and abdominal ultrasound);
Stage II. Stage of initial manifestations. It is characterized by frequent episodes of exacerbation of HP, which may be mistakenly regarded as OP. Recurrences of the disease can be light or heavy; There is a threat to the sickness of the patient. Already at this stage there may be complicated CP. The disease proceeds with progression trend: from repeated pain episodes to constant moderate pain accompanied by secondary disorders Appetite, neurotic disorders, and, as a result, to weight loss.
The quality of life does not change or reduced. Stage continues for several years. Over time, episodes become less severe, but during periods between exacerbations of the disease, clinical symptoms are saved. Sometimes the disease is very quickly progressing, the atrophy of the PJ is developing and the function of the organ is disturbed. A variant is possible when the disease manifests by exocrine and endocrine failure;
III stage. It is characterized by the development of constant clinical symptoms with the predominance of pain abdominal syndrome. Patients at this stage can be dependent on drugs, very little eaten. There are signs of exocrine and endocrine failure;
IV stage. The final stage of the disease characterized by the Atrophy of the PJ, the exocrine and endocrine failure, is clinically manifested by steatores, pronounced loss of body weight and diabetes. The pain becomes less pronounced, there are no sharp pain episodes. At this stage, the complications of HP are noted, in particular PJ cancer.
Tool and laboratory methods for diagnosing chronic pancreatitis
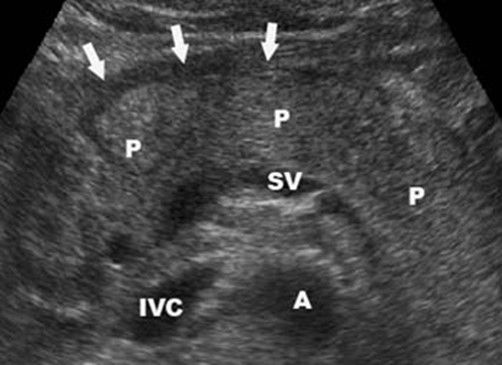
Abdominal Overview Radiography
The method in the era of the wide availability of ultrasound and CT for diagnosis of CP is practically not used. The study is performed quite simple, on an empty stomach, without special training. Perform pictures in two projections. In patients with Calcifying HP in the PJ parenchyma or in its ducts, the decisions are naturally detected on radiographs (see Fig. 4-18).Fig. 4-18. Overview radiograph. Multiple pancreatic calcifications are defined
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs
For HP outside the exacerbation, a heterogeneous increase in the echogenicity of the PJ or the alternation of medium and high density zones is characterized. This is due to the fact that the area of \u200b\u200bchronic inflammatory process, fibrosis or calcinates in the parenchyma are represented as separate sections of increased echogenicity. Depending on the size of the affected areas, the micro- and macronodular sonographic structure of the parenchyma is observed, the most pronounced in the case of calcifiable HP. Some large calcinates give a "acoustic shadow".With a pronounced increase in echoism (see Fig. 4-19 a) the entire PJ parenchyma councils detect only by the presence of "acoustic shadows". Linear location indicates their location in GPP (see Fig. 4-19 b). Announced a significant expansion of the duct, distal than the concreters located in it. The identification of large hypooehogenic areas Against the background of increasing the echogenicity of Parenhima indicates the presence of an active inflammatory process - exacerbation of HP (see Fig. 4-19 V).
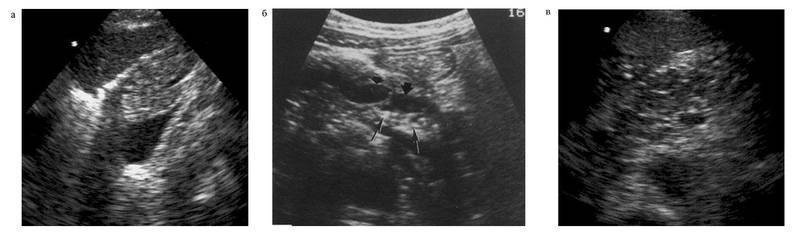
Fig. 4-19. Ultrasonogram of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis: A - visualizes the diffuse-inhomogeneous echoostructure of the pancreas with alternating zones of medium and elevated echo absorption, not clearly derogation from each other; b - visualized duct concrections (shown by thin arrows) and advanced segmented pancreatic duct (shown by wide arrows); B - visualizes hyperahogenic fields against the background of hypo echogenic zones in the pancreas
In a third of cases, at the XP, the iron contour is blurred, uneven, less frequently serrated, so with a hp the border between the PJ and the surrounding tissue in some cases it is impossible to determine exactly. In other cases, the PJ contours can be smooth, without jar, but with large smooth protractions, "humps", violating the form of the gland. When HP is out of exacerbation, the size of the gland is normal or reduced, sometimes significantly, so that only the extended GPP walls are visualized in the PJ projection, sometimes the duct is bent due to the fibrosis of the surrounding tissue.
Ultrasonic sign of progressive fibrosis and reduction of PZh size is an increase in the distance between the PJ and the aorta more than 20 mm. An increase in the size of the PJ is characteristic of exacerbation of HP. The increase is more commonly local associated with a segmental edema. An increase in the sizes of the PJ may be accompanied by a composer of the upper mesenteric vein, less often the lower hollow vein; Often determine the ultrasound signs of the thrombosis of the spleen vein. In the area in the area of \u200b\u200bthe PG head, it is possible to compress the overall gilt pass, leading to the expansion of the latter above the obstruction area at the high length.
Due to the peculiarities of two-dimensional echography, there is the possibility that when aggravating HP on an uneven hyperehogenic structure, areas of reduced echogenicity are superimposed, sometimes completely or partially masking signs of HP.
The ultrasound allows you to simultaneously examine the liver, a harsh bubble, reveal the phenomena of the gatro and duodenostasis, information about which may add an idea of \u200b\u200betiology, non -paccreatic complications, will provide an opportunity to establish the abdominal cavity. The main ultrasound signs of HP are presented in Table. 4-13.
Table 4-13. Ultrasound signs chronic pancreatitis

Currently, in most medical and prophylactic institutions, Russia uses the classification proposed by V.T. Ivashkin et al., Allowing to allocate characteristic, most common, morphological forms of the disease. Therefore, we present the main ultrasound signs allocated in the classification of clinical and morphological forms of pancreatitis, since it is in such a form most of the ultrasound diagnostic specialists give their conclusions to clinicians.
Interstitial
A variant of HP in the stages of exacerbation. According to ultrasound, a diffuse or local increase in the sizes of PJ is observed at the height of the exacerbation of the disease. It is characterized by revealing visualization of all PJ departments and its clear contours.The structure of the parenchyma gland is more often hypochogenic and inhomogeneous. More than 50% of patients with HP detect a small amount of fluid in a small gland bag, which is determined in the form of hypo echogenic liquid formation with a thickness of up to 2 mm between the rear wall of the stomach and the front surface of the PJ. Some patients have an outflow of yellow, which is evidenced by the increase in the volume of the horizontal bubble, containing thickly horizontal, and expanding the lumen of the overall grain duct more than 6 mm, in some cases, with a dynamic examination, the pseudokists are visualized during a dynamic survey. Pathological changes in the PJ Distant System according to ultrasound data are uncharacteristic.
Parenchimato form
When ultrasound in patients in this group, the size of the PJ does not change. In 50% of observations of contours are defined as fuzzy. Echogenicity of PJ Parenhim relative to the liver tissue is raised. The structure of the parenchyma is inhomogeneous, "coarse-frozen"; Alternation of increased and reduced echogenic zones of 2-4 mm. With a relatively small part of the patients, there is an expansion of the PJ dfice in the head of the head and body. Some patients determine the compression and convulsion of the spleen vein. Ultrasound diagnostics of the parenchymal form of HP is especially complex; Accuracy does not exceed 60%. Assessment of the structure and echogenicity of parenchyma with normal sizes of the PJ largely subjective. Help in the existence of HP is provided by clinical data, the experience of the doctor and the corresponding changes in the yellow ways, stomach and DPK.Fibrozno-sclerotic form
According to ultrasound, a diffuse or local decrease in the size of the PJ. Body sizes are within 7-11 mm. Parenchima PZ has diffuse-increased echogenicity, the contours of the gland are clear. In a relatively small group of patients, uneven, fine-maternal contours are determined, the structure of the gland is non-uniform with a small number of hypo echogenic point microcistal formations. Some patients have expanded PZh.In these cases, as a rule, with ultrasound, hyperheogenic small focal inclusions are visualized, similar to the concreteers, located both inside and outside the duct system. Ultrasound diagnostic difficulties occur in patients with increased nutrition, hypersthenical constitution. The absolute sizes of the PJ in these patients remain normal. In this case, lipomatosis of parenchyma cannot be distinguished from fibrosis as the consequences of the sclerotic process.
Hyperplastic form (pseudotumorous pancreatitis) Hyperplastic form HP is a rather rare version of the disease. Ultrasound examination visualizes a sharply enlarged PJ. More than 50% of patients define a diffuse increase in PJ, the rest is a local increase in the head of the gland. When localizing the process in the PJ head, it is possible to talk about the pseudotumorous XP with an increase in its size up to 40 mm and more.
The diffuse increase in PJ is accompanied by the formation of a bug-in contour. In a third of the patients, according to the ultrasound, the contours of the gland on the rear surface are inventious, which, in combination with the presence of adhesions in the suction area and signs of cholecystitis, is regarded as inflammatory changes in parapanque tissue. In many patients, the echogenicity of Parenhima was generally reduced, in some of them, on this background, the expressed heterogeneity of the acoustic structure with alternating large (10-15 mm) sections of increased and reduced echogenicity.
The expansion of the PJ flow in the head area of \u200b\u200bup to 4 mm is detected less than half of the patients. It should be emphasized that for most patients with this form of HP, difficulties occur during the differential diagnosis of limited areas of inflammation and the Karcinoma of the PJ due to the similar pattern of the available changes. To eliminate malignant lesions of PJ to these patients, under the control of ultrasound, produce puncture biopsy. The hyperplastic version of the CP should also be differentiated from the OP.
Kystosia form. PJ dimensions moderately increase or remain within normal limits. In all patients, multiple cystic formations are determined with a homogeneous hypooehogenic structure of a small (up to 1.5 cm) diameter, evenly located in all PJ departments, pronounced sclerotic changes in the surrounding parenchyma with the sections of its sightseeing. Most often they are localized in the body and head. PJ contours are clear, fine-maternal; GPP serve. In this case, most patients detect the intermittent areas of extensions (up to 0.5 cm) of the duct system with the total patients (0.5-1 cm) uneven contours lumen.
It should be indicated that when the PJ cyst is detected, there is a need to conduct differential diagnosis between the cystic form of HP and disonatogean and retention cysts, False PJ cysts arising from acute destructive pancreatitis, the cysts arising from the trauma of the abdomen, as well as ciladaitarcinoma. It should be borne in mind that disonatogenic and retention cysts are single, less often multiple, proper rounded shape with a thin uniform capsule, butched contours, are often localized in the body, less often the tail of the PZh. Usually such cysts are random finds.
Pseudokists, on the contrary, have an irregular shape and a thickened uneven capsule with seventure sites, the contents of the cyst are dense point and linear inclusions.
Endoscopic ultrasonography
EUS - a modern high-informative method of ultrasound diagnostics of PJ diseases, allowing to study in detail the structure of the tissue of the organ, the state of the duct system, carry out differential diagnosis PJ cancer pancreatitis (see Fig. 4-20), evaluate the size of parapaccreative lymph nodes and identify the cumoris of the PZh. EUS in the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis in patients with biliary-dependent formats of pancreatitis is launched, since EUS has significantly greater sensitivity than transabdominal ultrasound. In addition, EUS allows you to accurately identify areas of pancreatic and periccreatic liquid clusters with great accuracy, which may have a large prognostic value for heavy forms of CP and OP.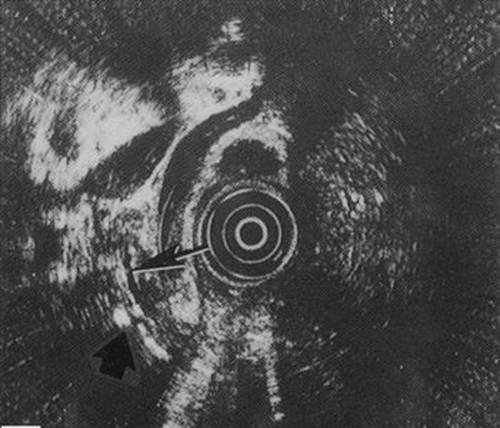
Fig. 4-20. Endoscopic ultrasonogram of the pancreas in chronic calculatory pancreatitis. The main pancratic duct is determined (shown by a thin arrow) with calcinate within the pancreas parenchyma (wide arrow). Round Target Structure in the Center - Tool
To date, the question of the introduction of clear diagnostic criteria for EUS with respect to the diagnosis of early HP or HP with minimal clinical and laboratory signs of the disease is unexcouted.
Main diagnostic signs of HP according to EUS:
. Changes in ducts: Conductors, hyperehogenic walls of ducts, curved walls of ducts, stricture, dilatation of ducts;
. Changes in Parenchim: Hyperehogenic trams, focuses and contours of robles, calcifications, cysts.
CT scan
CT makes it possible to diagnose, primarily at the stage of Pancreatitis complications, when the calcification, pseudokists, damage to neighboring organs, PJ and Malignization are most often found. Perhaps the only significant sign of an uncomplicated HP, which allows to identify this method, is a change in major gravel ducts (dilatation or stenosis). The sensitivity and specificity of CT largely fluctuate depending on the stage of the disease and amount to 80-90%. As criteria, HP according to CT data can be used various signs (Table 4-14).Table 4-14. Computer tomography data in chronic pancreatitis 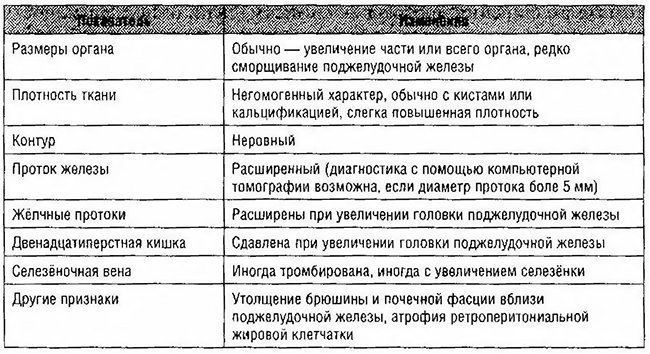
In exacerbation of the CP, the increase in PZ, the fuzzy of contours, infitthituration compromising, the heterogeneity of the body structure due to the areas of fibrosis, calcifications and calcifications in the tissue, PZh (Calcifying pancreatitis) (see Figure 4-21). For later stages of HP, it is also characterized by a decrease in the size of the PJ and the extension of Virsungov duct.
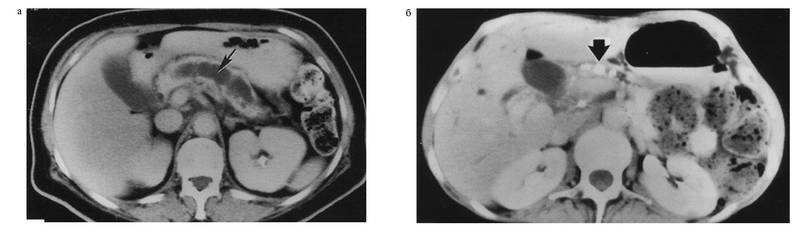
Fig. 4-21. Computer tomogram in patient chronic pancreatitis:a - determined by the significantly dilated main pancreatic duct (shown by the arrow), the atrophic parenchyma of the pancreas is significantly reduced in size; b - Multiple concrections are determined within the main pancreatic duct (shown by the arrow)
The main advantage of CT is the smaller frequency of failures that make a survey (obesity of patients, gases in the colon), which is observed when conducting an ultrasound. However, false-negative results are comparatively often; In a number of studies, unchanged tomograms were obtained in patients with a later proven HP.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancratography of the ERCPG according to most of the most modern scientific publications and guidelines - the "Gold Standard" of the diagnosis of HP. In the UK, the diagnosis of HP is only in the minimum number of cases on the basis of pancreatic laboratory tests, while the basic verification of the diagnosis is based primarily on the ERHP. It allows you to identify stenosis of the GPP and determine the localization of obstruction, detect structural changes in small ducts, intra-prototype calcinates and protein traffic jams, the pathology of the overall grain duct (stricture, choledocholiticiasis, etc.) (see Fig. 4-22 and 4-23). ERHPG is one of the most important research methods that allow differential diagnosis with pzh cancer.
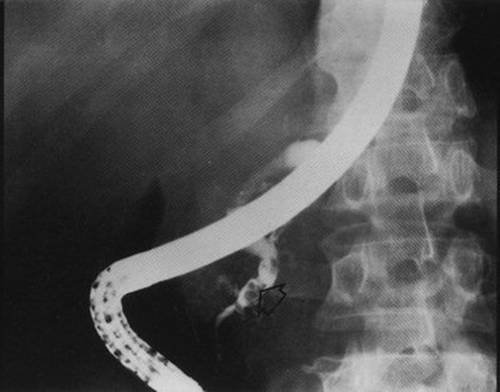
Fig. 4-22. A snapshot of a patient with obstructive calculose chronic pancreatitis is demonstrated. The concretion is defined in the main pancreatic duct (shown by the arrow). The terminal department of the main pancreatic duct contrasts to the level of intra-prototype
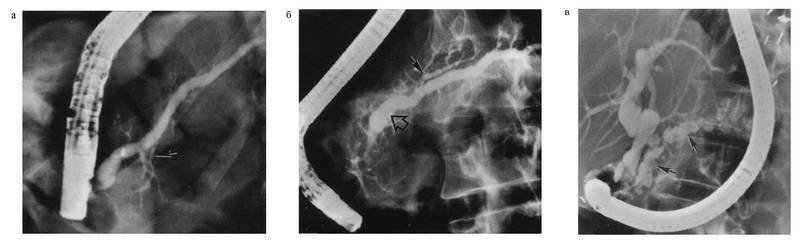
Fig. 4-23. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancratography in chronic pancreatitis.Device changes are demonstrated: A - unbearable changes with the minimum expansion of the main pancreatic duct (shown by the arrow); b - moderately pronounced changes in the pancreatic ductile system (the expansion of the main pancreatic duct is shown by a large arrow, the dilatation of small ducts is small); in - pronounced changes in the duct system ; Determined characteristic symptom "Chain-lakes" (shown by the arrow)
For HP, the irregularity of the contours of the ducts is characteristic, their tortileness, parts of the stenosis and dilatations - "clearly" duct, cystic expansion of the ducts - the symptom of the chain of lakes, the rigidity of the walls of the ducts, the presence of consolidation in them, expanding the side branches, their shortening and cliffs, slowing down Contrast in DPK. Similar changes may be celebrated by Kolado. The method also allows you to get pure pancreatic juice and carry out the endoscopic biopsy of the PJ.
Based on the results of the ERCP, you can set the stage of HP:
. probable hp (changed 1-2 small ducts);
. Light XP (more than three small ducts changed);
. moderate HP (defeat of the main duct and branches);
. Pronounced (change in the main duct and branches, intrappects defects or stones, duct obstruction, stricture or significant uneven lesion).
Table 4-15. Classification of pancreatomatograms in chronic pancreatitis 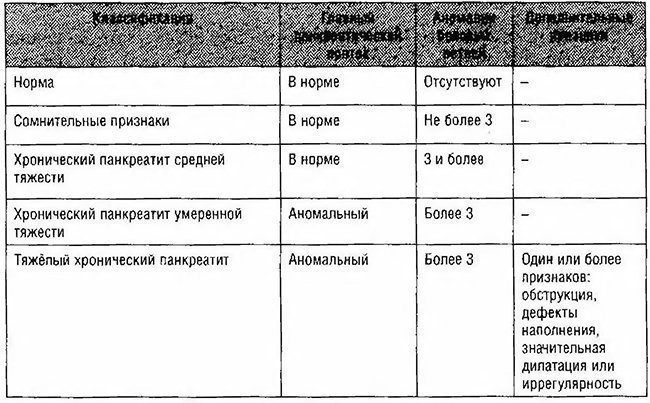
It is important to note that the degree of ductural disorders may not be correlated with the severity of the Functional Changes of the PJ, which makes a logical combination of ERHP with functional tests.
Erchpg- invasive procedure with low diagnostic performance with otchen pancreatitis and cholangitis. For this reason, at first should be used by an ultrasound or CT and resort to ERCP only in case of dubious diagnosis.
The ERHPG is of great importance for the diagnosis of autoimmune HP, allowing all patients to identify segmental or diffuse irregular narrowings of the GPP - a typical sign of this form of HP. In addition, ERCP allows dynamic monitoring for treatment in patients with autoimmune HP, since typical X-ray signs of autoimmune CP are reduced against the background of therapy with corticosteriodes, which allows the clinician to be confident in the adequacy of the therapy.
Maev I.V., Kucheryavy Yu.A.
Acute pancreatitis (acute inflammation of the pancreas) on ultrasound
In acute pancreatitis, pancreas increases in size. The increase in the pancreas is not always evenly. It is possible to increase only the head, sometimes the tail.
Three stages of acute inflammation of the pancreas are distinguished:
1. stage of edema,
2. Hemorrhagic-necrotic stage,
3. Destruction.
Edema.
The inflammation of the pancreas begins with edema, while the pancreas increases in size, the tendency to reduce its echogenicity, the structure of the gland does not change, the pancreatic contour is emphasized smooth.
Under the edema in the head area, the development of mechanical jaundice is possible.
It is possible to develop aggravating signs - accumulation into the glazing bag, effusion in pleural cavitieswhich can lead to lung atelectasis, intestinal atony.
With acute pancreatitis, an ultrasound is very hard - the belly will be taken, the patient experiences pain.
Hemorrhagically necrotic stage.
It is the second stage of acute inflammation of the pancreas. Microcharging occurs in the pancreas fabric, which leads to the dying (necrosis) of these areas of the pancreas. Pseudokists are formed - hypo echogenic or anechogenic sections are found. Pancreas has an uneven contour. Pseudokists look more likely as areas of reduced echogenicity. Anechogenic formations with smooth circuits are usually congenital cysts.
Destructive stage.
There is a destruction (destruction) of the pancreas tissue. The pancreas is practically unable to visualize the ultrasound. The organ is very loose, with sites of necrosis, fuzzy uneven contours. It is often accompanied by the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites), right-sided hydrotorax, the atelectasis of the lung, blocked bubble, flatulence.
Chronic inflammatory processes of the pancreas (chronic pancreatitis)
Chronic pancreatitis can leak without pain.
The ultrasound is revealed to increase the echogenicity of the pancreas, the contours are usually uneven, the dimensions usually remain normal, but when the fibrosis is developed, there is a tendency to reduce dimensions. Varsurung duct is usually not changed.
Diffuse pancreatic seal.
Most often arise against the background of violation of metabolic processes - with diabetes mellitus. Also often detected in old age. Diffuse changes Pancreatic gland is difficult to distinguish on ultrasound from chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas has increased echogenicity, normal dimensions, smooth contours. Virsurung duct is not changed.
The aggravation of chronic pancreatitis.
With the exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis, the pancreas increases in size, a tendency to reduce echogenicity appears, the Virsungov duct is possible, the appearance of pseudokists may appear.
Pseudokists There are intraparenhimatous and endophyte. Pseudocysts may have inhomogeneous internally content - pus, and also capable of mischievous.
With chronic inflammatory processes In the pancreas, it is possible to develop in its tissue calcinates, which look like small hyperehogenic structures with a weak acoustic shadow.
Fibroids of the pancreas
Fibrous changes in the pancreas occur under far-seated chronic inflammatory processes. This process is characterized by a decrease in the gland in size, the sealing structure, an increase in echogenicity. This process is irreversible.
Pseudotumorous form of inflammation of the pancreas
it is characterized by the development of morphological changes in inflammatory nature on a limited area of \u200b\u200bthe pancreas. When ultrasound, this process is almost impossible to distinguish from the true tumor. Recommended to perform CT or MRI.
Press on the pictures to enlarge.
Pancreatic cysts on ultrasound
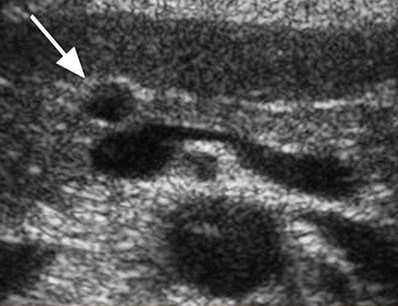
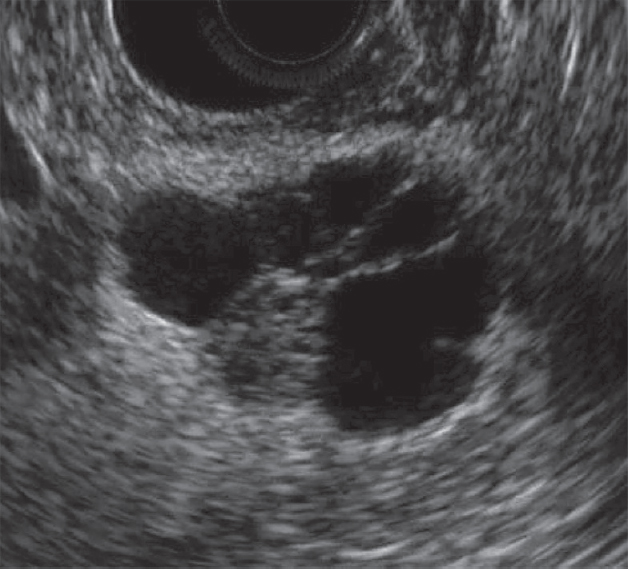
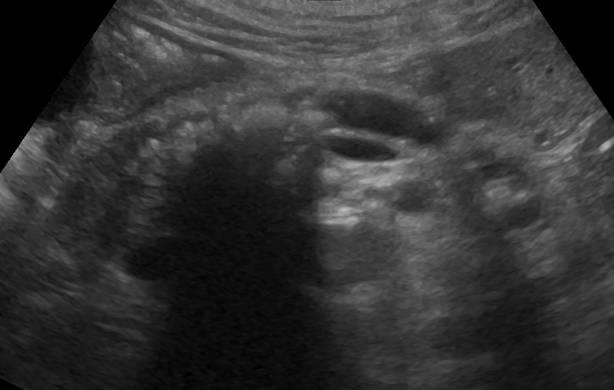
Single small simple cysts are found as random finds in a healthy pancreas. In chronic pancreatitis, small simple cysts are very common. When suspected of a cyst, pay attention to the gain of the outline of the far wall and the effect of the signal amplification in the tissues behind. Simple cysts are isolated from the parenchyma with a smooth thin wall. Inside there should be no partitions or irregularities of the wall, the contents of the cysts anechogenic. Simple cysts are always benign. But, if the cyst is not obvious "simple", further research is required.
| Photo. Simple pancreatic cysts on ultrasound. A, b - single simple cysts in the field of body (a) and neck (b) pancreas with a thin smooth wall and anechogenic content. In - classic signs of chronic pancreatitis: the main pancreatic duct is expanded against the background of the parenchyma atrophy, an outline of the gland is uneven with jar, in the parenchyma of ordinary and small cysts. | ||
 |
 |
|
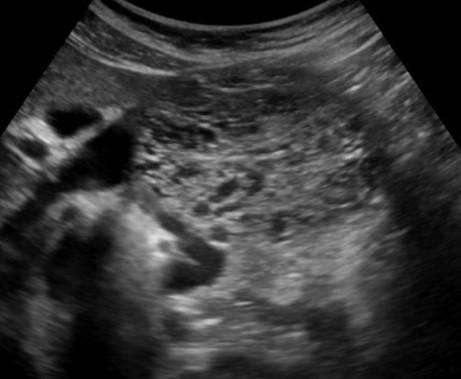
Important!!! Often there are simple pancreatic cysts, but do not forget about cystic tumors. Cancer is most dangerous disease pancreas.
There are two types of cystic pancreatic tumors: a benign microciste adenoma and malignant macrocyse adenoma. The microciste adenoma consists of a plurality of small cyst and looks like a dense education on ultrasound. Macrocyse adenoma, as a rule, includes less than five cyst of more than 20 mm. Sometimes in such cysts you can see polypoid formations.
| Photo. A, b - benign microciste pancreas adenoma: large cystic education In the pancreas head. B - pancreatic adenoma with the macro and microciste component. | ||
 |
 |
 |
With pancreatitis, the secretion of the pancreas digesors the surrounding tissues and pseudokists are formed. Pseudokists from abdominal cavity can go to chest and mediastinum. Often, pseudokists are found in patients who have undergone acute pancreatitis (see below).
As a result of a pronounced expansion of pancreatic duct, a distal place of obstruction can form retention pseudokists.
Acute pancreatitis on ultrasound
Acute pancreatitis is a severe complication of a gall-eyed illness or a consequence of toxic effects, such as alcohol.
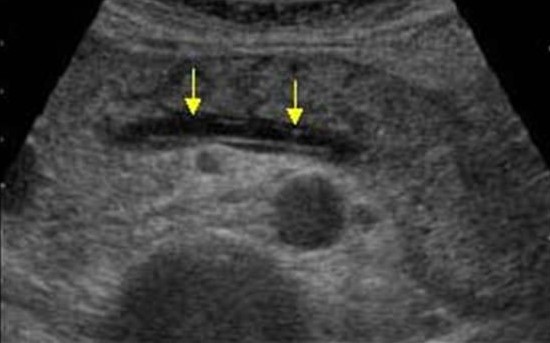
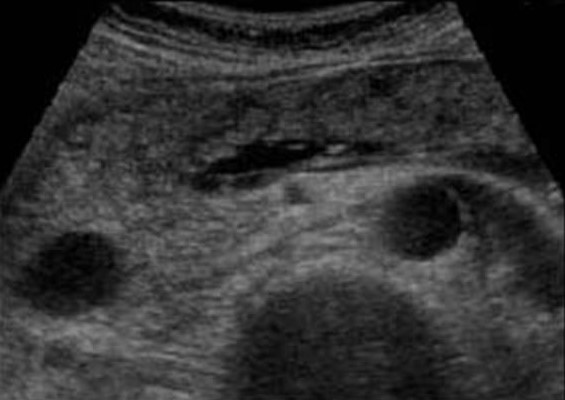
Light pancreatitis is not visible on the ultrasound (CT more sensitive method). Heavy pancreatitis is easily determined by ultrasound. When extraordinarily clear and contrasting pancreas stands out against the background of surrounding tissues, you can assume the edema of parenchyma and the surrounding fatty fiber. If around the pancreas, along the stomach, at the gate of the liver and spleen, a thin layer of free fluid is viewed, you can confidently diagnose pancreatitis.
| Photo. Acute pancreatitis on the ultrasound: a - edema of pancreatic parenchyma (P), the edge of the gland is extremely clear, a small cluster of the liquid along the boundary (arrows). B, B is a cluster of the liquid along the contour of the pancreatic body, the thin rim of the liquid in the course of the spleen vein (arrows), the parenchyma is inhomogeneous, the surrounding fiber of hyperhekin - swelling and inflammation, expanded the overall bile duct (B). In this case, it is necessary to exclude a gall-eyed disease. | ||
 |
 |
 |
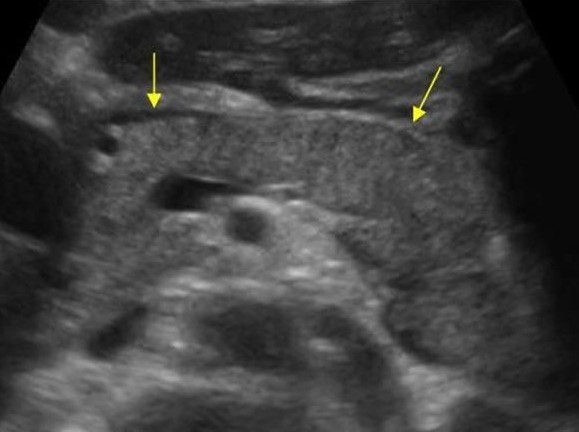
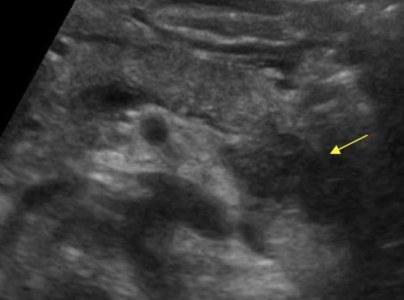
Almost all tumors of the pancreas are hypo echogenic compared to the normal pancreas. Only by ultrasound it is impossible to distinguish focal pancreatitis and pancreatic tumor. Tumor and pancreatitis can be combined.
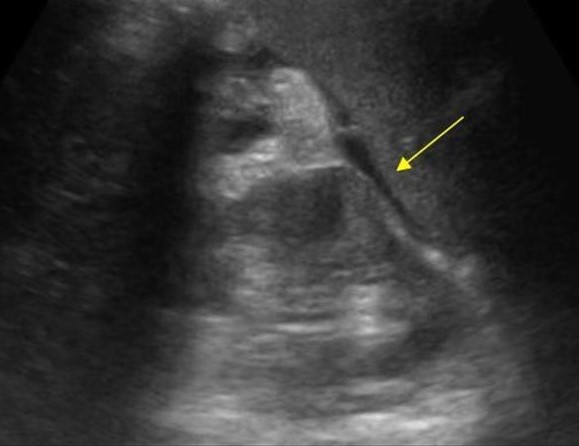
| Photo. Acute pancreatitis on the ultrasound: pancreas is unusually contrasted against the background of hyperheogenic surrounding tissues, a thin band of liquid along the contour (a), in the tail of a hypooehogenic focus (b), in the gate of the spleen liquid (B). A hypo echogenic tail can be mistaken for a tumor. | ||
 |
 |
 |
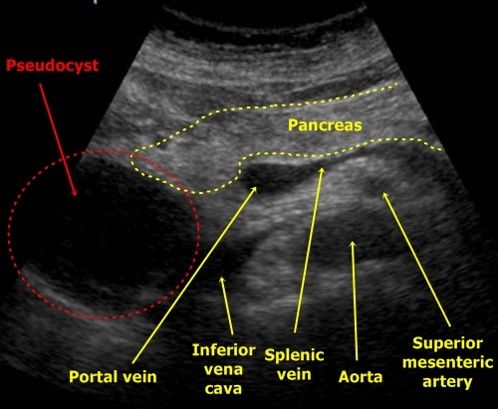
In severe cases of pancreatitis, pancreatic fluid digest the surrounding tissues, forming pseudocysts. Such cysts may be single or multiple. They can increase in size and break.
At ultrasound, pseudokists are defined as oval or rounded hypo echogenic formations with clear contours. In the early phases of the formation of a cyst, it represents a semi-liquid education and has a complex echostructure with internal reflections and fuzzy contours. Later, due to the autolytic processes and precipitates the suspension of blood and pus, clear signs of liquid content appear and a false capsule is formed with even walls. Often there is an infection of the pseudocyst, then internal echoes or thin tender partitions can be determined. When cyst is found, it is important to trace the connection of cysts with a duct, as it is important to determine therapeutic tactics. When a pseudokist is more than 10 cm in size, difficulties arise in determining its source.
| Photo. A is a large pseudocyst between the head of the pancreas and the liver after the transferred pancreatitis. B, B - heavy necrotic pancreatitis longitudinal (b) and transverse (c) cuts: extensive necrosis, melting surrounding in the area of \u200b\u200bthe tail, accumulation of fluid around the gland. | ||
 |
 |
 |
Chronic pancreatitis on ultrasound
Chronic pancreatitis can have different manifestations, from almost normal gland to pronounced atrophy and occurrence of parenchyma. Pancreas becomes thinner, pancreatic duct sometimes seems slightly expanded, the contour of the gland is often uneven with jar. Often there are simple cysts, and they can become quite large. Often, stones are formed in the pancreatic duct.
Calcifications in the pancreas on ultrasound
Important!!! If there is a dilatation of pancreatic duct, stones in the pancreatic duct and in the overall bile database should be searched.
Calcifications inside the pancreas can give an acoustic shadow, however, if they have small dimensions, they look like a separate bright echo essential shadow. In chronic pancreatitis, calcifications are distributed diffuse throughout the pancreas. Stones in the duct are located in the course of the duct. The bile stones in the distal choleret can be enrolled in the calcifications in the pancreas. Calcifications are clearly visible on the CT, and for unused stones, preferably MRI or ultrasound.
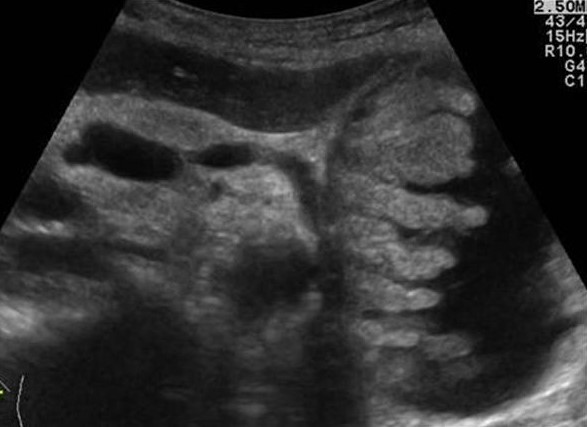
| Photo. A - in the extended dummy a small stone. B - in the extended pancreatic duct, a number of several stones with shading behind. B - in a patient with chronic pancreatitis huge stones in an extended dash. Pay attention to the intensive shading behind. | ||
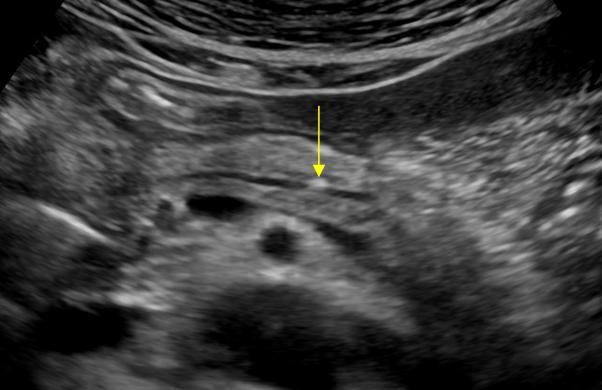 |
 |
 |
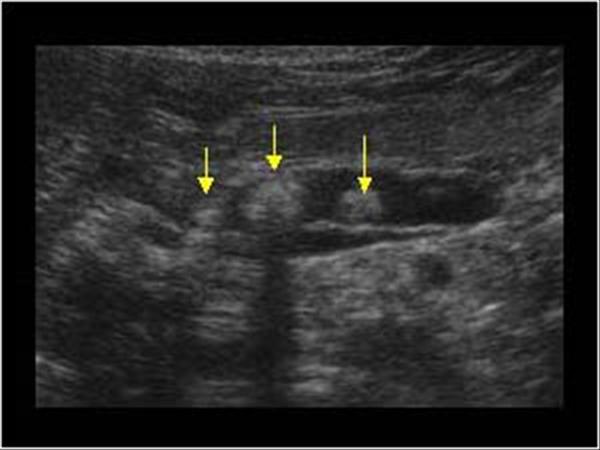
| Photo. A, b - calcifications in the pancreas parenchyma in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Some calcifications have a shadow. In - a boy of 5 years with chronic hereditary pancreatitis: Outbreaks (small arrows) and dilatation of pancreatic duct (big arrow). C is the merger of the upper mesenteric and spleen veins. | ||
 |
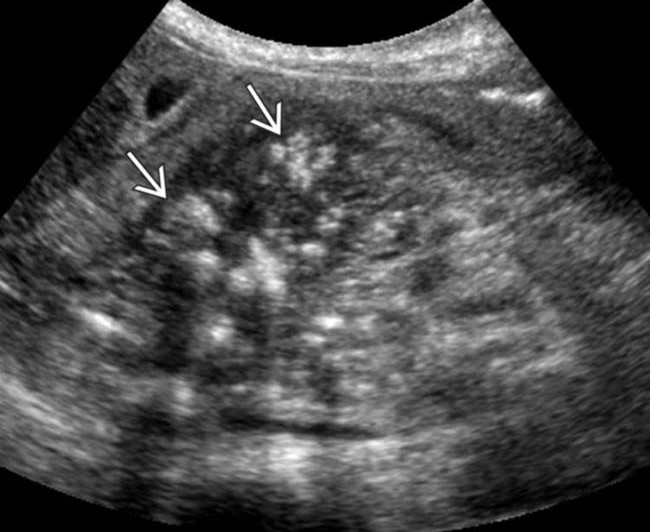 |
 |
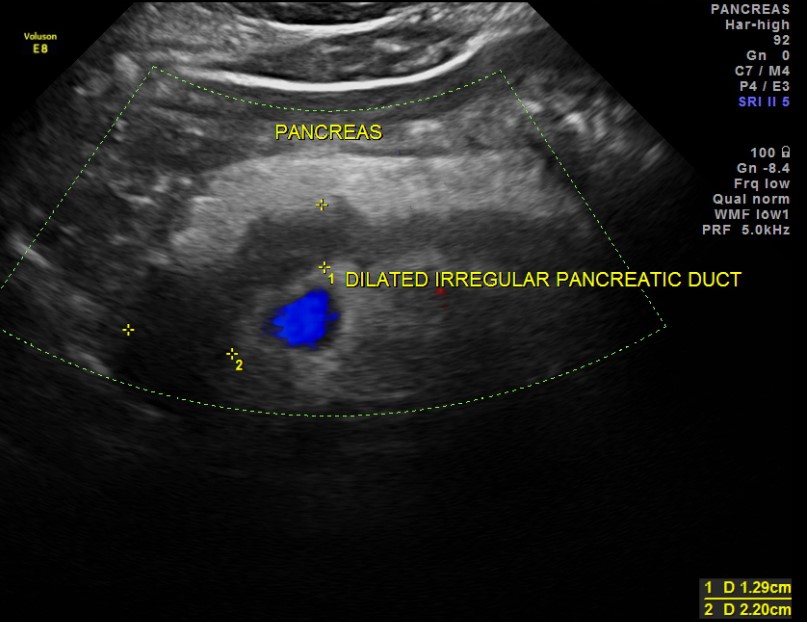
Advanced pancreatic duct on ultrasound
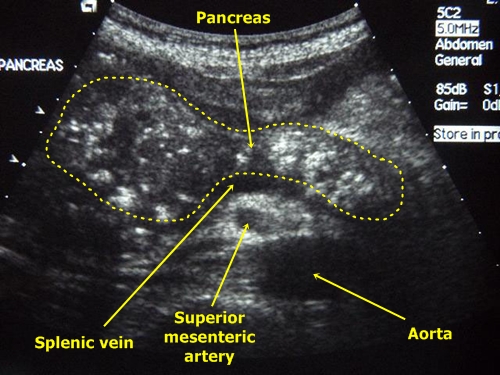
The internal diameter of the normal pancreatic duct is less than 3 mm. The duct is better visualized with transverse scanning in the middle third of the pancreas body. In order to make sure that you discovered the duct, you need to see the pancreas fabric on both sides of it. The spleen vein is behind or the stomach wall in front can be falsely interpreted as pancreatic duct.
The walls of the pancreatic duct should be smooth, and lumen clean. When the duct is expanded, the walls become uneven; Scan not only the head of the pancreas, but also the entire biliary tract.
The main reasons for the expansion of the pancreatic duct: the tumor of the head of the pancreas or the ampoule of the nipple of the nipple (combined with the jaundice and dilatation of the biliary tract); Stones of general gall or pancreatic duct; chronic pancreatitis; Postoperative spikes.
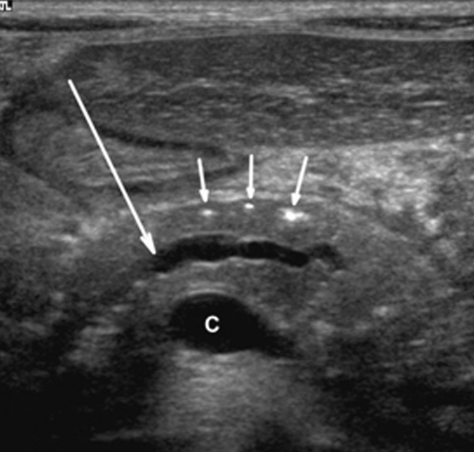
| Photo. A man with insulin-independent diabetes mellitus complains of weight loss and abdominal pain for a few months. On the ultrasound, the extensive overall dump of the pancreas with an uneven wall. With a further inspection, it is clearly visible in the calcification duct with the shadow behind (B). | ||
 |
 |
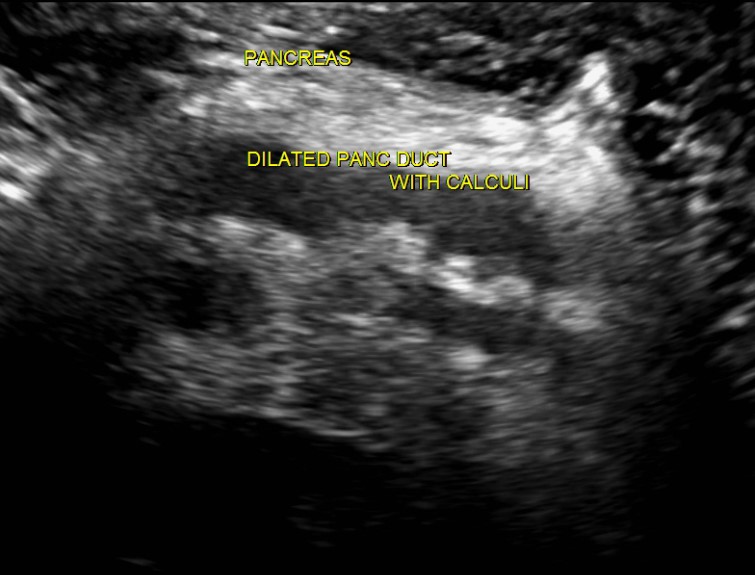 |
| Photo. Patient with sharp pancreatitis: a large pseudokist was formed at the tail level (see above), the extended pancreatic duct opens in the pseudokist. | ||
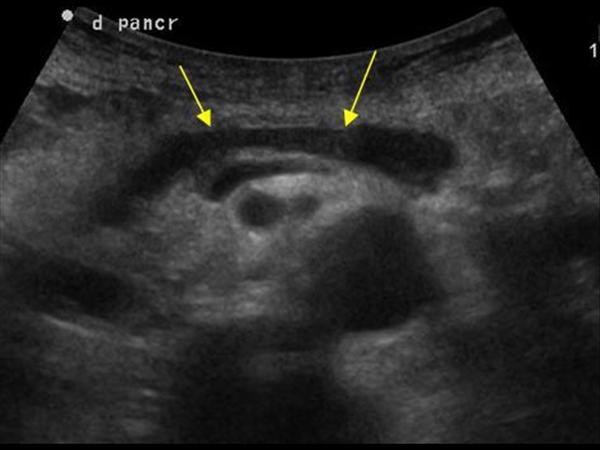 |
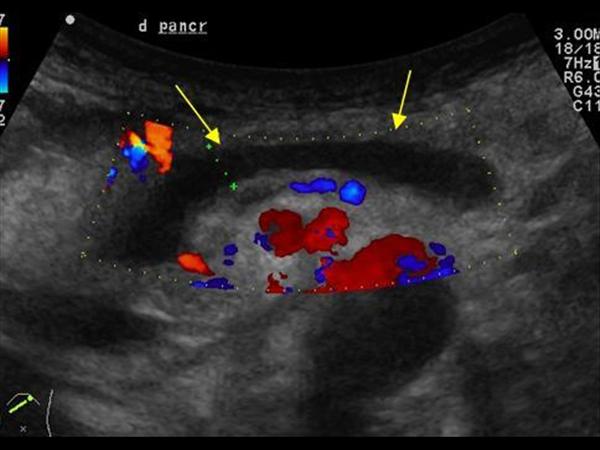 |
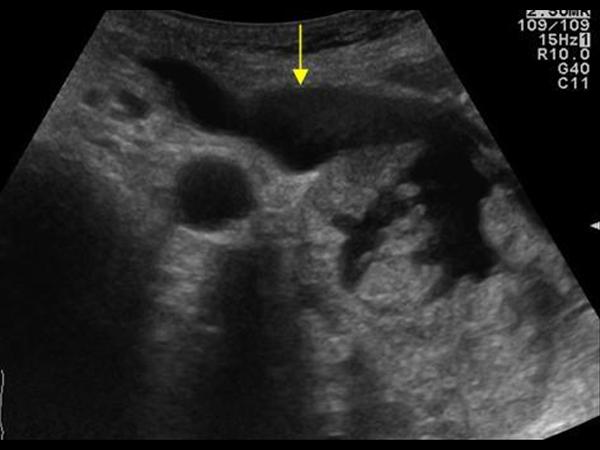 |
Pancreatic tumors on ultrasound
In most (50-80%) cases, the tumor affects the head of the pancreas. Head tumors squeeze the overall bull duct. When cancer contour pancreas, fuzzy, characterized by a local increase or esteem, sometimes embedded in the surrounding tissue in the form of languages \u200b\u200bor pseudopodies.
In most cases, the pancreas tumor is a hypo echogenic formation, almost deprived of internal echoes. However, there are tumors with diffuse scattered echoes and high-intensity echoes in the center in their absence on the periphery. Despite the fact that the border between the tumor and the rest of the parenchy gland is fuzzy, it can always be approximately carried out due to the difference in the echogenicity of normal tissue and tumor focus.
Although the hypo echogenic structure of the tumor, especially in the absence of small sections of increased density in it, resembles such at cysts, the absence of the effect of distal amplification makes it possible to eliminate the liquid nature of education. For a cyst, moreover, a much more flattened and clear boundary is characterized.
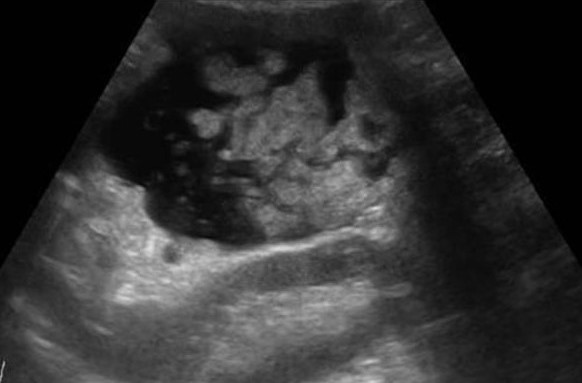
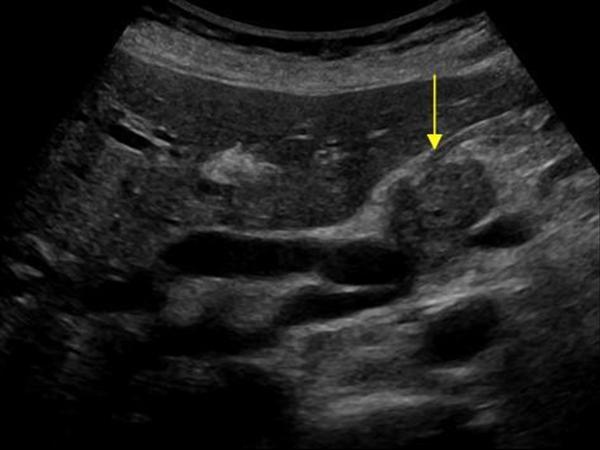
| Photo. The carcinoma of the pancreas head (arrow): the overall bull duct (A) and the pancreatic duct (b), hypo echogenic tumor surrounds the upper mesenteric vein (B). | ||
 |
 |
 |
In tumors of the pancreatic head, the overall biliary and pancreatic duct is very often expanded, unlike chronic wall pancreatitis, it is smooth and infertable.
Important!!! The visualization of the main pancreatic duct within the hypo echogenic zone indicates the benefit of local edema and against the tumor.
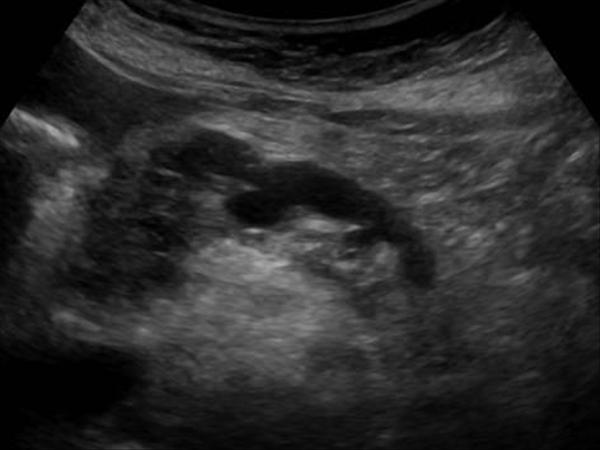
Sometimes in the pancreatic cancer, typical signs of chronic pancreatitis are revealed, as well as pseudokists distal than tumor obstruction site. This is a consequence of obstruction. Intrahranny metastases, enlarged currency, periportal and retroperitoneal lymph nodes indicate cancer.
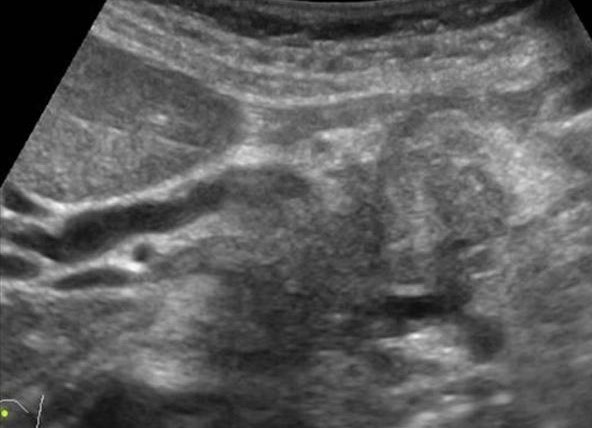
| Photo. The carcinoma of the pancreas head: the outline of the head is uneven due to volumetric hypochogenic education, the body parenchyma is very thin (atrophy), expanded pancreatic (a) and common bull (b) ducts, in the gate of the liver, a large rounded lymph node (B). | ||
 |
 |
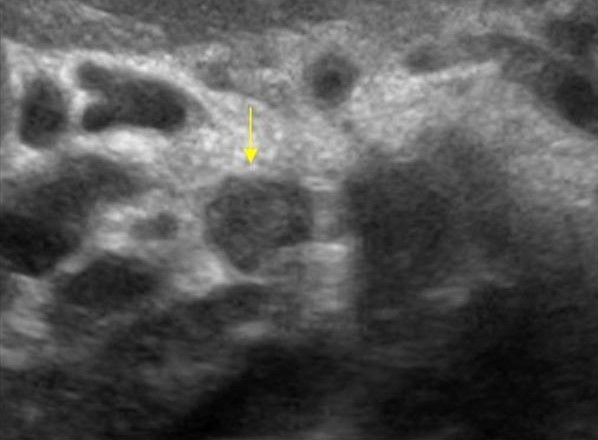 |
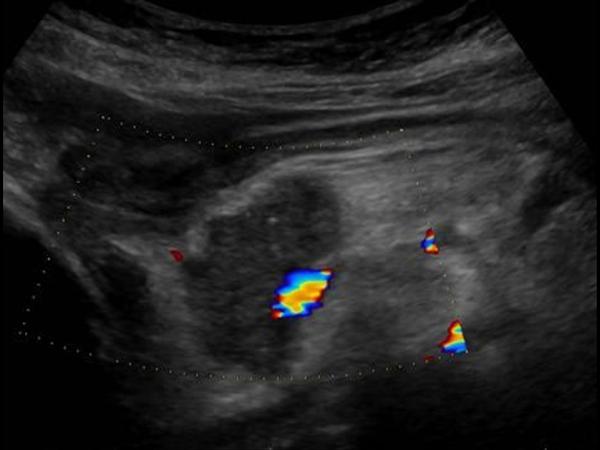
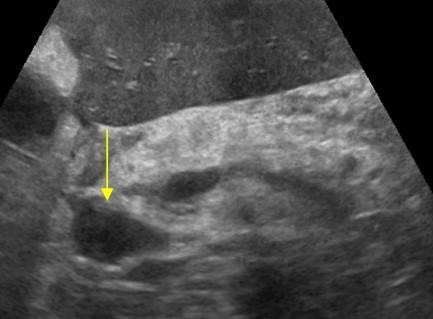
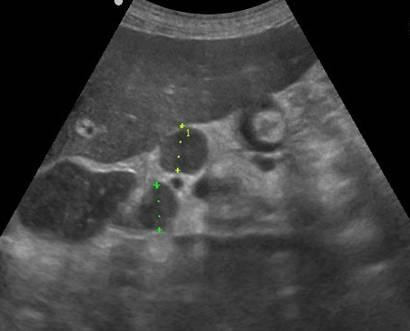
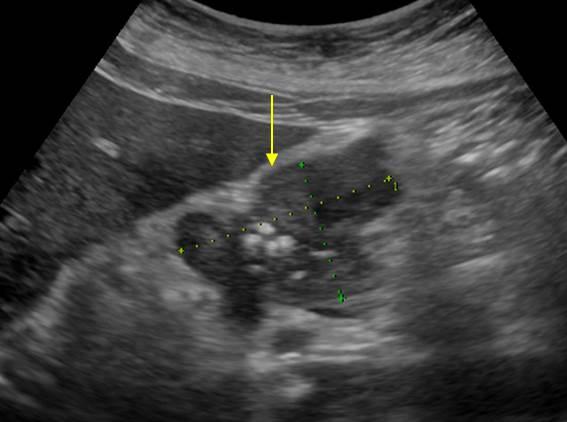
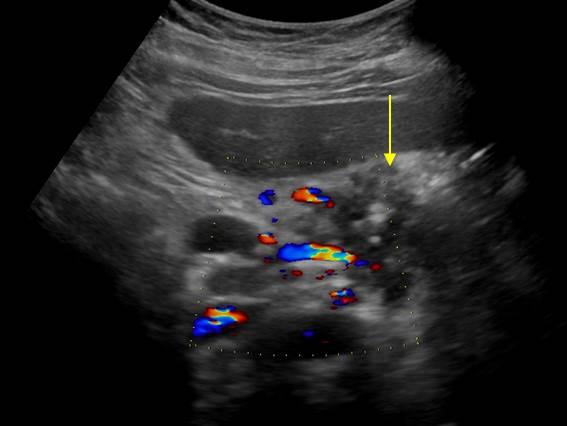
| Photo. Large lymph node (arrow) near the pancreas can be mistaken for a head tumor. Increased mesenteric lymph nodes of the rounded shape, hypo echogenic and without a central rutter, which indicates their malignancy. |
||
 |
 |
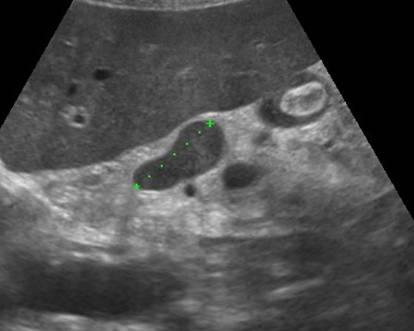 |
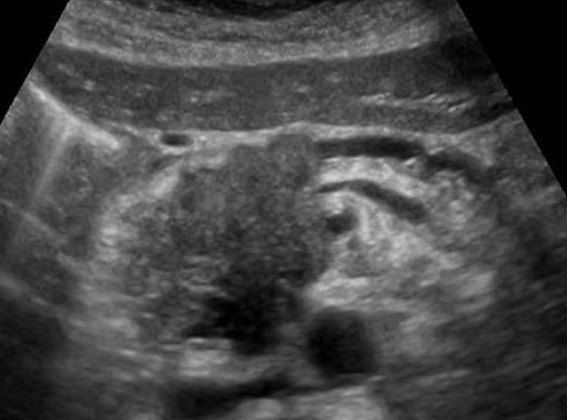
| Photo. Big neuroendocrine tumor (arrows) of the pancreas with observation and metastases in the liver (B). | ||
 |
 |
 |
Take care of yourself, Your diagnostic!
Read also ...
- The work of "Alice in Wonderland" in a brief retelling
- That transformation. "Transformation. Attitude towards the hero from the sister
- Tragedy Shakespeare "King Lear": the plot and the history of the creation
- Gargantua and Pantagruel (Gargantua et Pantagruel) Francois Rabl Gargantua and Pantagruel Brief



















