Hypogenesis of the corpus callosum what is it. Corpus callosum: functions and disorders What does the corpus callosum of the brain respond to?
The brain is responsible for all processes in the body. He constantly receives information in the form nerve impulses, processes it and sends it to the cells. This organ has a special structure and is divided into several sections: the medulla oblongata, cerebellum, pons, cerebral hemispheres, diencephalon, hind and midbrain, corpus callosum, pituitary gland and hypothalamus. These are not all parts of the brain.
Physiologically, the cerebral hemispheres must be connected. This is facilitated by 3 adhesions. The largest of them is the large commissure of the brain or the corpus callosum.
The greater commissure is one of the structures of the brain, which consists of more than 250 million processes of nerve cells. The main and, one might say, the only function of the large commissure is to connect the two hemispheres to each other.
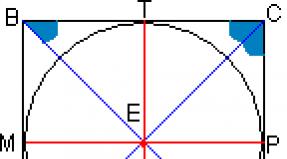
The corpus callosum of the brain has an elongated anteriorly elongated shape and reaches 6–9 cm in longitudinal section, and from 2 to 4 cm in cross section. It is located in the longitudinal slit of the large brain. This organ is divided into several sections:
- The body or trunk is an elongated part located in the middle.
- Roller - thickening of the back.
- The knee is an arcuate, curved portion at the front.
- The beak is the slender edge of the knee.
- A thin rostral plate is a layer of nerve cells that passes into the beak.
- The end plate is the extreme part of the rostral plate.
Just like the cerebral hemispheres, the corpus callosum of the brain is covered with a thin layer of gray matter. It forms 2 small grooves symmetrically. If we consider the brain in a median longitudinal section, a radiant divergence of whitish fibers in the hemispheres is noted. It is worth noting that on the medial (inner) surface of the hemispheres, just above the upper edge of the corpus callosum, there is a groove of the corpus callosum, which, continuing in front and downward, enters the deep groove of the hippocampus with its posterior end. The lower part of the greater commissure of the brain is close to the trunk.
Functions
The significance of the corpus callosum has long remained a mystery to scientists, and only in the middle of the twentieth century, in the course of experiments on animals, a little clarity was made about its structure and functions. Later, in his research on epilepsy, Dr. Sperry found that after surgery to separate the nerve fibers located between the hemispheres, epileptic seizures stop. However, in the course of research, his team came to the conclusion that such an operation changes the personality characteristics of the individual and his basic skills.
Vivid examples: patients recognized objects by touch, but could not pronounce their names aloud, or being absolutely right-handed after surgery were not able to draw elementary figures with this hand. It can be argued that this very experiment was the starting point in the study of the functions of the cerebral hemispheres.
The following functional features are assigned to the large commissure of the brain:
- Thanks to this structure, the collected information is transferred from one hemisphere to the cortical and subcortical structures of the other, which provides an adequate and timely response.
- When the corpus callosum is completely crossed, both hemispheres are completely isolated from each other, while consciousness is completely preserved.
V last years neuropathologists different countries drew attention to the anatomical features of the brain commissure in various people.
A group of scientists analyzed the images of magnetic resonance imaging of the middle age group of men and women without visible organic pathology of the brain. On the basis of this study, they identified 4 anatomical types of the greater commissure of the brain.
- Commissure with a raised middle part of the trunk and an angle open downward, while the outlines of the knee, trunk and ridge are rounded.
- The corpus callosum has an open upward and anteriorly angle between the knee and the anterior edge of the trunk.
- Corpus callosum with an open upward and posterior angle between the carina and the posterior edge of the trunk.
- Smooth, clear arc between the knee, trunk and corpus callosum.
According to the research results anatomical structure it is impossible to talk about the age or sex of any anatomical variant due to the small scale of the study. It is also worth noting that it is impossible to talk about the connection between the structure of the corpus callosum and anatomical features furrows of the corpus callosum.
Agenesis
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is usually attributed to genetically acquired diseases, which is characterized by the absence, reduction (truncation) or other anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the corpus callosum.
The literature describes cases of agenesis of the large commissure of the brain, when the trunk of the corpus callosum is presented in the form of single, not very wide and long isthmuses. The pillars are practically transparent. According to official data, this diagnosis is made in 1 out of 2,000 babies.
Pathology develops during a week of intrauterine development of the fetus during the formation and development of nerve fibers and their connections.
Doctors cannot explain all the features of the pathogenesis of the disease, but a hereditary factor is noted.
Symptoms characterizing the adhesion of the greater commissure of the brain:
- Microcephaly (a decrease in the size of the brain along with a decrease in the skull).
- Visual and hearing impairment.
- Cysts or tumors on a CT scan.
- Violation of sexual development (ahead of peers).
- Significant lag in the psychoemotional sphere.
- Structural disturbances spinal cord.
- Neoplasms in the digestive system.
- Lipomas are common.
- Aicardi syndrome.
The disease usually manifests itself during the first two years of a child's life.
Aicardi syndrome is a genetic disorder. There are no more than 500 known cases in the world.
The characteristic features of the pathology are:
- agenesis of the corpus callosum of the brain;
- specific lacunar changes in the fundus;
- early development of epileptoid states resistant to anticonvulsant therapy;
- facial dysmorphism;
- changes in the EEG;
- significant lag in psychomotor development, disturbances from the outside gastrointestinal tract.
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia of the large brain commissure is common. The disease is characterized by underdevelopment of nerve tissues and the corpus callosum as a whole. Such failures occur in utero. Reliably the etiology (cause) of the disease has not been clarified.
Although the disease is congenital, it can be corrected. The earlier treatment is started, the better results can be achieved. Therapy consists of regularly performing sets of exercises to develop and strengthen the connections between the two hemispheres of the brain, specially designed by neuropathologists and psychologists. In recent years, the method has been improved: information-wave brain stimulation has been added to physical exercises.
Write a comment
Would you like to move on to the next article "The hypothalamic-pituitary system and its functions"?
Copying of materials is possible only with an active link to the source.
A rare disease of the corpus callosum hypoplasia, a sentence or not?
The corpus callosum of the brain plays an important function in the body, but even such a small organ is susceptible to diseases - hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, one of the rare, but no less dangerous anomalies that affects the functioning of this organ.
What is the reason?
The corpus callosum is located exactly in the middle between the two hemispheres of the brain. Its functions were discovered relatively recently, around the 60s – 70s of the last century, and by chance. In the treatment of epileptic seizures, there was a practice of splitting a given body into two halves, as a result of which the seizures disappeared, but many side effects from such a procedure, which prompted the doctors who conducted the study to think correctly. The corpus callosum is a conductor of neurons between the two hemispheres, thanks to it, many important processes occur in our body, such as:
- physical activity;
- manifestations of feelings;
- cognitive processes.
It is impossible to say that all these processes will be limited for the patient, this is possible only in an extremely severe form of the disease, but the presence of deviations will be noticeable to the naked eye.
For example, when the corpus callosum was dissected in an adult with epileptic seizures, after a while they noticed that everything related to creativity (drawing, versification, etc.) a person could only do with his left hand, while ordinary procedures (technique food, rewriting text) only right.
What can we say about a person with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. In this case, the consequences are much more serious, but ... First things first.
The cause of this ailment is not fully known, but scientists agree that the lion's share lies in genetic abnormalities that are laid in intrauterine development, in particular, at 2-3 weeks of the embryonic period.
In addition, it is believed that the presence of hypoplasia is caused by mutations that affect brain development. Unfortunately, doctors are not able to give more accurate information.
The risk group includes mothers who:
- use alcoholic drinks during pregnancy;
- have had rubella during pregnancy, just like toxoplasmosis or severe flu;
- have been exposed to radiation;
- were subject to general intoxication of the body.
This disease belongs to the category of rare and, according to statistics, occurs in every 10 thousandth baby.
How to recognize?
Corpus callosum hypoplasia in a newborn is diagnosed, as a rule, after the first two months of life, but more often it occurs during intrauterine development.
If, before the birth of the child, the doctors overlooked the ailment, then during the first 2 years of life, the child will develop harmoniously, as befits a normal baby, and only after the specified time, parents may notice some deviations, such as:
- infantile spasms;
- convulsions;
- epileptic seizures;
- weakening of the cry;
- violation of touch, smell and vision;
- decreased communication skills;
- manifestations associated with muscle hypotension.
infantile spasms - seizures characterized by sudden flexion and extension of the arms and legs
muscle hypotension - a condition characterized by decreased muscle tone, can develop in combination with a decrease in muscle strength in the patient.
In the event that in childhood, for any reason, it was not possible to diagnose and recognize the presence of the disease, it will certainly manifest itself in adulthood, the symptoms include:
- violation of visual or auditory memory;
- hypothermia;
- problems with coordination of movement.
Hypothermia - problems with thermoregulation of the body (decrease in body temperature below 35 degrees)
How is the diagnosis carried out in a hospital setting?
As a rule, with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, a large number of concomitant diseases can develop, therefore, the presence of other (different from the above) symptoms is possible. In 80% of cases, the diagnosis of this disease occurs during intrauterine development using ultrasound diagnostics.
Nevertheless, it is possible to prescribe additional tests after birth (if during pregnancy the clinical picture was not completely clear) or after the parents turned to a specialist. The doctor conducts an initial survey and clarifies the presence of symptoms characteristic of this diagnosis, after which he usually prescribes:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- electroencephalogram of the head (EEG);
- other studies of a neurological nature.
Based on the data obtained from the results of the above studies, the doctor makes a conclusion and prescribes treatment.
Treatment features
Unfortunately, effective treatment to date, it has not yet been invented, and doctors are mostly struggling with the symptoms of the disease, so children with this diagnosis are doomed to constant treatment and supportive therapy.
The specific plan is selected by the attending physician individually for each. It all depends on the severity of the lesion of the corpus callosum and clinical picture ailment.
In 70-75% of cases, there is an unfavorable outcome. There is a high likelihood of mental retardation and the development of serious mental disorders such as schizophrenia, etc.
If your baby is diagnosed with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn, then your support and help will be important for him. Here are a few general recommendations, to provide preventive actions for the baby at home:
- Pay attention to general state baby, if he is tired or does not show interest in classes or communication, give him time to rest, he himself will make it clear when you can resume the procedure.
- Carry the child in the "airplane" position, this exercise has a strengthening effect on the body, the main thing is not to overdo it.
- Lay the baby on your chest, face to face, so that his hands are under the breast, stroke him with your hand from head to ass - this procedure will help him transfer weight from head to pelvis, you can also put him on the bed, and folded under his stomach towel roll.
- If the baby pronounces sounds, copy them and repeat after him, with the same intonation, try to maintain small pauses, this will stimulate him to repeat.
- While playing with the rattle, let the child fix his gaze on it, and slowly drive from side to side, encouraging him to follow the toy. If you lose sight of it, lightly rattle, attracting attention and continue the procedure. If the child has lost interest, do not push, give a break.
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of hypoplasia is serious and often does not come alone, you can only wish patience to parents with sick children, but you yourself should hope for the best, since 25-30% have a positive result, and perhaps you will be included in these percentages ...
Corpus callosum of the brain: functions
The corpus callosum is a dense group of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex into right and left. It connects the right and left halves, thereby providing communication between the hemispheres. This structure transfers motor (motor), sensory and cognitive information between the cerebral hemispheres.
Study history
The corpus callosum has long remained a mystery of human anatomy. Scientists could not determine in any way what function this part of the brain has. By the way, in 1981, the scientist who discovered the corpus callosum received the Nobel Prize for this. His name was Roger Sperry.
The first operations on the corpus callosum were aimed at treating epilepsy. So, breaking the connection between the hemispheres, doctors really cured many patients from epileptic seizures. But over time, scientists drew attention to the occurrence of specific side effects in such patients - behavioral reactions and abilities changed. So, as a result of experiments, it was found that after an operation that affected the corpus callosum, a person could write exclusively right hand, and draw only with the left. So the corpus callosum, the functions of which were still unknown to scientists, was no longer dissected in surgery to treat epilepsy.
Several years later, scientists discovered a link between the focus of the corpus callosum and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Corpus callosum: functions
The functions of this part of the brain are quite varied and important. The corpus callosum is the largest bundle of nerve fibers in the brain. It contains about 200 million axons and performs several important functions in the body:
- Communication between the hemispheres of the brain.
- The movement of the eyeballs.
- Maintaining a balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex.
- Tactile perception.
Localization
Spatially, this part of the brain is located under the hemispheres along the median line. From the front to the back, several different zones can be distinguished in the corpus callosum: the knee, middle part, body, rear end and cushion. The knee, bending downward, forms a beak, as well as a rostral plate. Above, the corpus callosum is covered with a thin layer of gray matter.
Another structure of this part of the brain is radiance. Cords of fan-shaped neurons stretch to the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
With agenesis, the corpus callosum of the brain is completely or partially absent. This brain anomaly can be caused by a number of various factors, including chromosomal mutations, genetic inheritance, intrauterine infections, and other causes that are not yet fully understood by scientists. Individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum may experience cognitive and communication impairments. They also have difficulty understanding spoken language and social reference.
But, given the function that the corpus callosum of the brain performs, how can people who do not have it from birth even live? How do they interact between the right and left hemispheres of the brain? Scientists have found that at rest, brain activity healthy person practically does not differ from that of a person diagnosed with agenesis of the corpus callosum. This fact indicates that the brain is being rebuilt under these conditions, and the functions of the absent corpus callosum are performed by other healthy areas. How exactly and by what structures this process is carried out, scientists have not yet figured out.
Symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum
Despite the extremely low occurrence of this diagnosis, scientists have studied its symptoms well. Some of the most common manifestations of agenesis of the corpus callosum are:
- Atrophy (complete or partial) of the auditory and (or) optic nerve.
- Cystic formations in the tissues of the brain (porencephaly).
- Connective tissue tumors - lipomas.
- The rarest disorder of intrauterine development of the fetus, schizencephaly, is a cleft brain.
- A significant decrease in the size of the brain and skull in general is microencephaly.
- Multiple pathologies of the digestive system.
- Spina bifida.
- Disorders of the structure of the retina (Ecardi syndrome).
- Early puberty.
- Retardation in psychomotor development.
These and many other disorders are in one way or another closely interrelated with the absence of the corpus callosum. As a rule, they allow a diagnosis to be made in the first 1-2 years of a child's life. The final confirmation of the diagnosis is considered to be an MRI scan of the brain.
Corpus callosum hypoplasia
Hypoplasia is a serious but fortunately rather rare diagnosis. In fact, this, like agenesis, is a violation of the intrauterine development of brain tissue. If, with agenesis, the corpus callosum of the brain is completely absent, then with gopoplasia it is underdeveloped. Of course, the treatment of this disease by means of modern medicine is impossible. Therapy provides for a set of measures that minimize deviations in the patient's development. Neuropsychologists recommend that patients regularly perform a specially designed complex physical exercise, contributing to the restoration of connections between the hemispheres, as well as information-wave therapy.
Sexual dimorphism
A number of Russian and foreign scientists believe that the difference in thinking and behavioral reactions between men and women is associated with the different structure and size of the corpus callosum. So, in the edition "Newsweek" there was an article explaining the nature of female intuition: in women, the corpus callosum is somewhat wider than in men. This fact, in the opinion of all the same scientists, also explains the fact that women, unlike men, are able to cope with several different tasks at the same time.
After a while, a group of French scientists reported that, as a percentage of the brain size in men, the corpus callosum is larger than in women, but the scientists did not draw any unambiguous conclusions. Be that as it may, all scientists agree only that the corpus callosum is one of the most important structural components that perform a number of vital functions.
MRI of the brain
on Tue 13 Sep: 16
Pathological changes in the intensity of the signal in the substance of the brain are not determined. Thinning of the corpus callosum. Intrasellar space is not changed, the height of the pituitary gland is 0.3 cm, the width is 1.3 cm, the length is 1.2 cm, the pituitary funnel is along the midline.
The left lateral, third ventricles are clearly expanded. Moderately - the right lateral and fourth ventricles. Moderately dilated subarachnoid space of the frontal-parietal regions of the cerebral hemispheres (more than the left), the rest of the cerebrospinal fluid-containing space within age norm... The craniovertebral junction is not changed. Paranasal sinuses the nose is not changed.
CONCLUSION. No focal pathology was revealed. Pronounced mixed hydrocephalus, especially on the left.
on Fri 16 Sep: 13
on Fri 16 Sep: 20
For example, one of the tests: if a child lying on the bed on his back tries to sit down, then the leg on the side of the paresis bends in the hip and knee joints, and the heel comes off the bed .. (I read it in the textbook on neurology)
on Sat 17 Sep: 53
on Sat 24 Dec: 50
on Mon 26 Dec: 04
Search for “agenesis of the corpus callosum” and “outcomes of hydrocephalus”.
on Thu 29 Dec: 01
Search for “agenesis of the corpus callosum” and “outcomes of hydrocephalus”. “Actually, I found information on this issue on the Internet. But there it is somehow terribly written that the thinning of the corpus callosum will cause severe mental retardation in the stage of imbicity, and in especially severe cases, it comes to death. Is it really so?
It's just that when I was being examined, the doctor told me that the thinning of the corpus callosum and hydrocephalus did not affect anything. But I can't believe it, that's why I decided to clarify
on Sun 1 Jan: 08
on Sat 18 Feb: 51
It's just, as it turned out, when I was little, the doctors first wrote to me with cerebral palsy syndrome, and then changed it to cerebral palsy.
on Sun 19 Feb: 31
on Tue 10 Apr: 41
Does this only apply to the mild form, or may the severe one also not show up on the MRI?
If I have a thinning of the corpus callosum, then how can I increase its thickness? On the Internet they write that this pathology is almost not amenable to treatment, and if it is treated, then with an emphasis on drug therapy. Doctors say little on this issue. Thank you for your help.
on Sat 14 Apr: 52
2. Severe may also not appear.
3. The development of the child, both hemispheres will also contribute to an increase in effective communication - the function of the corpus callosum.
on Wed 30 May: 37
the left lateral, third ventricles are clearly enlarged. Moderately - the right lateral and fourth ventricles. Moderately dilated subarachnoid space of the frontal-parietal regions of the cerebral hemispheres (more than the left), the rest of the liquor space within the age norm.
Severe mixed hydrocephalus, especially on the left.
Actually, I wanted to clarify some points:
1. Can such hydrocephalus progress?
2. How can it be removed? The fact is that, as I understand it, it is more correct to attribute mixed hydrocephalus not to hydrocephalus, but to brain atrophy, because. expansion of the ventricles and subarachnoid space is not due to a violation of the circulation process cerebrospinal fluid, and due to a decrease in the mass of brain tissue against the background of atrophy.
Actually, what can be done in this case?
3. Could such hydrocephalus be a consequence of meningitis?
on Sun 3 Jun: 19
3. Unlikely. Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes, not the brain itself ..
on Thu 7 Jun: 20
2. That's for sure. Help the brain - improve blood circulation, nootropics, etc.
3. Unlikely. Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes, not the brain itself .. "Hello! Could you explain:
1.How to determine if mixed hydrocephalus is progressing or not?
2.How to understand if my mixed hydrocephalus is true or not?
3. Why does true mixed hydrocephalus inevitably progress?
4. If I understand correctly, with mixed hydrocephalus, treatment is aimed only at combating the complications (consequences) of mixed hydrocephalus, and mixed hydrocephalus itself cannot be cured?
at Sat 9 Jun: 27
2.it is a matter of making the correct diagnosis
3.excessive "cerebrospinal fluid" does not go anywhere
4. on the contrary, they are treated surgically (shunts, etc.), but I think that everything is not so bad with you.
See. Recently, the diagnosis "hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome", "increased intracranial pressure", etc. has become extremely common. Most often, this comes from the data of the NSH and complaints of poor sleep. Practice shows that in many cases the diagnosis is made erroneously and increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is not associated with sleep / wake regulation problems. Those. There is overdiagnosis. Many doctors are aware of this and try to point out to colleagues. But the opposite effect is already taking place, when some are trying to gain cheap popularity precisely by combating overdiagnosis of increased ICP and stigmatize anyone who makes such a diagnosis “what the light is”. This is even worse. I witnessed several cases when the neurologist of my center, taking the child for conservative treatment, saved him from the hardest (and, even with a favorable outcome, disabling) operation ...
Now about the NSG. I am not commenting on the results of the study and, moreover, on the treatment prescribed based on its results. Indeed, in order to interpret the results, you need to know the device and the specialist who conducted the research. After all, it so happens that without attaching importance to one of the parameters, the doctor writes down it is not a "peephole". A colleague from the next office knows this (the first does this, knowing that the neurologist does not need it). I can rely on this figure and make a mistake with the recommendation.
In general, NSG is a visualization method. He, of course, does not show any pressure. But the doctor may decide that it is increased, because sees the expansion of the cavity system of the brain ("intracerebral" fluid presses on the brain tissue). But this is also doubtful, because the brain itself, by physical essence, water. And the water does not put pressure on the water (this, of course, is somewhat simplified). Secondly, an atrophic process is possible (the brain tissue itself decreases in volume) - then the pressure is even somewhat reduced. Etc.
In general, to judge ICP, in my opinion, it is more reasonable to use the Doppler study of cerebral blood flow TC USDG - the state of venous blood flow will tell us more than NSG ... This topic deserves a full-fledged book, but, I hope, I made minimal clarity ...
Corpus callosum
The brain is one unified system that constantly receives information and distributes a command to all organs and systems using impulses that are concentrated in the corpus callosum.
What is the corpus callosum?
The corpus callosum is a plexus of nerve fibers that unites the right and left hemispheres, coordinating the work of both halves of the brain into one whole.
The corpus callosum is presented in the form of a dense formation, white, elongated from front to back and centimeters long. It is located in the longitudinal slit of the brain.
On the upper surface of the corpus callosum is a thin layer of gray matter - a gray cover. It distinguishes the trunk of the corpus callosum, which bends to form a knee and passes into the beak of the corpus callosum. The beak extends into the end plate, but the dorsum of the corpus callosum is thickened.
The transversely fitting fibers of the corpus callosum are bred radially in any hemisphere and form the brightness of its body.
Callosal fibers of the brain connect symmetrical areas of the cortex of both hemispheres, passing to the nuchal part of the corpus callosum, the temporal and parietal lobes, but the interhemispheric fibers of the frontal part are located in the rostral area, forming its body.
The middle section, the corpus callosum, forms a bulge in the longitudinal direction and is the longest part of the brain. The posterior section is a thickening that freely hangs over the pineal body, roof plate and midbrain. There is a small layer of gray matter on the top surface. It forms four thickenings in the form of stripes, two on all sides of the median groove. When a horizontal section is taken, the corpus callosum is clearly visible: the side of the brain and the white matter.
Functions of the corpus callosum
The corpus callosum is the main "cable system" through which the right and left hemispheres quickly communicate. For example, if a person plays the harmonica, then instantly these hemispheres transmit a command to each other when the fingers are coordinated.
Its main function is to transmit the received information, which is collected in the cortex of one hemisphere, corresponding to the cortical spheres of the other hemisphere.
These functions are easier to explain with support for displaying the first studies. From the beginning, at the monkey, the corpus callosum is cut, the visual intersection is divided, and signals from any eye have every chance to act only to the cerebral hemisphere in the corner of the eye.
Then the monkey is taught to distinguish between different objects with its right eye, in this case, all the same, the left eye is covered.
After this experiment, cover the right eye and check whether it is able to identify these objects with the left-sided eye.
As a result, we can conclude that the left eye cannot recognize objects.
When re-examining, but only on another monkey, with cleavage of visual intersections with an intact corpus callosum, recognition by the first or second hemisphere of the brain is determined, that is, recognition is formed in the opposite direction from the other hemisphere.
The role of the corpus callosum is great, which is able to receive and transmit information to the cortex of the hemisphere.
The corpus callosum is a dense group of nerve fibers that divides the cerebral cortex into right and left. It connects the right and left halves, thereby providing communication between the hemispheres. This structure transfers motor (motor), sensory and cognitive information between the cerebral hemispheres.
Study history
The corpus callosum has long remained a mystery of human anatomy. Scientists could not determine in any way what function this part of the brain has. By the way, in 1981, the scientist who discovered the corpus callosum received the Nobel Prize for this. His name was Roger Sperry.
The first operations on the corpus callosum were aimed at treating epilepsy. So, breaking the connection between the hemispheres, doctors really cured many patients from epileptic seizures. But over time, scientists drew attention to the occurrence of specific side effects in such patients - behavioral reactions and abilities changed. So, as a result of experiments, it was found that after an operation that affected the corpus callosum, a person could write exclusively with his right hand, and draw only with his left. So the corpus callosum, the functions of which were still unknown to scientists, was no longer dissected in surgery to treat epilepsy.

Several years later, scientists discovered a link between the focus of the corpus callosum and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Corpus callosum: functions
The functions of this part of the brain are quite varied and important. The corpus callosum is the largest bundle of nerve fibers in the brain. It contains about 200 million axons and performs several important functions in the body:
- Communication between the hemispheres of the brain.
- The movement of the eyeballs.
- Maintaining a balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition in the cerebral cortex.
- Tactile perception.
Localization
Spatially, this part of the brain is located under the hemispheres along the median line. From the front to the back, several different zones can be distinguished in the corpus callosum: the knee, the middle, the body, the posterior end, and the ridge. The knee, bending downward, forms a beak, as well as a rostral plate. Above, the corpus callosum is covered with a thin layer of gray matter.
Another structure of this part of the brain is radiance. Cords of fan-shaped neurons stretch to the frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
With agenesis, the corpus callosum of the brain is completely or partially absent. This brain anomaly can be caused by a number of various factors, including chromosomal mutations, genetic inheritance, intrauterine infections, and other causes that are not yet fully understood by scientists. Individuals with agenesis of the corpus callosum may experience cognitive and communication impairments. They also have difficulty understanding spoken language and social reference.

But, given the function that the corpus callosum of the brain performs, how can people who do not have it from birth even live? How do they interact between the right and left hemispheres of the brain? Scientists have found that at rest, the activity of the brain of a healthy person is practically no different from that of a person diagnosed with agenesis of the corpus callosum. This fact indicates that the brain is being rebuilt under these conditions, and the functions of the absent corpus callosum are performed by other healthy areas. How exactly and by what structures this process is carried out, scientists have not yet figured out.
Symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum
Despite the extremely low occurrence of this diagnosis, scientists have studied its symptoms well. Some of the most common manifestations of agenesis of the corpus callosum are:
- Atrophy (complete or partial) of the auditory and (or) optic nerve.
- Cystic formations in the tissues of the brain (porencephaly).
- Connective tissue tumors - lipomas.
- The rarest disorder of intrauterine development of the fetus, schizencephaly, is a cleft brain.
- A significant decrease in the size of the brain and skull in general is microencephaly.
- Multiple pathologies of the digestive system.
- Spina bifida.
- Disorders of the structure of the retina (Ecardi syndrome).
- Early puberty.
- Retardation in psychomotor development.
These and many other disorders are in one way or another closely interrelated with the absence of the corpus callosum. As a rule, they allow a diagnosis to be made in the first 1-2 years of a child's life. The final confirmation of the diagnosis is considered to be an MRI scan of the brain.
Corpus callosum hypoplasia
Hypoplasia is a serious but fortunately rather rare diagnosis. In fact, this, like agenesis, is a violation of the intrauterine development of brain tissue. If, with agenesis, the corpus callosum of the brain is completely absent, then with gopoplasia it is underdeveloped. Of course, the treatment of this disease by means of modern medicine is impossible. Therapy provides for a set of measures that minimize deviations in the patient's development. Neuropsychologists recommend that patients regularly perform a specially designed set of physical exercises that help restore connections between the hemispheres, as well as information-wave therapy.

Sexual dimorphism
A number of Russian and foreign scientists believe that the difference in thinking and behavioral reactions between men and women is associated with the different structure and size of the corpus callosum. So, in the edition "Newsweek" there was an article explaining the nature of female intuition: in women, the corpus callosum is somewhat wider than in men. This fact, in the opinion of all the same scientists, also explains the fact that women, unlike men, are able to cope with several different tasks at the same time.

After a while, a group of French scientists reported that, as a percentage of the brain size in men, the corpus callosum is larger than in women, but the scientists did not draw any unambiguous conclusions. Be that as it may, all scientists agree only that the corpus callosum is one of the most important structural components that perform a number of vital functions.
A disease associated with abnormal development of the brain, congenital, rather rare, manifested in the complete or partial absence of structural formation connecting the hemispheres of the brain, is called adhesion of the corpus callosum.
The corpus callosum unites the cerebral hemispheres
Normally, the corpus callosum, or large commissure, is represented by a dense articulation of nerve fibers that unites the cerebral hemispheres, left and right, and provides coordination between them.
The formation of this structure from the point of view of morphology corresponds to the period of the week of pregnancy, the beginning of differentiation of the corpus callosum tissue is referred to the middle of the sixth week.
This pathology can have varying degrees of structural manifestation and be expressed in the form of total absence, partial (hypogenesis) or incorrect (dysgenesis) formation, underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the corpus callosum.
Instead of a normal structure that looks like a wide flat strip, a large joint takes the form of shortened partitions or transparent pillars of the vault.
As a rule, it is difficult to accurately determine the cause of a congenital structural malformation of the brain.
Predisposing factors
- Heredity (family cases of manifestation, with inheritance in an autosomal manner or linked to the X chromosome)
- Spontaneous mutations
- Rearrangement of chromosomes
- Intrauterine infections (usually of a viral nature) or trauma
- Impact toxic substances, teratogenic effect of drugs during uterine development
- Fatal fetal alcohol syndrome (due to maternal alcoholism during pregnancy)
- Nutrient deficiency in the fetus
- Metabolic disorders in the mother
To date, it is not possible to unequivocally name the cause of agenesis of the corpus callosum; one can only single out the factors that determine its occurrence.
You can get acquainted with the structure of the brain by watching the proposed video.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The clinic of the disease has a different nature of manifestation, depending on this, it can be detected in severe form in childhood, usually up to two years, or in adults, asymptomatic and sometimes completely accidental.
Children whose disease, for one reason or another, was not diagnosed in the prenatal period, look healthy at birth, their development is normal until they reach three months.
It is at this stage that the first symptoms of the disease appear, usually in the form of so-called infantile spasms, a variety of epileptic seizures, and seizures.
Symptoms
- Interruption of the formation and further development of the structure of the corpus callosum in the early stages
- Development of porencephaly, a defect in the brain mantle
- Hydrocephalus - lack of eye tracking ability, later - lack of voluntary movement
- Atrophic phenomena of the nerves, visual and auditory
- Microencephaly
- The appearance of neoplasms, cysts in the hemispheres
- Polymycrogyria (under-formed gyrus)
- Premature, early sexual development
- Manifestation of spina bifida syndrome
- Manifestation of Aicardi syndrome
- Lipomas development
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, tumor formation
- Slowdown and then inhibition of psychomotor development
- Manifestations in varying degrees retardation, mental and physical
- Coordination disorders
- Developmental delays, abnormalities of various organs
- Low muscle tone
- Skeleton anomalies
In patients with preservation of intelligence and motor functions, the manifestation of the anomaly consists in a violation of the exchange of information between the hemispheres, for example, in the difficulties experienced by a right-handed person, when asked to name an object in his left hand.
Diagnose the disease by scanning the brain
Diagnosis of the disease can be made by performing a brain scan procedure.
Carrying out prenatal diagnosis of such an anomaly as agenesis of the corpus callosum is fraught with great difficulties. Most often, an anomaly is diagnosed at the stage of the second or third trimester of pregnancy.
As the main method, the method of echography is used; MRI and ultrasound procedures are also used.
Carrying out the echography procedure in the prenatal period makes it possible to diagnose far from all cases of the disease, including due to the peculiarities of the presentation of the fetus.
In addition, with partial agenesis, it is even more difficult to detect the defect.
The diagnosis of the disease is complicated by the fact that agenesis is quite often combined with a number of malformations, with various genetic symptoms.
To obtain a complete picture of the examination, in case of suspicion of an abnormality, it is necessary to perform karyotyping, as well as a thorough ultrasound analysis, diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging.
Combination of various modern methods examination makes it possible to more reliably diagnose cases of agenesis of the corpus callosum in the prenatal period.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum: treatment and prognosis
Doesn't exist today effective methods treatment of the disease.
Treatment is aimed at minimizing symptoms of the disease
Therapeutic measures consist in the treatment of serious symptoms, reducing them to a minimum manifestation.
Medicines
- Antiepileptic
- From the benzodiazepine group
- Phenobarbital
- Corticosteroid hormones
Unfortunately, treatment is often ineffective, and even the use of potent drugs does not bring the desired results.
To correct the patient's condition, it may be necessary to carry out various surgical interventions, the use of methods of physiotherapy, physiotherapy exercises.
The prognosis for patients with agenesis of the corpus callosum depends largely on the type of abnormality. In the absence of a combination of the disease with any type of pathology, we can talk about a fairly favorable prognosis.
If there is a combination of agenesis and other pathology, we are not talking about a favorable prognosis, in such cases, manifestations of intellectual disabilities, neurological problems, developmental delay and other symptoms appear with high frequency.
Treatment of patients with agenesis of the corpus callosum is currently symptomatic and ineffective.
Brain pathology, agenesis of the corpus callosum, can be attributed to a group of diseases with multiple developmental abnormalities and an unfavorable prognosis.
Have you noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter to tell us.
Read about health:
Write in the comments what you think
Site search
Mailing list
Let's be friends!
direct permission of the administration of the journal "Dokotoram.net"
Everything about the corpus callosum: functions, anatomy and diseases
The human brain is a complex biological mechanism in which the processes that ensure the vital activity of the body are continuously occurring.
It is a single system that receives, processes and transmits information to all organs, cells and tissues. This happens due to impulses that are concentrated in the corpus callosum of the brain.
What is the corpus callosum: general information
The corpus callosum (MT) or large commissure, as this element is called by experts, is an accumulation of nerve fibers.
It brings together the two parts that form the brain - the right and left hemispheres. Also, the corpus callosum coordinates their stable work, ensures the coherence of transmission and reception of signals from each of the hemispheres. In addition, the corpus callosum unites the gray matter of each of the cerebral hemispheres.
The formation is a dense structure of white color. The anatomy of the corpus callosum is quite complex - in general, it is a structure elongated from front to back, the length of which, depending on age and gender, ranges from 7 to 9 cm.
The location of the large commissure is the longitudinal slit of the human brain.
Anatomy and function
The corpus callosum is covered with a small layer of gray medulla on top, which explains, accordingly, the gray cover on it. Upon visual examination, 3 main divisions can be distinguished:
- trunk (or midbrain);
- knee (part of the brain located in the front);
- beak or cushion of the corpus callosum (posterior section).
The brightness of a large commissure (when viewed in photographs or in a section) is provided by fibers that are located radially and are located in each of the hemispheres.
The middle section, when viewed, looks like a bulge, which is simultaneously the longest part of the entire brain. The posterior section is visually visible as a thickening relative to other sections and zones, which is freely located above the adjacent areas of the brain. The gray matter is represented by stripes and is located on top.
Functions provided by the corpus callosum:
- transmission of information important for the functioning of the body (impulses) from one hemisphere to another;
- the formation of the main characteristics that determine the personality and its characteristics;
- basic (basic, defining) skills and the possibility of their application during a person's life;
- work on the formation of the emotional and personal sphere.
Large commissure under attack ...
Disorders of the corpus callosum is a rare phenomenon, it occurs in 2% of all cases of diseases of the brain and central nervous system. In the case of diseases of the corpus callosum, the following are observed:
- disorders of various nature and intensity, manifested in the emotional - personal and cognitive spheres;
- physiological problems in the work of the limbs;
- problems with eyeballs and vision in general.
Corresponding diseases develop - agenesis, hypoplasia and dysplasia (dysgenesis) of the corpus callosum of the brain.
Agenesis: main causes, symptoms, treatment
Agenesis of the corpus callosum, as an independent disease, is a complex structural disorder. If it takes place, then the patient has, respectively, a violation of the associative connections between the right and left hemispheres of the brain, which is not observed in the normal state, since this organ is responsible for the unification of these areas.
The disease develops in the course of violations (abnormalities) in the course of development. It is rare - about 2%, congenital, manifests itself in complete or partial absence of this structural formation when viewed on photographs or studies.
Agenesis is expressed by the complete absence of a large commissure or by its underdevelopment, sometimes it is present only partially (there is no specific area). In this case, the formation, if it is underdeveloped or partially present, is presented in the form of significantly shortened septa or transparent pillars of the fornix.
Provoking factors and symptoms
Modern neurologists and scientists cannot accurately name the main reasons that affect the development of this pathology. The main predicted factors are:
- heredity (in 70% of cases, if the family has already had problems of a similar nature, then they will be repeated in future generations);
- genetic (including chromosomal) changes and mutations;
- rearrangement of chromosomes (during the period of fetal formation);
- the development of infections caused by the virus, occurring during pregnancy (in utero, especially dangerous in the early stages);
- trauma;
- ingestion of substances with toxic (poisonous) effects on the body or the developing fetus (including the effects of alcohol);
- the consequences of taking medication (side effects or complications);
- violation of the course of pregnancy (nutritional deficiency in the fetus during development);
- violation metabolic processes in the body of a pregnant woman.
The main symptoms indicating the presence of agenesis of the corpus callosum in a person and the need for immediate qualified diagnosis:
- hydrocephalus;
- disorders in the development and functioning of the optic and auditory nerves;
- the appearance of benign cysts and other types of tumors in the brain;
- insufficiently formed, to perform inherent functions, cerebral gyri;
- early puberty;
- development of lipomas;
- various problems and disorders in the work of the digestive tract (of different nature and intensity);
- violation of psychomotor skills;
- behavioral problems (especially acute in childhood);
- diagnosis of mild mental retardation (detected in childhood);
- impaired coordination of movements;
- low muscle tone;
- disorders of the development of muscles and bones of the skeleton.
A set of measures
Treatment is most often drug therapy. It includes taking antiepileptic drugs, as well as corticosteroid hormones. Also, in some cases, exercise therapy classes (physical education with a therapeutic bias) are shown.
Dysplasia and hypoplasia - abnormal or underdevelopment of MT
Hypoplasia, or, as this disease is also called, microcephaly, is complex pathology, during the course and development of which there is a significant decrease (the value is taken based on normal performance) the volume of the brain and, accordingly, the corpus callosum as well.
In most cases, along with the diagnosis of hypoplasia, other disorders are observed, including abnormal development of the present parts of the corpus callosum (dysplasia or dysgenesis), insufficient formation of the spinal cord, underdevelopment of the limbs and a number of internal organs.
Causes and clinic of pathology
The main cause of impaired development and a decrease in the size (or complete absence) of the corpus callosum is one or another congenital pathology. Factors causing such changes:
- the presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman (smoking, taking drugs or alcohol);
- intoxication;
- exposure to radiation (ionizing);
- consequences of complex and serious illnesses- rubella (carried over in adulthood or during pregnancy especially), influenza, toxoplasmosis.
- a decrease in brain volume relative to normal indicators (the main symptom);
- changes in the usual structure of the cerebral gyri and some structures (gyrus are flat);
- insufficient development of the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain in humans for normal functioning;
- reduction in the size of pyramids - elements medulla oblongata(pyramidal syndrome develops);
- violations and failures identified in the work of the cerebellum;
- dysfunction of the trunk (part of the brain);
- in most cases, there is a violation of intelligence;
- disorders of physical development;
- neurological disorders and characteristic disorders;
- pathology of the optic hillock.
The state of modern medicine
In hypoplasia, the cranium is smaller than normal in a person.
Despite the development of modern medicine, there is no high-quality and effective treatment for such a disorder. It is possible to minimize the manifestations of symptoms.
It is important to remember that this anomaly leads to a decrease in life expectancy. The main measure of influence is taking medications.
Consequences of hypoplasia
If at an early stage of development and formation of the anomaly, appropriate measures are not taken, then most patients in the future (already in childhood and adolescence) will experience various problems in the field of neurology.
Also, many patients with hypoplasia have moderate to severe intellectual disability, developmental delay, both mental and physical.
So, according to various medical studies, in at least 68-71% of cases of diagnosing hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, there is such a consequence as mental retardation. In addition, the disorder leads to the emergence of more serious mental disorders such as schizophrenia.
Dysgenesis consequences
Dysgenesis of the corpus callosum can cause changes in the muscle system and in the skeleton as a whole. It is a common cause of scoliosis.
There are lags in the mental and psycho-emotional development of children and adolescents. There are also intellectual disabilities, neurological problems, developmental delays, so patients in most cases need constant supervision and intensive treatment.
If measures are taken to eliminate manifestations, then children can learn the necessary skills, including mastering a simple school curriculum.
In dry but important residue
Thus, the corpus callosum of the brain, despite its tiny size, has a great impact on human life. It allows the formation of personality, is responsible for the emergence of habits, deliberate actions, the ability to communicate and distinguish between objects.
That is why it is extremely important to treat your health with care during pregnancy, since the main MT disorders are formed during this period.
It should not be forgotten that the corpus callosum forms the intellect, makes a person a person. Despite all attempts to study this structure, scientists have not yet been able to reveal all its secrets, therefore, very few methods of treating disorders, if any, have been developed.
The main ones are drug therapy and a special set of exercises - exercise therapy, which allows you to maintain optimal indicators of physical development. Measures should be taken to eliminate the symptoms of violations immediately, otherwise the desired improvements may not occur.
This section was created to take care of those who need a qualified specialist, without disturbing the usual rhythm of their own life.
A rare disease of the corpus callosum hypoplasia, a sentence or not?
The corpus callosum of the brain plays an important function in the body, but even such a small organ is susceptible to diseases - hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, one of the rare, but no less dangerous anomalies that affects the functioning of this organ.
What is the reason?
The corpus callosum is located exactly in the middle between the two hemispheres of the brain. Its functions were discovered relatively recently, around the 60s – 70s of the last century, and by chance. In the treatment of epileptic seizures, there was a practice of splitting this body into two halves, as a result of which the seizures disappeared, but there were many side effects from such a procedure, which prompted the doctors who conducted the study to think correctly. The corpus callosum is a conductor of neurons between the two hemispheres, thanks to it, many important processes occur in our body, such as:
- physical activity;
- manifestations of feelings;
- cognitive processes.
It is impossible to say that all these processes will be limited for the patient, this is possible only in an extremely severe form of the disease, but the presence of deviations will be noticeable to the naked eye.
For example, when the corpus callosum was dissected in an adult with epileptic seizures, after a while they noticed that everything related to creativity (drawing, versification, etc.) a person could only do with his left hand, while ordinary procedures (technique food, rewriting text) only right.
What can we say about a person with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. In this case, the consequences are much more serious, but ... First things first.
The cause of this ailment is not fully known, but scientists agree that the lion's share lies in genetic abnormalities that are laid in intrauterine development, in particular, at 2-3 weeks of the embryonic period.
In addition, it is believed that the presence of hypoplasia is caused by mutations that affect brain development. Unfortunately, doctors are not able to give more accurate information.
The risk group includes mothers who:
- drink alcoholic beverages during pregnancy;
- have had rubella during pregnancy, just like toxoplasmosis or severe flu;
- have been exposed to radiation;
- were subject to general intoxication of the body.
This disease belongs to the category of rare and, according to statistics, occurs in every 10 thousandth baby.
How to recognize?
Corpus callosum hypoplasia in a newborn is diagnosed, as a rule, after the first two months of life, but more often it occurs during intrauterine development.
If, before the birth of the child, the doctors overlooked the ailment, then during the first 2 years of life, the child will develop harmoniously, as befits a normal baby, and only after the specified time, parents may notice some deviations, such as:
- infantile spasms;
- convulsions;
- epileptic seizures;
- weakening of the cry;
- violation of touch, smell and vision;
- decreased communication skills;
- manifestations associated with muscle hypotension.
infantile spasms - seizures characterized by sudden flexion and extension of the arms and legs
muscle hypotension - a condition characterized by decreased muscle tone, can develop in combination with a decrease in muscle strength in the patient.
In the event that in childhood, for any reason, it was not possible to diagnose and recognize the presence of a disease, it will certainly manifest itself in adulthood, the symptoms include:
- violation of visual or auditory memory;
- hypothermia;
- problems with coordination of movement.
Hypothermia - problems with thermoregulation of the body (decrease in body temperature below 35 degrees)
How is the diagnosis carried out in a hospital setting?
As a rule, with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, a large number of concomitant diseases can develop, therefore, the presence of other (different from the above) symptoms is possible. In 80% of cases, the diagnosis of this disease occurs during intrauterine development using ultrasound diagnostics.
Nevertheless, it is possible to prescribe additional tests after birth (if during pregnancy the clinical picture was not completely clear) or after the parents turned to a specialist. The doctor conducts an initial survey and clarifies the presence of symptoms characteristic of this diagnosis, after which he usually prescribes:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- electroencephalogram of the head (EEG);
- other studies of a neurological nature.
Based on the data obtained from the results of the above studies, the doctor makes a conclusion and prescribes treatment.
Treatment features
Unfortunately, an effective treatment has not yet been invented, and doctors are mostly struggling with the symptoms of the disease, so children with this diagnosis are doomed to constant treatment and supportive therapy.
The specific plan is selected by the attending physician individually for each. It all depends on the severity of the lesion of the corpus callosum and the clinical picture of the disease.
In 70-75% of cases, there is an unfavorable outcome. There is a high likelihood of mental retardation and the development of serious mental disorders such as schizophrenia, etc.
If your baby is diagnosed with hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn, then your support and help will be important for him. Here are some general guidelines for taking preventive measures for your baby at home:
- Pay attention to the general condition of the baby, if he is tired or does not show interest in classes or communication, give him time to rest, he himself will make it clear when you can resume the procedure.
- Carry the child in the "airplane" position, this exercise has a strengthening effect on the body, the main thing is not to overdo it.
- Lay the baby on your chest, face to face, so that his hands are under the breast, stroke him with your hand from head to ass - this procedure will help him transfer weight from head to pelvis, you can also put him on the bed, and folded under his stomach towel roll.
- If the baby pronounces sounds, copy them and repeat after him, with the same intonation, try to maintain small pauses, this will stimulate him to repeat.
- While playing with the rattle, let the child fix his gaze on it, and slowly drive from side to side, encouraging him to follow the toy. If you lose sight of it, lightly rattle, attracting attention and continue the procedure. If the child has lost interest, do not push, give a break.
Unfortunately, the diagnosis of hypoplasia is serious and often does not come alone, you can only wish patience to parents with sick children, but you yourself should hope for the best, since 25-30% have a positive result, and perhaps you will be included in these percentages ...
Health, everyday life, hobbies, relationships
Corpus callosum hypogenesis
What about hypogenesis of the corpus callosum?
What about hypoplasia and agenesis of the corpus callosum?
If we talk about the corpus callosum itself, then we can say that it is a plexus of nerve fibers in the human brain, which connects the left and right hemispheres. This corpus callosum itself is made up of approximately two hundred million nerve fibers. Another thing about the corpus callosum is that it is itself the largest structure that connects the two hemispheres of the brain. When the corpus callosum has formed, then it begins to gradually grow further, both in width and in length. If we talk about the intersection of fibers, which subsequently begin to connect one hemisphere of the brain to the other, then it is worth saying that all this happens in a person for such a period of life as twenty weeks.
If the corpus callosum is partially absent or it is completely absent, then we can say that agenesis of the corpus callosum occurs in a person. It is worth saying that when a person experiences hypoplasia or agenesis of the corpus callosum, then the main adhesion, which was formed in a person with the help of commissural fibers, can either be completely or partially absent, and from this the third ventricle in a person remains open. When a person has agenesis, then there are special pillars of the vault, and there are also special transparent partitions. And when a person suffers from hypoplasia, then only the absence of a posterior adhesion can be noticed in a person, and the corpus callosum itself is shortened in a person. When a person has malformations of the corpus callosum, then most often they can begin to accompany any other disorders in the human brain, but they can also occur in isolation.
Most often, this kind of defects in a child can begin to appear literally two weeks after conception. If we talk about the frequency of manifestation of this, then it is worth saying that this disease develops in a person in coefficients of one in two or even three thousand.
What are the neurological defects?
If we talk about neurological defects, then we can say that they can be:
- Porencephaly;
- May be microgyria;
- It may be that a person may also develop atrophy optic nerves;
- They can also be interhemispheric and corpus callosum lipomas;
- If a person has hypoplasia of the limbic system;
- If a person suffers from interruption of the onset of the corpus callosum;
- If the person has schizencephaly;
- If a person has a cyst in the area of the corpus callosum;
- If there is spina bifida;
- If the person has colobomas. These include such as: a defect in the iris or tissues of the eyelids, a defect in the lens of the eye, a defect in the mesh or choroid of the eye in humans;
- When a person lacks a transparent septum and much more.
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn baby
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn is a very serious diagnosis, but at the same time, fortunately, it is quite rare. A similar disease, according to statistics, occurs in one out of two thousand babies born.
By its nature, the considered pathological condition, as well as agenesis of the specified structure, refers to defects in the intrauterine stage of development of brain tissue. However, unlike agenesis, which consists in the complete absence of the corpus callosum, in the case of hypoplasia, the latter is preserved, but is present in the brain in an underdeveloped state and, accordingly, does not fulfill the entire volume of functional duties assigned to it.
Taking into account the consequences of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn, this pathology should be considered as a disease with a not very favorable prognosis. Especially considering the fact that the pathological condition in question does not always proceed in isolation. Often, in conjunction with it, other disorders affecting the brain occur.
Causes of the corpus callosum hypoplasia syndrome
In order to clearly understand why hypoplasia of the corpus callosum of the brain in a child is dangerous, it is necessary to have an idea of what kind of structure it is and what is its role in the human body.
The corpus callosum has been an unsolved mystery to anatomists for many times. Researchers have not been able to establish for a long time what exactly this brain region is responsible for. But, as they say, if you dig for a long time, then you will definitely get to the bottom of something.
Today it is known that this structure is nothing more than a group of nerve fibers connecting the right and left halves of the brain and thereby providing a neural connection between them. It is through this anatomical formation that the transfer of motor, sensitive and cognitive information from one hemisphere to another, due to which there is a well-coordinated work of the whole organism.
The main reason due to which the baby develops the syndrome of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, doctors call the disorders that arise in the process of laying the structures of the brain, which occurs at the initial stages of the development of the embryo. But today even the most professional doctors are not able to intelligibly explain why such violations occur.
It's all about insufficient knowledge of the etiology of this pathological condition. Nowadays, perhaps, we can only talk about some of the factors that can cause the appearance of this disease. The first places among them are occupied by mutations affecting chromosomes, as well as heredity burdened by the disease in question.
Hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a child can develop as a result of intrauterine infections. Other possible reasons the described condition is still being studied by physicians.
Symptoms of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum in a newborn baby
The clinical manifestations of this pathology, as a rule, are of a varied nature. For this reason, the disease in question can be detected both in early childhood, which most often occurs in the period up to two years in the presence of severe course disease, and already in an adult, and quite by accident, which is characteristic of the asymptomatic course of the disease.
Babies who, for some reason, were not diagnosed with such a diagnosis in the prenatal period, at first seem to be quite healthy. The first symptoms of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum appear from the moment they reach three months of age. Prior to this, the development of the baby proceeds at the usual pace and does not differ from the norm.
The clinical picture begins with the onset of infantile spasms in the baby, to which seizures resembling epilepsy can join.
Children suffering from this pathology often have convulsions, such children usually lag behind in motor development, they also have a small modulation of cry, and impairments of sensory reactions develop. In the future, they have a low sociability.
In an older period of childhood, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum of the brain has consequences in the form of dysregulation of body temperature by the type of hypothermia, patients have a lack of coordination, visual and auditory memory suffers.
Treatment and consequences of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum
In relation to such a pathological condition as hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, treatment that could boast high efficiency, not yet developed. However, this does not mean that you should neglect the visit to the doctor.
At the present stage of development of medicine, the therapy of the disease under consideration provides only a set of measures aimed at minimizing deviations in the development of a patient suffering from this pathology.
Experts practicing neuropsychology recommend that such patients, with a certain frequency, perform a special set of physical exercises designed specifically for the treatment of the described ailment. Such exercises help to restore interhemispheric connections. In addition, information-wave therapy can be prescribed to the patient.
As mentioned above, the pathology under consideration can be combined with other diseases, due to which its prognosis is rather unfavorable.
Patients show various kinds of neurological problems, impaired intelligence, and delayed development. In particular, according to researchers, in at least 71% of cases, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum has consequences in the form of mental retardation.
In addition, the described anomaly of the corpus callosum often plays an important role in the occurrence of mental disorders, such as schizophrenia.
The corpus callosum is a white formation. Located in the brain. It is an important structure made up of strong connections from over two and a half hundred million nerve fibers. In the brain, there is no more powerful structure connecting its hemispheres - the left and right.
The shape is elongated and slightly flattened. The elongation of the body is directed from front to back. Connects the gray matter found in the cerebral hemispheres. Three parts of the body are located deep in the longitudinal slit of the brain.
The posterior section has a thickened shape - the body roller. It hangs over the pineal gland. The middle section is the trunk of the body. This is the longest part of the brain commissure. The front is the knee of the body, as it bends forward, backward and downward.
Its upper part is covered with a small layer of gray matter; in some areas it has small longitudinal thickenings that occupy each side of the median groove.
This is interesting: scientists have conducted research and found that the corpus callosum is absent in cloacal and marsupial animals.
If you look at a longitudinal section of the cerebral hemisphere, you will see the white matter of the hemispheres. The edges of the white matter are covered with a layer of gray all this is the cerebral cortex. The fibers extending from the body are the radiance of the corpus callosum.
Diseases
- Alien hand syndrome - the patient experiences a feeling of uncontrollability in one of the hands. The syndrome can manifest itself after a stroke, brain surgery, etc.
- Agenesis.
- Aicardi syndrome.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a disease that has a congenital pathology. It is believed that the main factors that influence the development of pathology and its spread are genetic.
The consequences of agenesis of the corpus callosum can be the most unfavorable, they are a component of most of various kinds of developmental pathologies and diseases, and are reflected in the mental abilities of the individual. In such situations, it has a complete or incomplete absence of the main adhesion, instead of their vault pillars, short partitions.
Fortunately, such defects are very rare: no more than one in two thousand. As a rule, they are inherited. Or they arise spontaneously, as a result of hard-to-explain abnormalities at the gene level, mutations and other pathologies.
From the history
The corpus callosum of the brain was discovered by Nobel laureate Roger Sperry and a group of scientists. They made this discovery in the early sixties of the last century. Twenty years later, he received the highest award for this.
Scientists were engaged in the treatment of epilepsy. Then they managed to conduct a number of successful scientific tests in which experimental animals participated. Only after that it was decided to perform an operation on the human brain.
During the operation, it was planned to divide the hemispheres that connect the nerve fibers of the brain. They are, these connections, and made up the corpus callosum of the brain. The end result of the operation was the elimination of epileptic seizures.
At the same time, it was noticed that after such an operation, certain moments in human behavior began to change, even some abilities changed. It was stated that the people who underwent the operation in Everyday life those using the right hand could not even write lines with their left hand, and depict anything with their right.
In another case, other features were noted in the behavior of the operated people. They could feel with their right hand any object and identify it, but they could not pronounce its name aloud. The results of these operations showed that people got rid of epileptic seizures, but acquired other problems that were unusual for them.
As a result, all these operations marked the beginning of a thorough study of numerous and different functions hemispheres of the brain.
Symptoms of agenesis
- Psychomotor skills have a retarded development.
- Lipomas may appear, which are of a different nature and pattern of occurrence.
- All kinds of pathologies of the optic nerves, which, as a rule, are expressed in their atrophy. The same goes for the auditory nerves.
- Various pathologies at the junction of the hemispheres, the formation of cysts, their localization, as well as all kinds of neoplasms.
- Symptoms can be expressed in deformities of the spine, one of the characteristic is its splitting.
- Disturbances in the work of the visual organs.
- Microencephaly.
- A case of seizures.
- The gastrointestinal tract has developmental abnormalities. Presence of benign and malignant tumors.
- Porencephaly
- Colobomas, expressed in various eye defects: lens, retina and others.
- Perhaps outstripping development in the sexual aspect, early maturation, and the like.
The symptoms of this pathology of the corpus callosum, it is clear that they are not limited to the list given above, and can manifest themselves in different organs and in different ways. But, as a rule, they find their expression in the backwardness of intellectual development in different degrees. Active vital activity is also impaired due to low motor physical activity. Many organs have growth abnormalities, skin lesions occur, and eye development is also impaired.
How and what we treat
Basically, the course of treatment for this pathology is to minimize the manifestation of the disease and to achieve the cessation of infantile spasms.
Therapeutic methods, according to experts, which are used in treatment, do not bring the desired effectiveness. In addition, the technique has not been improved and has not been fully worked out.
Mainly used drugs strong action, maximum doses and courses. Such shortcomings are explained by quite objective reasons. Since the method of treatment of agenesis is in constant search of new and improved methods of getting rid of this ailment.
The disease itself is carefully studied, but it is almost impossible to achieve tangible desired results, because it is very difficult to diagnose at the stage of development of the disease. All this is due to the position of the fetus, which does not allow for a clear and visual examination of the cavities and structures of the brain.
The pathology of the corpus callosum or its underdevelopment in children, as a rule, affects the state of their neurological development. At the same time, there are cases when, in the absence of any other anomalies, a normal karyotype was noted. The observation period in this case was quite long. Children were followed up to 11 years old.
Among the forms of agenesis manifestation, cases of Aicardi's syndrome are most observed. At the same time, there were about five hundred manifestations of this syndrome on the planet, the largest number in the country of the "rising sun" of Japan.
Those who had a similar pathology were noted for disorders associated with an abnormality in the development of the eyes. One of such anomalies is retinitis pigmentosa, which manifested itself in decreased visual acuity, cataracts, damage to the optic nerve and other pathologies.
Skeletal and other abnormalities
- These are mainly abnormalities that manifest as hemivertebrae and missing ribs.
- In medical practice, there are cases of jaw and facial anomalies. Of these, more than others were noted violations in the form of protruding incisors, a reduced angle of the nasal septum.
- Also, there were such abnormalities as the tip of the nose turned up, etc. It should also be noted that in almost a quarter of patients, various skin lesions were revealed, and a little more than seven percent had various pathologies of the extremities.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, frequent cases of oncological neoplasms were also noted.
An effective therapeutic treatment of the syndrome has not yet been created, although development is ongoing, therefore, symptomatic treatment is mainly used, which is mainly aimed at eliminating infantile spasms.
Although this technique is very complicated, it is ineffective. Medicines are used for application in maximum doses. Suffice it to say that the initial course of treatment is used sabrid, which is prescribed per day up to 100 mg per 1 kg of patient weight.
Corticosteroid hormones are used as an alternative.
Human differences
About whether the size of the corpus callosum affects the differences in intellectual development and abilities and behavior of people of different sexes, quarrels and discussions in the scientific community have been going on for a long time. This is even brought into the problem of sexual dimorphism, the direction that is just doing this.
At the beginning of the eightieth journal Science published material on its pages, which, according to the authors of the article, gave a clear establishment of sexual dimorphism in the structure of the brain. Among other claims, there was this: the size of the corpus callosum may help explain differences in intellectual abilities.
As often happens in such situations, new interpretations began to appear about the influence of the size of the corpus callosum on the behavior and ability of a person. One of the magazines, for example, in the early nineties published an article in which he indicated that in most cases, women have a wider body, which means that the hemispheres interact more closely - which fully explains the reason for female intuition.
And there are many such examples. Others argued that men have a larger corpus callosum, etc.
About ten years ago, in the course of scientific research, there were really significant differences in the morphological structure of the corpus callosum in men and women. However, whether they lead to any differences in behavior and abilities has not yet been scientifically proven.
The corpus callosum connects the left and right hemispheres and is made up of 200 million nerve fibers. Very rarely, a person can be born without a corpus callosum. This condition is known asagenesis of the corpus callosumwhich causes a variety of physical and behavioral symptoms. 
What is the corpus callosum?
Each side of the brain controls movement and feelings on the opposite side of the body. Therefore, physical coordination and information processing requires both hemispheres of the brain to work together. The corpus callosum acts as a connector.
The corpus callosum is located in the center of the brain, is about 10 centimeters long and resembles the letter "C" in shape. Typically, the corpus callosum forms in the brain 12-16 weeks after conception, towards the end of the first trimester of pregnancy. It develops throughout childhood. By the age of 12, the corpus callosum will be fully formed and will remain unchanged throughout life.
Until the 1950s, the exact function of the corpus callosum was unknown. In 1955, Ronald Myers, a graduate student at the University of Chicago, demonstrated the function of the corpus callosum in coordinating actions and solving complex problems.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum
Some babies are born without a corpus callosum, a rather rare abnormality, agenesis of the corpus callosum, which occurs in about 1 in 3000 people. The corpus callosum can also be damaged.
Disruption of corpus callosum formation can occur between the 5th and 16th weeks of pregnancy.
Risk factors for agenesis of the corpus callosum
The specific causes of developmental disabilities are not yet known, but possible factors include:
- Intrauterine infections or viruses such as rubella;
- Genetic abnormalities;
- Toxic metabolic disorders - ;
- Brain cyst.
Corpus callosum abnormalities can also be associated with a recessive genetic disorder. This means that the parents may be carriers of the gene that causes the abnormality.
While the presence of the corpus callosum is not essential to life, children who have corpus callosum abnormalities often lag behind their peers in development. Children with agenesis may be blind, deaf, and may never be able to walk or talk, while others may be sociable. "Sociability"Is a term often associated with autism. It is used when the autistic person has speech skills and is disproportionately high level IQ.
Anomaly of the corpus callosum is not a disease, many people with agenesis of the corpus callosum lead healthy image life. However, this can lead to problems such as seizures that require medical attention.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be combined with other brain abnormalities. These include:
An excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricular system of the brain, known ashydrocephalus;
Arnold-Chiari Syndrome;
Neural transmission disorders.
Agenesis of the corpus callosum can occur in conjunction with spina bifida - when there is a defect in the spinal canal.
Symptoms and diagnosis of agenesis of the corpus callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is usually diagnosed within the first 2 years of a person's life. Seizures are often the first sign of brain dysfunction. In mild cases, the disease can go unnoticed for several years.
Imaging of the brain is needed to confirm a problem with the corpus callosum. These tests may include:
Perinatal ultrasound;
Computed tomography (CT);
MRI.
But there are some common features of the agenesis of the corpus callosum, which can be broken down into four categories:
Physical signs, These include:
- Visual impairment;
- Low muscle tone;
- Wrong facial features;
- High pain tolerance;
- Sleep problems;
- Seizures;
- Hearing impairment;
- Chronic constipation.
Cognitive. Cognitive traits include:
- Problems with facial expression or tone of voice;
- Difficulty solving problems and complex problems;
- Does not assess risk;
- Difficulty understanding abstract concepts;
- Problems understanding sarcasm;
- Difficulty understanding emotions.
Features of motor developmentinclude:
- Delay in sitting, walking;
- Delays in speech and language acquisition;
- Clumsiness and poor coordination;
- Delay in toilet training.
Social and behavioral signs include:
Social immaturity;
Lack of self-awareness;
Difficulty understanding social cues
Problems understanding perspectives;
Difficulty maintaining attention
Hyperactivity;
Lack of fear;
Obsessive or compulsive behavior.
If the corpus callosum is not formed during the development of the fetus, then it will never be. Once the symptoms of agenesis of the corpus callosum are identified, they can be treated. Therapy and counseling can improve language and social skills.