Calculation of the nome index. Insulin resistance diagnostics, HOMA and caro indices
The World Health Organization has recognized that obesity has become an epidemic worldwide. Insulin resistance associated with obesity triggers a cascade of pathological processes leading to damage to almost all human organs and systems.
What is insulin resistance, what are its causes, and how to quickly determine it using standard analyzes - these are the main questions that interested scientists in the 1990s. In an attempt to answer them, many studies have been carried out that have proven the role of insulin resistance in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, female infertility and other diseases.
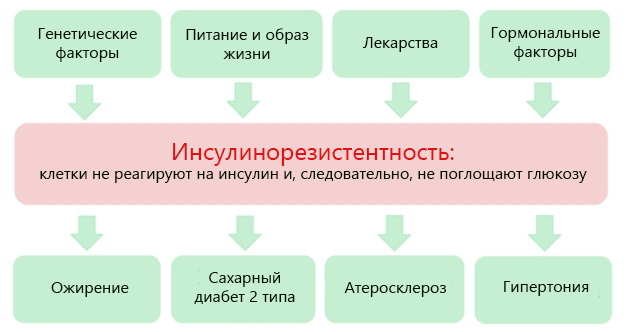
Insulin resistance is a decrease in the sensitivity of body tissues to the action of insulin.
Normally, insulin is produced by the pancreas in an amount that is sufficient to maintain blood glucose levels at a physiological level. It facilitates the entry of glucose, the main energy substrate, into the cell. With insulin resistance, the sensitivity of tissues to insulin decreases, glucose does not enter the cells, and energy hunger develops. In response, the pancreas releases more insulin. Excess glucose is deposited as adipose tissue, further enhancing insulin resistance.
The onset of insulin resistance
Over time, the reserves of the pancreas are depleted, cells that work with overload die, and develop diabetes.
An excess of insulin also has an effect on cholesterol metabolism, enhances the formation of free fatty acids, atherogenic lipids, this leads to the development of atherosclerosis, as well as damage by free fatty acids the pancreas itself.
Causes of insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is physiological, that is, it occurs normally in certain periods of life, and pathological.
Reasons for physiological insulin resistance:
- pregnancy;
- teenage years;
- night sleep;
- elderly age;
- second phase menstrual cycle among women;
- a diet rich in fat.
Causes of insulin resistance
Causes of pathological insulin resistance:
- obesity;
- genetic defects in the insulin molecule, its receptors and actions;
- hypodynamia;
- excessive consumption of carbohydrates;
- endocrine diseases(thyrotoxicosis, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, acromegaly, pheochromacytoma, etc.);
- taking certain medications (hormones, adrenergic blockers, etc.);
- smoking.
Signs and symptoms of insulin resistance
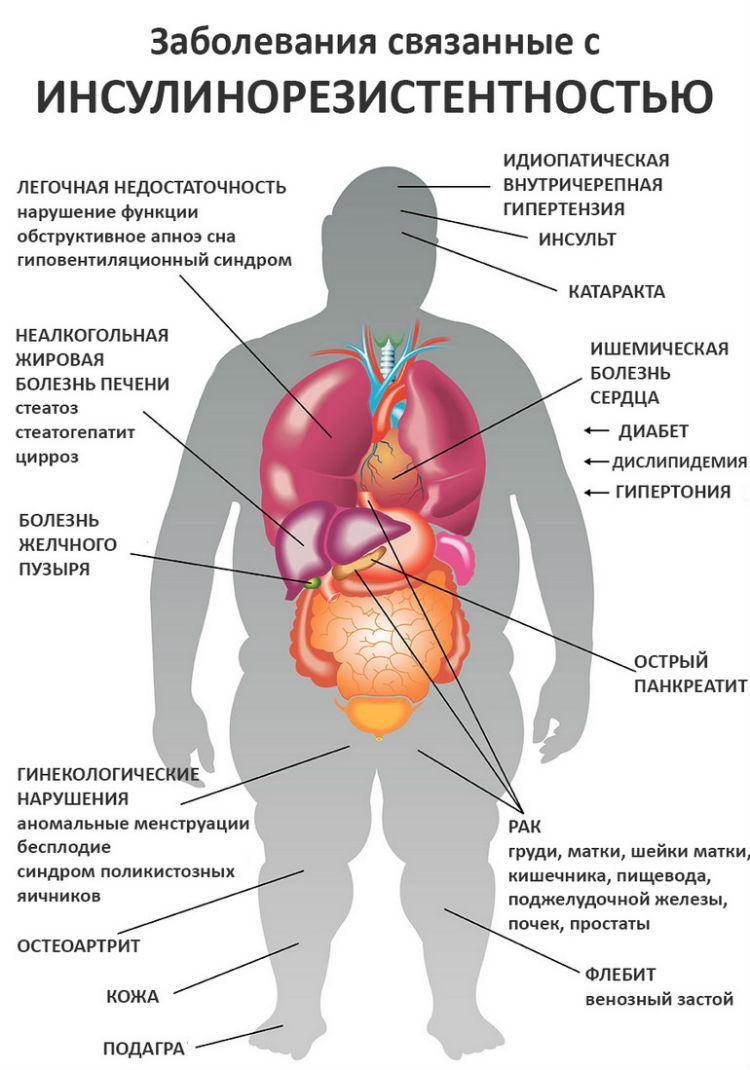
The main sign of developing insulin resistance is abdominal obesity. Abdominal obesity is a type of obesity in which excess adipose tissue is deposited primarily in the abdomen and upper body.
Internal abdominal obesity is especially dangerous when adipose tissue accumulates around the organs and interferes with their proper functioning. Is developing fatty disease liver, atherosclerosis, stomach and intestines are compressed, urinary tract, pancreas, reproductive organs are affected.
The fatty tissue in the abdomen is very active. A large number of biologically active substances are formed from it, which contribute to the development of:
- atherosclerosis;
- oncological diseases;
- arterial hypertension;
- joint diseases;
- thrombosis;
- ovarian dysfunction.
Abdominal obesity can be determined by yourself at home. To do this, you need to measure the waist circumference and divide it by the hip circumference. Normally, this indicator does not exceed 0.8 for women and 1.0 for men.
The second important symptom of insulin resistance is acanthosis nigricans. Acanthosis nigricans are changes in the skin in the form of hyperpigmentation and peeling in the natural folds of the skin (neck, armpits, mammary glands, groin, intergluteal fold).
In women, insulin resistance is manifested by polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). PCOS is accompanied by menstrual irregularities, infertility and hirsutism, and excessive male-pattern hair growth.
Insulin resistance syndrome
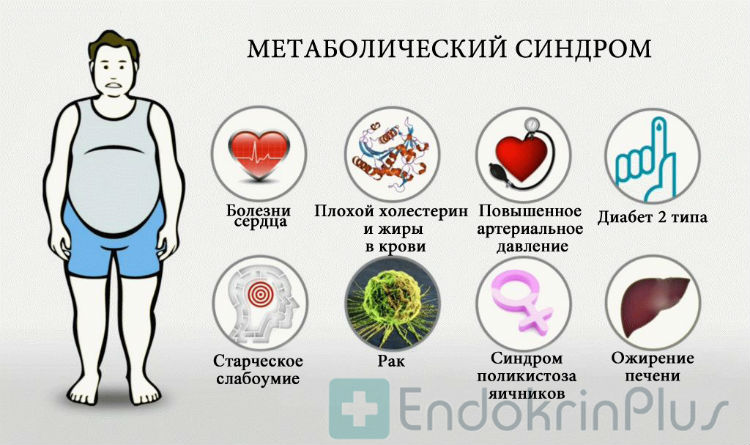
Due to the presence of a large number of pathological processes associated with insulin resistance, it was customary to combine them all into insulin resistance syndrome (metabolic syndrome, syndrome X).
Metabolic syndrome includes:
- Abdominal obesity (waist circumference:> 80 cm in women and> 94 cm in men).
- Arterial hypertension(persistent increase blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art.).
- Diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance.
- Disruption of cholesterol metabolism, an increase in the level of its "bad" fractions and a decrease in the "good" ones.
Danger metabolic syndrome- in a high risk of vascular accidents (strokes, heart attacks, etc.). They can be avoided only by reducing weight and controlling blood pressure levels, as well as glucose and cholesterol fractions in the blood.
Insulin resistance diagnostics
Insulin resistance can be determined using special tests and analyzes.
Direct diagnostic methods
Among the direct methods for diagnosing insulin resistance, the most accurate is the euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp (EHC, clamp test). Clamp test consists in the simultaneous administration of glucose and insulin solutions to the patient intravenously. If the amount of insulin injected does not match (exceed) the amount of glucose injected, they talk about insulin resistance.
Currently, the clamp test is used only for research purposes, because it is difficult to perform, requires special preparation and intravenous access.
Indirect diagnostic methods
Indirect diagnostic methods evaluate the effect of their own, and not injected from the outside, insulin on glucose metabolism.
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
An oral glucose tolerance test is performed as follows. The patient donates blood on an empty stomach, then drinks a solution containing 75 g of glucose, and retakes the analysis after 2 hours. The test measures glucose levels as well as insulin and C-peptide levels. C-peptide is a protein with which insulin is bound in its depot.
Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance are regarded as prediabetes and in most cases are accompanied by insulin resistance. When glucose levels are correlated with insulin and C-peptide levels during the test, a more rapid rise in the latter also indicates insulin resistance.
Intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT)
An intravenous glucose tolerance test is similar to OGTT. But in this case, glucose is administered intravenously, after which, after short periods of time, the same indicators are repeatedly assessed as in OGTT. This analysis is more reliable when the patient has a gastrointestinal tract disease that interferes with glucose absorption.
Calculation of insulin resistance indices
The simplest and most affordable way to identify insulin resistance is to calculate its indices. To do this, a person just needs to donate blood from a vein. The levels of insulin and glucose in the blood will be determined and the HOMA-IR and caro indices are calculated using special formulas. They are also called insulin resistance tests.
HOMA-IR index - calculation, norm and pathology
The HOMA-IR (Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance) index is calculated using the following formula:
HOMA = (glucose level (mmol / L) * insulin level (μIU / ml)) / 22.5
Normally, the HOMA insulin resistance index does not exceed 2.7, and this indicator is the same for both men and women, and after 18 years does not depend on age. In adolescence, it rises slightly due to physiological insulin resistance at this age.
Reasons for the increase in the HOMA index:
- insulin resistance, which indicates the possible development of diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, more often against the background of obesity;
- gestational diabetes mellitus (pregnancy diabetes);
- endocrine diseases (thyrotoxicosis, pheochromacytoma, etc.);
- receiving some drugs(hormones, adrenergic blockers, drugs that lower cholesterol);
- chronic diseases liver;
- acute infectious diseases.
Caro index
This index is also a calculated indicator.
Caro index = glucose level (mmol / L) / insulin level (μIU / ml)
Caro y index healthy person is at least 0.33.
A drop in this rate is a sure sign of insulin resistance.
Tests for insulin resistance are taken in the morning on an empty stomach, after a 10-14 hour break in eating. It is undesirable to take them after severe stress, during the period acute diseases and exacerbation of chronic.
Determination of blood glucose, insulin and C-peptide levels
 Determination of only the level of glucose, insulin or C-peptide in the blood, separately from other indicators, is not very informative. They should be taken into account in the complex, since an increase in only blood glucose may indicate improper preparation for the test, and only insulin - about the introduction of an insulin preparation from the outside in the form of injections. Only by making sure that the amounts of insulin and C-peptide are higher than those required for a given level of glycemia can we talk about insulin resistance.
Determination of only the level of glucose, insulin or C-peptide in the blood, separately from other indicators, is not very informative. They should be taken into account in the complex, since an increase in only blood glucose may indicate improper preparation for the test, and only insulin - about the introduction of an insulin preparation from the outside in the form of injections. Only by making sure that the amounts of insulin and C-peptide are higher than those required for a given level of glycemia can we talk about insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance treatment - diet, sports, drugs
After the examination, testing and calculating the HOMA and caro indices, a person is primarily concerned with the question of how to cure insulin resistance. It is important to understand here that insulin resistance is a physiological norm during certain periods of life. It has evolved as a way of adapting to periods of prolonged food shortages. And there is no need to treat physiological insulin resistance in adolescence, or during pregnancy, for example.
Pathological insulin resistance, leading to the development serious illnesses, needs correction.
It is possible to reduce insulin resistance by the most in a simple way- by reducing weight. A decrease in the amount of adipose tissue leads to an increase in the sensitivity of cells in the body to insulin.
In losing weight, 2 points are important: constant physical exercise and adherence to a low-calorie diet. 
Physical activity should be regular, aerobic, 3 times a week for 45 minutes. Running, swimming, fitness classes, dancing are well suited. During classes, muscles are actively working, namely, they contain a large number of insulin receptors. By actively exercising, a person opens up access for the hormone to its receptors, overcoming resistance.
Proper nutrition and adherence to a low-calorie diet is just as important a step in losing weight and treating insulin resistance as sports. It is necessary to drastically reduce the consumption of simple carbohydrates (sugar, candy, chocolate, baked goods). The menu for insulin resistance should consist of 5-6 meals, portions should be reduced by 20-30%, try to limit animal fats and increase the amount of fiber in food.
In practice, it often turns out that losing weight is not so easy for a person with insulin resistance. If weight loss is not achieved with a diet and sufficient exercise, drugs are prescribed.
The most commonly used drug is metformin. It increases the sensitivity of tissues to insulin, reduces the formation of glucose in the liver, increases the consumption of glucose by the muscles, and reduces its absorption in the intestine. This drug is taken only as directed by a doctor and under his control, since it has a number side effects and contraindications.
Oct 18, 2017 Inpire
- Description
- Preparation
- Indications
- Interpretation of results
The most common method for assessing insulin resistance is the basal (fasting) glucose to insulin ratio.
The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach, after an 8-12 hour period of overnight fasting. The profile includes indicators:
- glucose
- insulin
- calculated index of insulin resistance HOMA-IR.
Insulin resistance is associated with an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease and, obviously, is a component of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the relationship of obesity with these types of diseases (including metabolic syndrome). Most simple method the assessment of insulin resistance is the HOMA-IR insulin resistance index - an indicator derived from the work of Matthews D.R. et al, 1985, related to the development of a mathematical homeostatic model for assessing insulin resistance (HOMA-IR - Ho meostasis M odel A ssessment of I nsulin Resistance). It has been demonstrated that the ratio of basal (fasting) levels of insulin and glucose, reflecting their interaction in a feedback loop, largely correlates with the assessment of insulin resistance in the classical direct method for assessing the effects of insulin on glucose metabolism - the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp method.
The HOMA-IR index is calculated by the formula: HOMA-IR = fasting glucose (mmol / l) x fasting insulin (μU / ml) / 22.5.
With an increase in fasting glucose or insulin levels, the HOMA-IR index, respectively, increases. For example, if fasting glucose is 4.5 mmol / L and insulin is 5.0 μU / mL, HOMA-IR = 1.0; if fasting glucose is 6.0 mmol and insulin is 15 μU / ml, HOMA-IR = 4.0.
The threshold value of insulin resistance, expressed in HOMA-IR, is usually defined as the 75th percentile of its cumulative population distribution. The HOMA-IR threshold is insulin dependent and difficult to standardize. The choice of the threshold value, in addition, may depend on the objectives of the study and the selected reference group.
The HOMA-IR index is not included in the main diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome, but it is used as additional laboratory studies of this profile. In assessing the risk of developing diabetes mellitus in a group of people with glucose levels below 7 mmol / L, HOMA-IR is more informative than glucose or fasting insulin themselves. Use in clinical practice For diagnostic purposes, mathematical models for assessing insulin resistance based on determining the level of insulin and fasting plasma glucose has a number of limitations and is not always acceptable for deciding on the appointment of antihyperglycemic therapy, but can be used for dynamic monitoring. Impaired insulin resistance is noted with increased frequency in chronic hepatitis C (genotype 1). An increase in HOMA-IR among these patients is associated with a worse response to therapy than in patients with normal insulin resistance, and therefore correction of insulin resistance is considered one of the new goals in the treatment of hepatitis C. Increased insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) is observed in non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis ...
Strictly on an empty stomach after an overnight fasting period of 8 to 14 hours.
On the eve of the study, it is necessary to exclude increased psychoemotional and physical activity (sports training), alcohol intake, and an hour before the study - smoking.
Discuss with the referring physician whether the study should be carried out against the background of the current medication intake or their cancellation.
- In order to assess and monitor the dynamics of insulin resistance in a set of tests when examining patients with obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), patients with chronic hepatitis C, patients with non-alcoholic steatosis liver.
- When assessing the risk of development diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Interpretation of test results contains information for the attending physician and does not constitute a diagnosis. The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-medication. An accurate diagnosis is made by a doctor, using both the results of this examination and the necessary information from other sources: anamnesis, results of other examinations, etc.
Units: conventional units
Reference values HOMA-IR :
(2.7 is a threshold corresponding to the 75th percentile of the population values of adults 20-60 years old, without diabetes; the choice of the threshold value may depend on the objectives of the study)
Increasing values HOMA-IR is consistent with increased insulin resistance and an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Literature
1. Matthews DR et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985,28 (7) 412-419.
2. Dolgov V.V. et al. Laboratory diagnostics disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. Metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus. M. 2006.
3. Romero-Gomez M. et al. Insulin resistance impairs sustained response rate to peginterferon plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients. Gastroenterology, 2006, 128 (3), 636-641.
4. Mayorov Alexander Yurievich The state of insulin resistance in the evolution of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Abstract of thesis. diss. D. m. n, M, 2009
5.OO Khafisova, T.S. Polikarpova, N.V. Mazurchik, P.P. Ogurtsov Influence of metformin on the formation of a stable virological response during combined antiviral therapy chronic hepatitis with Peg-IFNa2b and ribavirin in patients with baseline insulin resistance. RUDN Bulletin. Ser. Medicine 2011, no. 2.
To indirectly determine how insulin works in the human body, a special method called the HOMA index is used. With the help of it, the endocrinologist can determine in what ratio the hormone insulin is in the patient and what is the glucose indicator. Such a study allows you to identify a terrible disease called "diabetes mellitus" in the early stages of the disease and promptly prescribe effective treatment to the patient.
What affects insulin production
With daily food intake, especially carbohydrates, gastrointestinal tract begins to break them down and turn them into glucose, which feeds the cells human body and all the muscles. Once glucose enters blood vessels, with the help of insulin, it is redirected to the cells, quickly penetrates the protective layer and provides them with vital energy.
The main function of insulin, which is produced in the pancreas, is to add, as they say, "strength" to glucose so that it can quickly penetrate the cell's defenses. If glucose is in the blood for a long time, then the sugar will be increased, as a large amount of the enzyme begins to accumulate.
With insulin resistance, insulin is not ready to cope with its main task. This means that glucose cannot get inside human cells. To improve the work of insulin, the pancreas begins to secrete more hormone, as a result, it also accumulates in excess. And the excess glucose turns into fat, envelops the outer walls of the tissues, which further aggravates the situation, because it is even more difficult for glucose to penetrate through the fat cells. Gradually, a person begins to gain extra pounds, the process of obesity begins.
NOMA index and its normal indicators
If, upon passing the analysis, the HOMA index does not exceed the 2.5-2.7 mark, then it will be normal. It should be clarified that the index-indicator can be different, depending on the research being carried out.
If studies indicate that the HOMA index is increased, then the following diseases often begin to progress in the patient:
- Diabetes.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Arteriosclerosis.
- Other diseases that can affect the work of the heart and blood vessels.
In order to start treating the disease on time, you should immediately visit a doctor at the first signs of the disease.
What are the first signs of insulin resistance
A person can notice the initial signs of insulin resistance on their own and make an appointment with an endocrinologist as soon as possible. On initial stage diseases in humans are observed:
- high blood pressure;
- deposition of adipose tissue, especially in the waist area;
- poor results of both blood and urine tests.
To accurately determine the degree of the disease and understand the causes of the disease, the doctor will prescribe diagnostic tests in the form of tests. To receive correct analysis, which will be shown by the index, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- do not eat any food before analysis, it is allowed to drink purified water;
- come to the clinic for examination in the early morning;
- in the evening, do not eat sweet or starchy foods, as well as fatty or salty foods.
When using various medications, you should discuss their name with your doctor in advance. The point is that some medications may affect the index, as a result, the calculation will turn out to be incorrect, and the doctor will prescribe, based on the tests received, the wrong treatment. A special formula is used for decryption. For example, if laboratory tests show that glucose is equal to 7.3, the insulin hormone is 19, then the HOMA index will be 5.77. Of course, the index will be greatly increased, because its normal level should not exceed 2.6-2.7.
Who is more susceptible to this disease
Resistance or diabetes mellitus is quite often transmitted with genes, that is, if one of the parents suffered from this ailment, then the possibility of the disease in children is very high.
But not only genetic causes lead to this ailment, the following factors can affect its occurrence:
- incorrect and unbalanced diet;
- hormonal disruption in the body;
- constant stress and a sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- addictions.
The patient has a malfunction in both fat and carbohydrate metabolism substances, the pressure is constantly increasing. Extra pounds are especially scary in the waist area, since they do not allow the normal release of insulin, which helps glucose to get inside the cells.
If a person feels some changes in his body, namely:
- frequent visits to the toilet to urinate;
- constant thirst and dryness in the mouth;
- weakness in the whole body and loss of previous performance;
- unwillingness to eat or, on the contrary, excessive appetite;
- poor healing of even the most minor wounds and bruises;
- headache;
- itchy skin.
With such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. The endocrinologist will examine the patient, tell you what laboratory tests need to be passed, and prescribe a comprehensive, effective examination. It is a timely visit to a doctor that will help bring the NORMA index to the desired indicator, and will greatly facilitate the patient's condition.
Treatment of the disease
After the results of the research, the doctor will prescribe medications taking into account the patient's individuality and develop a diet for him. When a diet is drawn up with an increased HOMA index, the basic rule will be observed - a decrease in the amount of carbohydrates from the diet of patients.
The diet must necessarily contain low-calorie food, all the substances and vitamins necessary for the body. The menu must include:
- foods containing protein;
- in a small amount of carbohydrates, which will be freely broken down and converted into glucose;
- natural fats.
Patients should take food in small portions, but often, that is, the diet should be fractional. Between meals should be kept for about 3-3.5 hours. During the day, you need to eat about 6 times. Exclude from the menu following products power supply:
- sugar in its usual form;
- semi-finished and fast food products;
- canned food and smoked meats;
- salty or sweet croutons and chips;
- sweet soda water.
The daily diet must include:
- fruits and vegetables, preferably fresh. If the food will be baked or boiled, do not sprinkle it with sugar;
- poultry or rabbit meat;
- lean fish varieties;
- brown rice, wheat grits;
- bread baked from wholemeal flour;
- low-fat dairy products.
- fruit drink or compote from fresh or dried fruits, without added sugar;
- rosehip decoction;
- freshly squeezed juices from fruits, especially citrus fruits.
If a person loves sweets very much, then it is advisable to replace sugar with jam, and the second courses are best cooked in steam or baked in the oven. Instead of butter, it is recommended to use vegetable oil, and try to remove figs, raisins and sweet grapes from the daily diet altogether.
In addition to diet and medications, patients should begin to lead a more active lifestyle, perform feasible daily physical exercises, quit smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
Insulin resistance syndrome is a pathology that precedes the development of diabetes. In order to identify this syndrome, the insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR) is used. Determination of the indicators of this index helps to determine the presence of insensitivity to the action of insulin in the early stages, to assess the estimated risks of developing diabetes, atherosclerosis, pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Insulin resistance - what is it?
Insulin resistance refers to the resistance (loss of sensitivity) of body cells to the action of insulin. In the presence of this condition, the patient's blood is observed as increased insulin and high glucose... If this condition is combined with dyslipidemia, impaired glucose tolerance, obesity, then this pathology is called metabolic syndrome.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
Insulin resistance develops in the following situations:
- overweight;
- hereditary predisposition;
- hormonal disruptions;
- the use of certain medications;
- unbalanced diet, carbohydrate abuse.
These are not all the reasons for the development of insulin resistance. Alcohol abusers also experience this condition. In addition, this pathology accompanies diseases thyroid gland, polycystic ovary disease, Itsenko-Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoma. Sometimes insulin resistance occurs in women during pregnancy.
 People who are resistant to the hormone have fat deposits in the abdomen.
People who are resistant to the hormone have fat deposits in the abdomen.
Clinical symptoms begin to manifest themselves in the later stages of the disease. Individuals with insulin resistance are obese (abdominal fat). In addition, they have skin changes - hyperpigmentation in the armpits, neck, and mammary glands. In addition, such patients have increased blood pressure, changes in the psycho-emotional background, and digestive problems.
Insulin resistance index: calculation
Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR), the HOMA index are all synonymous with the insulin resistance index. To determine this indicator, a blood test is required. The index values can be calculated using two formulas: the HOMA-IR index and the CARO index:
- HOMA formula: fasting insulin (μU / ml) * fasting plasma glucose (mmol / l) / 22.5 - normally no more than 2.7;
- KARO formula: fasting plasma glucose (mmol / l) / fasting insulin (μU / ml) - the norm does not exceed 0.33.
Analyzes and how to take it right
Patients initially need to be tested venous blood, and then do a test for insulin resistance. Diagnosis and determination of insulin resistance occurs subject to the following rules:
 No physical activity should be experienced 30 minutes before the test.
No physical activity should be experienced 30 minutes before the test. - smoking is prohibited for half an hour before the study;
- before the analysis, you can not eat for 8-12 hours;
- the calculation of indicators is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach;
- physical activity is prohibited half an hour before the test;
- the attending physician is required to be informed about the medications taken.