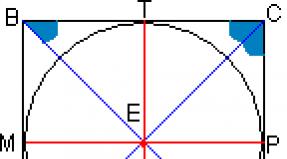
General psychology in diagrams and comments. Imagination as a cognitive mental process
Psychology: a textbook in diagrams, tables, comments. Zastavenko V.A.

SPb .: SPbGIKiT; 2015 .-- 177 p.
This study guide was developed in accordance with the requirements of federal state educational standards of higher professional education in the areas of training bachelors. The manual examines the issues that make up the theoretical foundations of psychology. In diagrams, tables and figures, as well as comments to them, the main phenomena of psychology are presented in the most acceptable form for perception and memorization. The structure and content of educational material correlates with the organization and content of educational information proposed in the work program for bachelors in the discipline "Psychology".
The manual is intended for students studying in the following specialties: 51.03.02 - Folk art culture; 03/38/01 - Economics; 11.03.04 - Electronics and Nanoelectronics; 11.03.01 - Radio engineering; 03.03.02 - Tourism; 42.03.02 - Journalism; 03/38/04 - State Medical University; 05.54.03 - Graphics.
Format: pdf
The size: 12.2 MB
Download: Rghost
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction 6
Chapter I. Introduction to psychology. The history of the development of psychological knowledge 7
1.1. The main stages of the development of psychological knowledge 7
1.2. The development of psychological knowledge in Antiquity 8
1.3. The development of psychological thought in the Middle Ages 9
1.4. Philosophical stage in the development of psychology 10
1.5. Scientific prerequisites for the emergence of psychology as a science 11
1.6. Experimental stage in the development of psychology 12
1.7. The current stage in the development of psychology 13
1.8. Periodization of the development of Russian psychology 14
1.9. The contribution of Russian psychology to world science 15
Comments 18
Self-check questions 22
Chapter IL Methodological Foundations of Psychology 23
2.1. The concept of the function of the methodology of science 23
2.2. Levels and structure of the methodology 24
2.3. Methodological principles of psychology 25
2.4. Development principle in psychology 26
2.5. The principle of reflection in psychology 27
2.6. Systems approach in psychology 28
2.7. Specific scientific level of methodological analysis of science 29
2.8. Subject and object of psychology as a science 30
2.9. Psychology in the system of sciences 31
2.10 Methods of Psychology 32
Comments 33
Self-check questions 36
Chapter S. Human psyche. Consciousness 37
3.1. Ideas about the essence and origin of the psyche 37
3.2. Essence of Psyche 38
3.3. Preconditions and conditions for the development of the human psyche 39
3.4. Nerve cell structure 40
3.5. Human nervous system 41
3.6. Human brain 42
3.7. Conditioned reflex as a physiological basis of behavior 43
3.8. Reflex arc as anatomical and physiological mechanism of reflex 44
3.9. Consciousness as the highest form of reflection of reality 45
3.10. Conscious and unconscious 46
Comments 47
Self-check questions 50
Chapter IV. Mental cognitive processes 51
4.1. The structure of the human psyche 51
4.2. Mental Processes 52
4.3. The concept and essence of sensations 53
4.4. Classification and features of sensations 54
4.5. Perception, essence and classification 55
4.6. Imagination, concept and types 56
4.7. Attention: essence, nature and characteristics 57
4.8. Memory: structure and classification 58
4.9. Speech, function and types 59
4.10. Thinking, concept and characteristics 60
4.11. Concepts of Intelligence 61
Comments 62
Self-test questions 65
Chapter V. Psychology of personality 66
5.1. Personality theories in psychology 66
5.2. The concept of personality in psychoanalysis 67
5.3. Behavioral personality theories 68
5.4. Humanistic psychology about personality 69
5.5. Ideas about personality in Russian psychology 70
5.6. The concept of personality and its description in various categories 73
5.7. Personality structure and factors of its formation 74
5.8. Human Temperament 75
5.9. Character: concept, nature and structure 76
5.10. Characterological personality traits 77
Comments 80
Self-check questions 83
Chapter VL Mental regulators of behavior and personality activity 84
6.1. The problem of needs in psychological science 84
6.2. The essence and classification of needs 85
6.3. Ideas about the essence and functions of a motive 86
6.4. Motive: structure and classification 87
6.5 Motivational sphere of personality 88
6.6. Schematic diagram of the process of motivational regulation of personality behavior 89
6.7. Emotions of personality: essence and functions 90
6.8. Emotion classification 91
6.9. Will as a regulator of personality behavior and activity 92
6.10. The structure of the will 93
Agreement
Rules for registering users on the QUALITY SIGN site:
Registration of users with nicknames like this is prohibited: 111111, 123456, ytsukenb, lox, etc.
It is forbidden to re-register on the site (create duplicate accounts);
It is forbidden to use someone else's data;
It is forbidden to use someone else's e-mail addresses;
Rules of conduct on the website, forum and in the comments:
1.2. Publication of personal data of other users in the profile.
1.3. Any destructive actions in relation to this resource (destructive scripts, guessing passwords, violation of the security system, etc.).
1.4. Using obscene words and expressions as a nickname; expressions that violate the laws of the Russian Federation, the norms of ethics and morality; words and phrases similar to the nicknames of the administration and moderators.
4. Violations of the 2nd category: Punished with a complete ban on sending any types of messages for up to 7 days. 4.1. Placement of information subject to the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation and contrary to the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
4.2. Propaganda in any form of extremism, violence, cruelty, fascism, Nazism, terrorism, racism; incitement of interethnic, interreligious and social hatred.
4.3. Incorrect discussion of the work and insults to the authors of texts and notes published on the pages "SIGN OF QUALITY".
4.4. Threats to the forum participants.
4.5. Placing deliberately false information, slander and other information discrediting the honor and dignity of both users and other people.
4.6. Pornography in avatars, posts and quotes, and links to pornographic images and resources.
4.7. Open discussion of the actions of the administration and moderators.
4.8. Public discussion and evaluation of the current rules in any form.
5.1. Mat and profanity.
5.2. Provocations (personal attacks, personal discrediting, the formation of a negative emotional reaction) and harassment of discussion participants (systematic use of provocations in relation to one or more participants).
5.3. Provoking users to conflict with each other.
5.4. Rudeness and rudeness in relation to interlocutors.
5.5. Transition to individuals and clarification of personal relationships on the forum threads.
5.6. Flood (identical or meaningless messages).
5.7. Intentional misspelling of nicknames and names of other users in an offensive manner.
5.8. Editing quoted messages, distorting their meaning.
5.9. Publication of personal correspondence without the explicit consent of the interlocutor.
5.11. Destructive trolling is the purposeful transformation of a discussion into a skirmish.
6.1. Overquoting (excessive quoting) of messages.
6.2. Use of a red font intended for corrections and comments by moderators.
6.3. Continuing discussion of topics closed by the moderator or administrator.
6.4. Creation of topics that do not carry semantic content or are provocative in content.
6.5. Creation of the title of a topic or message in whole or in part in capital letters or in a foreign language. An exception is made for the titles of permanent topics and topics opened by moderators.
6.6. Create signature with a font larger than the post font and use more than one palette color in the signature.
7. Sanctions applied to violators of the Forum Rules
7.1. Temporary or permanent ban on access to the Forum.
7.4. Deleting an account.
7.5. IP blocking.
8. Notes
8.1 The application of sanctions by moderators and the administration can be made without explanation.
8.2. Changes may be made to these rules, which will be communicated to all site members.
8.3. Users are prohibited from using clones during the period of time when the main nickname is blocked. In this case, the clone is blocked indefinitely, and the main nickname will receive an additional day.
8.4 A post containing obscene language can be edited by a moderator or administrator.
9. Administration Administration of the site "QUALITY SIGN" reserves the right to delete any messages and topics without giving any reason. The site administration reserves the right to edit messages and user profile if the information in them only partially violates the rules of the forums. These powers apply to moderators and administrators. The administration reserves the right to change or supplement these Rules as necessary. Ignorance of the rules does not relieve the user of responsibility for their violation. The site administration is not able to check all the information posted by users. All messages reflect only the opinion of the author and cannot be used to assess the views of all forum participants in general. The messages of the site staff and moderators are an expression of their personal opinion and may not coincide with the opinion of the editorial board and site management.
Agreement
Rules for registering users on the QUALITY SIGN site:
Registration of users with nicknames like this is prohibited: 111111, 123456, ytsukenb, lox, etc.
It is forbidden to re-register on the site (create duplicate accounts);
It is forbidden to use someone else's data;
It is forbidden to use someone else's e-mail addresses;
Rules of conduct on the website, forum and in the comments:
1.2. Publication of personal data of other users in the profile.
1.3. Any destructive actions in relation to this resource (destructive scripts, guessing passwords, violation of the security system, etc.).
1.4. Using obscene words and expressions as a nickname; expressions that violate the laws of the Russian Federation, the norms of ethics and morality; words and phrases similar to the nicknames of the administration and moderators.
4. Violations of the 2nd category: Punished with a complete ban on sending any types of messages for up to 7 days. 4.1. Placement of information subject to the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation and contrary to the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
4.2. Propaganda in any form of extremism, violence, cruelty, fascism, Nazism, terrorism, racism; incitement of interethnic, interreligious and social hatred.
4.3. Incorrect discussion of the work and insults to the authors of texts and notes published on the pages "SIGN OF QUALITY".
4.4. Threats to the forum participants.
4.5. Placing deliberately false information, slander and other information discrediting the honor and dignity of both users and other people.
4.6. Pornography in avatars, posts and quotes, and links to pornographic images and resources.
4.7. Open discussion of the actions of the administration and moderators.
4.8. Public discussion and evaluation of the current rules in any form.
5.1. Mat and profanity.
5.2. Provocations (personal attacks, personal discrediting, the formation of a negative emotional reaction) and harassment of discussion participants (systematic use of provocations in relation to one or more participants).
5.3. Provoking users to conflict with each other.
5.4. Rudeness and rudeness in relation to interlocutors.
5.5. Transition to individuals and clarification of personal relationships on the forum threads.
5.6. Flood (identical or meaningless messages).
5.7. Intentional misspelling of nicknames and names of other users in an offensive manner.
5.8. Editing quoted messages, distorting their meaning.
5.9. Publication of personal correspondence without the explicit consent of the interlocutor.
5.11. Destructive trolling is the purposeful transformation of a discussion into a skirmish.
6.1. Overquoting (excessive quoting) of messages.
6.2. Use of a red font intended for corrections and comments by moderators.
6.3. Continuing discussion of topics closed by the moderator or administrator.
6.4. Creation of topics that do not carry semantic content or are provocative in content.
6.5. Creation of the title of a topic or message in whole or in part in capital letters or in a foreign language. An exception is made for the titles of permanent topics and topics opened by moderators.
6.6. Create signature with a font larger than the post font and use more than one palette color in the signature.
7. Sanctions applied to violators of the Forum Rules
7.1. Temporary or permanent ban on access to the Forum.
7.4. Deleting an account.
7.5. IP blocking.
8. Notes
8.1 The application of sanctions by moderators and the administration can be made without explanation.
8.2. Changes may be made to these rules, which will be communicated to all site members.
8.3. Users are prohibited from using clones during the period of time when the main nickname is blocked. In this case, the clone is blocked indefinitely, and the main nickname will receive an additional day.
8.4 A post containing obscene language can be edited by a moderator or administrator.
9. Administration Administration of the site "QUALITY SIGN" reserves the right to delete any messages and topics without giving any reason. The site administration reserves the right to edit messages and user profile if the information in them only partially violates the rules of the forums. These powers apply to moderators and administrators. The administration reserves the right to change or supplement these Rules as necessary. Ignorance of the rules does not relieve the user of responsibility for their violation. The site administration is not able to check all the information posted by users. All messages reflect only the opinion of the author and cannot be used to assess the views of all forum participants in general. The messages of the site staff and moderators are an expression of their personal opinion and may not coincide with the opinion of the editorial board and site management.
Krysko V.G.Social Psychology: Schemes and Comments... - M .: Publishing house VLADOS-IPECC, 2001.-208 p.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SOCIAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL EVENTS
The most difficult task today is not to know and use the surrounding nature, but to understand the mechanisms of one's own and social behavior and learn how to manage it.
As the social life of people is multifaceted, so are the socio-psychological phenomena. However, they are all the result of human interaction.
From the point of view of philosophy, interaction is an objective and universal form of movement, development, which determines the existence and structural organization of any material system. Interaction as a material process is accompanied by the transfer of matter, motion and information. It is relative, carried out at a certain speed and "in a certain space-time.
In turn, psychological science considers interaction as a process of people influencing each other, giving rise to their mutual connections, relationships, communication, joint actions and experiences. Interaction, therefore, must be taken as the unit of analysis in social psychology.
Meanwhile, social and psychological phenomena and processes are very diverse. It is possible to understand and comprehensively comprehend them only if the grounds for their classification are correctly constructed, the general and the particular are naturally highlighted in them, and on this basis additional opportunities for comparison and comparison are found.
In all the diversity of social life, there is not and cannot be a single event or person to which it would be permissible to treat lightly and carelessly.
DI. Pisarev
Interaction- it is a process of direct or indirect influence of social objects (subjects) on each other, giving rise to their mutual conditioning and connection
It is causality that constitutes the main feature of interaction, when each of the interacting parties acts as the cause of the other and as a consequence of the simultaneous reverse influence of the opposite side, which determines the development of objects and their structures
In addition, interaction in social psychology usually means not only the influence of people on each other, but also the direct organization of their joint actions, which allows the group to realize the common activity for its members.
Interaction is always present as two components of content and style
Style interactions indicates how a person interacts with others
You can talk about productive and unproductive interaction styles Productive style is a fruitful way of contact between partners, contributing to the establishment and manifestation of relationships of mutual trust, the disclosure of personal potentials and the achievement of effective results in joint activities
Unproductive interaction style is an unproductive way of contact between partners, blocking the realization of personal potentials and the achievement of optimal results of joint activities
Usually, there are five main criteria that allow you to correctly understand the style of interaction.
1 The nature of activity in the position of partners (in a productive style - "next to a partner", in an unproductive style - "above a partner")
2 The nature of the goals put forward (in a productive style, partners jointly develop both near and distant goals, in an unproductive one - the dominant partner puts forward only close goals without discussing them with a partner)
3 The nature of responsibility (in a productive style, all participants in the interaction are responsible for the results of activities, in an unproductive style - all responsibility is attributed to the dominant partner)
4 The nature of the relationship that arises between partners (in a productive style - benevolence and trust, in an unproductive style - aggression, resentment, irritation)
5 The nature of the functioning of the mechanism of identification-isolation between partners

In interaction, a person's attitude to another person is realized as to a subject who has his own world.People-to-person interaction in society is also the interaction of their inner worlds, the exchange of thoughts, ideas, images, influence on goals and needs, influence on the assessments of another individual, his emotional state
Interaction, in addition, can be represented as a systematic, constant implementation of actions aimed at evoking an appropriate reaction from other people. Joint life and activity, in contrast to the individual, has at the same time more severe restrictions on any manifestations of the activity-passivity of individuals.This forces people to build and to coordinate the images of "I-He", "We-They", to coordinate efforts between them In the course of real interaction, a person's adequate ideas about himself, other people, and their groups are also formed The interaction of people is a leading factor in the regulation of their self-esteem and behavior in society
Interpersonal interaction - these are accidental or intentional, private or public, long-term or short-term, verbal or non-verbal contacts and connections
significant changes in their behavior, activities, attitudes and attitudes
The main features such interaction are
The presence of a goal (object) external to the interacting individuals, the achievement of which presupposes mutual efforts,
Explication (availability) for observation from the outside and registration by other people,
Reflexive polysemy - the dependence of its perception on the conditions of implementation and assessments of its participants
Intergroup interaction - it is a process of direct or indirect influence of multiple subjects (objects) on each other, giving rise to their mutual conditioning and a peculiar nature of relations.It usually takes place between whole groups (as well as their parts) and acts as an integrating (or destabilizing) factor in the development of society
Interaction has three levels of development - lower, middle and supreme, - each of which has its own distinctive characteristics (cm 2 3)
Consider the day and the hour unhappy when you haven't learned anything new.
Jan Amos Kamensky

On his initial (lower) level interaction is the simplest primary contacts of people, when between them there is only a primary and very simplified mutual or one-sided "physical" influence on each other for the purpose of information exchange and communication. For specific reasons, such interaction may not achieve its goal, and therefore may not receive all-round development.
The main thing that determines the success of initial contacts is the acceptance or rejection of each other by the interaction partners. Moreover, they do not constitute a simple sum of individuals, but are some completely new and specific formation of connections and relationships, which is regulated by real or imaginary (imagined) difference-similarity, similarity-contrast of people involved in joint activities (practical or mental) Any contact is usually begins with a concrete-sensory perception of the external appearance, features of the activity and behavior of other people.
The congruence effect also plays an important role in the interaction at its initial stage. Congruence - confirmation of mutual role expectations, complete mutual understanding, a single resonant rhythm, consonance of the experiences of the participants in the contact. It assumes a minimum of mismatches in the key moments of the lines of behavior of the participants in the contact, the result of which is the release of tension, the emergence of trust and sympathy at the subconscious level.
On middle level development of the process of human interaction is called productive joint activity. Here, the gradually developing active cooperation between them finds more and more expression in the effective solution of the problem of combining mutual efforts of partners.
At this time, there is a constant coordination of thoughts, feelings, relationships of partners in joint life. It is clothed in various forms of people's influence on each other. The mechanisms of suggestion, conformity and persuasion are the regulators of mutual influences, when, under the influence of the opinions, relations of one partner, the opinions and attitudes of the other change.
The highest level interaction is always an extremely effective joint activity of people, accompanied by mutual understanding. Mutual understanding between people is such a level of their interaction at which they are aware of the content and structure of the present and possible next action of the partner, and also mutually contribute to the achievement of a common goal. For mutual understanding, joint activities are not enough, mutual assistance is needed. It excludes its antipode - mutual opposition, with the appearance of which there is a misunderstanding, and then a misunderstanding of man by man.

Based on the results of the focus, several types of interaction are usually distinguished.
The most common is the dichotomous division of cooperation and competition (agreement and conflict, accommodation and opposition)
Cooperation - this is such an interaction in which its subjects reach a mutual agreement on the pursued goals and strive not to violate it as long as their interests coincide
Competition is an interaction characterized by the achievement of individual or group goals and interests in a confrontation between people
In both cases, both the type of interaction (cooperation or rivalry) and the degree to which this interaction is expressed (successful or less successful cooperation) determines the nature of interpersonal relationships between people
In the process of implementing these types of interaction, as a rule, the following leading strategies of behavior are manifested
1 Cooperation aimed at full satisfaction by the participants of the interaction of their needs (either the motive of cooperation or the motive of competition is realized)
2 Counteraction, which involves focusing on one's own goals without taking into account the goals of communication partners (individualism)
3 Compromise, realized in the private achievement of the goals of partners for the sake of conditional equality
4 Compliance, involving the sacrifice of self-interest to achieve the goals of a partner (altruism)
5 Avoidance, which is withdrawal from contact, the loss of one's own goals in order to exclude the gain of another
The division into types can also be based on intentions and actions of people, which reflect their understanding of the communication situationThere are three types of interactions: additional, intersecting and hidden
Additional is called such an interaction in which partners adequately perceive each other's position
Intersecting - this is such an interaction, in the process of which the partner, on the one hand, demonstrates an inadequacy of understanding of the positions and actions of the other participant in the interaction, and on the other hand, clearly manifests his own intentions and actions
Hidden interaction includes two levels at the same time, explicit, expressed verbally, and hidden, implied.It implies either deep knowledge of the partner, or greater sensitivity to non-verbal means of communication - tone of voice, intonation, facial expressions and gestures, since it is they who convey hidden content

In any act of interaction between people, their relationship to each other is always present.
The concept of "attitude" acts as a basic category of psychological science It finds concrete embodiment in any contacts, interactions of a person with a person, material and ideal things and phenomena. Attitude, as it were, emotionally colors any connection between an individual and the outside world. Even indifference to someone, something is attitude In other words, an attitude is an attribute of any human connection, direct and mediated, physical and ideal
Through the attitude, the system of needs, motives, drives of a person is determined.In this case, the attitude acts as an indicator and means of expression, objectification of all human actions
The attitude is thus - it is a socialized connection between the internal and external content of the human psyche, its connection with the surrounding reality and consciousness
Relations within the framework of "subject-object" and "subject-subject" are not identical. Thus, the activity (or severity) of the relationship, modality (positive, negative, neutral), breadth, stability, etc. are common for one and the other connection. At the same time, the one-directionality and reciprocity of relations differ significantly within the framework of the subject-object and subject-subject connection. Only under the condition of reciprocity of relations is it possible to form a "joint fund" of general and new intersubjective education (thoughts, feelings, actions), when it is difficult to say where one's own and where another's, both of which become ours.
Subject-subject relations are characterized by both constant reciprocity and variability, which is determined by the activity of not only one of the parties, as is the case with subject-object relations, where stability depends more on the subject than on the object.
Subject-subjective relations, in addition, include not only the relationship of a person with another person, but also the attitude towards oneself, that is, self-attitude. In turn, subject-object relations are all relations of a person to reality, excluding relations between people and self-relation.
Relationships can be divided into situational and sustainable. The last type of relationship is close to such a psychological phenomenon as attachment, which acts as a stable relationship characterized by dependence on something and someone

In the process of production and consumption of material goods, people enter into various kinds of relationships, which, as already mentioned, are based on their interaction with each other. In the course of such interaction, social relations arise. The nature and content of the latter are largely determined by the specifics and circumstances of the interaction itself, the goals pursued by specific people, as well as the place and role they occupy in society.
Public relations can be classified on the basis of different criteria: 1) according to the form of manifestation, public relations are divided into economic (production), legal, ideological, political, moral, religious,aesthetic etc.; 2) from the point of view of belonging to different subjects, relations are distinguished national (interethnic), class, confessional etc.; 3) based on the analysis of the functioning of connections between people in society, we can talk about relations on vertical and horizontal, 4) by the nature of the regulation, public relations are official and unofficial.
All types of social relations are permeated, in turn, by the psychological relations of people (synonym: relationships), i.e. subjective connections that arise as a result of their actual interaction and are already accompanied by various emotional and other experiences (likes and dislikes) of the individuals participating in them. Psychological relationships are the living human tissue of any social relationship.
Difference between social and psychological relations is that the former are by their nature, so to speak, “material”, are a consequence of a certain property, social and other distribution of roles in society and in most cases are taken for granted, are, in a sense, impersonal. In social relations, first of all, the essential features of social ties between the spheres of human activity, types of labor and communities are revealed.
Psychological relationships are the result of direct contacts between specific people endowed with certain characteristics, capable of expressing their likes and dislikes, realizing and experiencing them. They are full of emotions and feelings, i.e. the experience and expression by individuals or groups of their attitude towards interaction with other specific people and groups.
Psychological relationships are completely personified, as they are purely personal in nature. Their content and specificity depend on the specific people between whom they arise.

The general criterion for dividing interpersonal relationships into types is attractiveness
The constituent elements of mutual attractiveness-unattractiveness include sympathy-antipathy and attraction-repulsion.
Sympathy-antipathy represents the experienced satisfaction-dissatisfaction from real or mental contact with another person
Attraction-repulsion there is a practical component to these experiences
Attraction-repulsion is mainly associated with a person's need to be together, near Attraction-repulsion is often, but not always, associated with the experience of likes and dislikes (the emotional component of interpersonal relationships) something pulls, without visible satisfaction of the need to be together and near "
We can talk about the following types of interpersonal relationships relationship acquaintance, buddy, comradely, friendship, love, conjugal, kindred,destructive. This classification is based on several criteria 1) the depth of the relationship, 2) selectivity in the choice of partners, 3) the function of the relationship
The main criterion is the measure, the depth of the person's involvement in relationships. Different types of interpersonal relationships imply the inclusion of certain levels of personality characteristics in communication.The greatest inclusion of the personality, up to individual characteristics, occurs in friendly and marital relations.
Second criterion- the degree of selectivity in choosing partners for relationships Selectivity can be defined as the number of signs that are significant for the establishment and reproduction of a relationship.The greatest selectivity is found in relations of friendship, marriage, love, the least - in relationships of acquaintance
Third criterion- the difference in the functions of relations The functions are understood as a range of tasks, issues that are solved in interpersonal relationships.The functions of relations are manifested in the difference in their content, psychological meaning for partners
In addition, each interpersonal relationship is characterized by a certain distance between partners, assumes one or another measure of participation of role cliches.

Understanding- a socio-psychological phenomenon, the essence of which is manifested in 1) coordination of individual understanding of the subject of communication and 2) mutually acceptable bilateral assessment and acceptance of goals, motives and attitudes of interaction partners, in the course of which there is closeness or similarity (full or partial) of cognitive, emotional and behavioral responding to acceptable ways for them to achieve results of joint activities
The reasons for the misunderstanding may be
1) the absence or distortion of people's perception of each other,
2) differences in the structure of presentation and perception of speech and other signals,
3) lack of time for mental processing of received and issued information,
4) deliberate or accidental distortion of the transmitted information,
5) inability to correct an error or clarify data,
6) the lack of a single conceptual apparatus for assessing the personal qualities of a partner, the context of his speech and
behavior,
7) violation of the rules of interaction in the process of performing a specific task,
8) loss or transfer to another target of joint actions, etc.
To achieve mutual understanding between people, it is necessary to create special conditions.
The most important terms of understanding are:
1) understanding the speech of the interacting person,
2) awareness of the manifested qualities of the interacting personality,
3) identification of the influence on the personality of the situation of interaction with a partner,
4) the development of an agreement and its practical implementation in accordance with the established rules
Compliance with the conditions of mutual understanding in practice, in life is the criterion of the achieved mutual understanding
It will be the higher, the more the developed interaction rules are acceptable for joint activities.
They should not bind partners For this, they must be periodically corrected, that is, the joint efforts of people and the circumstances of their implementation must be coordinated
It is best to do this in a situation of equal status of individuals.

A person understands only what finds a response in his memory - for understanding, some knowledge about what is understood is always needed.
To achieve mutual understanding, people must proceed from the same postulates of communication and interaction and correlate the subject of discussion with the same social patterns and norms of behavior.
You cannot understand another person without entering into a personal relationship with him, without showing empathy towards him.
But first of all a person usually understands what corresponds to his predictions, hypotheses, goals:
- anticipation of possible situations allows you to comprehend those circumstances that will hinder mutual understanding;
- choosing your angle of view on an object provides an opportunity to defend their own positions in communication and relationships;
- point of view hypotheses partners allow you to avoid conflicts of understanding;
--- agreement on common points of view completely prevents possible mutual misunderstanding.
Mutual understanding can be predicted based on people's attitudes to the psychological and value-semantic positions of partners.
In this case, the criteria that help build assumptions about possible mutual understanding are:
Assumptions of each participant about knowledge of the subject of activity by partners, their competence;
Forecast of the attitude of partners to the subject of common activity, its significance for both parties;
Reflection: the subject's understanding of how the partner (s) perceive him;
Assessment of the psychological qualities of partners in communication and interaction.
Be able to understand the psychological qualities of other people, and then you will understand what their inner world is.
Lope de Vega

Communication-a complex multidimensional process of establishing and developing contacts and connections between people, generated by the needs of joint activities and including the exchange of information and the development of a unified strategy of interaction.
Communication is usually included in the practical interaction of people (joint work, learning, team play, etc.) and provides planning, implementation and control of their activities.
If the relationship is defined through the concept of "connection", then communication is understood as a process of human-human interaction, carried out using the means of speech and non-speech influence and pursuing the goal of achieving changes in the cognitive, motivational, emotional and behavioral spheres of persons involved in communication.
In the course of communication, its participants exchange not only their physical actions or products, the results of labor, but also thoughts, intentions, ideas, experiences, etc.
In everyday life, a person learns to communicate from childhood and masters its different types depending on the environment in which he lives, on the people with whom he interacts, and this happens spontaneously, in everyday experience. In most cases, this experience is not enough, for example, for mastering special professions (teacher, actor, announcer, investigator), and sometimes just for productive and civilized communication.
For this reason, it is necessary to improve the knowledge of its laws, to accumulate skills and abilities to take them into account and use them.
Each community of people has its own means of influence, which are used in various forms of collective life. They concentrate the socio-psychological content of the way of life. All this manifests itself in customs, traditions, rituals, rituals, holidays, dances, songs, legends, myths, in the visual, theatrical and musical arts, in fiction, cinema, radio and television. These peculiar mass forms of communication have a powerful potential for mutual influence of people. In the history of mankind, they have always served as a means of education, the inclusion of a person through communication in the spiritual atmosphere of life.
The human problem is the focus of all aspects of communication. Passion for only the instrumental side of communication can neutralize its spiritual (human) essence and lead to a simplified interpretation of communication as information and communication activity. With the inevitable scientific and analytical division of communication into its constituent elements, it is important not to lose a person in them as a spiritual and active force that transforms oneself and others in this process.
Communication in its content is the most difficult psychological activity of partners.

Communication usually manifests itself in the unity of its five sides - interpersonal, cognitive, communicative-informational, emotive and conative.
The interpersonal side communication reflects the interaction of a person with the immediate environment with other people and those communities with which he is associated with his life
The cognitive side communication allows you to answer questions about who the interlocutor is, what kind of person he is, what you can expect from him, and many others related to the personality of the partner
Communication and informationside is an exchange between people of various ideas, ideas, interests, moods, feelings, attitudes, etc.
Emotive side communication is associated with the functioning of emotions and feelings, mood in personal contacts of partners
Conative(behavioral) side communication serves the purpose of reconciling internal and external contradictions in the positions of partners
Communication has certain functions.
There are six of them:
1 Pragmatic function communication reflects its need-motivational reasons and is realized when people interact in the process of joint activities. At the same time, communication itself is very often the most important need.
2 Forming function and development reflects the ability of communication to influence partners, developing and improving them in all respects. Communicating with other people, a person assimilates common human experience, historically established social norms, values, knowledge and methods of activity, and is also formed as a person. In general, communication can be defined as a universal reality in which mental processes, states and human behavior arise, exist and manifest themselves throughout life.
3 Confirmation function provides people with the opportunity to know, validate and validate themselves
4 Merge-decouple function of people, on the one hand, through the establishment of contacts between them, it facilitates the transfer of the necessary information to each other and adjusts them to the implementation of common goals, intentions, tasks, thereby uniting them into a single whole, and on the other hand, it can be the cause of differentiation and isolation of individuals as a result communication
5 Organization and maintenance function relationship serves the interests of establishing and maintaining sufficiently stable and productive ties, contacts and relationships between people in the interests of their joint activities
6 Intrapersonal function communication is realized in a person's communication with himself (through internal or external speech, built according to the type of dialogue)

Communication is extremely versatile It can be presented in its variety by types
Distinguish between interpersonal and mass communication
Interpersonal communicationassociated with direct contacts of people in groups or pairs, constant in the composition of the participants
Mass communication- it is a lot of direct contacts of strangers, as well as communication mediated by various types of media
There are also interpersonal communication and role-playing. In the first case, the participants in communication are specific individuals with specific individual qualities that are revealed in the course of communication and organization of joint actions.
In the case of role-based communication, its participants act as carriers of certain roles (buyer-seller, teacher-student, boss-subordinate)
In role-based communication, a person loses a certain spontaneity of his behavior, since certain of his steps, actions are dictated by the role played
In the process of such communication, a person no longer manifests himself as an individual, but as a certain social unit that performs certain functions.
Communication can also be confidential and conflicting The first is distinguished by the fact that especially significant information is transmitted during its course.
Trust is an essential feature of all types of communication, without it you cannot carry out negotiations, resolve intimate issues
Conflicting communicationcharacterized by mutual opposition of people, expressions of displeasure and distrust
Communication can be personal and business Personal communication- this is an exchange of unofficial information
Business conversation- the process of interaction of people performing joint duties or involved in the same activity
Finally, communication can be direct and mediated. Direct(direct) communicationis historically the first form of communication between people On its basis, in the later periods of the development of civilization, various types of mediated communication arise.
Mediated communication- this interaction with the help of additional means (letters, audio and video equipment) *
" Some types of communication available on the diagram are not commented on, since their meaning is clear without explanation.

Communication is possible only with the help of sign systems. Distinguish between verbal means of communication (when speech is used) and non-verbal means of communication, when non-verbal means of communication are used.
V verbal communication * usually two versions of speech are used: oral and written Written speech is that which is taught in school and which is used to consider a sign of a person's education.
Oral speech, which in a number of parameters differs from written speech, is not an illiterate written speech, but an independent speech with its own rules and even grammar.
Non-verbal means of communication are needed in order to regulate the course of the communication process, create psychological contact between partners, enrich the meanings conveyed by words, guide the interpretation of the verbal text, express emotions and reflect the interpretation of the situation
They are divided into:
1 Visual means of communication are:
Kinesika - movements of arms, legs, head, torso,
Direction of gaze and eye contact,
The expression in the eyes
Facial expression,
Pose (in particular, localization, changing poses relative to the verbal text);
Skin reactions (redness, sweating),
Distance (distance to the interlocutor, angle of rotation to him, personal space),
Aids to communication, including physique features (gender, age) and means of their transformation (clothing, cosmetics, glasses, jewelry, tattoo, mustache, beard, cigarette, etc.)
2 Acoustic(sound) means of communication are:
Paralinguistic, that is, associated with speech (intonation, volume, timbre, tone, rhythm, pitch, speech pauses and their localization in the text),
Extra-linguistic, those not related to speech (laughing, crying, coughing, sighing, gnashing of teeth, sniffing, etc.)
3 Tactile-kinesthetic(touch-related) communication means:
Physical impact (leading a blind person by the hand, contact dance, etc.),
Takeshika (shaking hands, clapping on the shoulder)
4 Olfactory means of communication are:
Pleasant and unpleasant smells of the environment,
Natural and artificial human odors, etc.
* The characteristics of verbal communication are not included in the commentary, as they are well studied in general psychology

Communication- it is a connection during which information is exchanged between systems in living and inanimate nature.
Communication between people has a number of specific features:
1. Cash relationship of two individuals, each of whom is an active subject. At the same time, their mutual informing presupposes the establishment of joint activities.
The specificity of human exchange of information lies in the special role for each participant in the communication of this or that information, its significance.
2. Possibility of mutual influence of partners on each other through a system of signs.
3. Communicative influence only in the presence of a single or similar system of codification and decodification in the communicator (the person sending the information) and the recipient (the person receiving it).
4. Possibility of emergence of communication barriers. In this case, the connection that exists between communication and attitude clearly stands out.
Distribution media. The dissemination of information in society passes through a kind of "trust-distrust filter". Such a filter acts in such a way that true information may not be received, and false information may be received. In addition, there are means to facilitate the reception of information and weaken the effect of filters. The combination of these funds is called fascination. At-
the measure of fascination can be musical, spatial or color accompaniment of speech.
Content and type of information . In the process of communication, the participants in communication are faced with the task of not only exchanging information, but also achieving its adequate understanding by partners. That is, in interpersonal communication, the interpretation of the message coming from the communicator to the recipient is highlighted as a special problem. Barriers can arise during communication. Communication barrier- this is a psychological obstacle to the adequate transfer of information between communication partners.
The model of the communicative process usually includes five elements: communicator - message (text) - channel - audience (recipient) - feedback.
the main goal information exchange in communication - the development of a common meaning, a unified point of view and agreement about various situations or problems. It is characterized by feedback mechanism. The content of this mechanism lies in the fact that in interpersonal communication the process of information exchange doubles as it were, and in addition to the content aspects, the information coming from the recipient to the communicator contains information about how the recipient perceives and evaluates the behavior of the communicator.

Social perception -this is the process of perceiving social objects, which usually mean people and social groups
Features social perception are
1 The activity of the subject of social perception, meaning that he (an individual, a group, etc.) is not passive and not indifferent to the perceived, as is the case with the perception of inanimate objects And the object and the subject of social perception affect each other, seek to transform ideas about themselves in a favorable direction
2 The integrity of the perceived, showing that the attention of the subject of social perception is focused primarily not on the moments of generating an image as a result of the reflection of perceived reality, but on semantic and evaluative interpretations of the object of perception
3 The motivation of the subject of social perception, which indicates that the perception of social objects is characterized by a great fusion of his cognitive interests with emotional attitudes to the perceived, the obvious dependence of social perception on the motivational and semantic orientation of the perceiver.
Social perception usually manifests itself as:
1 Perception by group members
a) each other,
b) members of another group
2 Human perception:
a) yourself,
b) your group,
c) "outgroup"
3 Group perception:
a) your person,
b) members of another group
4 A group's perception of another group (or groups).
Social Perception Process represents the activity of its subject (observer) to assess the external appearance, psychological characteristics, actions and deeds of the observed person or object, as a result of which the subject of social perception develops a specific attitude towards the observed and forms certain ideas about the possible behavior of specific people and groups
Depending on these ideas, the subject of social perception predicts both his own relationships and behavior in various situations of interaction and communication with other people.

The perception of other people is greatly influenced by the process of stereotyping. Undersocial stereotype is understood as a stable image or idea of any phenomena or people characteristic of representatives of a particular social group
For a person who has mastered the stereotypes of his group, they perform the function of simplifying and reducing the process of perception of another person. Stereotypes are a tool of “rough adjustment” that allows a person to “save” psychological resources. They have their own “permitted” sphere of social application. group national or professional identity of a person
Identification is a socio-psychological process of cognition by a person or a group of other people in the course of direct or indirect contacts with them, in which a comparison or comparison of the internal states or position of partners, as well as role models with their psychological and other characteristics is carried out
Identification, as opposed to narcissism, plays a huge role in the behavior and spiritual life of a person. Its psychological meaning lies in expanding the range of experiences, in enriching inner experience. It is known as the earliest appearance of emotional attachment to another person. On the other hand, identification often acts as an element of psychological protection of people from objects and situations that cause fear, giving rise to anxiety and stress.
Empathy - this is emotional empathy for another person Through an emotional response, people know the internal state of others Empathy is based on the ability to correctly imagine what is happening inside another person, what he is experiencing, how the world around him assesses It is almost always interpreted not only as an active assessment by the subject of experiences and feelings knowing person, but also certainly as a positive attitude towards a partner
Attraction is a form of cognition of another person, based on the formation of a stable positive feeling towards him In this case, understanding of the interaction partner arises due to the appearance of an attachment to him of a friendly or deeper intimate-personal relationship
All other things being equal, people more easily accept the position of the person towards whom they experience an emotionally positive attitude.
Reflection - This is a mechanism of self-knowledge in the process of interaction, which is based on a person's ability to imagine how he is perceived by a communication partner. This is not just knowing or understanding a partner, but knowing how a partner understands me, a kind of doubled process of mirroring relationships with each other.
Casual attribution - the mechanism of interpretation of the actions and feelings of another person (causal attribution - the desire to clarify the reasons for the behavior of the subject).
Research shows that each person has their own “favorite” schemes of causality, ie. Common explanations for someone else's behavior:
1) people with personal attribution in any situation tend to find the culprit of what happened, attribute the cause of what happened to a specific person;
2) in the case of addiction to circumstantial attribution, people tend to blame the circumstances first of all, without bothering to find a specific culprit;
3) with stimulus attribution, a person sees the cause of what happened in the object to which the action was directed (the vase fell because it was not standing well) or in the victim himself (it is his own fault that he was hit by a car).
When studying the process of causal attribution, various patterns have been identified. For example, people most often attribute the cause of success to themselves, and failure to the circumstances. The nature of the attribution also depends on the degree of participation of a person in the event under discussion. The score will be different in cases if he was a participant (accomplice) or an observer. The general pattern is that as the significance of what happened, the subjects are inclined to move from adverbial and stimulus attribution to personal (that is, to look for the cause of what happened in the conscious actions of the individual).
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OF PERSONALITY
Personality is the subject and object of social relations.
A. G. Kovalev
The human psyche, the world of his mental phenomena - a derivative not only of his own development, but also the result of the impact of the surrounding world, social relations. The wealth of a person's psyche depends on the diversity of his connections with other people, on an active attitude to life. In this case, a person appears as a person, as a member of society.
The personality of a person as a member of society is in the sphere of influence of various relations emerging first of all in the process of production and consumption of material goods.
Personality is also in the sphere political relations. The psychology of the individual depends on whether she is free or oppressed, has political rights or not, can really elect and be elected, discuss issues of public life, or is the executor of the will of the ruling class.
Personality is in scope ideological relations. Ideology as a system of ideas about society has a huge impact on the individual, in many respects forms the content of her psychology, worldview, individual and social attitudes.
At the same time, personality psychology is influenced by relationships of people in a social group, which the person enters into. In the process of interaction and communication, people mutually influence each other, as a result of which a community is formed in views, social attitudes and other types of attitudes towards society, work, people, and their own qualities. At the same time, in a group, a person gains a certain authority, occupies a certain position, plays certain roles.
Personality is not only an object of social relations, but also their subject, i.e. active link. Entering into relationships with people, individuals create history, but they do it not arbitrarily, but out of necessity, under the influence of objective social laws. However, historical necessity does not exclude either the identity of the individual or his responsibility for his behavior to society.
Personality is an active and conscious being. She can choose one way or another way of life: resign herself to the position of the oppressed or fight against injustice, give her life to society or live for personal interests.

Personality- this is a specific person who is a representative of a certain society, a certain social group, engaged in a specific type of activity, realizing his attitude to the environment and endowed with certain individually psychological characteristics
The personality is distinguished first of all by its social essence. Outside of society, outside of a social and professional group, a person cannot become a person, i.e. nature creates a person, and shapes his society
Agreement
Rules for registering users on the QUALITY SIGN site:
Registration of users with nicknames like this is prohibited: 111111, 123456, ytsukenb, lox, etc.
It is forbidden to re-register on the site (create duplicate accounts);
It is forbidden to use someone else's data;
It is forbidden to use someone else's e-mail addresses;
Rules of conduct on the website, forum and in the comments:
1.2. Publication of personal data of other users in the profile.
1.3. Any destructive actions in relation to this resource (destructive scripts, guessing passwords, violation of the security system, etc.).
1.4. Using obscene words and expressions as a nickname; expressions that violate the laws of the Russian Federation, the norms of ethics and morality; words and phrases similar to the nicknames of the administration and moderators.
4. Violations of the 2nd category: Punished with a complete ban on sending any types of messages for up to 7 days. 4.1. Placement of information subject to the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation and contrary to the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
4.2. Propaganda in any form of extremism, violence, cruelty, fascism, Nazism, terrorism, racism; incitement of interethnic, interreligious and social hatred.
4.3. Incorrect discussion of the work and insults to the authors of texts and notes published on the pages "SIGN OF QUALITY".
4.4. Threats to the forum participants.
4.5. Placing deliberately false information, slander and other information discrediting the honor and dignity of both users and other people.
4.6. Pornography in avatars, posts and quotes, and links to pornographic images and resources.
4.7. Open discussion of the actions of the administration and moderators.
4.8. Public discussion and evaluation of the current rules in any form.
5.1. Mat and profanity.
5.2. Provocations (personal attacks, personal discrediting, the formation of a negative emotional reaction) and harassment of discussion participants (systematic use of provocations in relation to one or more participants).
5.3. Provoking users to conflict with each other.
5.4. Rudeness and rudeness in relation to interlocutors.
5.5. Transition to individuals and clarification of personal relationships on the forum threads.
5.6. Flood (identical or meaningless messages).
5.7. Intentional misspelling of nicknames and names of other users in an offensive manner.
5.8. Editing quoted messages, distorting their meaning.
5.9. Publication of personal correspondence without the explicit consent of the interlocutor.
5.11. Destructive trolling is the purposeful transformation of a discussion into a skirmish.
6.1. Overquoting (excessive quoting) of messages.
6.2. Use of a red font intended for corrections and comments by moderators.
6.3. Continuing discussion of topics closed by the moderator or administrator.
6.4. Creation of topics that do not carry semantic content or are provocative in content.
6.5. Creation of the title of a topic or message in whole or in part in capital letters or in a foreign language. An exception is made for the titles of permanent topics and topics opened by moderators.
6.6. Create signature with a font larger than the post font and use more than one palette color in the signature.
7. Sanctions applied to violators of the Forum Rules
7.1. Temporary or permanent ban on access to the Forum.
7.4. Deleting an account.
7.5. IP blocking.
8. Notes
8.1 The application of sanctions by moderators and the administration can be made without explanation.
8.2. Changes may be made to these rules, which will be communicated to all site members.
8.3. Users are prohibited from using clones during the period of time when the main nickname is blocked. In this case, the clone is blocked indefinitely, and the main nickname will receive an additional day.
8.4 A post containing obscene language can be edited by a moderator or administrator.
9. Administration Administration of the site "QUALITY SIGN" reserves the right to delete any messages and topics without giving any reason. The site administration reserves the right to edit messages and user profile if the information in them only partially violates the rules of the forums. These powers apply to moderators and administrators. The administration reserves the right to change or supplement these Rules as necessary. Ignorance of the rules does not relieve the user of responsibility for their violation. The site administration is not able to check all the information posted by users. All messages reflect only the opinion of the author and cannot be used to assess the views of all forum participants in general. The messages of the site staff and moderators are an expression of their personal opinion and may not coincide with the opinion of the editorial board and site management.