Why does the cheekbone and jaw hurt near the ear on the left and right, it hurts to chew: causes, treatment. The jaw clicks on one side and the jaw joint and cheekbone hurts when you open your mouth: what to do, which doctor to go to? Jaw arthrosis: symptoms, treatment. What to do
The jaw hurts when you open your mouth - a common complaint of people of any age. It is in vain to think that the unpleasant sensations will pass by themselves. The disease that caused them, in the absence of treatment, will progress. This will lead to other serious complications, pathology of the temporomandibular joint, and other health problems.
The structure and function of the temporomandibular joint
 The temporomandibular joint, or temporomandibular joint, is a paired organ in which the movement is synchronous. This ensures the performance of chewing functions and correct articulation. The joint is complex and subject to constant stress. Its structure and proximity to the nasal sinuses, ear and dentition makes the organ vulnerable to infectious lesions.
The temporomandibular joint, or temporomandibular joint, is a paired organ in which the movement is synchronous. This ensures the performance of chewing functions and correct articulation. The joint is complex and subject to constant stress. Its structure and proximity to the nasal sinuses, ear and dentition makes the organ vulnerable to infectious lesions.
The lateral pterygoid muscles are additionally involved in the movement of the jaw joints, which pull the ligaments, providing motor activity. Several joint functions are distinguished, each of which is unique. These are frontal movements when opening, closing the mouth, articulation. They also distinguish movements to the side and vertically when chewing food and sagittal - to advance lower jaw.
A healthy temporomandibular joint has the following structure:
- elliptical articular head of the lower jaw;
- the glenoid fossa, divided in half by the petrotympanic fissure;
- articular capsule - a strong shell of connective tissue(it protects the joint from bacteria);
- tubercle - a cylindrical protrusion in front of the glenoid fossa;
- a plate of cartilaginous tissue (disc) between the articular surfaces, thanks to which the joint performs movement in different projections;
- ligaments that regulate movement: lateral, wedge-mandibular, temporomandibular.
The structure of the human TMJ changes after tooth loss. The articular head gradually dissolves, reaching the state of the fossa. In addition, the posterior tubercle is flattened, which leads to limitation of mobility and disruption of work.
Joint dysfunction occurs due to various situations that can disrupt the bite, lead to asymmetry of the face, and jamming of the jaws.
The nature of pain and the mechanism of its occurrence
When it hurts to open the mouth wide, or it is completely jammed, this almost always indicates an inflammatory process, a violation of the anatomy and tissue functions. The pain can spread to all areas of the face, shoot into the ear, cause migraines, discomfort with visual stress. It can be different - long-term and short-term, aching and acute, which is taken into account when making a diagnosis.
Aching pain in the lower jaw accompanies the inflammatory process, burning disturbs with neuralgia. With cutting pain, bone injuries are usually diagnosed. People who find it painful to chew, open their jaws wide, often consider pathology to be the cause. skeletal system... However, the disease can also affect the surrounding tissues. If the patient ignores the pain, unpleasant symptoms will soon bother even with the jaw closed.

Under the influence of certain diseases, the jaw can jam, hurt on the left or right side. Pain on the left can indicate impaired blood circulation, problems with the vessels of the heart. Its right-sided character is observed with neoplasms, inflammatory processes... If the jaw hurts everywhere and constantly, an oncological factor can be suspected.
It happens that the jaw cracks after sleep, in the morning, at rest, cramps appear. Do not delay your visit to the doctor. Especially if the ailment is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- spasms with fever;
- throbbing pain with spasms;
- severe pain radiates to any ear, eye (we recommend reading: what to do if a toothache radiates to the ear?);
- swelling;
- mouth does not open;
- it hurts to chew for a long time;
- cramps in the lower part of the face.
When you open your mouth
Pain when opening the mouth is the result of a dislocation or fracture. If there has been no injury recently, these options are excluded. In this case, osteomyelitis is the cause of the discomfort. Other pathologies that lead to sharp, aching or sharp pain during the work of the jaws are dental diseases, among which caries ranks first. This also happens when dentures are not installed correctly.
When chewing and closing teeth
If the jaw system aches, aches, bothers when chewing, joining teeth, one can suspect its dislocation or osteomyelitis. Other ailments that lead to discomfort when teeth are closed include periodontitis, pulpitis, and complicated caries. With their exacerbations, the pain is of a pulsating nature, radiates to the temple, intensifies at moments of rest and night rest.
At chronic form pathologies, periodic It's a dull pain, which is exacerbated by the chewing load on the affected tooth or gum area. Certain foods and alcohol can also provoke unpleasant sensations when you chew. Leading to esophageal spasm, they also cause muscle spasm and jamming of the jaw.
Pressure
Pain in the cheeks when pressed has different causes. It can appear near the right or left side of the ears, and it can appear on palpation of the upper or lower part. The burning sensation is often caused by arteritis of the facial artery. With phlegmon, fistulas and abscess, the jaw will hurt even with light touch at rest, and others that cannot be ignored will be added to this symptom.
Pain when pressing on the teeth and gums speaks of their pathology, dental problems. Often she worries about abnormal eruption of a wisdom tooth, as well as accidental injury to the jaw.
Causes of pain in the jaw near the ear
Doctors often face complaints of patients about pain in the jaw near the ear, pain in the ear when chewing. This symptom is not always associated with dental problems, and painful sensations can be caused by the following reasons:

Often there is pain in the jaw near the ear and temple due to carotidinia. This disease is akin to migraine, which is characterized by aching pain in the ear, radiating to the area of the lower jaw and orbit. The pain is monotonous, but acute attacks occur that last from a couple of minutes to an hour. Carotidynia occurs when a dissection of the temporal artery, a tumor in the area of the carotid artery.
Associated symptoms
Any discomfort when the mouth does not open completely, or the jaw hurts on the right / left, cannot be ignored. Especially if it hurts a child. The fact that the pain is not random will tell the accompanying symptoms:

Diagnostic methods
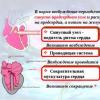
For complaints of pain near the cheekbones when yawning, eating, talking, a visual examination is carried out. After that, an X-ray, MRI, ultrasound, ECG is prescribed (if heart failure is suspected). The disease is differentiated depending on the type of origin:
- dental problems;
- neurology;
- pathology of the cardiovascular system;
- ENT diseases;
- trauma;
- neoplasms.
Diagnostics of cardiovascular, bone and ENT pathologies is carried out on the basis of analyzes and examination data. To identify why the skin on the face or tooth hurts, the mouth does not open, to identify neoplasms, X-ray and MRI will help.
Oncology is much more difficult to diagnose. This is helped by tests for tumor markers, tomography and other modern methods... Based on the results of the diagnosis, a treatment tactic is selected, the duration of which depends on the degree of neglect of the disease.
Which doctor should I go to?
What doctor will help if the lower jaw hurts? If it hurts to chew, and the problem is in the teeth and gums, you should make an appointment with the dentist. After an injury, with jamming of the jaw joints, incomplete opening of the mouth, it is worth seeing a maxillofacial surgeon.
Often, the patient does not find the cause, and the discomfort progresses: the ear on the right, the cheekbones, and the area around the neck hurts. In this case, you should consult a therapist. After the examination, he will tell you which doctor to contact, give a referral to an orthopedist, rheumatologist, neurologist, dentist-gnathologist, cardiologist, ENT, gastroenterologist and other specialized specialists.
How is the jaw joint treated?
Analgesics will help eliminate acute pain in the jaw joints. However, taking them will not solve the problem once and for all. It is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology, which becomes:

Folk remedies
Folk remedies against painful sensations when the jaw is opened, the pathology of its joints is used as an adjunct to the main treatment. They will not help if the jaw is jammed, but they will relieve pain symptoms. After consultation with the doctor, you can use the following recipes:

Additionally, according to the doctor's indications, you can do remedial gymnastics... The set of exercises is something like this (repeat 5 times every day):
- frown, then raise in surprise;
- squint your eyes;
- smile with closed lips, and then with an open mouth;
- stick out your lips with a tube;
- inflate and deflate cheeks;
- relax your face, stroke your temples and cheekbones.
There are many reasons for pain when opening the jaw, which are not easy to prevent. Experts recommend avoiding traumatic sports, monitoring the diet, and treating gingivitis, caries and other dental pathologies in time. You should beware of hypothermia, infectious diseases, stress, which adversely affect the state of the cardiovascular and nervous system.
Pain when opening the mouth is a symptom that can occur with various diseases: diseases of the teeth, gums, ENT organs, nervous system, as well as as a result of injuries. In this article, we will talk about the causes of pain when opening the mouth in the jaw near the ear on the left and right sides.
The mechanism of occurrence and nature of pain
Pain while opening the mouth in a person may indicate a dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. Depending on the intensity and duration of pain, there are:
- acute pain - appears suddenly and just as suddenly stops;
- chronic pain - bothers a person constantly, fades away for a short time and quickly returns again.
Acute pain when opening the mouth can occur against the background of prolonged fixation of the mandibular joint in one position, for example, in a dental chair. In this case, fluid or blood accumulates in the jaw joint and any movement of the jaw causes acute pain in it. As a rule, to eliminate this pain, it is enough to reduce the load on the mandibular joint - to refuse chewing gum, gently open your mouth when yawning.
Chronic pain when opening the mouth, which constantly bothers a person or occurs for no apparent reason, can signal the ongoing pathological processes in the jaw joint, for example, arthrosis. As a rule, such a disease develops due to the absence of lateral abutment teeth due to the increasing load on the bone and muscles.
Pain when opening the mouth can also occur with diseases of the middle ear, and in young children - during teething.
Causes of pain when opening the mouth
There are many reasons for the development of pain in the jaw and mandibular joint, the most common of which are:
- injuries and bruises of the jaw;
- fracture of the jaw;
- dislocation of the lower jaw;
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the mandibular joint;
- arthritis of the mandibular joint;
- chronic diseases teeth, pulpitis;
- sinusitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- inflammation of the tongue - glossitis;
- stomatitis oral cavity;
- carbuncle or furuncle in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- neuralgia;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- oncological processes in the lower jaw.
Symptoms
The accompanying symptoms of pain when opening the mouth largely depend on the cause of the development of the pathology, we will consider them in more detail.
Jaw injuries
A bruised jaw is the most common injury that causes severe pain with the slightest movement of the mouth. It is important to understand that a bruise is a violation of the integrity of soft tissues, while the bone and the joint of the lower jaw itself are not affected.
A bruise of the jaw usually occurs as a result of a strong blow to the face or after a person falls on the face. The most common symptoms of a bruised mandible are:
- pain when opening the mouth and chewing;
- hematoma in the chin and face;
- violation of the functioning of the jaw (inability to pronounce sounds, pain when chewing, yawning and any manipulation that requires opening the mouth).
Jaw dislocation
Dislocation of the temporomandibular joint is characterized by a displacement of the articular areas relative to each other. Distinguish between unilateral dislocation (with dislocation of 1 joint) and bilateral (with dislocation of 2 joints at the same time).
The reasons for the dislocation of the jaw are:
- blows to the face;
- falling on the face;
- excessive opening of the mouth, for example, when yawning, trying to bite off a large piece of food, yawning.
Dislocation of the lower jaw is most common in the elderly, which is associated with anatomical features joints and ligaments and much less often in children.
The clinical symptoms of dislocation of the temporomandibular joint are:
- severe pain in the area of the affected joint or on both sides in case of bilateral dislocation;
- the mouth is constantly open, and any attempt to close it causes a sharp pain in the victim;
- salivation;
- inability to speak normally.
In rare cases, chronic dislocation of the lower jaw may occur. This occurs against the background of stretching of the ligaments that fix the joint, therefore, with any predisposing factor, subluxations may occur.
Jaw fracture
A fracture of the lower jaw differs from a bruise by a violation of the integrity of the bone tissue; in traumatology, the following types of this pathology are distinguished:
- complete fracture with displacement of bone fragments;
- partial fracture, incomplete without displacement (as a rule, these are cracks in the bone region).
A complete fracture of the jaw can be open - when the integrity of the facial tissues is compromised or closed - without damaging the skin of the face.
The clinical symptoms of a jaw fracture are:
- sharp pain in the jaw area;
- hematoma;
- swelling of tissues, visible to the naked eye.
In the event of a fracture of the upper jaw, the victim develops blood bruises under the eyes within 1-2 hours, which is a consequence of hemorrhage from the bone into the tissue.
Osteomyelitis as a cause of pain when opening the mouth
Osteomyelitis is an inflammatory disease that occurs in the area bone marrow and periosteal tissues. The main reason for the development of this disease is the penetration of pathogens into the bone tissue of the jaw. The pathways for bacteria to enter are different:
- through diseased teeth that have not been treated for a long time;
- with blood flow from foci of infection (for example, as a result of boils and carbuncles);
- as a result of injury and infection of the wound surface.
Depending on the prevalence of the pathological process, osteomyelitis is limited (one or more teeth is affected) or diffuse (several parts of the jaw are affected).
The clinical symptoms of osteomyelitis are:
- a sudden increase in body temperature to 38.0-39.5 degrees;
- fever;
- chills;
- muscle pain;
- lack of appetite;
- throbbing acute pain in the area of localization of the inflammatory process;
- difficulty opening your mouth;
- general weakness;
- change in speech, indistinctness;
- inability to swallow and eat;
- swelling and sharp redness of the gums at the site of the lesion;
- there is a discharge of pus between the affected tooth and the gum;
- enlargement and soreness of large lymph nodes.
Furuncle
A boil is called purulent inflammation. sebaceous gland and hair follicle. When several nearby hair follicles are involved in the inflammatory process, they speak of a carbuncle. The favorite places for localization of carbuncles and boils are the face and neck, since these places are most often subject to dirt and microscopic damage (especially typical for women who squeeze out pimples or acne at home on their own). There are several reasons for the formation of carbuncles and boils on the body:
- damage to the integrity of the skin and the penetration of pathogenic bacteria with dirt;
- non-observance of the rules of personal hygiene;
- excessive oily skin;
- hormonal disruptions in the body;
- diabetes;
- inflammatory diseases of the nose, paranasal sinuses nose and middle ear;
- weak immunity.
The clinical symptoms of boils and carbuncles are:
- difficulty opening the mouth - the patient is in severe pain;
- an increase in body temperature (until the abscess breaks out);
- swelling and sharp soreness of the tissues in the affected area;
- headache and signs of general intoxication of the body;
- sharp redness of the inflamed area - within a few days a purulent "head" appears at the top of the swelling, from which a small amount of pus, lymph and blood is released.
Diseases of the teeth
Pain when opening the mouth often occurs with advanced dental diseases, namely:
- pulpitis;
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- periodontal abscess;
- tooth cyst;
- tooth trauma - tooth fracture, gum contusion, tooth dislocation.
With dental diseases, pain is usually so severe that it radiates to the ear, upper or lower jaw, and temple. Sometimes the patient himself cannot explain to the doctor where it hurts. Pain in most cases is of a sudden pulsating character and appears mainly at night.
Neuralgia as a cause of pain when opening the mouth
Neuralgia is a disease characterized by damage to peripheral nerves, as a result of which a person experiences severe pain along the innervation of this nerve.
Pain when opening the mouth can be caused by neuralgias of the following nerves:
1. Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve - this nerve innervates the oral cavity and face and is anatomically divided into 3 branches - the orbital nerve, maxillary and mandibular. As a result of damage to the maxillary and mandibular nerves, the patient experiences severe pain when trying to open his mouth. In most cases, pain occurs and intensifies at night and is similar in nature to a strong burning sensation. A sudden onset of pain occurs with a draft, washing your face cold water, eating hot food, touching the face. A few seconds before the onset of a painful attack, the patient has a feeling of "creeping" on the face or itching of the facial skin.
2. Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve - with inflammation of this nerve, pains take on an acute pulsating character. Pain sensations are localized in the area of the lower jaw and larynx with irradiation to the ear, temple, eyes. During an attack of pain, the patient may experience a cough, sore throat.
3. Glossopharyngeal nerve neuralgia - this nerve innervates the muscle responsible for raising the pharynx and parotid gland and provides gustatory sensitivity. With the defeat of the glossopharyngeal nerve, in addition to pain during opening the mouth, a person has pain in the throat, ear and lower jaw.
4. Neuralgia of the ear ganglion (node) - this node is affected as a result of complicated purulent otitis media, sinusitis, periodontitis. A person has acute pains of a pulsating nature radiating to the lower jaw, neck, back of the head.
Methods for diagnosing pain when opening the mouth
To establish the exact cause of pain when opening the mouth, the doctor prescribes a comprehensive examination for the patient, which includes:
- careful collection of anamnesis - what provoked the appearance of pain, whether there were injuries to the face, whether the teeth hurt, whether the patient was in a draft for a long time, etc.;
- consultation of the necessary narrow specialists - traumatologist, dentist, neurologist;
- general analysis blood and urine;
- jaw x-ray - helps to accurately identify the location of the inflammatory process and determine if there is a fracture;
- computed tomography - this study allows you to accurately identify the localization of the inflammatory process, the structural features of the teeth and the state of the periodontium, the state of the maxillary sinuses.
Treating pain when opening the mouth
The treatment of pain when opening the mouth directly depends on the causes of its occurrence, more on this is presented in the table.
|
The cause of the pain |
How to treat? |
|
Injury to the face and jaw (contusion, fracture) |
A fixing bandage is applied, analgesics are prescribed to eliminate pain, a cold heating pad or an ice pack is applied to relieve tissue swelling |
|
Diseases of the teeth |
Carious cavities are sanitized, cysts and abscesses are surgically removed, after which a course of antibiotics must be prescribed |
|
Neuralgia |
Prescribe B vitamins in injections, NSAIDs, antispasmodics, antiviral drugs... Physiotherapy treatment is added after significant improvement |
|
Sinusitis, glossitis |
Prescribe antibiotics, a course of physiotherapeutic procedures, restorative drugs |
|
Middle ear diseases |
Antibiotics, ear drops, pain relievers, antipyretics if necessary |
Forecast
The prognosis of pain when opening the mouth is favorable if a person immediately consults a doctor, and does not self-medicate. In the absence of timely medical care the disease can progress, complications arise, which in the future can lead to the patient's disability.
Pain when opening the mouth and chewing movements is familiar to many, as it often occurs with dental problems. Such a symptom may be transient or signal a serious pathology. To understand what to do in this situation, you need to pay attention to the accompanying signs.
Wisdom teeth
The last teeth in a row, the so-called "eights", are cut later than anyone else. When a person reaches the age of 14, mental development is considered complete, and wisdom develops. Therefore, the eighth teeth, or third molars, are called wisdom teeth.
When the eights are cut, the jaw hurts when opening the mouth, chewing, yawning and talking. The pain often does not subside even at rest, disturbing even at night. The gums can swell a lot, causing swelling of the cheeks, and it is also impossible to close the mouth completely.
Pain syndrome is most often caused by a lack of space in the jaw arch, which is why the tooth tries to take a non-physiological position and is cut incorrectly. The figure 8 can erupt at an angle towards the adjacent tooth, pressure on which is another cause of pain.
The appearance of wisdom teeth is sometimes accompanied by an increase in body temperature and an increase in lymph nodes. In some cases, the swelling is so strong that it prevents the mouth from closing.
Difficulty erupting a wisdom tooth is called pericoronitis, which in most cases does not go away on its own and requires an obligatory visit to a dentist-surgeon
To alleviate the condition, you can apply local funds- ointment Kamistad, Solcoseryl, Metrogyl-denta or Kalgel. Rinsing with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin) or herbs (chamomile, sage) helps to remove or reduce inflammation. You can eliminate puffiness with cold compresses.
Attention: if after a day or two the pain does not go away, you need to contact your dentist.
Trauma
Jaw injury is a fairly common occurrence that does not always go away without consequences. In case of bruises, people rarely go to the doctor, and in case of dislocations or fractures, difficulties with fixation arise. Therefore, tissue healing and bone healing often go wrong.
Almost any damage to the mandible negatively affects the function of the mandibular joint, the mobility of which is impaired. That is why, even after a while after the injury, it hurts to open your mouth.
In the absence or inadequate treatment of injuries, such signs as soft tissue swelling, jaw misalignment and its pathological mobility also appear. In this case, you should contact an emergency room or a surgeon who will restore the normal position of the jaw and apply a fixing bandage.
Injuries to the jaw are treated by a dental surgeon who will select prostheses that do not allow the patient to open his mouth wide, for example, the Petrosov apparatus.
Dental diseases
Painful sensations when opening the mouth and chewing can cause inflammation in the oral cavity. For example, with advanced caries, complications develop that do not disappear on their own:
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- granuloma (tooth cyst);
- phlegmon;
- periostitis (flux);
- osteomyelitis;
- multiple caries affecting a group of teeth.
Since in these diseases, the surrounding tissues are involved in the pathological process - to the right or to the left of the jaw joint, pulsating pain occurs and the mobility of the jaw is limited. The pain syndrome is especially strong with inflammation of the pulp of the molars (molars) and the hood of the eights.
Neoplasms
Neoplasms of the upper or lower jaw are either benign or malignant. They can be formed from dental, bone, cartilage and connective tissue. This pathology is characterized by chronic, persistent pain.
Benign neoplasms grow slowly, over the course of many years without causing harm to health and without manifesting themselves in any way. Malignant tumors on the contrary, they develop rapidly, often leaving no chance for recovery. In the absence of treatment, the prognosis for life is poor.
According to statistics, in about 4% of cases, a benign osteoma of the jaw is diagnosed - a bone tumor that manifests itself only under certain conditions. Reaching a significant size, it begins to put pressure on the nerve, and there are characteristic symptoms:
- pain and stiffness in jaw movements;
- violation of facial symmetry;
- deformation of the bone;
- change in bite.
If the mouth does not open completely, the cause may be an osteoma, which is located next to the coronal or condylar process.
Osteoblastoglastoma is another type of benign tumor that most often manifests itself as aching pain. A typical symptom is the appearance of ulcers and fistulas on the gums, an increase in the mobility of the teeth. Patients complain that the pain occurs when they chew, and over time it only gets worse.
The first sign of adamantinoma is a visual thickening of the jaw, which inevitably leads to a violation of the chewing process. Along with this, the intensity of pain in the jaw also increases. In advanced cases, the pain syndrome becomes pronounced, sharp, especially during meals.
Malignant tumors
Malignant neoplasms are of two types - cancer and sarcoma. The latter, in turn, can be formed from connective or bone tissue. A cancerous tumor forms from the skin and mucous membranes, causing first exposure of the dental necks, then loosening and loss of teeth. On early stages pain is mild or moderate, as the tumor grows, they increase.
Connective tissue sarcoma is a fast-growing tumor that can grow large in a short time. Almost always, its growth is accompanied by sharp, throbbing pains on the left side of the jaw or on the right. However, at the beginning of the development of sarcoma, only dulling of the tactile sensitivity of the skin of the face and gums is possible.
A typical sign of osteosarcoma (bone) sarcoma is a moderate chronic pain syndrome, which increases with palpation of the lower part of the face.
It should be noted that the detection of tumors of the jaws occurs most often at the later stages, which is explained by the blurring of the clinical picture. In addition, most patients do not visit the dentist regularly and try to manage their discomfort with home remedies.
Oral neoplasms are removed surgically, in some cases by a gentle curettage method.
Articular pathologies
If the jaw hurts when you open your mouth, the cause may be damage to the temporomandibular joint - arthritis, arthrosis, or dysfunction. In arthritis, inflammation develops in the joint due to injury or infection. This is manifested by soreness on both or only one side of the face, swelling, redness, difficulty chewing.

Arthrosis is a chronic disease in which a destructive degenerative process develops in the joint tissues
TMJ arthritis is also accompanied by a decrease in speech function and hearing, crunching during jaw movements. Pain syndrome ranges from weak, aching to sharp and intolerable. Patients complain that they cannot open their mouth completely; when trying to do this, the jaw "moves" to the side.
Since fluid accumulates in the joint during inflammation, there is a feeling of bloating and pressure, the resulting swelling prevents the teeth from closing. In the morning after a night's rest, the sensations are especially uncomfortable, which is explained by the large amount of exudate accumulated during the night.
The signs of arthrosis bear some resemblance to arthritis, since the pain is also localized in the joint. Osteoarthritis can develop due to the absence of one or more chewing teeth, when the main load is transferred to the jaw bone.
The most common signs of arthrosis are pain when moving - opening and closing the mouth, chewing, yawning, laughing or talking - as well as the characteristic crackling sound. With arthrosis, the jaw may hurt on the left or right side, but bilateral lesions also occur.
Attention: clicks in the jaw joint can be the only symptom of the disease, especially in the early stages. Having "captured" arthrosis at the very beginning of development, one can count on a complete recovery.
Dysfunction of the jaw joint means functional impairment symmetry in its structure, which leads to displacement of the disks and the appearance of pain. To the question of why dysfunction occurs, there are many answers, for the search of which narrow specialists are often involved - neurologists, psychologists and dentists.
Clinical picture dysfunction, or Kosten's syndrome, is very diverse and includes following symptoms:
- clicking and cracking when moving the jaw - sometimes these sounds can be very loud, and they are heard by people around them;
- pain can be felt not only at the point of the joint, but also in other places - the head, teeth, ears. Pain in TMJ dysfunction often imitates trigeminal neuralgia, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, acute otitis media and other diseases;
- blockage, or jamming in the joint. When a person opens his mouth, he must first "catch" the optimal position of the lower jaw, moving it from side to side.
The above symptoms are most typical for temporomandibular joint dysfunction, but others are often added to them:
- dizziness;
- intermittent sleep, snoring, respiratory arrest during sleep - sleep apnea;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- dry mouth due to decreased salivation;
- trouble swallowing food;
- pain and burning sensation in the tongue;
- noise in ears.
It is rather difficult to diagnose dysfunction, since it can be caused by trauma, dystrophic or inflammatory process, malocclusion, etc. Treatment of pathology is carried out by a dentist and in almost all cases includes the use of orthopedic devices - for example, night trainers.
Attention: if you suspect dysfunction, you should consult a specialist, because with a long course of the disease, the structure of the joint changes, and arthrosis develops.
Neuralgia
The jaw can hurt when peripheral nerves are damaged - trigeminal, superior laryngeal, glossopharyngeal, or ear. They have one common symptom - pain in the jaw area, but each type of neuralgia has its own characteristic signs.

Pain on one side of the face that occurs when the trigeminal nerve is affected is extremely severe and comparable to an electrical discharge
Trigeminal nerve so called because it is divided into three branches - orbital, maxillary and mandibular. With the defeat of the last two branches, pain occurs in the corresponding areas - the upper and lower jaw. Shooting pain syndrome appears when drinking cold or hot, being in a draft or outside in windy weather. Before the onset of a painful attack, tightness and slight itching of the skin may be felt.
The ear nerve becomes inflamed in diseases of the periodontal or ENT organs. Neuralgia auditory nerve accompanied by burning, throbbing pain behind the ear, which can spread to half of the lower jaw, back of the head and collar zone.
The glossopharyngeal nerve innervates the muscle of the same name and the muscle of the parotid salivary gland, and also provides gustatory sensitivity to the back of the tongue. The function of this nerve is impaired in infectious and inflammatory pathologies, aneurysm and brain tumors. Symptoms include sore throat, jaw, and ear pain.
Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve is a very painful phenomenon in which pains are observed in the larynx and lower jaw, radiating (radiating) to the ear, eye or temple. Often, a painful attack is accompanied by dry mouth and cough.
Neuralgia is diagnosed and treated by neuropathologists, who prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, neuroprotectors, anticonvulsants, antihistamines and sedatives, muscle relaxants.
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis of the jaw is a purulent inflammatory and infectious process that captures the entire jaw bone and leads to osteonecrosis (bone death). This pathology is quite common in dental practice and affects mainly males. Osteomyelitis of the lower jaw is diagnosed twice as often as the upper one.
In the overwhelming majority of cases, osteomyelitis is caused by dental diseases - caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, alveolitis, cyst at the root of the tooth. From the focus of the lesion, the infection penetrates the bone, which is largely facilitated by a decrease in immunity and some systemic diseases.
With an acute course of osteomyelitis, the temperature rises sharply to 38-39 °, pain appears in the area of the diseased tooth, which after a while spreads, "spills" to the ear and temple. The tooth begins to stagger, the gum swells under it, purulent contents are released from the formed gingival pockets.
The progress of the pathological process leads to the fact that the mouth almost does not open, it becomes difficult to swallow and even breathe, the lower lip goes numb from the outside and from the inside, sensitivity decreases in the chin area.
Attention: if you suspect osteomyelitis of the jaw, it is necessary to visit the dentist as soon as possible in order to prevent the development of severe complications.
From the above it follows that the main condition for the prevention of pain in the jaw is timely treatment and dental prosthetics. This is how most ailments can be avoided. Exceptions are tumors and injuries that cannot be prevented. In this case, the only way to minimize the consequences is early examination and treatment.
Sometimes such an unusual condition is noted, when the jaw does not open completely or does not open well. A person cannot fully eat, talk, and when trying to open his mouth a little wider, soreness appears, sometimes of a sharp nature. Trying to open the mouth sharply, a person feels severe pain in the area of the mandibular joint, and it can also be given to the temporal region. This condition, in which the jaw does not open completely, is called muscle contracture. Problems in the periarticular tissues of the temporomandibular joint can also cause such complaints.
A sharply limited opening of the mouth is observed with ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint. With this disease, there is a complete or partial fusion of the articular surfaces. Normal food intake becomes impossible, bite and breathing are disturbed. The face takes on a “birdlike” appearance. Treatment of this pathology is prompt. Additionally, massage, exercise therapy, drug therapy and a gentle diet are prescribed.
If contracture of the jaw apparatus appears, it is recommended to consult a specialist. He will be able after additional diagnostic activities determine why the mouth does not open fully, why painful sensations appear, and what to do in this case.
With contracture, there is a sudden difficulty in the mobility of the joint, which is responsible for the movement of the lower jaw, due to pathological processes in the muscle or ligamentous tissue. Often, such processes are triggered by injuries, diseases, reflex sharp muscle contractions.
There are certain reasons why it is impossible or difficult to open your mouth:
- contracture of the muscles of the jaw apparatus, which occurs as a result of injuries (for example, after a fall, impact), sprains of the muscular apparatus (with prolonged wide opening of the mouth at the dentist);
- myositis, which are obtained with the introduction of anesthesia (mandibular or torusal), which is used in the treatment or extraction of units on the lower dentition;
- inflammatory process in the muscular apparatus, which appeared as a result of hypothermia or infection;
- rheumatic diseases and, as a result, inflammation in the temporomandibular joint;
- injury to the joint or surrounding tissue;
- subluxation;
- periostitis of the alveolar process and inflammation, which has spread to all structures of the ligamentous apparatus of this area;
- processes of a purulent nature (phlegmon, abscesses) on the mandibular apparatus, which provoke an inflammatory process of the joint itself or the muscles that move the lower jaw.
All of these conditions can cause a condition in which the jaw cannot be fully opened, and the mouth opening range itself ranges up to one centimeter.
What to do
If the cause of the contracture of the muscular apparatus was the introduction of anesthesia, overstretching of the muscle with prolonged opening of the jaw, such conditions usually go away on their own for several days and do not require special treatment... If the reasons lie elsewhere, a visit to a specialist is mandatory.
In the event that this pathology is caused by adhesions, scars, tissue fusion, it is advisable to apply radical treatment, which involves surgery. Surgical treatment consists in excision of the modified tissue, replacement of the lost tissue sections. Typically, such procedures are performed by maxillofacial surgeons.
If additional soreness occurs
If, in addition to muscle contracture, pain appears when opening the mouth, there are probable causes such a state:
- Fracture. During it, soreness, difficulty moving the jaw, hematoma or bruising occurs. In such a situation, you should immediately visit a specialist.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. Treatment of the disease should be carried out immediately, since dangerous complications can arise.
- Arteritis of the facial artery.
- Dysfunctions in the jaw apparatus. May be congenital (eg, malocclusion), acquired (joint inflammation).
Regardless of the cause and severity of the symptomatology, it is recommended to timely contact a qualified specialist who can diagnose, determine the cause and prescribe the correct treatment regimen. If the use of conservative therapy options does not bring the desired result, it is advisable to undergo surgery to restore the full function of the temporomandibular joint.
If the cheekbone or jaw hurts, treatment is prescribed medication, folk remedies or physiotherapy procedures. Only a doctor will be able to choose the right tactics for treating the disease.
Pain in the cheekbones, jaw, near the ear is a frightening symptom. Such painful sensations may indicate the presence of a large number of diseases in organs and systems. Teeth, ears, gums, lymph nodes, sinuses, soft tissue face - diseases associated with these organs lead to pain.
- If unpleasant sensations appear in the cheekbone area, then you should immediately consult a doctor. But it is important to know which doctor to go to: dentist, otolaryngologist, surgeon or another.
- It is better to first contact a therapist who can refer you to the required specialist. Different laboratories and instrumental methods help doctors in diagnostics.
- To understand the factors behind the onset of pain, you can consider possible reasons using a special algorithm of actions. So, the jaw hurts, it hurts, it hurts when chewing - what to do in these cases and where to go? You will find answers to these and other questions in this article.
If there is pain in the jaw, then you do not need to indulge yourself in the hopes that this will go away by itself. This symptom occurs when a serious illness appears that needs to be treated. If this is not done in a timely manner, then the condition may worsen and the disease may develop into a chronic stage.
Causes of pain in the cheekbones, jaw near the ear on the left and right, and when it hurts to chew:
- Diseases of the dento-jaw apparatus, gums and temporomandibular joint... These problems are dealt with by dentists, maxillofacial surgeons. If you have jaw abscesses and phlegmon, you will need an operating dentist.
- Inflammation of the sinuses... On the sides of the nose are the maxillary sinuses, and behind the ear there is a cavity located inside the process at temporal bone... The mucous membrane of this cavity can become inflamed and give aching pain in the cheekbone area. An ENT specialist deals with such problems.
- Diseases of the larynx, tonsils and tissues around them. The disease appears as a result of a purulent-inflammatory process, infectious disease and tumors. An ENT doctor will be able to cure such a pathology.
- Disease of the peripheral nervous system. Nerve cells become inflamed, causing congestion and pain. You should contact a therapist or neurologist.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes... They become inflamed if infected lymph from the nose, throat, or ears gets into their tissues. Diseases of this system are dealt with by therapists or pediatricians (in children).


If the disease is started, delaying the trip to the doctor, then other concomitant, no less complex pathologies may develop:
- Purulent and inflammatory processes: abscesses, phlegmon.
- Infections in the mouth, nose, or ears.
- Dysmetabolic abnormalities in electrolyte balance.
- Injuries - can result from strong mouth opening when yawning, teeth opening bottles and other hard or metal caps.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Inflammation of peripheral vessels and nerves.
If the jaw hurts after going to the dentist or removing a tooth, then you need to urgently contact this specialist. Consultation may not be needed if a bracket system has been installed. In this case, mild or tolerable pain occurs when the correct bite is formed. But, if this condition does not go away after 2 months, then consultation with the attending dentist is necessary.


Important: A trauma surgeon should be consulted if the jaw or cheekbone began to hurt after an injury. In this case, pain can arise, both from a banal bruise, and from a serious fracture, dislocation or abscess.


Such pain can be associated with both dental problems and diseases of the nerve endings. What other causes of pain in the jawbone near the ear and in the muscles when pressed? Several important factors:
- Injury- a strong blow to the head area can lead to a violation of the integrity of the facial bone. Constant aching pain, as well as when pressed.
- Teething wisdom tooth... Such a process is almost always accompanied by painful sensations, in some people to a lesser extent, in others to a greater extent. Pain may occur when pressing on the cheekbone area.
- Jaw osteomyelitis- a disease that affects the entire bone. The cause of its occurrence is active pathogenic microorganisms that make their way into the root canals. The pain is severe and aching.
- Caries and pulpitis can cause pain that worsens at night, especially when pressing on the cheekbone in the area of diseased teeth.
- Arteritis- pain in the form of a burning sensation in the jaw area.
- Temporomandibular joint dysfunction- pain when opening the mouth and chewing food, when pressed.
- Boils, fistulas, phlegmon and abscesses- the jaw hurts when pressed and at rest.


Any discomfort cannot be ignored! If you experience pain in the jaw area, when pressed, at night, or if the discomfort is persistent, you should see a doctor.


Often the jaw crunches when yawning. But, if you open your mouth too wide, then in addition to a crunch, pain may appear. It does not go away for a long time, and appears during chewing, opening the mouth, or even at rest. What to do if your jaw cracked and it hurts?
If the pain persists the next day, then you should immediately consult a doctor. Such symptoms can occur with serious illnesses:
- jaw arthritis;
- bursitis;
- stretching of the ligaments of the jaw muscles;
- dislocation of the jaw joints.
The doctor will examine and order to take a picture. If the joints are in order, then the doctor may prescribe UHF and steroid anti-inflammatory drugs. Within 5-7 days after undergoing physiotherapy, the pain will disappear.
The clicking sound when opening the mouth is most often painless. Only discomfort is felt and a characteristic sound is heard.
- Many people get used to this crunch and stop paying attention to it.
- This condition is explained by the fact that the jaw joint leaves the articular bag during movement. It moves to the side and when it returns to its place, a crunch is heard.
- This can be due to an injury, malocclusion, excessive tension of the jaw muscles (singing, reading poetry).


What to do if the jaw clicks on one side and the jaw joint, cheekbone hurts when opening the mouth? A few tips:
- Correct diagnosis... Often people go to a doctor with a problem in advanced cases. It is difficult to determine the root cause, because you need to understand how this condition developed. To make the correct diagnosis, you must contact the doctor when the first pain... The doctor prescribes X-ray, MRI, computed tomography and arthroscopy.
- Dentists treat dysfunctions of the jaw joint... Complex cases require the consultation of a dental surgeon. For treatment, painstaking and lengthy work is carried out to correct the occlusion, refill teeth, replace prostheses, and so on. Treatment of dysfunction of the jaw joint is carried out by prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs.
- At home, you can alleviate the condition a little with warm compresses, and in case of inflammation, applying ice will help. Do not load the jaw: soft and grated food, complete rest.
- Relaxation techniques can help cope with pain... As a prevention of the appearance of such diseases, you can use.
Treatment of all diseases associated with clicking of the jaw joints and pain depends on the degree and nature of the development of the inflammatory process. General recommendations in this case, it is complete rest of the jaw.


Colds and runny nose are accompanied by the spread of pathogenic microflora throughout the body. Inflammation begins, which is accompanied by pain. Therefore, to the question: can the cheekbone and jaw hurt with a cold, runny nose, tooth extraction, we can confidently answer: yes.
- If pain occurs in the cheekbone area, almost under the eye, then this is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. Contact the ENT.
- Pain in the junction of the upper and lower jaw can occur due to colds and runny nose. Bacteria enter the articular sac, and its surface becomes inflamed. It will help get rid of the ENT problem.
- Colds can cause inflammation of the jaw nerve... A neurologist deals with the treatment of such a disease.
- Cheekbones can hurt with otitis media... In this case, the pain may be accompanied by an increase in temperature. The ENT doctor is engaged in the treatment of otitis media.
Jaw pain during tooth extraction may be minor. But, if the pain is severe and intensifies over time, then the surgeon may not have removed the entire tooth, so you should urgently consult a dentist.


Often, when pain occurs, people panic and do not know which doctor to contact. If such a situation arises, then you can contact a therapist, and he will already refer you to the right specialist. What other doctor can you contact if your cheekbone or jaw hurts? You will be received by the following specialists:
- dentist;
- dental surgeon;
- surgeon, orthodontist;
- neurologist;
If the pain is sharp and unbearable, as with a dislocation or fracture of the jaw, then an ambulance should be called.


From the above, it is clear that there are many reasons for the appearance of pain in the jaw joint. Diseases can be associated with ENT organs, neuralgia, inflammation of the articular and soft tissues, inflammation of dental tissues.
- Therefore, treatment for a sore jaw joint near the ear or in the cheekbone area should be prescribed only by a specialist.
- He will be able to make the correct diagnosis or refer to another highly specialized doctor.
- Often, when treating pain in the cheekbone area, it is accompanied by the appointment of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs... In almost any inflammatory process, the doctor prescribes UHF or other physiotherapy procedures.
Important: Do not self-medicate! It is hazardous to health.


Osteoarthritis of the jaw is a chronic disease of the bones of the skull in which the cartilage in the joints is destroyed, resulting in deformity, pain and decreased mobility.
Medication should only be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication can lead to a deterioration of the condition and an uncontrolled reaction of the body. The main groups of drugs used in the treatment of jaw pain are:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - non-steroidal drugs: diclofenac, ibuprofen, etoricoxib, ketorol. If there are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then drugs that reduce acidity in the stomach are prescribed in parallel: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole.
- Vitamins - ascorbic acid (vitamin C), cholecalciferol (vitamin D), calcium.
- Preparations that renew cartilage tissue - hyaluronic acid.
- Intra-articular injections for severe pain: Dysprospan. Such treatment is carried out once every 6 months.
Women may be prescribed hormone therapy, especially during menopause, but under the supervision of a gynecologist and an endocrinologist. It will also be effective to carry out physiotherapeutic procedures: current, paraffin, laser, magnet, massage, ultrasound.


In parallel with medications, in the treatment of arthrosis of the jaw joint, are used folk remedies... Apitherapy is a therapy performed using bee venom. It contains biogenic amines that relieve pain and act as an anti-inflammatory agent. Bee venom is used like this:


This method has many contraindications (allergies, chronic diseases, malignant neoplasms, hypertension, diabetes mellitus). Therefore, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment.
In addition to bee venom, honey and gelatin can be used to treat arthrosis:


Video: Why does the jaw click?
Read also ...
- Valentines: a big history of small postcards
- Sketch study of the basic version of the nightgown
- Presentation for the orkse lesson for primary grades "monastery"
- Presentation on the theme "development of a system of motivation and incentives for labor" Incentives and motivation of personnel labor presentation