Laminating fermentation reaction. Microbiology is a relatively young science. The most important representatives of nonypical lactic acid bacteria and their use
Vyatka State Agricultural Academy
Faculty of veterinary medicine
Department of Morphology and Microbiology
Course of microbiology and virology
On the topic "Local sampling"
Kirov 2012
1. Characteristics and chemistry of lactic fermentation
Characteristics of fermentation pathogens
Practical application of lactic fermentation in the national economy
In the future, functional products with lactic acid bacteria will have more high level Consumption and in the market there will be many products. New bacteria are expected to be discovered and, therefore, new biotechnological products with new nutritional and therapeutic useful results that are available to the consumer from childhood to old age.
Babe lactic acid bacteria are gram-positive, unfortunate, low, coconut and catalase-deficient. These are cocci and variable length bacillos and 5-8 μm thickness, optional anaerobic and catalase negative. They can be classified as heterophermentative and homofermentative. The first produce only 50% of lactic acid.
Products that get using lactic acid fermentation
1. Characteristics and chemistry of lactic fermentation
Lamp fermentation is the process of anaerobic oxidation of carbohydrates, the final product in which lactic acid is. The name obtained by the nature of the product - lactic acid. For lactic acid bacteria is the main way of catabolism of carbohydrates and the main source of energy in the form of ATP. Also, lactic acid fermentation occurs in animal tissues in the absence of oxygen at large loads.
Local bacteria are microorganisms that can be found in milk and dairy products certain, capable of fermentation of monosaccharides or polysaccharides to turn them into acids, such as dairy, lemon, propionic, exopolisaccharides, bacteriocins, hydrogen peroxide, non-ball sweeteners, vitamins, milk drinks , Silo, the formation of desirable flavors and flavors, ripening of cheeses and others. The above metabolites and others are produced through metabolic pathways using glucose as the main source of energy before obtaining the desired metabolite.
Milk proteins are an excellent source of nitrogenous nutrition for lactic acid bacteria, which split milk sugar, turning it into a lactic acid, increase the acidity of the medium, and the milk is cooled, forming a dense homogeneous clot.
Types of lactic acid fermentation. Different with homofermentative and heterofermentative lactic acid fermentation, depending on the released products in addition to lactic acid and their percentage ratio. The difference also lies in different ways of obtaining pyruvate in the degradation of carbohydrates homo- and heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria.
They are widespread in liquid and solid fermented products. Its benefit is a nutritious and therapeutic, giving sensory characteristics, very acceptable to consumers. Overview of lactic acid bacteria as a cellular factory for the production of food ingredients. International dairy magazine. Volume 18, p. 466.
Bacterlotsins and lactic acid bacteria - Billish. African magazine biotechnology. Classification of lactic acid and physiology. Introduction to food technologies. Technology of dairy products. Serum fermented by thermophilic lactic acid bacteria: the evolution of carbohydrates and protein content. Food microbiology. about.
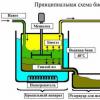
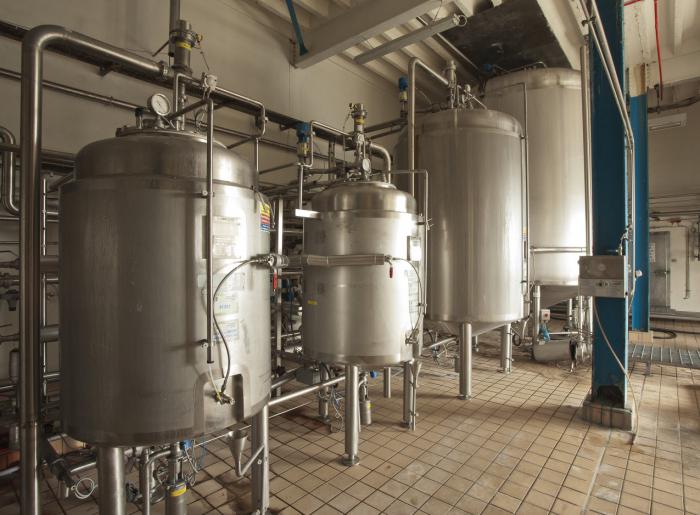
Homofermentative lactic acid fermentation. Since the cleavage of lactose occurs inside the cell of the microorganism, the key step of this metabolic path is the flow of glucose into the cell. When transferring lactose outside to the cytoplasmic membrane and in the microorganism cell, four proteins are involved (sequentially: enzyme II, II, I and HPR) participate in the phosphate of lactose. Lactose-6 phosphate hydrolyzed b. -phosphogalkotogenase ( b. -Pgal) on its monosaccharide components. Galactose and glucose are then catabolized through the Tagato Way and the Parnassa Embued-Meyergood Path (EMP). It is possible to dephosphorylation of galactose, and in this case it is not valid and excreted from the cell of the microorganism. In both cases, dihydroxyacetone-phosphate and glycerinaldehyde-3-phosphate and glycerinaldehyde-3-phosphate are converted in both cases of glucose and galactose, where the three-carbon sugars are oxidized further to phosphoenolpiruvat, and then form a lactic acid with lactate dehydrogenase. The product of homofermentable fermentation of fermentation is lactic acid, which is at least 90% of all fermentation products. Examples of homofermentable lactic acid bacteria: Lactobacillus Casei, L. Acidophilus, Streptococcus Lactis. Heterofermentative lactic acid fermentation. Lactose and glucose on the heterophermentation pathway are formed only bifidobacteria. When catabolized glucose with 2 it does not form, since there is no initial stage, including decarboxylation. Lactose is transported to a cage with a permeyase, and then hydrolyzed in glucose and galactose. There are no aldolaza and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase for this species. Hexoses subjected catabolism by hexosomonophosphate shunt with the participation of fructo-6-phosphate phosphocetolase. Fermentation products Bifidobacterium are lactate and acetate, and the fermentation of two glucose molecules gives three acetate molecules and two lactate molecules. By-products are: acetic acid, ethanol. Examples of heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria: L. Fermentum, L. Brvis, Leuconostoc Mesenteroides, Oenococcus Oeni. Characteristics of fermentation pathogens The effect of using propionic acid bacteria as an adjunct culture in the production of yogurt. Magazine "Milk Science". Volume 91, p. 892. Bacteriocinated food bioconservation strategies, international magazine on food microbiology, vol. 120, p. 51. Encyclopedia of food and nutrition. Preservation of aromatic compounds with acid milk bacteria in food media models. Preservation of antibiotics in food lactic acid bacteria - review. The appearance of lactic acid bacteria and beta-amines in biologically old wines. Biotype serum for lactic acid production Review, food chemistry. Volume 105, p. 1. Isolated on white background. International dairy magazine. Volume 18, p. +923. Aminolithic bacterial lactic acid fermentation. Review of heterologous production of bacteriocinnes by lactic acid bacteria. International Journal of Food Microblogging. Local bacteria are a group of microeerophilic gram-positive microorganisms that lose carbohydrates with the formation of lactic acid as one of the main products. All lactic acid bacteria (they are lactobacillia) - Gram-positive, optional anaerobes. Among the lactic acid bacteria there are mesophylls (they prefer about 30 ° C) and thermophilic (Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus Bulgaricus), the optimal temperature for which is the temperature of about 40-50 ° C. Local bacteria need a complete set of finished amino acids, in the vitamins of the group B12, in the components of nucleic acids, which determines their distribution in nature. Production of exopolishares when exposed to lactic acid bacteria and fermentation time. Professional biotechnology. The effect of the total content of solids in the lactic serum on the acidification profile and the viability of various lactic acid bacteria. Exopolisaccharides from lactic acid bacteria: prospects and problems, "Review of tendencies in biotechnology", vol. 38, p. 67. Evaluation of the probiotic Pottening of lactic acid bacteria isolated from the feces of infants in Egypt. Screening of lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria for the potential use of probiotics in Iberian dry fermented sausages. Lactic acid bacteria live mainly on plants, fruits, vegetables, in gastrointestinal, in milk and dairy products, as well as in places decomposition of plant residues. As a source of carbon is used lactose, maltose. The optimal pH value for the development of lactic acid bacteria is about 4. The lactic acid bacteria form from 1 to 3.5% of the lactic acid. fermentation lactic acid bacterium food Lamp fermentation is caused by several types of bacteria Antibiotic resestances of the starter and probiotic strains of lactic acid bacteria. Applied and ecological microbiology. American clinical food log. Bacteria associated with strong waves are prototypes of adkadas for La Masiasis de Mas acid. Insulation, identification and characteristics of lactic acid bacteria for the preparation of tropical cream cheese. Insulation, identification and characteristics of lactic acid bacteria for the production of tropical cream cheese. Based on the lowest pH, six strains were chosen for the production of "tropical cream cheese" with pasteurized milk. There were significant differences between the fermentation temperatures and the incubation time in each of the strains. In addition, milk acid, acetic acid, propionic acid and oil acid in fermented milk were evaluated with each strain, and there were no significant differences in the production levels of these metabolites. Typical lactic acid bacteria (almost completely convert carbohydrates into lactic acid) - acidophilic Bulgarian wand, cassea bacterium, cochazicum, as well as lactic acid cocci, leynestock, lactobacterium, streptococci and bifidobacteria. Ultipical (fermentation with the accumulation of a small amount of lactic acid) - proteus and intestinal wand. The lowest populations of these microorganisms were discovered in cheese obtained from pasteurized milk. The amount of dairy bacteria did not differ between both types of cheese. The purpose of this study was the allocation, identification and characteristics of 20 strains of lactic acid bacteria from "tropical cream cheese", traditionally prepared with nonpasteurized milk. Based on the lowest pH, 6 strains were chosen for the preparation of "tropical cream cheese" with pasteurized milk. Each strain represented significant differences in the temperature of fermentation and incubation time. In fermented milk for each strain, milk acid, acetic acid, propionic acid and oil acid, and there were no significant differences in the production levels of these metabolites. Corn cream cheese used as a reference. Lactic acid bacteria are combined into the Lactobacillaceae family. Although this group of morphologically heterogeneous (includes long and short chopsticks, as well as cocci), in physiological terms it can be described quite well. All bacteria relating to it are gram-positive, do not form a dispute (with the exception of Sporolactobacillus Inulinus) and in the overwhelming majority are fixed. The lowest indicators of microorganisms were found in cheese prepared by pasteurized milk. The amount of dairy bacteria was the same in both types of cheese. Tropical cream-cheese is cheese, which is perfectly accepted in the south-east of Mexico, mainly developed in the states of Chiapas and Tabasco. Although his historical origin is unknown, its production at the handling level is very similar in both states. Tropical cream cheese is made in a traditional way, acidifying with sour serum milk from the previous day. Then, one ml of calf serum is added for every 10 liters of milk to get cottage cheese, which is left for rest for 24 hours. After that, cottage cheese leaves for the day during the day, it is salted, form and pressed for four hours and, finally, packaged into the wax paper. All of them are used as a source of energy carbohydrates and isolated milk acid. Lactic acid bacteria are capable only for fermentation; They do not contain hemoproteins (such as cytochromes and catalase). They can grow in the presence of air oxygen: being anaerobam, they are still aeroclant. Another distinctive feature of lactic acid bacteria is their need for growth substances. No representative of this group can grow on a medium with glucose and ammonium salts. Most need a number of vitamins (Lakoflavina, Tiamine, Pantoten, Nicotinova and folic acids, biotine) and amino acids, as well as in purines and pyrimidines. Milk pasteurization allows you to get milk products with higher hygienic characteristicsBecause in this process, most pathogenic microorganisms are destroyed, which may be present in milk. However, that cheese can be prepared from pasteurized milk, it is necessary to add acidic microorganisms into milk to cover this part of the process. The microorganisms used should be part of the biota responsible for giving the typical characteristics of cheeses to be manufactured. Consumers value handicrafts due to their unique characteristics of aroma and aroma, which is usually explained by the metabolic activity of autochthonic microbiota present in the cheese milk. The use of commercial lactic acid crops helps to carry out the process of acidification, but usually they are associated with other organoleptic properties, since these microorganisms were selected from cheeses from other regions. In addition, the use of industrial lactic crops in the substitution of autochthonic microbiota can lead to the loss of autochon strains in the long run. Cultivate these bacteria mainly on complex media containing a relatively large amount of yeast extract, tomato juice, whey and even blood. Thus, lactic acid bacteria is a kind of "metabolic disabled", which, probably as a result of their specialization (growth in milk and other media rich in nutritional and rising substances), have lost the ability to synthesize many metabolites. On the other hand, many of them have the ability to which most other microorganisms do not have; They can use milk sugar (lactose). In this, they are similar to many intestinal bacteria. As a rule, the choice of autochon milk strains helped get dairy products with characteristics like products prepared from raw milk. There is a great interest in the study of local lactic crops for use in the industrial production of traditional cheeses, which retain their typical properties and are simultaneously safer from a hygienic point of view. The objectives of this work were to isolate, identify and characterize a dairy culture with autochthonic bacteria, which were inoculated into pasteurized milk to produce a product with the desired profile of cheese. Distribution and habitat. The propagation of lactic acid bacteria in nature is determined by their complex needs in nutrients and the method of producing energy (only fermentation). These bacteria are almost never found in soil and reservoirs. In natural conditions, they meet: in milk, places of its processing and dairy products (Lactobacillus Lactis, L. Bulgaricus, L. Helveticus, L. Casei, L. Fermentum, L. Brevis, Streptococcus Lactis, S. diacetilactis). Dilutions were seeded in two copies in the culture medium of a person, rogoz, Sharpe using the injection molding technology, incubated at 30 ° C for 48 hours. After five days of incubation, five drops of non-salar reagent were added to detect ammonium presence. Sequences were obtained from the database National Center biotechnology information. Graphic align showing areas with a high degree of identity that were used to design initiators. The initial denaturation was carried out at 94 ° C for 5 minutes and one final lengthening stage at 72 ° C for 10 minutes. Gels were performed within two hours. Precursors and metabolites of lactic acid were determined according to the Taylor method specified by Madrid et al. And the rest was determined quantitatively gas chromatography. on plants and on decomposing plant residues (Lactobacillus Plantarum, L. Delbriickii, L. Fermentum, L. Brevis, Streptococcus Lactis, Leuconostoc Mesenteroides). in the intestines and on the mucous membranes of man and animals (Lactobacillus Acidophilus, Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus Faecalis, S. Salivarius, S. Bovis, S. Pyogenes, S. Pneumoniae). Description of some types of lactobacteria: Bulgaricus (Thermobacterium Buldaricum). Forms long sticks and is homofermentative. Together with Streptococcus Thermophilus or with a greater degree of Lactobacillus Jughurti, it is used to prepare yogurt. Sometimes the Lactobacillus Bulgaricus is part of the bacteria of a frkic acid to prepare for lactic acid products. It is also used in the production of solid cheeses. The optimal temperature of its development is 40-45 ° C.Lactis (Thermobacterium lactis) forms long threads. Constantly is in the intestine of man and animals. It can be found on milking equipment, and more often than other types of lactobacilli, it is present in unprocessed (cheese) milk. Lactobacillus Lactis is identical to Lactobacillus Caucasicus, located in kefir. She often takes part in the ripening of solid cheeses. The optimal temperature of its development is approximately 40 ° C.Helveticus (Thermobacterium helveticum) is found in untreated (cheese) milk, in Sichuhhu and in the spontaneous enzyme calves. Used with Streptococcus Thermophilus for the preparation of Emmental and Gruyersky cheeses. It forms not only lactic acid, but also participates due to the presence of a proteolytic endoenzyme in ripening of cheeses.acidophilus (Bifidobacterium bifidum). With predominantly milk nutrition It is in large quantities in the intestines of children and adults. It is often discovered in the intestines of calves. From other lactobacilliomes found: Lactobacillus Casei (Streptobacterium casei) - strongly proteolytic, Lactobacillus Brevis (Betabacterium Breve), Lactobacillus Fermenti (Betabacterium Longum) .lactis. It is the first microorganism, which is highlighted in a clean culture (in 1873 by the Lister). Streptococcus Lactis occurs on plants. With dust and vegetable particles hits milking equipment and then into milk. It is found in the form of a short chain of two - six stars. Certain strains that do not form mucus and aromatic substances with unpleasant odorAs many wild strains are part of the starter. The optimal development temperature of Streptococcus Lactis is about 30 ° C. Separate strains, however, can also multiply, but slowly, at low temperatures (below 7 ° C). At a temperature of 25 ° C, Streptococcus Lactis due to the formation of lactic acid reduces the pH of about 4.5 and the milk is coagulated due to casein loss. DiaceTilactis. It forms not only lactic acid in milk, but also acetone and diacetyl, the most important aroma oils, as well as CO2. Streptococcus DiaceTilactis is contained in a significant amount in Zavask for the preparation of the oil. In each of the procedures, five repetitions were held. General acidity was reported to% of lactic acid? 1. The milk was standardized by 3% fat, pasteurized at a temperature of 63 ° C for 30 minutes, the temperature was reduced to 37 ° C, 1% of half of the skimmed milk was inoculated, acidified with selected milk crops. For every 10 liters of milk, 1 ml of the rennet enzyme was added. The production of cheeses was repeated five times. Dry substance. Samples 10 g of cheese were dried at 102 ° C for 4 hours, cooled in the desiccator and weighed. Statistical analysis For each of the processes, a dispersion of a pH reduction in relation to strains, times and temperatures was carried out. Local bacteria are a component of a normal microbiocenosis of the human digestive tract, and their quantitative composition serves as a criterion for assessing health status. Therapeutic effect Preparations that contain lactobacillias are due to the antagonistic effect of lactobacillia with respect to pathogenic microorganisms, including staphylococci, enteropathogenic intestinal sticks, protetes, Shigella, which determines the corrective effect of the drug in disabilities of bacteriocenosis. Preparations of lactobacilli improve exchange processes, prevent the formation of protracted forms of intestinal diseases, increase the nonspecific resistance of the body. For statistical analysis of these volatile fatty acids, six selected strains used a fully randomized design. Isolation, selection and purification of lactic acid bacteria from tropical cream cheese. Evaluation of the decrease in the pH of milk due to temperature, incubation and deformation time. The strength of the interaction x temperature x hour was not significantly different. In postoperative comparisons there was a decrease in the level of pH due to the influence of strains, 3 groups. Milk acid was a metabolite of the greatest presence in fermented milk with all strains. Physico-chemical estimates for tropical cream cheese with dairy cooling and tropical cream cheese with pasteurized milk. However, it seems that this species is not used as a starting culture for dairy products. Low pH inhibits the growth of unwanted and pathogenic microorganisms, which were found in some cheese in Tabasco. The low pH value leads to inhibiting the number of coliforms, especially with other stress mechanisms, such as a decrease in water activity and salt availability. The strains of lactic acid bacteria use in the production of medical drugs - probiotics intended for recovery normal microflora intestines and reproductive systems in women (after infectious diseases, antibiotic therapy). Practical application of lactic fermentation in folk farm Lactic acid fermentation is used in the dairy industry for the manufacture of prostromasses, cottage cheese, sour cream, kefir, butter, acidophilic milk and acidophilic prostropyl, cheese, sauer vegetables, when preparing bread starts, lactic acid. Local bacteria are widely used in the silage of feed, during the release of fur shkins and in the production of lactic acid. These bacteria have great importance when serving vegetables, feeding feed (vegetable mass) for animals, in bread maker, especially in the manufacture rye bread. Positive results provide research on the use of lactic acid bacteria in the manufacture of some varieties of sausages, salt-boiled meat products, as well as in the ripening of weakly salt fish to accelerate the process and give the products of new valuable qualities (taste, aroma, consistency, etc.). The use of lactic acid bacteria is also used to obtain lactic acid, which is used in non-alcoholic beverages. Spontaneously (spontaneously) arising milk acid fermentation in products (milk, wine, beer, soft drinks, etc.) leads to their spoilement (dismounting, turbidity, isleniation). The use of lactic acid bacteria in the household, agriculture And for the preparation of food. If the non-sterile solution containing along with sugars is also complex sources of nitrogen and growth factors, leave without access to air or simply pour a sufficiently large amount of such a solution into the vessel, then short bacteria will appear in it. They reduce pH to values< 5 и тем самым подавляют рост других анаэробных бактерий, которые не могут развиваться в столь кислой среде. Какие именно молочнокислые бактерии вырастут в таких накопительных культурах, зависит от прочих условий. Благодаря своему стерилизующему и консервирующему действию, основанному на подкислении среды, молочнокислые бактерии используются в сельском и домашнем хозяйстве и в молочной промышленности. Cooking silage. Milk acid bacteria living on plants play a large role in the integrity of the future of feed for livestock. For the preparation of silo, sugar beet leaves, corn, potatoes, herbs and alfalfa are used. The vegetable mass is pressed and added to her molasses to increase the ratio of C / N, and ant or any inorganic acid in order to provide preferential growth of lactobacilli and streptococcal. In such conditions, a controlled lactic acid fermentation occurs. Preparation of acidic cabbage. Acute cabbage is also a product, in the preparation of which lactic acid bacteria participate. In the finely chopped salt (2-3%) and spontaneous white-eyed fermentation begins, in which Leuconostoc (with C02 formation), and later Lactobacillus Plantarum begins participating at first LEUCONOSTOC. Milk products. Local bacteria, forming acid and giving products a certain taste, are widely used in the dairy industry. Sterilized or pasteurized milk or cream is fermented, adding clean ("starting") cultures of lactic acid bacteria as a start-up. Equal formal oil is prepared from cream, beaten with Streptococcus Lactis, S. Cremoris and Leuconostoc Cremoris. Diacetyl addresses in the fermentation process gives oil specific aroma. Explosives containing Streptococcus Lactis or Lactobacillus Bulgaricus and Streptococcus Thermophilus, cause casin coagulation when cooking cottage cheese and German cheeses (Garz and Mainzsky). In the manufacture of solid cheeses (in contrast to acidic milk cheeses), the casin coagulation uses a rennet enzyme. Lactobacillus Casei, Streptococcus Lactis) together with propio-Novokislavi participate only at the stage of ripening of cheeses. For the preparation of lactic acid products, start-up cultures of lactic acid bacteria, forming acid and some substances that give the product are also used. The fragrant smelling is obtained using the above-mentioned starters used for the preparation of fermented milk oil. Pakhtanyan along with lactic acid also contains acetic acid, acetoin and diacetyl. Yoghurt is obtained from pasteurized homogenized solid milk, inoculated Streptococcus Thermophilus and Lactobacillus Bulgaricus (after entering the swarm, milk is kept 2-3 hours at 43-45 ° C). Under the name Biogurt, sour milk fastened with a baked Lactobacillus Acidophilus and Streptococcus Thermophilus. Kefir belongs to lactic acids containing acid and ethanol; It is obtained from milk (cow, sheep or goat). Swiss prepare on so-called kefir grains, which consist of a non-fully studied community of organisms, including lactobacilli, streptococci, micrococci and yeast. Milk roding lead at 15-22 ° C for 24-36 hours. For the preparation of Kums, donkey milk is used, which is inoculated by a culture containing Lactobacillus Bulgaricus and the yeast of the Torula genus. Pure milk acid, which is used for various industrial purposes and as an additive to food products, is obtained as a result of fermentation. Milk or serum is fermented using Lactobacillus Casei or L. Bulgaricus. L. Delbruckii, L. Leichmannii or Sporolactobacillus Inulinus are used to fermentation of glucose and maltose. The source of the necessary growth factors serve melasse and malt. The formation of acid in an acidic test used for its lifting is also provided by lactic acid bacteria, in particular Lactobacillus Plantarum and L. Coryneformis. Starting crops Lactobacilli and micrococci are also used to prepare ferocular sausages (salami, servolet). Arriving milk acic acid and reducing pH, lactic acid bacteria are protected from damage those types of sausages that are not subjected to cooking. Products obtained using lactic fermentation At the heart of receipt equal milk products There is a directional and adjustable activity of certain types of lactic acid bacteria. As a result of the vital activity of lactic acid microorganisms, milk changes and becomes new taste, dietary, biological and therapeutic properties. Equal milk products are better and faster. If ordinary milk is as a hour after consumption, it is absorbed by 32%, then kefir, prostrochy, etc. are absorbed by 91%. When rushing milk, small, easily-friendly flakes are formed. The milk protein is subjected to partial cleavage (peptonization) and acquires a finely dispersed structure, and therefore, it does not require that processing in the stomach, which is undergoing ordinary milk. The most important component of fermented acidic acid, which possesses biological activity, creating optimal conditions for the manifestation of antibiotic substances and vital activity of lactic acid bacteria. At the same time, the lactic acid inhibits the development of grinding and other non-octic acids (including pathogenic) bacteria. Using fermented milk drinks, it is possible to limit and even completely discontinue education in the intestine harmful substances putrid microbes. Famous Russian scientist I.I. Mechnikov experimentally proved that with the introduction of animals in the intestine of these harmful products of rotational microbes in a few months, animals develop sclerosis of aorta. Apparently, in the development of atherosclerosis in person, the intensive vital activity of the intestinal rotary microflora plays a considerable role. Specific types of lactic acid bacteria are an acidophilic chopstick, lactic acid streptococcus, etc., capable of forming antibiotic substances in fermentation drinks with bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects. The study of the antibiotic properties of acidophilic bacteria revealed the ability to produce a number of thermostable antibiotic substances: lowland, lactoline, lactomine, streptotsin, etc., showing its effect mainly in an acidic environment. In all cases, disorders of the normal composition of intestinal microflora use of fermented acid, acidophilic products makes it possible to largely normalize the intestinal microflora, especially with respect to the reduction in the intensity of rotary processes. Local bacteria are produced by group V. vitamins by selecting crops of lactic acid bacteria, it is possible to obtain fermented dairy products with a high content of vitamins. Thus, ferocular products have versatile biological and medical properties. Known therapeutic effect of fermented milk products (drinks) in many diseases digestive system. They improve gastric secretion, normalize intestinal peristalsis, reduce gas formation. The biological properties of fermentation products have a healing effect on the beneficial intestinal microflora. In the USSR, industrial production of fermented milk products was organized on the basis of the wide use of pure crops of lactic acid bacteria and dairy yeast. A network of special laboratories for the selection of cultures and the production of starters, which are provided by the milk industry enterprises. In the production of fermented milk drinks, modern installations were used, providing high quality products (Fig. 1). Equality products are divided into lactic acid and mixed fermentation products. Fig. 1. Line of the production of fermented milk drinks with a cooling method in the stream. TMA-10 mild tank, 2 - centrifugal pumps - MCN-10, 3 - receiving tank, 4 - plate pasteurizer, 5 - Oma-2M-2M milkwritcher, 6 - double tank, 7 - Homogenizer, 8 - double-wall tanks, 9 - membrane Pump for a bunch, 10 - automatic drinks in bottles, 11 - automatic beverage bottling machine. Prostokvasha is an fervent drink, produced from pasteurized milk by driving it from the yoke, cooked on pure crops of lactic acid plants. Depending on the crops of lactic acid bacteria, they distinguish between the ordinary, Mesnikovskaya, southern, Ukrainian (ipayry), acidophone and varets. Ordinary prostone is prepared on pure cultures of lactic acid streptococci; It has a gentle clutch with a refreshing, pleasant, weakly acidic taste. Mesnikovskaya Prostokwash differs from an ordinary more dense clock and an acidic taste. This is explained by the fact that it is prepared from the pure cultures of the Bulgarian stick and lactic acid streptococci. South Prostokowa has a consistency of sour cream, slightly viscous, the taste is a sour, pinching, refreshing. When cooking apart from lactic acid streptococci and chopsticks use yeast. Varets is prepared from sterilized milk sustained at high temperatures for 2-3 hours (torrent). Varets has a dense, slightly viscous consistency, sour taste with a sweet taste of tomgear milk, cream color. Varetan is prepared on the same cultures as Mesnician Prostokow. Ryazhenka, or Ukrainian Prostokwash, cream color, to taste and consistency resembles sour cream, but has a peculiar taste. A sweet taste resembles tomlente milk. The fat content of rizhenka is 6%. For preparation it uses pure cultures of lactic acid streptococcus. The calorie content of ryazhenka is significantly higher than the calorie content of the prostruck of other varieties. Mazoni, Matsun, Katyk - In essence, these are different names of about the same type of southern acid milk produced from cow, buffalo, sheep, camel or goat milk. The main microflora of these beverages is the Bulgarian wand and thermal-loving lactic acid streptococci. Milk break down at elevated temperatures (48-55 ° С) and be keen in the device that saves heat. Jugurt is produced in the North Caucasus (mainly in Kabardino-Balkaria). This is a pressed sour milk, externally similar to sour cream or pasta. Fat in it is 12-13%, and water is not more than 70%. From such a pressed acidic milk prepare various dishes. It can be stored for a long time for consumption in the winter months in the form of a sour cream product "Brnatsmatsun". Kourung is an fervent drink, widespread in Northeast Asia in Buryats, Mongols, Tuvintsev and other peoples. The method of cooking Kurungi is known from deep antiquity. For Mongols and Tuvintsev, who conducted a half-hour lifestyle, in the summer of Kurunga was one of the most important products. Starting from the XVIII century, other nations (Buryats, Khakassy) have learned the secret of cooking Kurungi. Prepare Kurong through double fermentation - lactic acid and alcohol. The alcohol content usually does not exceed 1%. Ayran is a very common drink among the peoples of Central Asia, in the Caucasus, in Tataria, Bashkiria. Prepare from cow, goat, sheep milk. Several similar to Kumys (when preparation is used with lactic acid and alcohol fermentation). In some nations of our country, under the word "Ayran", a cool drink is meant, which is a mixture of sour milk with water. The Uzbek recipe, for example, provides for the dilution of the prostruck with cold digested water in a 1: 1 ratio, after which the drink is bottled into ice glasses. In Tajikistan and in Uzbekistan, another milk product of the chakca (probation) is produced - with the removal of a certain part of the water. In the Balkan Peninsula, yogurt for a long time makes sheep and buffalo milk. Since in this milk protein, fat and carbohydrates are greater than in a cow, yogurt is the thick of many other fermented dairy drinks. With the transition to industrial production, the yoghurt began to prepare from cow milk, to which dry milk is added or partially evaporated from cow milk moisture on vacuum devices. Exquisite used for the production of yogurt consists of lactic acid streptococci and Bulgarian sticks. By jointly developing, they give a higher breeding of lactic acid. Yoghurt quickly reduces thirst, quenching a feeling of hunger. It is useful to people of all ages, especially elderly, pregnant and nursing mothers. Daily use of yogurt contributes rapid restoration Forces, covers the needs of our body in amino acids, calcium salts, etc. "Kisel Malko" - Bulgarian acid milk, prepared with the use of the Bulgarian stick, open at the beginning of our century with Stamen Grigorov. In the secret archive of Louis XIV, evidence was discovered that the French king was very successfully used in order to heal from a serious gastric illness of this thick white drink, which he was brought from Bulgaria in special bags of sheep leather. "Food of real men to a deep old age" - so proudly called Bulgarians this elixir of youth and longevity. Mug "Colel Malko" is necessarily present in the Bulgarian menu. Chal (fur coat) is an acidic, strongly foaming drink with a pure milk taste and yeast smell, is prepared from milk camels. In Turkmenistan, he is called Chal, in Kazakhstan - Shubat. I. I. Mechnikov wrote that the nomads of Arabs, having excellent health and possessing a lot of physical strength, feed on almost exceptionally fresh or sakeful milk camels. The initial Zavskaya for the preparation of this drink is sour milk cameropers - "Katuk". Mightily attributed to the drink healing properties. There are even districts in Turkmenistan, where they go to the adoption of the course of treatment with Chalom. The most young fermented milk drinks include acidophilic drinks. The acidophilic stick, which is used to prepare acidophilies and other acidophilic drinks, is one of the varieties of lactic acid bacteria. It does not destroy under the action of digestive juices, better than other lactic acid bacteria carries out in thick intestines. For the preparation of acidophilies, equal amounts of acidophilic sticks, lactic acid streptococcus and kefir fungi are used. It turns out a damn drink slightly acute taste. Acidoofilin produces sweet, adding sugar. The same group of drinks includes acidophilic milk and acidophile-yeast milk. Like other sour milk drinks, this group is acidophilic, acidophilic and acidophilic-yeast milk - a valuable product for the nutrition of children, adults and the elderly. It contains the main necessary food substances necessary for our body, and in an easily-friendly form.
Nature allows a person to use those benefits that there are available in it. At the same time, people try to increase these wealth, create something new and know another unknown. Bacteria are the smallest creatures of nature, which also learned to use a person for their own purposes.
But not only the harm conjugate with pathogenic processes and diseases carry these prokaryotic organisms. They are still a source of an important industrial process, which since ancient is applied by people - fermentation. In this article, we will consider what this process represents and how specifically the lactic inflection of substances is carried out.
The history of the emergence and use of fermentation
The first references to the fact that the fermentation process was used by people to obtain certain products, appeared 5000 to our era. It was then that Babylonians used this way to obtain such products as:
- wine;
- prostokvash and other dairy products.
Later, such food began to receive both in Egypt, China, Sudan, Mexico and other ancient states. The yeast bread began to bake, ferment vegetable crops, the first attempts of canning appeared.
The process of lactic acid fermentation was used by the Millenniums. Cheeses, kefirs, yogurts were an important part of the meal at all times. All leeks and healers knew about the benefits of these products. However, the reasons for which the transformation of this kind is possible, remained unknown for a long time.

The fact that fermentation conditions require the presence of microorganisms, people could not even be assumed. In the middle of the XVII century, Van Gelmont will offer to introduce the term "fermentation" for those process cooking processes that are accompanied by gas release. After all, in translation, this word means "boiling". However, only in the XIX century, that is, almost two hundred years later, the French microbiologist, a chemist and physicist Louis Paster opened the existence of microbes, bacteria.
Since then, it became known that different fermentation requires the presence of various kinds of invisible to the eye of microorganisms. Their study made it possible with time to manage fermentation and direct him to the right side.
The essence of fermentation processes
If we talk about what is the process of fermentation, it should be indicated on its biochemical nature. After all, in its essence, it is just the activity of bacteria that makes themselves energy for life, producing various by-products at the same time.
In general, fermentation can be designated in one word - oxidation. Anaerobic disintegration of any substance under the influence of certain bacteria, which leads to the formation of a number of products. What substance underlies, and what happens as a result, is determined by the type of process itself. Several fermentation options are distinguished, so there is its own classification for transform data.
Classification
In total, there are three main types of fermentation.
- Alcohol. Lies in the oxidation of the original carbohydrate molecule before ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, water and ATP molecules (energy source). Transformation data is carried out under the action not only bacteria, but also mushrooms of different genera and species. It is in this way that ancient way to receive foods such as beer, wine, baking yeast, alcohol. That energy that is distinguished during the decomposition of the carbohydrate, goes to ensure the processes of the life of the microorganism. This is precisely the biological essence of the process.
- Friction of lactic acid It consists in oxidizing carbohydrates to lactic acid with a range of by-products. How it is carried out and which species happens, consider in more detail on.
- Oily acid. This type of fermentation is naturally important. It is carried out due to the vital activity of oily acid bacteria, which live in anaerobic conditions at the bottom of the swamps, river Ile and so on. Thanks to their work in nature, a huge number of organic components are processed. Products are many substances, the main among which is also allocated: acetone, carbon dioxide, acetic acid, dairy, and other compounds.

Each of the designated types is essential both natural and industrial scale. Types of organisms carrying out similar transformations are well studied today and many of them are cultivated artificially in order to obtain a large product output.
Friction of lactic acid: general concept
This type of fermentation is known from the most antiquity. Even before our era, the inhabitants of the ancient Egypt and other states could make cheese, cook beer and wine, bake bread, to escape vegetables and fruits.
Today special starters are used for fermented milk products, strains of the necessary microorganisms are artificially grown. The process is upgraded and brought to automatism, is carried out with the help of equipment. There are many manufacturers, which directly produce fermentation of a lactic acid.
The essence of the whole process can be set forth in several points.
- For the main product, the original carbohydrate is taken - simple (fructose, glucose, pentoses) or complex (sucrose, starch, glycogen and other).
- Anaerobic conditions are created.
- The strains of lactic acid bacteria of a certain species are counted into the product.
- All necessary external factors are provided, which are optimal for the desired product: illumination, temperature, the presence of certain additive components, pressure.
- After completion of the fermentation process, the product processing and allocation of all side connections occurs.
Of course, this is just a general description of what is happening. In fact, at every stage there are many complex biochemical reactions, because the process of lactic fermentation is the result of the vital activity of living beings.
Basics of the process of lactic fermentation
From a chemical point of view, these transformations are a number of consecutive stages.
- First there is a change in the source substrate, that is, a carbon chain of substance (carbohydrate) changes. This leads to the emergence of intermediate compounds of completely different nature relating to different classes. For example, if the original substrate is glucose, then it is rebuilt into gluconic acid.
- Redox reactions accompanied by gas release, by the formation of by-products. The main unit during the entire process is lactic acid. It is it produced and accumulated during fermentation. However, this is not the only connection. Thus, there is a formation of acetic acid molecules, ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide, water, sometimes and other accompanying.
- Energy output of the process in the form of adenosyntrifosphoric acid molecules (ATP). One molecule of glucose accounts for 2 ATP molecules, if the original substrate is a more complex structure, such as cellulose, then three ATP molecules. This energy uses lactic acid bacteria for further livelihoods.
Naturally, if you understand the biochemical transformations in detail, then all intermediate molecules and complexes should be indicated. Such, for example, as:

However, this issue deserves separate attention and should be considered from the point of view of biochemistry, so it will not affect it in this article. Let us consider in more detail what the technology of production of lactic acid products and what types of fermentation under consideration exist.
Homofermental fermentation
Homofermentative fermentation of the lactic acid implies the use of special forms of pathogens and differs from hetero-enzymatic product obtained and their quantity. It occurs according to the glycolytic pathway inside the cell of the microorganism. The essence consists, as in general, any fermentation, in the conversion of carbohydrates into milk acid. The main advantage of a similar process is that the yield of the right product is 90%. And only the remaining part goes to the side connections.
Bacteria fermentation of this type of species:
- Streptococcus lactis.
- Lactobacillus Casei.
- Lactobacillus Acidophilus and others.
What other substances are formed as a result of homofermental fermentation? These are such compounds like:
- ethanol;
- volatile acids;
- carbon dioxide;
- fumaric and succinic acid.
However, in industry, this method of obtaining fermented dairy products is practically not used. It has been preserved in nature as the initial stage of glycolysis, it occurs in mammalian muscle cells with extensive physical exertion.
The technology of production of the right products for food of people involves the use of such source carbohydrates as:

And homoferment bacteria are not able to oxidize many of these compounds, so their use is not possible as starters during production.
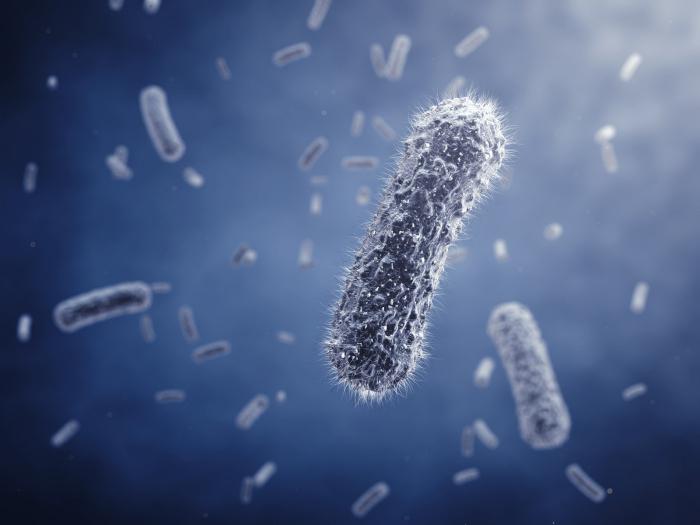
Heterofermentative lactic acid fermentation
This method is precisely those who are industrially applicable, due to which the production of all milk products is carried out, conservation of vegetables is carried out, the harvesting of silo feeds for livestock occurs.
The main difference from the previously described is that lactic acid fermentation pathogens are carried out with the formation of a larger number of by-products. Only 50% of sugar is recycled with bacteria into lactic acid, the rest goes to the formation of such molecules as:
- acetic acid;
- glycerol;
- carbon dioxide;
- ethyl alcohol and others.
What is it better and more profitable than the formation of 90% of pure lactic acid with a homofermentative method? The thing is that when the main product is produced too much, then the vital activity of many bacteria is oppressed at all. In addition, products lose many taste qualities that are purchased thanks to by-connects. For example, pleasant aroma Canned vegetables is provided by acetic acid and isoamyl alcohol. If these compounds are not, then the result of the conservation will become completely different.
The yield of lactic acid in 50% is quite sufficient to suppress the development and vital activity of all strangers and microorganisms in the system. Because even 1-2% cause too much acidification of the medium in which no other organisms can exist, except for lactic acid bacteria. The whole process is carried out by
The fermentation conditions with a heter-enzymal method must be as follows:
- good and fresh sourdough added at the initial stage;
- optimal external conditions that are selected for each product individually;
- high-quality and debugged equipment;
- all necessary technical devices for the process.
Among the external conditions, the temperature of the process is of particular importance. It should not be too high, but the cold will brake dramatically all the progress.
Today there is a specialized container for fermentation, which automatically creates all the necessary conditions for the correct and comfortable operation of microorganisms.
Necessary equipment
As we noted above, among the most important attributes it should be noted the container for fermentation. If we talk about the home procedure, then you should pay attention to the purity of the utensils used during conservation, the manufacture of prokobyvashi and other products. One way to reduce the number of foreign populations of microorganisms is the sterilization of containers before their use.
What kind of dishes is suitable for heterophermentation fermentation? It can be a glass or high-quality plastic (polypropylene, polyethylene) capacitance that is capable of tightly closed with a lid.
In industry, special devices use special devices for disinfection and cleansing containers before the start of the fermentation process.
Bacteria used in the process
If we talk about the cultures of bacteria that are used to create canned and fermented milk products, then you can designate several of the most common types of organisms.

Based on the combination and pure cultures of the designated organisms, start-up for fermented milk products. They are in open access, they can acquire them everyone. The most important thing is to comply with the conditions of fermentation process to benefit from the product being generated.
What products are obtained as a result of similar fermentation?
If we talk about what fermentation products can be obtained using lactobacilli, you can call several main categories.
- Nutrition (outer, yogurt, varents, kefir, cottage cheese, sour cream, butter butter, acidophilic products and others).
- Silo-type feed for farm animals.
- The lactic acid, which is used in the manufacture of soft drinks, stretch the fur skins and so on.
- Breadmaker, production of cheeses.
- Canning vegetables and fruits.
All this proves the importance of bacteria of certain species in the life of people, their industrial activity.