Recommendations of the European Society of Cardiologists to conduct patients with stable ischemic heart disease. Stenzardia, National Recommendations, 2010 Unstable National Recommendations
Citation:Sobolev G.N., Karpov Yu.A. Recommendations of the European Society of Cardiology on Stable IBS 2013: Mikrovascular angina // RMW. 2013. №27. P. 1294.
In September 2013, new recommendations were presented on the diagnosis and treatment of a stable ischemic heart disease (IBS). Among many changes in the recommendations, high attention attracted angina at unchanged coronary arteries (Ka), or microwave angina. The spectrum of clinical and pathological correlations between the symptoms and the nature of the changes in the walls of the walls is quite wide and varies from typical manifestations of angina, due to the stenosis lesion of the ka and transient ischemia of myocardium, to an atypical for angina of pain syndrome with unchanged. This range from atypical for the angina peeling syndrome against the background of meaningful stenosis in ka, ultimately acquiring the diagnosis of the "angina region", to a typical clinic of the disease against the background of unchanged KA, which is proposed to identify as "microwave angry" (MVS) in recommendations from 2013 . According to a stable angina, or earlier - cardiac syndrome X (CCM).
The definition of "CCM" was first applied in 1973 by Dr. H.G. Kemr, who addressed attention to the research of Canadian scientists R. Arbogast and M.G. Bou-Rassa. The pain syndrome in this group of patients may differ in the following characteristics:
1) pain can cover a small part of the left half chest, continue from several hours to several days and not to be taking a taking nitroglycerin;
2) the pain may have typical characteristics of an anginal attack on localization, duration, but at the same time arise in peace (atypical angina, due to vasospasm);
3) Perhaps the manifestation of pain syndrome with typical characteristics of an anginal attack, but more prolonged in time without a clear connection with exercise and a negative result of stress tests, which corresponds to clinical picture MVS.
Diagnosis and determination of treatment tactics in patients with MVS are a difficult task. In a significant portion of patients (approximately 50% of women and 20% of men) in the presence of angina, coronoagogeniography (kAg) does not reveal atherosclerosis of epicardial arteries, which indicates a violation of the function (coronary reserve) of the micrososud. The data of Women's ISChemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE), organized by the National Institute of Heart, Lungs and Blood, demonstrated the 2.5% annual risk of developing adverse cardiovascular events in this group of patients, including death, myocardial infarction, stroke and heart failure. The results of 20-year observation of 17,435 patients in Denmark with unchanged and unstructive diffuse damage with angina showed 52 and 85% increase in the risk of large cardiovascular events (cardiovascular mortality, hospitalization about them, heart failure, stroke) and 29 and 52% increase in the risk of total mortality, respectively, in these groups without significant differences in gender.
Despite the absence of a universal definition of the MVS, the main manifestations of the disease correspond to the presence of the triad of the signs:
1) Typical angina, due to the load (in combination or in the absence of angina rest and shortness of breath);
2) the presence of signs of myocardium ischemia according to ECG, Holter monitoring of ECG, stress tests in the absence of other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
3) unchanged or low-changed ka (stenosis<50%) . Наиболее чувствительным методом диагностики ишемии миокарда у этих больных является применение фармакологических тестов или ВЭМ-теста в сочетании с однофотонной эмиссионной компьютерной томографией миокарда при введении 99mTc-МИБИ (аналог таллия-201), позволяющего визуализировать дефекты перфузии миокарда как результат нарушенного коронарного резерва в ответ на повышенные метаболические потребности миокарда. Приступы стенокардии могут возникать достаточно часто - несколько раз в неделю, но при этом иметь стабильный характер. Таким образом, МВС является формой хронической стенокардии и по МКБ-10 относится к коду 120.8 «Другие формы стенокардии». Диагноз формулируется в зависимости от функционального класса стенокардии, например «ИБС при неизмененных коронарных артериях. Стенокардия ФК II. (Микроваскулярная стенокардия)».
The main cause of the MVS is the dysfunction of coronary microscopes, defined as an anomalous response of coronary microcirculation on vasoconstrictor and vasodilating stimuli. Figure 1 shows the main mechanisms and signaling paths of the regulation of coronary blood flow. Endothelium dysfunction, the hyperreactivity of smooth muscle cells and the increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system are discussed as the main causes of microvascular dysfunction. Estrogen deficiency can contribute to the development of CCS due to endothelium dysfunction (DE) in women in postmenopausal period. Famous traditional risk factors atherosclerosis, such as dislipidemia, smoking, obesity, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, can also affect the formation of endothelium dysfunction with the subsequent development of the MVS.
The coronary reserve, defined as the ratio of myocardial blood flow to the hyperemia phase with basal blood flow, decreases under the condition of increased basal blood flow or reduced hyperemia. Basal blood flow correlates with hemodynamic indicators (blood pressure, neurohumoral parameters, myocardial metabolism, heart rate - heart rate). Recently, data were obtained on the presence of a slow reverse seizure of norepinephrine in synapses in women, which can explain the specificity of the MVS for women and a disruption of the autonomous regulation of the tone of the microcosuds with a decrease in the coronary reserve. On the contrary, the hyperemic response is regulated by an endothelium-dependent and endotheline-dependent response. Mechanisms causing damage to hyperemic myocardial blood flow in patients with MVS are currently not clarified: some of the patients demonstrate endothelium dysfunction, others - an anomaly of endotheline-dependent vasodilant reactions, in particular the adenosine metabolism defect. We first demonstrated a decrease in the reserve of myocardial perfusion during the ATP-OECT of myocardium (Fig. 2). It is possible to use dipyridamole to evaluate the coronary reserve using transistorical ultrasonic doppler (Fig. 3), also convincing evidence in favor of a reduction in the coronary reserve were obtained in studies using positron-emission tomography of the heart.
Ischemic changes on the ECG and defects of the Miocardium Capture Tallolium during stress tests are identical in patients with MVS and obstructive atherosclerosis of epicardial ka, but differ in the absence of hykokinease zones at MVS, which is due to the small volumes of chemistry of ischemia, frequent localization of them in the subendocardial zone, quickly washing the anaerobic Metabolites and the emergence of zones with compensatory hypersochasitivity of neighboring myocytes, which significantly limits the possibility of visualizing such zones with a violated reduction. Nevertheless, compensatory release of adenosine may be sufficient to stimulate afferent fibers that cause a feeling of pain, which is particularly pronounced in the conditions of an increased pain sensitivity characterizing patients with MVS.
The MVS, as noted above, is established in the presence of angina attacks, documented myocardial ischemia in the absence of hemodynamically significant stenosis in the KA (stenosis of ≤50% or intact KA) and the absence of signs of vasospasm (as it takes place at the variant angina printela). The myocardial ischemia is usually loaded by load tests, which uses cycle ergometry (VEM), a Tredamil test, or 24-hour Holter monitoring of the ECG (HM-ECG) by identifying the horizontal depression of the ST segment by more than 1 mm from the point J to the ECG. The method of excluding the diagnosis of "IBS" is invalid by doctors only by identifying unchanged CA according to kag in patients with pain in the chest, refusal to conduct additional methods of study, the most precisely verifying myocardial ischemia, because This leads to the underestimation of the symptoms of the angina and the unassignment of the necessary drug therapy, which worsens the course of the disease, requires repeated hospitalizations. Thus, a reliable verification of myocardial ischemia in patients with CCM is represented by the determinant, which determines the strategy and tactics of treatment, and therefore the forecast of life in this group of patients.
For patients with MVS are characterized by low reproducibility of ischemic changes to the ECG during load tests and practically no possibility to identify hypokine zones according to stress-echochetus, which is due to the development of subendocardial ischemia due to the spasm of intramiocardial vessels, in contrast to patients with obstructive atherosclerosis of epicardial arteries corresponding to tranural ischemia and myocardial systolic dysfunction.
The verification of myocardial ischemia in this group of patients is possible:
1) when visualizing defects of myocardial perfusion in load or pharmacological tests;
2) confirmation by biochemical methods of metabolic disorders in myocardium.
Due to the complexity of the last methodology, the fundamental methods of verification of myocardial ischemia in patients with MVS are:
1. Single-photon emission computed heart tomography, combined with VEM test or pharmaceutical. In the first case, when reached the submaximal heart rate (heart rate) or ECG signs of myocardial ischemia during the implementation of the VEM test, patients are administered intravenously 99mtc-mibi (99mtc-methoxyisonitrile) with an activity of 185-370 MBC, followed by 1 hours of myocardium and evaluation Perfusion defects. In cases with insufficient informativeness of the samples with physical activity or under its negative results, an alternative method in conducting radionuclide studies of myocardial perfusion is a method using a pharmacological test. In this case, the VEM test is replaced by the introduction of intravenous pharmaceutical (dobutamine, dipyridamole, adenosine). Previously, studies were conducted in the FGBU RKNPK Ministry of Health of Russia with the introduction of Acetylcholine Intrakorokorno and 99MTC mibi intravenously with the aim of provocative myocardial ischemia due to endothelium dysfunction. These data are subsequently confirmed in the Acova study. The specified method has demonstrated high informativeness, but did not find widespread due to an invasive nature. The use of dobamine seems to be inappropriate in patients with MVS, because The expected effects of a reduction in myocardial cuttlens due to its ischemia will be extremely rare, as in the case of stress echoc. Currently, studies conducted in the FGBU RKNPK Ministry of Health of Russia make it possible to recommend that in broad clinical practice, the method of verification of myocardial ischemia in patients with MVS - OEECT myocardium combined with the introduction of adenosine trifhosphate available on the pharmaceutical market (ATP).
2. Intrakoronary administration of adenosine with an estimate of the blood flow rate by intravascular ultrasound research proves the presence of anomalous blood flow rate in patients with MVS.
3. Anomalous ratio of phosphocreatine / ATP in myocardium in patients with MVS according to MR-spectroscopy.
4. Sub-endocardial perfusion defects according to MRI heart.
In the treatment, all patients with MVS must be achieved the optimal level of risk factors. The selection of symptomatic therapy is empirical due to the unspecified cause of the disease. The results of clinical studies are not amenable to generalize due to the lack of uniform selection criteria and the few samples of patients, imperfect study design and the unacceptability of the effectiveness of the treatment of the MVS.
Traditional antianginal drugs are prescribed at the first stages of treatment. Short-effect nitrates are recommended for the relief of anginal attacks, but they often do not have an effect. Due to the dominant symptomatology of the angina angina, the treatment of β-blockers, the positive effect of which to eliminate the symptoms of angina is proved in several studies; These are preparations of first choice, especially in patients with obvious signs of increased adrenergic activity (high frequency of the pulse at rest or during exercise).
Calcium antagonists and prolonged nitrates have demonstrated ambiguous results in clinical studies, their effectiveness is obvious with an additional purpose to β-blockers in the case of angina conservation. Calcium antagonists can be recommended as the preparations of the first line in case of variability of the threshold of the stress angina. In patients with persistent angina, despite the optimal anti-inanal therapy, the following appointments may be proposed. ACE inhibitors (or angiotensin II blockers) are able to improve the function of micrososuds, neutralizing the vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin II, especially in patients with arterial hypertension and diabetes. It is possible to prescribe to some patients in order to suppress the increased sympathetic activity of α-adrenoblockers, whose influence on the symptoms of angina remains non-obvious. Improvement of tolerance to physical stress in patients with MVS has been demonstrated during Nicorandyl therapy.
Improving clinical symptoms was achieved due to the correction of the function of the endothelium under the treatment of statins and estrogen-agency therapy. Patients with continued angina, against the background of therapy with drugs mentioned above, treatment of xanthin derivatives (aminoophyllin, bamophillin) may be proposed in addition to antiagonal drugs in order to block adenosine receptors. New anti-naniginal drugs - Rolazine and Ivabradin - also demonstrated effectiveness in patients with MVS (Table 1). Finally, in the case of refractory angina, additional interventions should be discussed (for example, percutaneous neurostimulation).



Literature
1. 2013 ESC Guidelines on the Management of Stable Coronary Artery Disease. The Task Force On The Management of Stable Coronary Arttery Disease of the European Society of Cardiology. http://eurheartj.oxfordjournals.org/ Content / Early / 2013/08/28 / Eurheartj.eht296
2. ZIPES D.P., LIBBY P., BONOW R.O. et al. Braunwald's HeartCdisease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 8 EDN. Saunders-Elsevier, Philadelphia 66. Zorc-Pleskovic R., Vraspir-Porenta O., Zorc M. et al .2008.
3. Sharaf B.L., Pepine C.J., Kerensky R.A. et al. Detailed Angiographic Analysis of Women With Suspected Ischemic Chest Pain (Pilot Phase Data from The Nhlbi-Sponsored Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation Study AM. J. Cardiol. 2001. Vol. 87. P. 937-941.
4. Johnson B.D., SHAW L.J., buchthal s.d. et al. Prognosis in Women With Myocardial Ischemia in the Absence of Obstructive Coronary Disease. Results from the National Institutes of Health-National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute-Sponsored Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (Wise) // Circulation. 2004. Vol. 109. P. 2993-2999.
5. Jespersen L., HVELPLUND A., ABILDSTRØM S.Z. et al. Stable Angina Pectoris with No Obstructive Coronary Arttery Disease Is Associated with Increased Risks of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events // EUR. Heart J. 2012. Vol. 33. P. 734-744.
6. CANNON R.O. 3rd, Watson R.M., Rosing D.R., Epstein S.E. Angina Caused by ReducedVasodilator Reserve of The Small Coronary Arteries // J. AM. Coll. Cardiol. 1983. Vol. 1. P. 1359-1373.
7. Camici P.G., Crea F. Coronary Microvascular DYSFUNCTION // N. ENGL. J. Med. 2007. Vol. 356. P. 830-840.
8. Sergienko V.B., Samoilenko L.E., Sayutina E.V. et al. The role of endothelium dysfunction in the development of myocardial ischemia in patients with IHS with unchanged and low-change coronary arteries // Cardiology. 1999. No. 1. P. 25-30.
9. Lanza G.A., Giordano A., Pristipino C. et al. ABNORMAL CARDIAC ADRENERGIC NERVE FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH SYNDROME X DETECTED by Metaiodobenzylguanidine Myocardial Scintigraphy // Circulation. 1997. Vol. 96. P. 821-826.
10. Meeder J.G., Blanksma P.K., Van Der Wall E.E. et al. CORONARY VASOMOTION IN PATIENTS WITH SYNDROME X: Evaluation with Positron Emission Tomography and Parametric Myocardial Perfusion Imaging // EUR. J. NUCL. Med. 1997. Vol. 24 (5). P. 530-537.
11. Patent for the invention: a method for diagnosing myocardial ischemia in patients with cardiac syndrome on single-photon emission computed tomography with 99mts-mibi, in combination with pharmacological sodium adenosine trigger. Application No. 2012122649, Decision on issuing a patent of July 22, 2013. G.N. Sobolev, L.E. Samoilenko, I.E. Karpova, VB Sergienko, Yu.A. Carp.
12. GRAF S., KHORSAND A., GWECHENBERGER M. ET AL. Myocardial Perfusion in Patients with Typical Chest Pain and Normal Angiogram // EUR. J. Clin. Investig. 2006. Vol. 36. P. 326-332.
13. Zeiher A.M., Krause T., Schachinger V. et al. Impaired Endothelial-Dependent Vasodilatation of Coronary Resistance Vessels Is Associated with Exercise Induced Myocardial Ischemia // Circulation. 1995. Vol. 91. P. 2345-2352.
14. Rustamova Ya.K., Alekhin M.N., Salnikov D.V. and others. The value of stress echocardiography in patients with angiographically unchanged coronary arteries // Cardiology. 2008. No. 12. P. 4-9.
15. Camici P.G. Is the Chest Pain In Cardiac Syndrome X Due To Subendocardial Ischaemia? // EUR. Heart J. 2007. Vol. 28. P. 1539-1540.
16. Vermeltfoort i.A., Bondarenko O., Raijmakers P.G. et al. Is Subendocardial Ischaemia PRESENT in Patients with Chest Pain and Normal Coronary Angiograms? A Cardiovascular MR Study // EUR. Heart J. 2007. Vol. 28. P. 1554-1558.
17. ONG P., ATHANASIADIS A., Borgulya G. et al. High Prevalence Of A Pathological Response to Acetylcholine Testing in Patients with Stable Angina Pectoris and Unobstructed Coronary Arteries. The Acova Study (Abnormal Coronary Vasomotion in Patients with Stable Angina and Unobstructed Coronary Arteries) // J. AM. Coll. Cardiol. 2012. Vol. 59 (7). P. 655-662.
18. Gemignani A.S., ABBOTT B.G. The Emerging Role of the Selective A2A Agonist in Pharmacological Stress Testing // J. NUCL. Cardiol. 2010. Vol. 17. P. 494-497.
19. Rigo F., GHERARDI S., CORTIGIANI L. ET AL. Long-Term Survival of Patients with CHEST PAIN SYNDROME AND ANGIOGRAPHICALLY NORMAL OR NEAR-NORMAL CORONARY ARTERIES // EUR. Heart J. 2007. (Abstract).
The most important diagnostic method for complaints about pain in the chest is the collection of anamnesis.
At the diagnostic phase, it is recommended to analyze complaints and collection of anamnesis in all patients with suspicion of IHD.
Comments.The most common complaint with the walls of the voltage, as the most common form of a stable IBS, is the pain in the chest.
It is recommended to ask the patient about the existence of pain in the chest, the character, frequency of the occurrence and circumstances of the disappearance.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comments.Signs of typical (undoubted) stress angina:
Pain in the field of sternum, possibly with irradiation in the left hand, back or lower jaw, less often in the epigastric region, duration of 2-5 minutes. Equivalents of pain there are shortness of breath, the feeling of "gravity", "burning".
The pain described above occurs during exercise, or strong emotional stress.
The pain described quickly disappears after the discontinuation of the physical activity or after taking nitroglycerin.
To confirm the diagnosis of typical (undoubted) angina, it is necessary to have the patient of all three of the above features simultaneously.
There are atypical options for localization of pain and irradiation. The main sign of the angina of the voltage is the clear dependence of the occurrence of symptoms from physical exertion.
Equivalent of angina, there may be shortness of breath (up to choking), the feeling of the "heat" in the field of sternum, attacks of arrhythmia during exercise.
An equivalent of physical activity may be a critical increase in blood pressure (AD) with an increase in the load on myocardium, as well as abundant meals.
The diagnosis of atypical angina is placed if the patient has any two of the three above signs of typical angina.
Signs of non-English (non-monocardial) pain in the chest:
Pains are localized alternately and to the left of the sternum.
Pains wear local, "point" character.
After the occurrence of pain, more than 30 minutes continues (up to several hours or day), can be permanent, "shooting" or "suddenly punishing".
The pains are not associated with walking or other physical activity, however, occur during slopes and turns of the housing, in the position lying, with a long-term location of the body in an uncomfortable position, with deep breathing at the height of the breath.
Pains do not change after taking nitroglycerin.
Pains are enhanced with palpation of sternum and / or chest in the course of intercostal intervals.
The peculiarity of the pain in the chest with a vasospadic angina is that the pain attack is usually very strong, localized in a "typical" place - in the field of sternum. However, often such attacks happen at night and early in the morning, as well as when exposed to cold on open areas of the body.
The peculiarity of pain in the chest during microvascular angina is that angiosky pain, according to high-quality signs and localization of the corresponding angina, but arising after a while after exercise, and poorly bubbling nitrates may be a sign of microvascular angina.
When the stainless angina syndrome syndrome is identified, it is recommended to determine its functional class, depending on the portable physical exertion.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comments.There are 4 functional class (FC) of angina in the classification of the Canadian cardiology society (Table 1).
Table 1.Functional classes of angina.
| Functional class I. | Functional class II. | Functional class III | Functional class IV. |
| "Latent" angina. Attacks occur only with extreme voltage | Stenicard attacks occur at ordinary load: fast walking, lifting uphill, on the stairs (1-2 spans), after abundant food, strong stress | Stencardia attacks abruptly limit physical activity: occur with a slight load: walking in an average pace< 500 м, при подъеме по лестнице на 1-2 пролета. Изредка приступы возникают в покое | Inability to perform any, even minimal load due to angina disease. Attacks arise alone. Anamnesis is often a myocardial infarction, heart failure |
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to clarify the fact of tobacocuriasis at present or in the past.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask about cases of CVD for the nearest relatives of the patient (father, mother, siblings and sisters).
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask about cases of death from the CVD of the nearest relatives of the patient (father, mother, native brothers and sisters).
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask about previous cases of medical assistance and the results of such appeals.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to clarify the presence of previously recorded electrocardiograms in the patient, the results of other instrumental research and conclusions on these studies.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask the patient about the concomitant diseases known to it.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask the patient about all currently accepted drugs.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the collection of anamnesis, it is recommended to ask the patient about all the preparations that the reception of which was previously discontinued due to intolerance or inefficiency. The permissions level of recommendations IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C).
2,2 physical examination.
At the diagnostic stage, all patients recommended a physical examination.The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comments.Typically, a physical examination with an uncomplicated stable IBA has small specificity. Sometimes, with a physical examination, it is possible to identify signs of FR: excess body weight and, signs of diabetes (SD) (mass, dryness and leather flabbiness, reducing skin sensitivity). Signs of atherosclerosis of cardiac valves, aortic, trunk and peripheral arteries are very important: noise over the projections of the heart, abdominal aorta, sleepy, renal and femoral arteries, intelligible chromotype, cooling stop, weakening the pulsation of arteries and atrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities. Significant FR IHD, detected in physical examination - arterial hypertension (AG). In addition, you should pay attention to the external symptoms of anemia. In patients with family forms of hypercholesterolemia (HCC), when inspection, you can identify xanthomas at brushes, elbows, buttocks, knees and tendons, as well as xantellasm on centuries. The diagnostic value of the physical examination increases when the symptoms of the complications of the IBS are present - primarily signs of CH: shortness of breath, wheezes in the lungs, cardiomegaly, heart arrhythmia, swelling of the cervical veins, hepatomegaly, swelling of the legs. The identification of signs of CH in physical examination usually makes it impossible to assume post-infarction cardiosclerosis and a very high risk of complications, and therefore dictates the need for an urgent complex treatment, including with possible to revascular myocardium.
During a physical examination, it is recommended to carry out a general inspection, explore the skin of the face, torso and limbs.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
During the physical examination, it is recommended to measure the growth (M) and weight (kg) and determine the body mass index.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comments.The body mass index is calculated by the formula - "Weight (kg) / height (M) 2".
During the physical examination, it is recommended to draw auscultation of the heart and lungs, palpation of the pulse on the radial arteries and the arteries of the back of the stop, measure the hell in short in the patient's position lying, sitting and standing, to count the heart rate and pulse rate, draw auscultage of the projections of sleepy arteries, abdominal Aorts, iliac artery, carry out the palpation of the abdomen, parastinal points and intercostal intervals.
The level of persuasive recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
2.3 laboratory diagnostics.
Only a few laboratory tests have an independent prognostic value with a stable IBS. The most important parameter is the lipid spectrum of blood. The remaining laboratory tests of blood and urine make it possible to identify concomitant diseases and syndromes (thyroid dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, heart failure, anemia, eritremium, thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia), which worsen the IBS forecast and require accounting in the selection of drug therapy and with the possible direction of the patient to the operational treatment.All patients are encouraged to carry out a general analysis of blood with measuring hemoglobin levels, red blood cells and leukocytes.
In the presence of clinical bases, screening for the detection of type 2 SD 2 is recommended to begin with measuring the level of glycosylated hemoglobin of blood and blood glucose level on an empty stomach. If the results are unconvincing, it is recommended to carry out an oral test of glucose tolerance.
All patients are encouraged to study the level of creatinine blood with an assessment of the kidney function of creatinine clearance.
Level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (level of reliability of evidence B).
All patients are encouraged to study the lipid spectrum of blood on an empty stomach, including estimating the level of cholesterol of low density lipoproteins (HCLNP).
Comments.Dyslipoprotehemia is a violation of the ratio of the main classes of lipids in the plasma - the presenter of the atherosclerosis FR. Low density lipoproteins and very low density are considered protategenic, while high density lipoproteins are an anti-merogenous factor. With a very high content of HCLNP in Blood, IBS develops even in young people. Low high density lipoprotein cholesterol is an unfavorable prognostic factor. The high level of blood triglycerides is considered a significant predictor of the CSO.
In the presence of clinical grounds, it is recommended to screen the function of the thyroid gland to identify the thyroid diseases.
In patients with suspicion of heart failure, it is recommended to study the level of the N-terminal fragment of the brain sodium-eptic peptide of blood.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C);
When clinical instability of the state or at suspected OCS to exclude myocardial necrosis, it is recommended to re-measure the levels of blood troponin highly or ultra-high-sensitive method.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence A);
In patients who complained about the symptoms of myopathy against the background of the admission of statins, it is recommended to explore the activity of creating blood creatineinase.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C);
With repeated studies, all patients with a diagnosis of stable IHD it is recommended to conduct annual lipid spectrum control, creatinine and glucose metabolism.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
2.4 instrumental diagnostics.
Electrocardiographic study.All patients with suspicion of IBA when accessing a doctor is recommended to perform electrocardiography (ECG) alone and decrypt an electrocardiogram.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C);
To all patients during or immediately after the attack of the chest pain, allowing to suspect an unstable CHD current, it is recommended to record the ECG alone.
In suspected vasospadic angina, the ECG record is recommended during an attack of the chest pain.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C);
Comments.With an uncomplicated stable IBS outside the load, specific ECG signs of myocardial ischemia are usually absent. The only specific sign of the IBS on the EKGO EKGO is large-scapy myocardial changes after those transferred to them. Insulated changes of the teeth of T, as a rule, low-specific and require comparison with the clinic of the disease and data of other studies. Registration of ECG during a painful attack in the chest is much greater value. If there are no changes in the ECG pain, the probability of CDS in such patients is low, although it is not completely excluded. The emergence of any ECG changes during a pain attachment or immediately after it significantly increases the likelihood of IHS. Ischemic ECG changes immediately in several leads are an unfavorable prognostic sign. In patients with initially modified ECG due to post-infarction cardiosclerosis, the ECG dynamics during an attack even a typical angina may be absent, being a little specific, or false (reduction of amplitude and reversion of the initial negative teeth). It should be remembered that on the background of intraventricular blockade, the registration of ECG during a pain attack is also non-informative. In such cases, the doctor decides on the nature of the attack and tactics of treatment for related clinical symptoms.
Echocardiographical research.
The transstoracal echocardiogram (ECCG) is recommended to all patients with suspicion of a stable IBS and at a previously proven stable IHD.
Level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (level of reliability of evidence B).
Comments.The main goal of EchoCG alone is the differential diagnosis of angina with non-corona patient in the breast at the vices of the aortic valve, pericarditis, the aneurysms of the ascending aorta, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a mitral valve prolapse and other diseases. In addition, EchoCG is a basic way to identify and stratify hypertrophy of myocardium, local and general left ventricular dysfunction.
Transstoracal echocardiogram (ECCG) alone is carried out for:
The exceptions of other causes of the pain in the chest;
detecting local disorders of the mobility of the walls of the left ventricle of the heart;
measurements of the left ventricular emission fraction (FVL) and subsequent stratification of the risk of CSO;
estimates of the diastolic function of the left ventricle.
Ultrasonic study of sleepy arteries.
Ultrasound examination of the carotid arteries with a stable IHD is recommended to be carried out to detect atherosclerosis of carotid arteries as an additional FR CSO.
Comments.The identification of multiple hemodynamically significant stenosis in carotid arteries causes the risk of SSO to high, even with moderate clinical symptoms.
X-ray study with stable IBS.
At the diagnosis stage, the chest radiography is recommended to be carried out to patients with atypical symptoms of IBS or to eliminate the disease of the lungs.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
At the diagnostic stage, under the subsequent observation of the chest radiography, it is recommended to carry out at SN.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comment.Radiographic examination of the chest is the most informative in individuals with post-infarction cardiosclerosis, cardiac disorders, pericarditis and other reasons of concomitant CH, as well as if the aneurysm of the ascending part of the aorta arc is suspected. In such patients on radiographs, it is possible to estimate the increase in the departments of the heart and arc of the aorta, the presence and severity of abnormal hemodynamics (venous stagnation, pulmonary arterial hypertension). With atypical pain in the chest, X-ray studies are useful for identifying diseases of the musculoskeletal system during the differential diagnosis.
Monitoring ECG.
ECG monitoring is recommended to be carried out to patients with a proven stable IHD and suspicion of accompanying arrhythmia.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
ECG monitoring is recommended at the diagnostic phase to patients with suspected vasospadic angina.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C).
ECG monitoring is recommended at the diagnostic stage when loading samples are impossible due to concomitant diseases (diseases of the musculoskeletal system, interpretated chromotype, a tendency to a pronounced pressure increase under dynamic physical exertion, deregulation, respiratory failure).
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comment.The method allows you to determine the frequency of the occurrence and duration of pain and solemn myocardial ischemia. ECG monitoring sensitivity in the diagnosis of IBS: 44-81%, specificity: 61-85%. This diagnostic method is less informative to identify transient myocardial ischemia than tests with exercise. Prognostically unfavorable finds when monitoring ECG: 1) a large total duration of myocardial ischemia; 2) episodes of ventricular arrhythmias during myocardial ischemia; 3) myocardial ischemia at low heart rate (< 70 уд. /мин). Выявление суммарной продолжительности ишемии миокарда 60 мин в сутки служит веским основанием для направления пациента на коронароангиографию (КАГ) и последующую реваскуляризацию миокарда, поскольку говорит о тяжелом поражении КА .
Evaluation of the primary survey data and the predominant probability of IBS.
It is recommended when examining persons without previously the diagnosis of IBS, estimate the predestine probability (PTV) of this diagnosis on the basis of data obtained during the collection of history, physical and laboratory research, ECG in peace, echoCG and conducted on the testimony of chest radiological examination, ultrasound testing of the sleepy arteries and outpatient monitoring ECG.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comments.After primary research, the doctor builds a plan for further examination and treatment of the patient, based on the obtained primary data and PTV of the diagnosis of stable IBS (Table 2).
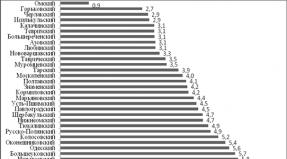
Table 2.The predominant probability of the diagnosis of stable ischemic heart disease, depending on the nature of the pain in the chest.
| Age, years | Typical angina | Atypical angina | Pain of nonorone character | |||
| men | women | men | women | men | women | |
| 30-39 | 59% | 28% | 29% | 10% | 18% | 5% |
| 40-49 | 69% | 37% | 38% | 14% | 25% | 8% |
| 50-59 | 77% | 47% | 49% | 20% | 34% | 12% |
| 60-69 | 84% | 58% | 59% | 28% | 44% | 17% |
| 70-79 | 89% | 68% | 69% | 37% | 54% | 24% |
| 80 | 93% | 76% | 78% | 47% | 65% | 32% |
Recommended in patients with PTV Diagnosis of IBS 65% Further research to confirm the diagnosis is not carried out, but to stratify the risk of CSO and the appointment of treatment.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Recommended.Patients with PTV Diagnosis IBS< 15% направить на обследование для выявления функционального заболевание сердца или некардиальных причин клинических симптомов.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Patients with intermediate PTV diagnosis of IBS (15-65%) are directed to additional non-invasive load and visualizing diagnostic studies.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Registration of ECG during samples with exercise.
Stress-ECG with physical activity is recommended as an initial method to establish a diagnosis in angina syndrome on the background of an intermediate PTV detection of IBS (15-65%) not taking anti-aishmic drugs.
Level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (level of reliability of evidence B).
Comments.Stress-ECG with exercise is not carried out in the case when the patient cannot perform physical activity, or if the initial ECG changes make it an impossible assessment.
Stress-ECG with physical activity is recommended in patients with a diagnosis of CHD and receiving treatment to assess its effect on symptoms and myocardial ischemia.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C);
Stress-ECG with physical activity is not recommended in patients receiving cardiac glycosides, as well as with the depression of ST segment per ECG at a closet of 0.1 mV.
The level of persuasive recommendations III (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comment.Typically, the stress test is a bicycle ergometry or a treadmill test. The sensitivity of the stress ECG with physical activity in the diagnosis of IBS is 40-50%, specificity of 85-90%. Sample with walking (Tredmil test) is more physiological and more often used to verify the functional class of patients with IBS. Veloergometry informatively in identifying the IBS in obscure cases, but it requires a patient, at least the initial cycling skills, is harder to be carried out by older patients and with concomitant obesity. The prevalence of exception to the atrial electrostimulation in the daily diagnosis of the IBS is lower, although this method is comparable by informativeness with cycle ergometry (VEM) and Tredmil test. The method is carried out according to the same indications, but is a means of choice if the patient is impossible to perform other load samples due to non-manual factors (diseases of the musculoskeletal system, interfering chromota, a tendency to a pronounced pressure increase under dynamic physical exertion, deregulation, respiratory failure). .
Stress methods for visualization of myocardial perfusion.
The stress methods of visualization of myocardial perfusion include:
Stress echoch with exercise.
Stress EchoCG with pharmacological load (dobutamine or vasodilator).
Stress echoch with a vasodilator.
Perfusion myocardial scintigraphy with exercise.
Stress EchoCG is one of the most sought-after and highly informative methods of non-invasive diagnosis of IBS. The method is based on the visual detection of local LV dysfunction, as equivalent to ischemia, during physical activity or pharmacological sample. Stress-echoca is superior to the usual load ECG on diagnostic value, has a greater sensitivity (80-85%) and specificity (84-86%) in the diagnosis of IBS. The method allows not only evidence to verify ischemia, but also to pre-define the symptom-bound to the localization of transient LV dysfunction. With technical capabilities.
Conducting stress-echoch with physical activity is shown to all patients with proven IBS for verification, symptom-related, as well as in questionable results of the usual load sample during the initial diagnosis.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C).
In suspected microvascular angina, it is recommended to conduct a stress echoch with exercise or dobutamine to verify the local hyokinesis of the LV wall, coming simultaneously with the angina and changes in the ECG.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C);
In suspected microvascular angina, it is recommended to conduct an ECOCH with a doppler study of the left coronary artery with measuring the diastolic coronary blood flow after B / in the administration of adenosine - to study the coronary reserve of blood flow.
The level of persuasive recommendations IIB (the level of reliability of evidence C).
Comment.Perfusion myocardial scintigraphy (single-photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography) is a sensitive and highly specific visualizing method of study with high prognostic significance. The combination of scintigraphy with physical activity or pharmacological samples (dosed in / to administration of dobutamine, dipyridamole) is much raising the value of the results obtained. The method of positron emission tomography allows you to assess the minute blood flow in a unit of myocardial mass and is particularly informative in the diagnosis of microvascular angina.
Conducting a scintigraphic study of myocardial perfusion in combination with physical activity is recommended for a stable IBC for verification, symptom-related and to assess the disease forecast.
The level of persuasive recommendations of IIA (the level of reliability of evidence C);
Conducting a scintigraphic study of myocardial perfusion in combination with a pharmacological breakdown (intravenous administration of dobutamine or dipyridamole) is recommended for stable IBS for verification, symptom-related and to estimate the disease forecast when it is impossible to perform a patient standard exercise (due to deregulation, musculoskeleting diseases apparatus and / or lower extremities, etc.).
Conducting a positron-emission tomographic study of myocardial perfusion is recommended when diagnosing microvascular angina.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations IIB (the level of reliability of evidence C);
The stress method of visualization is recommended as an initial method for the diagnosis of stable IBS under PTV 66-85% or at FVLG< 50% у лиц без типичной стенокардии .
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence B);
The stress method of visualization is recommended as an initial diagnostic method if the features of the ECG of rest prevent its interpretation during load.
Level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (level of reliability of evidence B).
The methods of visualization with exercise are recommended as preferable than methods with pharmacological load.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C);
The stress method of visualization is recommended as preferred in individuals, with the symptoms of the IBS, which previously had permissive coronary intervention (CCV) or coronary shunting (CH).
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations IIA (level of reliability of evidence B);
The stress method of visualization is recommended as preferable to estimate the functional significance of intermediate expressions of stenosis according to KAG.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations IIA (level of reliability of evidence B);
Patients with a stable IBS with a pacemaker recommended stress echoch or single-photon emission computed tomography.
The stress-method of visualization for stratification at risk of CSO is recommended in patients with non-informative results of stress-ECG with exercise.
Stratification for the risk of CSO with the help of a stress ECG or a stress method of visualization is recommended in patients with a stable IBS with a significant change in the frequency of the occurrence and severity of symptoms.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of evidence of evidence B).
With a concomitant blockade of the left leg of a beam of Gis, a stress echoca or single-photon emission computer tomography of myocardium with pharmacological load is recommended for stress-echoze at risk.
The permissions level of recommendations IIA (the level of evidence of evidence B).
Invasive studies with stable IBS.
Invasive coronarangiography (kAg) is traditionally the "gold standard" in the diagnosis of IWC and when stratifying the risk of complications.
With proven IBS, KAG is recommended for stratifying the risk of CCS in persons with severe stable angina (FC III-IV) or with clinical signs of high risk of CSO, especially when symptoms are poorly treatable.
The level of persuasiveness of recommendations I (the level of reliability of evidence C).
The manifestations of arterial hypertension are accompanied by significant negative changes in human health, therefore the diagnosis of this serious damage to the cardiac vascular system can be carried out at the early stage of development. Clinical recommendations Arterial hypertension has well-defined, since this disease tends to quickly aggravate with a multitude of negative health consequences.
Features of therapeutic effects in hypertension
Increased arterial pressure is accompanied by significant organic changes and is a real threat to human health. Pressure indicators must be constantly monitored by a cardiologist prescribed treatment with prescribed periodicity and frequency.
The main purpose of therapeutic effects in hypertension is to reduce blood pressure indicators, which becomes possible by eliminating the causes of this state and eliminate the consequences of hypertension. Since the causes of the disease can become both the hereditary factor and many external reasons that provoke a persistent increase in pressure, their definition will help to maintain the received positive result of treatment and prevent recurrences.
The main points of treatment of hypertension should be called the following:
- Elimination of parallel current organic diseases that can be provoking the factors for the development of hypertension.
- Power correction, which must contain a minimum amount of products rich in fats and cholesterol, which has the property is set aside inside the vessels and interfere with normal blood movement on them.
- Reception of medicines that will ensure the normalization of blood circulation in vessels, prevent oxygen fasting fabrics and restore the normal metabolic process in them.
- Control of the condition of the patient throughout the entire period of treatment, which will allow the necessary adjustments to the process of therapeutic effects in a timely manner.
The introduction of the required level of physical activity will speed up the processes of regeneration and the removal of slags from the body, which contributes to a more active blood movement by vessels, which makes it possible to eliminate the reasons provoking the resistant pressure lift.
The risk of aggravation of arterial hypertension consists in the high probability of the development of such dangerous and life of patient states, as ischemic heart disease, heart and renal failure, a stroke state. Therefore, to prevent the listed pathological conditions, it is necessary to pay attention to the indicators of blood pressure in a timely manner, which will avoid exacerbation in the future and maintain the patient's health, and in some cases, with the struck for the forms of diseases, and its life.

Risk factors hypertension
In hypertension, the most severe conditions occur during the following provoking factors:
- belonging to the male floor;
- age more years;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- elevated cholesterol level in blood;
- excess weight and obesity;
- metabolic disorders;
- hereditary factor.
The listed provoking factors are able to become a starting point in the development of hypertension, because if there are at least one of them, and even more so, it should be carefully referring to their own health, eliminate the situation and states that can cause exacerbation of hypertension. The beginning of treatment in the detection of an early stage of the disease allows minimizing the risks of the further development of pathology and transition to a more complex form.
Tips for the prevention and treatment of arterial hypertension, taking into account the characteristics of the patient's body, will rather eliminate the diseases of the disease, maintain the health of the cardiovascular system. Reception of any medicines should be carried out only on the appointment of a cardiologist who put a refined diagnosis on the basis of analyzes and research.

Hypertensive disease is a state in which most of the organs and their tissues do not surrelatinate the necessary volume of substances and oxygen, which causes the deterioration of their condition and the functioning of the entire body as a whole.
- accounting for the fact that arterial hypertension is currently diagnosed in an increasingly young age, which requires control of the health status of all groups of the population;
- preliminary diagnosis with a refined diagnosis, which will provide an opportunity for more effective treatment;
- application of the method of ranking drugs with initial use of monolation;
- reception prescribed by the doctor drugs to reduce blood pressure on a strict scheme;
- take into account the age indicator in the preparation of the medical circuit with AG, people over 80 should be treated according to a special scheme, taking into account their age and health status.
Emergency assistance in hypertensive crisis
Emergency assistance in hypertensive crisis have, trying to achieve as soon as possible to reduce blood pressure in the patient so that there is no severe damage to the internal organs.
Evaluate the effect of the accepted tablet after 30-40 minutes. If the blood pressure decreased by 15-25%, then it should be sharply reduced undesirable, this is enough. If with the help of the medication fails to facilitate the patient's condition, you need to call "ambulance".

Early appeal to the doctor, the challenge of ambulance with a hypertensive crisis will ensure efficient treatment and will help to avoid irreversible complications.
- The best way to recover from hypertension (quickly, easy, useful for health, without "chemical" drugs and dietary supplies)
- Hypertensive disease - a people's way to recover from her 1 and 2 stages
- Causes of hypertension and how to eliminate them. Analyzes with hypertension
- Effective treatment of hypertension without drugs
When you call the "ambulance" to cause urgent help brigade, you need to clearly formulate the dispatcher of the patient's complaints and the figures of its blood pressure. As a rule, hospitalization is not carried out if the hypertensive crisis in the patient is not complicated by the lesions of the internal organs. But be prepared and to the fact that hospitalization may be required, especially if hypertensive crisis arose for the first time.
Emergency assistance in hypertensive crisis before the emergency arrival is as follows:
- The patient should be taken in bed with a seven-time pillow. This is an important measure for the prevention of choking, difficulty breathing.
- If the patient is already treated from hypertension, he needs to take an extraordinary dose of his hypotensive drug. Remember that the drug will work most effectively if you take it sublingual, that is, to dissolve the tablet under the tongue.
- It should strive to reduce blood pressure indicators by 30 mm. RT. Art. For half an hour and by 40-60 mm. RT. Art. Within 60 minutes from the initial digits. If it was possible to achieve such a decline, then take additional doses of drugs lowering pressure should not be. It is dangerous to "knock down" blood pressure sharply to normal values, because it can lead to irreversible brain circulation disorders.
- You can take a soothing preparation, such as Corvalol, to normalize the psycho-emotional state of the patient, save it from fear, excitability, anxiety.
- A patient with a hypertonic crisis before the doctor's arrival is not at least one should not take some new drugs unusual for him. This is an unjustified risk. It is better to wait for the arrival of the brigade of emergency medical care, which will choose the most suitable drug and introduce it injectable. These same doctors, if necessary, will affect the hospitalization of the patient to the hospital or further treatment of outpatient (at home). After making a crisis, you need to consult a doctor or cardiologist to choose the best hypotensive tool for the "planned" treatment of hypertension.
Hypertensive crisis can happen by one of two reasons:
- Jumped pulse, usually above 85 beats per minute;
- Blood vessels narrowed, the bloodstream is difficult. At the same time, the pulse is not elevated.
The first option is called hypertensive crisis with high sympathetic activity. The second is the sympathetic activity is normal.
- Capoten (Captive)
- Corinthar (nifedipine)
- Cloofelin (Clonidine)
- Physiotense (Moxonidine)
- The rest of the possible medicines - about 20 drugs are described here.
We conducted a comparative study of the effectiveness of different tablets - nifedipine, captopril, clofelin and physiotension. 491 patients were involved, which appealed for emergency assistance in hypertension. In 40% of people, the pressure jumps out due to the fact that the pulse is sharply rising. The people most often take captopril to quickly bring down pressure, but to patients who have an elevated pulse, it helps badly. If the sympathetic activity is high, then the efficiency of the captitor is not more than 33-55%.
If a high pulse, it is better to take clofelin. It will work quickly and powerfully. However, Cloofelin in the pharmacy without a prescription can not sell. And when the hypertensive crisis has already happened, then the recipe goes late. Also from clofelin there are the most frequent and unpleasant side effects. An excellent alternative to him is the drug Physiotense (Moxonidine). The side effects of it rarely, and buy it in the pharmacy is easier than Cloofelin. Do not treat hypertension to clofelin daily! This is very harmful. The risk of heart attack and stroke rises. The life expectancy of hypertensive is reduced for several years. Physiotension from pressure can be taken daily only by appointing a doctor.
In the same study, doctors found that nifedipine lowers blood pressure in patients, but at the same time many of them increase the pulse. It can provoke a heart attack. Other tablets - hooks, clofelin and physiotension - pulse are not exactly increasing, but on the contrary, it is reduced. Therefore, they are safer.
Side Effects of Emergency Tablets in Hypertensive Crisper
Note. If dizziness has happened, enhancing the headache and the feeling of heat from taking physiotension or clopenign, then it is likely to pass quickly and without consequences. These are not serious side effects.

- If such sensations appeared for the first time - urgently adopt 1 tablet nitroglycerin or nitrosorbide under the tongue, 1 tablet aspirin and call "ambulance"!
- If for 5-10 minutes after taking 1 nitroglycerin tablets, the pain does not pass, re-accept the same dose. Maximum can be used sequentially not more than three nitroglycerin tablets. If after that pain, burning, pressure and discomfort behind the sternum are saved, you need to urgently cause "ambulance"!
- Complications of hypertensive crisis: angina and heart attack
- Aortic aneurysm - Complication of hypertensive crisis
- When hypertensive is needed urgent hospitalization
If you have heartbeat, "interruptions" in the work of the heart
- Consider the pulse if it is more than 100 shots per minute or he is irregular, call "ambulance"! Doctors will remove an electrocardiogram (ECG) and will take the right decision regarding further treatment tactics.
- It is impossible to make anticircraft drugs yourself, if you have not previously passed a complete examination at the cardiologist and your attending physician did not give specific instructions for the occasion of arrhythmia.
- On the contrary, if you know what arrhythmia you have, the diagnosis is set based on the results of a full-fledged examination at the cardiologist, you already accept one of the antiarrhythmic drugs or, for example, you know which the drug "takes off" arrhythmia (and if it is recommended by the doctor), then you You can use it in the dose specified by your doctor. At the same time, remember that arrhythmia often passes independently within a few minutes or several hours.
Patients with elevated arterial pressure should be known that the best prevention of a hypertensive crisis is a regular taking of a drug lowering blood pressure that prescribed your doctor. The patient does not follow without consultation with a specialist independently abruptly cancel himself a hypotensive drug, reduce its dosage or replace to another.
- Complicated and not complicated hypertensive crisis: how to distinguish
- Stroke - complication of hypertensive crisis - and how to treat it
- How to treat hypertensive crisis in pregnant women, after a surgical operation, with strong burns and when canceled Clofelin
Stenzard: stresses and rest, stable and unstable - signs, treatment
One of the most common clinical manifestations IHS (ischemic heart disease) is angina. It is also called "breast toad", although this definition of the disease has been very rarely determined.
Symptoms
The name is associated with signs of the disease that manifest themselves in a sense of pressure or compression (narrow - Stenos from Greek.), Feeling of burning in the heart (KardiA), for the sternum, passing into pain.
In most cases, pain occurs suddenly. In some people, the symptoms of angina are pronounced in stressful situations, others - during overvoltage when performing severe physical work or sports exercises. Third attacks are forced to wake up among the nights. Most often, it is associated with a stuffing indoor or too low ambient air temperature, increased arterial pressure. In some cases, the attack occurs during overeating (especially for the night).
The duration of pain - no more than 15 minutes. But they can give in the forearm, under the blades, neck and even the jaw. Often, the attack of the angina disease is manifested by unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region, for example, the severity in the stomach, gastric colic, nausea, heartburn. In most cases, painful sensations pass, as soon as a person is racing emotional excitement, if during walking it will stop, take a break in work. But sometimes to stop the attack requires the reception of a group of nitrates with a short action (nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue).
There are many cases when the symptoms of the attack of angina are manifested only in the form of discomfort in the area of \u200b\u200bthe stomach or headaches. In this case, the diagnosis of the disease causes certain difficulties. It is also necessary to distinguish pain attacks of angina from symptoms of myocardial infarction. They are short-term, and easily removed with nitroglycerin or nidefiline. While the pain in the heart attack does not stop with this drug. In addition, during angina, there is no stagnation in the lungs and shortness of breath, the body temperature remains normal, the patient does not feel excited during the attack.
Often this disease is accompanied by cardiac arrhythmia. External signs of angina and heart arrhythmia are manifested in the following:
- The pallor of the skin of the face (in atypical cases, redness is observed);
- On the forehead droplets of cold sweat;
- On the face - the expression of suffering;
- Hand brushes are cold, with loss of sensitivity in the fingers;
- Breath - superficial, rare;
- The pulse at the beginning of the attack - frequency, by the end its frequency is reduced.
Etiology (causes)
The most common causes of the occurrence of this disease are atherosclerosis of coronary vessels and hypertension. It is believed that the appearance of angina is caused by a decrease in the supply of coronary vessels and the heart muscle, which occurs when the influx of blood to the heart does not correspond to its needs. This causes myocardium ischemia, which, in turn, contributes to the violation of the oxidation processes occurring in it and the emergence of the oversupply of metabolic products. Often the heart muscle requires an increased amount of oxygen with pronounced left ventricular hypertrophy. The reason for this is the diseases such as dilatation or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic regurgitation, stenosis of aortic valve.

Very rarely (but such cases were noted), the angina of the heart occurs against the background of infectious and allergic diseases.
Course of the disease and forecast
For this disease, a chronic course is characterized. The attacks can be repeated when hard work is performed. Often they arise when a person is just starting to move (walking), especially in cold and wet weather, in stuffy summer days. Executed by attacks of angina emotional, mentally unbalanced people exposed to frequent stress. Cases were noted when the first attack of the angina resulted in a deadly outcome. In general, with a properly chosen treatment method, compliance with the recommendations of the physicians, the forecast is favorable.
Treatment
To eliminate angina attacks, used:
- Conservative treatments, including drug (drug) and non-drug therapy;
- Surgery.
Treatment of angina drugs is carried out by a cardiologist. It includes the following:
| 1 | ACF and F-Channel Inhibitors, B-Blockers | Holding blood pressure is normal, reduction of heart abbreviations and oxygen consumption by myocardium, increasing the degree of tolerance of physical exertion |
| 2 | Hydolipidemic drugs: polyunsaturated fatty acids omega-3, fibrates, statics | Slowing and stabilization of the formation of atherosclerotic plaques |
| 3 | Antiagregants (antithromboids) | Prevent thrombosis in coronary vessels |
| 4 | Calcium antagonists | Prevention of coronary spasms with vasospadic angina |
| 5 | Nitrates with a short action (nitroglycerin, etc.) | Saving an attack |
| 6 | Nitrates of prolonged action | Appointed as a prophylactic agent before the increased and long load or possible surge of emotions |
Non-drug treatments include:
- The use of diets aimed at reducing cholesterol in the blood;
- Bringing body weight in accordance with its growth index;
- Development of individual loads;
- Treatment with non-traditional medicine;
- Elimination of bad habits: tobacco and alcohol, etc.
Surgical treatment includes atherotomy, rotoring, coronary angioplasty, in particular - with stenting, as well as a complex operation - an aortocortonary shunting. The treatment technique is selected depending on the type of angina and severity of the disease.
Classification of angina
The following classification of the disease was adopted:
- Due to the occurrence:
- The walls of the voltage arising from the influence of physical exertion;
- Angina of rest, the attacks of which overtake the patient during night sleep, and during the day when it is in the lying position, without obvious to that.
- According to the nature of the course: as a separate type is highlighted by angina printela.
- Stable. The attacks of the disease appear with a certain, predictable frequency (for example, in a day or two, several times a month, etc.). It is divided into functional classes (FC) with I by IV.
- Unstable. For the first time arising (Air Force), progressive (PS), postoperative (early pre-infarction), spontaneous (variant, vasospast).
Each type and subspecies have its own characteristic features and features of the course of the disease. Consider each of them.
Stable angina stress
The Academy of Medical Sciences conducted studies, which types of physical work can perform people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, without experiencing discomfort and seizures in the form of gravity and pain in the chest. At the same time, the stable angina stress was divided into functional classes, which are allocated four.
I functional class
It is called the latent (hidiment) angina. It is characterized by the fact that the patient can perform almost all types of work. It is easily overcoming long distances on foot, easily rises the stairs. But only if all this is done measured and within a certain time. When accelerating the movement, or increase the duration and pace of work, an attack of angina disease occurs. Most often, such attacks appear with extreme loads for a healthy person, for example, when renewing sports, after a long break, the performance of the unbearable physical exertion, etc.
Most people suffering from the walls of this FC consider themselves healthy people, and do not resort to medical care. Nevertheless, coronary angiography shows that they have lesions of individual vessels of the average degree. Conducting a cyergometric sample, also gives a positive result.
II functional class
People exposed to the angina of this functional class often experience attacks at certain hours, for example, in the morning after awakening and a sharp rise from bed. In some, they manifest themselves, after overcoming the stairs of a certain floor, others - during movement in bad weather. Reduce the number of attacks, promotes the right organization of labor and the distribution of physical exertion. The fulfillment of them at an optimal time.

III functional class
The walls of the voltage of this type, inherent in people with strong psycho-emotional excitation, in which attacks appear when moving at normal pace. And overcoming the stairs to its floor for them turns into a real test. These people are often subjected to rest angina. They are the most frequent patients of hospitals, diagnosed with IHD.
IV functional class
In patients with angina, this functional class, any type of physical activity, even insignificant, causes an attack. Some are not capable of moving around the apartment, without painful feelings in the chest. Among them are the largest percentage of patients who have pains at rest.
Unstable angina
Angina, the number of seizures of which can increase, then decrease; Their intensity and duration is also changing, called unstable or progressive. Unstable angina (NA) differs according to the following features:
- Character and severity of occurrence:
- Class I. Initial stage of chronic angina. The first signs of the occurrence of the disease are noted shortly before applying to the doctor. At the same time, the aggravation of IBS is less than two months.
- Class II. Subighteous flow. Pain syndromes were noted throughout the prior visit to the doctor's doctor. But over the past two days were absent.
- Class III. The course is acute. Stenicard attacks were noted at rest over the past two days.
- The conditions of emergence:
- Group A. Unstable, secondary angina. The cause of its development is the factors provoking IBS (hypotension, tachyrhythmia, uncontrolled hypertension, infectious diseases, accompanied by a feverish condition, anemia, etc.)
- Group V. Unstabilic, primary angina. Developed in the absence of factors that enhance the course of the CHD.
- Group S. Early post-infarction angina. Arises in the coming weeks, after a stipulated acute myocardial infarction.
- Against the background of the therapeutic treatment:
- Developed with a minimum of therapeutic procedures (or not conducted).
- With a medical course conducted.
- Development continues when conducting intensive treatment.
Road angina
Patients, diagnosed with angina stable IV functional class, almost always complain about the appearance of pain at night, as well as early in the morning, when they just woke up and are in bed. The examination of the cardiological and hemodynamic processes of such patients, through continuous daily monitoring, proves that the precursor of each attack is to increase the ad (diastolic and systolic) and the increase in heartbeat. Separate people have pressure high and in the pulmonary artery.

Powered angina is a more severe flow of stress angina. Most often, the occurrence of the attack is preceded by a psycho-emotional load, causing an increase in blood pressure.
It is much more complicated to stop them, as the elimination of the causes of their occurrence is associated with certain difficulties. Indeed, as a psycho-emotional burden, any reason is a conversation with a doctor, a family conflict, troubles at work, etc.
When the attack of this type of angina occurs for the first time, many people feel a feeling of panic fear. They are afraid to move. After the pain passes, a person is experiencing excessive fatigue. Drops of cold sweat appear on his forehead. The frequency of the occurrences of the attacks is all different. They can only manifest themselves in critical situations. Other attacks attend more than 50 times per day.
One of the types of stenocardia rest is vasospadic angina. The main reason for the appearance of attacks is the spasm of coronary vessels, which occurs suddenly. Sometimes this happens even in the absence of atherosclerotic plaques.
For many, the elderly is characterized by spontaneous angina, which arises in the early morning watches, at rest or when they change the position of the body. There is no visible prerequisites for attacks. In most cases, their emergence is associated with nightmares, subconsciously fear of death. Such an attack can last a little longer than other types. Often it does not stop nitroglycerin. All this is angina, the signs of which are very similar to the symptoms of myocardial infarction. If you make a cardiogram, it will be seen that myocardium is in the stage of dystrophy, but at the same time clear signs of heart attack and the activity of enzymes indicating it is absent.
Stenria Prinzmetala
Ashhemal heart disease is a special, atypical and very rare type of coronary heart disease. It received such a name in honor of the American Cardiologist, who first discovered her. The peculiarity of this type of illness is the cyclicality of the occurrences of the attacks that follow one after another at a certain time interval. Usually they constitute a series of attacks (from two to five), which always arise at the same time - in the early morning. Their duration can be from 15 to 45 minutes. Often, this type of angina is accompanied by pronounced arrhythmia.
It is believed that this kind of angina is a disease of young people (up to 40 years). It rarely becomes the cause of a heart attack, but can contribute to the development of violations of heart rhythm dangerous to human life, for example, tachycardia of ventricles.
Character pain under angina

Most people, patients with angina complaints about pain. Some characterize it, as a gone or cutting, other it is felt like a compressive throat or burning heart. But many patients who cannot accurately convey the character of pain, as it irradiates in various parts of the body. The fact that this angina often testifies the characteristic gesture - a compressed fist (one or both palms) attached to the chest.
Pains during angina are usually followed by one after another, gradually amplifying and increasing. Having achieved a certain intensity, they almost immediately disappear. For the walls of the voltage, the occurrence of pain is at the time of load. The pain in the chest, appearing at the end of the working day, after the completion of physical work, has nothing to do with ischemic heart disease. It is not necessary to exercise anxiety and in case the pain lasts only a few seconds, and disappears with a deep breath or change.
Video: Lecture about angina and IBS in St. Petersburg State University
At-risk groups
There are features that can provoke the occurrence of various types of angina. They are called groups (factors) risk. Distinguish the following risk groups:
- Unmodified - the factors for which a person cannot affect (eliminate). These include:
- Heredity (genetic predisposition). If someone in the family in the male line died under the age of 55 years of heart disease, the son is included in the risk group of angina. On the female line, the risk of a disease arises if death came off from heart ailments to 65 years.
- Racial affiliation. It was noted that residents of the European continent, in particular the northern countries, angina region is significantly more often noted than residents of southern countries. And the lowest percentage of the disease is the representatives of the Negroid race.
- Sexuality and age. At the age of 55, angina region develops more often in men than women. This is due to the high formulation of estrogen (female sex hormones) during this period. They are a reliable protection of the heart from various diseases. However, during the period of menopause, the picture is changing and the risk of angina in representatives and the other sex becomes equal.
- Modified - a risk group in which a person may affect the causes of the development of the disease. It includes the following factors:
- Excess weight (obesity). During weight loss, the level of cholesterol in the blood decreases, the blood pressure decreases, which consistently reduces the risk of angina.
- Diabetes. Supporting blood sugar levels close to normal values, you can control the frequency of seizures of the IBS.
- Emotional loads. You can try to avoid many stressful situations, and therefore reduce the number of seasons of angina.
- Elevated blood pressure (hypertension).
- Low physical activity (hypodymna).
- Harmful habits, in particular smoking.
Emergency assistance in angina
People who have been diagnosed with progressive angina (and other species) are included in the risk group for the probability of sudden death and the occurrence of myocardial infarction. Therefore, it is important to know how to quickly cope with the main symptoms of the disease independently, and when the intervention of medical professionals is required.
In most cases, this disease is manifested by a sharp pain in the chest pain. This is due to the fact that myocardium is experiencing oxygen fasting due to a reduced supply to its blood during the load. First aid during the attack should be directed to the restoration of blood flow.
Therefore, each patient angina must have a high-speed drug to expand vessels, for example, nitroglycerin. At the same time, doctors recommend taking it shortly before the presumptive start of the attack. This is especially true if an emotional surge is predicted or difficult work is to be performed.

If you notice on the street of a walking person, who suddenly froze, badly turned pale and involuntarily concerns the chest with a palm or a compressed fist, this means that he was overtaking the attack of coronary heart disease and requires urgent assistance during angina.
In order to render it, you need to do the following:
- If possible, to take a person (if there is no bench nearby, then right to the ground).
- Open him chest, unbuttoning a button.
- Looking for a saving tablet Nitroglycerin (Walocordin or Validol) and put it under his tongue.
- Take time if within one or two minutes it won't be better, then you need to call an ambulance. At the same time, before the arrival of the physicians, it is advisable to stay next to him, trying to involve him in a conversation on distracted topics.
- After the arrival of the doctors, try to clearly explain to doctors a picture of what is happening from the moment of the occurrence of an attack.
Today, fast-acting nitrates are produced in various forms that act instantly and much more efficiently than tableted. These are aerosols called Nitro Mac, Isotke, Nitrosprey.
The method of their application is as follows:
- Shake the can
- Spraying device to send a patient to the oral cavity,
- Make him to delay your breath, make the injection of one dose of aerosol, trying to get under the tongue.
In some cases, it may be necessary to injected the medicine again.
Similar assistance should be provided to the patient and at home. It will remove a sharp attack and maybe it will be a saving, without allowing myocardial infarction to develop.
Diagnostics
After providing the first necessary assistance, the patient must necessarily seem to the doctor, which clarifies the diagnosis and selects optimal treatment. For this, a diagnostic examination is conducted as follows:
- The history of the disease is drawn up by the patient's words. Based on the patient's complaints, the doctor establishes the preliminary causes of the disease. After checking the blood pressure and pulse, measurement of heart rate, the patient is sent to laboratory diagnostics.
- In the laboratory, blood tests are investigated. Analysis is important for the presence of cholesterol plaques, which are prerequisites for the occurrence of atherosclerosis.
- Tool diagnostics are carried out:
- Holter monitoring, during which the patient has a portable recorder for a day, leading an ECG record and transmitting all the information received to the computer. Due to this, all violations are detected in the work of the heart.
- Load tests to study the heart reaction on various types of loads. They define the classes of stable angina. Testing is carried out on Treadmill (treadmill) or cyergometer.
- To clarify the diagnosis with pains that are not fundamental factors for angina, but also inherent in other diseases, computer multispiral tomography is performed.
- Choosing the optimal treatment method (between conservative and operational), a doctor can send a patient to coronary angiography.
- If necessary, to determine the severity of the damage to heart vessels, ECCG (endovascular echocardiography) is carried out.
Video: Diagnosis of elusive angina
Drugs for the treatment of angina
Medicinal preparations are necessary to reduce the frequency of attacks, reduce their duration and prevention of the development of myocardial infarction. They are recommended to take to all who suffer in any kind of angina. The exception is the presence of contraindications to the admission of a drug. Picks up a medicine for each particular patient Cardiologist.

Video: Opinion of a specialist about the treatment of angina with a clinical dissemination analysis
Alternative medicine in the treatment of angina
Today, many are trying to treat various diseases by the methods of alternative medicine. Some are fond of them, sometimes reaching fanaticism. However, it is necessary to pay tribute that many funds of traditional medicine helps to cope with the attacks of angina, without side effects inherent in some drugs. If the treatment with folk remedies is carried out in a complex with medication therapy, then you can significantly reduce the number of encouraging attacks. Many medicinal plants have a soothing and vasodilatory action. And you can use them instead of ordinary tea.
One of the most effective tools that strengthen the heart muscle and reduce the risk of heart disease and vessels is the mixture, which includes lemons (6 pcs.), Garlic (head) and honey (1kg). Lemons and garlic are crushed and poured with honey. The mixture is insteaded for two weeks in a dark place. Take a teaspoon in the morning (on an empty stomach) and in the evening (before bed).
You can read more about this and other methods of cleansing and strengthening vessels here.
No smaller wellness effect gives respiratory gymnastics by the method of Buteyko. She teaches to breathe correctly. Many patients who mastered the technique of performing breathing exercises, got rid of blood pressure jumps, and learned to tame the attacks of angina, returning themselves to live normally, to play sports and physical labor.
Painting angina
Everyone knows that the best treatment of the disease is its prevention. To be always in good shape, and not grab the heart at the slightest increase in the load, it is necessary:
- Keep track of your weight, growing preventing obesity;
- Forever to forget about smoking and other bad habits;
- In time to treat concomitant diseases that can be a prerequisite for the development of angina;
- With a genetic susceptibility to heart disease, more time to strengthen the heart muscle and increase the elasticity of vessels, visiting the Cabinet of Medical Physical Culture and strictly following all the advice of the attending physician;
- To lead an active lifestyle, because hypodymna is one of the risk factors in the development of angina and other heart disease and vessels.

Today, in almost all clinics there are hospitals of therapeutic physical education, the purpose of which is the prevention of various diseases and rehabilitation after complex treatment. They are equipped with special simulators and devices controlling the work of the heart and other systems. A doctor who is engaged in classroom in this office selects a set of exercises and a load that is suitable for a particular patient, taking into account the severity of the disease and other features. Visiting it can noticeably improve the state of his health.
Video: angina - how to protect your heart?
Ischemic heart disease is a common cardiovascular pathology resulting from a violation of the blood supply to myocardium.
Ischemic heart disease is most common in Russia among all cardiovascular diseases.
In 28% of cases, it is the reason for the appeal of adults in medical institutions.
At the same time, only half of patients with IHD knows about the presence of this pathology and is treated, in all other cases, ischemia remains unrecognized, and its first manifestation is a sharp coronary syndrome or myocardial infarction.
↯ More articles in the magazine
 Diagnoses on the ICD-10
Diagnoses on the ICD-10
- I20.1 angina with documented spasm
- I20.8 Other walls of angina
- I20.9 angina angina
- I25 chronic ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease is the defeat of the heart muscle associated with the impaired blood flow by coronary arteries.
This violation, in turn, is organic (irreversible) and functional (transient).
In the first case, the main cause of the IBS is stenping atherosclerosis. The factors of the functional damage to the coronary arteries are spasms, the transit platelet aggregation, as well as intravascular thrombosis.
The concept of "ischemic heart disease" includes both sharp transient (unstable) and chronic (stable) states.
Most often, the main reasons for the development of IBS are the stable anatomical atherosclerotic and / or functional stenosis of epicardial vessels and / or microvascular dysfunction.
The main risk factors of ischemic heart disease:
- High blood cholesterol.
- Diabetes.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Tobacco
- Excessive body weight, obesity.
✔ Distribution of patients with IBS according to the degree of risk based on non-invasive diagnostic methods, download a table in the Consilium system.
Download Table
In addition, the risk factors for which cannot be influenced are:
- belonging to the male floor;
- age;
- burdened heredity.
In addition, there are social risk factors that increase the frequency of the ESS of the population of developing countries:
- urbanization;
- industrialization;
- economic backwardness of the population.
Human ischemia is developing when the need for the heart muscle in oxygen exceeds the possibility of its delivery with blood by coronary arteries.
The mechanisms of development of the IBS are:
- reduction of the coronary reserve (ability to increase coronary blood flow while increasing myocardial metabolic needs);
- primary reduction of coronary blood flow.
The need for the heart muscle in oxygen is determined by three factors:
- Voltage of the walls of the left ventricle.
- Myocardial reduction.
The higher the value of each of these indicators, the higher the need of myocardium in oxygen.
The magnitude of the coronary blood flow depends on:
- resistance of coronary arteries;
- heart rate frequencies;
- perfusion pressure (so called the difference between diastolic pressure in the aorta and they are also in the left ventricle).
Angina
Angina - the most common form of heart ischemia. Its frequency increases with age in both men and women. The annual mortality from the IBS is about 1.2-2.4%, and from fatal cardiovascular complications every year dies with 0.6-1.4% of patients, while the percentage of myocardial infarction infarction - 0.6-2, 7 per year.
However, in subpoments with various additional risk factors, these values \u200b\u200bmay be different.
Patients with diagnosed stable angina dying die from ischemia 2 times more often than patients without this diagnosis. There are no epidemiological data on microvascular and vasospadic angina.
Revascularization of the heart muscle in order to relocate angina attacks, reducing its functional class and improving the quality of life is recommended to all patients with angina in the presence of a coronary stenosis\u003e 50 percent with documented myocardium ischemia or a fractional reserve of blood flow (FRK) ≤ 0.80 in a complex with angina: and / or its equivalents) refractory to drug therapy.
It must be said that for the stenosis of the coronary arteries less than 90%, additional tests are needed to prove their hemodynamic significance (documented myocardial ischemia, including according to the data of the load samples with the myocardial visualization or the definition of the FRK).
Myocardial revascularization to improve the forecast of the main pathology is shown in all patients with an extensive zone of ischemia (\u003e 10% in the left ventricle), as well as to all patients with a single preserved artery with stenosis\u003e 50 percent.
Operation on coronary artery improves the prognosis of patients with an extensive zone of ischemia.
About the big zone of the defeat of the heart muscle can be judged by the presence of a hemodynamically important lesion of a large coronary artery:
- left coronary artery trunk;
- proximal department of anterior downward artery;
- two- or three-sided lesions with a decrease in the function of the left ventricle;
- the only preserved coronary vessel.
When choosing a method, it is necessary to consider such factors as:
- Anatomical features of the defeat of the coronary arteries.
- Related diseases and possible risks.
- The consent of the patient to the specific method of surgical treatment.
In the event that it is possible to carry and Aosh, and PCV with stenting, and the patient agrees to any type of intervention, the choice of technique is determined anatomical features The defeat of the coronary direction.
Ischemic heart disease: treatment
Based on conservative treatment Stable Heart Ischemia is the elimination of risk factors that can be affected, as well as complex drug treatment. The patient must be informed about all risks and about the treatment strategy.
When collecting an anamnesis and examination, you must pay attention to the accompanying pathologies, especially if we are talking about arterial hypertension, sugar diabetes and hypercholyterene.
Elimination of risk factors - a complex and vaguely long task. The most important role is played by informing and patient training, since only aware and trained patient will clearly follow medical recommendations and will be able to further make important decisions depending on the symptoms.
- discuss with the patient perspective as medical treatmentand surgical intervention;
- stipulate the need and frequency of passing instrumental and laboratory research;
- to talk about the most common symptoms of unstable angina, Oim, emphasize the importance of the speedy treatment of specialists in their occurrence;
- give clear recommendations for the maintenance of a call, emphasize the importance of treating related diseases.
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating clinical manifestations of IBS, as well as to prevent complications from the heart and blood vessels. It is recommended to prescribe a patient at least one drug to eliminate the symptoms of angina in a complex with preventive preparations.