The composition of the unemployed. Indicators of the composition and structure of occupied and unemployed. Distribution at the place of residence
Unemployment in its total mass causes great interest and the need for action by the state. However, no less attention is deserved and the unemployed themselves separately. Who are these and whom we can rightfully consider the unemployed?
We present the interpretation of the unemployed, this M.G.Nazarov in the textbook "course of socio-economic statistics". This author suggests that the unemployed is the persons who have reached a certain age adopted in national legislation as the lower border of working age, which during the period under review did not have the work (income), but they were engaged in the search and were ready to start working immediately or during a period defined by national legislation. Note that the authors of other sources are quite solidar with MG Nazarov on the issue of determining the unemployed.
Speaking about searching for work, it means an active search for it. That is, the unemployed should apply to public or private employment services or directly to the administration of enterprises and organizations, put ads in the press, use personal connections or take attempts to organize your business.
In addition, the unemployed includes persons studying in the direction of employment services. As an unemployed, students and students, people with disabilities and pensioners are taken into account if they are actively engaged in looking for work and are ready to proceed.
The above-described criteria for the unemployed correspond to the methodology for determining the number of unemployed, proposed by the International Labor Organization (ILO). The unemployed calculation according to the ILO method can be carried out only on the basis of periodic sample surveys (population surveys) on employment issues organized by the State Statistics Committee.
But also as part of the unemployed, persons who are not engaged in employment registered in the employment service as job seekers, as well as recognized as unemployed.
The Ministry of Labor and Social Development keeps accounting for unemployed through public employment services. In accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation "On Employment of the Population in the Russian Federation" of April 19, 1991, the unemployed is recognized by the working citizens who are not working, seeking work, ready to begin it and in the established manner registered in the employment service bodies. So determine the number of official unemployed.
Speaking of unemployment, it is impossible not to note the composition of the unemployed. The social composition of the unemployed funds of statistics is obtained in analyzing the data of the sample survey on employment issues and from the employment authorities on annex to form No. 1-T (employment) "Report on employment and employment" for the year. The report contains information on the qualitative composition of the unemployed (distribution of them by sex, age, level of education for the reasons for dismissal, the presence of children, profession, specialty). The study of the qualitative composition of the unemployed contributes to the development of a more effective employment policy (subsidies for expanding jobs, the system of training and retraining of labor, promoting entrepreneurial activities, etc.).
In order to correctly assess the situation in the labor market, it is necessary to analyze the reasons that led citizens to the status of the unemployed.
An analysis of the distribution of unemployed by the floor refutes a very common thesis that the unemployment is "female" face. In the total number of unemployed, the share of men has always exceeded the proportion of women, in 2000 the share of unemployed men was 54.3%. However, women were dominated among the official unemployed - 69.7%. See: Statistics: studies. / I.I. Eliseeva, I.I. Egorova etc.; under. ed. Prof. I.I. Eliseeva. - M.: TK Velby, Publishing House Prospekt, 2004. - s. 306 .. This suggests that women experience more difficulties in solving the problem of employment, and the unemployed men are more often trying to work independently.
On the unequal position of men and women in the labor market, the fact that, despite a higher level of education, the work of unemployed women remains unclaimed. Higher and incomplete higher education, according to the survey in November 2000, had 18.5% of unemployed women and 12.4% of unemployed men, secondary vocational education -, respectively, 26.2 and 19.3%.
The age of unemployed reflects the problems of the employment of young people, which has special social significance. The average age of the unemployed is 35.1 years. The share of young people up to 30 years is 37.7% of the total number of unemployed, while their share in the total number of employed - 23.6%. The share of unemployed older ages (over 50 years) is much lower than their share in the numbers of employed (12.2 and 17.9%, respectively). Consequently, the availability of work experience is one of the factors that increase the likelihood of employment. At the same time, in 2000, 18.1% of the unemployed did not have experience.
The situation in the labor market is characterized by an increase in the number of persons, for a long time not working, and their shares in the total number of unemployed. Under the duration of unemployment V.N. Salin, along with E.P. Shpakovskaya in the textbook "Socio-economic statistics" understand the duration of the period during which the unemployed is looking for work. There is a duration of unfinished unemployment - time from the moment of finding work to the period under consideration (the moment of the survey), and the duration of complete unemployment - the time since the start of job finding until the time of employment. For long unemployment believes unemployment for 12 months or more. The share of a long unemployed is constantly growing.
Along with the information about the unemployed employment services, they collect information about the needs of enterprises and organizations in labor. In particular, the need for enterprises and organizations the need for employees is the number of vacancies (vacancies). Based on these data, the amount of demand for labor is calculated - the total number of jobs equal to the sum of the actual number of working and number of vacancies.
It should be noted that in the existing system of information support of the labor market (not only in Russia, but also in almost all CIS countries) the weak link is the statistics of demand for work. Currently, the analysis of the balance of demand and supply of labor, as a rule, is based on the data of employment services, although it is not known that information about vacancies reported by enterprises to these services (that is, the application for labor) is clearly underestimated. The study of demand statistics is advisable to build on the basis of information collected directly by state statistical authorities from enterprises and organizations, while achieving the confidence of information based on inspections, personal surveys, etc.
A balanced labor market is if there is a number of vacancies in it approximately coincides with the amount of unemployed. Such a condition does not mean the achievement of professional qualification compliance, but only indicates the quantitative coincidence of supply and demand, to evaluate which the coefficient of tension in the labor market is calculated - the ratio of the number of unemployed to the number of stated vacancies.
ProvocumenisySectoral prey, formations of the formation Economic Economics, Technical Power SuppliesPert-FEFFECTICFECTIONINGTRUKTRUEEEKOMIKOVEKOVEYCOVERSION is the mobility of labor. The category of mobility reflects the combination of various types of labor movement in the labor market: professional, qualifying movement, the movement of labor between enterprises, industries, regions. Mobility pledge is the polivalence of the employee. The polivalent worker has the appropriate stage of development of professional training, it is capable of working not only on its own, but also on related specialties, to quickly adapt to changing production conditions, mastering new skills and technologies, quickly respond to changing demand for labor, its price, etc. .
The combination of employee polivalence, its mobility and good health meets modern working conditions and is the main criterion for the competitiveness of the employee in the labor market.
Since 2001, the Ministry of Labor and Social Developed RF has introduced the practice of determining the constituent entities of the Russian Federation related to territories with a tense situation in the labor market. The procedure for identifying such territories is provided for by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 2, 2000 No. 875 "On the rules for attributing territories to territories with a tense situation in the labor market."
Goskomstat annually until March 15 presents data on the Russian Federation as a whole and on the subjects of the Russian Federation in the last 2 years in six indicators:
employment level in% of the total population aged 15-72 years;
the level of common unemployment (ILO unemployment);
the level of registered unemployment;
the share of unemployed, job seekers 12 months or more, in the total number of unemployed;
share of working part-time and holidays on the initiative of the administration in the total number of employees (on large and secondary organizations);
The coefficient of tension in the labor market.
Regions of the Russian Federation are ranked by values \u200b\u200bof indicators, i.e. They are assigned a number within a certain dependence on the value of the indicator: the greater the value of the indicator, the greater the sequence number. Only indicators of the level of employment are ranked in the inverse dependence on the value. With an equal size of one indicator, the same sequence number is assigned in different territories. For each subject of the Russian Federation and for the Russian Federation as a whole, the average sequence number (general indicator) is calculated in the middle arithmetic formula.
The level of tension in the labor market is determined by dividing the average sequence number (middle rank) in a given territory to a similar overall figure in the Russian Federation as a whole. If the average sequence number on the territory exceeds the overall figure in the Russian Federation by more than 1.5 times, then this subject of the federation is considered a territory with a tense situation in the labor market.
The commissioned procedure was intended to contribute to the development of practical measures, purposeful, addressing policy to stabilize the labor market of concrete territories, taking into account regional characteristics and interests.
When calculating the unemployed, attention should be paid to the problem that appeared in Russia and a number of other countries and which must be solved. We are talking about employees of enterprises sent to the so-called administrative leave, which can be both partial maintaining content and without maintaining content. In this case, the duration of this vacation is quite significant. In this case, although these individuals have formal relationships with the employer, many of them are looking for another job and are ready to proceed.
Analysis of foreign experience shows that in other countries there are also persons in a similar situation. But at the same time, the duration of administrative leave does not exceed 2-3 weeks, a maximum of one month. After that, the individuals are taken into account in the unemployed category.
Taking into account the fact that persons who are in administrative leave are often in a situation with more severe than those officially recognized as unemployed and have the right to receive unemployment benefits, appropriate adjustments should be made to the definition of unemployment, which would allow both persons having Formal ties with employers, as they are in administrative leave, after the expiration of a certain period (for example, a month), take into account as unemployed.
Based on the foregoing, we see that the composition of the unemployed is diverse, and it can be considered through the prism of various categories, and the number of unemployed may vary depending on the method of calculating the unemployed. For example, the number of officially unemployed is usually significantly lower than the number of unemployed, determined by the ILO methodology. And how to celebrate domestic and foreign scientists, the adopted unemployment accounting system in our country does not reflect actual trends in the development of the Russian labor market, since most of the unemployed are not registered on labor exchanges, preferring to look for work independently or resorting to the services of non-state intermediary structures (recruitment agencies, etc. .). In addition, the labor market in the Russian Federation is not balanced and, in the context of the global crisis, it is not yet necessary to count on an equal number of unemployed and vacancies. We can assume that at present, the consideration of Russia has a significant number of territories with a tense situation in the labor market. And the problem of increasing the number of administrative unpaid vacations today is becoming more acute.
The social composition of the unemployed funds of statistics is obtained in analyzing the data of the selective examination on employment problems and from the employment service authorities on annex to form No. 1 -T (employment) "Report on employment and employment" for the year.
The report contains information on the qualitative composition of the unemployed (distribution of them by sex, age, level of education, reasons for dismissal, the presence of children, profession, specialty). The study of the quality of the unemployed contributes to the development of a more effective employment policy (subsidies for expanding jobs,
Tab L and Tsa 9.6 The structure of the unemployed for the availability of work experience and reasons (%) Indicator October 1995 November 1999. Total unemployed including: Do not have experience 100 100 have experience: 16.8 18.9 left the former Place of work 83.2 81.1 in connection with: release, reduction of states, liquidation of enterprises, own business 28.3 32.4 at their own desire 39.4 21.3 ending with temporary, seasonal work, contract 4.8 5.1 dismissal from the Armed Forces 1.5 0.6 by other reasons 9.2 21.7 the workforce preparation and retraining, encouraging entrepreneurial activities, etc.).
In order to correctly assess the situation in the labor market, it is necessary to analyze the reasons that led citizens to the status of the unemployed. In Russia, the acuteness of the problem of unemployment depends largely on changes in the structure of the economy and the conversion of the military industrial complex. Therefore, among the reasons for the dismissal, the first place in 1999 was engaged in the release of employees, the dismissal of them in connection with the reduction of states, the liquidation of the enterprise, their own business (Table 9.6).
As can be seen from the table. 9.6, among the reasons for the loss of work, not only the release of employees was played with a significant role in connection with the reorganization of production, but also their dismissal on their own desire, which is often hidden not only dissatisfaction with the content and working conditions, its payment, but also structural changes in production. Velika share and persons who were resolved by other reasons not disclosed today: 21.7% in 1999
Among the unemployed registered in the employment service bodies, women prevail, in the overall number of unemployed, calculated on the ILO methodology - men (53.9% in October 1995; 54.2% in October 1997; 59.4% in October 1998; 52.4% in November 1999). For the reasons for unautability among men, the dismissal at their own desire is more common: for 1995-1999. The proportion of persons without work for this reason were fluidated in the following limits: 43.9% in October 1995 and 24.2% in August 1999, and among women - 34.1% in October 1995 and 15 , 4% in August 1999
The acuteness of employment problems largely depends on structural changes in the economy. The release of workers is often connected with technical progress, and with a decrease in production volumes, and with its reorganization, and with the conversion of the military-industrial complex. Different reasons for reducing jobs determine the relevant system of social protection measures unemployed. At the same time, the uneasy real possibilities of help in employment with significant differences in the labor market situation lead to strong differentiation of regions in terms of officially registered unemployment.
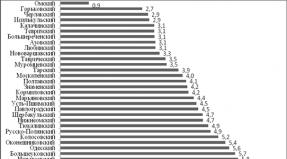
Distribution of Russia regions in unemployment in 1998
Such:
Unemployment rate,% regions up to 8 3
8,1-12 12,1 - 16 16,1-20 20.1-
32.1 or more
The unemployment range of the unemployment in the regions is quite wide: the coefficient of variation was 40.6%. The most acute problem of unemployment is in Ingushetia (51.1% unemployed), Kalmykia (30.8% unemployed), Dagestan (30% unemployed).
The educational level of unemployed in Russia is one of the highest in the world: at the end of November 1999, 41% of the unemployed had a higher and secondary special education, in major cities this figure even higher. The unemployed women tend to have a higher level of education than men: So, in Russia as of December 1, 1999. Among the unemployed women, 48% had a higher and secondary special education, which is 13 percentage points higher than among men. The educational composition of the unemployed can be compared with the similar composition of those employed according to selective studies of the population of Russia in November 1999 (Table 9.7).
Differences in the share of persons with higher education in the composition of the economically active population - occupied and unemployed - the percentage of persons with higher education among the economically active population The population of employed unemployed total economically active, thousand people 60 631,9070 69,701 persons with higher education,% 20 , 9 10.3 19.5 Estine: 10.6 percentage points. This means that education acts as an important employment factor.
At the same time, education is not a factor in social protection against unemployment. In the future, we can expect the growth in the sustainability of the position of the employee in production with the growth of its educational level. This trend can be observed in Western countries.
From the position of the professional orientation of the unemployed, it is necessary to study their age composition. The main part of the unemployed in Russia makes up people of mature age. Distribution of unemployed in Russia by age at the end of November 1999, if they take their amount per 100%, such1: age (years)% 16-19 7.4 20-24 15.9 25-29 12.8 30-34 13,4 35-39 15.4 40-44 12.3 45-49 10.2 50-54 4.5 55-59 5.4 60-72 2.8 The average age of the unemployed was 33.9 years.
Age can be taken into account when developing concrete assistance measures unemployed. For example, in France after the expiration of the unemployment benefit (65 months), unemployment assistance is allocated, the value of which depends on the age of the unemployed: from 65 to 130 fr. per person per day.
Special social significance has unemployment among young people. At the end of November 1999, 36% of the unemployed was people under the age of 30. In a number of regions, the employment of young people are engaged in the country's employment employment service, youth labor exchanges, as well as an interregional employment center.
To predict employment and unemployment, information about the duration of unemployment is necessary. This kind of data is used in most countries of the world.
Unemployment duration in Russia at the end of November 1999
g. reached six groups:
Time interval (month)% to the total number of unemployed
and more than 47.3
Compared to the countries with a developed economy in Russia, the proportion of the first group is too small and very high.
For example, in the USA in 1990 less than 1 month. There were no work about 47% of those who lost it, and only every twentieth did not have it over 1 year25. The high proportion of persons who did not have a job less than 1 month, means that unemployment does not lead to social explosions in society. On the contrary, a high percentage of persons with the status of unemployed more than 1 year is one of the signs of chronic unemployment.
Based on the distribution of the unemployed, it is possible to approximately determine the average duration of unemployment as an average arithmetic weighted:
T \u003d i tjnj / zni, where g, - the time of lack of work in the group;
L /, - the number of unemployed / among the group.
Since the time of lack of operation is set in the intervals, then in the calculation, the middle of the interval is used, i.e. 0.5; 2.0; 4.5; 7.5; 10.5 and 13.5 months. Due to the fact that unequal time intervals are used as weight for calculating the average duration of unemployment, it is more correct to apply not initial data on the number of unemployed in each group, but relative to the distribution density, i.e., the percentage of the unemployed percentages for the same value Unemployment time interval, for example, 1 month. In our case, the relative density of the distribution will be in groups: 0.5; 4,733; 3.375; 2,125; 2.475 and 11,825. You can determine the relative distribution density per 4 months., Then only the percentage of the unemployed first and second groups is subjected to recalculation, i.e. we will have the following values \u200b\u200bas weights: 26.4; 18.9; 13.5; 8.5; 9.9; 47.3. Using both weighing systems, we get the same result of g S \u003d 7.4 months. However, due to the very large "weight" for the last group with an open interval, this calculation gives an inaccurate result.
If, as "weight", use the initial data of the variational series, then the average duration of unemployment will be equal to 9 months, which is slightly lower than its real value of 9.7 months. Median duration of unemployment is 11.2 months. Calculation of medians was produced by the formula
NME ~ ^ i-1 ^
where * o is the lower boundary of the median interval (9), i.e. the first interval with the accumulated frequency of 50 and more%;
/ - the magnitude of the median interval (3);
NMC - median sequence number (50);
^ ms - ~ ~ accumulated frequency of the premedified interval (42.8);
fME is the local frequency of the median interval (9.9).
The magnitude of the median shows that about half of the unemployed are looking for work more than 11.2 months.
The search time of work is quite closely related to the age of the unemployed and differs significantly on the floor. A large duration of the average time to find a job is observed in unemployed older age groups: the variation range was 4.5 months in November 1999., including for men - 3.7 months, for women - 5.5 months. The strength and tesne of this relationship also differ in the floor (Table 9.8).
The correlation coefficients indicate a fairly close connection, since their values \u200b\u200bare close to 1 (especially in women). Determination coefficients reflect the dependence on 89% of the average time for finding work in women from age-related changes. For men, this figure below is 75%. They differ in the floor and regression coefficients: with an increase in age for 1 year for men, the average duration of unemployment increases by 0.064 months., I.e., for 1.9 days, for women - by 0.093 months, or 2.8 days. The results of the analysis of the dependence of the average time to search for work unemployed (y - months) by age (x - years),
november 1999, Russia Regression equation Correlation coefficient, r determination coefficient, r2 F-criterion * All unemployed y \u003d 6,897 + 0.076x 0.925 0,856 47.6 Men y \u003d 6,849 + 0.064x 0,866 0,750 24.0 women y \u003d 6,806 + 0.093x 0.943 0.890 64.7 * Table value of the F-criterion at the level of significance of 0.05 and the number of degrees of freedom 1 and 8 is 5.32. The difference of data differences is confirmed by the Fisher's F-Criterium value, which for all equations above the table value. The calculation of the F-criterion is carried out by the formula
F \u003d -c-gp-2l 1
where n is the number of age groups.
The definition of the value of G2 and the construction of the regression equation is carried out in accordance with the methods set forth in the theory of statisticals26.
Similarly, it is possible to study the composition of unemployed for the duration of receipt of unemployment benefits: through the distribution of the unemployed in the duration of the time of receipt of the benefit.
Since 1994, in statistical reporting, there is information on the duration of unemployment of persons with disabilities as one of the socially not protected segments of the population requiring special care from the state. The average unemployment period in persons with disabilities is longer than as a whole throughout the totality of the unemployed. To disabled realized employment assistance, in many countries, enterprises are obliged to provide a certain part of jobs to disabled or deduct the relevant amounts to the disabled assistance fund. In Russia, enterprises in the number of employed people with disabilities account for at least 50%, have some tax benefits.
Unemployment is a social phenomenon involving the lack of work in people who make up the economically active population.
According to the definition of the International Labor Organization, a person aged 10-72 years (in Russia 15-72 years) is recognized as unemployed, if the critical week of public survey on employment issues is simultaneously:
Did not have work
I was looking for a job
Was ready to start work
Tab. 6 Number of unemployed citizens of the Omsk region
The smallest number of unemployed citizens was observed in 2008, then an increase in the number of unemployed and in 2010 reached 101 thousand people. In comparison with 2000, the number of unemployed significantly decreased. But, if we consider the number of unemployed citizens registered in government agencies of the employment service, then the smallest value is 2000, only 15.4 thousand people. The greatest number of unemployed citizens registered in government agencies of the employment service falls for 2009, in 2010 there is a decrease in 3 thousand people.
You can sum up with small results in 2011. To do this, it is necessary to analyze the following table.
Tab. 7 The number of unemployed citizens registered in government agencies of the employment service in 2010-2011
1) According to the General Directorate of the State Employment Service of the Omsk Region.
2011 began with an increase in the number of unemployed. For the month, the number of unemployed increased by 0.4 thousand people. Accordingly, unemployment benefits were more paid.
Also analyzing 2011, you can view the unemployed 2011 in the total number of employees.
Tab. 8 The number of employees and the unemployed 2011.
1) organizations with more than 15 people are taken into account.
It can be seen from the table that all indicators are less than the indicators of the same period of the previous year. The unemployed status has about 17% of the average number of employees of organizations.
Fig. 3.
Fig. four The level of registered unemployment (by municipal regions of the region) on March 1, 2011,% of EAN


Fig. five
For all 3 months, the smallest level of registered unemployment was in the Omsk district. Such areas like the Claork, Gorky, Bolshechensky, Iscikulsky, Tevrisian, Azov, Falisin have a level of unemployment equal to approximately 3. The worst situation with the unemployment rate is observed at the Nazivsky, Sargat, Kratutinsky, Babevsky, Odessa and Sadelniki districts. Here the unemployment rate is greater than 5.
From the data of the General Directorate of the State Employment Service of the Omsk Region, the number of registered unemployed in the Omsk region as of April 1, 2011 is 18861 people (on April 1, 2010 - 22,399). The level of registered unemployment is 1.8 percent of the economically active population (as of April 1, 2010 - 2.1%). According to forecast estimates, the level of registered unemployment in March of the current year will be 1.8%. The need declared by employers the need for replacement of free jobs (vacant posts) in the first quarter of 2011 amounted to more than 18.4 thousand vacancies, which is 19.3% more than in 2010. Within three months of 2011, almost 1800 employers addressed the employment service for assistance in the selection of the necessary workers. According to data on April 1, 2011, the city and inter-seat banks of vacancies contain 11.5 thousand vacancies of employers of the city of Omsk and municipal areas of the Omsk region, about 30% of them constitute vacancies for employees (on April 1, 2010 -6.0 thousand vacancies, Of which about 52% - to replace vacancies of employees). With the assistance of the employment service in January - March 2011, they found the work (income lesson) more than 40 percent of citizens (4982 people), who applied to employment assistance. The number of employed unemployed citizens in the reporting period of 2011 amounted to 3091 people. The government service promotion in the search for suitable work is provided to everyone without exception to citizens who applied to the employment service of the Omsk region, from among those who work, or those who wish to change the place of work or lost work, regardless of the cause of dismissal.
Professional guidance services in the first quarter of 2011 took advantage of more than 20.1 thousand people, state services for psychological support and social adaptation in the labor market received more than 4 thousand unemployed citizens. During January - March 1194 people have the opportunity to improve the qualifications, pass vocational training.
As already noted, as part of EAN, in addition to those engaged, Unemployed
Unemployment entails serious economic, social and psychological consequences.
TO firstyou can attribute:
· Non-slip products, under-utilization of the Company's production opportunities. The dependence between the unemployment rate and the lag of the volume of the gross national product (GNP) is reflected in the OKUN's Law (Okun's LAW) excess on 1% of the actual unemployment level over natural leads to the lag of the actual volume of the GNP by 2.5% of the potential;
· A significant reduction in the living standards of people being unemployed, since work is the main sources of means of existence for them;
· Slow growth of the wage level engaged as a result of emerging competition in the labor market;
· An increase in the tax burden in employed due to the need for social support for the unemployed: payments of benefits and compensation.
In addition to the economic consequences, unemployment has serious social and psychological consequences, often less obvious, but even more significant than economic. The main ones include the following:
· Strengthening political instability and social tensions in society;
· Exacerbation of the criminal situation, crime growth;
· Increasing the number of suicides, mental and cardiovascular diseases, alcoholism mortality;
· Loss of non-working qualifications and practical skills;
· The aggravation of family relationships and an increase in divorces;
· Reducing social bonds unemployed;
the unemployed in accordance with the definition that the ILO made belongs to the ages set to measure economic activity (15-72 years), which in the period under review can be simultaneously described in the following categories:
· There were no work (income);
· We were looking for work for four weeks preceding the surveyed week, i.e. Applying the state or commercial service of employment or directly to the administration of the enterprise (employer), they used or placed ads in the press, tried to use personal connections, etc. Or took steps to the organization of their own business;
· Were ready to start work during the surveyed week;
· Students, students, people with disabilities and pensioners were taken into account as unemployed if they were looking for work and were ready to start her
the unemployed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation includes able-bodied citizens who do not have work and earnings (labor income) living in the territory of the Russian Federation registered at the employment center at the place of residence to search for work, seeking work and ready to start it.
Unemployed according to the legislation of the Russian Federationcitizens cannot be recognized:
1) under the age of 16, as well as citizens who, in accordance with pension legislation, were appointed a pension by age (old age), for long service;
2) who refused for 10 days from the day of appeal to the employment service from two options for suitable work, including a temporary nature, and for the first time job seekers who do not have a profession (specialty) - in the case of two failures from obtaining training or proposed paid work, including a temporary nature;
3) who did not appear without good reason within 10 days from the date of registration, in order to search for suitable work in the employment authorities to offer them a suitable work, as well as those who have not come to the period established by them for registration as unemployed.
Information about the numbers and composition of the unemployed is reflected in the following characteristics:
· The floor (with the allocation of the least protected socially protected unemployed - women);
· Age (with the allocation of unemployed youth);
· Place of residence (with the allocation of urban and rural population);
· Education level;
· Family position;
· Reasons for dismissal;
· Duration and ways to find work;
· Availability of work experience;
· Types of activity.
End of work -
This topic belongs to the section:
Population statistics
The natural movement of the population is the fertility fertility and population changes as their result .. Indicators .. Absolute ..
If you need additional material on this topic, or you did not find what they were looking for, we recommend using searching for our work base:
What we will do with the material obtained:
If this material turned out to be useful for you, you can save it to your social networking page:
| Tweet |
All the themes of this section:
Population statistics
The population is a combination of people living within a certain territory: parts of the country, the whole country, groups of countries, the whole globe and continuously renewing due to births and deaths
At the place of residence
Ø rural Ø city city is considered to be the population with a population of 20 thousand and more provided that<85% семей составляют рабочие и служащие.
Ø Current accounting Ø One-time observation · Micro census · Selective census · Solid census of population 5) Calculate
Relative
1) General Indicators Ø fertility rate Ø Mortality rate Ø Natural growth ratio Ø Nationality coefficient
By reasons
Ø Economic Ø Demographic Ø Social Ø Political Ø Cultural and Ethnic Ø Military & Oslas
On economic feasibility
· Economically appropriate (profitable) · economically unprofitable 9) largest indicator: · net migration · Gross migration · Sal
Demographic processes and forecasts
To evaluate demographic processes and forecasts, knowledgeable indicators of the demographic situation 1) the dynamics of the population 2) dynamics of the natural movement are considered
The concept of "household" and their structure
Household - a set of persons living in one residential premises or its parts related either not related relationship relations fully or partially united their individuals
Main indicators of population statistics
Directions of study Indicators The number, composition and structure of the population The number of cash and permanent population, including
Main indicators of labor market statistics and labor resources
Directions of study Indicators Economic activity of the population The number of economically active population and its structure on p
Employment and unemployment statistics
The entire population on actual participation in production can be divided into 2 groups: ü Economic active population ü economically inactive population
Non-standard employment forms
These include: · Part-time employment; · Seasonal work; · Random earnings; · Temporary job; · Employment part-time; · N.
Types of unemployment and their characteristics
Congestion; · Chronic; · Hidden; · Classical; · Technological; · Voluntary; · Forced; frictional (current);
Economically inactive population
The economically inactive population is faces aged 15 to 72 years, which are not considered busy or unemployed during the period under consideration: · Population, N
statistics of labor resources
Labor resources are the faces of both sexes engaged in economic activities and persons who could potentially participate in the production of goods and services, but do not work
Balance of labor resources for 200_
No. P / p Name of the indicator The number million people I. Sources of formation of labor resources & NBS
Relative indicators
· The coefficient of natural replenishment of labor resources KEST. Pop. \u003d · The coefficient of natural disposal of labor resources KEST.Leb \u003d 1000 ‰ · coefficient
Relative
1) The working capacity of the population is the proportion of the working capacity of the population in its total number 2) the working capacity of the working age population - the proportion of cooperation
Workforce statistics
One of the most important areas in the study of the situation in the labor market is the analysis of the number of employees of enterprises, labor structures in various directions, as well as movement and use
The presence (number) of employees of the enterprise
The number of employees of the enterprise can be expressed: torque indicators (on date); Interval (average for the period). For their calculation use
Relative Motion Indicators
1. The coefficient of turnover by reception: Kob.PR. \u003d TPR / T̅P * 100% 2. The coefficient of turnover on the disposal: Kob.W. \u003d TUV. / T̅SP * 100% 3. The gain (loss) of workers: KPRR (UB) \u003d &
Statistics of labor productivity
Productivity is its effectiveness, the effectiveness of expedient productive activities for creating a product for a certain period of time. Split
Methods for determining the production
1) Natural (conditional) for calculation must be complied with the following conditions: the products must be homogeneous and the same name; When comparing natural display
Analysis of the dynamics of labor productivity
In order to study the dynamics of labor productivity, labor productivity indices are used. Under the production of homogeneous products, the following methods are used; Based on individual
Index analysis of the dynamics of average labor productivity
One of the directions of economic analysis of labor productivity is the study of the dynamics of the average level of labor productivity on the aggregate of the enterprise of the industries. 1) index produce
Work time statistics
Working hours - part of the calendar fund of time spent on the production of products or to perform a certain type of work. Analysis - the use of a worker in
Balance of working time
Working time resources Using working time 1. Calendar Foundation of working time 2. Festive and weekends 3. Tabel fund
Working Time Use Indicators
1. The average number of hours worked by one employee \u003d 2. The average duration of the working period in days (T̅) \u003d 3. The average actually duration of the working period
Salary fund
FZP is the total amount of funds in monetary and natural forms distributed among employees of the organization in accordance with the number and quality of labor. As part of the wage fund
Foundation statistics
Remuneration - regularly obtained remuneration for production products or service provision, or for spent time, including vacations, holidays, other time paid
Study of the interrelation of average wages and labor productivity
In the economic and statistical analysis of wages, the interrelationship of average wages and productivity is of great importance. It is believed that inequality should be observed
Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation
FGOU VPO "Orenburg State Agrarian University"
Department of Statistics and Economic Analysis
COURSE WORK
on the topic: " Statistical analysis of unemployment in the Russian Federation "
Performed: student 34 gr. specialties
"Economics and Management
in the enterprise (by industry)
Atamanova A.P.
Checked: Ph.D., Associate Professor Khabarova S.V.
Introduction
At present, unemployment becomes an integral element of Russia's life that has a significant impact not only on the socio-economic, but also on the political situation in the country, which is the relevance of the subject of the study.
Unemployment becomes an integral attribute of the market economy system, seriously affects the effectiveness of the economic activities of the subjects of the market economy, the economic and social life of the entire society. Unemployment is a macroeconomic problem that has the most direct and strong impact on each person. Therefore, unemployment cannot be considered only as an economic phenomenon. It is necessary to take into account its social parties. Loss of work for most people means a decline in living standards and causes serious psychological trauma. Therefore, it is not surprising that the problem of unemployment is often the subject of political discussions.
The most threatening factor in the growth of unemployment and mass release of people from production was the destruction of links between sectors and coagulation for this reason for large and super-brood enterprises. The gap of horizontal economic relations, violation of contractual obligations for the supply of products led to a decrease in production volumes, reducing the number of jobs and working.
The economically active population could not satisfy the requirements of the new economy, which needed active workers who can study independently, actively act, not afraid to take responsibility. The negative attitude towards small businesses at that time prevented the creation of new jobs, thereby contributing to unemployment.
In the last decade, the labor market varies dynamically. High technologies are introduced into an increasing number of spheres of vital activity. Therefore, the significance of highly qualified labor increases. The end of the 20th century was marked by the Boom of Higher Education, which was expressed in a significant increase in the number of graduates of schools, continuing training in the university. At the same time, the recent past remained the socio-economic transformation of Russia, the signs of which became the crisis situation in the labor market and the leakage of the minds.
The purpose of this course work is to study unemployment as an economic category, its theoretical aspects and manifestations in the practice of economic activity. In accordance with this purpose, the following tasks define:
Determine the concept and essence of unemployment, the causes of its occurrence, as well as economic and social consequences;
Consider the classification of unemployment species, identify their specificity;
Make a statistical analysis of the structure and dynamics of unemployment in the Russian Federation;
Determine the paths and methods of preventing unemployment, consider anti-crisis policies in the field of employment.
The subject of the research is the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of the unemployed, as well as changes in the economic activity of the Company accompanying unemployment.
The object of research is the unemployed Russian Federation.
Problems in the labor market were considered in the works of many authors: A.D. Popova, S.V. Kurysheva, F.T. Prokopova, A.E. Lapina, V.V. Skobeeva, I.I. Egorova V.D. Areschenko and others. Scientists examined in detail unemployment, its structure and dynamics. This work is devoted to the analysis of unemployment based on existing research.
1. Theoretical foundations of unemployment
Unemployment for all countries of the world is social evil. However, if in countries with a developed market economy, in the presence of a more or less significant level of unemployment, the economy and the population of decades exist safely, the Russian labor market and the relevant unemployment do not have analogues in the world due to the relatively low material security of our population and the unemployed in Features, higher social tensions in a society capable of providing significant social shocks in Russia.
Unemployment - This is a socio-economic phenomenon in which part of the labor force (economically active population) is not occupied in the production of goods and services. The unemployed, along with busy, form the country's labor. In real economic life, unemployment acts as an excess of the supply of labor over demand for it.
The entire population of the country in working age, capable of working (i.e., less disabled people, mentally ill and prisoners), is divided into 2 categories:
· Economically active;
· Economically inactive.
The economically active population, or labor, consists of busy and unemployed:
where LF is an economically active population or labor;
E - busy;
U - unemployed.
The unemployed belongs to persons in working age, which in the period under review:
Did not have work (income class);
We were looking for work - apply to state or commercial employment services, used or placed ads in the press, directly appealed to the administration of the enterprise or the employer, used personal connections, etc. Or took steps to the organization of their own business;
Were ready to start work.
The unemployed also includes persons who in the period under review:
Did not have work, but agreed on the period of starting work (within two weeks after the period under review) and did not continue its further search;
We had no work, they were ready to start, but did not look for work, as they expected an answer from the administration or an employer to the appeal earlier. At the same time, the period waiting for the answer should not exceed one month.
Students, students, pensioners and people with disabilities are taken into account as unemployed if they have been looking for work and were ready to start it.
Unemployment should be distinguished as an economic category from its accounting and statistical dimension. The essence of unemployment as an economic category is that part of the economically active population of the country can not apply their labor force (ability to work), becomes "excessive population", deprived of opportunities for a different period of time to work, receive labor income and the threat of skillful qualifications , profession, social status, reducing living standards. Accounting and statistical measurement of unemployment carries an element of conventionality, depending on the criteria for assigning certain persons to the discharge of the unemployed and the base, with which their number is compared (able-bodied population, the occupied population, economically active population, etc.). Currently, an indicator characterizing the unemployment rate is calculated as the ratio of the number of unemployed to the number of economically active population, i.e., for the number of employed and unoccupied, including unemployed persons.
With unemployment, Russia came closely since 1992, when, after adoption in 1991, the Law of the Russian Federation on Employment Employment began to officially assign the status of the unemployed people looking for a job.
"Unemployment violates one of the fundamental human rights - the right to work" - notes the Declaration of Human Rights. In the Law of the Russian Federation "On Employment of the Population" (Article 5 of Chur.1) recorded: "The state ensures the policy of facilitating the realization of the rights of citizens to full, productive and freely elected employment."
In Russia, obtaining unemployed status has a tougher character than in international documents. In art. 3H1 It is indicated that the status of the unemployed is assigned to able-bodied citizens who do not have work and earnings, registered in the employment service in order to search for suitable work and are ready to start it.
According to the ILO Convention No. 168 of 1988, "On Promoting Employment and Unemployment Protection" Complete Unemployment is understood "How loss of earnings due to the impossibility of getting appropriate work on a person who can work, ready to work and really looking for work."
Thus, if the state of unemployment in Russia is based on five criteria, then in the ILO Convention - only three, mainly related to the activities of a person for a specific period of time and independent of legal norms due to registration of unemployed in the employment service and payment of unemployment benefits How it is practiced in Russia.