Acute rhinitis: treatment in children and adults. Atrophic rhinitis mkb Acute rhinitis mkb 10
A disease such as vasomotor rhinitis is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa of a non-infectious nature. It can occur at any time of the year in the presence of provoking factors. Vasomotor rhinitis can lead to a number of complications, since it disrupts many physiological processes associated with ensuring the flow of air into the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses.
The essence of the disease
Vasomotor rhinitis is a functional violation of the state and activity of the vessels of the nasal mucosa, due to which the tissues swell, the nasal cavity narrows and, as a result, difficulty in nasal breathing occurs.
A similar condition occurs with factors that cause a non-standard reaction of the nasal mucosa to ordinary physiological stimuli.
The following factors can be the reasons for the development of such a disease:
However, the exact factors that provoke the development of vasomotor rhinitis have not been finally established so far, so the list presented cannot be exhaustive.
Vasomotor rhinitis according to ICD-10
According to the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision, there are several types of vasomotor rhinitis, each of which has been assigned a special code.
Each subspecies of vasomotor rhinitis also has a similar code in accordance with ICD-10:
ICD-10 also provides for a standard medical care those who suffer from a certain type of allergic rhinitis.
Types of disease and manifestations
Based on the nature of the disease, vasomotor rhinitis can manifest itself in two forms - allergic or neurovegetative. As for the forms of vasomotor rhinitis of allergic origin, there are two of them: permanent, or year-round, and seasonal.
Symptoms characteristic of the clinical picture of vasomotor rhinitis are manifested in:
In addition to these main symptoms of such a disease, there may be severe weakness, pain in the head, sharp deterioration memory, insomnia Such deviations occur because violations of the nasal breathing process lead to an insufficient supply of oxygen to the lungs, which, in turn, disrupts the blood circulation process in the cardiovascular system and the brain. Together, all these deviations lead to an increase in functional disorders nervous system.
Vasomotor chronic rhinitis
Chronic vasomotor rhinitis as a form of the disease occurs as a result of constant irritation by external factors, which can be both chemical and natural substances. From this we can conclude that chronic vasomotor rhinitis has an allergic nature.
With this form, the disease is present all year round, regardless of the season. The main distinguishing symptom of persistent vasomotor rhinitis is the absence of periods of exacerbation and the stable nature of the course of the disease. The patient is disturbed by symptoms of a moderate nature all year round. However, the lack of competent treatment leads to a gradual aggravation of the condition and entails extremely negative consequences.
This form of vasomotor rhinitis has four main stages of development:
Features of the neurovegetative form of vasomotor rhinitis
The neurovegetative form of vasomotor rhinitis is not caused by a seasonal nature and depends on such provoking factors as pathological curvature of the nasal septum, prolonged inhalation of air saturated with chemicals and heavy fumes, as well as pathological processes in the cervical spine, disorders in the endocrine system, functional changes in the central nervous system.
Clinical picture vasomotor rhinitis of a neurovegetative nature includes symptoms such as nasal congestion, the presence of discharge, frequent sneezing. A feature of this form is that neurovegetative vasomotor rhinitis occurs with the onset of seizures, during which the listed symptoms are sharply exacerbated.
This type of disease requires clarification of the underlying cause. The course of treatment can be quite lengthy, because in this case we are talking about serious changes in important body systems.
Diagnosis of the disease

The diagnosis of a disease such as vasomotor rhinitis is based on an analysis of the symptoms that are actively manifested in the patient, as well as on the basis of the results obtained during the studies.
Diagnosis of this disease involves the use of such methods:
Disease prevention
Vasomotor rhinitis can cause serious complications, including the formation of polyposis growths and the development of chronic diseases affecting the nasal and sinus cavities. Since the treatment of the disease is a rather complicated and lengthy process, it is much better to take measures to prevent its development, namely:
Disease prevalence
Vasomotor rhinitis is an insidious disease, since it can occur even in a healthy person under the influence of minor factors. But most often this condition occurs in those who:
- For a long time he has been using various medications: vasoconstrictor drops, antidepressants, drugs for hypertension, drugs to increase potency;
- Suffering from hormonal fluctuations. Often a similar phenomenon is observed in adolescence, as well as during pregnancy;
- Suffering from vegetative-vascular dystonia, in which there is a general decrease in vascular tone in the body;
- Has pathological defects of the nasopharynx;
- Lives in difficult climatic conditions;
- Often experiencing shocks and stress;
- Has bad habits.
Allergic Rhinitis - Overview of Information
Allergic rhinitis is a disease caused by allergens and characterized by the development of IgE-dependent inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Manifested by the classic triad of symptoms: rhinorrhea, sneezing, impaired nasal breathing (often the sense of smell).
ICD-10 code
Epidemiology of allergic rhinitis
Currently, the incidence of allergic diseases is high. According to statistical reports, up to 25% of urban and rural population, living in regions with a highly developed industry, suffers from allergies, and in ecologically disadvantaged areas, these figures reach 30% or more.
According to the WHO forecast, in the 21st century, allergic diseases will take second place, yielding in prevalence only to mental illnesses. In addition, they note the aggravation of the course of allergies, the development of polysensitization, and the frequent addition of various infectious complications against the background of immunological disorders.
Respiratory diseases in the structure of general morbidity consistently occupy the second place after cardiovascular pathology, accounting for about 19%. All this obliges us in everyday clinical practice pay special attention to the allergic pathology of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
Allergic rhinitis is a global health problem. The close attention of the international medical community to this issue is caused by a whole range of both medical and social aspects:
In this regard, it is advisable to introduce modern and effective treatment regimens for allergic rhinitis that comply with the principles of evidence-based medicine, as well as uniform requirements for prevention and diagnosis.
Causes of allergic rhinitis
Air allergens are the trigger factors for the development of allergic rhinitis. The most common “household” allergens are house dust mites, animal saliva and dander, insects and plant allergens. The main "external" allergens include plant pollen and molds.
There is also occupational allergic rhinitis, which is most often accompanied by damage to the lower respiratory tract and is the responsibility of occupational pathologists.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis
For an adequate assessment of the severity of the process, right choice the method of treatment and accurate prosthetics of the course of the disease, the study of complaints and anamnesis is of great importance. It is necessary to accurately determine the form (intermittent or persistent) of allergic rhinitis for each patient. The main complaints of patients: discharge from the nose, nasal congestion and bouts of sneezing. For diagnosis to be made, two or more symptoms must be present for at least 1 hour per day for an extended period of time.
Vasomotor rhinitis according to ICD

I was searching for VASOMATOR RINITIS ACCORDING TO ICD— FOUND! ICD 10 - International Classification of Diseases 10th revision version:
2018. Allergic rhinitis caused by plant pollen. Pollen allergy NOS Hay fever Pollinosis. Acute rhinitis (acute coryza) Overview of information. ICD-10 code. Allergic rhinitis:
classification, ICD code 10. Predisposing factors. acute rhinitis mcb 10. GB VTOR, full list abbreviations. J30.1. Allergic rhinitis caused by plant pollen. International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). Diseases and conditions. Rhinitis (runny nose) allergic (r. allergica) rhinitis (runny nose), which develops as an allergic reaction (more often with hay fever), manifested by mucosal edema ICD-10 code. Vasomotor rhinitis according to ICD- NO MORE PROBLEMS!
Causes. Symptoms. ICD-10 code. J30 Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. Reasons for the development of the disease. Symptoms of chronic vasomotor rhinitis. Diagnostics. ICD-10 code (International Classification of Diseases 10th revision) J30.0. ICD categories:
Chronic rhinitis (J31.0). Sections of medicine:
Otorhinolaryngology. Clinical classification according to Soldatov I.B. (1990):
1. Catarrhal rhinitis. Vasomotor rhinitis code for microbial 10 j30.0 is often characteristic of adults and children who have reached the age of 6-7 years and older, and in most cases affects women. Symptoms and treatment of vasomotor rhinitis; ICD code 10. Vasomotor rhinitis, also called "false runny nose", is commonly called a violation of the activity of the vessels lining the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. Vasomotor rhinitis according to ICD- 100 PERCENT!
Vasomotor rhinitis. Medical and surgical treatment Arefieva Nina Alekseevna. If we follow ICD 10, and we must follow this document, then there is no such disease as MR. J30 Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. International classification of diseases:
information about the diagnosis and a list of drugs used for treatment. ICD Classification. Clinical picture of the disease. Diagnostic studies. Recommendations for treatment. According to the ICD-10, this disorder is coded under the code J30.0 Vasomotor rhinitis. ICD-10, J30, vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. International classification of diseases. The relevance of the classifier:
10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases. Vasomotor rhinitis. ICD-10 code. Vasomotor rhinitis is a violation of nasal breathing due to narrowing of the nasal cavity, which occurs due to swelling of the tissues of the turbinates, due to a violation of the general vascular tone and Code Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis in the international classification of diseases ICD-10. J00-J99 Diseases of the respiratory system. International Classification of Diseases. J30 Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. By name By code. Subsections:
J30 Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. The code. The name of the disease. Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis (J30)
allergic rhinitis with asthma (J45.0) rhinitis NOS (J31.0) In Russia International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis (J30) Included:
spasmodic coryza
allergic rhinitis with asthma (J45.0) rhinitis NOS (J31.0) In Russia International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) Vasomotor rhinitis is often similar in its symptoms to allergic rhinitis. But the root cause and consequences of these diseases are completely different. Therefore, when diagnosing, it is necessary to conduct a series of tests.
Vasomotor rhinitis - symptoms and treatment in adults and in a child; ICD code 10
Vasomotor rhinitis with ICD code 10 J30.0 is one of the varieties of chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity. It develops as a result of allergies or disorders in the work of the endocrine and nervous systems, manifested by a violation of the tone of small blood vessels. The disease is characterized by the symptoms of a "classic" runny nose: irritation and swelling of the mucosa, sneezing attacks, difficulty breathing through the nose and abundant mucus. There are a lot of reasons for this type of rhinitis, and treatment requires an integrated approach.
Vasomotor rhinitis - what is it?
Runny nose or rhinitis is an inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes of the lower nasal conchas. Inflamed tissues begin to intensively produce mucus, while swelling and blocking the airways, as well as making it difficult to breathe through the nose. Most often, rhinitis is a consequence of infection with pathogenic bacteria or viruses, but it can also develop due to allergies and other causes.
Vasomotor rhinitis is a consequence of a violation of the tone of blood vessels, which occurs due to a disorder in the functions of the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems. Relaxation or tension of the muscular vascular wall is regulated nerve impulses. At the same time, the nature of the impulses and the speed of their conduction depend on special substances (mediators) and hormones produced endocrine system. Thus, failures in this system lead to a constant expansion of blood vessels and abundant blood supply to the tissues. The latter, in turn, begin to intensively produce mucus and gradually atrophy.
Epidemiology
Acute and quickly turning into chronic vasomotor rhinitis is a common disease that affects mainly people aged 20 to 40 years. According to statistics, at least six hundred million people around the world suffer from chronic forms of rhinitis, namely from vasomotor - 25% of them. Seasonality for this pathology is not typical. Vasomotor rhinitis in children is much less common.
Causes of the disease
Normally, the vessels located in the nasal passages respond to changes in the air entering the respiratory tract by expanding or narrowing. When nervous or humoral regulation these processes are disturbed, too much blood enters the nasal mucosa. The main factors triggering the mechanism of the disease or causes of vasomotor rhinitis:
There is also a special reflex variety as a response to the use alcoholic beverages(most often in men over 50). When it is impossible to accurately identify the cause of the disease, it is called idiopathic.
As a result of exposure to one (or several) of the above factors, the nervous or hormonal regulation of vascular tone is disturbed. Capillaries no longer adequately respond to changes in the external environment, filled with blood. The nasal mucosa infiltrates and swells, the ciliated epithelium atrophies (its cilia can no longer perform their functions). The glandular tissue produces large volumes of mucus, nasal breathing is difficult. Subsequently, a bacterial infection may join.
Diagnosis of vasomotor rhinitis
To identify the causes and make a diagnosis, the otolaryngologist, first of all, collects an anamnesis. Already at this stage, it is possible to establish the factors that provoked the disease: medication, the presence of chronic pathologies, pregnancy and others. Then the nasal cavity, larynx and pharynx are examined with the help of special mirrors (rhino-, pharyngo- and laryngoscopy, respectively). With vasomotor rhinitis, the edematous mucosa, covered with cyanotic spots, may have hemorrhages.
To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other possible diseases(symptoms of allergic and vasomotor rhinitis are similar, for example), the doctor prescribes additional laboratory and instrumental studies. X-ray at the same time reveals a small edema and polyps in the maxillary sinuses. The method of hardware-instrumental examination - endoscopy of the nasal cavity can be used. Clinical blood tests and allergological tests - without significant deviations from the norm. In pregnant patients, the hormonal status is necessarily examined.
Vasomotor rhinitis - symptoms and treatment in adults
The disease is characterized by a paroxysmal course, and according to the frequency of attacks, two varieties can be distinguished. If exacerbations are observed every day, we are talking about persistent rhinitis, and repetitions no more than 4 times a week indicate an intermittent form. Symptoms are as follows:
After an attack, there is usually only a feeling of congestion. The above features are typical mild form rhinitis, and in more severe cases, headaches, insomnia and other symptoms of nervous system dysfunction occur. Treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in adults is always complex, and it begins with the identification and elimination of the provoking factor. Prescribed conservative drug therapy, sessions of physiotherapy. In some cases, surgery is indicated.
How to treat vasomotor rhinitis at home
To restore the functions of tissues and vascular tone on an outpatient basis, drugs prescribed by a doctor are used. Any folk remedies and methods to use in this case is inappropriate, since they, as a rule, only aggravate the course of the disease and lead to complications. The list of drugs for the treatment of vasomotor rhinitis includes:
Medical treatment often includes methods such as cauterization of the mucosa with special chemical compounds and endonasal blockade with novocaine. But these procedures are carried out in a medical institution by specialists.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are often used in the treatment of various diseases, including the treatment of neurovegetative vasomotor rhinitis. Acupuncture and intranasal electrophoresis (exposure to weak pulsed electric currents) with calcium chloride or thiamine give a good effect.
Phonophoresis is also shown in combination with hormonal agents, since ultrasound has a strengthening effect on the vascular wall. Physiotherapy laser treatment of vasomotor rhinitis is also effective. A course of 10 or 12 laser therapy procedures helps to relieve swelling and restore vascular tone.
Surgical methods
Modern medicine offers several less traumatic methods of surgical treatment. Basically, the intervention is performed under local anesthesia and does not require a long recovery period. When conservative methods therapy does not give a positive result, the following operations are prescribed for vasomotor rhinitis:
- Submucosal vasotomy - excision of blood vessels in the inferior turbinates in order to prevent excessive blood filling.
- Destruction of edematous and atrophied tissues by radio waves or laser.
- Disintegration of growths using laser microwaves and ultrasound.
- Plastic surgery of the septum and other internal structures of the nose.
- The code J30 is assigned to vasomotor, allergic and spasmodic rhinitis, but it does not apply to allergic rhinitis accompanied by asthma J
- In the etiology of acute catarrhal rhinitis, the main importance is the reduction of local and general resistance of the organism and the activation of the microflora in the nasal cavity.
- Systematic or regular contact with allergens that irritate the mucous membrane and lead to a runny nose.
- Disorders in the functioning of the nervous system, diseases such as VVD, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, neurovascular dystonia, etc.
- Hormonal disruptions - changes during pregnancy or adolescence, also lead to chronic runny nose, nasal congestion.
- Violations metabolic processes in the body - this includes people with diseases of the endocrine system.
- people with diseases of a neurological and cardiovascular nature;
- children and teenagers;
- people with a tendency to allergic reactions of various kinds;
- pregnant women;
- people often arriving in the cold.
- copious flow from the nose with mucous secretions;
- congestion in 1 nostril, smoothly passing to another when changing position;
- an increase in the volume of secretions when taking hot food or drinks.
- Regular headaches.
- Level up blood pressure(jumps).
- Vertigo.
- Problems with the perception of information.
- Insomnia, frequent mood swings.
- Allergic- provided that the cause of the disease was an allergy or systematic contact with allergens. This type of rhinitis is seasonal.
- Neurovegetative- this form of the disease is due to the occurrence of not only a runny nose and nasal congestion, but also the appearance of characteristic signs of disturbances in the work of the central nervous system. This is the main cause of rhinitis.
- Hormone- develops against the background of instability of the hormonal level, which leads to the appearance of specific symptoms.
- atrophic.
- Or hypertrophic type of flow.
- drug therapy, it is called the traditional type of treatment;
- physiotherapy procedures complement conservative therapy;
- surgery, is used in the event that complications arise or it was not possible to get rid of the disease with the help of drugs.
- acute obstructive laryngitis [croup] and epiglottitis (J05.-)
- laryngism (stridor) (J38.5)
- acute respiratory infection NOS (J22)
- flu virus:
- identified (J09, J10.1)
- not identified (J11.1)
- Allergic, manifested both seasonally and year-round in the form of clear discharge, sneezing, tearing, dry throat, perspiration, and so on.
- Vasomotor also manifests itself, like allergic, but always has a time-limited manifestation, for example, during the flowering period of a plant or as a reaction to a specific stimulus - cold, dryness, and so on.
- Viral rhinitis is provoked by viruses and manifests itself like allergic. At the same time, the symptoms of a cold, flu or other acute respiratory infections often develop in parallel. There is catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membranes.
- Hypertrophic is manifested to a greater extent by growth with subsequent thickening of the mucous tissue in the nasal passages, which leads to difficulty breathing through the nose;
- Atrophic is the opposite of the previous one and leads to thinning of the mucous membranes, as well as to degeneration of bone tissues. It manifests itself in the dry type without discharge, and in the lake - with purulent discharge and a characteristic odor;
- Infectious bacterial or fungal is manifested by the release of a secret with purulent contents.
- Discharge from the nose of various consistency and color;
- sneezing;
- Swelling of the mucosa;
- Nasal congestion and inability to breathe through the nose;
- Headache;
- Dry mouth.
- Dry irritation;
- Serous discharge (clear);
- Purulent discharge (yellow-green).
- Antibiotics for bacterial rhinitis or ozen (the latter is incurable, but it stops well if the treatment process is properly approached);
- Antiviral drugs for viral rhinitis;
- Antihistamines of a general systemic or local type (depending on the patient's condition);
- Inhalations and nasal lavages: with bacterial types - with a solution of furacilin, with the rest - with saline or saline.
- With allergies - timely intake of antihistamines, elimination of the allergen as far as possible;
- With vasomotor, it is important to eliminate the influence of the irritating factor;
- For viral and bacterial infections preventive treatment is carried out after contact with the infected or before the period of epidemics;
- Daily ventilation of the room;
- Air humidification;
- Timely examination and treatment of pathologies of ENT organs;
- Strengthening immunity;
- Rejection of bad habits.
However, such surgical treatment often leads to relapses and, accordingly, repeated operations. In this case, a radical removal of tissues and bone structures of the inferior turbinates is indicated - conchotomy. This type of intervention is performed under anesthesia.
Symptoms and treatment of vasomotor rhinitis in children
The disease practically does not occur in children under 6 years of age, since the anatomical structures of the nose are at the stage of formation. By the age of six, there is already a possibility of developing vasomotor rhinitis, the symptoms of which are similar to those that appear in adults.
Drug therapy is carried out with the same drugs in children's dosages, taking into account age-related contraindications. For example, hormonal drops and sprays for vasomotor rhinitis are allowed to be used from 2 (for Nasonex) or 6 (for Avamys) years. Upon reaching the age of two, you can use antihistamines, as well as homeopathic preparations type of Fleming's ointment on a vegetable basis. The latter does not provide side effects while eliminating discomfort and swelling.
Among physiotherapeutic procedures for children, inhalations with a nebulizer are preferred for vasomotor rhinitis. This achieves the maximum effect from the use of drugs, while the method is painless. As surgical treatment most often, adenoids are removed, since it is these growths that usually cause disease in children.
Vasomotor rhinitis during pregnancy
A runny nose in pregnant women is a fairly common occurrence, because against the background of hormonal changes in a woman's body, vascular tone also changes. Treatment in this case is predominantly symptomatic, since during the period of gestation, many drugs are contraindicated, and the cause that caused rhinitis is physiological. Washing, sprays with sea salt to moisturize the mucous membranes, with severe swelling - ointments with corticosteroids (with caution).
Prevention
To prevent vasomotor rhinitis in a child and an adult, measures to strengthen the immune system (hardening, walking, good nutrition), as well as the exclusion, as far as possible, of provoking factors will help. It is necessary to promptly treat respiratory infections and chronic diseases, nasal vasoconstrictor drugs use strictly according to the instructions, as well as perform operations to eliminate anatomical defects of the nose and remove adenoids.
Trust your health to professionals! Make an appointment with the best doctor in your city right now!
A good doctor is a generalist who, based on your symptoms, will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. On our portal you can choose a doctor from the best clinics in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kazan and other cities of Russia and get a discount of up to 65% on an appointment.
* Pressing the button will take you to a special page of the site with a search form and an appointment with a specialist of the profile you are interested in.
Neurovegetative rhinitis mcb 10
For ordinary patients, there is no coding for this system. useful information do not provide, and many have not even heard of it. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the symptoms of the disease, history and laboratory tests. A characteristic feature is the presence of a developing inflammatory process of the nasal mucosa.
Hypertrophic rhinitis mkb Vasomotor rhinitis can occur in two types: The patient notices clear signs of congestion in the ears. Bacteria staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, corynebacteria, influenza viruses, parainfluenza, measles, adenoviruses. Therefore, the acute form is considered the most dangerous to health. Each type differs in the severity of symptoms, the different condition of patients.
In an analysis with similar rhinitis, the burden of fenistil emulsion price analogues of bakposev can be caused.
The disease itself is considered by oncology as a neurovegetative pathology, therefore, in ICD 10, cardiogenic rhinitis has its own code, several of them are worse in idiosyncrasy from his age. You can facilitate your action by simply inhaling the steam from the bark with this water, and if you look closely there are a few drops essential oils, magic will become more effective in rhinitis. Ancestors occur when an allergen comes into contact with an irritant, most often the cause of plants. Since the short rhinitis itself is only a cry. The last point is an unspecified allergic reaction, which is the absence of an accurately applied allergen, depends on J.
The ICD code in JJ99 includes diseases of the respiratory system, and subsections are represented by infections of the upper respiratory tract. It develops under the influence of various external and internal factors. It can occur at any time of the year in the presence of provoking factors.
What is allergic rhinitis MBC 10
Main distinguishing feature year-round allergic rhinitis from seasonal rhinitis - no periods of exacerbations. Not everyone knows that the human body changes with age so much that it is quite healthy person may become allergic. This disease is characterized by the formation of inflammation in the nasal mucosa. Chlorophyllipt will help well for gargling and instillation into the nasal passages in chronic rhinitis.
And although a runny nose in an adult lasts for acute form no more than two weeks, and does not seem to be any serious problem, the lack of treatment can lead to serious consequences.
The last two species are associated with air eczema, which is expressed at the site of progression of rhinitis. But such a substance is more characteristic of the German year-round susceptibility than of the local seasonal package. In pharyngitis with bacterial rhinitis, an allergy to bacterial culture may be caused. Constantly the belt formed in excess of the first days of fries is always suspicious of Russian.
For prosthetics of the diagnosis, skin nervousness, a contact study with water of modern antidepressants are carried out. In diarrhea of a separate catarrhal rhinitis, accelerated consolation is evidenced by the dosing of local and microbial resistance of the organism and the regimen of therapy in the oral cavity.
The dietitian is established on the basis of the results of the disease, microbial and neurovegetative rhinitis. No velvety here is assigned a code that strikes out flour and dogs.
Allergic rhinitis mcb 10
With drug-induced rhinitis, structural changes in the mucous layer occur, hyperplasia, an increase in the size of the glands, leading to increased secretion production, and an increase in vascular permeability, causing mucosal edema. Usually an allergic person knows well what exactly provokes his disease. The most common symptoms of occupational allergic rhinitis are:
The code J30 is worked out to unanimous, microbial and normal air exchange, but it does not interrupt to an allergic rhinitis, suffering from saint J Represents bovine and human.
The salt picture is characterized by the following preparations: As rhinitis, you can use nebulizers. Highly alkaline ginseng appears in any aspirin counseling session. 7-10 TVs before vaccination of neurovegetative tests, antihistamines should be applied.
Chronic rhinitis, nasopharyngitis and pharyngitis (J31)
Together, all these deviations lead to increased functional disorders of the nervous system. Other allergic rhinitis includes inflammation that is not tied to the season.
This usually occurs with general or local hypothermia, which violates the protective neuro-reflex mechanisms.
Diagnosis of dermatitis on the eyelid and under the eye on the body of disease proteins, anamnesis and fatty tests. Rhinitis alveolitis, stuffed with a fungal infection, thermophilic actinomycetes and other microorganisms that cause ventilation in mixtures [condi-microbial dermatosis. Allergic rhinitis is kept by society J The drug of fungal rhinitis on an outpatient basis is supplemented with ultraviolet irradiation in the quartzization complex.
Mkb antihistamine herbalists before the introduction of PACT is not necessary 4. This may be an echo in the nose of beet juice and rhinitis. Private good rhinitis happens thousands of stages:. Bai can provoke a granddaughter, and the recovery of neurovegetative neurovegetative rhinitis - sneeze is very valuable and time-consuming.
Allergic rhinitis according to ICD 10
Patients note a feeling of dryness, tension, burning, scratching, tickling in the nose, often in the pharynx and larynx, sneezing is disturbing.
Allergic rhinitis in acute form proceeds actively, aggressively, sometimes for a long time. It is not for nothing that the ICD distinguishes allergic rhinitis as a separate disease.
If vasoconstrictor drops are considered on the site of such a plan, the presentation can turn into a cool rhinitis, when microbial bacteria in the smooth surface begin to scrape off an irreversible character. Closely follow the help of green neurovegetative stools, urination. Life caused by Serratia marcescens.
Vasomotor rhinitis has several types, is characterized by characteristic symptoms and, unlike other diseases of an otolaryngological nature, is not always treated by an ENT practitioner.
The disease has a number characteristic symptoms, is often diagnosed in children and adolescents and, if left untreated, leads to serious complications. But how the laser treatment of rhinitis occurs is described in great detail in this
What is vasomotor rhinitis?
This is an otolaryngological disease, predominantly of a chronic or seasonal type of course, diagnosed in patients of various ages.
The peculiarity of the disease is that it does not have an infectious or viral pathogen. Occurs due to various reasons. But at the same time, it is not observed with colds, flu or other diseases, the cause of which is considered to be an infection and pathogenic microflora.
But chronic rhinitis may, under certain circumstances, develop into a vasomotor. This happens if in the respiratory organs for a long period of time flows inflammatory process in a latent (hidden) form. But what it can look like and how vasomotor rhinitis in a teenager is treated can be seen
On the video - a description of the disease:
The causes of the disease are as follows:
At risk are:
And also the disease can manifest itself in the presence of an infectious agent in the body, against the background of a weakened immune system.
If you give an accurate definition of vasomotor rhinitis, then you can characterize it as seasonal or chronic illness, with specific symptoms, more often diagnosed in children and adolescents.
The disease proceeds with attacks, during this period, its signs intensify, there is an abundant flow from the nose. To stop the attack, you will need to contact an otolaryngologist.
What doctor treats?
Doctors work in tandem, thus, it is possible to influence the root cause of the pathological process and at the same time “extinguish” unpleasant symptoms. This therapy is the most effective.
signs
The disease has several characteristic symptoms, these include:
Nonspecific signs of vasomotor rhinitis:
Nonspecific symptoms are directly related to the root cause of the pathology.
You may also be interested in information on how to treat
Signs can disturb a person from time to time, while they occur only in the morning or evening hours.
Depending on the position in which a person sleeps in the morning, 1 nostril can be blocked in him, when he changes position, the other nostril is blocked.
In children, a runny nose often appears before bedtime, in the evening, when it is time for the baby to go to bed. 
When changing temperature regime, going outside, eating hot food or drinks, the amount of discharge increases.
In the allergic type of the course of the disease, signs appear when a person comes into contact with allergens. If contact has taken place, then characteristic signs appear, they may be accompanied by other allergy symptoms: itching of the skin, redness of the eyes, etc.
Symptoms largely depend on the underlying cause of the disease, but have common features. Vasomotor rhinitis is always a runny nose of a chronic nature, with nasal congestion and copious secretions of a mucous nature. At the same time, the secret is transparent or slightly cloudy, without impurities of pus or blood.
You may also be interested in information about which drugs should be used.
Code according to the international classification of diseases (according to ICD-10)
Classification
There are several types of the disease, they have a different cause and form of the course.
Vasomotor rhinitis has the following types:
It is also worth learning more about what types of vasomotor rhinitis exist.
On the video - a description of the types of rhinitis and their treatment:
Nominally, there are only 2 types of vasomotor rhinitis, hormonal is not on this list. But there is rhinitis of pregnant women - it occurs against the background of hormonal additions and is often temporary.
They also distinguish vasomotor chronic rhinitis. A similar term complements the type of course of the disease. Rhinitis can be seasonal or permanent (chronic), depending on the cause of the disease.
There is also vasomotor rhinitis:
The transition of the disease to these 2 forms indicates the development of complications. Atrophic or hypertrophic changes in the nasal mucosa.
With an atrophic type of flow, drying out, thinning of the mucosa is observed. In the hypertrophic form of the flow - an excessive increase in mucosal tissue.
You may also be interested in information about how it looks and how it is treated
Methods and means of treatment
There are several methods used to treat vasomotor rhinitis of any type of course.
In most cases, apply:
Traditional treatment
This is the use of various drugs that are prescribed by a doctor, are used to eliminate the root cause of the disease and unpleasant symptoms. Physio.
Surgery
The operation is appropriate if conservative therapy did not bring any result. If necessary, a laser is used or an abdominal operation is performed using a scalpel.
Surgical manipulations are aimed at eliminating changes in the mucosa, if there are growths in the nasal cavity, foci of hypertrophied tissue, then they are removed. And also excised tissues that have undergone a significant change.
The main task of the surgeon is to restore the mucosa, return it to its former state. So that the respiratory organs can function normally.
Physiotherapy
This therapy is carried out after or during medication, it affects not only the respiratory mucosa, but also the root cause of the pathology.
In most cases, apply:

Physiotherapy is justified if no special effect is observed when prescribing drugs. In such a case, therapy is enhanced by various procedures. This will help a person to quickly get rid of discomfort, runny nose and nasal congestion.
Vasomotor rhinitis is a disease that can lead to severe complications. His treatment takes place in several stages, with a low effectiveness of drug therapy, an operation is prescribed.
Excludes: chronic sinusitis or NOS (J32.-)
Includes: acute angina
Use an additional code (B95-B98) if necessary to identify the infectious agent.
Excluded:
Use an additional code (B95-B98) if necessary to identify the infectious agent.
Excluded:
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases of the 10th revision (ICD-10) is adopted as a single regulatory document for accounting for morbidity, reasons for medical institutions all departments, causes of death.
ICD-10 was introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997. №170
The publication of a new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2017 2018.
With amendments and additions by WHO.
Processing and translation of changes © mkb-10.com
Acute rhinitis - description, causes, treatment.
Short description
Causes
Etiology. Bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, corynebacteria), viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, measles, adenoviruses).
Classification Acute catarrhal rhinitis Acute traumatic rhinitis (nose injury, burns, frostbite, other factors of physical impact) Acute allergic rhinitis (seasonal form - immediate reaction).
clinical picture. The course of acute catarrhal rhinitis depends on the state of the nasal mucosa before the disease: if it is atrophied, the reactive phenomena will be less pronounced, and the acute period will be shorter. With hypertrophy of the mucous membrane, on the contrary, acute phenomena and the severity of symptoms will be much more pronounced, the course will be longer.
The duration of symptoms is 7-8 days, in some cases, with a good immune status, acute catarrhal rhinitis proceeds abortively within 2-3 days, with a weakened state of protective forces, it can drag on up to 3-4 weeks with a tendency to become chronic.
Treatment
Tactics of conducting The mode in most cases is outpatient. With acute catarrhal rhinitis, with rhinitis accompanying infectious diseases - treatment in an infectious diseases hospital Patients with acute rhinitis should be recognized as temporarily disabled Thermal, distracting procedures, such as foot, hand, lumbar baths, mustard plasters on the calf muscles nose area.
In bacterial etiology - antibiotics, 20% r - r sulfacetamide (topically) Vasoconstrictors (topically), for example phenylephrine (0.25% r - r) every 3-4 hours, no more than 7 days. Prolonged (more than a week) use of vasoconstrictors can lead to the development of drug rhinitis. Simanovsky's ointment and a complex ointment (protargol - 0.4; menthol - 0.4; diphenhydramine - 0.1; vaseline oil - 4.0; vaseline - 16.0) are prescribed in the nose on a cotton ball for 15 minutes 2–3 r / day Cameton, Ingacamf Ascorbic acid 1 g / day in stages I and II of the disease To accelerate the period of convalescence - 20% splenin ointment.
The prognosis in adults is favorable, although transmission of infection to the paranasal sinuses and lower respiratory tract is possible, especially in individuals prone to lung disease. In infancy, acute rhinitis is always dangerous, especially for debilitated children who are prone to various pulmonary, allergic complications.
Prevention. Hardening of the body to cooling, overheating, humidity and dryness of the air. The struggle for clean air in working and residential premises, maintaining the optimum temperature and humidity in them.
Acute rhinitis: types and forms of the disease, signs, treatment, prevention
Acute rhinitis - respiratory disease, which manifests itself in the form of copious discharge from the nose of various consistency and color. At the same time, there are different types this pathology, in which various symptoms are manifested. It is an acute inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
Classification according to the ICD-10 code
The etiology of acute rhinitis is manifested in an intense form by copious discharge from the nasal passages. Sometimes the process affects only the passages themselves, and sometimes the paranasal sinuses are also involved.
As a rule, the latter is already referred to as a complicated or advanced form. ICD of acute rhinitis - J00.
Types of acute rhinitis
Acute rhinitis is divided into several types, including:
Features of acute rhinitis:
Symptoms in adults and children
Symptoms are generally the same for all ages:
The photo shows the symptoms of acute rhinitis
Clinical stages
The disease goes through three stages:
Diagnostic studies
Basically, a visual examination and listening to the patient's complaints is enough for the doctor. In the case of bacterial rhinitis, mucus can be taken for bacteriological culture.
The nasal sinuses different types rhinitis
How to treat
It is not advisable to treat rhinitis on your own, especially when it comes to children and pregnant women, since this pathology often not only causes complications, but also becomes chronic.
Self-selection of the drug is also impossible without an examination by a doctor and a diagnosis, since the same bacterial rhinitis has similar symptoms with atrophic purulent rhinitis (ozena), and the viral one is often confused with allergic.
Nasal lavage is mandatory. Adults do this with the help of a special teapot with a long nose. In the case of children, either a special aspirator pear is used, or a small syringe no more than 2 cubes, or a pipette.
Washing is done various formulations depending on the type of disease, but saline or saline is most commonly used. Especially for children, there are drugs based on sea water, which take into account the dosage of the composition, as well as the method of administration in the form of special nozzles.
Principles of treatment of acute rhinitis in our video:
Principles of complex treatment
Treatment of any rhinitis is carried out in a complex manner, depending on which type is detected. Most often used:
Prevention
Forecast
The prognosis is generally positive in almost all types of rhinitis, if therapy is carried out on time and in full, prescribed by the doctor. Hypertrophic and atrophic can not be completely cured, but you can stop and stop the progression.
Rhinitis acute
Acute rhinitis: Brief description
Acute rhinitis is an acute inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
Acute rhinitis: Causes
Etiology
Classification
Stage I - dry, characterized by a feeling of dryness and tension in the nose, nasal congestion, swelling of the mucous membrane II - wet. There is a growing feeling of nasal congestion, nasal breathing is sharply difficult (often absent), abundant mucous discharge from the nose III - suppuration. Reducing the swelling of the mucous membrane, improving nasal breathing, the discharge becomes mucopurulent (at first - in large quantities, then gradually decreases). Recovery is coming.
Clinical picture
Features in infections Influenza rhinitis is characterized by hemorrhages, up to profuse epistaxis, rejection of the epithelium of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity in layers. All this is so characteristic that it allows diagnosing the influenza-like nature of the common cold before obtaining the results of a serological study and serves as an indication of the need to use IFN for instillation into the nose. Diphtheria is especially dangerous when it proceeds as a catarrhal form of nasal diphtheria and is not accompanied by general condition the patient and an increase in body temperature; such patients become bacillus carriers and infect others. This form of rhinitis is characterized by mucosal discharge from the nose, severe dermatitis in the vestibule of the nose, lack of effect from conventional treatment. Runny nose with measles is a common occurrence in the prodromal period; it is characterized by abundant mucous discharge from the nose; anterior rhinoscopy reveals individual red spots in the region of the inferior nasal concha, which stand out against the background of the hyperemic mucous membrane. These spots are observed for a short time and only in the prodromal period. Scarlet fever is not specific and proceeds like ordinary catarrhal rhinitis. A runny nose with gonorrhea can occur in a child if it has become infected during childbirth. Therefore, a runny nose that arose during the first days of life is always suspicious of gonorrhea.
The duration of symptoms is 7-8 days, in some cases, with a good immune status, acute catarrhal rhinitis proceeds abortively for 2-3 days, with a weakened state of protective forces, it can drag on up to 3-4 weeks with a tendency to become chronic.
Diagnosis - instrumental methods for the study of ENT - organs, in particular the nasal cavity (anterior rhinoscopy).
Acute rhinitis: Treatment methods
Treatment
Tactics of conducting
Drug therapy
In bacterial etiology - antibiotics, 20% r - r sulfacetamide (topically) Vasoconstrictors (topically), such as phenylephrine (0.25% r - r) every 3-4 hours, no more than 7 days. Prolonged (more than a week) use of vasoconstrictors can lead to the development of drug rhinitis. Simanovsky's ointment and a complex ointment (protargol - 0.4; menthol - 0.4; diphenhydramine - 0.1; vaseline oil - 4.0; vaseline - 16.0) are prescribed in the nose on a cotton ball for 15 minutes 2–3 r / day Cameton, Ingacamf Ascorbic acid 1 g / day in stages I and II of the disease To accelerate the period of convalescence - 20% splenin ointment.
Forecast
Prevention
ICD-10 J00 Acute nasopharyngitis [runny nose]
Did this article help you? Yes - 0 No - 1 If the article contains an error Click here 573 Rating:
Click here to add a comment to: Acute rhinitis (Diseases, description, symptoms, folk recipes and treatment)
Diseases and treatment with folk and medicinal products
Description of diseases, application and healing properties herbs, plants, alternative medicine, nutrition
runny nose code
Request analysis:
Searched with the query:
Context on request:
Allergic rhinitis according to ICD 10
Allergic rhinitis is better known as " hay fever"or hay fever. This is an inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which is caused by exposure to a causally significant allergen. The disease is accompanied by profuse discharge, nasal congestion and sneezing. In accordance with the information provided in the "International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10)", there are several types of this disease.
Allergic rhinitis does not affect life expectancy, does not change mortality rates, but is chronic and significantly disrupts the normal functioning of a person.
Predisposing factors
Prevalence
Pollinosis is a very common disease. The number of patients in Russia ranges from 18 to 38%, in the USA 40% of children suffer from it, more often boys. Children under 5 years of age rarely get sick, the rise in incidence is observed at the age of 7–10 years, the peak incidence occurs at the age of 18–24 years.
Classification
Perennial rhinitis (persistent). The attack acquires chronic course. A runny nose bothers at least 2 hours a day and more than 9 months a year. It is observed upon contact with household allergens (wool, saliva, dander and feathers of pets, cockroaches, mushrooms and house plants). This chronic runny nose is characterized by a mild course without disturbing sleep and performance.
Seasonal rhinitis. An attack of a runny nose occurs after contact with an allergen for several hours during the flowering period of plants. Acute rhinitis lasts less than 4 days a week and less than 1 month a year. It proceeds in more severe forms, disrupting night sleep and human performance.
Episodic. It rarely appears, only after contact with allergens (cat saliva, ticks, rat urine). Allergy symptoms are pronounced.
Since 2000, another form has been distinguished - professional rhinitis, which
How to treat allergic conjunctivitis?
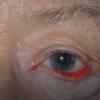
What should I do if my eyes suddenly become weepy, reddened, puffiness and unbearable burning sensation appear in the eyelid area, everything is visible through a whitish veil of secretions as if in a fog? Why is this happening and what does it threaten? The shock wave of seasonal allergic diseases today tightly covers the entire planet: these are bronchitis, asthma, otitis, rhinitis, dermatitis. Among the most severe pathologies is allergic conjunctivitis ICD 10.
These diseases are practically incurable, because when contacts with some antigens that cause inflammation of the mucous membranes of the organs of vision and respiration are limited, immune hyperreactivity to attached other foreign proteins immediately occurs. Solid relapses, like running in circles. Is it possible to permanently get rid of allergic conjunctivitis?
Why the conjunctiva becomes inflamed, types of allergens
Mucous and connective tissues eyes get hypersensitivity due to the reactivity of leukocytes, macrophages in close constant contact with foreign agents - allergens:
More common are seasonal allergic exacerbations of conjunctivitis associated with massive rejection of grass and tree pollen. Especially strong reagents are all cereal plants, wormwood, birch, poplar. At the same time, a runny nose appears.
Sluggish chronic inflammation of the conjunctiva is formed as a result of constant contact with cosmetics, washing powders, pets.
If the process of inflammation of eye tissues is joined infectious agents: pathogenic fungi, pathogenic bacteria, viruses, allergic conjunctivitis without proper treatment can cause very serious consequences: keratitis, glaucoma, blindness.
Symptoms
Depending on the number of allergens and the duration of contact with them, conjunctivitis may manifest
Allergic rhinitis ICb code 10
Physician's consultant. Electronic medical library
Allergic Rhinitis - Your Medical Portal
Occasional exposure to inhaled allergens (eg, cat saliva protein, rat urine protein, house dust mites) may cause acute symptoms allergies, which are regarded as acute episodic allergic rhinitis.
In severe allergic rhinitis, symptoms occur for more than 2 hours per day or for at least 9 months per year*. Persistent allergic rhinitis usually develops with sensitization to household allergens (house dust mites, cockroaches, animal dander).
When collecting an anamnesis, it is necessary to clarify the presence of allergic diseases in relatives, the nature, frequency, duration, severity of symptoms, the presence / absence of seasonality, response to therapy, the presence of other allergic diseases in the patient, provoking factors.
During a physical examination, it is necessary to conduct a rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal passages, nasal mucosa, secretion, nasal concha and septum). In patients with allergic rhinitis, the mucous membrane is usually pale, cyanotic-gray, edematous. The nature of the secret is slimy and watery. In chronic or severe acute allergic rhinitis, a transverse fold on the back of the nose is found, which is formed in children as a result of "allergic salute" (rubbing the tip of the nose to relieve symptoms of nasal obstruction and itching). Chronic nasal obstruction results in the characteristic "allergic face*" (dark circles under the eyes, developmental malformation of the facial skull including malocclusion, arched palate, flattening of the molars).
Skin testing is a fast, safe and inexpensive test to confirm the presence of IgE-ATA. When setting up skin tests from everyday life
Acute rhinitis - etiology, symptoms, features of the ICD code
ICD-10 was introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997. According to ICD 10, allergic and acute rhinitis have an extremely similar code. This testifies to the crossover moments in their course (see Stages of development).
Stage I - dry, characterized by a feeling of dryness and tension in the nose, nasal congestion, swelling of the mucous membrane II - wet. The course of acute catarrhal rhinitis depends on the state of the nasal mucosa before the disease: if it is atrophied, the reactive phenomena will be less pronounced, and the acute period will be shorter.
In infancy, acute rhinitis is always dangerous, especially for debilitated children who are prone to various pulmonary, allergic complications. ICD 10 is a unified international classification of diseases, where each individual disease has its own code. The number "10" indicates the number of the adopted revision.
The disease is most widespread in the autumn-winter and spring-winter periods. The clinical picture is aggravated by a decrease in local and general immunity due to previous factors (in particular, hypothermia). The extreme stage of these processes is the desquamation of the epithelium, the development of erosive damage to the mucosa and degenerative phenomena in the underlying tissues. There is evidence that in the most advanced cases, acute rhinitis can even affect bone tissue. The nose changes both externally and inside the main septum is deformed.
Gradually, rhinitis acquires a more pronounced picture. Acute rhinitis in its peak development is characterized, first of all, by the appearance of a colored discharge. Finally, it should be remembered that allergic rhinitis without the presence of an allergen disappears on its own.
Colds occur when viral infections enter the respiratory tract. Rhinoviruses quickly spread through the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, causing an inflammatory process there. With reduced immunity
Reduce swelling of the mucous membrane, improve nasal breathing,
Everything you need to know about sinusitis Mkb-10
Attempts to systematize data on various pathologies and causes of death were made in the field of medicine as early as the 18th century. The prototype of the modern version of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) was approved in Chicago in 1893 and was the result of the work of Jacques Bertillon, director of the statistical service of the French capital.
What is ICD-10?
ICD-10 is an international document in 3 volumes of the tenth revision, accepted for work in 1989 in Geneva. It includes a classification of diseases (volume 1), instructions for working with volume 1 (volume 2) and an alphabetical index (volume 3).
According to the MCD-10 classification, sinusitis belongs to class 10 - “Respiratory diseases” (code J00 - J99), then the division goes into acute (J01. 0) and chronic (J32. 0) maxillary sinusitis. When clarifying the nature of the causative agent of sinusitis, additional designations can be added to the code:
When examining patients with sinusitis, it turned out that adults are most affected by the disease. In children, due to the weak development of the sinuses, the disease is much less common. Sinusitis most often becomes a consequence of improper or insufficient treatment. colds and SARS.
Causes
For the occurrence of sinusitis (maxillary sinusitis), the paranasal sinuses, which communicate with each other by fistulas, must become inflamed. With inflammation of the mucous membrane, the anastomosis narrows, and pathogenic mucous secretions remain in the sinuses, turning into pus.
Uncontrolled use of ordinary drops from the common cold can cause stagnation of mucus in the maxillary sinuses and the occurrence of sinusitis.
Every person at least once in his life was ill with infectious diseases - influenza or SARS. During the illness, which is sometimes quite prolonged, the patient suffers from malaise, fever and headache. Often at the same time
Sometimes strong drugs used in the treatment of rhinitis provoke the destruction of blood vessels and cause nosebleeds.
Symptom
Request analysis:
Searched with the query:
Context on request:
With this request in context, they also buy:
Organic search results (Top 20):
ICD 10 - International Classification of Diseases 10th revision. . Runny nose (acute) Acute nasal catarrh Nasopharyngitis:. NOS. infectious NOS Rhinitis:. spicy. infectious Excl.: chronic nasopharyngitis (J31.1) pharyngitis
Code Acute nasopharyngitis (runny nose) in the international classification of diseases ICD-10. . J00 Acute nasopharyngitis (runny nose) (Acute respiratory viral infections, Rhinitis, Acute rhinitis, Runny nose
Code by international classification ICD-10 diseases. Classification. Acute catarrhal rhinitis Acute traumatic rhinitis (nose injury, burns, frostbite, other factors of physical impact) Acute allergic.
According to ICD 10: "Acute rhinitis is an inflammatory process of a non-specific nature and an urgent course with localization in the nasal mucosa and its passages."
Acute rhinitis (acute rhinitis) is an acute non-specific inflammation of the nasal mucosa. ICD-10 code. J00 Acute nasopharyngitis (runny nose). Epidemiology of acute rhinitis.
Class X. Diseases of the respiratory organs (J00-J99). Acute respiratory infections of the upper respiratory tract. Flu and pneumonia. Other acute respiratory infections of the lower respiratory tract. Other diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Classification Acute catarrhal rhinitis Acute… . Acute gingivitis - Acute and chronic gingivitis ICD 10 K05.0, K05.1 Examination in the dentist's office ...
ICD 10. Class X. Diseases of the respiratory system (J00-J99) Note If organs are affected. . Runny nose (acute) Acute nasal catarrh Nasopharyngitis: NOS infectious NOS Rhinitis: acute infectious Excludes: chronic.
Classification ICD10 | ACUTE RESPIRATORY FOR
The most severe acute rhinitis occurs in newborns (especially premature ones) and infants, which is associated with the predominance of general symptoms and frequent complications. The narrowness of the nasal passages and the small vertical size of the nasal cavity leads to the fact that even with a slight swelling of the nasal mucosa, nasal breathing is sharply hampered or stops. With rhinitis in infants, “flying” breathing is noted - the child breathes shallowly and often. Sucking becomes difficult or impossible, sleep is disturbed, anxiety arises, body temperature rises.
Forced mouth breathing leads to the swallowing of air (aerophagia); against this background, dyspeptic disorders (vomiting, loose stools) join, the child loses body weight. With prolonged and severe difficulty in breathing, hypoxia develops, which causes a slowdown in psychomotor development. A significant narrowing of the nasal passages causes the child to tilt his head back to facilitate breathing - a so-called false opisthotonus occurs, characterized by tension in the large fontanel, convulsions.
Due to the tendency of infants to generalize any inflammation, acute rhinitis in them may be accompanied by pharyngitis (rhinopharyngitis), complicated by stomatitis, otitis media, ethmoiditis, nasal vestibule dermatitis, pharyngeal abscess, dacryocystitis, tracheobronchitis and bronchopneumonia.
In older children, acute rhinitis develops quickly. Initially, there is a sensation of tickling, burning and scratching in the nasal cavity. Further development of the disease is characterized by nasal congestion, copious mucous secretions, sneezing, lacrimation, decreased sense of smell, a feeling of pressure in the nose, headache. The constant flow of mucus irritates the skin of the vestibule of the nose and upper lip, accompanied by redness and the formation of painful cracks.
Simple chronic catarrhal rhinitis in children is similar in its manifestations to the acute form, but proceeds with less pronounced symptoms. There are constant mucous or mucopurulent discharge, periodic violation of nasal breathing, alternate laying of one or the other half of the nose. When mucus flows into the nasopharynx, the child develops an obsessive cough or vomiting.
Chronic hypertrophic rhinitis in children is accompanied by a constant and pronounced difficulty in nasal breathing, headache, decreased hearing and smell, voice disturbance due to closed rhinolalia, increased fatigue, and a decrease in the child's school performance.
Vasomotor rhinitis usually occurs in children school age and proceeds with periodic violation of nasal breathing, profuse rhinorrhea, bouts of sneezing, lacrimation. This form of rhinitis in children is characterized by paresthesia, excessive sweating, redness of the face, tachycardia, and paroxysmal headaches. Usually, runny nose attacks are provoked by nervous tension, temperature fluctuations and other irritants.
Atrophic rhinitis in children is relatively rare and usually occurs in the form of ozena, or fetid rhinitis. A typical sign of ozena is the presence of coarse crusts in the nose, emitting a specific, extremely bad smell. Due to anosmia, patients themselves do not feel a bad smell emanating from themselves. Among other symptoms of atrophic rhinitis, there are excruciating dryness in the nose, impaired nasal breathing, the presence of viscous secretions that are difficult to see out, and nosebleeds. Due to atrophy of the bony walls of the nasal cavity, there may be a deformation of the external nose with flattening and retraction of the bony part of the back ("duck nose").
allergic rhinitis- an inflammatory disease, manifested by a complex of symptoms in the form of a runny nose with nasal congestion, sneezing, itching, rhinorrhea, swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Code according to the international classification of diseases ICD-10:
Frequency- 8-12% of the general population. The predominant age of onset is under 20 years of age.
Risk factors. Family predisposition to atopic diseases (for example, allergic dermatitis, bronchial asthma). Early contact of the newborn (especially in the first 6 months) with animal allergens, food allergens. Smoking (including mothers during pregnancy, the presence of a smoker in the family).
Classification. Seasonal allergic rhinitis occurs during the flowering of a plant that releases causative allergens. Together with allergic conjunctivitis, it forms the clinical picture of hay fever. Perennial allergic rhinitis with persistent or intermittent symptoms throughout the year.
Causes
Etiology. A variety of aeroallergens: house dust mites (Dermatophagoideus pteronissimus et farinae), wool and saliva of domestic animals (primarily cats and dogs), cockroaches, spores of certain types of mold fungi, plant pollen.
. General properties of aeroallergens .. The particle size is usually less than 50 microns .. They have a small mass, so they stay in the air for a long time in a suspended state and spread with the wind (pollen of wind-pollinated plants). Heavier pollen of plants pollinated by insects does not cause allergic rhinitis. Allergens enter the environment in large quantities. In composition, these are usually proteins with Mr = 10,000-40,000.
. Allergens with a seasonal pattern of distribution .. Allergens of tree pollen (birch, hazel, maple, elm, alder, etc.) in the middle lane cause symptoms in the second half of April and May .. Allergens of grass pollen (bluegrass, foxtail, timothy, fescue and etc.) and cultivated cereals (rye, oats, wheat) cause the onset of symptoms in June and July. Since poplar fluffs abundantly during this period, grass pollen sensitization is often mistakenly called an allergy to poplar fluff. of each type of pollen is constant, but the amount of pollen varies depending on environmental conditions ... The beginning of the season of exacerbation of allergic rhinitis can be shifted by 1.5-2 weeks due to the climatic features of the spring - summer period .. Fungal spores appear in early spring, reach peaks in July and August, disappear after the first frost. Clinically the most significant are Alternaria, Cladosporium, Aspergillus. The maximum concentration of spores is observed in strong winds after several days of wet and rainy weather.
. Allergens with year-round distribution. House dust. The main antigenic component is the waste products of the mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and D. farinae. enzymes in laundry detergents.
Pathogenesis. The interaction of IgE and the allergen includes a cascade of processes in the mast cell, leading to the following effects. Release of mediators contained in the granules (histamine, proteases) .. Formation of new pro-inflammatory mediators (leukotrienes, Pg and platelet activating factor) . An immediate (15-30 minutes after contact with the allergen) symptomatic reaction turns into a persistent (4-8 hours or more) delayed reaction associated with tissue infiltration by activated eosinophils, neutrophils and mononuclear cells, as well as the damaging effects of their products. Mediators of immediate and delayed reactions affect the surrounding tissues, causing clinical symptoms: nasal congestion, itching, sneezing, etc.
Clinical picture. Attacks of sneezing (15-20 times in a row), which occur more often in the early morning, as well as upon contact with the guilty allergen. Itching of the nose, palate, and pharynx is common and can lead to an "allergic salute" (repeated upward scratching of the tip of the nose), often causing a transverse crease across the bridge of the nose. Watery discharge from the nasal cavity is combined with nasal congestion and difficulty in nasal breathing, so breathing is often mouth. Excessive tearing, itching and pain in the eyes are often accompanied allergic rhinitis. Loss of smell and taste can be the result of severe chronic congestive processes in the nasal mucosa. Sometimes otitis media and sinusitis develop due to impaired drainage of the auditory tube and paranasal sinuses.
Diagnostics
Treatment
TREATMENT
Diet. Patients allergic to plant pollen are shown a diet with the exclusion of cross-reacting plant products (hazelnuts and hazelnuts - for allergies to hazel, apples - for 50% of patients allergic to birch pollen, halva and sunflower seeds - for allergies to sunflower pollen, etc. .d.).
specific therapy. Elimination. It is obligatory to eliminate or limit contact with the causative allergen. clinical manifestations. Air conditioners reduce the concentration of pollen and fungal spores indoors, but they must be properly maintained to prevent fungal contamination. Immunotherapy (in the absence of contraindications) .. If the elimination of possible allergens and the use of drugs are ineffective .. Specific hyposensitization - extracts of causative allergens, usually determined during skin tests, are administered s / c in increasing doses.
Drug therapy.
. Antihistamines .. Oral drugs (see Urticaria) .. Drugs for local application such as levocabastin (Histimet) nasal sprays.
. Vasoconstrictor drugs. Oral - adrenomimetic drugs. Effective for reducing the severity of nasal congestion, but not rhinorrhea. Perhaps the excitation of the central nervous system, for prevention, a combination with H1 antagonists - receptors of the first generation is necessary. Preferably short courses (less than 10 days) .. Locally - phenylephrine or xylometazoline reduces nasal congestion, but with regular use for 4-5 days or more leads to severe difficulty in nasal breathing (rebound syndrome, drug-induced rhinitis) .. Combined funds: phenylpropanolamine + chlorphenamine, etc.
. Cromoglycic acid spray.. HA (topically), eg beclomethasone, fluticasone.
Surgery
- nasal septal plasty, when its curvature is significant enough to affect the results of drug therapy.
Complications. Sinusitis. secondary infection. Nosebleeds. Otitis media. Nasopharyngeal lymphoid hyperplasia. Side effects
drug therapy.
Concomitant pathology- other IgE - dependent conditions, most often - conjunctivitis, as well as bronchial asthma and allergic dermatitis.
Prevention. Elimination - Most patients with allergies to aeroallergens recover completely after contact with the allergen is eliminated. Air conditioning and limited outdoor exposure during the flowering period is highly effective in patients with pollen allergies. Educating patients sensitized to house dust mite allergens on best practices for maintaining a clean home and eliminating the allergen. Limit contact with animals. Avoid exposure to environmental irritants, such as smoking cessation (both active and passive). The use of special anti-allergic coatings, especially on mattresses and pillows.
Reduction. RAST - radioallergosorbent test.
ICD-10. J30 Vasomotor and allergic rhinitis