Suspected diabetes symptoms. Folk remedies. Treatment of complications of diabetes mellitus
Today there are two types of diabetes. This is due to the fact that, on the one hand, these are diseases of different origin, and on the other, they have a common feature - increased content blood sugar, which unites them into one disease - diabetes mellitus. While type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes is a rare disease, type II (non-insulin dependent) diabetes is quite common. For example, in Germany there are approximately 150-200 thousand type I diabetes patients and about 5 million type II diabetics. With non-insulin-dependent diabetes, the body either lacks insulin, or too much of it, but it cannot be used correctly.
Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with damage, dysfunction, and failure of various instruments, especially the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels... In young people, diabetes is caused by the destruction or destruction of the cells in the pancreas responsible for the production and secretion of insulin. This type of diabetes is called type 1 diabetes, type 1 diabetes, or type 2 diabetes.
In older people, usually obese and overweight, diabetes causes insulin resistance. This type of diabetes is called type 2 and requires continuous intake of appropriate oral medications... Often, insulin injections will also need to be given over time.
There are several main reasons for the development of non-insulin dependent diabetes:
1. Obesity.
2. Unhealthy diet (high-calorie food, excess consumption of animal fats, systematic consumption of alcohol, smoking, lack of coarse fiber dietary fiber), which leads to obesity and disease gastrointestinal tract that contributes to the development of diabetes.
Untreated or improperly treated diabetes is a major direct and indirect cause of disability and early death. The long-term effects of hyperglycemia are the cause of chronic complications of diabetes. Diabetes occurs in all human races as well as in animals. They described the symptoms of type 1 diabetes. The first clinical description of this disease was given by the Greek physician Arteus from Cappadocia.
To explain diabetes mellitus, we get a sweet leak. The name of this disease is associated with the secretion of excess sugar in the urine. This was the first symptom that led to the diagnosis of diabetes. Initially, there was no reason for her. Currently, over 3.1 million Poles suffer from diabetes in Poland. Over the past decade, the number of patients with diabetes has doubled.
3. A sedentary lifestyle, in which the use of glucose by tissues is reduced.
4. Mental and emotional overload, frequent stress, causing increased secretion of hormones, which contributes to the development of diabetes. Chronic gastritis, cholecystitis, accompanied by disruption of gastrointestinal hormones that regulate insulin and glucose levels.
More than 30% of them still remain unrecognized. It is estimated that about 1 million patients in Poland are completely unaware of their illness. 60% of Poles who are at high risk of diabetes do not know or suspect that they can get diabetes. Patients inform the doctor when he is already very advanced.
Diabetes is a metabolic disease that is difficult to diagnose and does not initially show any symptoms, but people who have risk factors for developing it should be tested regardless of symptoms. If the diagnosis is not diagnosed, it can lead to a number of health complications. Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by elevated level glucose in the blood, which is caused by insufficient production of insulin, which the body cannot process. This leads to functional disorders and symptoms suggestive of diabetes.

5. Ischemic disease heart, contributing to the development of diabetes, as the body's sensitivity to insulin decreases.
7. The use of certain drugs, especially diuretics, antihypertensive drugs (clonidine, Gemiton, etc.), drugs containing adrenaline, cytostatic agents, hormonal drugs(including prednisone), some contraceptives.
Diabetes has many symptoms, many of which can easily be attributed to other ailments such as stress, pallor, cold sweats, bowel problems, heart palpitations, anxiety, lack of concentration, and this can make a quick diagnosis difficult. Symptoms common to diabetes include increased thirst, visual disturbances, weight loss, itchy skin, and relapses. At an advanced stage of the disease, the warning signal may also be panic attacks as well as dizziness, speech disorders, vision and concentration, such symptoms should not be underestimated and consult a doctor as soon as possible!
Such diabetes can be “managed” through diet and combinations of antidiabetic pills that regulate the body's production of insulin or lower blood sugar levels. Such diabetes most often manifests itself gradually, with obvious signs. As a rule, it is discovered by accident during a medical examination.
Prevention and treatment of diabetes
The body converts the carbohydrates consumed into glucose, which in the event of an insulin deficiency cannot be used, so the blood sugar will rise. It is very important to maintain correct blood sugar levels to prevent damage to the blood and nerves. From a preventive point of view, it is important to monitor blood sugar levels every six months, and it is also important to know that if you are overweight or if you smoke, your risk of developing the disease can be significantly increased. People with diabetes should pay particular attention to a diet rich in fiber and should avoid foods high in sugar and fat.
This type of diabetes also occurs in adolescents (about 5% of patients under the age of 20), but the likelihood of the disease is highest in those over 40. By the age of 50-60, the risk increases even more.
This form of diabetes is often a hereditary disease. 85% of people suffering from it have close relatives - diabetics. If obese diabetics lose weight, they can get rid of the signs of the disease. If you follow a certain diet, regularly engage in port, constantly monitor your condition, you can reduce or completely eliminate the need for pills or injections. But this form of diabetes is not always caused by overeating. Sometimes the reason may be poor functioning of the pancreas.
You must consume good quality, natural foods and maintain digestive system taking probiotics. This is remarkable because with diabetes they have digestive problems. It is also advisable to cleanse the intestines to remove toxic residues. When performing a cleansing treatment, you must use a set of drugs that remove.
Type 1 diabetes, otherwise referred to as adolescent or insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, is an autoimmune disease. As a result of malfunctioning immune system he recognizes his own healthy beta cells in the pancreas as foreign. Consequently, antibodies destroy insulin-producing cells.
Another type of disease, much more complex - insulin-dependent diabetes... This type of diabetes is detected by sharp, vivid symptoms: frequent urination, intense thirst, significant weight loss, weakness, irritability. As already mentioned, in this case, ketoacidosis may develop, and then - hyperglycemic coma, life-threatening. If you have insulin-dependent diabetes, pills and diet will not help, insulin injections are required. But if you are not obese, but rather, on the contrary, very thin and even weak, additional doses of insulin in combination with a proper diet, exercise, taking decoctions from medicinal plants will almost always maintain the required amount of sugar in the blood. The amount of food, the dose of insulin and the amount of exercise should be balanced.
The incidence of this type of diabetes is due to a predisposition to autoimmune diseases and possibly to different types external factors, among others. environmentally friendly, but the reasons are not entirely clear. The diagnosis of type 1 diabetes occurs in 50% of children under the age of 14, and the remaining 50% in young people under the age of 35. Symptoms are acute and rapidly progressing.
People with type 1 diabetes account for about 9% of all diabetics. Diabetes Type 1 must continuously administer insulin by administering insulin or using an individual insulin pump and monitoring blood sugar levels daily. Insulin plays a very important role in the human body because it allows us to use energy from the outside. Insulin is a protein hormone that produces the beta cells of the pancreas, precisely located on the so-called. Langerhans. It affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
The fact is that insulin gives the body the ability to obtain energy from food, and exercise reduces blood sugar levels. That is, if you eat more, you need a large dose of insulin and more physical activity, if you eat less, on the contrary. It's very simple, you just need to remember it all the time. But whatever form of the disease we are talking about, you need to know: the life of a diabetic is, first of all, constant self-control. Uncontrollable diabetes affects all organs and systems, causing many complications. If you train yourself to control the disease, all suffering will pay off. Remember that you are responsible for your health. You need to lead a well-planned life: eat at the same time, take pills and do insulin injections on a schedule, constantly do tests (you can also at home using glucotests - urine tests for sugar or using a special apparatus for blood tests), go to the doctor.
Insulin acts as a key to cells - connecting to a receptor on their surface dissolves the cell membrane and allows glucose to enter the cell. Diabetes was a disease already known in antiquity, but no one knew how to effectively treat it. The first records of diabetes speak of unfulfilled desire, frequent urination, and a very rapid halt in the body, which ends shortly after death. The Latin name "Diabetes mellitus" comes from a large amount of sweet urine, which patients gave, despite the constant drinking of water.
The doctor will diagnose you, write a prescription and prescribe treatment, but only you will live your life. See your doctor more often, it doesn't matter if you take insulin or not, but you should definitely monitor your blood sugar level. Your doctor will monitor your blood sugar levels to prevent possible complications, and will also help you plan your diet, exercise, and in general - life. To manage diabetes you only need a diet, see your doctor at least once every 3 months. Do this regularly, on a schedule, not when you feel like it. And if you are injecting or taking pills, visit your doctor more often, depending on your condition, but at least once a month. It is also necessary to establish a solid diet.
A diabetic person with severe hypoglycemia may not be able to help themselves and will need your help! The behavior of a diabetic with very low level blood sugar can partially resemble alcohol intoxication and, unfortunately, is often mixed with it, and the patient does not receive adequate help. This is why it is extremely important not to pass by indifferently when someone might be in danger to health and life! The diabetic may have silicone tape or diabetes ID.
If pregnancy is diagnosed in a woman with hyperglycemia, it is gestational diabetes. In most cases, treatment involves a diet, sometimes requiring insulin. Improperly treated or untreated gestational diabetes can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby. Women who have had gestational diabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
You must have breakfast, lunch, dinner and snacks every day. It will be difficult until you get into a rhythm, but this routine will pay off. It is better and cheaper to eat right than to suffer and be treated with expensive medications later. Perseverance will make you feel better now and in the future. It will become your way of life. So you will prevent possible complications and live to a ripe old age, while maintaining your health.
It is found in adults over 35 years of age and usually does not require insulin therapy for the first 6 months. Type 3 diabetes is not exactly a medical condition, but it can affect people in its own way. It is said that diabetes is a disease of the whole family - a person with diabetes not only needs psychological support and education.
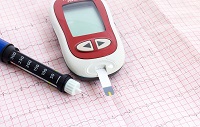
Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia. Depending on the causes of diabetes, we are divided into types - different, in particular. Course and method of treatment. The word diabetes does not always mean the same thing. A blood glucose meter is a diagnostic tool for accurately monitoring blood sugar levels in a controlled manner. With its small size and quick measurement, it provides freedom of choice for people with diabetes. The test involves inserting a test strip into a meter that draws a small drop of blood from your finger and the result is shown on the display.
In diabetes mellitus, the pancreas is unable to produce the required amount of insulin or produce insulin of the required quality. Why this is happening has not yet been clarified. There are separate hypotheses with varying degrees of reliability; a number of risk factors can be pointed out.
There is an assumption that type I diabetes is caused by a viral infection. Type II diabetes is often caused by genetic defects. One thing scientists know for sure - you cannot get diabetes like you get the flu or tuberculosis. It can be assumed that the cause of type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent) is a decrease in insulin production or its complete cessation due to the death of beta cells of the pancreas that produce insulin. One of the factors of this decrease may be the autoimmune processes occurring in the body.
Blood glucose meters differ in appearance, size and interpretation depending on the brand. A person with type 1 diabetes must have injected insulin by injection or subcutaneous infusion. This is due to damage in the autoimmune process of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas.
An insulin pump is a small device that mimics a normal pancreas. An electronic pump delivers insulin through a subcutaneous infusion set - an infusion tube consisting of a thin, punctured tube that, on the other hand, is connected to an insulin reservoir short acting in the pump. Only when using an insulin pump can you deliver the same type of insulin differently. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion is divided into two types: the base pump delivers a user-specified base dose 24 hours a day, regardless of food intake.
In type 2 diabetes, which is four times more common than type 1 diabetes, beta cells initially produce insulin in normal or even large amounts. However, the tissues of the body are immune to its action, and therefore the pancreas increases the production of insulin in order to overcome tissue resistance, and for a while it manages to do this - due to excess secretion of insulin, normal blood sugar levels are maintained. The pancreas cannot work in this mode for a long time - it is depleted, insulin secretion decreases, and diabetes mellitus occurs.
The pen is a special pen that resembles a fountain pen, because it is similarly mentioned in the cartridge - the pen contains ink cartridges, pints of an insulin bottle. The needle is attached to the tip of the pen, just like the tip is on a pen. The length and thickness of the needle is individual choice user, there is a wide selection of needles suitable for different groups. age. The feed button handle is equipped with a bucket usually divided into 0.5 units.
We found that the pancreas was damaged in people who died of diabetes. They were the first to discover and describe the role of the pancreas in regulating blood sugar levels, but they could not isolate the responsible substance. However, it was a huge step towards saving people with diabetes. Today, the European Association for Diabetes Research presents an annual award to Talented Young Diabetes Researchers in recognition of Oskar Minkowski's accomplishments. Soon after these events, special beta cells were discovered on the previously mentioned islands of Langerhans, which produce insulin and make up only 2% of the mass of the pancreas.
There are a number of factors that predispose to the onset of diabetes mellitus.
In the first place, hereditary predisposition should be indicated. Almost all experts agree that the risk of developing diabetes increases if someone in your family has diabetes or has had diabetes - one of the parents, brother or sister. The closest hereditary relationship is observed in type II diabetes. It is inherited with a probability of 80% on both the maternal and paternal lines, and if both parents are ill with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, the probability of its manifestation in children is close to 100%. These numbers are not a verdict. From an early age, the child needs to be explained that there is a certain risk of the disease, but if he excludes the action of other predisposing factors, he will closely monitor his health, he will be able to avoid the development of diabetes mellitus.
Only they were able to extract the substance from the dog's pancreas, which is why they are considered the pioneers of insulin. The purified insulin solution was obtained through collaboration with chemist Bertram Collip. This year also became the first chemically synthesized protein. Initially, insulin was injected into glass syringes, which were then prepared - unfortunately, after a while they began to leak. After a while, they replaced them with insulin, and it was not until the 1980s that they appeared on the market.
Since then, the development of insulin pump technology has led to the development of an artificial pancreas. Type 2 diabetes is a disease that develops from insulin resistance, primarily in adults and the elderly. As a result of obesity or overweight, the cells in the body become resistant to insulin and the secondary beta cells that produce it are damaged. Abnormal eating habits and decreased physical activity are additional factors. In this type of diabetes, when the diagnosis is diagnosed, about 50% of the beta cells are active, the body also produces its own insulin.
Hereditary predisposition must be taken into account in many life situations - for example, when marrying and when planning a family. If heredity is associated with diabetes, then children need to be prepared for the fact that they too can get sick. It should be clarified that they constitute a "risk group", which means that their lifestyle should minimize all other factors affecting the development of diabetes.
The second leading cause of diabetes is obesity. This factor, fortunately, can be neutralized if a person, realizing the full extent of the danger, will strenuously fight overweight and win this fight.
The third reason is pancreatic diseases - pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, diseases of other endocrine glands, as a result of which beta cells that produce insulin are damaged.
The fourth reason is a variety of viral infections (rubella, chicken pox, epidemic hepatitis, influenza, etc.), which can lead to the death of cells that produce insulin, and, consequently, to the development of diabetes mellitus. They play the role of a trigger mechanism, as it were, triggering the disease. Have healthy person these diseases will not cause diabetes. But when combined with other factors, especially heredity and obesity, the development of diabetes is likely.
You should be especially careful about your condition in the period from November to March, because most cases of diabetes occur during this period due to the influence of a viral infection. The situation is complicated by the fact that the ailments of a patient with diabetes mellitus can be mistaken for viral infection... It is possible to establish an accurate diagnosis only on the basis of an analysis of the glucose content in the blood.
In fifth place is nervous stress as a predisposing factor. Nervous and emotional overstrain should be especially avoided for people with aggravated heredity and overweight.
In sixth place among risk factors is age. Some studies indicate that for every 10 years, the likelihood of developing diabetes is about doubled. But, on the other hand, such a predisposing factor as heredity loses its significance with age. Scientists have come to the conclusion that if one of the parents is sick with diabetes, then the probability of the disease is 30% at the age of 40 to 55 years, and after 60 years - about 10%.
Diabetes is rightly referred to as a disease of civilization, that is, in many cases, it is caused by excess, rich in easily digestible carbohydrates, "civilized" food.
In rare cases, some hormonal disorders lead to diabetes, sometimes diabetes is caused by damage to the pancreas, which occurs after the use of certain drugs or as a result of prolonged alcohol abuse. With regard to type II diabetes, in almost all cases, weight loss and significant exercise stress help prevent the progression of the disease and normalize blood sugar levels. At the same time, it is obvious that with the development of type I diabetes mellitus, immediate insulin therapy is necessary.
It should be noted that any one of these reasons very rarely leads to the development of diabetes. Usually, the disease occurs under the influence of several predisposing factors. Also, in rare cases, causes such as hormonal disorders, some medications or long-term alcohol abuse.
It must be remembered that not only the very fact of an increase in blood sugar levels is terrible, but also the consequences of prolonged hyperglycemia - it is this that leads to the development of the main complications of diabetes mellitus - damage to the kidneys, eyes, cardiovascular vascular system... Therefore, the earlier the treatment of diabetes mellitus is started, the more chances you have to maintain your health and well-being for many years.
With the development of type I diabetes, symptoms usually appear quickly, and the diagnosis is not particularly difficult. Type II diabetes flows unnoticed, the doctor may discover it by accident. So, an optometrist, when examining the fundus, can see certain features.
Diabetes is characterized by typical, long-known Clinical signs... A person begins to worry about a general deterioration in well-being, weakness, fatigue, insomnia, itching of the skin and mucous membranes, difficult and long healing of wounds, weight loss in type I diabetes, in type II diabetes, overweight is usually noted. Pathological changes in the cardiovascular system develop for the second time, nervous systems and other organs. Excess glucose is excreted in the urine, resulting in frequent urination with an increase in the total amount of urine up to 3-7 liters per day. Loss of fluid leads to increased thirst and consumption of large amounts of water, dry mouth.
Type I diabetes is sometimes present sharp deterioration states when severe weakness occurs, abdominal pains, vomiting, the smell of acetone from the mouth (ketoacidosis) appear. Type II diabetes usually develops gradually over time.
Diabetes mellitus, or diabetes mellitus, was known to the ancient Egyptians. They called this disease "sweet death." The term diabetes was first coined by the Roman physician Aretheus in 100 AD. The word "diabetes" in translation from Greek means "expiration" and, therefore, the expression "diabetes mellitus" actually means "expiring sugar", or "losing sugar", which reflects one of the characteristic features of the disease - the loss of sugar in the urine.
Centuries and millennia passed before people understood the mechanism of development of "sweet death".
In the 17th century, physician Thomas Willis first discovered the sweet taste of urine in diabetics, which was then used by doctors to diagnose the disease.
In 1776, the English physician Dobson (1731-1784) found out that the sweetish taste of the urine of patients is associated with the presence of sugar in it, and from that date, diabetes, in fact, began to be called sugar.
In 1788 it was found that the occurrence of diabetes mellitus is closely related to changes in the pancreas.
Since 1796, doctors began to talk about the need for a special diet for diabetics, in which part of the carbohydrates was replaced by fats. Physical activity began to be used as a treatment for diabetes.
A hundred years later, in the middle of the 19th century, Paul Langerhans, a disciple of the famous Virchow, discovered in the pancreas certain clusters of cells that in appearance resemble islets (later they were called "islets of Langerhans"), when they were removed, a disease arose in animals, resembling diabetes mellitus. The experiments of the experimenter Minkowski confirmed this assumption. When the pancreas was transplanted to dogs with a previously removed pancreas, the manifestations of diabetes mellitus disappeared. As soon as the transplanted organ was removed, the animal showed signs of disease again.
In 1921, from the "islet cells of Langerhans" Canadian scientists F. Benting and C. West obtained a drug called "insulin" (Greek insula - islet). Since 1926, insulin began to be obtained industrially, it still saves the lives of millions of patients with diabetes mellitus. In addition to insulin, which is considered the most effective remedy for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, other antidiabetic drugs are currently available, many of which are used in pill form. With a mild course of the disease, this greatly simplifies the treatment.
Diabetes mellitus is a fairly common disease characterized by an increase in blood sugar levels that most often affects people over 40. It is based on absolute or relative insufficiency of insulin.
With absolute insulin deficiency, the insulin content in the blood of patients is usually sharply reduced and they need constant insulin administration. This type of diabetes is called insulin-dependent.
With relative insulin deficiency, the level of insulin in the blood of patients usually approaches normal. In this case, insulin-dependent diabetes develops. This type of diabetes does not require the administration of insulin; compensation is achieved with pills or diet therapy.
With diabetes mellitus, all types of metabolism are disrupted, but most of all it suffers carbohydrate metabolism... In conditions of insular insufficiency, the permeability of the cell membranes of insulin-dependent tissues decreases. The loss or weakening of the action of insulin leads to a slowdown in the entry of glucose into muscles and adipose tissue, inhibition of its phosphorylation. This leads to disruption of glycogen synthesis. In cells, oxidation processes slow down, the transition of carbohydrates to fats is inhibited. Glucose is transferred in large quantities from the liver into the bloodstream, which causes hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). The latter is accompanied by glycosuria (increased sugar content in the urine) due to increased filtration in the renal glomeruli and its insufficient reabsorption in the urinary tubules.
Insulin deficiency in diabetes mellitus is believed to be the reason for the slow passage of amino acids through the cell membrane and inhibition of protein synthesis. This violation underlies the weakening of immunobiological reactions (inhibition of the formation of antibodies), slowing down the healing of wounds and the occurrence of trophic ulcers.
There are three main stages of diabetes mellitus: prediabetes, latent diabetes, and overt diabetes. Most early stage the disease is prediabetes. At this stage, fasting blood sugar and glucose tolerance test are normal.
The assumption about the possible onset of the disease arises at the birth of large fetuses in women (more than 4500 g), with repeated death of the fetus, and especially in the presence of unfavorable heredity. Obesity also plays an important role in diagnosis. Most often, the diagnosis of prediabetes can only be made retrospectively.
With latent diabetes, the fasting blood sugar level is normal, there is no glycosuria, but the glucose tolerance test is pathological.
With overt diabetes, there is an increased sugar content in the blood and urine (hyperglycemia and glycosuria).
Every person knows what diabetes mellitus is today. This is an ailment due to the violation of complex metabolic processes, namely, carbohydrate. The disease is accompanied by an uncontrolled increase in blood glucose. Determined glucose in excessive quantities and in the urine (normal - it is not there). The progression of the disease entails more or less life-threatening consequences. All organs and organ systems are damaged, there is always a high risk of coma (hypoglycemic, hyperglycemic). Comas are often the cause of death.
With diabetes mellitus, serious metabolic disorders occur in the body. Diagnosis is based on characteristic symptoms and high-precision laboratory tests.
Historical reference
There is no reliable data on when exactly people first encountered a dangerous ailment. We can say that the earliest mentions of a disease similar in description to diabetes mellitus date back to the third century BC. The ancient Egyptian healers and the ancient Greek, Roman, and Eastern Aesculapians were already well acquainted with him. In medieval Europe, there were also attempts to explain "what diabetes is", to describe the nature of the disease that people of different classes suffered from. In those days, it was not possible to establish the real causes of diabetes mellitus, so most of the sick people were doomed to death.
The definition "diabetes" was originally used by Aretius (2nd century AD), a Roman physician. He described the disease as “intolerable suffering, prevalent mainly among males, which dissolves the body in urine. The ailing people continuously excrete urine, experience an unquenchable thirst, their life is painful, short-lived. " In ancient times, the diagnosis was based on external signs.
If a child or a young man (type 1 diabetes) fell ill, he soon died from a coma. When the disease developed in an adult patient (according to modern classification- type 2 diabetes), with the help of a special diet, medicinal herbs he received primitive help.
Further research brought medicine closer to finding out the true causes of the disease, methods of its treatment:
- 1776 - eng. Dr. Dobson determined that the sugary taste of urine excreted by a sick person was due to the increase in sugar in the urine. Therefore, diabetes began to be called "diabetes mellitus";
- 1796 - the importance of adherence to a diet and proper physical activity by diabetics was substantiated;
- 1841 - physicians learned how to determine the laboratory content of glucose in urine, and then in the blood;

- 1921 - insulin was synthesized for the first time, which in 1922 was used to treat patients with diabetes mellitus;
- 1956 - investigated the properties of a special group of drugs that can make the body produce insulin;
- 1960 - describes the structure of human insulin;
- 1979 - full-fledged synthesized human insulin thanks to genetic engineering.
Modern medicine allows you to maximize the life and optimize the activity of diabetics.
A timely diagnosed condition and the patient's adherence to medical recommendations helps him to keep the sugar level at more or less normal level and avoid dangerous complications of the disease.
Classification
Diabetes mellitus is usually classified into two main types - insulin-dependent (IDDM) and non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM). There are also gestational diabetes and pathological conditions associated with disruptions in carbohydrate metabolism.
Depending on the body's ability to produce insulin, there are:
- 1st type - IZSD. This type of diabetes is inextricably linked to acute insulin deficiency in the body. The damaged pancreas (PZH) is unable to perform its functions. It does not produce insulin at all or releases it in critically small amounts. As a result, high-quality processing and assimilation of glucose becomes impossible. Get sick in childhood or before the age of 30. Patients are usually not overweight. They have to take injectable insulin.

- 2nd type - NIDDM. Insulin in this type of diabetes is produced by the corresponding cells of the pancreas in sufficient or even excessive volume, however, tissue receptivity to it is lost, it is "useless". NIDDM is determined, as a rule, in adults, after 30-40 years. Patients usually suffer from varying degrees of obesity. IN subcutaneous injections insulin for such patients is usually not urgently needed. For the treatment of such diabetes, tableted dosage forms... Medications work to reduce the insulin resistance of cells or to stimulate the pancreas to produce insulin.
Gestational diabetes develops during the period when a woman is carrying a child, which is associated with a change in hormonal levels, the need to "share" glucose with the fetus. With gestational diabetes mellitus, the health of both the woman and the fetus suffers.
Sometimes there is a secondary nature of impaired glucose tolerance, arising against the background of cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, pancreatectomy, chronic pancreatitis... A variety of genes are capable of acting as causes, endocrine diseases, some medicines and toxins.
Degrees of diabetes
In the classification of diabetes, it is important to subdivide it into degrees of severity, based on the level of glycemia, an indication of the compensatory capacity of the body, and the presence of complications.

- Diabetes mellitus of the 1st degree is characterized by its more or less favorable course for the patient. The process is compensated, there are no chronic complications, glucose in the blood is about 6-7 mmol / l, it is not in the urine.
- Diabetes mellitus of the 2nd degree of severity allows us to speak about its partial compensation. The first manifestations of complications appear. The level of sugar in the blood is 7-10 mmol / l. There is still no glucosuria. There are also no irreversible organic violations.
- DM grade 3 is characterized by its pronounced progression. The glucose content is 13-14 mmol / l, there is stable glucosuria (sugar in the urine), significant proteinuria (protein in the urine). With this diabetes mellitus, chronic complications of the disease develop (decreased visual acuity, hypertension, angiopathy, etc.).
- DM 4th degree - decompensation. Severe complications develop (diabetic foot, gangrene of the extremities, frequent coma, failure of the kidneys, liver, organic defects of various organs and vital systems). Glycemia reaches critical, uncontrolled levels (15-25 mmol / l and more). In the urine is determined high level proteins and sugar.
Symptomatic picture
Diabetes mellitus in many cases is determined by chance, in the course of laboratory preventive studies. The first signs of diabetes may appear later.
The asymptomatic course of the disease delays the diagnosis and initiation of treatment, which significantly complicates the process in the future. The symptoms of diabetes mellitus depend on the individual characteristics of the organism, the clinical stage of the disease, and its type.
Signs of diabetes mellitus:

- frequent urination, abundant excretion of urinary fluid, including at night;
- a constant feeling of thirst, a person cannot quench it;
- dizziness, severe weakness, chronic fatigue, quickly onset fatigue (develops as a result of inadequate absorption of the main source of energy - glucose);
- dry skin (a sign of progressive dehydration), dry mouth;
- itching of both the skin and mucous membranes - especially in the perineum;
- loss of body weight or its increase in excess of a measure;
- violation of appetite;
- emotional instability;
- problems with visual ability - "fog, a cloudy veil" appears before the eyes, visual acuity decreases;
- numbness of the limbs, an attack of muscle cramps, tingling, heaviness in the legs due to impaired blood microcirculation;
- sexual dysfunction;
- slow "tightening" (healing) of wounds, cuts, pustular skin lesions (furunculosis).
There are additional symptoms of diabetes. Dysfunctions of different systems are observed. Heart attack can often occur, liver and kidneys are affected.
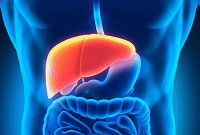
If diabetes is not adequately treated, liver cells are gradually replaced connective tissue(cirrhosis develops) or "get fat" (hepatosis).
The above listed signs of diabetes report formidable malfunctions in the body, forcing a person to consult a doctor.
Causal factors of the disease
Diabetes cannot be contracted, but the role of heredity in the mechanism of the disease has been proven.
If one of the parents has diabetes, the chance that the child will develop diabetes is about 30%. If both the mother and the father are sick, the risk that their offspring will develop symptoms of diabetes rise to 60%.
What are the causes of diabetes mellitus? The cause of type 1 diabetes is the death of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas due to autoimmune pathology, when antibodies to their own cells are produced in the body and destroy them. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, the pancreas produces insulin, but in insufficient volumes, therefore, the sensitivity of tissue receptors to insulin decreases.

Negatively influencing factors, in addition to genetic predisposition, are:
- overweight;
- sharp or chronic diseases pancreas (pancreatitis, viral, infectious lesions), its injuries, tumors;
- emotional shock;
- age - the risk of getting sick increases over the years;
- pregnancy;
- taking some medications.
Render bad influence gross flaws in the diet (excessive consumption of sweets, food containing carcinogenic, toxic substances), alcohol abuse. Nicotine also contributes to diabetes by constantly poisoning the body and the pancreas in particular. To protect yourself from diabetes, you should avoid bad habits.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the doctor takes into account the patient's complaints, the existing signs of diabetes and laboratory data. Initially, blood taken from the patient in the morning is examined on an empty stomach. Excessive blood sugar levels oblige the doctor to conduct additional tests (for glucose tolerance, for example).
Indicators in adults:
The doctor will be able to reliably interpret the test data; it makes no sense to panic prematurely. To clarify the diagnosis, the level is also determined glycated hemoglobin, insulin in the blood, C-peptide, antibodies to insulin, etc. Such tests can distinguish type 1 from type 2 diabetes.
To determine the degree of complications, to identify concomitant ailments, various additional methods studies (ultrasound, X-ray, ECG, rheovasography, MRI), which are necessarily periodically prescribed to all people with diabetes. Consultation of an ophthalmologist, neuropathologist, surgeon is mandatory.
Complications of diabetes
Untreated diabetes, constant violation of medical recommendations, inaccuracies in nutrition and other factors lead to the development of life-threatening complications of diabetes mellitus.
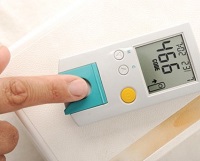
Sharp surges in blood sugar provoke acute (hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia) and chronic complications (damage to the liver, CC-system).
Acute complications, delay in the elimination of which can lead to the death of a person:
- Hypoglycemia - a drop in blood sugar below 3.3 mmol / l. Its initial and main signs: hunger, drowsiness, an attack of tachycardia, headache, an attack of severe weakness, trembling in the body and sweating. Further, visual impairment, pallor of the skin, an attack of aggression join. If appropriate measures are not taken at this stage, lethargy, loss of consciousness, coma appear. Hypoglycemia can be provoked by: an overdose of a sugar-reducing agent, fasting, unusual physical activity, and alcohol intake. If the patient has received an injection of insulin but has not eaten after that, the sugar level will drop critically.
- Hyperglycemia - an excess of blood sugar concentration over 5.5-6.7 mmol / l. It occurs in cases when a person with diabetes misses taking the prescribed antihyperglycemic agent, if the prescribed dose is no longer enough, it has not been corrected by the doctor for a long time, if the patient has suffered severe stress and others. It is manifested by thirst, dry mouth, visual impairment and loss of consciousness. This is a life-threatening attack.
- Ketoacidosis develops as a result of the accumulation of "ketone" bodies in the blood. Symptoms: the smell of "acetone", which is felt from the patient's mouth, weakness, headache and pain in the abdomen. The nature of breathing changes.
The prolonged course of the disease, its severe forms lead to the development of complications from the nervous, vascular system, provoke damage to the feet. Nephropathy is damage to the smallest renal vessels. The patient feels pain and heaviness in lumbar spine, thirst, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea, swelling, unpleasant taste. Protein appears in the patient's urine.
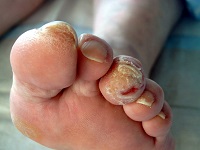
"Diabetic foot" is a change in the structure of tissues on the feet that occurs during prolonged and severe diabetes mellitus. Cuts, cracks or calluses can provoke the development of trophic ulcers on the feet in diabetes mellitus. Treatment diabetic foot often untimely due to late detection of lesions.
Principles of diabetes treatment
Diabetes treatment must be comprehensive. The choice of a therapeutic strategy depends on the type of disease, the severity of its course, the presence of complications, and other factors. How is diabetes treated?
The main directions are as follows:
- Normalization of blood glucose levels with medications and maintenance of the desired level. In type 1 diabetes mellitus, regular subcutaneous insulin administration is required. Insulin is short-acting and with varying degrees of prolongation. It can only be prescribed by an endocrinologist, starting from the patient's blood glucose levels, the severity of symptoms. Before each administration of the drug, the patient must measure sugar, recording the result, using a special portable device - a glucometer. It is necessary to strictly follow the doctor's recommendations regarding insulin treatment. How is type 2 diabetes treated? The doctor usually prescribes medications in . There are many varieties of them; in each specific clinical case, the endocrinologist selects the appropriate medication for diabetes mellitus.

- Correct diet. Nutrition in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus performs an auxiliary function, while in type 2 diabetes it plays a key role. Diet can qualitatively adjust blood sugar levels. If dietitian nutritional recommendations are regularly violated, this leads to undesirable consequences... The diet of a diabetic is naturally different from that of a healthy person. There are quantitative and qualitative nutritional restrictions. The diet should not contain foods that can excessively increase sugar levels (sweets, hydrogenated fats, alcohol, fast food, etc.). The goal of the diet for an overweight patient is not only to control the intake of carbohydrates, but also to stabilize the weight. Underweight diabetics are prescribed a diet to increase body weight.
- Moderate physical activity. Adequate physical activity contributes to lowering blood sugar. Its type and volume in diabetes mellitus should be agreed with the doctor. Insulin-dependent patients should be especially careful, hypoglycemia should not be allowed.
- Herbal medicine (treatment of diabetes mellitus with herbs should be discussed with the attending doctor).
- Adequate therapy of concomitant diseases and complications (treatment of diabetic pathology of the feet, kidneys, liver, blood vessels, etc.), including surgery diabetic progressive foot, which has affected the deep layers of tissues.
Requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels in diabetes. In addition to measuring with a glucometer, you need to check sugar in a clinical laboratory. People with diabetes are registered at the clinic. Treatment is prescribed and corrected only by a doctor.
Forecast
So, can diabetes be cured? This question is asked by every person who has received a disappointing diagnosis. Unfortunately, there is no way to completely cure diabetes.
Attentive attitude to one's own well-being, adherence to medical prescriptions, physical exercise, herbs, diet, you can only maintain the level of sugar in the blood at the proper level, to avoid the development of life-threatening complications in diabetes mellitus.
Trying to cure the disease, patients resort to various unconventional methods. It should be remembered that such attempts are often fatal.