Sugar diabetes in the elderly: causes, symptoms and treatment. Sugar diabetes in old age
Diabetes - this is a disease that arises against the background of violations in endocrine system. It is characterized by a chronic overestimated blood sugar content. The disease is diagnosed at any age, but most often it affects people after 40 years.
The peculiarities of diabetes in the elderly are that it is often not stable and easy. But characteristic sign Diseases are an extra weight that has a greater half of retirees.
Since at the old age there is a lot of health problems, there are few obesity pays attention to the obesity. However, despite the long and hidden course of the disease, its consequences can lead to a fatal outcome.
There are two types of diabetes:
- The first type is developing with insulin deficiency. Often diagnosed at a young age. This is an insulin-dependent diabetes, which proceeds in severe form. In this case, the absence of treatment leads to a diabetic coma and diabetics may die.
- The second type - appears in the excess of insulin in the blood, but even such a number of hormone is not enough to normalize the level of glucose. This type of disease is mainly occurring after 40 years.
Since type 2 diabetes is mainly appearing in the elderly patients, it is worth considering the causes of the symptoms and the treatment of this type of illness in more detail.
Provoking factors and causes of development
From fifty years, most people decreases glucose tolerance. Moreover, when a person ages, every 10 years, the concentration of sugar in blood sutra will increase, and after making food - to rise. So, for example, you need to know what.
However, the risk of diabetes is determined not only age peculiarities, but also the level of physical activity and the daily diet.
Why does the old people appear postprandial glycemia? This is explained by the impact of a number of factors:
- age decrease in insulin sensitivity in tissues;
- the weakening of the action and secretion of intricantine hormones in old age;
- insufficient production of insulin by pancreas.
Sugar diabetes in people of elderly and senile age is due to hereditary predisposition. The second factor contributing to the appearance of the disease is considered overweight.
Also, the occurrence of pathology lead problems in the work of the pancreas. These may be failed in the functioning of the domestic secretion glands, cancer or pancreatitis.
Another old diabetes can develop against the background of viral infections. These diseases include influenza, rubella, hepatitis, chickenpox other.
In addition, endocrine disorders often appear after nervous stress. Indeed, according to statistics, old age, accompanied by emotional experiences, not only increases the likelihood of a second-type diabetes in the elderly, but also complicates its current.
And in patients engaged in intellectual labor, high level Glucose is celebrated much more often than those whose work is related to physical activities.
Clinical picture and complications
Sugar level
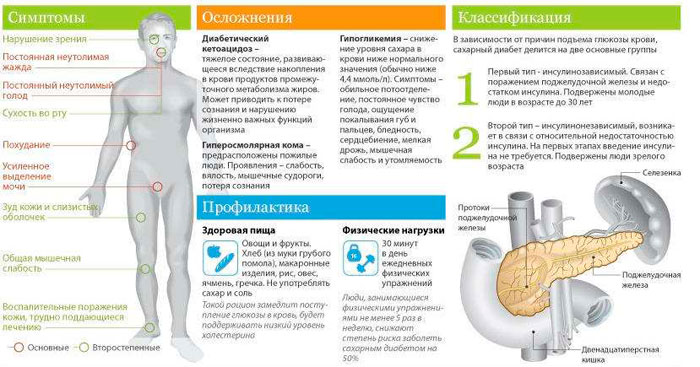
General diabetes symptoms in people over 40 years old - this is:
- weakening of view;
- itching and drying the skin;
- convulsions;
- permanent thirst;
- euchness lower extremities;
- frequent urination.
 However, to confirm the diagnosis is not necessarily the presence of all signs. It is enough to occur 1 or 2 symptoms.
However, to confirm the diagnosis is not necessarily the presence of all signs. It is enough to occur 1 or 2 symptoms.
Sugar diabetes mellitus 2 in patients of retirement age is often manifested by a strong impairment of vision, thirst, malaise and long healing of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
An old age is dangerous with frequent disorders in the cardiovascular system, exacerbated by diabetes. So, atherosclerosis often appears in patients. coronary arterieswhich affect the vessels of the legs, which can develop. And this leads to massive foot lesions and its further amputation.
Frequent complications of diabetes - this is:
- the formation of ulots;
- worsening view (cataract, retinopathy);
- heartache;
- swelling;
- infectious diseases of the urinary tract.
Another dangerous consequence of diabetes is renal failure. In addition, the nervous system may be affected, which leads to the appearance of neuropathy.
For this state, such symptoms like pain, burning in the legs and loss of their sensitivity are characteristic.
Diagnostics and drug treatment
Sugar diabetes in older people to diagnose quite difficult. This is due to the fact that even when the blood glucose content is increased, then in the urine sugar may generally be absent.
Therefore, the elderly age obliges a person every year to be examined, especially if it is worried about atherosclerosis, hypertension, IHS, nephropathy and purulent skin diseases. Install the presence of hyperglycemia allow parameters - 6.1-6.9 mmol / l., And the results of the glucose tolerance indicate the results - 7.8-11.1 mmol / l.
However, the responses of the study for glucose tolerance can be inaccurate. This is explained by the fact that with age, the sensitivity of cells to the sugar is decreased, and the level of its blood content remains an overestimated long time.
Moreover, the diagnosis of coma at this state is also hampered, since its signs are similar to the symptoms of lesion of light, heart failure and ketoacidosis.
All this often leads to the fact that diabetes is revealed at the later stage. Therefore, people, age from 45 years old, it is necessary to take tests every two years to the concentration of glucose in the blood.
Treatment of diabetes in older patients is a rather difficult task, because they already have others chronic diseases and overweight. Therefore, to normalize the state, the doctor prescribes a patient various drugs from different groups.
Medical therapy for elderly diabetics implies the reception of such varieties medicines as:
- Metformin;
- glitazones;
- derivatives of sulfonylurea;
- clay;
- gliptins.
Increased sugar is most often reduced by metformin (keyfall, syphorn). However, it is prescribed only with sufficient filtering functionality of the kidneys and when there are no diseases causing hypoxia. The advantages of the drug are intensifying exchange processesAlso, it does not deplete the work of the pancreas and does not contribute to the appearance of hypoglycemia.
Glitazones, like Metformin, can increase the sensitivity of fat cells, muscles and liver to insulin. However, when the pancreas is depleted, the use of thiazolidindiones is meaningless.
Also, glitazones are contraindicated in problems with heart and kidneys. Moreover, drugs from this group are dangerous in that they contribute to the washout of calcium from the bones. Although such funds do not increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Sulfonylurea derivatives affect the beta cells of the pancreas, which is why they begin to actively produce insulin. The use of similar drugs is possible until the pancreas is depleted.
But derivatives of sulfonylurevines lead to a number of negative consequences:
- increase in the likelihood of hypoglycemia;
- absolute and irreversible depletion of the pancreas;
- a set of body weight.
In many cases, patients begin to take derivatives of sulfonylurea despite all the risks only in order not to resort to insulin therapy. However, such actions are harmful to health, especially if the patient's age comes to 80 years.
Hinides or meglitinides, as well as sulfonylurea derivatives, activate insulin production. If you drink preparations before meals, the duration of their impact after reception is from 30 to 90 minutes.
Contraindications to the use of meglitinides are similar with sulfonylurea derivatives. The advantages of such funds are that they can quickly reduce blood sugar concentration after eating food.
Gliptins, in particular glucagon-like peptide-1, are hormones-increspension. Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitors are caused by the pancreas to produce insulin, inhibiting glucagon selection.
However, GPP-1 is effective only when sugar is really enhanced. The composition of glyptins is saksagliptin, sytagliptin and Wildagliptin.
These means neutralize a substance that has a devastating effect on GPP-1. After taking such drugs, the level of hormone in the blood increases almost 2 times. As a result, the work of the pancreas is stimulated, which begins to actively produce insulin.
Diet and therapy and preventive measures
Sugar diabetes in old age requires compliance with a certain diet. The main task of the diet is weight loss. To reduce the admission of fats in the body, a person needs to go to low-calorie food.
So, the patient should enrich the diet fresh vegetables, fruit, low-fat varieties of meat and fish, fermented milk products, cereals and croups. And from sweets, baking, butter, nutrition broths, chips, pickles, smoked, alcoholic and sweet carbonated drinks should be refused.
Also diet with diabetes mellitus involves meals with small portions at least 5 times a day. And dinner should be 2 hours before sleep.
Physical activity - good prevention Development of diabetes in pensioners. With regular sports, the following results can be achieved:
- reduce blood pressure;
- prevent the appearance of atherosclerosis;
- improve the susceptibility of body tissues to insulin.
However, the loads must be seamless depending on the patient's well-being and its individual characteristics. The ideal option will be walking for 30-60 minutes in the fresh air, swimming and cycling. You can also perform morning charging or make special gymnastics.
But for the elderly patients there are a number of contraindications to physical exertion. These include a hard form renal failure, unsatisfactory diabetes compensation, the proliferative stage of retinopathy, unstable angina and ketoacidosis.
If diabetes was detected in 70-80 years, then such a diagnosis is extremely dangerous for the patient. Therefore, he may need a special care in the boarding house, which will improve the overall health of the patient and will extend his life as much as possible.
Another important factor that slows the development of insulin addiction is to preserve emotional equilibrium. After all, stress contributes to the increase in pressure, which becomes the cause of the failure in carbohydrate exchange. Therefore, it is important to maintain calm, and in case of need, taking sedatives based on mint, Valerians and others natural components. The video in this article will tell about the peculiarities of the flow of diabetes in old age.

Sugar diabetes in the elderly, symptoms and treatment
Sugar diabetes is a lack of insulin in the human body, this disease belongs to the group of endocrine diseases. In diabetes, a large amount of blood glucose is formed, which negatively affects life abilities.
Today, medicine has a sharp question that affects the scale of incidence of diabetes. These problems are acute in all countries of the world, people of different ages are subject to this disease, from the smallest to the elderly.
More distribution occurs in people of the older age generation, more often after 60 years.
A significant increase in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus is directly related to the peculiarities of physiological changes in aging. human organism, There is a violation of the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Risk of development of diabetes in old age
In the age group, over 50 years, there are practically irreversible changes that are accompanied by a decrease in glucose tolerance.
This means that it is gradually an increase in the presence of blood sugar on an empty stomach, after eating there is a process of glucose concentration in human blood. Also do not forget about the heredity of this disease.
All changes in the human body are coming individually, each in different ways. Someone processes proceed faster, someone has much slower.
The development of diabetes in the people of the elderly age is much higher than that of the younger generation
The changes affect the lifestyle, which leads a pensioner, what is used in food, physical exertion.
And in the elderly, the secretion and action of such hormones, as intrescans, are significantly reduced and weakened, the sensitivity of the body tissues is reduced to insulin. All this leads to not very good results, health begins to deteriorate.
Contributing factors for the development of sugar diabetes
- Lack of physical activity of man;
- Reduction of muscle mass;
- Poor-quality nutrition;
- Incorrect carbohydrate exchange.

When improving blood sugar levels, the body is experiencing a serious deficit of energy, and this is the problem of developing diabetes in widespread.
Types of diabetes
There is a division of diabetes in two groups. If in the body is a lack of insulin, it is considered a diabetes of the first type.
And when there is a violation of excessive insulin - this is diabetes mellitus. Consider all types of disease in more detail.
Diabetes of the first type
Sugar diabetes of 1 type, it is also called youthful diabetes, the disease is manifested at different ages.
Video: type 1 diabetes
A feature of this type of disease is insulinant failure, which is lifelong character, is accompanied by the destruction of betta cells.
The first type of disease is distinguished, autoimmune and idiopathic.
The diabetes of the second type
Sugar diabetes mellitus is a defect of insulin secretion, the background for this is insulin resistance. This is associated with a metabolic violation.
At the same time, an increase in insulin is observed in the blood, which affects the metabolism.
Video: Signs of type 2 diabetes
Having considered the main types of the disease, it should be borne in mind that further identified several forms of diabetes, they include:
- Defects of insulin genetics;
- Diabetes due to the use of medicines;
- Diabetes transformed after infection in the body.
Decrease in insulin secretion with age
Hazardous insulin resistance, with significant obesity, is manifested even with the normal amount of insulin produced in the pancreas.
When eating a person in food products with large content Carbohydrates, there is an increase in the amount of glucose in the blood, which leads to the development of insulin by the pancreas.
This process takes place in two phases:
- Intensive intensive insulin of the pancreas, the process lasts about 10-15 minutes;
- Smooth filling of blood insulin, flows this moment throughout one to two hours, after eating food.
All sorts of medical studies have proven that a person with an increase in age has a significant decline.
If a old man It has a normal body weight, a decrease in glucosinase activity is noticed.
This gene contributes to ensuring the sensitivity of the betta cells in the pancreas, while stimulating the effects of glucose. As a result of such a nuance, there is a decrease in insulin secretion in old age.
2-type diabetes symptoms
That layer of the population that suffers from type 2 diabetes, it feels a lack of insulin in the blood, which forces people to make people insulin-dependent throughout life.
As a result, insulin lack is observed increased content In the blood of glucose, which adversely affects the condition blood system and other internal organs.
The symptoms of the diabetes of the second type are:
- Constant thirst, man always wants to drink;
- Reinforced urination, the patient is constantly visiting a toilet exceeding the number of times from the usual;
- Unjustified body weight loss;
- Increased fatigue;
- Constant weakness;
- Unreasonable nervousness and irritability;
- Vomit reflex and nausea.
If a person has these symptoms, it is necessary to immediately contact a specialist for help.
When a person drags his appeal to the doctor, there is a risk of obtaining a number of complications that can manifest themselves in the diseases of the renal system, violations in neurological manifestations, there is a special risk of heart attack, stroke, even loss of vision may occur.
Sugar diabetes type 2 enough dangerous diseasewhich can lead to death
Diagnosis of diabetes in the elderly
When contacting the hospital, the first doctor will appoint, it is to pass blood from the finger to the analysis, where the level of sugar is determined. All people over 40 are recommended to take tests for sugar at least once every two years.
- Blood test for hemoglobin;
- Urine analysis for the presence of protein;
- When a person has a fatigue complaint;
- Significantly impairment of vision;
- Problems with lower limbs.
Sometimes the diagnosis of the disease is hampered by the absence of symptoms. Especially problematic identification of the disease in people of old age.
This is associated with the age fatigue, memory problems, dizziness, many of this are concluded that old state dementia comes, and they do not appeal on the doctor.
When a person does not treat diabetes, the disease progresses, and the consequences are unpredictable.
Treatment of 2-type diabetes
Sugar diabetes of the 2nd type is quite difficult to treat, but still amenable to treatment.
Unfortunately, patients over the age of 45 have a large number of concomitant diseases that do not allow to be treated in the complete required amount.
There are several ways to treat:
- Therapy without drugs. To such a course of treatment include the finding of a person on a permanent diet, accompanied in physical activity. The diet is restricted food containing animal fats and carbohydrates. It is categorically impossible to use sugar-containing products, sugar substitutes will help. The diet should be constant in time, you can not pass food. Attention is also paid to the physical condition, to maintain a simple gymnastics, and yoga for the elderly will be appropriated;
- Medical methods. To reduce sugar in the blood there are a large number of drugs. The main applied groups of medicines, this is: Biguanides derived from thiazolidinone, acarbosis, inhibitors, incritons and others. All medicines are used only by appointing the attending physician;
- Insulinotherapy. This is a complex necessary measureswhich implies balancing violations carbohydrate exchangeoriginating due to insulin administration to the patient's body.
Such a disease, like diabetes, it often leads to irreversible processes in the body, thereby significantly reduces the vitality.
Conclusion
Of all the above listed, it should be understood that the earlier go to the hospital, having the slightest symptoms, the most likely to start treatment in time.
The main responsibility for the state of health bear people themselves for themselves. Take care of your health and your loved ones.
 Sugar diabetes (SD) - A group of metabolic (exchange) diseases characterized by hyperglycemia, which develops as a result of insulin secretion defects, insulin actions or both of these factors.
Sugar diabetes (SD) - A group of metabolic (exchange) diseases characterized by hyperglycemia, which develops as a result of insulin secretion defects, insulin actions or both of these factors.
People of the elderly and senile age most often occur in the 2nd type diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes).
In diabetes mellitus of the 2nd type plays a role genetic predisposition. Provide to the occurrence of sugar diabetes obesity, stressful situations, a low-wear lifestyle, unbalanced nutrition. The basis of the type 2 diabetes mellitus is the phenomenon of insulin resistance and violation of the β cell function.
Insulin resistance - decrease in tissue sensitivity to insulin.
Patients over 60 years old suffering from diabetes are noted elevated levels Confinixular hormones - STS, ACTH, Cortisol.
Clinical picture.
Elderly and senile people are sometimes difficult to establish the time of the first signs of the disease. Often the disease is diagnosed by chance. More often there are low-almptomatic forms of diabetes. Patients complain of general weakness, fast fatigue, skin and genital itch. There are a tendency to bronchitis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, mercant diseases and others inflammatory processes, slowing down wound healing. For patients, excessive mass of the body is more characteristic.
The deterioration of the state occurs most often against the background of stress, injuries, infections, hypertensive crisis, myocardial infarction, acute brain circulation disorders.
Often the main manifestation of diabetes in people of elderly and senile age becomes its complications (progression ischemic Disease Hearts, damage to the nervous system, kidneys, reducing vision, etc.). Diagnostic criteria for violations of carbohydrate metabolism are shown in Table. 5.1.
Table 5.1
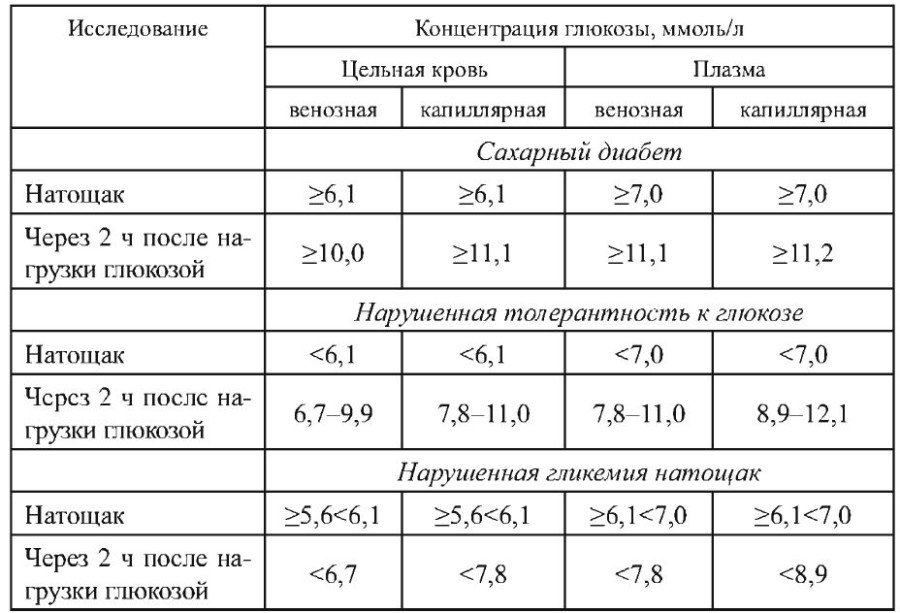
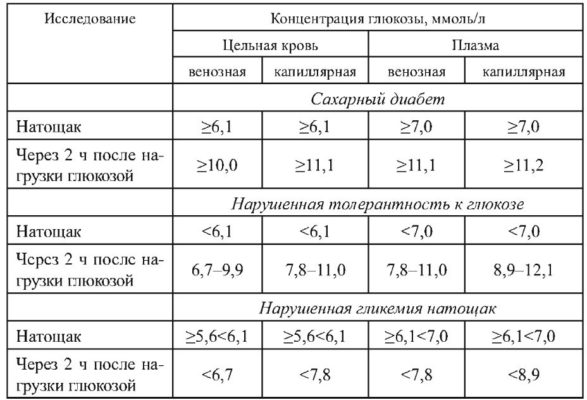
Complications.
Elderly and senile people expressed vascular complications. Macroangiopathy arise (damage to large and medium caliber vessels) and microangiopathy (lesion of arterioles, capillaries and Vullet).
Atherosclerosis is based on macroangiosagatia. There is a progressive course of ischemic heart disease, a tendency to myocardial infarction, lesion of brain vessels, oblique atherosclerosis of the vascular of the lower extremities.
MicrangioNatia Develop the elderly before young people. The vision is reduced, dystrophic processes in the retina (diabetic retinopathy) and closet of lens are developing. Engaged kidney (nephlohangiopathy, which is often accompanied by chronic pyelonephritis). The vessels of the microcirculatory line of the lower extremities are affected.
Syndrome diabetic foot - Against the background of a reduction in sensitivity on the skin of the feet, microcracks appear, the skin becomes dry, loses elasticity, swelling appears.
The shape of the foot ("Cubic Stop") changes. In the later stages, there is a severe defeat of the stop, unkind ulcers are formed. In the launched cases, the limb amputation is necessary.
Diabetic Ninearopathy- One of the manifestations of the damage to the nervous system during diabetes mellitus. There are pains in the limbs, numbness, the feeling of "crawling Murashey", a decrease in sensitivity, reflexes.
Acute states.
Diabetic ketoacidosis in the elderlyit is rare. Ketoacidosis can develop in patients with insulin-independent diabetes mellitus under stress conditions and with concomitant diseases leading to decompensation of diabetes mellitus.
Hypoglycemia in the elderly meets less often than young people.
The reasons- intense physical activity (increase in glucose recycling), alcohol intoxication, an overdose of assigned insulin, receiving β-adrenoblocators. The basis is the energy starvation of cells under conditions of low blood glucose. Develops quickly.
Symptoms: total weakness, sweating, trembling, muscular tone elevated, feeling hunger, patients can be excited, aggressive, tachycardia is noted, raising arterial pressureFor further development, the loss of consciousness, a decrease in muscle tone, blood pressure.
Hypoglycemic states develop at different levels of glycemia (more often than 3.3 mmol / l).
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
Repeated studies of blood glucose content, urine study on glucose, acetone, blood definition glicated hemoglobin (Compound glucose with hemoglobin, showing the average level of glycemia over the past 3 months), fructosamine (glycated albumin), diagnosis of kidney function, inspection of the oculist, neuropathologist, study of blood flow in brain vessels, lower extremities.
Treatment and care.
Patients with diabetes are prescribed a table D. EXCLUSIVE ACCESSIBLE CARBOBERS (Sugar, confectionery), instead of sugar replacements are recommended: xylitis, fructose, tsukley. Limited animal fats. The diet includes products containing slow suction carbohydrates (black bread, buckwheat, oatmeal, vegetables).
Value exercise must correspond to the state of the patient. Muscular work increases muscle glucose absorption.
Medicia treatment It is to apply the following oral saccharincing drugs:
- biguenides (Currently, from this group, only metformin is in demand, elderly patients are appointed with caution);
- preparations of sulfanylmichevines (glyclaside, glinenkelamide, glurerenorm);
- tiaglitazones (roseglitazone) - a new class of antidiabetic drugs.
Insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetesit can be used with ketoacidosis, vascular complications, surgical interventions, when attaching other diseases, ineffective treatment.
Sugar diabetes in a child often proceeds much harder than an adult. This disease can develop in newborns, its etiology is associated with hereditary factors and a certain way of life. Basically, the disease appears at the age of 6-12 years.
It was found that diabetes arising in 2 years is more malignant than chronic hyperglycemia that occurs in 10-12 years. Often, children develop an insulin-dependent form of the disease.
But occasionally at an older age (for example, adolescents) 2 type of disease can be diagnosed, which is often developing against the background of obesity. However, there are other types of diabetes, the causes of which are diverse.
Types and factors for the development of diabetes
Many people think that the causes of the disease are often reduced to immune failures, but this is not quite so. In fact, the etiology of the disease is quite varied. All the factors of diabetes have a newborn baby, a preschooler, schoolchildren and a teenager are divided into 2 main categories - type 1 diabetes (idiopathic, autoimmune) and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
If there is no type 1 diabetes, then the child can be detected such types of diabetes as:
- insulin independent;
- MODY;
- neonatal (develops in newborns);
- diabetes accompanying genetic syndromes.
It is noteworthy that the last 2 forms of the disease identify quite simply, and for the differences in type MODY, 1 and 2 forms that are often accompanied by obesity, it will be necessary to conduct a complex differential diagnosis.
The reasons for the development of diabetes in children have not yet been studied. However, it was found that the combination of hereditary predisposition and adverse external factors leads to the emergence of chronic hyperglycemia in a child.
Type 1 diabetes is divided into idiopathic and autoimmune. In the latter case, the autoantibodes that kill the beta cells of the pancreas occurs.
But with the idiopathic form of the disease, these antibodies are not detected, so the factors of the appearance of problems with the pancreas are unknown, but the result is the same as in the autoimmune form of the disease.
Often the disease is detected in 5-16 years at the time of Pubertata. And in newborns and young people, such a type of diabetes is practically not found.
At an autoimmune insulin-dependent form of the disease, antibodies are found to:
- glutamatdecarboxylase - GAD (80-95% of cases);
- islated beta cells - ICA (60-80%);
- tyrosine phosphatase - IA-2Bet (70-80%);
- antinsulin antibodies - IAA (30-60%).
The conditions for the appearance of 1 type of diabetes of the child are heredity and factors of the external environment. It is worth noting that the genetic cause of the occurrence of the disease is not inheritance of a mutated gene, which in 100% of cases leads to the emergence of chronic hyperglycemia.
Such a state is developing when normal genes are built into a certain combination. Therefore, the likelihood that a close relative of the patient will also be sick with such diabetes is 50%.
However, for the implementation of this theory, a combination of a number of factors is needed. So, the appearance of type 1 diabetes often contributes viral infection. It may be cytomegalovirus, cokesacks, Epstein-Barr, Echo, parotitis, rubella and more.
Also, the premises of diabetes can be said that power factors contribute to its appearance. So, it was found that artificial feeding using mixtures with cow milk and gluten-containing products can provoke the development of diabetes. Another likelihood of chronic hyperglycemia increases the regular use of preservatives and nitrates.
In addition, insulin-dependent diabetes in children arises against the background of chronic or acute stress. Toxic impact also leads to the emergence of such a disease. So. Cyclicheptadine, Rodentcid and Streptozotocin can have a detrimental effect on the pancreas cells.
But what are the causes of diabetes in children not caused by immune disorders? Type 2 hyperglycemia increasingly affects patients early age Even a weight. Obesity in the child arises due to an inactive lifestyle and nutrition.
The principle of development of such a state in children is the same as in adults. However, the flow of insulin dependent diabetes is different:
- In 5-25% of patients at the initial stage of diabetes, there is a lack of insulin and severe glucosotoxy.
- Often the disease proceeds asymptomatic or with unfriendly signs.
- Due to the rapid progression of the disease, the rapid development of vascular complications occurs.
- Sometimes children detected by autoantibodies, as with 1 form of diabetes, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
- 40% of children initial stage The disease is accompanied by ketosis, sometimes hyperosmolar states are joined to it.
All of these features can lead to the fact that the child will be delivered the wrong diagnosis. Therefore, all children with overweight should be examined for the presence of type 2 diabetes. Distinctive features of this form of the disease are insulin resistance, overweight, normal or increased content of C-peptide concentration, age from 10 years, absence of autoantibodies, the presence of relatives with a similar disease.
Mature form diabetes in young people occur due to the genetic defect of the pancreatic beta cells. Moreover, the autosomal dominant type of inheritance does not depend on the floor.
There are 9 diabetes subtypes, each of which is triggered by a defect of one or another gene. Therefore, to diagnose the disease, it is necessary to carry out a special genetic study.
Often diabetes mody proceeds softly, so there is no need for insulin therapy most often. The reason for the examination on this form of the disease can be such factors as the presence of chronic hyperglycemia in relatives, normal content C-Petida, long honeymoon (from year), lack of communication with the HLA system, low dose insulin and high compensation.
There is also an neonatal form of diabetes, which develops in the first half of the year of life. The course of the disease may be different, it is a monogenic form.
There are 2 subspecies of neonatal diabetes - transient and permanent. In the transient type, the need for insulin's introduction disappears in a few months, and the likelihood of relapses in the future is 50%. In the case of permanent form in insulin therapy, there is no need.
As a rule, neonatal diabetes mellitus in children of the causes of which are linked in the genetic failure, it appears due to the mutation of the AVSS8 and KCNI11 genes. It is worth noting that with such a type of violations, the patient is translated from insulin on drugs containing sulfanylmic.
Also diabetes can accompany genetic syndromes. The reasons for such a form is also a genetic failure, but this happens extremely rarely.
Such diabetes may occur immediately after birth, school age Either during puberty. Examples of genetic disorders requiring insulin therapy are tungsten syndrome, Rackson-Medellhall, Rogers, lipodystrophy and so on.
The probability of the appearance of the disease in relatives
Sugar level
The overall risk of diabetes is 0.4%. Thus, in the family where no one is sick 1 type of disease, the probability of the appearance of chronic hyperglycemia is minimal.
But if there is an insulin-dependent diabetic in the family, then the chances of the occurrence of a disease in someone from his relatives increase. So, in children whose father was ill diabetes, the risk of developing endocrine disorders is 6.1%, and the sisters and brothers probability is 5%.
If Mom is sick, then much depends on its age. For example, if it is under 25 years old, then chances are 3.6%, older - 1.1%.
In the diversified twins, the probability of the appearance of diabetes in the second is 5%, at one-time - 30-50%. Children of parents who are both diabetics are ill in 30% of cases. It is noteworthy that it happens that the parents have a much later illness than their children.
Crop of Togo, the chances of the emergence of diabetes at the sisters, brothers and parents depend on the age when a man fell ill. So, if the disease appeared at 20 years, then the probability of its development for sisters and brothers is 6.4%, and for parents - 2.3%. In the case of a later occurrence of chronic hyperglycemia, for sisters and brothers, the chances are significantly reduced - 1.6%.
In addition to the relaxing factors and genetic failures, the presence of diabetes can be suspected if you pay attention to the characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Clinical picture and complications of diabetes in children
Leading signs of illness - rapid rapid slimming, increased urination and thirst. The accompanying manifestations refers to the weakening of immunity (frequent fungal and purulent skin lesions), fast fatigue, increased appetite and indisposition. Little children appear diameters in the crotch or on the hips, and girls often bother vulvit.
At the same time, urine becomes bright and transparent. And on diapers and underwear with urin residues, starch spots are formed, which are sugar.
If all these symptoms are not seen earlier than 4 weeks at a schoolboy or a few days later baby, Diabetic ketoacidosis will be developed. This state appears when due to glucose deficiency, the body begins to use fats and other substances. However, with their decay, ketones are formed together with glucose - derivatives of acetone.
Since the sugar of the body needs a lot, then with its receipt, a variety of ketones are formed that do not have time to be output. All this can lead to the development of a diabetic coma.
Often, symptoms of diabetes mellitus in children are found in the ketoacidosis state. Therefore, parents should know how it manifests itself.
Ketoacidosis is developing gradually, for several hours or even days. If the medical intervention is not timely, then there is a coma or a patient dies.
At the initial stage of the disease, the following manifestations are noted:
- strengthening characteristic diabetic signs;
- bad appetite, vomiting and nausea;
- top-like abdominal pains, in the right hypochondrium and in the zone near the navel;
- impairment;
- dizziness;
- malaise;
- headache.
At the same time, a "diabetic blush" appears in the patient, his lips crack, dry, and the skin begins peeling. Also emerges characteristic symptom - Acetone from the oral cavity.
When the patient is in a state state, all the above-described manifestations are more pronounced. So, pain in the stomach becomes sharp, there is a strong vomiting with blood impurities, the breath and the work of the heart is disturbed.
The patient's skin becomes gray, pale, dry and diryab. His tongue and lips are covered with brown raid.
If a diabetic coma developed, then there is no vomiting, urination is stopped, and the patient is unconscious. In addition, there is a strong disorder of the circulatory system and respiratory function. In this case, urgent medical care is needed.
Complications can develop with any type of diabetes, which has a negative impact on the life of the patient and can lead to disabilities. So, the consequence of diabetes can be the rebirth of the liver. At the same time, the organ becomes dense and disruption of the outflow of bile.
Also in the patient often develops angiopathy. But at the initial stage, irreversible consequences of pathology can be prevented if you have adequate therapy.
As a rule, the first manifestations occur 15-20 years after the start of the disease. However, in case of poor compensation and in case of insufficient monitoring of the health status of the child, the consequences will appear much earlier - 3-5 years.
Basic complications of diabetes in children:
- nephropathy - contributes to the emergence of renal failure;
- retinopathy - manifests itself a worsening of vision, which can lead to retinal detachment and blindness;
- polyneuropathy - characterized by the damage to the peripheral nerves, which is manifested by low sensitivity and weakness in the legs;
- encephalopathy - manifests itself mental, intellectual and emotional disorders.
In addition, in the absence of adequate and timely treatment In small vessels of the lower extremities, adverse changes occur. The first thing is violated blood supply, and ulcers are formed on the legs, the feet are cold, and with a reinforced load, pain occurs. In the launched cases, it is formed, but this phenomenon is more characteristic of elderly diabetics.



















