The negative impact of the profession on a psychological condition is called. The problem of mental functional states in professional activities. Questions for repetition
As a rule, labor has a positive effect on man and his personal features. However, professional development can be and descended. The negative impact of the profession on the identity can be partial or full. With partial regression professional development Some one element is affected. Complete regression means that negative processes affected the individual structures of the psychological activity system, leading to their destruction, which can reduce the effectiveness of activities. A sign of the negative impact of the profession to the personality is the emergence of various professional deformations or specific states, such as mental burnout.
The word "deformation" (from the lat. deformatio. - distortion) means changing the physical characteristics of the body under the influence of the external environment. Under professional deformation, everyone is a change caused by the profession that occurs in the body and acquires a persistent nature ("History of Soviet Psychology of Labor", 1983). The deformation extends to all parties to the physical and mental organization of a person who change under the influence of the profession. This effect is clearly negative, which is obvious from the examples given by researchers (the curvature of the spine and the myopia in the office employees, the flatteriness of the Swiss). Professional deformation can lead to difficulties in everyday life and reduce labor efficiency.
The mechanism of occurrence of professional deformation has a rather complicated dynamics. Initially, unfavorable working conditions cause negative changes in professional activities in behavior. Then, as difficult situations are repeated, these negative changes can accumulate in personality, leading to its restructuring, which further manifests itself in everyday behavior and communication. It has also been established that first negative mental states and installations appear first, then positive qualities begin to disappear. Later at the site of positive properties, negative mental qualities arise, changing the personality profile of the employee (Markova A. K., 1996).
Professional deformation can have a rather complicated dynamics of manifestations in labor activity Man and affect various sides of the psyche: motivational, cognitive, scope of personal qualities. Its result can be specific attitudes and representations, the appearance of certain features (Eagle V. E., 19996).
The deformation of certain individual structures may arise as a consequence of the progressive development of certain traits of character, cognitive entities, motives as a result high degree Specialization activities. The hypertrophied development of these characteristics leads to the fact that they begin to manifest themselves not only in professional activities, but also penetrate other people's lives. Implementation of professional duties does not significantly suffer.
Professional deformation of the motivational sphere can manifest itself in excessive wiping by any professional sphere with a decrease in interest in others. A well-known example of such deformation can serve as the phenomenon of "workolism", when a person spends most of the time in the workplace, he says and thinks only about work, losing interest in the rest of life. In this case, according to the expression of L. N. Tolstoy, it turns out to be "morally anesthetic like smoking or wine to hide from itself the irregularity and vanity of life" (quot. By: Markova A. K., 1996). Labor in this case is a kind of "defense", an attempt to escape from those difficulties and problems that arise in a person's life. On the other hand, personality can highly work in any area devoting all its time, which leads to the absence of interests and activity in other areas. In particular, Ch. Darwin expressed regret that strengthened classes in the field of biology completely held all his time, as a result of which he had no opportunity to follow the innovations of fiction, interested in music and painting.
Professional knowledge deformation may also be a result of deep specialization in any one professional sphere. A person limits the scope of his knowledge by the fact that he needs to effectively fulfill his duties, demonstrating complete ignorance in other areas. "The ignorance of Holmes was as striking as his knowledge. He almost did not have any idea about modern literature, politics and philosophy. I happened to mention the name of Thomas Carlejle, and Holmes asked naively - who he is so famous. But when it turned out that he exactly knows nothing about the theory of Copernicus, neither about the structure of the solar system, I just took it from amazement. - ... on my damn she? - He interrupted impatiently. - Well, well, let, as you say, we rotate around the sun. And if I found out that we rotate around the moon, would this have helped me or my work? " *
* Conan Doyle A. Etude and the Baghro Tones. - M., 1991. - P. 17.
Another form of manifestation of this phenomenon is professional stereotypes and installations (Granovskaya R. M., 1988; Petrenko V. F., 1988). They represent a certain level of the achieved skill and manifest themselves in knowledge, automated skills and skills, subconscious installations that do not load consciousness. The negative effect of stereotypes is manifested in a simplified approach to solving problems, in the idea that this level of knowledge and ideas can ensure the success of activities (Markova A. K., 1996). In a number of professions, these stereotypes and installations are very dangerous. An example of such a profession can be the activities of the investigator. Suspicious as the type of deformation inevitably leads to bias, to an indictment bias in investigative activities. This phenomenon was called "accusatory bias" and represents an unconscious installation that a person whose wines has not yet been proven, definitely committed a crime. The studies have identified the availability of a charge for accusing all the specialties of the legal profession, starting with the employees of the prosecutor's office and ending with lawyers (Panasyuk A. Yu., 1992). Formed from professionals stereotypes and installations can also interfere with the development of new professions. In particular, in the studies we spent, it was shown that the presence of stereotypes in consciousness may make it difficult to adapt the adaptation of doctors who receive the specialty of a medical psychologist to a new profession and affects the idea of \u200b\u200bit. The ideas about the profession of a psychologist from doctors and teachers and psychologists who have basic education and successfully working in their field have certain differences. So, both groups allocate such qualities as the ability to position to themselves, goodwill, care to people. However, if psychologists refer these qualities to the category of professional competence, the doctors and teachers do not. The reason for this may be the transfer of old models to new conditions. AT traditional medicine and pedagogy There is an image of a doctor (teacher) as a professional manipulator, including characteristics such as dominance, authoritarianism, demanding, patient behavior management or student. In contrast to doctors and teachers, psychologists build their image in the context of a psychologically oriented model (Eagle V. E., 1996).
The level of professional deformation of personal features has been studied slightly worse. It is noted that personal features formed under the influence of a profession significantly make it difficult to interact in society, especially in unprofessional activities.
In particular, many teachers are distinguished by the didactic behalf of speech, the desire to teach and educate. If such a tendency is absolutely justified at school, then in the field of interpersonal relationship, it annoys people. For teachers is also characteristic of a simplified approach to problems. This quality is necessary at school in order to make explanable material more affordable, but outside professional activity it generates rigidity and straightness of thinking (Granovskaya R. M., 1988; Rogov E. I., 1998).
Professional deformation of personal features may also arise as a result of the excessive development of one feature necessary for the successful performance of professional duties and spreading its influence on the "non-professional scope of the subject of the subject. For example, the investigator in its work faces deception, cunning and hypocrisy. Based on this, he can produce increased criticality and excessive vigilance. Further sharpening of these features can lead to the development of excessive suspicion, when the investigator in each person sees the criminal, and this feature is manifested not only in professional activities, but applies to family and domestic relations (Granovskaya R. M., 1988).
The deformation of some personal features can be compensated by the development of others. So the employees of corrective labor institutions under the influence of the profession are formed such specific personal characteristics as the rigidity of behavior and the cognitive sphere, the narrowing of the circle of interests and communication. The deformation of the specified characteristics is accompanied by high levels The severity of such personal features, like accuracy, punctuality, conscientiousness. In addition, various psychological structures are subjected to different degrees. According to our data, the emotional-motivational sphere is deformed to a greater extent than the block of personality characteristics (Eagle V. E., 1996).
Another manifestation of the negative impact of the profession is the phenomenon of mental burnout is widely known in the West and practically not investigated in domestic science. Unlike professional deformation, mental burnout can be more attributed to the case of complete regression of professional development, since it affects the person as a whole, destroying it and has a negative impact on the efficiency of work. For the first time, this phenomenon was described by L. Fredereberger, who observed a large number of workers who experience gradual emotional exhaustion, loss of motivation and efficiency. The researcher called this phenomenon term burnout. (burnout) used in colloquial speech to designate the effect of chronic drug dependence. Simultaneously with the observations of X. Fredereberger, a social psychologist K. Masolch, studying the cognitive strategies of people used to combat emotional excitement, found that the studied phenomena affect the professional identification and behavior of employees. She found that lawyers also call this phenomenon by burnout ( Professional Burnout., 1993).
· Mental burnout - Sundar, which includes emotional exhaustion, depersonalization and reduction of professional achievements.
Currently, there are many diverse approaches to the description of mental burnout, which are combined into three large categories depending on the source of its occurrence.
Representatives of interpersonal approaches see the traditional cause of burnout in the asymmetry of relations between workers and clients, which emphasizes the importance of interpersonal relationships in the emergence of burnout. In particular, K. Maslach believes that the main cause of burnout is the tense relationship between customers and employees. The psychological danger of such relationships is that professionals deal with human problems that carry a negative emotional charge that the heavy burden falls on their shoulders.
Among the individual approaches, an existential approach is the most popular representative of which A. Pines. In her opinion, burnout with the greatest probability arises from the social sphere workers with a high level of claims. When highly motivated specialists who identify themselves with their work and consider it a highly valued and socially useful, fail in achieving their goals and feel that they are not able to make a significant contribution, they are burning apart. Work that was the meaning of life for an individual causes him disappointment, the development of which leads to burnout.
Unlike the above approaches, the organizational approach focuses on the work environment factors as the main sources of burnout. Such factors include a large amount of work and above all its routine component, a narrowed area of \u200b\u200bcontacts with clients, the lack of independence in operation and some others. Despite the presence of a variety of approaches, all researchers of this phenomenon converge in the following:
1. Mental burnoutit is a syndrome that includes emotional exhaustion, depersonalization and reduction of professional achievements. Under emotional exhaustion means a sense of emotional devastation and fatigue caused by its own work. Depersonalization implies a cynical attitude towards labor and objects of its labor. In particular, in the social sphere, depersonalization involves an insensible, inhuman attitude to customers coming to treatment, consultation, education and other social services. Finally, the reduction of professional achievements is an emergence of incompetence in workers in their professional sphere, the awareness of failure in it.
2. This phenomenon is professional. To some extent, he reflects the specifics of working with people - a professional sphere, which was first discovered. At the same time, the study of recent years has made it possible to significantly expand its sphere of distribution, including professions in it, not related to the social sphere.
3. This phenomenon is irreversible. Having aroused in humans, it continues to develop, and you can only slow down this process in a certain way. Studies show that short-term waste from labor temporarily removes the action of burnout, but after the resumption of professional duties, it is completely restored.
The classic description of this phenomenon we find the German writer T. Mann in his famous Romance "Buddenbok", where the image of a person containing the main features of burnout, such as extreme fatigue, loss of ideals and following them, as well as loss of love for work. "Thomas Buddenbroch felt immensely tired, broken. That he was given to achieve, he reached and perfectly gave himself a report that the top of his life path was already passed, unless he corrected himself, on such an ordinary and low-lying path, you can generally talk about the vertices ... it was empty on him Heart: He no longer hatched any plans, did not see him in front of him, which could be boring with joy and inspiration ... the lack of interest capable of capturing it, impoverishment, emptying the soul - the devastation is such a complete that he almost felt him as stupid, oppressive longing, - in conjunction with an inexorable inner debt, with a stubborn determination to hide his disigma and observe les Dehors. Made the existence of Thomas Buddens artificial, far-fetched, turned every word, every movement, each, even the most daily act in the tense, pushing the forces of the hyseride "*.
* Mann T. Buddenbok. - M., 1982.- with. 540-544.
The burnout is an independent phenomenon, not conducible to other states found in professional activities (stress, fatigue, depression). Although some researchers tend to consider mental burnout as a long worker stress, the experience of stressful factors, most researchers converge that stress and burnout are also related, but relatively independent phenomena. The ratio between burnout and stress can be considered from the standpoint of the temporary fractation and the success of adaptation. The difference between stress and burnout lies primarily in the duration of the process. The burnout is a long, "stretched" working stress in time. From the point of view of Selre, stress is an adaptive syndrome that mobilizes all sides of human psyche, burnout is a breakdown in adaptation. Another difference between stress and burnout is the degree of their prevalence. While stress may experience each, burnout is the prerogative of people having a high level of achievements (Eagle V. E., 1999). Unlike stress arising in countless situations (for example, war, natural disasters, illness, unemployment, various situations at work), burnout more often manifested when working with people. Stress does not necessarily be the cause of burnout. People are able to work perfectly in stressful conditions, if they believe that their work is important and meaningful (Eagle V. E., 1999).
Thus, although there is some generality between stress and burnout, the latter can be considered a relatively independent phenomenon.
Some researchers bind burnout with depression and disappointment in work. Indeed, these concepts can be closely correlated with each other, and it is quite difficult to find differences between them. X. Fredereberger pointed out that depression is always accompanied by a sense of guilt, burnout is always accompanied by a sense of anger. Unfortunately, this thesis had only clinical evidence. At the same time, the difference between burnout and depression is caused by a greater degree of universality of the latter. If burnout is manifested only in professional activities, depression is more global, and its action is viewed in various life contexts. Research of the connection of depression and constituent burnouts show the presence of a close correlation of depression and emotional exhaustion. As for the relationship between depression and the rest of the components of mental burnout, it is pretty poorly visible. Consequently, the conclusion of many authors about the coincidence (overlap) of the concepts of "burnout" and "depression" is true only in part (Eagle V. E., 1999).
The main difference between burnout and fatment is that in the latter case, a person is able to quickly recover, and in the first - no. An analysis of the subjective sensations of people experiencing burnout syndrome shows that although they feel physically exhausted, but describe this feeling as significantly different from the "normal" physical fatigue. In addition, fatigue as a result of physical exercises may be accompanied by a sense of success in achieving any goals and from this point of view is positive experience. The burnout is associated with a sense of failure and is negative experience (Eagle V. E., 1999).
Among the factors causing a burnout, the individual features of the individual and socio-demographic characteristics are occupied, on the one hand, and the factors of the working medium - on the other. Among the socio-demographic characteristics, the most close relationship with burnout detects age.
As for personal characteristics, the high level of burnout is closely related to passive resistance tactics, external "control locus", a low degree of personal endurance. There is also a positive connection between burnout and aggressiveness, anxiety and negative - between burnout and a sense of group cohesion. Among the factors of the working environment are the most important degree of independence and independence of the employee in the performance of its work, the presence of social support from colleagues and leadership, as well as the opportunity to participate in decision-making important for the organization.
Studies of recent years not only confirmed the vitality of this structure, but allowed to significantly expand its sphere of distribution, including professions in it, not related to the social sphere. In some foreign studies, there is a burnout in the professions of engineering labor, among television service workers and some others. For example, psychological studies of sailors show that a long stay away from home, labor automation on ships, leading to a reduction in personnel, contribute not only to the development of traditional states of loneliness and longing for the house, but also burnout.
The study of a number of other professional phenomena in the professions of the "non-social sphere" confirms the above. In particular, the phenomenon of "islet" described in the literature at the pilots is defined as the loss of the pilot's directivity to fulfill their professional activities. The pilot loses interest in his work, he appears fear of flights, uncertainty in his abilities, loss of responsibility for the outcome of the flight. Ultimately, pilots have a desire to change the profession, to write off for a non-money work (Ponomarenko V. A., 1992). The description of this phenomenon is largely consistent with the description of mental burnout. Symptoms of burnout and "islet" are equally manifested in loss by a person satisfying from their true professional activities, in reducing motivation in the professional sphere, in emotional, mental and physical exhaustion. This allows you to consider "islee" as a manifestation of burnout in the flight profession.
Naturally, the presence of mental burnout causes people to look for various ways to overcome it, for example, an appeal to psychotherapeutic services, optimization of working conditions, etc.
Thus, the profession can significantly change the character of a person, leading both positive and negative consequences. The difficulty of combating professional deformation is that it is usually not aware of the employee. Therefore, professionals are very important to know about the possible consequences of this phenomenon and more objectively refer to their shortcomings in the process of interaction with others in everyday and professional life.
Questions for repetition
1. What are the four basic stages of professionalization you know?
2. What is the negative impact of professional development?
3. In which directions are the formation of motivation of professional activities?
4. What are the aspects of the formation of cognitive structures in the process of professional development?
5. What is a production situation?
6. What are the qualities of the subject called professionally important?
7. What are the main stages of the formation of professional abilities in the process of mastering the profession?
8. How is the development of personal characteristics of the floor by the influence of the profession?
9. What is the mechanism for the occurrence of professional deformation?
10. In which areas of human vital activity can professional deformation be manifested? How does the deformation affect human behavior?
11. What is the essence of the phenomenon of mental burnout?
12. What is the main difference between mental burnout and fatigue?
Abulkhanova-Slavskaya K. A. Strategy of life. - M., 1991.
Ananyev B. G. On the problems of modern personnel. - M., 1980. T. 1.
Granovskaya R. M. Elements of practical psychology. - L.: LHA, 1988.
History of Soviet Psychology Labor: Texts / Ed. V.P. Zinchenko, V. M. Muninov, O. G. Noscova.
Klimov E. A. Psychology of a professional. - M., 1996.
Kudryavtsev T. B. Psychology of vocational training and upbringing. - M., 1986.
Markova A. K. Psychology of professionalism. - M., 1996.
Eagle V. E. Study of the phenomenon of mental burnout in domestic and foreign psychology // Problems of general and organizational psychology. - Yaroslavl, 1999 - P. 76-97.
Eagle V. E. Psychological study of the impact of the profession on personality // Abstract collection of elected work on grants in the field of humanitarian sciences. - Ekaterinburg, 1999., P. 113-115.
Panasyuk A. Yu. Indictor in the mirror of psychological research // Psychol. g. - 1992. - T. 13. - № 3. - P. 54-65.
Petrenko V. F. Psychosmantics of consciousness. - M., 1988.
Povarnok Yu. P. Psychology of formation of a professional. - Kursk, 1991.
Rogov E. I. Teacher as an object of psychological research. - M., 1998.
Povarnovkov Yu. P., Shadrikov V. D. Investigation of the dynamics of the information basis of activities on different attacks of the formation of PSD // Problems of industrial psychology. - Yaroslavl, 1979.
Ponomarenko V. A. Psychology of the life and labor of the pilot. - M., 1992.
Profcofing work with high school students / Ed. B. A. Fedorishin. - Kiev, 1980.
Shadrikov V.D. Problems of system genesis of professional activity. - M., 1982.
Shadrikov V. D. Introduction to the psychological theory of vocational training. - Yaroslavl, 1981.
Shadrikov V. D., Druzhinin V. N. Formation of the subsystem of professional and important qualities in the process of professionalization // Problems of industrial psychology. - Yaroslavl, 1979. -s. 3-18.
Schreander R. V. The level of professionalization as a factor determining the structure of professional-important qualities // The problem of system generation activities. - Yaroslavl, 1980. - P. 56-67.
Crites S. The Vocational Choice. - N.Y., 1964.
Professional Burnout: Recent Developments in Theory and Research / Ed. W. B. Shaufeli, CR. Maslach & T. Marek. Washington DC: Taylor & Francis, 1993.
Question 2. The main content of this type of work is the interaction between people ...- Answer: "Man - man"
- Answer: Operation
- Answer: "Do not harm!"
- Answer: reduction
- Answer: Classification
- Answer: Profession content
- Answer: Means
- Answer: Goals
- Answer: Conditions
- Answer: Final
- Answer: Motor
- Answer: Objectivity
- Answer: "Man - Nature"
- Answer: Selection
- Answer: Internal
- Answer: "Man - man"
- Answer: Sociology of Labor
- Answer: occupation
- Answer: Tasks
- Answer: Morality
- Answer: Efficiency
- Answer: separation
- Answer: Privacy
- Answer: Propaganda
- Answer: Organic
- Answer: "Man - Technique"
- Answer: Personality Prepared
- Answer: external
- Answer: module
- Answer: deformation
- Answer: Diagnostic
- Answer: Socio-Communicative
- Answer: semi-automatic
- Answer: Nonprofhesionalism
- Answer: Self
- Answer: Regulatory
- Answer: Age
- Answer: template
- Answer: Abilities
- Answer: subject
- Answer: Secondary Professionalization
- Answer: Primary Professionalization
- Answer: Cognitive
- Answer: clients
- Answer: important qualities
- Answer: Subject activities are given to them from birth
- Answer: Preparatory
- Answer: "Man is a sign system"
- Answer: Free
- Answer: Professional Competence
- Answer: Item (guns)
- Answer: Self
- Answer: Selection
- Answer: Acts of Professional Activities
- Answer: spiritual
- Answer: Wheel tools
- Answer: Motive
- Answer: "Man - Technique"
- Answer: Professional Competence
- Answer: Goals
- Answer: Orientation
- Answer: Objectivity
- Answer: template
- Answer: Productivity
- Answer: Functional
- Answer: Social
- Answer: burnout
- Answer: specialty
- Answer: self-regulation
- Answer: Object
- Answer: The ability of the subject and features of the person
- Answer: Information
- Answer: Communicative actions
- Answer: Stabilization
- Answer: Enlightenment
- Answer: Requirements for professionally important qualities of a person
- Answer: SuperProfhesionalism
- Answer: Pedagogical School
- Answer: "Man - Technique"
- Answer: Ergonomics
- Answer: "Man is an artistic image"
- Answer: Privacy
- Answer: Labor Psychology
- Answer: Professional development
- Answer: Psychodiagnity
- Answer: Objectivity
- Answer: Domestic
- Answer: Universal
- Answer: Labor Psychology
- Answer: Professional Ecology
- Answer: Functional
- Answer: "Man - man"
- Answer: Automatic
- Answer: subject
- Answer: Subject
- Answer: Action
- Answer: Performance
- Answer: Microelements actions
- Answer: Services
- Answer: psychoprophylactic consultation
- Answer: Regulation
- Answer: Operational
- Answer: Goal
- Answer: Introductory
- Answer: "Man - Nature"
- Answer: "Man is an artistic image"
- Answer: entry into activities
- Answer: Consultation
- Answer: Activity
- Answer: Labor Statistics
- Answer: The system of professional tasks, forms and types of professional activities, professional features of the personality, ensuring the satisfaction of the needs of society in achieving the necessary society of a significant result, product
- Answer: Professionalization
- Answer: Knowledge
- Answer: Employee of Fine Arts
- Answer: Akmeology
- Answer: Suitability
- Answer: Professiona
- Answer: Acts
- Answer: Needs
- Answer: Reorientation
- Answer: Labor Hygiene
- Answer: Perceptual
- Answer: Material
- Answer: Motivation
- Answer: individual
- Answer: Labor Physiology
- Answer: "Man - Technique"
- Answer: Activities through which a person participates in the life of society and which serves to him by the main source of material livelihoods
- Answer: Communicative
- Answer: Organizing actions
- Answer: "Man - Nature"
- Answer: Object
- Answer: Labor Psychology
- Answer: Optimality
- Answer: Correctional
- Answer: Correctional
- Answer: Compliance with the culture of dignity
- Answer: Gnostic
- Answer: Professional Action
- Answer: Basic
- Answer: tool
- Answer: Ethics
- Answer: Thinking
- Answer: "Man - man"
- Answer: Activity
- Answer: Macroelements actions
- Answer: Information
- Answer: Professionalization
- Answer: Svetva
- Answer: Pedagogical Technical School
- Answer: Subject
- Answer: Personality Motivational Sphere
- Answer: Conditions
- Answer: "Man is a sign system"
- Answer: Tools
The labor mainly has a positive effect on man and his personal features. However, professional development can be and descended. The negative impact of the profession on personality has a partial or full nature. With a partial regression of professional development, some kind of element is affected by the progressive development of the system and its effective functioning. Complete regression means that negative processes affected the individual structures of the psychological activity system, leading to their destruction, which can reduce the effectiveness of activities. The manifestations of the negative impact of the profession on personality is the emergence of various professional deformations or specific states, such as, for example, a phenomenon of mental burnout.
Professional deformation of the person. The word deformation comes from Latin deformatio. (distortion) and means changing the physical characteristics of the body under the influence of the external environment. In relation to the profession, the deformation is understood by any change caused by the profession that occurs in the body and acquiring persistent nature. From this point of view, the deformation applies to all aspects of the physical and mental organization of a person who change under the influence of the profession. As for the impact of the character itself, it is clearly negative, as evidenced by the following examples: the curvature of the spine and the myopia in the office employees, the flatteringness of the Swiss. Based on this, traditionally understanding the professional deformation is associated with the negative impact of the profession on the psychological characteristics of a person who makes his behavior in everyday life and ultimately able to reduce labor efficiency.
The mechanism of occurrence of professional deformation has a rather complicated dynamics. Initially emerged, the unfavorable working conditions cause negative changes in professional activities in behavior. Then, as difficult situations are repeated, these negative changes can accumulate in personality, leading to its restructuring, which further manifests itself in everyday behavior and communication. It has also been established that first negative mental states and installations appear first, then positive qualities begin to disappear. Later at the site of positive properties, negative mental qualities arise, changing the personal profile of the employee.
When recuiting situations, negative states are fixed and posed positive qualities whose share is reduced. There is a steady distortion of the configuration of the personal profile of the employee, which is deformation.
Professional deformation, as a rule, has a rather complicated dynamics of manifestations in human labor activities and affects the various sides of the psyche: the motivational, cognitive, scope of personal qualities. Its result may be specific attitudes and submissions, the November of the definite features.
The deformation of certain individual structures sometimes arises as a consequence of the progressive development of certain features of individuals, cognitive entities, motifs as a result of a high degree of specialization of activity. The hyperbolization of the development of these characteristics leads to the fact that they begin not only to manifest themselves in professional activities, but also penetrate other areas of human life, making it difficult to behave in them. Implementation of professional duties does not significantly suffer.
Manifestation of professional deformation in the motivational sphere. Professional deformation of the motivational sphere can manifest itself in excessive wiping by any professional sphere with a decrease in interest in others. Famous example Such deformation is the phenomenon of workolism when a person spends most of the time in the workplace, he says and thinks only about it, losing interest in the rest of life. Labor in this case is a kind of protection, an attempt to get away from those difficulties and problems that arise in a person's life. On the other hand, personality can highly work in any area devoting all his time to this, which leads to the lack of interests and activity in other areas. In particular, Ch. Darwin expressed regret that strengthened classes in the field of biology completely held all his time, as a result of which he had no opportunity to follow the innovations of fiction, interested in music and painting.
The deformation at the value and motivational level may manifest itself in reducing the values \u200b\u200bof value orientations associated with activity, creativity, spiritual satisfaction. In particular, the investigators are observed low level Streetings to enhance their education, unwillingness to make elements of creativity in professional life. In the field of hobbies, the main value is a passive vacation, the lack of desire to find a hobby, opening opportunities for creativity.
Manifestation of professional deformation in the cognitive sphere. Professional deformation of knowledge may also be a result of deep specialization in a professional sphere. A person limits the sphere of his knowledge of only those necessary for him to effectively fulfill their duties, demonstrating complete ignorance in other areas.
Another form of manifestation of this phenomenon is the formation of professional stereotypes and installations. They represent a certain level of the achieved skill and manifest themselves in knowledge, automated skills and skills, subconscious installations that do not load consciousness. The negative effect of stereotypes is also manifested in a simplified approach to solving problems, to the creation of the idea that this level of knowledge can ensure the success of activities. In a number of professions, these stereotypes are very dangerous, for example, in the profession of the investigator, suspicion as a type of deformation inevitably leads to bias, to the indictment in investigative activities. This phenomenon was called an accusatory bias and is an unconscious installation on a person whose wine has not yet been proven, as a person definitely committed a crime. Research has identified the availability of a charge for accusing all the specialties of the legal profession, starting with the prosecution workers and ending with lawyers.
Formed from professionals stereotypes and installations can also interfere with the development of new professions. In particular, studies conducted by the authors showed that the presence of old stereotypes in consciousness may make it difficult to adapt the adaptation of doctors receiving the specialty of a medical psychologist, to a new profession and affects the idea of \u200b\u200bit. The ideas about the profession of a psychologist among representatives of medical and pedagogical areas and in psychologists who have basic education and successfully working in their field have differences in the classroom of the qualities of the psychologist's profession to different areas. Thus, both groups allocate such qualities as the ability to arrange people, goodwill, care to people. However, if psychologists include these qualities in the category of professional competence, then doctors and teachers do not. The reason for this may be the transfer of old models to new conditions. In traditional medicine (and pedagogy) there is an image of a doctor (teacher) as a professional-manipulator, including characteristics such as dominance, authoritarianism, demanding, patient behavior management or student. In contrast to the doctors and teachers, psychologists of relevant specializations are building their image in the context of a psychologically oriented model.
Professional deformation of personal characteristics. The level of professional deformation of personal features has been studied slightly worse. Personal features formed under the influence of a particular profession significantly make it difficult to interact in society, especially in unprofessional activities. In particular, many teachers are distinguished by the didactic behalf of speech, the desire to teach and educate. If such a trend is justified at school, then in the sphere of interpersonal relationship, it annoys people. For teachers is also characterized by a simplified approach to problems. This quality is necessary at school in order to make the explanable material more affordable, but outside professional activity it generates rigidity and straightness of thinking.
Professional deformation of personal characteristics may also arise as a result of the excessive development of one feature necessary for the successful performance of professional duties and has spread its influence on the non-professional scope of the subject. For example, the investigator in his work faces deception, cunning and hypocrisy, so he can have increased criticality and excessive vigilance. The further development of these features can lead to an increase in excessive suspicion, when the investigator in each person sees a criminal, and this feature is manifested not only in professional activities, but it spreads on family and domestic relations.
The deformation of some personal features can be compensated by the development of others. Thus, the employees of corrective labor institutions, the influence of the profession form specific personal characteristics: the rigidity of the behavior and the cognitive sphere, the narrowing of the circle of interests and communication. The deformation of these characteristics is accompanied by the bright severity of such personal features, as accuracy, punctuality, conscientiousness. In addition, different psychological structures are subjected to different degrees. According to the authors of the data, the emotional-motivational sphere is deformed to a greater extent than the personal characteristics unit.
Phenomenon of mental burnout. Another manifestation of the negative impact of the profession is the phenomenon of mental burnout is widely known in the West and practically not investigated in domestic science. Unlike professional deformation, mental burnout can be attributed to a greater extent to the case of complete regression of professional development, since it affects the person as a whole, destroying it and has a negative impact on the efficiency of work.
The main characteristics of the phenomenon of mental burnout.
1. Mental burnout is a syndrome that includes emotional exhaustion, depersonalization (cynicism) and the reduction of professional achievements. Under emotional exhaustion means a sense of emotional devastation and fatigue caused by its own work.
Depersonalization implies a cynical attitude towards labor and objects of its labor. In particular, in the social sphere, depersonalization involves an insensible, inhuman attitude to customers coming to treatment, consultation, education and other social services. Customers are not perceived as living people, but all their problems and troubles with whom they come to a professional, from his point of view, there is a blessing for them.
Finally, the reduction of professional achievements is an emergence of incompetence in workers in their professional sphere, the awareness of failure in it.
- 2. This phenomenon is professional. To some extent, he reflects the specifics of the professional sphere, which was first discovered: work with people and assistance. This is especially true of its second component. At the same time, the studies of recent years have significantly expanded the scope of its distribution, including the profession not related to the social sphere.
- 3. Mental burnout has a negative impact on all directions of personality and its behavior, reducing ultimately the effectiveness of professional activities and satisfaction with labor.
- 4. This phenomenon is irreversible. Having aroused in humans, it continues to develop, and you can only slow down this process in a certain way. Studies show that short-term waste from labor temporarily removes the effect of this phenomenon, but after the resumption of professional duties, it is completely restored.
Currently, there are many diverse approaches to the description of mental burnout, which are combined into three large categories depending on the source of its occurrence.
Representatives of interpersonal approaches see the traditional cause of burnout in the asymmetry of relations between workers and clients, which emphasizes the importance of interpersonal relationships in the emergence of burnout. In particular, K. Maslak believes that the main cause of burnout is the tense relationship between customers and employees. The psychological danger of such relationships is that professionals deal with human problems that carry a negative emotional charge that the heavy burden falls on their shoulders.
Among the individual approaches, an existential approach is the main representative of which A. Paine. In her opinion, burnout with the greatest probability arises from the social sphere workers with a high level of claims. When highly motivated specialists who identify themselves with their work and consider it a highly valued and publicly useful, fail in achieving their goals and feel that they are not able to make a significant contribution, they are burning apart.
Work that was the meaning of life for an individual causes him disappointment, the development of which leads to burnout.
Unlike the above approaches, the organizational approach focuses on the work environment factors as the main sources of burnout. These factors include: a large amount of work, and above all its routine component; The narrowed area of \u200b\u200bcontacts with customers, the lack of independence in work and some others.
The burnout is an independent phenomenon, not conducible to other states found in professional activities (stress, fatigue, depression).
Although some researchers tend to consider mental burnout as a long working stress, the experience of the impact of stressful factors, most converge in the opinion that stress and burnout are also related, but relatively independent phenomena. The ratio between burnout and stress can be considered from the position of the temporary factor and the success of adaptation. The difference between stress and burnout lies, first of all, in the duration of this process. The burnout is a long, stretched working stress. From the point of view of Selre, stress is an adaptive syndrome that mobilizes all sides of human psyche, burnout is a breakdown in adaptation. Another difference in stress and burnout is the degree of their prevalence. While stress may experience each, burnout is the prerogative of people having a high level of achievements. In contrast to stress arising in countless situations (for example, war, natural disasters, disease, unemployment, as well as situations at work), burnout is very often manifested when working with people. Stress does not necessarily be the cause of burnout. People are able to work perfectly in stressful conditions, if they believe that their work is important and meaningful.
Thus, although there is some generality between stress and burnout, but the latter can be considered a relatively independent phenomenon.
The main difference between burnout and fatigue is that in the latter case, a person can quickly recover, and in the first - years. An analysis of the subjective sensations of people experiencing burnout syndrome shows that they although they feel physically exhausted, but describe this feeling as significantly different from normal physical fatigue. In addition, fatigue as a result of physical exercises may be accompanied by a sense of success in achieving some goals and from this point of view is positive experience. The burnout is associated with a sense of failure and is negative experience.
Some researchers bind burnout with depression and disappointment in work. These concepts can be closely correlated with each other, and it is quite difficult to find differences between them. Fredereberger Indicates that depression is always accompanied by a sense of guilt, burnout - a sense of anger. Unfortunately, this thesis had only clinical evidence. At the same time, the differences between burnout and depression are caused by a greater degree of universality of the latter. If burnout is manifested only in professional activity, then depression is more global: its action is visible but all the situations of the individual. Research of the connection of depression and constituent burnouts show the presence of a close correlation of depression and emotional exhaustion. As for the relationship between depression and the rest of the components of mental burnout, it is pretty poorly visible. Consequently, the conclusion of many authors about the coincidence (overlapping) of the concepts of burnout and depression is true only in part.
Among the factors causing burnout, special attention is paid to individual identity features and socio-demographic characteristics, on the one hand, and the factors of the working environment, on the other. Among the socio-demographic characteristics, the most close relationship with burnout detects age.
As for personal features, the high level of burnout is closely related to passive resistance tactics, external "locus of control", low degree of personal endurance. There is also a positive connection between burnout and aggressiveness, anxiety and negative - with a sense of group cohesion. Among the factors of the working environment are the most important: the degree of independence and independence of the employee in fulfilling its work, the availability of social support for colleagues and leadership, as well as the ability to participate in decision-making important for the organization.
Studies of recent years not only confirmed the vitality of this structure, but allowed to significantly expand its sphere of distribution, including the profession not related to the social sphere. In particular, in some foreign studies, there is a burnout in the professions of engineering labor, television workers and some others. For example, psychological studies of sailors show that a long stay away from home, labor automation on ships, leading to a reduction in personnel, contributes not only to the development of such traditional states for this sphere, such as loneliness and longing to house, but also burnout states.
The study of a number of other professional phenomena in the professions of the non-social sphere confirms said. In particular, the phenomenon described in the literature in the pilots is defined as the loss of the pilot's directivity to fulfill its professional activities. The pilot loses interest in his work, he manifests the flight, the fear of uncertainty in his abilities, loss of responsibility for the outcome of the flight. Ultimately, Pilotov has a desire to change the profession, to engage in unlawful work. The description of this phenomenon is largely consistent with the description of mental burnout. Symptoms of burnout and isletness are equally manifested in loss by a person satisfying from their true professional activities, in reducing motivation in the professional sphere, in emotional, mental and physical exhaustion. This suggests the consideration of the islet as manifestation of burnout in the flight profession.
The presence of mental burnout causes people to look for various ways to overcome it, from circulation to the appropriate psychotherapeutic services and optimization of working conditions before using alcohol and other not quite adequate ways, up to commit suicide.
Thus, the profession can significantly change the character of a person, leading both positive and negative consequences. The difficulty of combating professional deformation is that it is usually not realized by the employee, the PI of its manifestations is detected by other people. Therefore, professionals are very important to represent the possible consequences of this phenomenon, more objectively refer to their shortcomings in the process of interaction with others in everyday and professional life.
Knowledge of these phenomena and their accounting in the practice of the work of the psychologist are especially important in professional counseling of people, or, as they are called in foreign psychology, career counseling. This type of consulting appeared in our country relatively recently as a result of economic change and unemployment as a social phenomenon. He is designed to help a person go to new professional activities, find forms of full or partial realization of its past experience, personality and individuality, reduce the influence of old professional stereotypes that prevent the mastering of a new profession. In particular, the developing burnout phenomenon in a professional can lead to stress, the emergence of high mental tensions, negative professional expectations. The result of the impact of burnout can be a change in the place of work and the search for new options. In this regard, it is important to help a person in finding the necessary information, the development of the skills of the competent analysis, the psychological readiness of the search for new work, taking into account its past professional experience.
The concept of mental states. Classification of mental conditions: emotional, cognitive, volitional and states arising in the process of human labor activities. Factors affecting the state of the employee and their determination. Adaptation of the employee at the production and problem of mental states. Activity manager for adaptation management. Regulation and self-regulation of mental states.
Mental states - psychological category characterizing the mental activity of the individual for a certain period of time. This is the background on which human mental activity flows. It displays the peculiarity of mental processes and the subjective ratio of the individual to the reflected phenomena of reality. Mental states have the beginning and end, change over time, but they are intertwined, relatively constant and stable. Kk Platonov determines mental states as occupying an intermediate position between mental processes and personality properties.
Mental states include joy, sadness, concentration, boredom, fatigue, tension, apathy, etc. At the given point in time it is a mental state, two groups of factors are influenced: environmental factors and individual actors.
Types of mental states:
1. Emotional states. Depending on the depth, intensity, duration and degree of differentiation, the following types of emotional states are distinguished: sensual tone of sensations, affect, mood, passion and emotion itself.
2. Cognitive states are associated with cognitive activity.
3. The volitional states arise in situations based on the need: replenishing the deficit of the motivation to actions in the absence of sufficient motivation; selection of motifs, goals, types of action in their conflict; arbitrary regulation of external and internal actions and mental processes.
4. Psychological conditions arising as a consequence of the characteristics of working conditions were called Praxic (from Lat. Praxis - work) of states. States arising from a person in the process of employment are divided into the following three groups:
1) with respect to sustainable And long-lasting status. Such states determine the attitude of a person to this production and a specific type of labor. These states (satisfaction or dissatisfaction with work, interest, work or indifference to it, etc.) in most cases reflect the general psychological attitude of the team.
2) temporary, situational, rapidly passing states. They arise under the influence of various types of problems and troubles in the manufacturing process or in relationships in the team.
3) states arising periodically in the course of work. There are many such states (for example, a state of work, improving performance, final impulse, etc.).
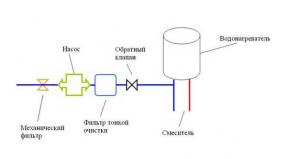
Since the psychological (or - functional) states under consideration are a consequence of human professional activity, it is advisable to proceed from the approaches to the description of the work in the psychology, taking into account the working conditions. In a psychological analysis, working conditions come from the fact that any activity is characterized by three main elements: the awareness of the goal, the availability of funds and the result obtained.
Pursued goal - Getting some product. In the production of a real product, the goal may be described in the form of quantitative requirements, in the form of drawing or set in the form of an exemplary sample, a list of signs, etc.
Used to achieve the goal facilities - This is a technique, energy, information. The main requirement to the result obtained: the result must correspond to the goal.
Depending on the ratio of the three items of activity in a person in the process of labor arise various stateswill be discussed below.
Functional comfort characterizes the ideal case when a person has all the conditions necessary for activity (in the structure "Purpose" - "means" - "result"). But in most real cases, a person is forced:
1) independently formulate a specific goal of its actions in these conditions (find it in official or technical instructions, to receive from the head, to accept responsible decisions, etc.).
2) conduct an independent search for funds (and methods) of activities, "design" them or "reconstruct" available equipment, knowledge, information in relation to a specific production situation.
3) to seek a positive result for how long, making great efforts, work in the conditions of the deficiency of information on the results of its activities (and in some cases even about the appointment of their actions).
Table 1 provides an analysis of the combinations of possible situations in labor activity, producing the relevant patux states. The sign (+) identifies the presence of this component working conditions, sign (-) - the absence of it.
Another pole (relative to the status of functional comfort, see Table 5.1), is the so-called indifferent state. The indifferent state occurs in a person who is absolutely not interested in the production situation: the employee is not known for the organization's goal nor the list of necessary funds, the resulting result is unknown.
Table 5.1 - Communication of psychological states with working conditions
Components of labor conditions
A variety of situations that arise in real employment, produce a fairly wide spectrum corresponding to them psychological states.
In very general adaptation (Lat. Adapto-fitting) - the process of adapting an employee to the conditions of the external and internal environment. The term "adaptation" is extremely wide and applied in various fields of science. In sociology and psychology allocate social and production adaptation. To a certain extent, these two types of adaptation intersect with each other, but each of them has independent areas of application: social activities are not closed in production, and production - includes technical, and biological, social aspects.
From the position of personnel management, the production adaptation is the greatest interest. It is she who is a tool in solving such a problem as the formation of the new working required level of productivity and quality of labor in a shorter time.
The reasons for changing the conditions of labor activity are diverse: admission to a new place of work, the transition to another unit, to a new position, the introduction of new forms of labor organization, its payment, etc.
This problem is of one way or another concerns all categories of working, but it is most acute for young workers and young professionals.
The change of the workplace involves not only the change in working conditions, the change of the collective, but also is often associated with a change in the profession, the type of activity, which gives adaptation is a new, more complex character.
In the process of adapting a person to a production environment, a lot of questions arises: whether it is necessary to accept employee Wednesday as properly and all forces adapt to it or require changes and environment itself, what are the ways and means of influencing a person and on Wednesday, where the criteria for the possibility and need to take into account the requirements of the employee etc. Therefore, it should be distinguished by active adaptation when the individual seeks to influence Wednesday in order to change it (including those norms, values, forms of interaction and activities that it must master), and passive when it does not seek such an impact and change.
Adaptation is most effective as the process of active adaptation of an individual to a changing medium with the help of the appropriate control effect and use of various means (organizational, technical, social and psychological, etc.).
In its impact on the employee, the progressive results of adaptation and regressive are distinguished. The latter take place in the case of passive adaptation to the medium with a negative content (for example, with low labor discipline).
In addition, there is a primary production adaptation when a person is first included in permanent employment at a particular enterprise, and secondary - upon subsequent change of work.
The components (components) of the production environment as an adaptation object is very diverse. Among them, it is possible to allocate: working conditions and its organization, wage and forms of material incentives, labor content, rigidity of norms, psychological climate in the team, etc. Some researchers also distinguishes the factors of the non-productive sphere of the enterprise (adaptation to living conditions, exproductive communication with the team, organization of leisure in the enterprise).
Production adaptationAs a complex phenomenon, you can consider from various positions, highlighting the psychophysiological, professional, socio-psychological part of it.
Each of them has its own object, its targets, performance indicators.
Psychophysiological adaptation - Adaptation to labor activity at the level of the employee's body as a whole, the result of which are smaller changes in its functional state (less fatigue, adaptation to high physical exertion, etc.).
Professional adaptation - Full and successful mastering a new profession, i.e. Addictive, adaptation to the content and nature of labor, its conditions and organization. It is expressed at a certain level of mastering professional knowledge and skills, in the ability, in accordance with the nature of the personality character of the profession.
Socio-psychological adaptation A person to production activities is adaptation to the nearest social environment in the team, to traditions and unwritten standards of the team, to the style of work of managers, to the peculiarities of interpersonal relations that have developed in the team. It means the inclusion of an employee into the team as an equal one, taken by all its members.
Among the components of the production environment, to which the employee needs to be adapted, along with such as the conditions and maintenance of labor, duties, there are components with a socio-economic tint: the organization of labor, labor and material incentives, the socio-household sphere of the enterprise, the organization of leisure employees etc. It is no coincidence that some researchers identify the socio-economic aspect of industrial adaptation.
Figure 5.1 - Communication between the types and factors of adaptation
Professional adaptation determines the timing of the development of a new profession, which affects the choice of personnel policy (orientation to a set of workers from or on the redistribution of its own), on the duration of the period of maintaining reduced production indicators, characteristic of a non-adaptive employee, the period of formation of a labor stereotype.
In the process of adapting, as well as labor activities, various negative mental conditions may arise, which affect the overall extent satisfaction with labor activity.
Figure 5.1 provides a link between the types and factors of adaptation.
Types of states depending on a variety of production situations:
Mental fatigue occurs when obtaining the desired result required long work, even if it was not too heavy. The status waiting for the result causes a sense of fatigue (according to the table 5.1, the goal is realized, funds are enough, difficulty - in achieving the desired result).
The state of waiting for the result, the lack of result with excessive strengths causes a sense of fatigue. No wonder they say that there is nothing worse than waiting and catching up. In a state of mental fatigue, a person feels "squeezed lemon." He is ready to work, because he knows why and what to do, but does not have enough forces for this: everything is hard to remember, the solutions come the most trivial, it is difficult to focus on attention for a long time. The decrease in the intensity of mental activity may cause depression, and together with it it comes irritability and outbreaks of anger in relation to innocent people, most often the closest.
From the point of view of the production assessment of the work performed, fatigue is accompanied by a decrease in performance (quantitative indicator) and efficiency (indicator characterizing the quality) of labor. Fatigue is considered from 3 sides:
a) on the part of the subjective - as a mental state;
b) from the physiological mechanisms;
c) from the side of reducing productivity and quality of labor.
In labor psychology, fatigue is considered as special, peculiar experienced mental state N.D. Levitova), comprising the following components:
1. Feeling vysiasia . Fatigue affects that a person feels a decrease in performance, even when labor productivity is still preserved at the same level. This reduction in performance is expressed in the experience of special, painful voltage and uncertainty. A person feels that he cannot properly continue to work.
2. Disorder attention . Attention is one of the most tired mental functions. In the case of fatigue, attention is distracted, becomes sluggish, larger, or vice versa, chaotic movable, unstable .
3. Disorders B. touch region. Such disorders under the influence of fatigue are subjected to receptors who take part in the work. (For example, if a person reads a long time without a break, he starts to "break out" in the eyes of the text of the text. With a long and tense listening of music, the melody's perception is lost. Long handmade can lead to weakening tactile and kinesthetic sensitivity).
4. Violation of B. motor sphere. Fatigue affects the slowdown or disorderly inadequacy of movements, the disorder of their rhythm, in the weakening of the accuracy and coordination of movements, their deutomatization.
5. Impairment of memory and thinking.
7. Drowsiness - as an expression of security braking.
The degree of fatigue changes over time, with long work, the manifestation of one or a component characterizing phase fatigue, appear and develop subsequent (in time) components. So we are talking about dynamics Treatment characterized by a combination stadium .
a) a relatively weak sense of fatigue. Labor productivity drops slightly. Fatigue is often manifested when a person, despite the heavy exhaustive work, feels even well-efficient (the effect of motivation). This stage is characterized by increasing fatigue resistance.
b) The decrease in performance becomes noticeable and more and more threatening. In the present stage, this decrease often applies only to quality, not to the number of labor.
c) acutely experienced fatigue that can take form overwork. The performance indicators are either sharply reduced, or they take a "feverish" form, reflecting a person's attempts to preserve the proper pace of work, which at this stage of fatigue can even accelerate, but to be unstable. In the end, working actions may be so disorganized that a person feels the impossibility of continuing to work, experiencing a painful state.
The state of mental tension is caused by the excessive magnitude of the mental effort necessary to a person when solving the tasks set before him. Arises, as a rule, in the context of complex activities caused by the following factors:
– deficiency of funds: information, conditions, equipment (failed, or "unaware of" funds available from a specialist);
- limit intensity psychic processesassociated with the "provision of" activities.
The emotional component of mental tensions is due to the degree of responsibility for the decisions made, a time deficit, the deficit of the information necessary for the decision-making. Emotions regulate the flow of incoming information, participate in search management (i.e., with the activities related to the search for information necessary for the decision-making). There is general rule Estimates number and sign emotions depending on the volume informationnecessary to solve the task. P.V. Simonov expressed him in 1970 as a formula, E \u003d P * (IR - IN) connecting the following indicators:
E - quantity and quality emotions;
In - necessary the amount of information (to solve the task, satisfying the need, etc.), that is forecast;
See also: Miramistin 0 01 150ml with sprayer
IR - real (or actual) The number of information available in humans.
Mental tensions can affect human behavior differently, which is generally manifested in two forms:
but) excitable, - characterized by increased engine reactions, fussiness, excessive talkativeness, etc.
b) brake, - characterized by oppression, slowed down reactions, "fading" until the complete inability to respond to various types of influences.
The state of mental tension occurs in cases of increased responsibility, a shortage of time or collision with particularly difficult tasks. For all these situations, the general is that they require new, non-standard actions from a person.
Depending on the degree Intensity, this condition affects the performance of the activity in different ways. In some cases, it worsens the performance indicators leads to personality disintegration. In other cases, on the contrary, has a beneficial effect. Moreover, some people can effectively work only in a state of mental tension and therefore create certain difficulties themselves, for example, postponement until the last moment the fulfillment of an important case, and then on the energy lift wave ("Behind Moscow, to retreat nowhere") in a short time Many cases.
The state of the lack of motivation (or reduced motivation) occurs even more often than the states of mental fatigue or mental tension. This is explained by the fact that there are quite a few production situations in which the activity does not have an internal motive motive, and the goal is made from the outside in the form of coercion. The condition under consideration is more characteristic of employees than for the owners of enterprises or responsible persons. The employee is secured by all necessary means and, following the requirements of its managers, more or less easily can obtain the result (Table 5.1). But its performance is steadily declining. Moreover, unwanted functional shifts are observed, resembling symptoms of fatigue or subjective feeling of malaise.
Thus, indifference to the goal is naturally leading to a decrease (and in the limit - absence) of motivation and, ultimately, leads to the deactivation of mental processes of the subject of labor.
Despite the external similarity with the state of mental fatigue, the reduction in motivation differs from it causes of occurrence and psychophysiological manifestations. Therefore, the prevention measures of this state are fundamentally different from the prevention of mental fatigue. If in the latter case a person needs rest, then with the fall of motivation, it, on the contrary, needs activity. Often this activity is to find a new or special meaning of activity.
Stress and Stress factors
Stress is a state of mental stress that occurs in a person in the most difficult, difficult conditions both in everyday life and labor activity and under special circumstances. The state of emotional stress arising from a person in the process of activity is associated with extreme, special conditions Labor (Table 5.1). With regard to professional activities, this is the situation when the goal is, adopted, but there are no funds to achieve it, to solve the task. Yes, and the result (outcome of the work) is practically independent of man. There is a sense of helplessness of the employee in the established conditions.
The concept of stress (from the English stress - pressure, tension) introduced the Canadian physiologist Hans Selle in 1936. Stress - This is a comprehensive process that includes certainly physiological and psychological components. With the help of the stress reaction, the body seems to mobilize himself on protection, to the adaptation to the new situation. Non-specific protective mechanisms are entered into operation, providing resistance to an unfavorable person to situations and adaptation to them.
When analyzing the external causes of stress, the concept of stressors and extreme conditions is used.
Stressors - These are unfavorable, significant external and internal exposure and duration, leading to the emergence of stressful states. Distinguish physiological and psychological stressors. Physiological stressors include strong physical, blood loss, large physical exercise, infections, ionizing radiation, sharp changes in temperature, etc. Psychological stressors are associated with mental injuries; They affect their alarm values: a threat, danger, offended. In labor activity, according to data given by MA The following psychological factors are the most powerful stress, the most powerful stress motivities: dissatisfaction with work, low motivation to work, depression and lack of self-affirmation [Kitty, 1981]. Psychological stressors include such factors as disrespect for the personality of the performer, the lack of opportunity to act in its characteristic style, the unwillingness to bear responsibility assigned to him.
Information stress There is an information overload situation when a person does not cope with the task, it does not have time to make faithful solutions at the required pace at a high degree of responsibility for the consequences of the decisions made.
Emotional stress manifests itself in situations of threats, danger, insults, etc. The forms of its manifestation, as well as the forms of manifestation of mental tension, are different. This can be an active form (the so-called "Lion stress" - characterizes the most efficient, constructive line of behavior), or passive reaction (The so-called "Stress of Rabbit").
Known point of view, [Bodrov, 1998], according to which any variety of stress (personal, interpersonal, family, professional, etc.) is at its basis information. The source is served by a message, information on the current (real) and estimated (probabilistic) impact adverse events, their threat, or "internal" information in the form of past ideas extracted from the memory of information about the injury events, situations or their consequences. These reactions are usually associated with producing negative emotions. In these types of psychological stress information about an unfavorable, dangerous event is start torquedetermining the threat of its occurrence and forming a sense of anxiety, mental tension, etc.
Depending on the degree of development (in dynamics), the following phase stress:
1) The alarm reaction is characterized by the process of mobilizing the protective properties of the body, an increase in protective properties with respect to the traumatic effect. The body functions with a large load. By the end of the first phase, most people increase efficiency.
2) The resilience phase (or resistive phase) is characterized by a balanced cost of the body's adaptation resources.
3) the phase of depleting the adaptation resources of the body.
Thus, depending on the phase of stress and the "polarity" of its manifestations, we can talk about the stresses of "good" and "bad".
As numerous studies have shown, stress in labor activity, depending on its level, generates very different, and sometimes even opposite results. Stress manifests itself in universal adaptation syndrome as the necessary and useful vegetative and somatic reaction of the body on a sharp increase in its overall external load. This reaction is manifested in the growth of the bioelectric activity of the brain, in increasing the heart rate, the growth of systolic pressure of blood, the expansion of blood vessels, increase the content of leukocytes in the blood, i.e. In a number of physiological shifts in the body, contributing to the increase in its energy capabilities and the success of the fulfillment of complex activities. Therefore, as emphasizes M.A. Cat, "In itself, stress is not only appropriate protective reaction The human body, but also a mechanism that promotes the success of labor activity in conditions of interference, difficulties and danger "[Cattle, 1981].
However, the relationship between stress level and flowing out of it activation The nervous system (NA), on the one hand, and the effectiveness of work activity - on the other, is nonlinear. It was noted at the beginning of the 20th century English psychologists R. Yerks and J. Dodson. They experimentally showed that with an increase in the activation of the nervous system to a certain level, the productivity of behavior increases, while with a further increase in activation, it begins to fall.
Stress has a positive effect on the results of labor (mobilizes the energy reserves of the body and contributes to overcoming the obstacles arising in the work) only as long as it has exceeded a certain critical level. Such stress that increases the resistance of the organism to adverse external influences is called estrass. If this level is exceeded, the so-called hypermobilization process is developing in the body, which entails a violation of the mechanisms of self-regulation and deterioration of the results, up to its breakdown. Stress, exceeding critical levelIn extreme terms, can lead to the disease and death of a person called Distress.
The state of psychological stress (as well as the state of mental stress) is developing in unfavorable conditions of activity and extreme situations. For modern production, the extreme situations of two extreme types are typical.
The first type of extreme situation occurs when the requirements of the intensity of work and tight restrictions in time force a person to strain the forces extremely and mobilize the internal reserves. At the same time, the extremality of such labor can often increase due to the negative effect of strong external factors - stressors (noise, vibration, etc.).
The second type of extreme situation arises, on the contrary, due to the lack or heterogeneity of the incoming information, disadvantages of interpersonal contacts, as well as low motor activity. In such conditions, a person develops a state of monotonia. The required level of wakefulness, attention in such conditions, a person has to be supported by the volitional effort.
Thus, for stressful situations of the other type, one common feature is characterized - the emergence of an acute internal conflict between the requirements that work presents to him and its capabilities. In the first case, this conflict arises mainly as a result of the growth of the requirements for man. In the second - due to the reduction of human capabilities to fulfill the requirements.
Excessive burden of responsibility is a constant source of stress, which ultimately can lead to severe depression. And while this burden will not decrease, it is almost impossible to remove stress. Try some of the responsibility to shift on the shoulders of another person. After all, this does not mean that you are an irresponsible person or a bad worker. Too much load ultimately adversely affects not only your mental and physical health, but also on the quality of work. If this is not possible, then you need to frankly talk to the boss, which often does not even represent the load of subordinates (because no one has complained). The fact that a person is not taken for a larger amount of work than can perform means that he refers to his duties is responsible.
Try not to be overworked at work, do not take over greater responsibility and load. In addition, each person needs a regular and full-fledged vacation.
In many satirical works, a typical official who drinks one for another sedative pill, and he constantly happens the attacks of anger. If a person really became such a thing, he is in a constant condition of stress and is no longer able to cope with his professional duties. In order to work well, first of all it is necessary to calm down and focus. In addition, it is desirable to include in your diet foods with a high content of magnesium (for example, vegetables, nuts, seeds). Improve mood can a piece of chocolate or portion of macaroni. Regularly allow yourself to relax and restore forces, for this change the situation. You can go to the sea or relax in the nature of the lake. Very helpful to relax in a sanatorium or a holiday home.
Refer to the removal of stress
A person who is constantly suffering from strong stress, very rarely can solve all his problems. Therefore, it is recommended to seek help to an experienced and qualified psychologist or psychotherapist and talk to him about your problems. A specialist together with the patient will try to find a way to escape from the enchanted circle of problems and constant stress.
Vitaminotherapy. Stressful state forces human body include all internal reserves to support its performance. Eat in food. healthy foodssaturated with vitamins C (apples, tomatoes, rosehips) and in (dried fruits, cabbage, beets, almonds, chicken liver, fish, etc.).
Aromatherapy. Since ancient times, the favorable effect of fragrant essential oils is known. Soothing the essential oils of roses, lavender, jasmine and cypress act.
Sophisticated conversationAs a method for removing stress is very effective. Sometimes a person in the emotional voltage state is simply necessary to speak, often to see the problem at a different angle just just voice it. In our conditions will help to cope with stress, replacing expensive medicationsClose people, best girlfriend or friend.
Extreme in the fight against bad mood. Another effective way to remove stress is to undergo a new type of stress. Accept the cold shower, go through the acupuncture procedure, sign up for extreme sports, such as dumping or parachute jumps.
Take care of sports. Fighting with stressful situations help sports, as well as they make the body more resistant to emotional effects. This is a wonderful way out for many - do physical exercise. Moreover, it does not matter what. Perhaps it will be running, push-ups, bike, power workouts. Try and you make sure it really acts! The greatest effect will be from the exercises, where regular repetitions are needed (for example, running) causes the body to relax. And this, in turn, makes your body and brain react to stress adequately. Simply put, the heart rate is reduced, blood pressure decreases, the voltage in the muscles is reduced. It is enough thirty minutes of classes on the simulator to reduce by 25% emotional stress caused by stress.
The oldest system - yoga. With yoga, you can relax, sort out yourself, and also strengthen the muscles. Try to meditate. Closing my eyes, breathe deep and slowly. On each breath and exhale, repeat some nice phrase or word. This simple exercise is able to bring the body into balance, help relax and relieve stress.
be careful. Avoid situations that can lead to emotional disorder.
Smile more often. If you smile more often, you can call a good mood at the subconscious level. Praise yourself. It seems to be simply, but many of us only aggravate stressful state, drowning inner voice. But studies show that positive feedback in their address is stimulated by the production of cortisol hormone, which is responsible for the neutralization of stress. Next time, having caught yourself on self-esteem, say out loud, and even better write about yourself something good.
The state of monotonia occurs when a person is represented only to the means of activity in the form of source material, equipment, technologies, an algorithm of work. However, excessive simplification of operations, (or, on the contrary, the excessive complexity of the process or product produced) often leads to the fact that the employee is separated from the actual goal and does not see and does not know the results of its labor costs, the degree of their contribution to the achievement of the general (also unknown to it) goals. As a result - the lack of satisfaction from embodied efforts.
See also: Aspirin UPSA Instructions for cold
The mental state of the experience of monotonia is caused by the actual or apparent monotony of the movements and actions performed at work. Under the influence of the monotony of actions (and as a result of monotonia as a psychological state), a person becomes sluggish, indifferent to work. Monotony state also negatively acts on the human body, leading to premature fatigue. At the physiological level, this is manifested in reducing the heart rate, respiratory frequency, reaction rate.
If in the work there are inevitable monotonous movements or actions, a person with a higher level of intelligence is experiencing a sense of monotony (monotony state) to a lesser extent. This is due to the fact that he possessing a broader outlook and ability to analyze, better understands the need for these actions to achieve a common goal. This means that it can better activate its performance, seeing in a monotonous - diversity. The ability to see a variety in monotonous inherent in highly qualified specialists. A small-skilled worker cannot catch the changes to seemingly "monotony" for him and becomes a victim of wildlifelessness, manifested sometimes in the most cruel forms of monotonia and psychological, and at the physiological level.
Anxiety - This is a multi-valued psychological term, describing both a certain state of the individual at a limited period of time and the sustainable property of a person.
The state of anxiety is associated with the peculiarities of production and has a significant impact on the success of professional activities. None of the activities fail to regulate official duties, relations, the technological process as a whole, to such an extent to completely exclude uncertainty. The employee often pursues the premonition of failure in labor due to the unclear ongoing behavior in the current situation and insufficient orientation in the means of permission.
Anxiety is understood as an individual psychological peculiarity, consisting of an increased inclination to experience anxiety in a wide variety of situations, including such, the objective characteristics of which are not available to this. Anxiety - This is the property of a person, which manifests itself in the frequency, regularity and threshold of the occurrence of concerns and insecurity in their actions, the experiences of real and alleged "omissions" in the actions or deeds, excitement about those who have occurred or possible events, etc.
There are personal anxiety (RT) and situational, or reactive (LT) anxiety.
Personal anxiety It characterizes the readiness of a person to experience fear and excitement about the wide range of subjectively significant phenomena. Personal anxiety can be considered, on the one hand, as a rather sustainable personality property, and on the other hand, as one of the results of the "accumulated" personality of the state of "chronic" mental stress arising in the process of interaction between the personality and its environment.
Situational (or reactive) anxiety - This is a temporary, transient state, which is the form of an emotional reaction of an individual to a situation containing real or imaginary danger. The state of reactive anxiety is characterized by stress, anxiety, concern, nervousness.
Anxiety V. various degrees Determines efficiency different species Professional activities, success of social and professional adaptation. It should be understood that anxiety as such in itself is not a negative condition or personality line. A certain level of anxiety is a natural and mandatory feature of an active, active personality. At the same time, for each person there is its optimal "useful anxiety". The normal level of anxiety is necessary for efficient and coordinated behavior. A person who has a significant deviation of the magnitude of the RT and LT indicators from the average, or moderate level of anxiety requires special attention.
High anxiety, in particular, implies a tendency to emerge alarm state in situations to assess its professional competence. In this case, the supervisor needs to be somewhat displaced with external demands for the employee, categorical in the formulation of professional tasks - to a substantive understanding by the performer of the upcoming activity and its specific planning for subtasks, and also help form a sense of confidence in success. Excessively overestimated, hypertrophied development of anxiety (as a chronic, "accumulated" state of mental stress and as a personality property) can switch to the clinical form of neurosis.
Low anxiety, on the contrary, requires the head of efforts to encourage the activity of personality, more attention to the motivation of activities, initiating the interest of the contractor, focusing in front of the employee of public and personal significance and the need to solve certain objectives.
Time deficit in specialist
The time deficit as a specialist activity factor can be viewed on both sides:
but as limitdisabling of time to perform the task in specific conditions (objective factor);
b) as limit of human capabilities Perform this activity in the temporary range under consideration (subjective factor).
Accordingly, you can allocate objective and subjective Conditions (or prerequisites) The emergence of a time deficit. TO objective Prerequisites include the following:
1) High speed flow or functioning managed by an object by a specialist.
2) The short-term admission of information or signals.
3) the complexity and multi-element of the managed object or process (for example, the need for parallel processing by a specialist of a variety of information, etc.).
4) sharp, sudden disorders in the operation of a managed object or process (for example, emergency occurrence, a sudden change in the conditions of the task of activity, etc.).
but psychological time deficit problem It occurs only when those listed above objective The prerequisites are combined with certain subjective conditions. They can be expressed in the language of mathematical symbols:
t 1 - Time to receive information about the problem situation;
t 2 - time processing and decision making;
t 3 - the implementation of the decision taken (the implementation of the control influences).
Then the main condition for the efficiency of the specialist (lack of a sense of time deficiency) will be expressed as a formula:
a source
The sales profession teaches tricks and trembleness. The ability to imagine a product that is not for sale is a whole art, and often a very low quality of the goods makes itching and cut.
Lawyers can be seen from afar. Neat hairstyle, a strict business suit and case - an image, a la Keanu Reeves from the "Devil Lawyer". In addition, restrained behavior is emphasized in addition to such official appearance.
These people are very clearly and consistently answered questions and love to pour professional terms. "Formalism of lawyers is not so harmless," Nadezhda Kuzmina explains, psychologist-consultant center "Navigator". - The awareness of the laws may exceed the framework of the permissible, and over time they simply turn into a bore. "
These people from the young years are getting used to the atmosphere of the strictest discipline. As a rule, the military "build" homework, and disagreeous suppress the power to be aligned. Military retired is a classic image of a homely tyrant and dictator.
According to psychologists, the military acquire that type of professional deformation of the person, which cannot be overcome. The officer is not a profession, but a lifestyle. Here, even a sense of humor will not save, which, must be said, the military is either missing, or is too specific.
The work of the doctor implies a huge responsibility, and the service in extreme conditions imposes its mark. The well-known cynicism of physicians becomes a kind of psychological protection against fear and daily suffering of patients. Black humor, which a doctor can afford colleagues in society, is automatically transferred to friends and loved ones, and it can touch the feelings of others.
Sometimes physicians are so much accustomed to hide the emotions that they prefer not to talk about work and their experiences. Tragic events occurring in ordinary life, doctors perceive in Spartan and with a certain share of indifference. However, what seems indifference is actually a personally erected psychological wall.
Both in work and in life, journalists are quite superficial. This is understandable: the profession does not imply a detailed study of the material, so the interests of the journalist are directed by Wishing, and not deep into.
"In two of three cases, people go to study at a psychologist to try to sort out themselves," says Denis cleaner. "They are bothering them, and they want to learn how to cope with problems." At the same time, oddly enough, until the end of the life, psychologists cannot end with their "cockroaches". In some cases, they do not notice the context and begin to analyze and dig in the problems of other people. They are satisfied with the interlocutor interrogations with the addiction and, most terrible, try to impose advice to him. "In business, it is not always necessary," says Denis cleaners. - I will give an example. Sales managers often arrange special training on NLP, where they are taught how to influence people. But in the end, all negotiations are broken, because instead of listening to the interlocutor, people study how someone looked at who, who got like and who did what movement. "
Some experts joke: an accountant is a diagnosis. "It seems to me, in order to change the specialty, the accountant will have to spend much more effort than an employee of any other profession," the CEO of Protraining Company Denis Cleanikov smiles. Many people are so fit in the business image that they carry the meticulousness and love for a privacy protocol. "Accountants do everything right," says Denis cleaners. - All extreme scares them and is alarming. They learn at school on the top five, ends the institute with a red diploma. They would prefer to immediately get a job where to retirement. " Pedantism Accountants are often transferred to the family. The spouse or spouse can not worry: planning family budget It turns out in safe hands, and the apartment will be kept clean and order.
a source
The labor mainly has a positive effect on man and his personal features. However, professional development can be and descended. The negative impact of the profession on personality has a partial or full nature. With a partial regression of professional development, some kind of element is affected by the progressive development of the system and its effective functioning. Complete regression means that negative processes affected the individual structures of the psychological activity system, leading to their destruction, which can reduce the effectiveness of activities. The manifestations of the negative impact of the profession on personality is the emergence of various professional deformations or specific states, such as, for example, a phenomenon of mental burnout.
Professional deformation of the person. The word deformation comes from Latin deformatio. (distortion) and means changing the physical characteristics of the body under the influence of the external environment. In relation to the profession, the deformation is understood by any change caused by the profession that occurs in the body and acquiring persistent nature. From this point of view, the deformation applies to all aspects of the physical and mental organization of a person who change under the influence of the profession. As for the impact of the character itself, it is clearly negative, as evidenced by the following examples: the curvature of the spine and the myopia in the office employees, the flatteringness of the Swiss. Based on this, traditionally understanding the professional deformation is associated with the negative impact of the profession on the psychological characteristics of a person who makes his behavior in everyday life and ultimately able to reduce labor efficiency.
The mechanism of occurrence of professional deformation has a rather complicated dynamics. Initially emerged, the unfavorable working conditions cause negative changes in professional activities in behavior. Then, as difficult situations are repeated, these negative changes can accumulate in personality, leading to its restructuring, which further manifests itself in everyday behavior and communication. It has also been established that first negative mental states and installations appear first, then positive qualities begin to disappear. Later at the site of positive properties, negative mental qualities arise, changing the personal profile of the employee.
When recuiting situations, negative states are fixed and posed positive qualities whose share is reduced. There is a steady distortion of the configuration of the personal profile of the employee, which is deformation.
Professional deformation, as a rule, has a rather complicated dynamics of manifestations in human labor activities and affects the various sides of the psyche: the motivational, cognitive, scope of personal qualities. Its result may be specific attitudes and submissions, the November of the definite features.
The deformation of certain individual structures sometimes arises as a consequence of the progressive development of certain features of individuals, cognitive entities, motifs as a result of a high degree of specialization of activity. The hyperbolization of the development of these characteristics leads to the fact that they begin not only to manifest themselves in professional activities, but also penetrate other areas of human life, making it difficult to behave in them. Implementation of professional duties does not significantly suffer.
Manifestation of professional deformation in the motivational sphere. Professional deformation of the motivational sphere can manifest itself in excessive wiping by any professional sphere with a decrease in interest in others. A well-known example of such a deformation is the phenomenon of workolism, when a person spends most of the time in the workplace, he says and thinks only about her, losing interest in the rest of life. Labor in this case is a kind of protection, an attempt to get away from those difficulties and problems that arise in a person's life. On the other hand, personality can highly work in any area devoting all his time to this, which leads to the lack of interests and activity in other areas. In particular, Ch. Darwin expressed regret that strengthened classes in the field of biology completely held all his time, as a result of which he had no opportunity to follow the innovations of fiction, interested in music and painting.
The deformation at the value and motivational level may manifest itself in reducing the values \u200b\u200bof value orientations associated with activity, creativity, spiritual satisfaction. In particular, the investigators have a low level of aspirations for improving their education, the unwillingness to make elements of creativity in professional life. In the field of hobbies, the main value is a passive vacation, the lack of desire to find a hobby, opening opportunities for creativity.
Manifestation of professional deformation in the cognitive sphere. Professional deformation of knowledge may also be a result of deep specialization in a professional sphere. A person limits the sphere of his knowledge of only those necessary for him to effectively fulfill their duties, demonstrating complete ignorance in other areas.
You probably heard that at the genetic level we inherit from our parents the peculiarities of the nervous system, which, in turn, determines our temperament.
The external environment to which our organism is adapted, contributes to the emergence of excitation and braking processes in our nervous system, which leads to certain mental and physiological conditions, which affect the general state of the health of the body.
And now let's look at:
- As a medium where we are, affects our internal states;
- How our activities affect our states.
And then trace the relationship between the peculiarities of the work of the nervous system and our professional activities. After that, we draw conclusions about whether we work and whether we are engaged in terms of maintaining health in our body.
A brief course on an important (medium and mental state, environment and physiological states)
The adaptation mechanism is responsible for adaptation to new living conditions. Adaptation occurs at the level of psyche and physiology.
At the physiology level, the system of organs correspond to the adaptation: the immune system, Endocrine system, nervous system. These systems are interconnected and affect each other. A failure in one of the systems leads to failures in other systems.
Interacting with the external environment, our body exchanges with it chemicals, energy, information (reacting to the stimulus; perception and processing of information; changes inside and outside to maintain the necessary balances that provide survival or maintenance of life).
All changes in the medium immediately forcing our body to adapt to new conditions (changes in temperature and humidity, the appearance of threats or other organisms nearby).
For adaptation for the most part, our vegetative nervous system is responsible (Next VNS), and we do not need to think about how and what to change in the body so that it continues to live (chemical reactions, hormone exchange, heart rate, breathing intensity, etc. P.). In fact, when you consciously change something in your behavior, fulfilling your professional duties (we are going somewhere, do something), then you forced your VNS to fulfill additional work to maintain the functional state of your body.
VNS has a sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system. The first responds, simply speaking, for acceleration / excitement. Second - for suppressing activity and relaxation.
The activity of one nervous system (from the above) leads to a decrease in the activity of another system.
Conscious fulfillment of some kind of activity (related to motor activity) adds excitation to the central nervous system and enhances the operation of the sympathetic nervous system. And this changes your mental processes (speeding up / slowing out thinking and work with information, improving or worsening the work of imagination, etc.).
Any changes in the outer medium are also enhanced or slowed down one of the systems (sympathetic or parasympathetic). In other words, changes are surrounded by physiological processes (due to the adaptation of the body to new conditions) and form new mental states that can be useful or harmful to your health.
Strong stress does not pass without a trace for health (this can manifest themselves with time, for example, in the form of "post-stress syndrome").
Wednesday affect our states and our health. By changing consciously environmental conditions, you can maintain your health or harm him.
Now we will tire in more detail the relationship between activities and states.
Relationship of activities and conditions
As mentioned above, conscious changes in behavior affect the relationship between the body with the environment, which affects the changes in the internal balances in the organ systems and in general on the physiological states of the whole body. Changes in physiological processes entail changes in mental processes that can harm the normal functioning of the organism (health violations).
In other words, while you, for example, spend a presentation for the client, in your body there are many changes and at the level of physiology (as a result of the impact of stress factors). To maintain your behavior and adapting to the environment in which you found yourself, the body has to work out. The work done may eventually bring the body (and more specifically, for example, the psyche) to a non-functional state (to uncomfortable and painful sensations).
Strong stress in the form of stimuli / impacts from the medium forces the body to work in another mode. If the potential of the body is insufficient (there is not enough energy, certain chemicals), then this may cause certain deviations from the norm (health violations).
Changes in the activity increase or weaken the interaction of the body with the medium, which ultimately changes internal states. These states can harm health.
And now it is time to mention the peculiarities of the nervous system and professional activity.
Psychological characteristics of temperament - features of mental processes and behaviors that are generated by a combination of the properties of the nervous system:
- Activity. As far as a person is able to focus, concentrate their attention, imagination, memory and thinking on a specific object (how fast the corresponding mental processes work, producing periodic or cyclic operations). Different people (per unit of time) have time to make different work on the volume.
- Productivity. High, if a person without signs of fatigue can do more (see, hear, remember, submit, decide). That is, perform a large amount of work. Ability to maintain a high pace of work enough.
- Ecavitability, brakesiness and switchability. The speed of the occurrence, termination or switching of a cognitive process from one object to another, the transition from one practical action to another. Some people quickly switch from one thread reflection on the other, others slower.
These characteristics determine the type of temperament, which over time acquires the features of the dynamic features observed in human behavior and received often at its temperament. However, they are only it some kind of modification, and in scientific circles it is called an individual activity style.
That is, an adult may have two types of "temperament": the main (since childhood) and purchased (artificially created by adapting behavior to the medium).
Ideally (for the most efficient professional activity) "Individual Style Activity" must coincide with temperament, but it is rare. Most often, the person has to adapt with its temperament to the requirements of professional activity and environment. Therefore, the mismatch of the style of activity and natural temperament is a typical situation.
The discrepancy between the "natural" temperament and "acquired" (individual style of activity) adversely affects well-being (health) and on the successful performance of activities (results of labor).
When the individual style of activity coincides with temperament, the following positive consequences are associated:
- When performing relevant activities, a person feels comfortable, experiencing positive emotions and enjoying what operates at a certain pace with a given speed and elected activity.
- In the course of its activities, it allows relatively few mistakes and is able to work with high quality.
- A person can work for a long time without signs of fatigue or fatigue.
In the event of a significant discrepancy between the natural temperament (hereinafter PT) and the individual style of activity (hereinafter ISD), negative consequences may be observed:
- A person has a sense of discomfort when performing activities at a given pace or at a given speed.
- It allows a considerable amount of errors and is not able to fully control them.
- It quickly gets tired and tired (when the pace of work and communication proceeds in a rhythm inherent for him).
Favorable combinations of temperament and individual style of activity to fulfill professional obligations:
- Choleric (PT) and Sanguine (ISD).
- Sanguine (PT) and choleric (ISD).
- Phlegmatic (PT) and Melancholic (ISD).
- Melancholic (PT) and phlegmatic (ISD).
Adverse combinations:
- Phlegmatic (PT) and Sanguine (ISD).
- Melancholic (PT) and choleric (ISD).
Summary
Temperament affects the quality of activity. Professional activity may not approach the type of temperament (a person has to produce an individual style of activity, taking into account the requirements of the profession and environment).
Temperament is associated with mental properties and affects the formation of character traits. The mismatch of the characteristics of the temperament and the created individual style of behavior leads to diseases of the body and personality disorders.
Findings:
- Our temperament and individual activity style or interfere, or help us at work (profession).
- Activities affect mental states that may disclaim the nervous system, and this, in turn, may interfere with maintaining the normal functional condition of the body (health).
- Since the external environment (place) can enhance or smooth the effect of "the influence of professional activity on the nervous system", then, therefore, it can be concluded that the environment can help support health or harm him.
If you read this article, we realized that your professional activity may be the cause of physical ailments, it makes sense to think about her shift. Either, as an option with "smaller victims", it is worth considering the possibility of changing the external environment where your activity takes place, that is, to change the place of work.
Remember - ignorance prevents us from being healthy, successful and happy. And knowledge allows you to avoid problems and help gain the desired.
You now know how your activity is interrelated, the external environment and features of your nervous system. Take for yourself the right solution!
P.. S..
Some tips:
- Consciousness, personality, activities are interconnected! Affecting one thing, change the other.
- Changing activities leads to changes in consciousness and personality.
- The personality image is formed gradually through the practice (as a result of activity).
If in priorities material needs, then the change of work or activity can improve a comfortable and safe existence. But it is necessary to take into account even how the change of activities will affect your social and spiritual needs (they can become more relevant, or the change of activity will not allow them to satisfy). As well as how the change of activity will affect your morality (which is for you good, and what evil). Changing activity or place of work may affect the moral side of your life (they pay a lot, but you have to do what your conscience cannot close your eyes).
In an aggressive environment, a person with high morality do nothing to do. These are constant internal conflicts: surviveYou have to do what is contrary to internal beliefs and values. Before changing activities or place of work, you need to take into account to avoid in the future internal conflicts.