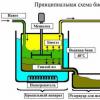
Beta blockers with vasodilatory action. Adrenoblockers (alpha and beta blockers) - a list of drugs and classification, mechanism of action (selective, non-selective, etc.), indications for use, side effects and contraindications. Mechanism of action
Catecholamines are important in the regulation of the functions of the organism: adrenaline and norepinephrine. They stand out in blood and act on special sensitive nerve endings - adrenoreceptors. The latter are divided into two large groups: alpha and beta-adrenoreceptors. Beta-adrenoreceptors are located in many organs and tissues and are divided into two subgroups.
When the β1-adrenoreceptors are activated, the frequency and power of heart abbreviations increase, expand coronary arteryThe conductivity and automaticism of the heart improves, the decay of glycogen in the liver and energy formation increases.
When the β2-adrenoreceptors are excited by the walls of the vessels, the muscles of the bronchi, the tone of the uterus is reduced during pregnancy, insulin and disintegration of fat increases. Thus, the stimulation of beta-adrenoreceptors using catecholamines leads to the mobilization of all the body for active livelihoods.
Beta-adrenoblastors (Bab) are a group of medicinal substances that bind beta-adrenoreceptors and impede the action of Catecholamines on them. These drugs are widely used in cardiology.
 Babs reduce the frequency and strength of heart abbreviations, reduce blood pressure. As a result, oxygen consumption with cardiac muscle decreases.
Babs reduce the frequency and strength of heart abbreviations, reduce blood pressure. As a result, oxygen consumption with cardiac muscle decreases.
Diastola is lengthened - the rest period, relaxation of the heart muscle, during which there is a filling of coronary blood vessels. Improving the coronary perfusion (myocardial blood supply) contributes to the decrease in intracardiac diastolic pressure.
The redistribution of blood flow occurs from normal blood ducts to the ushised, as a result, the portability of physical exertion is improved.
Bab has an antiarrhythmic action. They suppress the cardiotoxic and arrhythmogenic effect of catecholamines, and also prevent the accumulation of calcium ions in the heart cells, worsening energy exchange in myocardium.
Classification
Bab is an extensive group of medicines. They can be classified for many signs.
Cardooselectivity - the ability of the drug to block only β1-adrenoreceptors, without affecting β2-adrenoreceptors, which are in the wall of the bronchi, vessels, uterus. The higher the selectivity of Bab, the safer to apply it in concomitant diseases respiratory tract and peripheral vessels, as well as diabetes mellitus.  However, selectivity is the concept of relative. When prescribing a drug in large doses, selectivity decreases.
However, selectivity is the concept of relative. When prescribing a drug in large doses, selectivity decreases.
Some women inherent internal sympathomimetic activity: the ability to some degree to stimulate beta-adrenoreceptors. Compared to ordinary women, such drugs slow down the heart rhythm and the strength of its abbreviations, less often lead to the development of cancellation syndrome, less adversely affect lipid exchange.
Some women are able to additionally expand the vessels, that is, there are vazodilative properties. This mechanism is implemented using pronounced internal sympathomimetic activity, alpha-adrenoreceptor blockades or direct action on vascular walls.
The duration of action most often depends on the peculiarities of the chemical structure of Bab. Lipophilic facilities (propranolol) act several hours and quickly derived from the body. Hydrophilic preparations (atenolol) are effective for a longer time, can be assigned less frequently. Currently created lipophilic substances long action (Metoprolol Retard). In addition, there are women with a very small duration of action - up to 30 minutes (esmolol).
Scroll
1. Noncardiodelective Bab:
BUT.  Without internal sympathomimetic activity:
Without internal sympathomimetic activity:
- propranolol (Anaprilin, Obizant);
- nadolol (Corgard);
- satolol (Sotagexal, Tensol);
- timolol (blocarden);
- nipradilol;
- flestrolol.
- oplespolol (trazicor);
- pindolol (wqquen);
- alprenolol (APTIN);
- penbutolol (Betapressin, Levatol);
- bopindolol (Sandonorm);
- bucindolol;
- dilealol;
- carolol;
- labetalol.
2. Cardooselective women:
A. Without internal sympathomimetic activity:

B. With internal sympathomimetic activity:
- acelebalol (acecor, sectal);
- talinolol (Cordanum);
- coleiprolol;
- emolol (Vasakor).
3. BB with vazodilative properties:
A. Narkdiodelective:

B. Cardooselective:
- carvedilol;
- nebivolol;
- coleiprolol.
4. Long-term women:
A. Narkdiodelective:
- bopindolol;
- supolyol;
- penbutolol;
- satolol.
B.  Cardooselective:
Cardooselective:
- atenolol;
- betaxolol;
- bisoprolol;
- empapolol.
5. Babs of ultrashort action, cardiolective:
- eSMOLOL.
Application for diseases of the cardiovascular system
Threw stress
In many cases, women are one of the leading means to treat and prevent attacks. Unlike nitrates, these funds do not cause tolerance (drug sustainability) with long use. Babs are capable of cumulating (accumulating) in the body, which allows you to reduce the dosage of the drug after a while. In addition, these funds protect the heart muscle itself, improving the forecast by reducing the risk of myocardial repeated infarction.
Antianginal activity of all women is about the same.  Their choice is based on the duration of the effect, the severity of side effects, costs and other factors.
Their choice is based on the duration of the effect, the severity of side effects, costs and other factors.
We begin treatment with a small dose, gradually increasing it to effective. The dosage is selected in such a way that the frequency of the heart abbreviations at rest was not lower than 50 per minute, and the level of systolic blood pressure is at least 100 mm RT. Art. After the onset therapeutic effect (The cessation of angina seizures, improving the tolerance of physical exertion) The dose is gradually reduced to the minimum efficient.
Prolonged use of high doses of women is inappropriate, as it significantly increases the risk of side effects. With insufficient effectiveness of these funds, it is better to combine them with other groups of drugs.
Babs can not be abruptly canceled, as it may occur with cancellation syndrome.
Babs are especially shown if the stroke angina is combined with sinus tachycardia, glaucoma, constipation and gastroofine reflux.
Myocardial infarction
Early use of women when it helps to limit the cordial muscle necrosis area. At the same time, mortality decreases, the risk of myocardial infarction and the heart stop decreases.
 Such an effect is provided by women without internal sympathomimetic activity, it is preferable to use cardio selective tools. They are especially useful in combining myocardial infarction with arterial hypertension, sinus tachycardia, post-infarction angina and a tachiisistolic form.
Such an effect is provided by women without internal sympathomimetic activity, it is preferable to use cardio selective tools. They are especially useful in combining myocardial infarction with arterial hypertension, sinus tachycardia, post-infarction angina and a tachiisistolic form.
Bab can be prescribed immediately when the patient is admitted to the hospital with all patients in the absence of contraindications. In the absence of side effects, the treatment of them continues at least a year after the myocardial infarction.
Chronic heart failure
The use of women in heart failure is studied. It is believed that they can be used when combined with heart failure (especially diastolic) and angina stress. Rhythm disorders, arterial hypertension, a tachiisistolic form of atrial fibrillation in combination with also the grounds for the appointment of this group of drugs.
Hypertonic disease
Babs are shown in the treatment hypertensive diseasecomplicated. They are also widely used in young patients leading an active lifestyle. This group of drugs is prescribed by combining arterial hypertension with stress angina or violations of the heart rhythm, as well as after the myocardial infarction.
Disturbance of cardiac rhythm
 Women are used with such violations heart RhythmAs fibrillation and fluttering atrial, sucanementaricular arrhythmias, poorly tolerated sinus tachycardia. They can also be appointed during rhythm violations, but their effectiveness in this case is usually less expressed. Bab in combination with potassium preparations are used for the treatment caused by glycoside intoxication.
Women are used with such violations heart RhythmAs fibrillation and fluttering atrial, sucanementaricular arrhythmias, poorly tolerated sinus tachycardia. They can also be appointed during rhythm violations, but their effectiveness in this case is usually less expressed. Bab in combination with potassium preparations are used for the treatment caused by glycoside intoxication.
Side effects
The cardiovascular system
Bab depress the ability of a sinus node to produce pulses that cause heart cuts and cause sinusovoy bradycardia - Slowing the pulse to the values \u200b\u200bless than 50 per minute. This side effect is significantly less pronounced in women with internal sympathomimetic activity.
Preparations of this group can cause an atrioventricular blockade of varying degrees. They reduce the strength of heart abbreviations. The last side effect is less pronounced in women with vazodilative properties. Babs reduce blood pressure.
Medicines of this group cause spasm of peripheral vessels. A cooling limbs may appear, the Raino syndrome is worse. These side effects are almost deprived of preparations with vazodilative properties.
Babs reduce the renal blood flow (except for the supolyol). Due to the deterioration of peripheral blood circulation in the treatment with these means, there is sometimes a pronounced general weakness.
Respiratory system
Bab causes the spasm of the bronchi due to the concomitant blockade of β2-adrenoreceptors. This side effect is less pronounced in cardiodelective funds. However, their doses, effective in relation to angina or hypertension, are often sufficiently high, while cardioselitivity is significantly reduced.
The use of high doses of women can provoke apnea, or a temporary stop of breathing.
Bab worsen the flow of allergic reactions to insect bites, medicinal and food allergens.
Nervous system
Propranolol, metoprolol and other lipophilic women penetrate blood into the cerebral cells through the hematorencephalic barrier. Therefore, they can cause headache, sleep disorders, dizziness, worsening memory and depression. In severe cases, hallucinations arise, convulsions, coma. These side effects Hidely expressed hydrophilic women, in particular, atenolol.
Treatment of women can be accompanied by a violation of neuromuscular conductivity. This leads to the emergence of muscle weakness, decrease in endurance and fast fatigue.
Metabolism
Non-selective women suppress insulin production in the pancreas. On the other hand, these drugs brake mobilization of glucose from the liver, contributing to the development of prolonged hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes. Hypoglycemia contributes to the heating into the blood of adrenaline acting on alpha-adrenoreceptors. This leads to a significant rise in blood pressure.
 Therefore, if necessary, the appointment of women patients with accompanying diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to prefer with cardiolalective drugs or replace them with calcium antagonists or other groups.
Therefore, if necessary, the appointment of women patients with accompanying diabetes mellitus, it is necessary to prefer with cardiolalective drugs or replace them with calcium antagonists or other groups.
Many women, especially non-selective, reduce the content of "good" cholesterol (high density alpha-lipoproteins) and increase the level of "bad" (triglycerides and lipoproteins of very low density). This disadvantage is deprived of drugs with β1-internal sympathomimetic and α-blocking activity (carvedilol, labetolol, pindolol, dilellol, celiprolol).
Other side effects
Treatment of women in some cases is accompanied by sexual dysfunction: violation of the erection and loss of sexual entry. The mechanism of such an effect is unclear.
Bab can cause skin changes: rash, itching, erythema, symptoms of psoriasis. In rare cases, hair loss and stomatitis is recorded.
One of the serious side effects is the oppression of blood formation with the development of agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenic purpura.
Cancellation syndrome
If women are used for a long time in high dosage, the sudden cessation of treatment can provoke the so-called cancellation syndrome. It is manifested by the participation of angina attacks, the emergence of ventricular rhythm disorders, the development of myocardial infarction. In easier cases, the abolition syndrome is accompanied by tachycardia and an increase in blood pressure. Cancellation syndrome is usually manifested several days after the cease of reception of women.
 To avoid the development of cancellation syndrome, you need to follow the following rules:
To avoid the development of cancellation syndrome, you need to follow the following rules:
- cancel Babe slowly, for two weeks, gradually reducing the dosage for one reception;
- during and after the abolition of women, it is necessary to limit physical exertion, if necessary, increase the dosage of nitrates and other anti-naniginal products, as well as drugs that reduce blood pressure.
Contraindications
Bab is absolutely contraindicated in the following situations:
- swelling of lungs and cardiogenic shock;
- severe heart failure;
- bronchial asthma;
- atrioventricular blockade II - III degree;
- the level of systolic blood pressure is 100 mm Hg. Art. and below;
- cardiac frequency less than 50 per minute;
- poorly controlled insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Relative contraindications to the appointment of women - Riino and atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries with the development of interspersed chromium. 
Beta-adrenoblocators They are called drugs that are reversible (temporarily) block various species (β 1 -, β 2 -, β 3 -) of adrenoreceptors.
The value of beta adrenoblockers It is difficult to overestimate. They are the only class of drugs in Cardiology, for the development of which is presented. Awarding the Prize in 1988, the Nobel Committee called the clinical significance of beta-adrenobloclars " the greatest breakthrough in the fight against heart disease after the opening of Digitalisa 200 years ago».
DiGitalis preparations (plants of fluttering, lat. Digitalis) call a group cardiac glycosides (digoxin, Stroofantin et al.), which are used to treat chronic heart failure from about 1785.
Brief classification of beta adrenoblockers
All beta-adrenoblocators are divided into non-selective and selective.
Selectivity (cardooselectivity) - The ability to block only beta1-adrenoreceptors and not affect beta2 receptors, since the useful effect of beta-adrenoblockers is due to the mainly blockade of beta1 receptors, and the main side effects are beta2 receptors.
In other words, selectivity is selectivity, selectivity of the action (from the English. selective - selective). However, this cardooselectivity is only relative - in large doses, even selective beta-adrenoblastors can partially block both beta2-adrenoreceptors. Please note that cardiolective preparations are stronger reduce diastolic (lower) pressurethan non-selective.
Still some beta adrenobloclars have the so-called Vs. (internal sympathomimetic activity). Less often call it SSA (own sympathomimetic activity). BCA is the ability of beta adrenoblor partially stimulate The beta-adrenoreceptors suppressed by them, which reduces the side effects ("softens" the effect of the drug).
For example, beta adrenoblockers from the BCA to a lesser extent reduce heart rateAnd if the heart rate is source low, then sometimes they can increase it.
Beta adrenoblays with mixed action:
- Carvedilol - Mixed α 1 -, β 1 -, β 2 -adrenoblocator without BCA.
- Labetalol. - α-, β 1 -, β 2 -adrenoblocator and partial agonist (stimulator) β 2 receptors.
Useful effects of beta adrenoblockers
To understand what we can achieve from the use of beta-adrenerboators, we must understand the effects that occur at.
Cardiac Regulation Scheme.
Adrenoreceptors and Catecholamins acting on them [ ], as well as adrenal devices that allocate adrenaline and norepinephrine directly into the bloodstream, are combined into sympatoadrenal system (CAC). Activation of the sympathoadrenal system occurs:
- w. healthy people with stress,
- in patients with a number of diseases:
- myocardial infarction,
- acute and chronic heart failure (the heart does not cope to pump blood. At CXN, shortness of breath arise (in 98% of patients), fatigue (93%), heartbeat (80%), swelling, cough),
- arterial hypertension and etc.
Beta1 adrenoblastors limit the effects of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body, thereby leading to 4 Effects:
- reduction of heart cutness
- reducing heart rate (heart rate),
- decrease in conductivity in the conductive heart system,
- reducing the risk of arrhythmias.
Now more for each item.
Reducing heart rate
The decrease in heart rate leads to the fact that the heart pushes the blood in the aorta with a smaller force and creates a smaller level of systolic (upper) pressure. Reducing the reduction of abbreviations reduces the work of the heart And, accordingly, the need of myocardium in oxygen.
Reduced heart rate
The decrease in the heart rate allows the heart more rest. This is perhaps the most important thing about which I wrote before. During the abbreviation (systole), the muscle tissue of the heart is not heavily, as the coronary vessels in the thickness of myocardium are shifted. Blood supply myocardium Perhaps only during his relaxation (diastole). The higher the heart rate, the smaller the overall duration of the heart relaxation periods. The heart does not have time to relax fully and may experience ischemia (lack of oxygen).
So, beta-adrenoblays reduce the power of heart abbreviations and the need of myocardium in oxygen, and also lengthen the period of rest and blood supply to the heart muscle. That is why beta blockers are pronounced anti -cehetic action and often used for treating anginawhich is one of the forms of IBS ( ischemic Disease Hearts). Old name angina - angina pectorisLatin angina Pectoris., therefore, the opponentical action is also called antianginal. Now you will know what is the antichangal effect of beta-adrenobloclars.
Please note that among all Cardiology Classes beta adrenoblocators without It is better to reduce the heart rate ( frequency of heart abbreviations). For this reason, heartbeat and tachycardia (CSS above 90 per minute) First of all, they are prescribed.
Since beta blockers reduce the work of the heart and blood pressure, they contraindicated In situations where the heart does not cope with its work:
- heavy arterial hypotension (Hell is less than 90-100 mm Hg. Art.),
- acute heart failure (Cardiogenic shock, pulmonary edema, etc.),
- Hsn ( chronic heart failure) In the Stage decompensation.
It is curious that beta blockers should be used (in parallel with three other classes of lek. Drugs - ACE inhibitors, cardiac glycosides, diuretic) treatment initial stages chronic heart failure. Beta blockers protect the heart from excessive activation of the sympathetic system and increase the life expectancy patients. I'll tell you more about modern principles The treatment of HSN in the topic about heart glycosides.
Conduct reduction
Conduct reduction ( reducing the velocity of electrical impulses by ) As one of the effects of beta blockers is also of great importance. Under some conditions, beta blockers may disrupt preservative conductivity (slow down impulses from atria to ventricles in AV-node) What causes an atrioventricular blockade (AV blockade) of varying degrees (from I to III).
AV-block diagnosis Various degrees of gravity is put on ECG and manifests itself in one or more signs:
- constant or cyclic interval lengthening P-Q View More 0.21 s,
- losing individual ventricular cuts,
- reduced heart rate (usually from 30 to 60).
A steadily increased duration of the P-Q interval from 0.21 s and above.
a) periods of gradual elongation of the P-Q interval with the fallout of the QRS complex;
b) loss of separate QRS complexes without gradually elongation of the P-Q interval.
At least half of the ventricular QRS complexes falls.
The impulses from the atria to the ventricles are not conducted at all.
From here council: If the patient has a pulse less often 45 blows per minute or an unusual uneven rhythm appeared, it is most likely to adjust the dose of the drug.
In what cases are elevated risk of conducting conductivity disorders?
- If the beta adrenoblocator is prescribed to the patient with bradycardia (Heart rate below 60 per minute)
- if it is originally available violation of atrioventricular conduction (increased the time of the electric. pulses in AV node more than 0.21 C),
- if the patient is individually high sensitivity to beta blockers
- if a exceeded (incorrectly selected) dose of beta adrenoblocker.
To prevent conduction disorders, you need to start with small doses of beta blocker And raise the dosage gradually. If the side effects occur, the beta-adrenobloclater cannot be canceled sharply due to the risk of tachycardia (heartbeat). Need to reduce the dosage and cancel the drug gradually, within a few days.
Beta adrenoblastors are contraindicated if the patient has hazardous deviations on the ECG, for example:
- violations of conductivity (Atrioventricular blockade II or III degree, synoatrial blockade, etc.),
- too rare rhythm (CSS less than 50 per minute, i.e. sharp bradycardia),
- sinus node weakness syndrome (SCC).
Reducing the risk of arrhythmia
Reception of beta adrenoblockers leads to reducing the excitability of myocardium. In the heart muscle, there are fewer excitation foci, each of which is capable of leading to cardiac arrhythmia. For this reason, beta blockers are effective in treating, as well as for prevention and treatment and stomacle Rhythm disorders. Clinical studies have shown that beta blockers significantly reduce the risk of fatal (deadly) arrhythmias (for example, ventricular fibrillation) and therefore are actively used for prevention sudden death , Including with the pathological elongation of the Q-T interval on the ECG.
Any myocardial infarction due to pain and necrosis (dieting) of the heart muscle site is accompanied by pronounced activation of the sympathetic system. The purpose of beta-blockers with myocardial infarction (if there is no indicated above contraindications) significantly reduces the risk of sudden death.
Indications for the use of beta blockers:
- IBS (angina, myocardial infarction, chronic heart failure),
- prevention of arrhythmias and sudden death,
- arterial hypertension (treatment of increased blood pressure),
- other diseases with an increase in the activity of catecholamines [ adrenaline, Noradrenalin, Dopamine] in organism:
- thyretoxicosis (thyroid hyperfunction),
- alcohol abstinence (), etc.
Side Effects of Beta Adrenoblockers
Part of side effects due to excessive action of beta adrenoblockers on the cardiovascular system:
- sharp bradycardia (Heart rate below 45 per minute),
- atrioventricular blocada,
- arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 90-100 mm Hg. Art.) - more often intravenous administration beta adrenoblockers,
- strengthening heart failure up to the edema of the lungs and stop the heart,
- worsening blood circulation in the legs With a decrease in cardiac emissions - more often in older people with atherosclerosis of peripheral vessels or endarterity.
If the patient has feochromocytoma (a benign tumor of the brain layer of adrenal glands or nodes of sympathetic vegetative nervous systemhighlighting catecholamines; occurs in 1 for 10 thousand people and up to 1% of patients with hypertension), T. beta blockers may even increase blood pressure Due to the stimulation of α 1 -adrenororeceptors and spasm arterioles. To normalize hell, beta blockers need to be combined with.
In 85-90% of cases of pheochromocytoma is a tumor of adrenal glands.
Beta blockers by themselves show antiarrhythmic effectbut in combination with other anti-anhythmic drugs possible provocation attacks of ventricular tachycardia or ventricular bigemia (constant alternate change of normal reduction and ventricular extrasystole, from lat. bI - two).
Bigemia.
The rest of the side effects of beta blockers are easy-smart.
The narrowing of bronchi and bronchospasm
Beta2-adrenoreceptors expand bronchi. Accordingly, beta-blockers acting on beta2-adrenoreceptors are narrowing the bronchi and can provoke bronchospasm. This is especially dangerous to patients with bronchial asthma , smokers and other people with lung diseases. They have cough and shortness of breath increases. To prevent this bronchospasm, you need to take into account the risk factors and be sure to apply only cardio selective beta blockerswhich in ordinary doses do not act on beta2-adrenoreceptors.
Reducing sugar levels and lipid profile deterioration
Since the stimulation of beta2-adrenoreceptor causes the splitting of glycogen and the growth of glucose levels, the beta blockers can reduce the level of sugar in blood with development moderate hypoglycemia. People with normal carbohydrate exchange There is nothing to fear, and patients with, should be careful. Moreover, beta blockers mask such symptoms of hypoglycemia like tremor (jitter) I. heartbeat (tachycardia), due to excessive activation of the sympathetic nervous system due to the emission of contrincing hormones during hypoglycemia. note that sweet glands They are controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, but they are m-cholinoreceptors that are not blocked by adrenoblockers. Therefore, hypoglycemia during the reception of beta blockers is characterized especially strong sweating.
Patients with diabetes in insulin must be informed about the increased risk of development when using beta-adrenoblockers. For such patients are preferred selective beta blockersnot acting on beta2-adrenoreceptors. Patients with diabetes mellitus in an unstable condition ( poorly predictable blood glucose levels) Beta blockers are not recommended, in other cases, please.
Sexual violations
Perhaps development impotence (Modern name - erectile dysfunction), for example, when taking propranolola For 1 year it develops in 14% of cases. Also noted development fibrous plaques In the body of the penis with its deformation and the difficulty of erection when taking propranolola and metoprolol. Sexual violations are more often in persons with (that is, problems with potency when taking beta blockers usually arise from those who are possible without drugs).
I am afraid of impotence and for this reason do not take medicines for arterial hypertension - a mistake solution. Scientists find out that long increased blood pressure leads to erectile dysfunction Regardless of the availability of accompanying atherosclerosis. With high hell walls of vessels thicken, become denser and can not supply internal organs the right amount of blood.
Other side effects of beta adrenoblockers
Other side effects When taking beta blockers:
- from side gastrointestinal tract (in 5-15% of cases): constipation, less often diarrhea and nausea.
- from side nervous system: Depression, sleep disorders.
- from side skin and mucous membranes: rash, urticaria, eye redness, reducing the secretion of tear fluid (relevant for contact lenses using contact lenses), etc.
- when receiving propranolola Occasionally happens laryingospasm (Difficult noisy, whistling inhale) as a manifestation of an allergic reaction. Laringostasm arises as a reaction to an artificial yellow dye tartrazine In a tablet approximately after 45 minutes After taking the drug inside.
Cancellation syndrome
If you take beta-blockers for a long time (several months or even weeks), and then suddenly stop receiving, arises cancellation syndrome. In the coming days after the cancellation occurs heartbeat, anxiety, angina attacks, ECG worsens, maybe the development of myocardial infarction and even a sudden death.
Development of cancellation syndrome is due to the fact that during the reception of beta-blockers the body adapts to the reduced influence (NOR) of adrenaline and increases the number of adrenoreceptors in organs and tissues. In addition, since propranolol slows down the transformation of the hormone of the thyroid gland tyroxina (T 4) in hormone triiodthththinine (T 3), then some signs of cancellation syndrome (anxiety, trembling, heartbeat), especially expressed after the abolition of propranolol, can be caused by excess thyroid hormones.
For the prevention of cancellation syndrome recommended gradual cancellation of the drug for 14 days. If necessary, surgical manipulations on the heart exist other diagrams of the discharge of the drug, but in any case the patient must know your medicine: What, in which dosage, how many times a day and how long he takes. Or at least write them on the leaf of paper and wear with you.
Features of the most significant beta blockers
Propranolol (Anaprilin) - non-selective beta blocker without BCA. it the most famous drug from beta blockers. Act briefly - 6-8 hours. Characterized by the abolition syndrome. Fat solvent, so penetrates the brain and possesses soothing action. Non-selective, therefore, has a large number of due beta2-blockade of side effects ( sensing bronchi and enhances cough, hypoglycemia, cooling limbs).
It is recommended for receiving under stress situations (for example, before the exam, see). Since there is sometimes increased individual sensitivity to beta-blocator with a rapid and significant decrease in blood pressure, its first purpose is recommended to be conducted under the control of the doctor with a very low dose (for example, 5-10 mg anaprilin). To increase blood pressure should be introduced atropine (and not glucocorticoid hormones). For permanent reception propranolol It is not suitable, in this case another beta blocker is recommended - bisoprolol (below).
Atenolol is a cardioslelective beta blocker without BCA. Previously was a popular drug (as well as metoprolol). Applied 1-2 times a day. Water soluble, so does not penetrate the brain. Honor cancellation syndrome.
Metoprolol - cardioslelective beta blocker without BCA, similar to atenolol. Accepted 2 times a day. Atenolol and metoprolol have now lost their importance due to the distribution bisoprolol.
Betaxolol (Locase) - Cardooselective beta blocker without BCA. Mainly used for treatment arterial hypertension. Accepted 1 time per day.
Bisoprolol (Concorp) - Cardooselective beta blocker without BCA. Perhaps the most important drug today from beta blockers. Convenient form of reception (1 time per day) and reliable smooth 24-hour antihypertensive effect. Reduces blood pressure by 15-20%. Does not affect the level of thyroid hormones and blood glucose, so allowed in diabetes mellitus. Bisoprolol is weaker than the cancellation syndrome. There are many on the market bisoprolol Different manufacturers, so you can choose inexpensive. In Belarus, the cheapest generic today - Bisoprolol-Lugal (Ukraine).
Esmolol - is available only in a solution for intravenous administration as antiarrhythmic drug. Duration of 20-30 minutes.
Nebivolol (root) - Cardooselective beta blocker without BCA. Also an excellent drug. Causes a smooth decrease in blood pressure. The pronounced antihypertensive effect occurs after 1-2 weeks of reception, the maximum - after 4 weeks. Nebivolt enhances production azota oxide (NO) in the endothelium of blood vessels. The most important function of nitrogen oxide - expansion of vessels. In 1998 was awarded Nobel Medicine Prize with wording " For the opening of the role of nitrogen oxide as a signal molecule in the regulation of the cardiovascular system" Nebivolol has a number additional useful effects:
- vasteransior [Vasodilative] (from Lat. vAS. - vessel dilatatio. - expansion),
- antiagregant (inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombosis),
- angioprotective (Protects the vessels from the development of atherosclerosis).
Carvedilol - α 1 -, β-adrenoblocator without BCA. Thanks to the blockade of α 1 -receptors, has vasodilative action And additionally reduces blood pressure. Less atenolol reduces heart rate. Does not impair the tolerance of physical exertion. Unlike other blockers, reduces blood glucose levels, therefore it is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Possessed antioxidant properties, slows down atherosclerosis processes. Accepted 1-2 times a day. Especially recommended for treatment of chronic heart failure (CHF).
Labetalol - α-, β-adrenoblocator and partially stimulates β 2-receptors. Well reduces blood pressure with a minor increase in heart rate. It has an antiagonal effect. It is capable of raising blood sugar. In large doses, bronchospasm can cause cardioslelective beta blockers. Used intravenous with hypertensive cries and (less often) inside 2 times a day for the treatment of arterial hypertension.
Medicinal interactions
As I already indicated above, combination of beta blockers with other antiarrhythmic drugs Potentially dangerous. However, this is the problem of all groups of antiarrhythmic drugs.
Among antihypertensive (hypotensive) drugs prohibited Only a combination of beta blockers and calcium channel blockers from the group verapamila and diltiazem. This is associated with an increased risk of cardiac complications, since all these drugs act on the heart, reduce the power of abbreviations, heart rate and conductivity.
Overdose of beta adrenoblockers
Symptoms overdose Beta blockers:
- sharp bradycardia (heart rate below 45 per minute)
- dizziness up to the loss of consciousness,
- arrhythmia,
- akricyanosis ( scorn in fingertips),
- if the beta-blocker is fat soluble and penetrates the brain (for example, propranolol), then a coma and cramps can develop.
Assistance in overdose Beta blockers depends on the symptoms:
- for bradycardia - atropine (parasimpatic effect blocker), β 1 -stimulators ( dobutamine, Isoproterenol, Dopamine),
- for heart failure - cardiac glycosides and diuretic,
- for low hell (hypotension below 100 mm Hg. Art.) - adrenaline, Meston and etc.
- for bronchospaisme - aminoophyllin (efufillin), isoproterenol.
For local application (instillation in the eyes) beta blockers reduce the education and secretion of waterthat reduces intraocular pressure. Local beta blockers ( timolol, Proksodolol, Betaxolol et al.) Used for treating glaucoma (eye disease with gradual due to elevated intraocular pressure ). Perhaps development system side effects, caused by the hit of anti-chloroous beta-blockers on the tears and nose channel and from there in the stomach, followed by suction in the gastrointestinal tract.
Beta blockers are taken into account as possible doping and athletes should be used with serious restrictions.
Supplement about Koraxan
In connection with frequent issues in the comments about the drug Koraxan (Ivabradin) Highlight its similarities and differences with beta blockers. Koraxan blocks i f -Channels of the sinus node and therefore does not apply to beta adrenoblockers.
| Koraxan (Ivabradin) | Beta blockers | |
| Impact on the occurrence of pulses in the sinus node | Yes, inhibits | Yes, suppress |
| Influence on heartbreaking | Reduces heart rate with sinus rhythm | Reduce heart rate at any rhythm |
| Effect on the conduct of pulses by the conductive system of the heart | Not | Slow hold |
| The effect on the reduction of myocardium | Not | Reduce myocardial reduction |
| Ability to warn and treat arrhythmia | Not | There are (apply to the prevention and treatment of many arrhythmias) |
| Antianginal (anti-chemic) effect | Yes, used in the treatment of stable angina | Yes, used in the treatment of any angina (in the absence of contraindications) |
| Impact on blood pressure | Not | Reduce blood pressure and are often used to treat hypertension |
In this way, coraxan Used to gear sinus rhythm with normal (slightly reduced) hell and the absence of arrhythmias. If a Hell elevated or there are cardiac arrhythmias, you need to use beta blockers. A combination of shoquacan with beta blockers is allowed.
More about Coraxan: http://www.rlsnet.ru/tn_index_id_34171.htm.
Beta blockers in the treatment of hsn
(update from 19.07.2014)
A group of beta blockers refers to the basic (mandatory) for treatment Xsn (chronic heart failure). According to the results of clinical studies now for the treatment of HSN recommended 4 drugs:
- carvedilol,
- bisoprolol,
- extended form metoprolol Sukcinate,
- people over 70 years old are also allowed nebivol.
These 4 drugs proved to clinical studies Its ability to improve the condition and increase the survival of patients with HSN.
- atenolol,
- metoprolol Tartrate.
The aim of treating beta-blockers with CHSN is a decrease in the heart rate at least 15% of the initial level below 70 ° C. per minute (50-60). It has been established that the decrease in the heart rate for every 5 blows reduces mortality by 18%.
The initial dose of CXN is 1/8 from therapeutic And slowly rises every 2-4 weeks. In case of intolerance and the inefficiency of beta-blockers, they are combined or completely replaced by a blocker I f -Channels of a sinus node - ivabradin (see above Supplement about Koraxan).
Read more about the use of beta blockers in the treatment of HSN, read in national recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of HSN of the 4th revision, approved in 2012-2013. (PDF, 1 MB, in Russian).
Traditionally, beta blockers are considered.
These drugs help not only effectively reduce the level of blood pressure when he reaches increased valuesBut also contribute to the decrease in heart rate, and sufficiently.
What is beta and alpha blockers
Preparations that are found to the category of adrenoblastors are taken, in turn, classify into several subgroups, and this is despite the fact that they can all be effectively used during the treatment of pressure jumps.
Alpha-adrenoblocators are biochemically active substances that affect alpha receptors. They are accepted with hypertension of essential and symptomatic. Thanks to the tablets, the vessels are diverted, due to which their resistance to the periphery weakens. Due to this effect, the bloodstream is greatly relieved, and the pressure level decreases. In addition, alpha-adrenoblockers lead to a decrease in the number of harmful cholesterol and fat in the blood.
Beta adrenoblocators are also classified into two categories:
- Act only on type 1 receptors - such drugs are commonly referred to as selective.
- LS, which affect both types of nervous endings - they are already referred to as non-selective.
Note that the adrenobloclars of the second type do not at all prevent the sensitivity of the receptors through which those implement their clinical effect.
Note that due to the ability to reduce heart rate, beta-blockers can be applied not only for the treatment of essential GB, but also to eliminate manifestations.
Classification
Based on the preferential action on beta-1 and beta-2, adrenoreceptors, beta blockers are classified on:
- cardooselective (as such includes metaprolol, atenolol, betaxolol, nebivolol);
- cardionialective (beta blockers - a list of drugs with hypertension looks like this: propranolol, supolyol, thymolol,).
There is another classification - according to the biochemical features of the structure of the molecule. Based on the ability to dissolve in lipids or water, representatives of this LAN group are classified into three groups:
- Lipophilic beta-adrenoblockers (Sleprenolol, propranolol, alprenolol, carvedilol, metaprolol, thymolol) - they are recommended alone in low doses in case of hepatic and stagnant heart failure in running stages.
- Hydrophilic beta-adrenoblockers (among them Atenolol, Nadolol, Talinolol, Satolol) are noted. Used at less running stages.
- Amphipal blockers (representatives - Acebotolol, Betaxolol, Pindolol, Coleiprolol) - It was this group that got the most distribution due to its wide range of action. Amphipal blockers are most often used in GB and IBS, and in different variations of this pathology.
It is important!
Many are interested in what drugs (beta-blockers or alpha - adrenoblocator) are better in hypertension. The thing is that to relieve hypertensive syndrome for a long period of time (that is, for systematic reception) better beta-blockers with high selectivity, that is, the effect of selectively, selectively (List - Bisoprolol, Metaprolol, Carvedilol ).
If you need an effect, the duration of which will manifest themselves briefly (the reading is a resistant GB, when it is urgent to reduce the blood pressure level, to avoid cardiovascular disaster), then you can assign alpha blockers, the mechanism of action of which is still different from BAB.
Cardooselective beta adrenoblays
Cardooselective beta blockers in therapeutic doses show biochemical activity mainly in relation to beta-1-adrenoreceptors. An important point is that with an increase in the dosage of beta-blockers, their specificity is noticeably reduced, and even the most highly selective drug blocks both receptors. It is very important to understand that selective and non-selective beta-blockers lower the level of blood pressure is about the same, however, the cardiodelective beta-blockers have significantly less side effects, it is easier to combine them in the presence of concomitant pathologies. Typical highcardo-selective drugs include metoprolol (trade name -), as well as atenolol and bisoprolol. Some β-adrenoblays, among them -carreedylol, block not only β1 and β2-adrenoreceptors, but also alpha adrenoreceptors, which in some cases inclined the choice of clinician in their direction.

Internal sympathomimetic activity
Some beta adrenobloclars have internal sympathomimetic activity, which is also of great importance. These drugs include pindolol and acebutol. These substances or practically do not reduce, or lower, but not particularly, the indicator of the heart rate is alone, but it repeatedly block the increase in the heart rate during the physical exertion or the action of beta-adrenomimetics.
Preparations with in one way or another internal sympathomimetic activity are uniquely shown in bradycardia of varying degrees of severity.
It should also be noted that the area of \u200b\u200busing beta-adrenobloclars from the BCMA in cardiological practice has narrowed enough. These drugs acquire their relevance, as a rule, for the treatment of uncomplicated forms AG (there is even a hypertension in pregnancy - oxprenolol and pindolol).
In patients with angina, the use of this subgroup is largely limited, because They are less effective (relative to β-adrenoblasts without ATSMA) in terms of providing negative chronotropic and battle effects.
Beta blockers from the BCMU should not be used in patients with acute coronary syndrome (Abbreviated ACS) and in post-infarction patients due to the high risk of increasing the frequency of cardiogenic complications and mortality in comparison with beta-adrenobloclars without ATSMA. Preparations from ACMA do not have relevance in the treatment of persons with heart failure.
Lipophilic drugs
All lipophilic beta blockers unambiguously should not be used during pregnancy - this feature is dictated by the fact that they are largely penetrated through the placental barrier, and after some time after the reception begin to provide unwanted impact on the fruit. Accordingly, taking into account the fact that beta blockers can also be applied in pregnant women only if the risk is at times lower than the expected benefit, the category of drugs in question is not allowed at all.
Hydrophilic drugs
One of the most important properties of hydrophilic drugs is their longer half-life (for example, atenolol is derived from the body for 8-10 hours), which allows them to be prescribed 2 times a day.
But here there is another feature - given the fact that the main load when removing lies on the kidneys, it is not difficult to guess that this organ during a stable increase in pressure was amazed to take drugs from this group.
Last generation beta blockers
A group of beta-adrenoblockers currently includes more than 30 items. The need to include them in the treatment program of cardiovascular diseases (abbreviated-CVD) is obvious and confirmed by statistical data. Over the past 50 years, the cardiological clinical practice of beta-adrenoblastors has taken confident positions in carrying out the prevention of complications and pharmacotherapy of various forms and stages of AG, IBS, HSN, metabolic syndrome (MS), as well as at various types of tachyarhythmias of both ventricular and sugaryaricular.

According to the requirements of generally accepted standards, in all uncomplicated cases, drug treatment AG starts with beta-adrenoblockers and an AEAPF, repeatedly reduce the risk of developing OIM and other cardiovascular disasters of various genes.
Smella, there is an opinion that the best beta blockers today are drugs such as bisoprolol, carvedilol; Metoprolol Sukcinate and Nebivolol.
Please note that only the attending physician has the right to assign a beta blocker.
Moreover, in any case, it is recommended to choose drugs of only a new generation. All experts agree that they cause a minimum of side effects and help to cope with the task, in no case leading to a deterioration in the quality of life.
Application for diseases of the cardiovascular system
Preparations from this group are actively used in the treatment of both both symptomatic ags, as well as tachycardia, prudged pains and even atrial fibrillations. But before taking, you should pay for some fairly ambiguous qualities of these drugs:
- Beta blockers (abbreviated BAB) are largely oppressed by the ability of a sinus node to generate pulses leading to an increase in heart rate, thereby cause sinus bradycardia - slowing down the pulse to the values \u200b\u200bbelow 50 per minute. This side effect is less pronounced in women with internal sympathomimetic activity.
- Pay attention to the fact that the drugs of this group with a high probability can lead to an atrioventricular blockade of varying degrees. In addition, they significantly reduce the strength of heart abbreviations - that is, there is also a negative battle effect. The latter is less pronounced in vazodilative properties.
- Babs lower blood pressure. Medicines of this group are the cause of the present spasm of peripheral vessels. Because of this, a cooling of the limbs may appear, in the case of the Reyny syndrome, its negative dynamics is noted. The above side effects are practically deprived of preparations with vazodilative properties.
- Baby significantly reduce the renal blood flow (with the exception of supolyol). Due to the reduction in the quality of peripheral blood circulation in the treatment with these drugs, there is a pronounced general weakness.
Threw stress
In most cases, women are a drug to choose the treatment of chest toads and cardial attacks. Note that in contrast to nitrates, these drugs do not completely cause tolerances with their prolonged use. Babs are capable of accumulating in the body, which allows me to slightly reduce the dosage of the drug somewhat. In addition, these tools are perfectly protected by myocardia itself, optimizing the forecast by reducing the risk of a relapse of the OIM recurrence.
Antianginal activity of all Bab is relatively identical. Their choice is based on the following advantages, each of which is very important:
- the duration of the effect;
- the absence (in the case of competent use) of pronounced side effects;
- relatively low cost;
- the possibility of combining with other drugs.
The course of therapy is started with a relatively small dose, and it increases gradually efficiently. The dosage is selected so that the heart rate is at rest is not lower than 50 per minute, and the level of the garden did not fall less than 100 mm Hg. Art. After the onset of expected therapeutic effect (The cessation of the occurrence of seizures of the progressive pain, the normalization of portability of at least an average physical activity) of the dose for a certain period of time is reduced to the minimum efficient.
The positive effect of women is especially noticeable in the event that the stress angina is combined with sinus tachycardia, symptomatic hypertension, glaucoma (increase), constipation and gastroesophageal reflux.
Myocardial infarction
Preparations pharmacological group Bab with OIM bring dual benefits. Their introduction to / in the first hours from the moment of manifestation of the OUT reduces the need for the heart muscle in oxygen and improves its delivery, significantly reduces the pain, contributes to the demarcation of the necrotic region and reduces the risk of gastric arrhythmias representing the direct hazard to human life.

Long reception of women reduces the risk of infarction recurrence. It has already been scientifically proven that in / in the introduction of women, followed by the transition to the "tablet" significantly reduces the mortality, risk of stopping blood circulation and recurrence of cardiovascular disasters without a deadly outcome by 15%. In the event that an early thrombolysis is conducted in the urgent situation, women do not give a decrease in mortality, but significantly reduce the risk of stress angina.
Regarding the formation of the demarcation zone of necrosis in the heart muscle - the most pronounced effect is provided by women who do not have internal sympathomimetic activity. Accordingly, it will be preferable to use cardiodelective tools. They are especially effective in combination of myocardial infarction with ag, sinus tachycardia, post-infarction angina and the TachiSistolic form of FP. Bab can be prescribed immediately with the hospitalization of the patient, subject to the absence of absolute contraindications. If there is no unwanted side effects, the treatment of these medications continues at least a year after the transferred to Oim.
Chronic heart failure
Beta blockers have a multidirectional effect, which makes them among the drugs of choice in the situation under consideration. Below will be given those of them that are of the greatest value when the HSN is stopped:
- These drugs reproduce the pumping function of the heart repeatedly.
- Beta blockers well reduce the direct toxic effect of norepinephrine.
- Babs strongly reduce the heart rate, in parallel with this, leading to the prolongation of diastoles.
- They have a significant antiarrhythmic effect.
- LS are able to prevent remodeling and diastolic dysfunction of the left ventricle.
Of particular importance was therapy of Bab after a generally accepted theory explaining the manifest of CXN, the neurogormonal theory was the reason for which the uncontrolled increase in the activity of neurogormons is the cause of the progression of the disease, and the leading role in this is given to Noraderenlin. Accordingly, beta-blockers (clear cause, which only do not possess sympathetic activity), blocking the effect of this substance, prevent the development or progression of the CHF.
Hypertonic disease
Beta blockers have been successfully used for a very long time and successfully used in the therapy of hypertensive disease. They block the undesirable effect of the sympathetic nervous system on the heart, which repeatedly facilitates its work, while at the same time reducing its blood need and oxygen. Accordingly, the result of this is the reduction of the load on the heart, and this, in turn, leads to a decrease in the digits of blood pressure.
The designated blockers help hypertensive controls and are used in the treatment of arrhythmia. It is very important when choosing a suitable beta blocker, consider the features of drugs from different groups. In addition, various side effects should be taken into account.
So if the doctor adheres to an individual approach to each patient, then even on some beta-blockers, he will be able to achieve significant clinical results.
Disturbance of cardiac rhythm
Given that the reduction in heart force significantly reduces the need of myocardium in oxygen, women successfully apply under the following heart rate disorders:

- fibrillation and fluttering atrial
- supported arrhythmias,
- poor tolerant sinus tachycardia,
- Preparations from this pharmacological group and with ventricular rhythm violations are used, but here they will already be less pronounced.
- Bab in combination with potassium preparations is successfully used to treat various arrhythmias that were provoked by glycoside intoxication.
Side effects
A certain part of the side effects is used by the excessive action of women on the cardiovascular system, namely:
- sharp bradycardia (in which the EFS indicator falls below 45 per minute);
- atrioventricular blocks;
- arterial hypotension (with a fall in the garden level below 90-100 mm Hg. Art.), Note that this kind of effects are usually developing with intravenous administration of beta-adrenoblastors;
- increasing the intensity of signs of XSN;
- reducing the intensity of blood circulation in the legs, subject to a decrease in cardiac output - this kind of problem usually occurs in the elderly with or manifesting endarterity.
There is another very interesting feature of the action of these drugs - for example, if the patient has a feuhromocytoma (a benign tumor of adrenal glands), then the beta-blockers can lead to an increase in the digits of the blood pressure due to the stimulation of α1-adrenoreceptors and spasms of the hematomycocreational vessels. All other unwanted side effects, one way or another, associated with the reception of beta-blockers, are nothing more than the manifestation of individual intolerance.
Cancellation syndrome
If you take beta blockers for a long period of time (meant in mind a few months or even weeks), and then suddenly stop the admission, the abolition syndrome occurs. Its indicators will be the following symptoms: heartbeat, concern, many times the attacks of angina, occurrence pathological signs On the ECG, and also does not exclude the likelihood of developing Oim and even a sudden death.
The dedication syndrome manifesto can be explained by the fact that during the reception the body is already adapted to the reduced influence of norepinephrine - and this effect is implemented by increasing the number of adrenoreceptors in organs and tissues. Taking into account the fact that Bab slows down the process of transformation of the thyroid thyroid hormone (T4) in the hormone triiodothironine (T3), then some manifestations of cancellation syndrome (anxiety, trembling, heartbeat), especially pronounced after the abolition of propranolol, can be due to excess thyroid hormones .
To implement preventive measures, the cancellation syndrome should be abandoned from them gradually, within 14 days - but this principle is relevant only under the condition of oral administration.
Drugs from hypertension categories of beta-adrenobloclars can easily learn from the scientific name with the ending "Lol". If the doctor prescribes a beta blocker, tell him that he discharges the prolonged action medication. Such a medication can cost more, but the prolonged means is accepted only once a day. It is of great importance for men and women of old age, which are prone to forgetfulness and may accidentally skip the time of reception of the tablets.
Pills
Beta-adrenoblastors did not show hypotensive properties to the first clinical experiments. Scientists and did not wait for them. However, as it turned out, the first beta-blocker was capable of reduced the pressure value in patients with arterial hypertension and angina. In the future, the hypotensive property was found in propranolol and other beta blockers.
Classification
 Classification
Classification Chemical composition Drugs of the category of beta-adrenoblockers are not ungeneged, and therapeutic effects do not depend on it. It is more important to consider the specifics of the interaction of drugs with specific receptors and how compatible they are. The more specificity to beta-1 receptors, the less negative concomitant actions. Therefore, beta-adrenobloclars - a list of drugs of a new generation - will be properly present:
- First generation: non-selective preparations for the first and second receptors: Satolol, propranolol, ndolol, oxprenolol, thymolol;
- Second generation: selective drugs to the first-type receptors: Acelebalol, metaprolol, atenolol, anaprilin, esmolol;
- Third generation: Cardooselective blocking agents for beta-1 receptors with additional drug actions: Talinolol, betaxalol, nebivolol. This also includes non-selective blocking compounds of beta-1 and beta-2, having concomitant drug properties: bucindolol, carvedilol, labetalol. Carolol.
The listed beta-adrenoblasts in different periods were the main category of drugs used and used in the diseases of heart and vessels. Most of the prescribed drugs refers to the last two generations. Thanks to them pharmacological actions There was an opportunity to keep under control the heart rate, to conduct an ectopic pulse to ventricular departments, reducing the risks of anginal angina attacks.
The most first medicines among beta adrenoblockers are tools from the first category indicated in the classification table - non-selective beta blockers. These drugs block the first and second type of receptors, providing, in addition to therapeutic effect, a negative effect in the form of bronchospasm. Therefore, they are not recommended when chronic pathologies lungs and bronchi, asthma.
In the second generation, beta-adrenerboators are indicated, whose principle of operation is conjugate with the blockade only for the first type of receptors. They have a weak relationship with beta-2 receptors, so the side effects in the form of a spasm of bronchi in patients suffering from pulmonary diseases, rarely occur.
Features of the mechanism of drugs
The effect of reducing blood pressure of this category is determined directly to their beta-adrenoblocking property. Blocking adrenoreceptors quickly acts on the heart - the number of abbreviations is reduced, and its efficiency increases.
 The mechanism of operation of blockers
The mechanism of operation of blockers Beta adrenoblockers on people in healthy and calm state do not affect, that is, pressure remains normal. But in patients with hypertension, this effect is necessarily present. Beta blockers work with stressful situations and physical Loads. In addition, on the background of blocking beta receptors, the production of renin substance is reduced. Therefore, the intensity of the production of an angiotensine of the second type decreases. And this hormone affects hemodynamics and stimulates the production of aldosterone. Thus, the activity of the renin-angiotensin system decreases.
Medical properties
Beta-adrenobloclars of different generations differ from each other by selectivity, solubility in fats, the presence of internal sympathomimetic activity (the property is selectively activated by the suppressed adrenoreceptors, which reduces the number of side effects). But at the same time, all drugs have the same hypotensive effect.
Important! Almost all beta-blockers reduce the bloodstream in the kidneys, but this is not reflected in the functional ability of the organ even with long-term reception of drugs.
Reception rules
Adrenoblockers receptors give an excellent effect with hypertension of all degrees. Despite the substantial pharmacokinetic differences, they have a rather long hypotensive effect. Therefore, one or two drug receptions are enough per day. Beta blockers give a less pronounced effect in people with dark skin and patients of mature age, but there are exceptions.
 Tablet reception
Tablet reception The reception of these drugs in hypertension does not lead to water delay and salt compounds in the body, so it does not have to prescribe diuretics to prevent hypertensive edema. It is worth noting that diuretic medicines and beta-adrenoblays enhance the overall effect of pressure drop.
Side effects
Beta-adrenoblockers doctors are not prescribed astmatics, patients with a weakness of a sinus node, patients with pathologies of atrioventricular conductivity. The reception of beta-blockers during pregnancy is prohibited, especially in the last months.
Adrenoblockers are not always prescribed to people suffering from simultaneously IBS, hypertension, hsn or cardiomyopathy, since these drugs reduce myocardial reductions and at this time increase the overall resistance of vascular walls. Beta blockers are not suitable for diabetics with insulin addiction. They cannot be used in conjunction with calcium channel blockers.
These drugs without ACC increase the content of triglycerides in the blood plasma. In this case, the concentration of HDL cholesterol decreases, but the total cholesterol in the blood remains unchanged. Beta-adrenoblockers from the BCA practically do not change the lipid picture and can even increase the value of HDL cholesterol. Further consequences of this action were not studied.
 Side properties
Side properties If sharply cancel the use of β-adrenobloclars, this can cause a ricochetic syndrome, which manifests itself with such symptomatic signs:
- Tachycardia;
- A sharp increase in pressure;
- Heart impairment, arrhythmias;
- Ischemic attacks;
- Tremble in body and chills limbs;
- Acute attacks of angina;
- The risk of infarction;
- In rare cases, death.
Attention! Almost under strict control and with constant observation, slowly reducing the dose over two weeks, while the body is not accustomed to function without medication.
The hypotensive effect of the β-adrenoblocker can be weakened by the reception of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, for example, indoentacin.
A significant increase in the pressure in the vessels in response to the use of adrenobloclockers can be observed in patients with hypoglycemia and a peochromocytoy. This side effect sometimes occurs when the adrenaline dose is introduced.
First generation adrenoblors
These non-selective drugs block adrenoreceptors β1 and β2. However, they have several side effects: reducing the lumen of the bronchi, cough stimulation, increasing the tone muscular system uterus, hypoglycemia, etc. in the list of first-generation drugs are presented:
- Propranolol. This medicine in a certain respect has become the standard with which the remaining adrenoblocators are compared. It does not have ACM and no selectivity with alpha-adrenoreceptors. It has good fat solventness, so quickly gets to the central nervous system, soothing and reducing pressure. The duration of the therapeutic effect is 8 hours.
- Pindolol. In the preparation there is an ACA. The tool has an average fat solventness, a weakly pronounced stabilizing effect.
- Timolol. The adrenoblocator in which there is no WSA. He got widespread use in ophthalmological practice For therapy, glaucoma, relieving eye and cilia inflammation. However, in the case of the use of thymolol for eye in the form of droplets, an acute systemic effect may be observed, accompanied by a chopping, decompensation of heart failure.
 Timolol
Timolol Second generation of drugs
Adrenoblockers with cardiodelectivity to beta-1 receptors have much less side effects, but during the reception of elevated doses, the remaining adrenoreceptors can be blocked, that is, they have relative selectivity. Consider briefly the properties of drugs:
- Atenol - used earlier in demand in cardiological practice. This is a water-soluble medicine, therefore it is difficult for him to pass through the hemat andthelical wall. Does not have in the composition of the BCA. As side effect A ricochet syndrome may appear.
- Metoperol is a highly selective adrenoblocator that has excellent fat solventness. Therefore, it is used in the form of saline compounds of succinate and tartrate. Due to this, its solubility is improved and the duration of transportation in the vessels is reduced. The production technique and the type of salt provide long-term therapeutic action. Metoprolol Tartrate is a classic form of metoprolol. The duration of its effect is 12 hours. It can be produced under such names: Methodogramard, Betalok, Egilov, etc.
- Bisoprolol is the most popular beta adrenoblocator. It does not contain ACC. The medicine has high indicator Cardooselectivity. The purpose of the bisoprolol is allowed with diabetes and thyroid diseases.
Third generation drugs
Adrenobloclars of this category have an additional vasodilator action. The most effective from the point of view of therapy with the preparations of the Third Group is considered:
- Carvedilol is a non-selective type blocker that does not have ACC. Increases the lumens of peripheral vascular branches, blocking alpha-1 receptors. It has antioxidant properties.
- Nebivolol - remedy with vasodilatory effect and high selectivity. Such properties ensures stimulation of nitrogen oxide. A steady hypotensive effect begins two weeks of treatment, in some cases four weeks later.
 Carvedilol
Carvedilol Attention! It is impossible to assign beta adrenoblastors without a doctor. Before therapy, you must need medical recommendations, study the instructions for the medicine, read about it in Wikipedia.
Contraindications
Adrenoblockers, like many drugs, have certain contraindications. Since these tools affect adrenoreceptors, they are less dangerous compared to their antagonists - ACE inhibitors.
Common list of contraindications:
- Asthma and chronic pulmonary diseases;
- Any types of arrhythmias (rapid or slow heartbeat);
- Sinus node weakness syndrome;
- Ventricular atrial blockade in the second stage of development;
- Hypotension with severe symptoms;
- Tooling the fetus;
- Childhood;
- Decompensation XSN.
Allergies to the constituent drug becomes contraindication. If for some kind of medicine begins allergic reaction, it is replaced. In various sources of literature, analogs and substitutes of drugs are indicated.
Efficiency of adrenoblocators
Under angina, adrenoblockers significantly reduce the risks of systematic seizures and the severity of their flow, reduce the likelihood of progression of vascular pathologies.
In case of insufficiency, myocardial beta-blocking agents, inhibitors, adrenolics and diuretic medicines increase the lifetime. These medicines effectively regulate tachycardia and arrhythmia.
In general, these funds help keep control of any heart disease under control, keeping pressure at a normal level. In modern therapeutic practice, the blockers of the third group are predominantly used. The second category is prescribed, with selectivity to beta-1 receptors. The use of such drugs makes it possible to keep under control arterial hypertension And deal with cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of the development of the Aneurysm of the BCA, Diagnostic Methods, Treatment and Forecast What is better: Corinthar or Kioten Action, how to choose the best preparation?