Realization of crop production. Cost of agricultural products. Profitability of agricultural production Growing rye in Russia
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted by http://allbest.ru.
Introduction
1. Theoretical foundations for the sale of agricultural products
1.1 Concept and conditions for the sale of agricultural products
1.2 Channels and ways to sell agricultural products in market conditions
2. Analysis of the current state of production and sales of crop production in SPK "Koltoz" Krasavsky "...
2.1 Organizational and economic characteristics of the economy
2.2 Analysis of production and sales of crop production
2.3 Analysis of financial results from the sale of crop production
2.4 Effect of Channels for the Financial Results on the sale of crop products
3. The main directions and reserves of increasing market efficiency of crop production
3.1 Reserves for an increase in production and sales of crop production
3.2 Profit profit reserves and profitability from sales of crop production
3.3 Ways to increase the efficient sales of products in the farm
Conclusions and offers
Bibliography
Introduction
The current state of the agricultural market is characterized by an increase in market channels in the product market structure. The market development on the village is on the way of gradual reorientation of the agrarian sector from the sale of products to the procurement organizations on alternative channels, including the sale in the markets, through its own trading network and catering enterprises, on the barter and others. Principal miscalculations in the organization of agricultural relationships with processing sectors, as well as agroservice and agricultural failure, make rural producers engage in product processing directly in farms.
The emergence of new form of implementation on the market of agricultural products, the redistribution of sales volumes between those existed earlier and new channels indicate qualitative changes.
Problems of the implementation of agricultural products are reflected in Russian and foreign economic literature. The ideas of the optimization of agriculture and the implementation of its products were worried A. Smith, D. Ricardo, T, Malthus and subsequent outstanding economists.
Contributed to the development of problems of implementing M. I. Tugan-Baranovsky, A. V. Chayanov, E.E. Slutsky. The current problems of the implementation of agricultural products are covered in the works of economic scientists G.V. Savitskaya, I.A. Minakova, N.A. Volkova, O.A. Stolyarova, V.P. Georgian, N.Ya. Kovalenko, M. Kolesova, A.D. Sheremete and a number of others (their works are reflected in the literature list).
The purpose of the course project is the economic analysis of the sale of crop production, identifying reserves for an increase in production and sales of crop production, reserves of increasing profits and profitability, outline ways to increase the efficiency of crop production.
In accordance with the purpose of the following tasks:
· Consider the conditions and channels for the sale of agricultural products
· Examine the organizational -economic state of the analyzed farm
· Conduct analysis of production and sales of crop production
· Analyze financial results from the sale of crop production
· Examine the impact of the implementation of the channels for the financial results from the sale of crop production
· Note way of increasing the efficient product sales in the farm
The subject of the study is the realization of plant production in the exercise farm.
The Object of Research -SPK "Kolhoz" Krasavsky "Lyssogorsk district of the Saratov region.
Research methods: monographic, comparison, calculating graphic method.
When writing a course project, the following sources of information were used: the accounting financial statements of the enterprise, works of scientists -Economists, methodological benefits.
1. Theoretical basis for the sale of agricultural products
1.1 The concept and conditions for the sale of agricultural products
The market of agricultural raw materials and food is the scope of the exchange of agricultural goods and other industries. His emergence is closely related to the liquidation of the monopoly of the state for the purchase of agricultural products and food on "solid" prices, with a wide deployment of product sales directly by the manufacturers themselves. With its formation, the state should widely use the methods of economic regulation, ensure parity of prices for industrial and agricultural products.
The fully functioning market of agricultural raw materials and food is a combination of several components - specialized markets, market infrastructure and market mechanism. The absence or insufficient development of at least one of them leads to a decrease in the efficiency of promoting goods from the manufacturer to the consumer, and therefore, to a decrease in the profitability of the entire agro-industrial production.
The agricultural raw materials and food market are characterized by certain features arising from the characteristics of the most agro-industrial production:
1. Dependence of the proposal of agricultural products from weather conditions that limit the possibilities of control from the rural producer over the amount and quality of products. It must be taken into account both by the manufacturers themselves and government regulatory organizations.
2. The presence of guaranteed demand for agricultural products, since it satisfies the most pressing needs of the population. To a certain extent, this feature of the agricultural market compensates for the negative effect of the previous one.
Agricultural enterprises can use it to improve their performance. To do this, they need not to produce from year to year the same products, but to maneuver the assortment, develop the production of new goods in demand to increase their competitiveness and find new sources of income.
3. A large volume of supplies of perishable types of products strengthen the need, on the one hand, in storages (primarily for vegetables, potatoes, fruits), on the other, - in the maximum compressed periods of implementation. It is necessary to avoid significant losses of the crop, and therefore, and reducing production yields.
4. The concentration of consumption of agricultural products in cities, especially in large, causes the need for its sale through a different kind of intermediaries. This leads to the loss of a certain share of income of commodity producers; They are forced to share with intermediaries part of the value of final products.
The agricultural raw material and food market also has a number of features that do not allow to make prices on it completely free. This is due to the duties of the state as a guarantor of the country's food security, with the need to take into account the natural and economic conditions of production and the high capital intensity of industries of the APK. Need an extensive and flexible price regulation system, including the definition of target prices, providing profitability sufficient to cover the current costs and expansion of production; establishing guaranteed (protective) prices that may be lower than the target prices and are used when market prices fall below their level; Introduction of the mechanism of collateral and the corresponding quotas for guaranteed procurement of products.
The creation of federal and regional food funds is also necessary for the implementation of commodity investments in cases where the state intervention is needed to eliminate food deficit, stabilization and lower prices, ensuring freedom of movement of products within the country.
The total volume of products manufactured at the enterprise, in the industry, etc. For a certain period of time is called gross products.
Gross agricultural products include crop production and animal husbandry. The gross production of crops includes gross fees of crops, taking into account by-products, the cost of planting perennial plantings, the cost of growing young perennial plantings and an increase in work in progress. The gross production of animal husbandry includes finished products that are not associated with the cloth of animals (milk, wool, eggs), the rating, the increase in grown young and adult cattle, as well as side products.
Gross agricultural products are taken into account in physical and value terms. In natural indicators, it is determined by certain types of products.
Gross products of agriculture is determined by the gross turnover method. This means that when calculating, the products produced during a certain period by all units regardless of whether it was then used within the enterprise for further production or was implemented to the side.
Gross products - an important economic indicator; It characterizes the total production, is necessary to determine the specific gravity of the agricultural industries in the aggregate social product, the industry's industry structure, the role of individual categories of farms in products. At the same time, it has a number of disadvantages that do not allow it to objectively assess the results of the economic activity of the enterprise. First, gross products include the costs of material resources and does not provide an idea of \u200b\u200bthe amount of newly created (added) product. Secondly, the gross products of agriculture, calculated as the sum of its volume on crop and animal husbandry, allows for a repeated account (feed produced in the enterprise and consumed in the same year will be taken into account twice: as part of crop production and as part of animal production costs) . Thirdly, when assessing gross products at current prices, its actual cost is distorted, since the non-unique part of the products is estimated at cost, which can be both lower and above the current market prices. Fourth, the gross production indicator calculated in comparable prices does not reflect the quality of products.
Commodity Products are part of gross products intended for implementation. Products actually released outside the industry (enterprise) and paid by the consumer or trading organization are called implemented (both indicators are calculated in current prices). However, both in practice and in the literature, these expressions are often used as synonyms; Under the commodity products are often understood by the implemented cash revenue. In reporting and statistical materials of agricultural enterprises, marketable products are not specified.
It is necessary to distinguish the commodity products of the enterprise as a whole and by industry. The main indicators characterizing the marketability of the enterprise, industry and certain types of products are the level of marketability and total marketable products; In agriculture, indicators of commercial products are also used per unit area and livestock head.
In determining the level of marketability of individual types of products (grains, sugar beets, milk, etc.), the volume of gross and realized products is calculated in physical terms, and when it is determined by an industry or an enterprise as a whole, the cost indicators apply. In this case, it is important that gross and realized products are calculated in uniform prices (for example, in comparable).
The level of rationality is the ratio of products sold to gross, expressed as a percentage.
The level of agricultural production by categories of farms differs significantly. He is highest in agricultural enterprises, the lowest - in households. It is natural, since agricultural enterprises produce products mainly for sale, and households - to meet the needs of the family in food. At the same time, in recent years, the level of production in agricultural enterprises has also decreased.
The main directions for the growth of the level of agricultural and processing industries include:
an increase in the extraction of gross production by increasing the yield of crops and livestock productivity, increase the yield of final products from raw materials (sugar, sunflower oil, juice, etc.).
improving the quality of seeds and feed, economical spending;
reduction of product losses and raw materials in the process of production, storage, transportation;
improving product quality;
organization of effective marketing service at the APK enterprises.
In modern conditions, the level of marketability of agro-industrial production is largely determined by the market situation, supply and demand.
In a market economy, the competitiveness of any enterprise, its sustainable position in the market is largely determined by the quality of products.
Product quality-- This set of properties characterizing its ability to satisfy the need caused by its appointment. The buyer considers high-quality products that he needed; The same product can get a high marker assessment when used for some purposes and low for others. Thus, the increase in protein content in barley increases its feed value, but reduces its value as raw materials for brewing.
Solving problems related to product quality, primarily depends on the organization and technology of standardization.
Standardization-- This is an activity aimed at developing and establishing rules, rules, characteristics of production technology and product quality, providing consumer rights to purchase good quality goods for an appropriate price; It is expressed in the development, publishing and application of standards.
The standard is a regulatory document developed on the basis of the agreement of most stakeholders and approved by the relevant authority (State Statistics Committee of Russia, Ministries, Individual Enterprises), which establishes general principles, characteristics, requirements and methods related to certain standardization objects. Such an object can be products, services and processes.
Product standards define the requirements that products should meet the product quality indicators; They also regulate methods for measuring, control and testing. Standards are divided into mandatory and recommended. Mandatory are intended for steady execution; Recommended (promising) standards are distinguished by the fact that they are laid as not only already applied in the production parameters of quality, but also to be developed in perspective. These standards orient the manufacturer to higher requirements for product quality, which will be generally accepted in a few years.
The standards used in agriculture can be divided into the following groups:
standards for agricultural products that establish requirements for its quality, the order of delivery of procuring and implementing organizations;
standards for products used in agricultural production (fertilizer, machinery, materials, etc.);
technical standards for typical technology of mechanized cultivation, cleaning, processing, packaging, transportation and storage of agricultural products.
Quality management - actions carried out when creating, operating or consuming products in order to maintain the required level of its quality. The objects of control in this case, as a rule, are technological processes (soil treatment, sowing, plant care, etc.), on which the quality of the products obtained depends.
Development of management solutions is made by comparing information on the actual state of the technological process with the characteristics provided by the regulatory documentation (standards, technical conditions, production tasks, etc.). It is necessary to ensure the production of products that meets the requirements of the consumer complies with the applied standards and specifications, allows to make a profit.
The essential element of the quality management system is certification; certificate or conformity sign confirms that the goods or service meets certain standards or other regulatory documents. With the help of certification, the final quality assessment is carried out.
Certification can be mandatory or voluntary. Mandatory certification is carried out on the basis of laws and legislative provisions; It confirms the compliance of the product with the mandatory standards requirements. Voluntary certification is carried out in cases where strict compliance with the requirements of existing standards or other regulatory documentation for products is not provided.
1.2 Channels and ways to sell agricultural products in market conditions
The economic efficiency of industries of the APC largely depends on the organization of the sale of products, selecting its implementation channels. Most manufacturers offer their products to the consumer through intermediaries, which reduces the amount of work related to the sale of goods.
Product sales channel-- This is a combination of legal entities and individuals who act as intermediaries or sales participants, take on or help to convey to someone else ownership of a specific product on its way from the manufacturer to the consumer.
Each type of product realizable corresponds to its sales channel and the organizational form of trade. Depending on the number of intermediaries, the channels for the implementation of the zero level, one-, two-, three-level and so on.
The zero-level channel consists of a manufacturer who directly sells his goods to consumers. The most common way to directly sell is trade through own shops.
A single-level channel includes one intermediary; This is usually a retail enterprise.
The two-level channel includes two intermediaries (wholesale and retail), three-level - three (wholesale, fine-powered and retail).
The main part of crop production (grain, sunflower, sugar beet, etc.) and industrial products are implemented through wholesale trade.
The role of an intermediary in promoting goods to the final consumer takes on a wholesale and retail system.
Wholesale trade is a combination of legal entities and individuals who acquire and store goods, and then resell them (retail merchants or other wholesalers). Wholesale purchases of agricultural products are carried out by procurement organizations, commodity exchanges, processing enterprises; This allows producers to quickly sell their products in its production places.
Retail is entrepreneurial activities related to the sale of goods to end users for personal (family) use. In this area, there are both large firms and numerous private entrepreneurs. Wholesale trade through stock exchanges, auctions, fairs received the greatest distribution.
From an economic point of view, the commodity exchange is organized in a certain place, regularly operating on the established rules of the wholesale market, which comes in trade in samples and standards or contracts for their supply in the future. The result of trading on the stock exchange is the conclusion of transactions between sellers and buyers.
Exchange transaction is an agreement on mutual transmission of rights and obligations regarding the goods admitted to the exercise on the stock exchange, which was reflected in the Exchange Agreement (contract) concluded by the participants during the exchange trading. These transactions are customary to divide into two groups: with a real product and without it.
The simplest type of transaction with a real commodity is a transaction with immediate delivery (or with a short delivery time). These are transactions for a cash product, that is, the goods at the time of trading in the stock exchange or expected on this day to arrive.
Another kind of transactions with a real product - forward (urgent) transactions; In this case, the mutual transmission of rights and obligations occurs immediately, but the delivery of goods (execution of the contract) is postponed to a specific date in the future.
Transactions without real goods are divided into futures and optional.
Futures transactions are mutual transmission of rights and obligations regarding standard contracts for the supply of stock goods. A distinctive feature of such a transaction is that its object is not a product, but a stock exchange contract. Futures transactions are characteristic of agricultural stock exchanges; They can conclude long before harvest.
Optional transactions - logical continuation of futures. The owner (acquirer) of the option receives the right to buy or sell a certain number of futures contracts on the price agreed in advance for a certain period in the future. Such contracts are mainly used to insure risks associated with futures trading.
Exchange trade in the market infrastructure of developed countries occupies its definite place; Through this system usually takes no more than 5--10% of the total volume of goods, but this is enough to identify prices in the market. Wholesale food markets provide sales of 20--25% of goods, and their main mass (65--75%) is sold by manufacturers through various mediation organizations to commercial structures and consumers of raw materials.
Until recently, government procurement was played in the prevailing role in the realization of agricultural products. Purchase is a form of organized acquisition by the state of agricultural products, raw materials, food producers (suppliers) for subsequent processing or implementation by the consumer (buyer) on mutually beneficial conditions. In addition, there is a system for the supply of agricultural products and food to federal and regional funds. With the advent of a variety of trade and procurement structures on the market, sales of products on state channels declined sharply.
Direct links of commodity producers with enterprises of the processing industry and trade are very effective; They allow you to reduce the loss of agricultural products at the stages of its production, transportation, processing and storage. In addition, the deadlines for the delivery of products to the consumer are significantly reduced, its quality increases, the costs of implementation are reduced.
Most often, agricultural producers sell their products to federal and regional food funds, processing enterprises, farm employees on wage, through their own shopping points, trade exchanges, auctions, cooperative pricing organizations, contracts, direct links and based on barter transactions. In the current economic conditions, the successful implementation of products of industries of the APK largely depends on the level of development and nature of the functioning of agricultural markets.
2. Analysis of the current state of production and sales of crop production in SPK "Koltoz" Krasavsky "
2.1 Organizational and economic characteristics of the economy
The enterprise studied is a agricultural production cooperative (SEC). Agricultural production cooperative is created by citizens and legal entities for joint activities for the production, processing and marketing of agricultural products, as well as to fulfill other non-prohibited activities based on the personal labor of the members of the cooperative.
Complete name - Agricultural production cooperative "Krasavsky collective farm". Located in the Lyssogorsky district of the Saratov region. The main activities are crop production and animal husbandry.
The constituent document of the production cooperative is its charter, approved by the general meeting of its members.
The highest management body of the cooperative is the general meeting of its members.
The executive bodies in the SEC "Krasavsky collective farm" are the Board of the Cooperative and Chairman of the Cooperative. They carry out the current management of the cooperative activities.
In addition to the Chairman, the Board is the main accountant.
The Chairman of the Cooperative, the Board of the Cooperative is elected by the General Meeting of Members of the Cooperative Members of the Cooperative For a period of no more than 5 years. The Chairman of the Cooperative is a member of the Board of the Cooperative and heads it.
The service life of the cooperative is not limited.
Table 1- Composition and structure of fixed assets of SPK "Koltoz" Krasavsky "
|
Types of fixed assets |
|||||||
|
Construction and transfer devices |
|||||||
|
cars and equipment |
|||||||
|
Vehicles |
|||||||
|
Production and Economic Inventory |
|||||||
|
Cattle: Worker |
|||||||
|
productive |
|||||||
|
Other types of fixed assets |
|||||||
Table 1 shows that the main stake in the structure of fixed assets is occupied by cars and equipment of 25518 thousand rubles. and buildings 24226 thousand rubles.
Also, a significant share has a productive livestock 12030 thousand rubles, structures and gear ratios 6824 thousand rubles., Production and economic equipment of 2399 thousand rubles, vehicles 1552 thousand rubles. In the magnitude, the composition and structure of fixed assets occurred both favorable and adverse changes.
The proportion of the active part of the funds is increased: working and productive livestock. There is a constant increase in the first place of agricultural production facilities.
In addition, the company has developed the structure of fixed assets, relevant manufacturing activities of the economy: high proportion of OPF S.-H. Appointments: buildings, machinery and equipment, productive livestock (83.1% in 2012). These categories are important for S.-H. Enterprises.
An analysis of land resources is presented in Table 2.
Table 2- composition and structure of land in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
|
Types of land |
|||||||
|
Specific weight,% |
Specific weight,% |
Specific weight,% |
|||||
|
General land area, total |
|||||||
|
including: Agricultural Labor |
|||||||
|
of them: Pashnya |
|||||||
|
pasture |
|||||||
|
non-agricultural land |
|||||||
|
of these: Roads (km) |
|||||||
|
other land |
It can be seen from this table that in the reporting year the total land farm decreased by 67 hectares. This happened mainly by reducing agricultural land and pasture. At the same time, the area of \u200b\u200bPashnya increased. The size of non-agricultural land has not changed. The greatest specific weight in the structure of land includes arable land -6213 hectares (67.8%), pastures -2951 hectares (32.2%). Non-agricultural land -786 hectares (7.9%), roads -66 km (8.4%), other Earth -221 hectares (2.2%). Such a structure indicates the rational use of land resources.
The share of agricultural land is very high - 92.1%, and the distribution of land resources within them corresponds to the specialization of the economy and allows you to successfully meet the needs of production.
The production specialization of the enterprise is determined by the main commodity industries and products that ensure the greatest revenue from the implementation.
Consider the revenue structure for implemented product products in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm.
Table 3- Revenue structure for implemented products in 2010-2012.
|
Indicator |
|||||||
|
Structure,% |
Revenue from sales, thousand rubles. |
Structure,% |
Revenue from sales, thousand rubles. |
Structure,% |
|||
|
Grain and leguminous - all |
|||||||
|
Barley - total |
|||||||
|
Other grain and leguminous |
|||||||
|
Other products |
|||||||
|
Total on crop production |
|||||||
|
Sale of cattle on meat and tribe |
|||||||
|
Total in cattle breeding |
|||||||
|
Products of animal husbandry of own production, implemented in a processed form |
|||||||
|
Total animal husbandry |
|||||||
|
Total by farming |
The specialization coefficient is 0.1, which indicates a weak economy. The main share of commercial products is made up of milk of 19727 thousand rubles, grain and leguminous volumes are only 5560 thousand rubles. and the sale of cattle on meat and a tribe 2790 thousand rubles. In the reporting year, the cultivation of other grain and leguminous crops was established. Based on Table 3 data, it is possible to conclude a milk with the developed production of grain and leguminous crops the direction of specialization.
From the provision of the supply process, production and sales of finished products, the staff and the effectiveness of its use depends on the volume and timeliness of agricultural work, the fullness of the use of technology and as a result is the volume of production, its cost, profit and a number of other economic indicators. Consider the security of the company with human resources as a whole and in categories of workers. These tables also allow you to familiarize yourself with the dynamics of the wage fund for 3 years, a change in labor costs in various industries.
Table 4- number and salary of employees of the organization
|
Indicators |
|||||||
|
number, people |
Photo, thousand rubles. |
number, people |
Photo, thousand rubles. |
number, people |
Photo, thousand rubles. |
||
|
On the enterprise - just |
|||||||
|
including |
|||||||
|
Employees occupied in production, total |
|||||||
|
Permanent workers |
|||||||
|
including |
|||||||
|
Tortanist-machinists |
|||||||
|
Machine milking operators, Diarai |
|||||||
|
Cots cattle |
|||||||
|
Employees of horse breeding |
|||||||
|
Workers pig breeding |
|||||||
|
Servants |
|||||||
|
Officers |
|||||||
|
Specialists |
In the period 2010-2012 The company has a decrease in the number of employees with a simultaneous increase in the wage fund. In the reporting year there was an increase in the number of tractor drivers-machinis for 8 people. At the same time, the number of permanent workers per 18 people decreased by reducing machine milking operators per person who serve 2, managers per person and specialists for 3 people.
Table 5- Financial results of the enterprise, thousand rubles.
|
Indicators |
||||
|
Product revenue |
||||
|
The cost of realized products |
||||
|
Gross profit |
||||
|
Profit (loss) from sales |
||||
|
Interest to getting |
||||
|
Percentage to be paid |
||||
|
Other income |
||||
|
other expenses |
||||
|
Profit (loss) before taxation |
||||
|
Other payments from profits |
||||
|
Net profit (loss) of the reporting period |
During the analyzed period, the company has consistently received profits. In the reporting year, the net profit indicator is significantly lower than the previous years. This is due to significant increase in the reporting year of production costs -44335 thousand rubles., Interest to payment -2376 thousand rubles., Other expenses -5256 thousand rubles, other payments from profits -284 thousand rubles. and a decrease in revenue from the sale of products -42374 thousand rubles. Increase the amount of other income up to 2376 thousand rubles. It did not have a significant impact on the financial results of activity in 2012.
So, the analysis of the company's security by resources showed that the presence of land, labor financial resources allows the company to successfully solve production tasks
2.2 Analysis of production and sales of crop production
The production volume of agricultural products is one of the main indicators characterizing the activities of the agricultural enterprise. The amount of product sales depends on its magnitude, and therefore the degree of satisfaction of the needs of the population in food products, and the industry - sir. The level of its cost, the amount of profit, the level of profitability, the financial position of the enterprise, its solvency and other economic indicators depend on the production volume.
The size and structure of sowing areas is significantly affected by the production of crop production. Consider and analyze the size and structure of the sowing space in the SEC "Krasavsky collective farm.
Table 6 - Size and structure of scenery
|
Name of culture |
Sowing Square, ha |
Structure of sowing areas,% |
|||||
|
Cereals - total |
|||||||
|
including: Winter grains |
|||||||
|
skin grains |
|||||||
|
scented tops |
|||||||
|
Sunflower |
|||||||
|
Perennial herbs |
|||||||
|
Annual herbs |
|||||||
|
Silosal cultures |
|||||||
|
All sowing square |
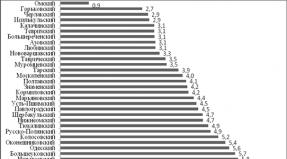
In the reporting year, compared with the previous year there was an increase in the sowing area at 473 hectares and it was 5735 hectares. This happened mainly due to the expansion of the seed area under spring grain at 500g, perennial herbs on 547 hectares and corn on the silage and green feed for 51 hectares. At the same time, the sowing area was significantly reduced under winter grains by 242 hectares, gentlemen on 16 hectares, sunflower on 80 hectares, annual herbs at 267 hectares and silo cultures of 20 hectares.
Grain -2673 (46.6%), including tark grain -1467 hectares (54.9%), winter grain-911 hectares (34.1%), grain-1911 hectares (34.1%), occupy the main share in the structure of the seed area. 11.0%) and perennial herbs -1214 hectares (21.2%). The share of corn on the silage and green feed was 529 hectares (9.2%), annual herbs - 525 hectares (9.1%), silage crops -100 ha (1.7%) ..
Table 7 -Valova Collection and yield of agricultural crops in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
|
Name of culture |
Gross Collection, C |
Yield, c / ha |
|||||
|
Grain and leguminous, including: |
|||||||
|
winter grains |
|||||||
|
skin grains |
|||||||
|
scented tops |
|||||||
|
Sunflower |
|||||||
|
Perennial herbs most, including: |
|||||||
|
on seeds |
|||||||
|
on green feed |
|||||||
|
Annual herbs - including, including: |
|||||||
|
on seeds |
|||||||
|
on green feed |
|||||||
|
Corn on Silo and Green Feed |
Table 7 Analysis shows a reduction in the reporting year of gross grain and leguminous collection to 30612 c, sunflower up to 5780 C, perennial herbs per hay to 9633 c and for seeds up to 6120 centners, annual grasses for seeds up to 5488 centners. Significantly reduced gross collection of winter grains to 19440 c and spring grain to 8262. At the same time, there was an increase in the gross gauge of the grainbobs -2910 C, perennial herbs on the green feed -199 c, the annual herbs on the hay -9947 C and corn on the silage and green feed -67551 c.
In 2012, there is an increase in the yield of grain and leguminous products to 15.38 c / ha, including winter grain -21.34 c / ha, grain-volume -9.86 c / ha; Annual herbs on the hay -33,38 c / ha and corn on the silage and green feed -127,70 c / ha. The yield of such types of products has decreased as spring grain -8.39 c / ha, sunflower -8.3 c / ha, perennial herbs on hay -27.44 c / ha.
The production of crop production depends on the size of the sowing areas and the yield of crops. Consider the influence of these factors on the change in gross production.
Table 8 - Reliance of the yield and size of seatic areas to change the production of gross products in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
|
Type of products |
Square sowing, ha |
Yield, c / ha |
Gross Collection, C |
Deviation 2012 from 2010, C |
||||||
|
including due to |
||||||||||
|
S yield |
||||||||||
|
Winter grains |
||||||||||
|
Skin grains |
||||||||||
|
Scented tops |
||||||||||
|
Sunflower |
Analyzing Table 8 It can be concluded that the decline in the reporting year of the gross collection of winter cereals on 1026 c occurred due to the decrease in the seed area at 1520 hectares, the spring grain to 9070 ° C by reducing the yield at 2.29 centners / ha. At an increase in the size of the gross collection of sunflower on 437 C affected the increase in yield by 0.8 c / ha ..
Commodity products are called part of gross products intended for implementation. The main indicator characterizing the marketability of the enterprise is the level of marketability. Vehicle level is the ratio of sales and gross, expressed as a percentage:
where TP -Ronalized products rubles;
Navel products, rub.
Calculate the level of products of crop production for SEC "Krasavsky collective farm for 3 years:
Item level in the period 2010-2012. It averages 80%. This suggests that the main proportion of crop production produced enterprise is implementing and only a small part uses for his own needs. At the same time, the largest level of rationality was observed in 2011 - 103%, which indicates a reduction in excessive stocks of crop production. Surplus reserves were formed due to the low level of production of crop production, which in 2010 was 62%.
Agricultural enterprise can implement its products in the following areas: product sale by other organizations and enterprises, selling products on the market, on barter transactions, the sale of the population and in the account of wages to employees of the economy.
Consider the channels for the sale of crop production in SPK "Koltoz" Krasavsky "
Table 9 - Channel sales of crop production
|
Channels implementation |
Type of products |
Specific weight in total product sales,% |
|||
|
grain and leguminous, thousand rubles. |
sunflower, thousand rubles. |
Total implemented, thousand rubles. |
|||
|
Organizations, markets |
|||||
|
Employees of the enterprise |
|||||
|
For payment dividend |
|||||
The economy in the reporting year realized the products of crop production to other organizations, in markets, employees of the enterprise and the payment of dividends. Revenue for all realized products amounted to 10120 thousand rubles. The largest share in the total volume of sales is occupied by markets and other organizations -80%. Revenue according to this channel is 8046 thousand rubles.
2.3 Analysis of financial results from the sale of crop production
Consider financial results from the sale of crop production SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
Table 10 -financial results from the sale of crop production
|
Type of products |
|||||||||||
|
Profitability level,% |
Number of products sold, c |
Complete cost of realized products, thousand rubles. |
Revenue from the sale of products, thousand rubles. |
Profit (+), loss (-), thousand rubles. |
Profitability level,% |
||||||
|
Grain and leguminous, total |
|||||||||||
|
Sunflower |
|||||||||||
Analyzing the data of the table can be concluded that the financial results of the enterprise in the reporting year compared with the Basine Year. This is due primarily to obtain a loss from the sale of grain and grain - (- 480) thousand rubles. and a decrease in the profit from the sale of sunflower at 1776 thousand rubles. In 2012, there is a significant increase in the cost of grain and leguminous capacity by 2586 thousand rubles. and sunflower for 1164 thousand rubles.
I will identify the influence of individual factors on the volume of sales and financial results of the enterprise.
Table 11 -Factor analysis of the volume of production of crop production
|
Type of products |
Production volume, C |
Product sales, c |
Item level,% |
Deviation from Plan, C |
||||||
|
including due to |
||||||||||
|
Production volume |
Material level |
|||||||||
|
Sunflower |
The data analysis of the table shows that in 2012 there was a significant increase in the sale of grain -18688 C and sunflower -6127 century. The main factor that influenced the volume of products sold is the level of rationality. In the reporting year, it amounted to 61% on grain and 106% on sunflower.
Table 12-Factory analysis of profitability of crop production
In the reporting year there is a significant decrease in the level of profitability of grain by 41% and sunflower by 102%. This is due to a decrease in the average price of the sale of cereals by 20% and sunflower by 72%, as well as an increase in the cost of 1Cs by 21% and 30% of grain and sunflower, respectively.
2.4 The impact of the implementation channels for financial results from the sale of crop products
We define financial results from the sale of crop production for each channel of the implementation used by the SEC "Krasavsky collective farm in 2012.
Table 13-sale of grain and leguminous crops
|
Channel implementation |
Number of products sold, c |
Complete cost of realized products, thousand rubles. |
Price implementation of products, rub. |
Revenue from sales, thousand rubles. |
Profit (+), loss (-), thousand rubles. |
Profitability level,% |
|
|
Organizations, markets |
|||||||
|
Employees of the enterprise |
|||||||
|
For payment dividend |
|||||||
Analyzing the data of the table, it can be concluded that the economy sells grain and leguminous crops to other organizations, in markets, employees of the economy and for payment of dividends.
The main channel of implementation is the sale of other enterprises and markets in the markets. Revenue according to this channel is 3486 thousand rubles., Full cost -3791 thousand rubles, loss - (-480) thousand rubles, loss rate - (- 8)%.
A significant excess of the indicator of the full cost of products above the revenue led to negative results from the sale of grain and leguminous crops in 2012.
Table 14-Upalization of sunflower
In the reporting year, the farm made the sale of sunflower only in markets and other enterprises. Complete cost of sales products -3330 thousand rubles, revenue -4560 thousand rubles. The company received profits from the implementation of 1230 thousand rubles. The level of profitability was 37%.
3. The main directions and reserves of raising the efficiency of the sales of crop products
3.1 Reserves for an increase in production and sales of crop production
The important tasks of the analysis of economic activity include the identification of reserves for the increase in production of crop production. Economic reserves are the possibility of improving the productivity of the enterprise by maximizing the use of available production potential, achievements of scientific-equipment and best practices.
Table 15 - Classification of reserves
|
Sign of classification |
Types of reserves |
|
|
1. at the place of education |
outlogenian |
|
|
2. By time use |
perspective |
|
|
3. By resource types |
live work basic and working capital |
|
|
4. By the nature of the impact on the results of production |
formed by extensive factors educated at the expense of intense factors |
The identification of reserves for increasing production of crop production can be carried out in the following areas:
expansion of sowing areas
improving the structure of the sowing
preventing the death of crops
increased crop yields
Calculate the reserve for the increase in production by expanding the sowing space for sunflower. To do this, the reserved reserve of the expansion of the sowing Sunflower Square to multiply on the actual yield of this culture.
Table 16 - Prev to increase product production due to the more complete use of land resources
When sowing sunflower at 40 hectares after the event performed, the farm may receive 328 cm. A significant reserve for increasing production of crop production is to improve the structure of the sowing space, i.e. The increase in the share of more crops in the overall sown area. To calculate this reserve, it is necessary to develop a more optimal structure of crops, and then compare the actual production volume with possible, which will be obtained with the same actual area with actual yield, but with an improved sowing structure.
Table 17 - reserve increase production volume due to improving the structure of sowing
|
Name of culture |
Structure of crops,% |
Sowing Square, ha |
Actual yield on average for 3 years, c \\ ha |
Production volume with the structure of crops, c |
||||
|
actual |
possible |
actual |
possible |
actual |
possible |
|||
|
Winter grains |
||||||||
|
Skin grains |
||||||||
|
Scented tops |
||||||||
|
Grain-information |
Increasing the share of winter cereals by 15.9% by reducing the share of spring grain and grainbobov, a reserve for an increase in production volume of 4399.1 C is obtained.
An important reserve for increasing production is the prevention of losses when harvesting. To determine these reserves, the area of \u200b\u200bthe victims or in time not cleaned crops multiplied to the planned or actual yield of the respective crops.
Table 18 - reserve increase production volume due to liquidation of losses when harvesting
After carrying out activities to eliminate losses when harvesting, the yarre grain cereal revealed Possible reserve was 5730.4 c.
By summarizing the results of the calculations of reserves for increasing production of crop production in Table 20.
Table 19 - production increase production
Due to the above mentioned events, the farm can obtain an additional amount of products equal to 10457.5 c.
The reserve for an increase in production volume is determined by multiplying the average market for profit, obtained from the sale of a unit of products.
Reserve for increasing sales of grain crops is:
Reserve reduction loss from the sale of grain crops is -21c.
Reserve for increasing sales from the sale of sunflower:
The reserve for an increase in the volume of sunflower sales is 161.
3.2 Profit profit reserves and profitability from sales of crop production
The main sources of increasing the amount of profit are an increase in the volume of product sales, price increase and decrease in product costs.
Table 20-Growth of profit profit due to an increase in product sales
The revealed profit growth reserve is 32900.7 thousand rubles.
Calculate the reserve of increasing the level of profitability. It is determined by the formula:
As a possible level of profitability, we will take the indicators of 2010, because This year, the enterprise had the best results of its activities.
Reserve for increasing the level of profitability of production of grain crops:
The revealed reserve of profitability growth was 45%.
Determine the reserve of growth in the profitability of sunflower production:
Reserve increase in profitability is 102%.
3.3 Ways to increase the efficient sales of products in the farm
Currently, the enterprise sells most of the products to other organizations and markets.
Selection of sales channels affects costs and profits. The company that takes on all functions should pay them, respectively, it receives all incomes.
Currently, most manufacturers work through intermediaries who deliver goods to the market and form the distribution channel of goods (which is also called the trading channel or marketing channel).
Distribution channel is a set of interdependent organizations that make a product or service available for use or consumption.
Manufacturers resorting to intermediaries receive certain benefits. Appeal to intermediaries is explained by their unsurpassed efficiency in bringing goods to target markets. Thanks to its contacts, experience, specialization and understanding of activities, mediators usually offer manufacturers a big profit than they are capable of getting themselves.
The role of the distribution channel is to move goods from manufacturers to consumers. Thanks to the channel, breaks in time, place and right of ownership, separating goods and services from those who would like to take advantage of them are eliminated.
The efficiency of sales products on the market directly depends on the quality of products. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out various measures to improve it.
Similar documents
Studying the economic essence of the sale of products, the features of this process in JaVeo-Agro. Analysis of the composition and structure of crop goods. Reserves of improving the sales results of crop production and increase its level of profitability.
course work, added 08/14/2013
Classification of profits. Factor analysis of financial results from the sale of products. Analysis of profit and profitability in the "Direct-Kosting" system with the calculation of margin income. Reserves increase profits from product sales.
course work, added 31.10.2014
Theoretical aspects of analyzing the sale of products and financial results. Dynamics and implementation of the plan for the implementation of products of OJSC "Planet". Determination of the break-even point, security zone, critical level of constant costs, profitability.
thesis, added 09.12.2007
Theoretical foundations of statistics of financial results of products. Characteristics of activities and analysis of production of crop production in "Vintage XXI Century" LLC. Analysis of indicators affecting the financial results of the sale of grain.
coursework, added 03/27/2011
Basics of statistics of financial results of implementation. Analysis of financial results from the sale of crop production of OJSC ODH PZ "Lenin Path". Economic and statistical analysis of the farms of the Leningrad and Novopokrovsky districts of the Krasnodar Territory.
course work, added 12/27/2009
The role of revenue from the sale of products in the production process. Types of sales channels and the composition of agricultural products implemented. Methodology and indicators system when analyzing implementation. The state of the branch of crops and animal husbandry.
course work, added 10/23/2011
Calculation of profits from the sale of crop production as a difference between revenue and full cost. Distribution of farms at the cost of gross production of crop production in the calculation of 100 hectares of agriculture. Comparative analysis of the output of this product.
course work, added 10/16/2011
The composition and dynamics of profits. Financial results from sales of products. Indicators profitability of the enterprise. Economic characteristics of Sundugach LLC, analysis of gross income and profits from sales, works, services.
coursework, added 11/29/2010
Organizational and economic characteristics of the economy. Costs as an economic category, ways to reduce. Classification and structure of costs of agricultural production. Factor analysis of the cost of crop production.
course work, added 31.10.2014
The overall characteristics of the demand, price and sales of products. Methodological foundations of sales and evaluation of demand. Organizational and economic characteristics of the enterprise of Metal OJSC, the analysis of profit and profitability, the impact on them demand for products.
Determine the relative values \u200b\u200b(share) of products (D) of crop production and animal husbandry in periods. Make conclusions.
Decision:
We will find the share of crop production and animal husbandry by the formula d.\u003d N / N:
In the reporting period:
d p \u200b\u200b\u003d \u003d 0.52, or 52%;
d g \u003d \u003d 0.48, or 48%;
In the reporting period:
d p \u200b\u200b\u003d \u003d 0.54, or 54%;
d И \u003d \u003d 0.46, or 46%.
The share of crop production is larger than the share of livestock products in the overall production of agricultural products in both the reporting and in the previous period. In the reporting period, there is a decrease in the share of crop production and, accordingly, the increase in the share of animal husbandry products (by 2%).
Task 5.
Determine the relative amount of coordination, if for the period production of linen fabrics amounted to 116 thousand m 2, wool - 147 thousand m 2.
Decision:
Coordination \u003d 116/147 \u003d 0.8, i.e. The volume of linseed fabrics was 0.8, or 80% of the production of woolen tissues.
City of Polotsk - 82 814;
Novopolotsk city - 99 295.
Calculate the relative magnitudes of comparing the population of Novopolotsk city in relation to the population of Polotsk city.
Decision:
OI comparing the population of Novopolotsk city in relation to the population of the city of Polotsk will be:
99 295/83 632 \u003d 1,187, or 118.7%
Output: The population in Novopolotsk is more than in the city of Polotsk 1.187 times or 18.7%
Task 7. As of January 1, 2010, the population in Polotsk - 83,632 people. During the reporting period, 878 people were born; Died - 1 188 people.
Determine the relative value of fertility, mortality.
Decision:
The fertility rate is defined as the ratio of the number of people born to the population in settlement by 1000 people.
Bakeries \u003d * 1000 \u003d 10.5 (people)
The mortality rate is defined as the ratio of the number of those who died to the average annual population per 100 people.
Ov mortality \u003d * 1000 \u003d 14.2 (people)
The number of dead exceeds the number of born (natural decline).
Task 8. The number of cattle (goal) in the farm - 1220 goals. Including cows make up 30% of the total flock of cattle. Average annual fishing - 4670kg. Agricultural land -
Calculate the density of cattle, cows and milk production on 100ga agricultural land.
Decision:
Livestock cows, goal: 1220 0.30 \u003d 366;
Gross Naughty Milk, C: 4670 366 \u003d 1709220 (kg) \u003d 17092.2 (C);
CRS density, goal: 100 \u003d 43;
Cow density, goal: 100 \u003d 13;
Milk production per 100 hectares of agricultural land, C: 100 \u003d 607.8.
Task 9. Potato yields in the current year amounted to 120 c / ha, with an area of \u200b\u200b40 hectares. Planned to obtain yield - 130 c / ha at the area of \u200b\u200b35 hectares.
Decision:
Gross harvest according to plan, C: Sun pl \u003d 130 35 \u003d 4550;
Gross collection actual, C: Sun F \u003d 120 40 \u003d 4800;
The percentage of the implementation of the Plan on the Gross Collection:
OV. PL \u003d 100.
OB statepl \u003d 100% \u003d 105.5%;
Percentage of the implementation of a yield plan
OV. pl \u003d 100%;
OV. Pl \u003d 100% \u003d 92.3%
Output: Gross potato collection in the reporting year compared to the basic increased by 5.5%, including by increasing the size of the seed area, it increased by 14.3%, but reduced yield by 7.7,% reduced gross fee for 8.8 %.
Task 10. There are data:
Production of milk per 100 hectares of agriculture;
The increase in cattle on 100 hectares of agriculture.
Make an economic output.
Decision:
Calculated by 100 s / k land:
Oh intensity \u003d ![]() 100%;
100%;
Output: In the reporting year, compared with the basic milk production by 100 hectares of agriculturals decreased by 42.6 tons (6.5%), the increase in CRS increased by 0.7 tons (16.7%).
Task 11. There are data on the economy of the size of land, hectares:
Land area - 2830;
Total with / x land - 2812;
Pashnya - 1408;
Senokos - 881;
Pastures - 523.
Calculate the structure of C / x land, the share of agricultural land in the total land area. Take output.
Decision:
The structure of C / x land is calculated by the formula:
S structure \u003d 100%;
Then: - Pashnya - 100% \u003d 50.1%;
Senokos - \u003d 31.3%;
Pastures - \u003d 8.1%.
Share of agricultural land in total land area: 100% \u003d 99.3%.
Output:The greatest share in the structure of the land is taken by arable land.
Task 12. There are data on grain yield, c / ha:
1) The absolute size of the scheduled task for 2010:
23,9 1,1 \u003d 26.3 (c / ha)
2) the absolute size of the actual yield:
26.3 0.94 \u003d 24.7 (C / ha).
Task 13. For two agricultural enterprises, calculate relative comparison indicators by:
Grain yields, c / ha;
Average annual Fdo, kg.
Make conclusions.
Initial data:
Decision:
One of the agricultural enterprises are accepted for the comparison base, for example, the "Zelenka" KPP, then
According to the yield of grain, c / ha:
OB comparison \u003d 100% \u003d 158.8%;
On the average annual fee, kg:
Obsites \u003d 10% \u003d 99%
Output:In the KUSP "POLYTY", the yield of grain higher than in the CASP "Zelenka" by 58.9%, but the average annual fishing is below 1%.
Topic: "Average values"
Task 1.
Decision:
The average yield for each culture is variants of the signs (x).
The average yield in the grain group as a whole is determined by the formula of the middle arithmetic weighted, since the area (F) is not the same:
= ![]() 23.8 (c / ha)
23.8 (c / ha)
Task 2.
Decision:
The conditions of the problem differ from the condition of the first, source data, there is a yield () and gross collection (), but the area (F) is not given. In this case, we calculate the average by the formula of the average harmonic. And since the gross collection (-Aves) is not the same, according to the formula of the average harmonic suspended
substituting the values \u200b\u200bin the formula and lead to the same measurement units
Garm \u003d \u003d \u003d 26.9 (c / ha);
Implementation of a plan:
% to be performed \u003d 100%;
% to perform \u003d 100% \u003d 101.5
The farm has exceeded the yield plan by 1.5%.
Task 3.
The yield of potatoes on the farms of the district is characterized by the following data:
Calculate the middle yield in areas.
Decision:
The average yield is the options for signs (), but they are presented in the form of intervals. Therefore, first, it is not necessary to determine the interval of each of the intervals in (as the floor of the lower and the upper border). Determining the size of the open interval (first) focus on the magnitude of the subsequent interval, the latter on the magnitude of the subsequent interval. Then the middle of the interval of the first \u003d 85; The latter - \u003d 150. The average yield is determined by the formula of the average arithmetic value
= = ![]() \u003d \u003d 105 c / ha
\u003d \u003d 105 c / ha
Task 4.
There are data:
Calculate: - average yield for the grain group, c / ha;
The average cost of 1t, thousand rubles;
Average labor cost per 1t grain, person.
Decision:
To calculate the average yield, we take yield and gross collection, we expect the formula for harmonic suspended:
Garm \u003d \u003d \u003d 21.7 (c / ha).
To calculate the average cost, we take the cost of 1T () and gross collection (F). The average is calculated by the formula of the middle arithmetic weighted:
= ![]() =
= ![]() \u003d 401.3 (thousand rubles).
\u003d 401.3 (thousand rubles).
To calculate the average cost of 1 ton, we take the cost of all products () and the amount of products manufactured (F):
12.9 (s).
Topic: "Variation Indicators"
Task 1.
There are data on the delivery of the session in two groups
Decision:
The average exposability score is determined by the average arithmetic weighted:
As
The averaged sign (score) is given in the form of an interval - we define the middle of each of the intervals, then:
Medium exposure score on the first group:
= ![]() = = = 6,0;
= = = 6,0;
Medium exposure score on the second group:
= ![]() = = = 5,5.
= = = 5,5.
Humane performance is higher in the first group, but in order to characterize where the academic performance is more stable. Calculate the indicators of variations (oscillations):
The average square of deviation and coefficient of variation.
The average square of deviation (dispersion) on the first group:
= ![]() = = 4,4;
= = 4,4;
= = ![]() = = 1,85.
= = 1,85.
The variation coefficient characterizes the deviation as a percentage:
100% = 7,3%;
100% = 4,2%.
The average performance of the performance is higher in the first group, however, more stable performance (homogeneous) in the second, since the indicator of variation (oscillations) of academic performance in the second group is below.
Topic: "Rows of speakers"
Task 1.
There are data:
The yield of potatoes (in farms of all categories of the Republic of Belarus; centners with one hectare)
| Years | |||||
| Yield |
Describe a dynamic series.
Absolute increase;
Growth coefficient;
Growth rate;
Rate of increase.
Decision:
The dynamic range of interval, complete, levels are expressed by absolute averages.
Absolute increase, c / ha
Basic method:
Valuable way:
186 – 221 = -35
Rosta coefficient
Basic method.
The main directions of increasing production of crop production are presented in Fig. 2.
You can trace how the production of products will change due to the expansion of the sowing space i. The use of land resources (inclusion in agricultural turnover of lands engaged in shrubs, deposits, wetlands, under the roads and drives, etc.).
Unused reserves for increasing production of products due to incomplete use of land resources are considered to be those related to the foreclosure of measures to improve land improvement.
The production of crop production is carried out on Earth, which in agriculture acts as the main means of production. The spatial disgrace of agricultural production and its close dependence on the natural and climatic conditions, as well as the maintenance of agricultural activities on various soils in terms of quality, determine the need for a rational placement of cultures, which, in combination with a specialization, is capable of providing a significant impact not to obtain results. Thus, a significant reserve for increasing production in crop production is to improve the structure of the sowing space, i.e. The increase in the share of more crops in the overall sown area. To calculate the magnitude of this reserve, it is first necessary to develop a more optimal structure of crops for this economy, taking into account all its capabilities and restrictions, and then compare the actual volume of products with a possible one, which will be obtained with the same common actual area, with the actual crop yield, but with improved The structure of crops.
Figure 2. The main directions of increasing production of crop production
For example, the farm has the opportunity to increase the share of more yields of vegetable crops due to the reduction of the share of less crops. To determine the increase in production of vegetables, it is necessary to make a calculation based on the method of the chain substitution
An increase in production of crop production also depends on the growth of crop yields. Economic studies, as well as the work of many Agrarian scholars, show that the high level of crop yields can be achieved only with a high culture of agriculture, the use of mineral fertilizers and plant protection products, using high-quality seeds, which implies the need for additional costs. In the production of grain, sugar beet and other crops based on the use of intensive technologies, a three-four-fold increase in profits is achieved, with an increase in the total costs of material and cash by 1 hectare by 20-60%, while ensuring the timely payback of additional funds invested. Thus, the growth of crop yields can occur due to:
- a) increase the dose of fertilizers;
- b) increase their payback;
- c) the introduction of more crop crops;
- d) reduce product loss when harvesting;
- e) improvement of hayfields and pastures and other agrotechnical events.
In order to calculate the increase in production due to additional fertilization, it is necessary for the number of additional fertilizers under the I-YU culture in recalculation to the active ingredient multiplying the actual increase in the crop of this culture, which 1 C NRC is provided in the economy.
A significant increase in production in crop production occurs due to the increase in fertilizer payback, which in turn depends on the dose and quality of fertilizers, their structure, deadlines and methods of entering into the soil. The increase in payback (efficiency) of fertilizers is determined when analyzing their use by developing specific measures (construction of warehouses for storage, balance of fertilizers for each culture, etc.). Then a possible increase in fertilizer payback is multiplied by their planned volume of application in the soil for each culture and thus determines the reserve for an increase in production production.
Increased yields largely depends on the level of seeding, quality and varieties of seeds. The lack of seeds, lowering the seeding rate, the use of substandard seeds reduce the number of plants on each hectare, create conditions for breeding weeds, reduce crop yields. It is necessary to establish whether the seeding norms were performed, taking into account the quality of seeds, what is the actual germination of seeds (according to the control examinations of sites and fields). If there was a degree of fields as a result of a decline in the seeding rate, poor quality of seeds, disorders of the deadlines and methods of Seva, it is necessary to calculate how much the yield of culture has decreased due to this factor.
A great impact on the yield has a plan to implement more promising and high-yielding varieties. Due to the not fulfillment of the plan of sowing of some varieties and over-fulfillment, the relationship between them is changing. If the share of more crop varieties increases, then as a result, the average yield of culture increases and vice versa. Calculate the influence of this factor on the change in the yield of the culture can be a way of chain substitution or absolute differences.
Significant loss of crop production may be due to impaired methods and cleaning. Their total volume can be defined as the difference between the biological and actually obtained mass of the harvest. In case of violation of harvesting, grain squeezing occurs, the loss of the physical mass of the majority of crops. The difference in yields when cleaning at an optimal time and later than these deadlines, multiplied by the area deployed with a delay, in this case will show the real amount of the reserve. To reduce losses in the harvesting of potatoes in farms, it is envisaged after harvesting harvesting a potato field, then peaks and re-harrow. If these events were not conducted or were carried out in an incomplete amount, it is necessary to calculate the unused potato production capabilities. Counting is carried out as follows: Non-fulfillment of the plan for each type of post-harvesting works is multiplied by the average collection of tubers with 1 hectare when conducting an appropriate event.
Without the last place in increasing production of crop production, it is possible: ways and quality of land processing, methods of sowing and crops, alternation of crops in the fields of crop rotation, limestorming of the soil, improving meadows and pastures, etc. This can be determined if you compare the yield of crops in the fields, on which the corresponding event was conducted and was conducted.
An important reserve for increasing production is the prevention of losses when harvesting. In case of violation of the coupling time, the grain is obsessed, the loss of the physical mass of most agriculturals ...
The production volume of agricultural products is one of the main indicators characterizing the activities of the agricultural enterprise. The amount of product sales depends on its magnitude, and therefore the degree of satisfaction of the needs of the population in food products, and the industry - sir. The level of its cost, the amount of profit, the level of profitability, the financial position of the enterprise, its solvency and other economic indicators depend on the production volume.
The size and structure of sowing areas is significantly affected by the production of crop production. Consider and analyze the size and structure of the sowing space in the SEC "Krasavsky collective farm.
Table 6 - Size and structure of scenery
|
Name of culture |
Sowing Square, ha |
Structure of sowing areas,% |
||||
|
Cereals - total |
||||||
|
including: Winter grains |
||||||
|
skin grains |
||||||
|
scented tops |
||||||
|
Sunflower |
||||||
|
Perennial herbs |
||||||
|
Annual herbs |
||||||
|
Silosal cultures |
||||||
|
All sowing square |
In the reporting year, compared with the previous year there was an increase in the sowing area at 473 hectares and it was 5735 hectares. This happened mainly due to the expansion of the seed area under spring grain at 500g, perennial herbs on 547 hectares and corn on the silage and green feed for 51 hectares. At the same time, the sowing area was significantly reduced under winter grains by 242 hectares, gentlemen on 16 hectares, sunflower on 80 hectares, annual herbs at 267 hectares and silo cultures of 20 hectares.
Grain -2673 (46.6%), including tark grain -1467 hectares (54.9%), winter grain-911 hectares (34.1%), grain-1911 hectares (34.1%), occupy the main share in the structure of the seed area. 11.0%) and perennial herbs -1214 hectares (21.2%). The share of corn on the silage and green feed was 529 hectares (9.2%), annual herbs - 525 hectares (9.1%), silage crops -100 ha (1.7%) ..
Table 7 -Valova Collection and yield of agricultural crops in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
|
Name of culture |
Gross Collection, C |
Yield, c / ha |
||||
|
Grain and leguminous, including: |
||||||
|
winter grains |
||||||
|
skin grains |
||||||
|
scented tops |
||||||
|
Sunflower |
||||||
|
Perennial herbs most, including: |
||||||
|
on seeds |
||||||
|
on green feed |
||||||
|
Annual herbs - including, including: |
||||||
|
on seeds |
||||||
|
on green feed |
||||||
|
Corn on Silo and Green Feed |
Table 7 Analysis shows a reduction in the reporting year of gross grain and leguminous collection to 30612 c, sunflower up to 5780 C, perennial herbs per hay to 9633 c and for seeds up to 6120 centners, annual grasses for seeds up to 5488 centners. Significantly reduced gross collection of winter grains to 19440 c and spring grain to 8262. At the same time, there was an increase in the gross gauge of the grainbobs -2910 C, perennial herbs on the green feed -199 c, the annual herbs on the hay -9947 C and corn on the silage and green feed -67551 c.
In 2012, there is an increase in the yield of grain and leguminous products to 15.38 c / ha, including winter grain -21.34 c / ha, grain-volume -9.86 c / ha; Annual herbs on the hay -33,38 c / ha and corn on the silage and green feed -127,70 c / ha. The yield of such types of products has decreased as spring grain -8.39 c / ha, sunflower -8.3 c / ha, perennial herbs on hay -27.44 c / ha.
The production of crop production depends on the size of the sowing areas and the yield of crops. Consider the influence of these factors on the change in gross production.
Table 8 - Reliance of the yield and size of seatic areas to change the production of gross products in SEC "Krasavsky collective farm"
|
Type of products |
Square sowing, ha |
Yield, c / ha |
Gross Collection, C |
Deviation 2012 from 2010, C |
|||||
|
including due to |
|||||||||
|
S yield |
|||||||||
|
Winter grains |
|||||||||
|
Skin grains |
|||||||||
|
Scented tops |
|||||||||
|
Sunflower |
Analyzing Table 8 It can be concluded that the decline in the reporting year of the gross collection of winter cereals on 1026 c occurred due to the decrease in the seed area at 1520 hectares, the spring grain to 9070 ° C by reducing the yield at 2.29 centners / ha. At an increase in the size of the gross collection of sunflower on 437 C affected the increase in yield by 0.8 c / ha ..
Commodity products are called part of gross products intended for implementation. The main indicator characterizing the marketability of the enterprise is the level of marketability. Vehicle level is the ratio of sales and gross, expressed as a percentage:
where TP -Ronalized products rubles;
Navel products, rub.
Calculate the level of products of crop production for SEC "Krasavsky collective farm for 3 years:



Item level in the period 2010-2012. It averages 80%. This suggests that the main proportion of crop production produced enterprise is implementing and only a small part uses for his own needs. At the same time, the largest level of rationality was observed in 2011 - 103%, which indicates a reduction in excessive stocks of crop production. Surplus reserves were formed due to the low level of production of crop production, which in 2010 was 62%.
Agricultural enterprise can implement its products in the following areas: product sale by other organizations and enterprises, selling products on the market, on barter transactions, the sale of the population and in the account of wages to employees of the economy.
Consider the channels for the sale of crop production in SPK "Koltoz" Krasavsky "
Table 9 - Channel sales of crop production
The economy in the reporting year realized the products of crop production to other organizations, in markets, employees of the enterprise and the payment of dividends. Revenue for all realized products amounted to 10120 thousand rubles. The largest share in the total volume of sales is occupied by markets and other organizations -80%. Revenue according to this channel is 8046 thousand rubles.
Cost of agricultural products. Profitability of agricultural production
1. The essence of production costs and cost of production, types of cost
Classification of production costs when calculating products
Methods for calculating the cost of crop production (on the example of grain crops) and animal husbandry
The structure of the cost of crop production and animal husbandry and the main ways to reduce costs
Gross and Commodity Products, Gross and Pure Income, Profit, Profitability
1. The essence of production costs and cost of production, types of cost
Production of agricultural products is associated with the use of industrial resources of the industry - labor, land, water, material, in the course of which they are partially or fully consumed or transferred to the created products. The combination of production resources consumed and transferred to products is costs of its production. Distinguish public costs and costs of manufacturing enterprise. Public coststhis is a combination of the cost of society as a whole to produce a particular type of product. They constitute the cost of products and include: 1) labor costs, 2) cost of consumed material resources and 3) the cost of the surplus product created by the labor of employees for society and to cover the cost of education management, health care, defense and other public Needs, as well as on the expansion of production.
The first two parts of the cost are costs of production of the enterprise, they consist of the cost of labor and the cost of consumed material resources - annual depreciation of fixed assets (warehouses) participating in the production of products - machinery, equipment, buildings, etc., as well as the cost of the production process (objects) - Seeds, feed, fertilizers, fuel, etc.
In production costs include the cost not applied, but consued production resources. So the costs of the necessary work are part of the production costs not largely created by this labor work, but on labor costs. In production costs include not the cost of land resources and fixed assets, but only costs associated with their use, not the cost of material working capital, but only the value of material costs. The combination of current costs for the production and sale of products expressed in cash is costs of products.Thus, the cost of production expresses the value of the consumed part of the production potential of agriculture.
Product costs It is one of the most important indicators of economic efficiency of agricultural production, it shows that the production of agricultural products, including in the enterprise. The cost is reflected in the cost of the economic activity of agricultural enterprises: the efficiency of the use of production resources, the state of technology and the organization of production, the introduction of the achievements of science and best practices, the level of management of the economy. The cost of the cost of products is necessary to substantiate the placement and specialization of agricultural production, the determination of its economic efficiency, establishing zonal procurement prices.
The sum of all production costs of the enterprise to obtain products is the cost of gross production (SV), it can be expressed by the formula:
SV \u003d PZ or SV \u003d from + A + MW.
According to economic content (cost composition), the following types of cost are distinguished: technological, industrial and complete.
Technological cost Includes costs due to production technology, as well as the cost of organizing and managing production in brigades, farms.
Production cost It is the sum of the technological cost and costs of managing the enterprise and the organization of production in general (generality expenses).
Complete cost- The sum of production costs and exproductive expenses.
Planned cost Calculate in the preparation of annual production and financial plans for agricultural enterprises, and in the intra-economic calculation it is also calculated for departments, farms, brigades. The calculation of the planned cost is based on progressive labor costs, materials, depreciation (depreciation standards), management costs, as well as on adopted technology and organization of production and planned amount of gross production.
Regulatory cost Determine on progressive norms of labor costs, material and cash on hectares of sowing, livestock head, unit of products.
Provisorial (expected) cost, As a type of planned, includes the actual costs of manufacturing products for 9 months and planned costs in the fourth quarter combined.
Reporting, or actual cost Products are calculated when summing up the economic activities of agricultural enterprises based on the annual production report. The reporting cost is calculated according to the accounting report on the number of products obtained and the actual labor costs and material resources for its production.
Comparison of actual indicators with planned or regulatory costs allows to identify the permissible workpiece of labor and means, to establish its causes and schedule measures to reduce product costs.
2. Classification of production costs when calculating products
All production costs included in the cost of production in agriculture are grouped by various features. According to the role in the production process, costs are divided into basic and invoices. TO the main costs These include those directly related to the production of a certain type of product, they take into account the main part and are predominant in the overall amount of costs. Thus, when calculating the cost of milk to the main costs include wages of production workers, the cost of feeds, the cost of maintaining fixed assets DB. When calculating the cost of grain-wages of mechanisters, the cost of seeds, the cost of operation of machines, etc. overheadbelow the cost of organizing production and managing the industry or farm as a whole.
According to the method of assigning products and inclusion in the cost price, costs are divided into direct and distributed. Direct costsdirectly relate to the production of a certain type of product. Distributed costsassociated with the production of several types of products, by virtue of which the distribution of them between individual types of products is carried out indirectly.
In terms of production, the costs included in the cost of production are divided into simple (single-element) and complex (multi-element). Simple- These are the costs consisting of homogeneous elements (the cost of seeds, feed, salary, etc.). Comprehensive costs Consist of several simple - for example, the cost of milk includes the salary of farm workers, the cost of feed, depreciation and the current repair of cowners. In relation to the volume of production, costs are divided into conditional variables and conditionally constant. Costs whose size changes in proportion to volume change change is called conditional variables. For example, an increase in sowing area causes a corresponding change in seeds, wages, damping machines, etc. Costs whose size does not change or changed little due to changes in production, called conditionally permanent (Depreciation of office premises, the content of administrative and management personnel, etc.).
By the time of participation in production, costs are divided into the costs of the current year and the costs of next year.
3. Methods for calculating the cost of crop production (on the example of grain crops) and animal husbandry
The calculation of the cost of products in agriculture has a number of features caused by its specificity.
First feature It is that the annual production cycle of production in agriculture, as well as the difference between production time and the working period, determine the possibility of calculating the cost of products only after the end of the economic year. Production of individual types of livestock production (milk, rack, growth, etc.) occurs more or less evenly during the year, but their cost is impossible to calculate monthly, since the cost of maintenance of production and management can be distributed only after determining the amount of direct costs in all Industries. In addition, a significant part of crop production is used as animal feed; Therefore, initially determine the actual cost of production, and then calculate the cost of animal husbandry production.
Second feature It consists of many crops and animal husbandry of several types of products from many agricultural crops. In this regard, there is a need to distribute the costs between the specified types of products.
Third singularity is the definition of the incomplete amount of production only at the end of the year as of January 1. These costs include the cost of the crop of next year.
Fourth feature characterized by the procedure for calculating the reporting cost at the end of the year; During the year, all products are taken into account by planned cost, which does not allow the end of the year to identify the actual amount of costs.
In agriculture, the cost of all the main types of crop production and animal husbandry, as well as serving industries. Objects calculating costs in crop production and are groups of cultures (grain without corn, vegetables of closed and open soil, junk, perennial and annual herbs, etc.) or individual cultures (potatoes). In animal husbandry, the objects of calculation of the cost are a milk herd (milk and indelod); young cattle and adult cattle on fattening (increase); Pigs (increase); Bird adult (egg); Young bird (growth) Bee (honey, wax and swari).
When calculating the cost of certain types of products, the number of obtained main, conjugate, and by-products obtained by type is determined. It is almost impossible to organize separate accounting for the production of each type of production. Therefore, the distribution of production costs between all kinds of products is carried out using the following methods:
method of direct class attribution to the relevant types of products;
the cost of the costs of the costs between the types of products of individual crops, animal species in proportion to the quantitative value of one of the signs common to the types of products obtained (for example, in proportion to the amount of full-fledged grain contained in them, the supply of nutrients, etc.);
the method of distribution of costs is proportional to the cost of products in the assessment at realized prices.
Costs for cultivation and cleaning grain crops (Including the costs of cleaning and drying the grain for the current) make up the cost of grain, grain consists and straw. The cost of straw is determined by costs of costs established on its workpiece and is excluded from the total amount of production of grain crops. The grains are counted into full grain at the specific grain content in them. The cost of 1 C grain is determined by dividing the total amount of costs (minus the cost of straw) for the total amount of grain, taking into account the grain consists (full grain). To calculate the cost of 1 C of grain consists, it is necessary for the cost of 1 C of full grain to multiply on the specific weight of the grain content in the grain consides.
where: Sensitiveness 1 C Grain, r.;
The cost of 1 C of grain seeds, r.;
PZ- total amount of the cost of cultivation of grain crops (without the cost of straw), r.;
LED grain. c;
The number of grains, c;
Dual grain in grain.
IN dairy cattle breeding The costs of the maintenance of cows after the exclusion of the cost of by-products (manure) is distributed in accordance with the flow rate of feed: for milk - 90%, on the range - 10%:
where: cm - the cost of 1 c milk, r.;
ST - Cost 1 of the source head, r.;
PZ - the total amount of the cost of the maintenance of cows (less the cost of manure), p.;
VPM is the amount of milk, c;
VPT- amount of ranges (calves), goal;
nine; 0.1 The proportion of the cost of the maintenance of cows to the distribution by types of products.
In animal husbandry, it is also possible to calculate the cost of 1 c increase in the living mass of livestock, which is determined by dividing the total amount of production costs for livestock for the year on the gross increase in vibrant mass. Along with this, the cost of 1 s living livestock mass is also calculated by the formula:
where: PZ- production costs of the increase in livestock, r.;
BS- Balance cost of livestock at the beginning of the year, r.;
The cost of cattle received during the year to grow and fattening, r.;
SPR - the cost of the rating, r.;
a- livestock, remaining at the end of the year, c.
basic livestock mass dropped during the year, c.
4. The structure of the cost of crop production and animal husbandry and the main ways to reduce costs
By economic maintenance costsrelated to product production is divided into a number of homogeneous groups - economic elements of costs:
- Costs for labor with social insurance deductions.
- Material costs.
- Depreciation of fixed assets.
- Insurance plates
- Other costs.
Cost division by economically homogeneous elements Used in collective farms and state farms when planning and accounting to determine wage funds, depreciation deductions, the cost of creating or acquiring new material resources. Cost accounting for economically homogeneous elements is valuable in that it does not contain a re-invoice and does not include an intravenial turnover. However, economically homogeneous elements of costs are not possible to determine the cost of individual types of products, since the specified grouping costs is carried out in general by the economy or by industry without distributing them by types of products.
The composition of the costs included in this or that article of unequal, and their value depends on the number of industrial resources consumed in physical terms and monetary assessment of them.
Cost of production of crop production:
Costs for labor.
Seeds and planting material.
Fertilizers.
Plant protection products.
Work and services.
The cost of maintaining fixed assets.
Costs for the organization of production and management
Insurance payments.
Other costs.
Cost of livestock production.
- Costs for labor.
- Animal protection means.
- Stern.
- Work and services.
- The cost of maintaining fixed assets.
- Costs for the organization of production and management
- Insurance payments.
- Other costs
- Losses from the case of animals (in account).
The ratio of individual cost articles, expressed in percent characterizes product cost structure. The structure of the cost of various sectors of agriculture and types of products of Nonodynakov. It depends on the type of product, the nature of production, the number and value of the technique used and the level of mechanization, the number and cost of fertilizers, feed and other means of production, the yield of crops and livestock productivity, the organization of production, labor productivity and other factors. IN crop productionthe main share of costs production production consists of maintenance costs, labor payment, the cost of seeds, and animal husbandry - the cost of feed and pay for labor. The relatively high propellation weight of the goods in the cost of production indicates the insufficient level of mechanization of work in the production of products (potatoes, vegetables, dairy cattle breeding). With a high level of production mechanization, the share of wages in the cost structure is lower, but above the share of the cost of maintaining the main funds and current repairs, fuel and lubricants (grain production, pig breeding, poultry). The high proportion of the cost of feed (pig breeding, poultry farming) is mainly due to the use of expensive feed-feeds, potatoes, etc.
Reducing the cost of agricultural products is an important agricultural problem, one of the main conditions for increasing agricultural efficiency. Reducing the cost of production is one of the main sources of savings, ensuring expanded reproduction on the basis of accelerating scientific and technological progress.
The main ways of reducing production costs on agricultural products are:
- Reducing the complexity of production due to the introduction of more advanced machines, the growth of the level of integrated mechanization, which leads to a reduction in the cost of living labor and labor costs per unit of production, however, the reduction in production costs will occur if the costs of remuneration to decrease more extent than There will be increased cost-related machines. A prerequisite for reducing the cost of products by reducing remuneration is also ahead of the growth rate of productivity compared to the rate of increasing its payment.
- Reducing the durability of productiondue to the high-performance use of fixed assets, productive livestock, buildings and structures, etc. An important way to reduce the durability of production in agricultural enterprises- an increase in the intensity of the use of those elements of labor, which directly affect the increase in fertility of land and livestock productivity. The increase in the intensity of the use of fixed assets leads to the fact that depreciations are attributed to the cost of certain types of products in a smaller size, which leads to a decrease in its cost. It is also possible to reduce the tract capacity of production by removing unnecessary, as well as unused fixed assets and transmitting them to other farms. Construction of the most economical production buildings.
- Reducing the material intensity of productionmust go , on the one hand, by reducing costs in physical terms based on improving the quality and economical spending of material working capital, on the other hand, by reducing their value. Material intensity of production B. crop production Many extent depends on the level of costs for seeds and planting material, which in turn is determined by the value of the sieved seeds and their value. It is also possible to achieve a decrease in the material intensity of production in crop production by reducing the expenditures on the operation of equipment (fuel and lubricants, the cost of car repair). IN animal husbandrythe decrease in the material intensity of production can be ensured primarily by reducing the cost of feed. Since the value of the costs on this article depends on the number of feed consumed and their cost, all activities contribute to the full ensuring the livestock of all types of livestock with high-class own feeds and a decrease in the cost of one feed unit due to the growth of the yield of feed crops and the mechanization of feed production will influence the decrease in material consumption Products.
- Reducing the cost of organizing production and management.
The main way of reducing these costs is the reduction of administrative and management personnel on the basis of improving production management.
5. Improvement of specialization and increased production concentration. Rational specialization and strengthening of agricultural production make it possible to efficiently use production resources, grow those cultures, breed the breeds of livestock for which there are most favorable natural and economic conditions, along with this deepening specialization and enhancement of production concentrations create favorable conditions for the introduction of complex mechanization, progressive technology and organization of production. IMPORTANT, to reduce production costs, rational intra-economic specialization and production concentration.
6. Implementation of resource and energy-saving technologies.Intensive and industrial technologies Production of products in crop production and animal husbandry contribute to both increasing the productivity of land and livestock, so t in the economical and savings of production resources- labor, land, water, material, due to the way such technologies act as resource-saving. An important economic lever of ensuring the efficient use of production resources is scientifically based on their rationing.
7. Improving the organization of labor. Progressive forms of organization (and payment) of labor, especially a collective contract in agriculture and animal husbandry, with the payment of gross income. Promotes labor productivity in agriculture.
5. Gross and Commodity, Gross and Pure Income, Profit, Profitability
cost Cost Cost Agricultural Profitability
The ultimate result of the production activities of agricultural enterprises is gross agricultural products.Under Gross Products of Agriculture Understand its amount produced during a certain time (usually per year). It includes products of crop production and animal husbandry:
- main products, i.e. that for the sake of which agricultural production is carried out - grain, potatoes, vegetables, milk, wool, etc.;
- slodes, the increase in live livestock and bird mass;
- the cost of perennial plantings and incomplete production (costs for sowing winter and soil preparation for the crop of next year);
- by-product, i.e. obtained simultaneously with the main stralav and others.
Gross Products of Agriculture It is planned and taken into account in natural and cost Indicators. Natural indicators reflect the size and composition of consumer values \u200b\u200bcreated in agriculture. An indicator of gross production of crop production in physical terms is the gross collection of a separate culture or group of homogeneous cultures, and animal husbandry- production of certain types of products, calculated in centners, tons, etc.
Gross products Agriculture, depending on the destination, is divided into two parts. One part (seeds, feed, milk for avoiding calves) is consumed directly in agriculture for production purposes. Other (remaining) - is the final products used mainly to implement. It is the final product that the real contribution of each enterprise, the area, areas into the production of gross social product is determined.
For a cumulative expression gross Products of Agriculture Rate in comparable or current Prices.
To determine the physical volume of products, its changes over the years, as well as the calculus of annual and watch productivity, foundation and other targets of gross products estimated in comparable prices 1983.
Evaluation gross products in current prices Used with the calculation of gross and net income of agriculture. In this case, all implemented products Estimated according to the actual existing realization prices, and the rest (non-universal) part is at cost. In agriculture cumulative gross products It is defined as a simple amount of products of various industries, i.e. With the inclusion of mutual turnover taking place between them (gross turnover).
Gross products of agriculture in value expression gives a generalized characteristics of all material goods created in the industry.
However, the indicator gross products in terms of valuation In agriculture, there is a number of shortcomings that affect the magnitude of the indicators of economic efficiency of production, using gross products:
Gross products are the result of the costs of not only living, but also last labor, as a result of which the indicators calculated on gross products can be high not only by saving live labor, but due to the increase in the material intensity of products related to the overpowering of material resources.
The active methodology for determining the cost of gross products as the amount of it on crop and animal husbandry is allowed to repeat.
When assessing gross products in current purchasing prices, the actual value of it is incorporated, since the universal part of gross products is estimated at cost, which is usually below the procurement prices for pure income, i.e. The cost of gross products does not take into account the surplus product expended on the production of the universal part of gross agricultural products.
The gross product indicator does not reflect its quality, due to the specified shortcomings of the scope of the gross production indicator, is limited.
The final products of agriculture develops from products intended for implementation (but not yet realized) and implemented. Implemented Call products of crop production and animal husbandry sold by agricultural enterprises on all channels - the state, cooperative organizations, the rural population, through their dining rooms, etc. TO commodity Believe the products implemented outside the farm and enrolled in the people's turnover. When implementing, commercial products from a natural form goes into the value in the form of monetary revenue or cash income, some of the gross products immediately takes the value of the value for the service to the services rendered and the work performed for other enterprises and individuals.
Essential for society also has vehicle level. Under volost levelagricultural production understand the ratio of commercial products to gross, expressed as a percentage. When determining the level of marketability of certain types of products, the value of gross and commercial products in physical terms is used, and in determining the level of markets of all agriculture, a separate enterprise or to compare the markets for various industries that give inhomogeneous products, use the value of gross and commercial products.
Gross income Includes the necessary and surplus product. Clean income - There is a monetary expression of the cost of the product for society. It includes the entire surplus product and the part of the required product, which goes to the personal consumption of material production workers through public consumption funds. Quantifying income is the difference between the cost and production cost (SP) of gross agricultural products:
SVP - SP \u003d CH.
Profit It is a realized part of pure income and is calculated as a difference between the value of the (commodity) product or, which is the same, monetary revenue from its implementation (DV) and commercial (full) cost of commercial products (SC):
STV (DV) - SC \u003d CDD (PR).
If you do not have the entire amount of commercial (full) cost, but only material costs, then as a result will remain income:
STP (DV) -MZ \u003d D.
Profit or income are synthetic indicators of the effectiveness of human enterprises. They characterize the final economic indicators of farms, including activities not only in the field of production, but also in the sphere of circulation, implementation. Profit or income - as if focus, in which all the components of the economic activity of enterprises are reflected. First of all, they reflect the cost of living labor, as they are based on the gross income - the newly created value, produced by the living labor of workers, beyond the part of its part that reimburses the costs of wages.
However, profit or income indicators are not the only and inclusive to characterize production efficiency. As a generalizing indicator of the trade-economic efficiency of agricultural production of agricultural enterprises, profitabilitySince it finds a reflection of the efficiency of the use of industrial resources of industry, land, water and material, the level of management and organization of production and labor, the quality and results of product implementation, the possibility of extending the reproduction and economic stimulation of workers.
Profitability It is an economic category reflecting the profitability, the profitability of the enterprise, expressed in the indicators of gross, net income, profits or income.
There are profitability of two species: an economic and national economic. Hosiest profitability - This is the profitability of a separate agricultural enterprise or a separate type of product. It depends on the number and quality of products, the level of purchasing prices and the cost of production costs. However, the state through purchasing prices is withdrawn by a part of the surrender of the surcharge product at its disposal for nationwide needs. If we take into account this part of the surplus product (through retail prices) and move it from those additional costs that are manufactured at the stages of the processing, storage and sale of finished products, then the profitability is calculated in this way will be profitable than national economic.
Relative indicators of product profitability, Called by the norm (during planning) or level (under analysis) profitability (PB), calculated in percentage of gross or net income on the magnitude of potential, applied or consumed resources (production costs) and multiplying the result obtained by 100:
These indicators characterize the effectiveness of gross production and show how many gross or net income is obtained based on the ruble of production resources. Relative indicators of profitability of implemented (commodity) productsAlso called the norm or level of profitability (PP) are calculated as a percentage division of the amount of profit or income on the magnitude of potential, applied or consumed resources - commercial (full) production costs and multiplying the result obtained by 100:
This indicator characterizes the effectiveness of the implemented (commodity) products and shows how much profits or income is obtained for the ruble of resources. If the level of profitability of realized products for consumed resources is 40%. This means that for every 100 rubles of costs after its compensation, 40 rubles of profit (income) were obtained.
The level of profitability of implemented (commodity) products for consumed resources can also be determined using several other formulas:
All of the above profitability characterize the economic efficiency of using current production costs for products, however, agricultural enterprises produce on only current production costs, but also carry out capital investments on the increase and updating of fixed assets, the cost of which is incorporated in the production costs of each year not fully, but Part equal to the sums of depreciation deductions. Therefore, it is important to know the effectiveness of not only current production costs, but also the effectiveness of the use of one-time costs materialized in production facilities. To this end, relative profitability indicators calculated as the percentage of net income, profit or income to the average annual value of the main and material working capital are separately, as well as total (basic and material revolving combined) funds called round profit:
These indicators characterize the efficiency of use in the first case of the main, in the second - material revolutions, in the third total means of production. They show how much profits or income is obtained per unit value of relevant means of production. The more profit received the ruble of the means of production, the therefore they are more efficiently used.
Tutoring
Need help to study what language themes?
Our specialists will advise or have tutoring services for the subject of interest.
Send a request With the topic right now, to learn about the possibility of receiving consultation.