What is the frontal sinus. Mucocele of the frontal sinus. Symptoms of hypoplasia and aplasia of the frontal sinuses
Frontal sinusitis, or frontal sinusitis, is inflammation of the frontal sinuses. According to statistics, over the past decade, this type of pathology is considered one of the most common in the world. Currently, more than ten percent of the population suffers from sinusitis, and about one percent of people suffer from the pathology of the frontal sinuses.
frontal sinuses
The following sinuses are adjacent to the nasal passage:
- wedge-shaped;
- frontal;
- lattice;
- maxillary.
These cavities look like small voids located in the skeleton of the skull and opening into the nasal passages. In the normal state, the sinuses are empty and contain no contents other than air. The cavities themselves perform a number of specific functions:
- warm and humidify the air;
- perform a protective role in trauma;
- perform the function of a voice resonator;
- protect eyes and teeth from temperature extremes.
There are two frontal sinuses in the frontal lobe. In shape, they resemble a pyramid with the base down. In the center, it is divided into two parts by a bony septum.
The frontal sinuses have four walls: anterior, posterior, septum, or internal, lower. The sizes of the sinuses in humans are different. On average, it is four centimeters long. Some people do not have this sinus at all. Usually such an anomaly occurs due to heredity.
From the inside, the frontal sinuses are lined with mucous membranes. It is a continuation of the nasal mucosa, but thinner and without cavernous tissue. The sinus itself is connected to the nasal cavity by a narrow canal open in front of the nasal passage.

The causes of inflammation
With inflammation of the mucous membrane, a pathology occurs, called frontal sinusitis. It can have different causes, which determine the severity of the course of the disease, its form.
Infection
In more than half of cases of frontal sinusitis, the frontal sinuses become inflamed due to an infection that enters the cavity through the tubules. The inflammatory process can occur in several sinuses at once, for example, the maxillary sinus and the frontal sinus can be affected. The cause of inflammation can be SARS, diphtheria, tonsillitis and other infections.
The most common causative agents of inflammation are:
- rhinoviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- coronaviruses;
- different types of bacteria;
- fungi.
Allergy
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses, swelling of the mucous membranes can occur as a complication of an allergic reaction. This can be observed when bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis... With edema, there is an overlap of the channel through which the contents of the frontal sinus exit.

Polyps
Polyps may develop in the nose. These are benign formations with round shape... Polyps are formed as a result of the degeneration of the mucous membrane. During this process, swelling of the mucous membrane may occur, breathing becomes difficult, the outflow from the cavities is blocked.
Trauma
The maxillary sinus and frontal sinus can become inflamed due to injuries. Even minor tissue injuries can cause serious circulatory problems in the mucous membrane and sinuses.
Septal abnormalities
Sinus inflammation may occur. Such an anomaly of the structure can be congenital or acquired as a result of trauma, postponed pathologies. The curvature of the septum can disrupt the free flow of contents from the sinuses, which contributes to the creation of favorable conditions for the reproduction of microbes.
Foreign bodies
Sometimes there are situations when it enters the nasal passages foreign body... The result is inflammation that spreads to the nasal cavity and adjacent sinuses.
Clinical manifestations
Inflammation of the frontal sinuses is very serious illness, which is much more serious than other ailments. By its nature, it can be divided into two forms: chronic and acute. Each of them has special clinical symptoms, according to which the doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis.

Acute form
The structure of the frontal sinuses characterizes the symptoms of the disease. So, with frontal sinusitis, there is a sharp pain in the forehead, which can increase with pressure on the anterior wall of the sinus. You can check this by pressing yourself on the area above the bridge of the nose. With increased pain, frontal sinusitis can be assumed. Also, with pathology, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain in the eyes;
- photophobia appears;
- profuse discharge appears from the nose;
- sometimes there is a change in the color of the skin above the eye;
- symptoms of general intoxication are observed;
- the body temperature rises to 39.
During the examination, the ENT can detect swelling, hyperemia of the nasal mucosa.
During acute frontal sinusitis, in case of violation of the outflow of mucus from the sinuses, pain syndrome increases. However, as soon as the lumen of the tubule increases and the contents can be released, the pain subsides. Periods of stagnation are usually observed in the morning hours. At this time, the pain can radiate to the eyes, temples.
Chronic form
If the acute form of pathology is not treated, then it becomes chronic. This can also happen due to improperly selected treatment.
Clinically chronic inflammation of the frontal sinus occurs with the following symptoms:
- pressing pain in the frontal cavity, which increases with tapping;
- profuse purulent discharge is observed from the nose;
- in the morning hours there is abundant purulent sputum.
All these symptoms are less pronounced. Because of this, many believe that the disease has receded. In fact, she moved from acute form into chronic. If not cured, the disease can cause serious complications.
Diagnostics
In order for the doctor to be able to prescribe the correct treatment, it is necessary to carry out a diagnosis. It includes:
- Collecting anamnesis. The doctor collects complaints, clarifies the clinical manifestations, determines the cause of the disease.
- Rhinoscopy. During the examination, the ENT assesses the condition of the nasal mucosa, determines whether the contents can leave the sinus and where it flows out.
- Ultrasound of the sinuses.
- Endoscopic examination. During the examination, the doctor determines the condition of the nasal mucosa and sinuses, looks at the structure of the cavities.
- Fluoroscopy. This is the most commonly used method. With the help of X-ray diagnostics, the doctor determines the shape and condition of the frontal sinuses, sees inflammation, swelling, and determines the nature of the contents.
A bacteriological study of the contents of the nose is required to clarify the cause that led to the inflammation. Only after the results of the diagnosis, the specialist can choose a treatment regimen for the frontal sinuses.

Treatment
The method of treatment is determined by the form of the disease. With a mild course of the disease, the doctor selects a conservative treatment using several types of drugs. To reduce swelling, the nasal passages are irrigated with drugs based on adrenaline. Inside, the following medications are prescribed:
- Antibiotics ENT selects drugs wide range actions. As soon as the cause of the disease is determined, antibiotics are selected for a narrowly targeted action.
- Analgesics. They help relieve pain.
- Allergy medications that help alleviate the patient's condition.
- Physiotherapy.

With the right treatment, the pain subsides on the third day, breathing improves, and body temperature normalizes. You can not self-medicate, because the contents of the frontal sinusitis can cause serious complications, up to meningitis.
The frontal sinuses are an integral part of the paranasal air cavity system and perform a number of functions related to the protection of the body, the organization of normal breathing and speech. They are located in the immediate vicinity of the meninges, so their diseases can threaten with serious complications.
The structure and functions of the front cameras
The frontal sinuses, like the maxillary sinuses, in their location belong to the anterior voids, which communicate with the nose through the sinuous and long middle frontal-nasal passage. This anatomy predetermines much more frequent infectious diseases anterior cavities.
The frontal chambers are a paired organ located in the thickness of the frontal bone.
Their size and configuration can vary significantly from person to person, but on average, each frontal sinus has a volume of about 4.7 cubic centimeters. Most often it looks like a triangle, lined with a mucous membrane inside, with four walls:
- The orbital (lower) is the thinnest, most of its area is the upper wall of the orbit, with the exception of the edge adjacent to the ethmoid bone. On it there is an anastomosis of a canal 10-15 mm long and up to 4 mm in diameter, extending into the nasal cavity.
- The front (front) is the thickest, represented by the outer part of the frontal bone, which has a thickness of 5 to 8 mm.
- The cerebral (posterior) - consists of a thin but strong compact bone, bordered by the anterior cranial fossa and the dura mater.
- The inner (medial) one separates the two chambers, in its upper part it can deviate to the left or right.
A newborn child does not have frontal sinuses, they begin to form only at 3-4 years of age and finally develop after puberty.
They appear at the top inner corner orbits, consist of cells of the ethmoid bone, the nasal mucosa grows into them. In parallel with this, the process of resorption of the spongy bone, which is located between the inner and outer plates of the frontal bone, takes place. In the vacated space, frontal voids are formed, which sometimes can have niches, bays and internal partitions in the lumen. Blood supply comes from the ophthalmic and maxillary arteries, innervation - from the orbital nerve.
The cavities are most often not the same, since the bone plate separating them is usually not located exactly in the center, sometimes it may be absent, then a person has one large cavity. In rare cases, the dividing bone is located not vertically, but horizontally, and the chambers are located one  over the other. According to various studies, 5-15% of people have no frontal sinuses at all.
over the other. According to various studies, 5-15% of people have no frontal sinuses at all.
The main functions of front cameras today are:
- protection of the brain from injury and hypothermia (act as a "buffer");
- participation in the formation of sounds, increased vocal resonance;
- regulation of the pressure level in the nasal passages;
- warming and humidifying the inhaled air;
- decrease in the mass of the skull during its growth.
Acute frontal sinusitis: etiology and symptoms
Since the paranasal compartments are covered with mucous membranes inside, the main disease is the inflammatory process in them. If we are talking about the frontal sinuses, then their inflammation is called frontal sinusitis. The inflammation has a wave-like course, it can quickly turn from an acute stage into a chronic one and then proceed asymptomatically or pass without treatment.
The main cause of the disease, as a rule, is an inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract, from where it passes to the frontal compartments in an ascending way.
In case of untimely or insufficient treatment due to a change in the pH of the secretion, the immune barrier from the ciliated epithelium weakens, and the pathogenic microflora penetrates into the chambers, covering the mucous membranes. Many doctors are of the opinion that acid-base balance mucus can break drops with a vasoconstrictor effect, which are used for a long time.
The main prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- a runny nose that does not go away for a long time;
- poorly cured or transferred "on the legs" colds;
- hypothermia of the body, in particular of the legs;
- stress;
- trauma to the front of the head.
The inflammatory process is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes, as a result of which there is an increased secretion with simultaneous obstruction of the outflow of fluid. Oxygen supply is sharply limited or completely stopped. The gradually increasing internal pressure is the cause of severe pain in the forehead.
Symptoms of the disease are divided into general and local, which together give a characteristic clinical picture of acute frontal sinusitis. 
Local signs:
- complete absence or severe difficulty in nasal breathing;
- throbbing and pressing pain above the eyebrows, which intensifies when the head is tilted forward or when the hand is pressed on the forehead;
- profuse purulent discharge from the nasal passages (one or both);
- leakage of secretion into the oropharynx;
- on upper eyelid or the orbital angle of the eye may be swelling.
Simultaneously with the local, general signs are growing, indicating an intoxication of the body:
- temperature rise to 37.5-39 degrees, chills are possible;
- blood reaction (increased ESR, leukocytosis);
- muscle weakness;
- spilled headaches;
- hyperemia of the skin in the projection of the affected organ;
- aching bones and joints;
- rapid fatigue and drowsiness.
Diagnostics and conservative treatment of frontal sinusitis
To study the clinical picture and make the correct diagnosis, you must contact an otolaryngologist. The ENT doctor interviews the patient, after which he performs a rhinoscopy - a visual examination of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses in order to determine the place of discharge of pus and the state of the mucous membranes. Palpation and percussion (tapping) help reveal tenderness in the anterior wall of the forehead and the corner of the eye on the affected side.
To confirm the alleged diagnosis, the patient donates blood for analysis, in addition, X-ray (in lateral and direct projection) or computed tomography is performed.
These methods are the best way to determine the lesion focus, the amount of accumulated pus, the depth and shape of the chambers, and the presence of additional partitions in them. The secreted mucus undergoes a microbiological examination to determine the pathogen and prescribe adequate treatment.
In most cases, conservative treatment is used, including anti-inflammatory therapy, unclogging of the frontal-nasal canal and restoration of drainage of the cavity. In this case, the following drugs are used:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics in the presence of high fever (Klacid, Avelox, Augmentin) with subsequent correction if necessary;
- analgesics (askofen, paracetamol);
- antihistamines (claritin, suprastin);
- drugs to reduce the secretion of mucous membranes by high adrenalization (sanorin, nasivin, galazolin, sinupret, naphthyzin);
- means for strengthening the walls of blood vessels (vitamin C, rutin, askorutin).
In the absence of severe intoxication, the body shows high efficiency physiotherapy (laser therapy, UHF, compresses). The YAMIK sinus catheter is also used, which allows flushing the chambers with medicinal substances.
In case of inefficiency conservative treatment(persistence of a high temperature, headache, disturbed nasal breathing, the release of thick mucus or pus) for three days, and if pus in the cavities is detected by X-ray or computed tomography, sinus trepanopuncture is prescribed. Today this is a very effective technique that gives high level recovery. This is a fairly simple operation that is well tolerated by patients, regardless of their age.
The essence of the operation consists in mechanical penetration under the bone tissue in order to:
- removal of purulent contents;
- restoration of drainage through the connecting channel;
- reducing the swelling of the membranes;
- suppression of pathogens that caused inflammation.
To carry out the surgical intervention, a manual drill with a length of no more than 10 mm with a penetration depth limiter and a set of plastic or metal cannulas for washing are used.
When determining the optimal entry point, special calculations are used, which are confirmed by X-ray images in different projections.
Trepanopuncture is performed in the inpatient department of the hospital, while local infiltration anesthesia is mainly used (ledocaine, novocaine). With the help of a drill, a hole is made in the thick anterior wall of the bone, through the opening of which the entire organ is probed. A special cannula is inserted into the hole and fixed through which medicines are injected over the next few days. In addition, the sinus and the connecting canal are washed with antiseptic solutions, followed by the evacuation of blood clots, polyps, cystic formations, granulation tissue.
Less commonly, otolaryngologists use the method of punching the bone with a chisel. The vibration generated in this case is contraindicated in:
- meningitis;
- abscesses;
- osteomyelitis of the cranial bones;
- thrombophlebitis.
 There is also a method of puncturing the lower wall of the cavity with a sharpened special needle, which is much thinner than the front, and is widely used in practice. In this case, a thin subclavian catheter which attaches to the skin after the removal of the needle and serves as a path for rinsing and delivery drugs into the camera. However, this operation is considered less preferable and more difficult due to the presence in the immediate vicinity of the orbit.
There is also a method of puncturing the lower wall of the cavity with a sharpened special needle, which is much thinner than the front, and is widely used in practice. In this case, a thin subclavian catheter which attaches to the skin after the removal of the needle and serves as a path for rinsing and delivery drugs into the camera. However, this operation is considered less preferable and more difficult due to the presence in the immediate vicinity of the orbit.
Due to the location near the lesion focus meninges, delay in seeking medical attention or attempts to self-medicate can lead to serious consequences, up to and including death. Complications of frontalitis can be diseases such as purulent inflammation of the orbit, meningitis, osteomyelitis of the cranial bones, etc.
Traditional methods of treatment and prevention of frontal sinusitis
Folk recipes are mainly aimed at reducing edema and removing mucus, their use must be agreed with the attending physician:
- Boil bay leaves (5-10 pcs.) In a saucepan, transfer to low heat and breathe, covered with a towel, for five minutes. Repeat for several days in a row, this promotes the outflow of pus.
- A teaspoon of salt, some baking soda, and three drops of tea tree oil are mixed in a glass of warm water. To clear the nose, then, tilting the head forward, using a small syringe under pressure, pour the solution into one nostril so that it flows out of the other. Repeat 2-3 times a day, then apply drops for the common cold.
Prevention of the disease is as follows:
- timely treatment rhinitis and sinusitis, if the runny nose has not passed in three days, you should contact the clinic;
- strengthening immunity through hardening and exercise;
- vitamin therapy in the autumn and spring periods;
- control of the purity of the nose and free nasal breathing.
Sources: medscape.com,
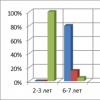
In 12-15%, they may be completely absent. Moreover, in 71% of cases they are absent on one side only, in 29% they are absent on both sides. In 45% of cases, hypoplasia is observed, in 55% - complete aplasia. Quite often, there is a multichamber sinus. In most cases, it is divided by a bony septum into two cavities. The volume of underdeveloped sinuses usually does not exceed 0.5 ml. But sometimes there are also huge sinuses, the volume of which is about 500 ml.
Causes of hypoplasia and aplasia of the frontal sinuses
There can be many reasons. Most of them are genetically determined. Some were formed during the period of intrauterine development. The formation of the frontal sinuses and their anomalies are mainly due to endogenous or exogenous factors that affect the development of the fetus. With hypoplasia, the facial bones are incompletely fused, with aplasia, they do not fuse at all.
The formation of hypoplasia or aplasia can be indirectly caused by previous infectious diseases, persistent viruses, hidden infections, a progressive fungus that is not completely cured acute rhinitis, a tumor in the sinus, in any other facial area. Injuries to the nose, allergic reactions, the consequences of surgical interventions, neuralgic diseases and impaired metabolism also contribute to the malformation of the frontal sinuses.
Risk factors
The risk group includes people who have relatives in the family with genetic anomalies in the development of the frontal sinuses. Also at risk are children whose mothers were exposed during pregnancy to various adverse factors, with complicated pregnancy, difficult childbirth. If during childbirth the child is injured, especially the facial part of the skull, the risk of hypoplasia or aplasia is significantly increased. Also at risk are children who, in early childhood or during intrauterine development, have suffered severe infectious diseases, allergies, and neuralgia.
Pathogenesis
They represent the paranasal sinuses, which are located in the frontal bone and are directed backward, beyond the region of the eyebrows. They have four walls, with the lower one being the upper wall of the eye sockets. With the help of the posterior walls, the sinus is separated from the frontal lobes of the brain. From the inside, the sinuses are lined with mucous membranes.
At birth, the frontal sinuses are completely absent, they begin to form by the age of 8. They reach their maximum size after puberty. Most often, symmetry between the sinuses is not observed, the bony septum deviates from the midline in one direction or another. Sometimes additional partitions are formed. They stop developing by the age of 25.
Sizes may vary. Sinus development is sometimes delayed or simply not developing. Similar phenomena can develop against the background of an inflammatory process, which is transmitted from the focus of infection to the frontal sinuses.
As a result of the development of inflammation, a reverse development of the sinuses can be observed. Hypoplasia refers to a condition in which the development of the sinuses began normally, and then either a delay or reverse development began. Aplasia means the absence of frontal sinus formation. As the pathology develops, ossification occurs, during which the bone in the region of the eyebrows becomes denser.
Symptoms of hypoplasia and aplasia of the frontal sinuses
Quite often, pathology does not bother a person at all. it is discovered quite by accident during inspection. But sometimes there are cases when such pathologies cause discomfort to a person. There may be a feeling of space at the site of the sinus, filled with fluid or air. When pressed, a depression forms, redness occurs.
At the site of the frontal sinus, edema forms, the mucous membrane becomes denser. When tapping or tilting the head down, soreness, a feeling of pressure may be felt. There may be pain in the eye area, especially in the corners of the eyes, on the inside. Many patients note increased tearing, swelling of the area around the eyes, nose bridge. There is a nasal congestion, sometimes mucous, serous or purulent discharge may appear.
The condition may not bother a person if he is in healthy condition, but begins to cause discomfort and aggravate the condition during the illness. Against the background of any disease, especially a cold, severe pain develops in the sinus area, which is transmitted to the head. Less often, pain radiates to other parts of the body. Later, cases of pain may become more frequent, it may acquire a pulsating character. Sometimes there is a feeling of heaviness, throbbing pain in the temples.
The condition is accompanied by chills, dizziness, weakness. Frontal sinusitis may develop, which must be treated. If treatment is neglected, the disease is transmitted to the bones of the orbit, and through them to the outer meninges.
The earliest signs of pathology can be pain in the forehead, which increases with bending, tapping, palpation. The pain can be aggravated by sudden movements, jumping, sudden changes in position, and even when trying to blow your nose. For many, the usual blowing of their nose leads to cramping and dizziness.
There may be pressure in the forehead, or the filling of areas with air, liquid, which move when you move them from side to side. Sometimes the sensations give a person discomfort, sometimes they do not cause any anxiety. When the first signs appear, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible and undergo an examination.
Hypoplasia of the right frontal sinus
The term implies insufficient development of the frontal sinus. That is, it first began its development, after which it slowed down or stopped. May be symptomatic or asymptomatic. It is often detected during examination by percussion and palpation. When tapping, a characteristic percussion sound is heard, and pain on palpation can also be detected.
Asymmetry can indirectly indicate hypoplasia. In this case, the left side is slightly larger than the right. There may be swelling, pain that worsens when bending over. There is a sensation as if fluid is flowing to the right side of the forehead. All this can be accompanied by temperature and general weakness... Sometimes there is abundant discharge of a mucous or purulent character.
The examination is carried out mainly in frontal or lateral projections, which makes it possible to assess the volume and depth of the sinus, as well as to reveal the presence of a pathological process, pathological substances in it. It is imperative to make sure that the sinus is not inflamed and that there is no purulent or other exudate in it. This is due to the fact that the frontal sinus is connected through the orbit with the brain, respectively, in the presence of an infection, it can quickly be transmitted to the brain, causing various infectious diseases, including meningitis.
Hypoplasia of the left frontal sinus
This term means that the left frontal sinus is underdeveloped. At the same time, the right one is fully developed. Usually the sinus begins its development, then for some reason it slows down, or a complete stop of development. Often this pathology does not manifest itself in any way, proceeds absolutely asymptomatic, without causing any discomfort to the patient. It can be diagnosed during the examination. It is easily detected with percussion and correct palpation, causing painful sensations.
Aplasia of the left frontal sinus
Often, aplasia is hereditary pathology and means the complete absence of the frontal sinuses, their underdevelopment. Pathology is formed when the process of normal formation of various cranial regions is disturbed. First of all, there is an incorrect formation of the facial surface of the brain.
It is often manifested by a slight depression or confluence of the frontal lobe of the head. At the same time, there is a complete or partial narrowing of other paranasal sinuses and nasal canal. There is excessive pressure on the facial or nasal wall, slight asymmetry. There may be a slight indentation in the canine fossa. It ends with the complete fusion of the nasal and facial walls.
Aplasia of the right frontal sinus
Unilateral pathologies develop quite often. In this case, facial asymmetry is well developed. The main symptom is also underdevelopment of the opposite sinus. When trying to puncture with a puncture, the needle falls immediately into soft tissue cheeks. Most often found in men. Often it becomes the cause of sinusitis, affects the frequency of the formation of pathologies of the nasal passages. Pain is usually heard only on palpation or percussion.
Complications and consequences
The disease in many is completely asymptomatic, does not cause any consequences and complications. Usually, aplasia does not cause any inconvenience to a person at all. Whereas hypoplasia can lead to some complications. For example, underdeveloped sinuses can be complicated by sinusitis, otitis media, and other inflammatory and exudative processes. The frontal sinus is connected through various channels to the other paranasal sinuses, the nasopharynx, the ear and the nasolacrimal canal. As a result, the existing infection can persist in these channels as in a single system, transmitting the infectious and inflammatory process to any of the sites.
The danger is that the frontal sinus is connected through the bottom of the orbit with the brain. Accordingly, inflammation can be transmitted to the brain. Also, if the bones are thin and porous, the infection can penetrate into the brain, causing inflammation of the meninges.
Outside, severe swelling and redness may appear, which are transmitted and spread to other sinuses and parts of the body. The danger is that the entire system can be damaged. In this case, along the descending paths, the infection can spread to the lungs, bronchi, trachea, causing corresponding inflammatory reactions. May affect the eye, contributing to the development of the inflammatory process. Most often, conjunctivitis develops, vision is impaired, and tearing appears.
The danger lies in the accumulation of infection, which is accompanied by general weakness, elevated temperature, decreased alertness and performance. Pus, purulent-mucous exudate may form, which is capable of further spreading to neighboring areas, especially to the brain, which can have extremely negative consequences.
The presence of pus in the sinuses is also dangerous, since the canal that connects the nasopharynx to the sinuses is very thin and can easily become clogged with purulent masses. Also, in the presence of pus, the mucous membrane increases, which makes the canal even narrower. Thus, the removal of pus to the outside will be impaired, and surgery may be required. It is important to carry it out in a timely manner to prevent pus from entering the meninges.
Diagnostics of the hypoplasia and aplasia of the frontal sinuses
Diagnosing sinus malformations is usually not difficult. The diagnosis can be made already on the basis of a survey and a visual examination of the patient, since the clinical picture is quite pronounced and specific. A standard physical examination is performed using methods clinical research... With the help of percussion, you can identify a characteristic sound that will indicate the development of hypoplasia or aplasia. With the help of palpation, you can feel the frontal sinus, determine its border, volume. Auscultation is rarely used, since in this case it is not very informative.
If there is insufficient information to confirm the diagnosis, special laboratory and instrumental studies may be prescribed. Differential diagnosis carried out if several diseases have a similar clinical picture and makes it difficult to differentiate.
Analyzes
A bacteriological study may be required in the presence of inflammation and the need to determine the causative agent of the disease, select the optimal dosage medicinal product... If you suspect viral infection virological and bacteriological studies are carried out. If an allergic reaction is suspected, allergological tests and an analysis for immunoglobulin E, which is the main indicator of allergy in the body, are performed.
Instrumental diagnostics
For the study, the X-ray method is used, which allows you to view in various projections the main sinuses of the nose, including the frontal, to identify possible foci of infection, signs of inflammation, bone defects. It is possible to differentiate hypoplasia from complete aplasia, to determine on which side the pathology is located.

An equally informative method is microrinoscopy, in which the nasal cavity is probed with rubber catheters or metal probes. The study makes it possible to assess the condition of various sinuses, nasal passages, as well as determine the degree of sinus underdevelopment, or diagnose their complete absence. It is performed under local anesthesia.
The most informative method is computed tomography, which can be used to comprehensively assess the condition of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, identify possible anomalies and birth defects, assess the degree of pathology, consider the presence or absence of an inflammatory process, a focus of infection. Various tumors can be detected at an early stage of their formation. Allows you to assess not only the condition skeletal system but also soft tissues. It is important to differentiate hereditary and non-hereditary diseases, as well as to determine the type of inheritance in each family, based on clinical and genealogical research methods. The aim is to determine the likelihood of a patient with a genetically determined pathology appearing in the family. It is important to choose the best method of treatment and rehabilitation as soon as possible.
Treatment of hypoplasia and aplasia of the frontal sinuses
Treatment is used if the pathology causes discomfort to the patient. In the absence of any complaints, treatment may not be carried out. In the presence of pain, discomfort, shortness of breath, an inflammatory process, a conservative method of therapy is used, mainly the medication route is chosen.
Are applied various drugs, in particular, vasoconstrictor drops, sprays, solutions for rinsing the nasopharynx, oral cavity... For allergies and swelling, antihistamines are used. Mucolytic agents are used to stimulate the outflow of the contents of the sinuses and restore mucociliary clearance. On indications, antibiotics can be prescribed, antiviral drugs, antimycotics, immunomodulators.
Vitamin therapy is often performed. Physiotherapy procedures are carried out if necessary. Most often, physiotherapy is resorted to after punctures, freeing the sinus from purulent contents, which helps prevent relapses. In this case, warming up, UHF therapy is usually required.
The therapy allows to reduce atrophic processes in the mucous membrane, to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. In some cases, even pathological changes in bone tissue can be prevented. Physiotherapy is not used with a pronounced allergic reaction, since you can only aggravate the pathology by increasing the edema.
It is recommended to carry out complex therapy, which will also include folk remedies, homeopathic remedies, medicinal herbs... You can carry out steam inhalation at home using various herbal decoctions, essential oils. Inhalation is contraindicated in the presence of pus, as this can cause complications. They also carry out various warming ups, make compresses, rinses, rinses. Massage and manual therapy are excellent treatments.
To relieve puffiness and inflammation, hormonal and other agents are used. Adrenalization of the mucous membrane has proven itself well. To do this, make frequent and abundant lubrication or irrigation of the mucous membrane with drugs containing adrenaline. Similar drugs can also be used for instillation into the nose. Such therapy helps to reduce the thickness, looseness of the mucous membrane, respectively, the inflammation decreases and an excessive amount of mucus ceases to be produced.
Surgical methods are rarely used, only if they are ineffective conservative therapy... Trepanopuncture is performed, in which a puncture of the frontal sinus is performed in order to cleanse it of accumulated transudate or exudate.
It's important to know!
Since acute sinusitis is an infectious disease, it is natural that the attention of doctors is primarily drawn to antibacterial treatment... However, the inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses occurs in unusual conditions of a closed cavity, impaired drainage, deterioration of the function of the ciliated epithelium, and sinus aeration.
- This is an integral part of the paranasal cavities. This area is responsible for several functions, but the main task is to protect the body and normalize the airway pressure.
It is important to know that the frontal sinuses are located in close proximity to the brain, so inflammation in this area is especially dangerous. It is known that almost fifteen percent of people suffer from diseases in this area.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to warn this side against the penetration of microbes, cyanobacteria, shigella, enterobacteria, enterococci and other numerous harmful elements, therefore, when an infection enters the body, in which the temperature rises and is characterized by inflammation of the respiratory tract, as well as with pain in the ears or head, the frontal zone should be checked.
Sometimes the frontal sinuses are undeveloped or completely absent. With this anatomical structure, a person often complains of headaches.
Paranasal sinuses, localized in the forehead area, is located just above the nose and in its structure is voids, and is connected to the area of the nasal sinuses with the help of a certain frontal-nasal fold. The penetration of harmful elements into the head region occurs precisely through this element. When germs enter the nasal fold, the patient experiences severe discomfort and other unpleasant symptoms.
Note that the depression in the forehead is a paired organ and therefore the disease always occurs on both sides.
This side resembles a triangle of five centimeters in size., but the cubic size may vary depending on the individual structure of the patient's body. Inside the sinus is the mucous part that envelops all four parts of the frontal sinus:
- Front side.
- Bottom part.
- Medial area.
- Back part.
All four parts help protect the brain from the penetration of viruses and bacteria, as well as changes in atmospheric pressure, trauma to the skull, as well as adaptation of the body to weather changes. In addition, this part is responsible for the following functions:
- transmission of sound impulses;
- increase in air temperature and its adaptation for subsequent processing;
- moisturizing the mucous area;
- regulation of pressure in the nasal sinus;
- with the development of the skull, this side reduces its mass.
Frontal sinuses are not developed - what does this mean
It is known that at birth in newborns, the frontal cavity is not fully developed or is completely absent. The accessory cavities begin their formation, being in the mother's abdomen, but complete their formation only closer to 18 years of age or during puberty.
 If, upon examination, the doctor diagnosed that the child's frontal sinus is not developed, you should not be afraid. The largest area, called the maxillary region, is only formed in adulthood, and until that time, each section of the frontal sinus can be.
If, upon examination, the doctor diagnosed that the child's frontal sinus is not developed, you should not be afraid. The largest area, called the maxillary region, is only formed in adulthood, and until that time, each section of the frontal sinus can be.
If an adult is suspected of underdeveloped frontal sinuses, the doctor may send for additional examinations. This is necessary when there is a risk of the formation of a disease against the background of the penetration of viruses or microbes, as well as the risk of a tumor or cyst.
It is known that when a disease occurs This most often occurs when the area of the lower septum is too elastic. In addition, if the right frontal sinus or both parts are undeveloped, the patient often complains about the temporal region, as well as feeling of constant pressure on the bridge of the nose.
 A common reason diseases of the frontal part becomes anatomical structure.
When viewed on x-rays at this time, it is clear that the paranasal cavities are filled with air. In this case, the patient is provided with treatment in which the general state and excess air flows are removed. With poor-quality or incorrect therapy, the disease in this area leads to consequences that are dangerous to health in general.
A common reason diseases of the frontal part becomes anatomical structure.
When viewed on x-rays at this time, it is clear that the paranasal cavities are filled with air. In this case, the patient is provided with treatment in which the general state and excess air flows are removed. With poor-quality or incorrect therapy, the disease in this area leads to consequences that are dangerous to health in general.
It is important to note that children have no frontal sinuses at all. Before the age of eighteen, they are just beginning to form and are formed in the upper part of the eyes. Closer to the completion of formation, this side grows into the mucous region of the nose and becomes covered with a mucous membrane.
At the same time, the cancellous bone dissolves., which is located between the inner bone and the outer part of the skull.
Conclusion
For severe pain in the head or nasal region, doctors often diagnose cavities in the frontal sinus. In this case, patients complain of a feeling of pressure in the region of the bridge of the nose, pain in the forehead, profuse discharge of tears, as well as anemia.
On palpation on the wall of the eyes, sharp shooting pains are often formed. In this case, an individual course of treatment is prescribed.
It is important to know that the frontal sinuses are located in close proximity to the brain, so inflammation in this area is especially dangerous. It is known that almost fifteen percent of people suffer from diseases in this area.
About the frontal lobe and pneumatization
Unfortunately, it is impossible to warn this side against the penetration of microbes, cyanobacteria, shigella, enterobacteria, enterococci and other numerous harmful elements, therefore, when an infection enters the body, in which the temperature rises and is characterized by inflammation of the respiratory tract, as well as with pain in the ears or head, the frontal zone should be checked.
Sometimes the frontal sinuses are undeveloped or completely absent. With this anatomical structure, a person often complains of headaches.
The paranasal sinuses, localized in the forehead area, are located just above the nose and are voids in structure, and are connected to the nasal sinus area using a certain frontal-nasal fold. The penetration of harmful elements into the head region occurs precisely through this element. When germs enter the nasal fold, the patient experiences severe discomfort and other unpleasant symptoms.
Note that the depression in the forehead is a paired organ and therefore the disease always occurs on both sides.
This side resembles a triangle of five centimeters in size, but the cubic size can vary depending on the individual structure of the patient's body. Inside the sinus is the mucous part that envelops all four parts of the frontal sinus:
All four parts help protect the brain from the penetration of viruses and bacteria, as well as changes in atmospheric pressure, trauma to the skull, as well as adaptation of the body to weather changes. In addition, this part is responsible for the following functions:
- transmission of sound impulses;
- increase in air temperature and its adaptation for subsequent processing;
- moisturizing the mucous area;
- regulation of pressure in the nasal sinus;
- with the development of the skull, this side reduces its mass.
Frontal sinuses are not developed - what does this mean
It is known that at birth in newborns, the frontal cavity is not fully developed or is completely absent. The accessory cavities begin their formation, being in the mother's abdomen, but finish their formation only closer to 18 years of age or during puberty.
If, upon examination, the doctor diagnosed that the child's frontal sinus is not developed, you should not be afraid. The largest area, called the maxillary region, is only formed in adulthood, and until that time, each section of the frontal sinus can be pneumatized.
If an adult is suspected of underdeveloped frontal sinuses, the doctor may send for additional examinations. This is necessary when there is a risk of the formation of a disease against the background of the penetration of viruses or microbes, as well as the risk of a tumor or cyst.
It is known that with reduced pneumatization, a disease of the maxillary region occurs. This most often occurs when the area of the lower septum is too elastic. In addition, if the right frontal sinus or both parts are undeveloped, the patient often complains of pain in the head and temporal region, as well as a feeling of constant pressure on the bridge of the nose.
Anatomical structure becomes a common cause of frontal lobe disease. When viewed on an x-ray at this time, it can be seen that the paranasal cavities are filled with air. In this case, the patient is given treatment, in which the general condition is normalized and excess air flows are removed. With poor-quality or incorrect therapy, the disease in this area leads to consequences that are dangerous to health in general.
It is important to note that children have no frontal sinuses at all. Before the age of eighteen, they are just beginning to form and are formed in the upper part of the eyes. Closer to the completion of formation, this side grows into the mucous area of the nose and becomes covered with a mucous membrane.
At the same time, the cancellous bone dissolves, which is located between the inner bone and the outer part of the skull.
Conclusion
For severe pain in the head or nasal region, doctors often diagnose cavities in the frontal sinus. At the same time, patients complain of a feeling of pressure in the bridge of the nose, pain in the forehead, profuse discharge of tears, and anemia.
On palpation on the wall of the eyes, sharp shooting pains are often formed. In this case, an individual course of treatment is prescribed.
Directory of major ENT diseases and their treatment
All information on the site is for informational purposes only and does not claim to be absolutely accurate from a medical point of view. Treatment must be carried out by a qualified doctor. Self-medication can hurt yourself!
Frontal sinuses
The frontal sinuses are the paranasal sinuses located in the frontal bone behind the eyebrows. Their lower walls are represented by the anterior walls of the orbit, the posterior walls protect the sinuses from the frontal lobes of the brain. The cavities are lined with mucous membranes from the inside. It is worth noting that such cavities are absent in children. early age, they begin to develop only by the age of 8, completing their formation by years. The height of the frontal sinuses in an adult reaches 30 mm, width 25 mm, depth mm, the volume does not exceed 8 ml.
The absence of the frontal sinuses is not a pathology; it is diagnosed in 5% of the population. Frontal sinuses are essential for the normal functioning of the body. Due to the fact that newborns and children younger age these cavities are absent, doctors conclude that one of the main functions of such formations is to reduce the mass of the skull. In addition, the sinuses provide:
- protecting the brain from shocks;
- in the cavities, the air comes into contact with the mucous membranes, while it is moistened and warmed;
- participate in the formation of the human voice, enhance the response.
Do not forget that the frontal sinuses have unlimited access to the mucous membrane, respectively, these formations can be quite vulnerable. It is not excluded the possibility of the development of inflammation that flares up against the background of the penetration of a virus or infection into the human body. The determining factor for the onset of inflammation is the weakening of the immune system and its inability to destroy the virus.
Features of the structure of the frontal sinus
The frontal sinus is located in the frontal bone behind the superciliary arches. The cavities are presented in the form of paired formations in the form of a pyramid with three faces. The frontal sinus septum separates the right and left sinuses. In most cases, they are asymmetrical, this is due to the fact that the bony septum has an inclination to one side. Their inner surface is lined with mucous membranes.
The cavities consist of the following walls:
The base of the sinus is the upper wall of the orbit. The anterior wall of the sinus is the most dense, it can be felt, it is located 1-2 cm above the eyebrows. The back and bottom walls are aligned at right angles. It is worth remembering that deviations in the structure of the frontal sinuses are not uncommon, for example, in some patients, the internal septum is located not vertically, but horizontally. The cavities in this case are located one above the other.
Diseases of the frontal sinuses
It is worth remembering that the frontal sinuses are void formations, the surface of which is lined with mucous membranes. Such formations are often affected by bacteria and viruses. Representatives of pathogenic microorganisms enter the human body with the inhaled air, and if the immune system the person failed, the following diseases occur:
With frontalitis, inflammation forms on the mucous membranes, after which it penetrates through the nasolacrimal canal to the frontal sinuses. As a result, edema occurs, the excretory canal is blocked, as a result of which the outflow of mucous contents from the sinus is limited or blocked. It should be remembered that the treatment of such a disease should be complex; it is impossible to cure frontal sinusitis without antibiotics.
The cyst is a small, round, thin-walled container. It can be of various sizes. The causes of cysts are similar to the prerequisites for the occurrence of frontal sinusitis. During the inflammatory process, fluid is constantly produced (possibly in an increased volume), but its outflow does not occur. Consequently, due to the accumulation of mucus, a cyst forms. Drug treatment in this case it is ineffective, the operation is indicated.
Inflammation causes
The bones of the skull, which have a porous structure, are lined with mucous membranes in order to ensure the protective function of the body, which is to prevent the penetration of various particles and microorganisms that can become a source of pathology. But it is worth remembering that with a decrease in immunity, pathogenic microorganisms can freely enter the human body.
Due to the fact that the frontal sinuses are connected to the nasopharynx, with the development of a strong pathology, pathogens penetrate them and become the cause of the development of polysinusitis - inflammation of all paranasal sinuses, including the frontal ones. Hypothermia, violation of the blow-out technique, lack of correct treatment underlying disease, interruption antibacterial therapy, non-compliance with the treatment regimen.
Therapy technique
Medical treatment of frontal sinusitis does not differ from the treatment of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, therefore it is performed in the same directions:
- Application antibacterial drugs macrolides, cephalosporins, penicillins.
- The use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Taking anti-allergic drugs to relieve puffiness.
- Steam inhalation.
- Irrigation of the nasal cavity with saline.
- The use of nasal drops and sprays of various effects.
- Physiotherapy.
- Respiratory gymnastics Strelnikova.
- The use of immunostimulating drugs.
It should be remembered that only a doctor should prescribe treatment. Self-medication is unacceptable, it can lead to a number of irreversible consequences.
Consequences and complications
Among possible complications inflammation of the frontal sinus of the nose is distinguished by:
- Shortness of breath leading to chronic hypoxia. This condition negatively affects the state of all organs and systems of the body. It is worth remembering that this complication is especially dangerous for children - it can cause developmental delays.
- Breathing disorder during sleep. Against this background, constant drowsiness arises.
- The development of blindness is not excluded. Against the background of chronic inflammation, photophobia develops, a decrease in visual acuity.
- Development of inflammatory processes in the ENT organs.
- Meningitis.
- Encephalitis.
- Brain abscess.
At the very beginning of the inflammatory process, it is extremely important to consult a doctor and unquestioningly follow all his recommendations and instructions. It is worth remembering that only correct and timely treatment will allow you to defeat the pathology and cope with the symptoms of inflammation. In the absence of therapy, the consequences can be irreversible.
All about the frontal sinuses and their treatment
The frontal sinuses are an integral part of the paranasal air cavity system and perform a number of functions related to the protection of the body, the organization of normal breathing and speech. They are located in the immediate vicinity of the meninges, so their diseases can threaten with serious complications.
The structure and functions of the front cameras
The frontal sinuses, like the maxillary sinuses, in their location belong to the anterior voids, which communicate with the nose through the sinuous and long middle frontal-nasal passage. This anatomy predetermines much more frequent infectious diseases of the anterior cavities.
The frontal chambers are a paired organ located in the thickness of the frontal bone.
Their size and configuration can vary significantly from person to person, but on average, each frontal sinus has a volume of about 4.7 cubic centimeters. Most often it looks like a triangle, lined with a mucous membrane inside, with four walls:
- The orbital (lower) is the thinnest, most of its area is the upper wall of the orbit, with the exception of the edge adjacent to the ethmoid bone. It contains the fistula of a canal with a length of mm and a diameter of up to 4 mm, which extends into the nasal cavity.
- The front (front) is the thickest, represented by the outer part of the frontal bone, which has a thickness of 5 to 8 mm.
- The cerebral (posterior) - consists of a thin but strong compact bone, bordered by the anterior cranial fossa and the dura mater.
- The inner (medial) one separates the two chambers, in its upper part it can deviate to the left or right.
A newborn child does not have frontal sinuses, they begin to form only at 3-4 years of age and finally develop after puberty.
They appear at the upper inner corner of the orbit, consist of ethmoid cells, and the nasal mucosa grows into them. In parallel with this, the process of resorption of the spongy bone, which is located between the inner and outer plates of the frontal bone, takes place. In the vacated space, frontal voids are formed, which sometimes can have niches, bays and internal partitions in the lumen. Blood supply comes from the ophthalmic and maxillary arteries, innervation - from the orbital nerve.
The cavities are most often not the same, since the bone plate separating them is usually not located exactly in the center, sometimes it may be absent, then a person has one large cavity. In rare cases, the dividing bone is located not vertically, but horizontally, and the chambers are located one above the other. According to various studies, 5-15% of people have no frontal sinuses at all.
The main functions of front cameras today are:
- protection of the brain from injury and hypothermia (act as a "buffer");
- participation in the formation of sounds, increased vocal resonance;
- regulation of the pressure level in the nasal passages;
- warming and humidifying the inhaled air;
- decrease in the mass of the skull during its growth.
Acute frontal sinusitis: etiology and symptoms
Since the paranasal compartments are covered with mucous membranes inside, the main disease is the inflammatory process in them. If we are talking about the frontal sinuses, then their inflammation is called frontal sinusitis. The inflammation has a wave-like course, it can quickly turn from an acute stage into a chronic one and then proceed asymptomatically or pass without treatment.
The main cause of the disease, as a rule, is the inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract, from where it passes to the frontal compartments ascending.
In case of untimely or insufficient treatment due to a change in the pH of the secretion, the immune barrier from the ciliated epithelium weakens, and the pathogenic microflora penetrates into the chambers, covering the mucous membranes. Many doctors are of the opinion that the acid-base balance of mucus can be disturbed by drops with a vasoconstrictor effect, which are used for a long time.
The main prerequisites for the development of the disease:
- a runny nose that does not go away for a long time;
- poorly cured or transferred "on the legs" colds;
- hypothermia of the body, in particular of the legs;
- stress;
- trauma to the front of the head.
The inflammatory process is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes, as a result of which there is an increased secretion with simultaneous obstruction of the outflow of fluid. Oxygen supply is sharply limited or completely stopped. The gradually increasing internal pressure is the cause of severe pain in the forehead.
Symptoms of the disease are divided into general and local, which together give a characteristic clinical picture of acute frontal sinusitis.
- complete absence or severe difficulty in nasal breathing;
- throbbing and pressing pain above the eyebrows, which intensifies when the head is tilted forward or when the hand is pressed on the forehead;
- profuse purulent discharge from the nasal passages (one or both);
- leakage of secretion into the oropharynx;
- swelling may spread to the upper eyelid or corner of the orbit of the eye.
Simultaneously with the local, general signs are growing, indicating an intoxication of the body:
- temperature rise to 37.5-39 degrees, chills are possible;
- blood reaction (increased ESR, leukocytosis);
- muscle weakness;
- spilled headaches;
- hyperemia of the skin in the projection of the affected organ;
- aching bones and joints;
- rapid fatigue and drowsiness.
Diagnostics and conservative treatment of frontal sinusitis
To study the clinical picture and make the correct diagnosis, you must contact an otolaryngologist. The ENT doctor interviews the patient, after which he performs a rhinoscopy - a visual examination of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses in order to determine the place of discharge of pus and the state of the mucous membranes. Palpation and percussion (tapping) help reveal tenderness in the anterior wall of the forehead and the corner of the eye on the affected side.
To confirm the alleged diagnosis, the patient donates blood for analysis, in addition, X-ray (in lateral and direct projection) or computed tomography is performed.
These methods are the best way to determine the lesion focus, the amount of accumulated pus, the depth and shape of the chambers, and the presence of additional partitions in them. The secreted mucus undergoes a microbiological examination to determine the pathogen and prescribe adequate treatment.
In most cases, conservative treatment is used, including anti-inflammatory therapy, unclogging of the frontal-nasal canal and restoration of drainage of the cavity. In this case, the following drugs are used:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics in the presence of high fever (Klacid, Avelox, Augmentin) with subsequent correction if necessary;
- analgesics (askofen, paracetamol);
- antihistamines (claritin, suprastin);
- drugs to reduce the secretion of mucous membranes by high adrenalization (sanorin, nasivin, galazolin, sinupret, naphthyzin);
- means for strengthening the walls of blood vessels (vitamin C, rutin, askorutin).
In the absence of severe intoxication of the body, they show a high efficiency of physiotherapy (laser therapy, UHF, compresses). The YAMIK sinus catheter is also used, which allows flushing the chambers with medicinal substances.
Trepanopuncture
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment (persistence of a high temperature, headache, disturbed nasal breathing, secretion of thick mucus or pus) for three days, as well as if pus in the cavities is detected by X-ray or computed tomography, sinus trepanopuncture is prescribed. Today it is a very effective technique that gives a high level of recovery. This is a fairly simple operation that is well tolerated by patients, regardless of their age.
The essence of the operation consists in mechanical penetration under the bone tissue in order to:
- removal of purulent contents;
- restoration of drainage through the connecting channel;
- reducing the swelling of the membranes;
- suppression of pathogens that caused inflammation.
To carry out the surgical intervention, a manual drill with a length of no more than 10 mm with a penetration depth limiter and a set of plastic or metal cannulas for washing are used.
When determining the optimal entry point, special calculations are used, which are confirmed by X-ray images in different projections.
Trepanopuncture is performed in the inpatient department of the hospital, while local infiltration anesthesia is mainly used (ledocaine, novocaine). With the help of a drill, a hole is made in the thick anterior wall of the bone, through the opening of which the entire organ is probed. A special cannula is inserted into the hole and fixed through which medicines are injected over the next few days. In addition, the sinus and the connecting canal are washed with antiseptic solutions, followed by the evacuation of blood clots, polyps, cystic formations, and granulation tissue.
Less commonly, otolaryngologists use the method of punching the bone with a chisel. The vibration generated in this case is contraindicated in:
There is also a method of puncturing the lower wall of the cavity with a sharpened special needle, which is much thinner than the front, and is widely used in practice. In this case, a thin subclavian catheter is inserted into the lumen of the needle, which is fixed on the skin after removing the needle and serves as a passage for washing and delivering drugs to the chamber. However, this operation is considered less preferable and more difficult due to the presence in the immediate vicinity of the orbit.
Due to the location near the lesion of the meninges, delay in seeking medical attention or attempts to self-medicate can lead to serious consequences, including death. Complications of frontalitis can be diseases such as purulent inflammation of the orbit, meningitis, osteomyelitis of the cranial bones, etc.
Traditional methods of treatment and prevention of frontal sinusitis
Folk recipes are mainly aimed at reducing edema and removing mucus, their use must be agreed with the attending physician:
- Boil bay leaves (5-10 pcs.) In a saucepan, transfer to low heat and breathe, covered with a towel, for five minutes. Repeat for several days in a row, this promotes the outflow of pus.
- A teaspoon of salt, some baking soda, and three drops of tea tree oil are mixed in a glass of warm water. To clear the nose, then, tilting the head forward, using a small syringe under pressure, pour the solution into one nostril so that it flows out of the other. Repeat 2-3 times a day, then apply drops for the common cold.
Prevention of the disease is as follows:
- timely treatment of rhinitis and sinusitis, if the runny nose has not passed in three days, you should contact the clinic;
- strengthening immunity through hardening and exercise;
- vitamin therapy in the autumn and spring periods;
- control of the purity of the nose and free nasal breathing.
Comments and Feedback
You will also be interested in
Actual prices and products
A drug made according to an old folk recipe. Find out how he got on the coat of arms of the city of Shenkursk.
Famous drops for disease prevention and immunity enhancement.
Monastic tea for ENT diseases
For the prevention and assistance in the treatment of diseases of the throat and nose according to the prescription of Shhiarchimandrite George (Savva).
Any use of the site materials is allowed only with the consent of the portal editorial staff and the installation of an active link to the source.
The information published on the site is intended solely for information and in no way calls for self-diagnosis and treatment. To make informed decisions on treatment and taking medications, it is imperative to consult a qualified doctor. The information posted on the site was obtained from open sources. The editorial staff of the portal is not responsible for its accuracy.
Higher medical education, anesthesiologist.
Frontal sinuses: structure, function, diseases
TO sinuses of the nose, in addition to the ethmoid labyrinth, wedge-shaped and maxillary, also include the frontal sinuses. All these air cavities are also called paranasal sinuses. Distinctive feature frontal sinuses - the absence at the time of birth of a person. They develop only by the age of eight and are fully formed only after puberty.
The structure of the frontal sinuses
The frontal sinuses are located in the frontal bone behind the eyebrows. These cavities are paired, in the form of a trihedral pyramid. The inner surface is covered with a mucous membrane. They are formed by several walls:
- front or front;
- back or cerebral;
- bottom;
- an internal or sinus septum.
The internal part divides the frontal bone into two parts - left and right. Most often they are not symmetrical, since the bony septum is deflected to one side of the midline. The base of the sinus is the upper wall of the orbit, and the apex is located at the junction of the anterior wall with the posterior wall. With the help of the frontal-nasal canal, it is also called an anastomosis, each frontal sinus opens into the nasal passage.
The front wall of the sinus is the thickest - we can feel it by running our hand over the forehead just above the eyebrows. In its lower part, between the brow ridges, there is the bridge of the nose, and the frontal tubercles are located just above. The back wall is connected to the bottom at a right angle.
However, the structure of the sinuses is not always the same as described above. There are rare cases when the internal septum separating the sinuses is located not vertically, but horizontally. In this case, the frontal sinuses are located one above the other.
There are other deviations in the structure of the cavities. For example, incomplete partitions can be observed inside them - a kind of bone ridges. Such a bosom consists, as it were, of several bays or niches. Another, more rare anomaly is complete septa - they divide one of the cavities into several, forming multi-chambered frontal sinuses.
Functions of the frontal sinuses
Along with other paranasal cavities, the frontal sinuses are used for the efficient functioning of the body. Given the fact that they are absent at birth, there is a hypothesis that the main function of the frontal sinuses is to reduce the mass of the skull. In addition, the frontal cavities:
- act as a kind of shockproof "buffer" that protects the brain from injury;
- participate in the breathing process: air from the nasal passages enters the cavities, where, interacting with the mucous membrane, it is additionally moistened and warmed;
- take part in the formation of sounds, increase voice resonance.
Diseases of the frontal sinuses
Given that the frontal sinuses are hollow formations lined with mucous membranes, they can be affected by viral or bacterial infections... Pathogenic microbes penetrate along with the inhaled air. With low body resistance, an inflammatory process can occur.
Frontit
Inflammation "arises", as a rule, on the nasal mucosa, and then through the nasolacrimal canal spreads to the frontal sinuses. Edema occurs, as a result of which the canal is blocked, and the outflow of fluid from the sinuses becomes impossible. This is how the frontitis develops. The isolated environment that forms is ideal for bacteria to grow and pus to form.
Basically, the treatment of frontal sinusitis is carried out with the help of drugs. In this case, complex therapy is prescribed: vasoconstrictor, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are used. Physiotherapy can be carried out according to the doctor's prescription. An operation to open the cavities is required only in cases where treatment does not lead to recovery and there is a possibility of complications.
Unlike others, the thinnest posterior wall is formed not by bone tissue, but by spongy tissue. Therefore, even with insignificant inflammatory processes it can collapse and allow infection to spread to other organs.
Cyst of the frontal sinuses
A frontal sinus cyst is a small, spherical container filled with fluid that has thin, elastic walls. The size and location of such a neoplasm may vary. This tumor occurs under the same circumstances as frontal sinusitis.
As a result of inflammation, the outflow of fluid is disturbed, but mucus continues to be produced and accumulated. And since she has nowhere to go, over time, the formation of a cyst occurs. The treatment of such a disease is surgery.
Diagnosis of sinus diseases
The symptoms of frontal sinus disease, whether it be frontal sinusitis or a cyst, are the same. The only difference is that a cyst, if it is small, may not appear in the form of any signs for quite a long time. In addition, a minor neoplasm is not always detected during routine examinations at the ENT.
Disease symptoms
The main symptoms of frontal sinus disease are:
- pain in the forehead, which increases with pressure and with overwork;
- purulent nasal discharge, often odorless;
- violation of normal breathing, usually from the side of the affected cavity;
- swelling and redness of the skin at the site of the inflamed sinus;
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- general weakness.
Survey
If there is even the slightest suspicion that a frontal sinusitis or cyst is developing, you should immediately contact an otolaryngologist. After interviewing the patient, this doctor will perform a rhinoscopy - an examination of the nasal cavity and paranasal cavities. An x-ray may be done to confirm the diagnosis and to determine the presence and level of pus.
In especially advanced cases, computed tomography is performed. This type of study also allows you to determine how large the frontal sinuses are, the presence of additional partitions in them, which is important when performing a surgical intervention. To identify the causative agent of the disease, microbiological studies of the secretions are carried out.
X-ray is often used if the maxillary sinuses are inflamed - the frontal cavities are also clearly visible on the images. For the diagnosis of other sinuses, this type of study is ineffective, since they are poorly visible in the image.
Potential consequences and prevention
In cases of incomplete recovery or with advanced frontalitis, the disease can take on a chronic form. This is dangerous with frequent relapses and other serious consequences in the form of meningitis or inflammation of the brain.
In order to prevent the disease, try to avoid hypothermia, temper the body, treat acute respiratory diseases and a runny nose. And then you will not have to study the frontal sinuses with the help of a photo, their structure and functions, resort to consulting an otolaryngologist and carry out treatment.
performed only by a doctor!
- About the disease
- Sinusitis
- Varieties
- Sinusitis
- Rhinosinusitis
- Frontit
- About symptoms
- Runny nose
- Snot
- About procedures
- Others ...
- About drugs
- Library
- news
- Questions to the doctor
Copying of materials is allowed only with indication of the source