Permanent disability Permanent disability is long-term. Temporary disability, its types and forms of social security Certification of persistent disability sse
Permanent disability- This is a long-term or permanent disability resulting from a chronic illness or injury that led to a significant dysfunction of the body. Adopted November 1995 The federal law "social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation" has defined a new concept of disability, defining such fundamental concepts as "disabled person", "limitation of life activity", "medical and social expertise", etc.
Disabled person- a person who has a health disorder with a persistent disorder of the body's functions, caused by diseases, consequences of trauma or defects, leading to limitation of life and necessitating social protection.
Medical and Social Expertise (ITU)- this is the determination in the prescribed manner of the needs of the examined person in measures of social protection, including rehabilitation, based on an assessment of the disabilities caused by persistent disorder of the body's functions.
ITU is carried out by the State Service of Medical and Social Expertise, which is part of the system of social protection bodies of the Russian Federation. ITU establishes the cause and group of disability, the degree of disability, determines the types, scope and timing of rehabilitation, social protection measures, and gives recommendations on employment
Restriction of life activity- this is a complete or partial loss by a person of the ability or ability to carry out self-service, independently move, navigate, communicate, control his behavior, learn and engage in work.
The classification of the parameters of limitation of vital activity is carried out in three degrees:
mild functional dysfunctions
moderately severe dysfunctions
significantly pronounced dysfunctions.
The basis for recognizing a person as a disabled person is:
health disorder with persistent disorder of body functions caused by diseases, injuries or defects
limitation of life activity
the need to implement measures of social protection of the citizen.
2 group - social insufficiency. requiring social protection, due to health problems, with a persistently expressed disorder of body functions as a result of illness, injury or defect, leading to a pronounced restriction of one of the categories of vital activity - 2nd degree. These patients do not need outside care, but all types of work are contraindicated for them for a long period.
Group 3 - social insufficiency. requiring social protection, due to a health disorder, as a result of a disease, with a moderately pronounced disorder of body functions as a result of an illness, injury or defect leading to a slightly pronounced restriction of one of the categories of vital activity - 1st degree. These patients have a significantly reduced ability to work, due to the state of their health, a change in working conditions is required.
The criteria for establishing disability, without a term for re-examination, are:
the impossibility of eliminating and reducing the social deficiency of a disabled person due to prolonged restriction of his life activity (with a follow-up period of at least 5 years) caused by a health disorder with persistent irreversible morphological changes and impaired body functions.
Ineffectiveness of rehabilitation measures, which leads to the need for constant social protection.
Other criteria stipulated by the current legislation
The ITU public service institutions include: the ITU Bureau and the ITU Head Office
The formation of the ITU bureau network is based on the population living in the territory, as a rule, one institution for 70-90 thousand people.
City ambulance medical care;
Central (city, district);
Regional, including children's (regional, republican, district).
1.1.2. Specialized hospitals, including:
Rehabilitation treatment, including for children;
Gynecological;
Geriatric;
Infectious, including children;
Narcological;
Oncological;
Ophthalmic;
Psychoneurological, including children's;
Psychiatric, including children's;
Psychiatric (hospital) specialized type;
Psychiatric (hospital) specialized type with intensive supervision;
Tuberculous, including children.
1.1.3. Hospital.
1.1.4. Medical and sanitary unit, including the central one.
1.1.5. Nursing home (hospital).
1.1.6. Hospice.
1.1.7. Leprosorium.
1.2. Dispensaries:
Medical and physical education;
Cardiological;
Skin and venereal;
Mammological;
Narcological;
Oncological;
Ophthalmic;
Anti-tuberculosis;
Neuropsychiatric;
Endocrinological.
1.3. Outpatient polyclinic institutions
1.3.1. Outpatient clinic.
1.3.2. Polyclinics, including:
City, including children's;
Central district;
Dental, including children's;
Consultative and diagnostic, including for children;
Psychotherapeutic;
Physiotherapy.
1.4. Centers, including scientific and practical:
Rehabilitation therapy for internationalist warriors;
Restorative Medicine and Rehabilitation;
Geriatric;
Diabetic;
Narcological rehabilitation;
Occupational pathology;
On the prevention and control of AIDS and infectious diseases;
Clinical and diagnostic;
Speech pathology and neurorehabilitation;
Rehabilitation;
Medical and social rehabilitation;
General medical (family) practice;
Consultative and diagnostic, including for children;
Hearing rehabilitation;
Physiotherapy and sports medicine;
Manual therapy;
Medical and preventive nutrition;
Specialized types of medical care;
Psychophysiological diagnostics.
1.5. Ambulance facilities
and blood transfusion facilities
1.5.1. Ambulance station.
1.5.2. Blood transfusion station.
1.5.3. Blood Center.
1.6. Institutions for the protection of mothers and children
1.6.1. Perinatal center.
1.6.2. Maternity hospital.
1.6.3. Women's consultation.
1.6.4. Family Planning and Reproduction Center.
1.6.5. Center for Reproductive Health of Adolescents.
1.6.6. Children's home, including specialized ones.
1.6.7. Dairy cuisine.
1.7. Spa facilities
1.7.1. Balneological hospital.
1.7.2. Mud bath.
1.7.3. Resort clinic.
1.7.4. Sanatorium, including for children, as well as for children with parents.
1.7.5. Sanatorium-preventorium.
1.7.6. Sanatorium health-improving camp of year-round operation.
2. Health care facilities of a special type
2.1. Centers:
Medical prevention;
Disaster medicine (federal, regional, territorial);
Medical mobilization reserves "Reserve" (republican, regional, regional, city);
Licensing of medical and pharmaceutical activities (republican, regional, regional);
Quality control and certification of medicines;
Medical information and analytical;
Informational and methodological for the examination, accounting and analysis of the circulation of medical products.
2.2. The Bureau:
Medical statistics;
Pathological anatomical;
Forensic medical examination.
2.3. Control and analytical laboratory.
2.4. Military medical commission, including the central one.
2.5. Bacteriological laboratory for the diagnosis of tuberculosis.
3. Health care institutions for supervision
in the field of consumer protection and human well-being
3.1. Hygiene and Epidemiology Centers.
3.2. Centers for State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance.
3.3. Plague control center (station).
3.4. Disinfection center (station).
3.5. Center for Hygienic Education of the Population.
4. Pharmacy institutions
4.1. Pharmacy.
4.2. Pharmacy.
4.3. Pharmacy booth.
4.4. Pharmacy store.
Notes:
1. Treatment-and-prophylactic institutions (hospitals, dispensaries, maternity hospitals and other institutions) used for teaching by higher medical educational institutions (faculties) or for scientific purposes by medical scientific organizations are clinical institutions.
2. The health care institutions provided for in subsection 1.1 "Hospital establishments" of this Nomenclature may include a polyclinic (outpatient clinic).
3. In the presence of two or more healthcare institutions of the same name, subordinate to one state or municipal authority, each of them is assigned a serial number.
4. Feldsher-midwife stations (FAP) are structural subdivisions of health care institutions.
5. Health centers (medical, paramedic) are structural units of health care institutions or organizations and are designed to provide first aid to workers, employees and students.
6. Sanitary aviation may be part of a regional, territorial, republican hospital or a disaster medicine healthcare institution and acts as its department.
7.Clinics - medical and preventive institutions (hospitals, maternity hospitals and other health care institutions), which are part of higher medical educational institutions, medical scientific organizations or subordinate to medical universities and scientific organizations are their structural units.
8. Specialized homes for children include:
WITH organic defeat central nervous system with a mental disorder;
With organic damage to the central nervous system, including infantile cerebral palsy, without mental disturbance;
With dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system and other defects of physical development without disturbing the psyche;
With hearing and speech impairments (deaf and dumb, deaf, hard of hearing);
With speech disorders (stuttering, with alalia and other speech disorders);
With visual impairments (blind, visually impaired);
- with tuberculous intoxication, small and fading forms of tuberculosis;
Sanatorium.
9. The center of medical and social rehabilitation includes:
Department of permanent residence for adolescents and adults with disabilities with severe forms of children cerebral palsy, who do not move independently and do not serve themselves.
10. The full name of the health care institution provided for by this Nomenclature may contain information on departmental affiliation (Roszdrav, the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, etc.) and functional affiliation (clinical).
Educational edition
Shkor Nadezhda Mikhailovna
Health Economics and Management
Examination of permanent disability
Permanent disability- long-term or permanent disability or significant disability caused by chronic disease(trauma, anatomical defect), leading to a pronounced dysfunction of the body. Depending on the degree of permanent incapacity for work, disability is established through a medical and social examination.
Medical and social expertise(ITU ) - determination of the needs of the examined person in measures of social protection based on an assessment of the disabilities caused by persistent disorder of the body's function.
In Russia, a three-stage system of federal state institutions of the ITU has been created, which includes the Federal Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise, the Main Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise, as well as the Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise in municipalities, which are branches of the main bureaus.
Citizens who have persistent disabilities and disabilities and who need social protection are sent to the ITU, according to the conclusion of the medical commission when:
Obvious unfavorable clinical and labor prognosis, regardless of the timing of temporary disability, but no later than 4 months from the date of its onset;
Favorable clinical and labor prognosis with temporary disability lasting over 10 months (in some cases: conditions after injuries and reconstructive operations, in the treatment of tuberculosis - over 12 months);
The need to change the vocational rehabilitation program for working disabled people in the event of a worsening clinical and work prognosis, regardless of the group of disability and the timing of temporary disability.
Citizen goes to medical and social expertise an organization that provides him with medical and preventive care (a body that provides pensions, a body for social protection of the population), after carrying out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures in the presence of data confirming a persistent violation of body functions caused by diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects. At the same time, in the "Direction for medical and social expertise" (f. 088 / y-06), data on the state of a citizen's health is indicated, reflecting the degree of dysfunction of organs and systems, the state of the body's compensatory capabilities, as well as the results of the rehabilitation measures taken.
If an organization that provides medical and preventive care has refused a citizen to be sent to the ITU, he is given a certificate, on the basis of which he has the right to apply to the bureau on his own. The bureau's specialists conduct an examination of a citizen and, based on its results, draw up a program of additional examination and rehabilitation measures, after which they consider the question of whether he has disabilities
A citizen recognized as a disabled person is issued a certificate confirming the fact of establishing a disability, indicating the disability group and the degree of restriction (or without restriction) of the ability to work, as well as an individual rehabilitation program.
A citizen who is not recognized as a disabled person, at his request, is issued a certificate of the results of the ITU.
A citizen can appeal against a decision of the Bureau by submitting a written application to a higher authority: the Main Bureau or the Federal Bureau of ITU. A citizen can appeal against decisions made in the ITU bureau (three instances) in court in accordance with the procedure established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
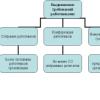
Disability
Disability indicators are an important medical and social indicator public health. Handicapped (lat. invalidus- weak, infirm) it is considered to be a person who has a health disorder with a persistent disorder of the body's functions, caused by diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects, leading to a limitation of life and necessitating his social protection.
In 2013. in the Russian Federation, 13.2 million people with disabilities were registered, including 574.4 thousand children with disabilities. Annually, for the first time, about 1.5 million people are recognized as disabled.
Recognition of a person as a disabled person is carried out on the basis of a comprehensive assessment of his health status based on an analysis of his clinical, functional, social, professional, labor and psychological data and only when conducting a medical and social examination.
Depending on the degree of limitation of life activity,
caused by a persistent disorder of the body's functions resulting from diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects, a person recognized as a disabled person is assigned a disability group I, II or III, and a child under the age of 18 is assigned the category “disabled child”.
Criteria for determining disability
The criterion for determining I group disability is a social failure that requires social protection or assistance, due to health disorders with persistent, significantly pronounced dysfunction of the body, caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects, leading to a pronounced restriction of one of the categories of life or their combination.
♦ Indications for the establishment of I group of disability:
Inability to self-service or complete dependence on others;
Inability to move independently and the need for constant help from others;
Inability to orientate (disorientation);
Inability to communicate;
Inability to control your behavior.
The criterion for establishing II group disability is a social failure that requires social protection or assistance, due to health disorders with persistent severe disorders of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of trauma or defects, leading to a pronounced restriction of one of the categories of life activity or their combination.
The ability to self-service with partial help from others and the use of assistive devices;
Ability to move independently using assistive devices and (or) with the help of other persons;
Inability to work or the ability to perform work in specially created conditions with the use of aids and (or) a specially equipped workplace, with the help of other persons;
Learning disability or ability to learn only in special educational institutions or special programs at home;
The ability to orientate in time and space, requiring the help of others;
Ability to communicate using assistive devices and / or with the help of others;
A progressive decrease in criticism in relation to one's own behavior and the environment with the possibility of partial correction only with the regular help of others.
The criterion for determining III group disability is a social deficiency that requires social protection or assistance, due to health problems with persistent insignificantly or moderately severe disorders of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of injuries or defects leading to a mild or moderate restriction of one of the categories of life activity or their combination.
♦ Indications for establishing the II group of disability:
Self-service ability using assistive devices;
The ability to move independently with a longer investment of time, fragmentation of execution and a reduction in distance;
Ability to study in educational institutions general type subject to a special regime of the educational process and (or) using special methods and training regime, with the help of other persons (except for training personnel);
The ability to self-orientate only in a familiar situation, provided that assistive devices are used;
The ability to communicate, characterized by a decrease in speed, a decrease in the volume of assimilation, reception and transmission of information.
When establishing a disability group, they simultaneously determine the degree of restriction of his ability to work(III, II or I degree of restriction), or a group of disability is established without limiting the ability to work.
When assessing the degree of restriction of the ability to work, determine the ability to work in normal production conditions, in specially created conditions, or the inability to work.
Depending on the circumstances of the onset of disability during the medical and social examination, it is determined the following reasons disability.
1. Disability due to general illness It is the most common reason disability, with the exception of cases directly related to occupational diseases, work injury, military injury, etc.
2. Disability due to work injury is established for citizens whose disability has occurred as a result of damage to health associated with an accident at work.
3. Disability due to occupational disease is established for citizens whose disability has occurred as a result of acute and chronic occupational diseases.
4. Disability since childhood: a person under the age of 18 who is recognized as a disabled person is assigned the status of a “disabled child”; upon reaching the age of 18 years and older, these persons are determined to be “disabled since childhood”.
5. Disability among former military personnel established in case of diseases and injuries associated with the performance of military duties.
6. Disability due to radiation accidents is established for citizens whose disability has occurred as a result of the elimination of accidents at Chernobyl nuclear power plant, PA "Mayak", etc.
A person recognized as a disabled person is issued a certificate confirming the fact of establishing a disability, indicating the disability group and the degree of limitation of the ability to work, or indicating the group of disability without limiting the ability to work.
In order to dynamically monitor the state of health and predict the development of compensatory and adaptive capabilities of disabled people, they are systematically reexamined.
Disabled persons of II and III groups undergo re-examination annually, invalids of group I - once every 2 years. Despite the fact that today about 30% of disabled people have an indefinite certificate of disability, such a frequent re-examination is often unreasonable and causes criticism from patients, in connection with which, since 2008, the indications for indefinite recognition of a person as a disabled person have been expanded. In accordance with the new rules, citizens are assigned a disability group without specifying a re-examination period, and citizens under the age of 18 are assigned a category “disabled child” in the following cases:
No later than 2 years after the initial recognition of a disabled person (establishment of the category of “disabled child”) of a citizen who has diseases, defects, irreversible morphological changes, dysfunctions of organs and body systems listed in a special List approved by a resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation;
Not later than 4 years after the initial recognition of a citizen as a disabled person (establishment of the category of "disabled child"), when it is revealed that it is impossible to eliminate or reduce the degree of restriction of a citizen's vital activity caused by persistent irreversible morphological changes, defects and dysfunctions of organs and body systems during the implementation of rehabilitation measures.
Establishing a disability group without specifying a term
in the absence of positive results of rehabilitation measures carried out to the patient before his referral to a medical and social examination. At the same time, it is necessary that the direction contains data on the absence of positive results of such rehabilitation measures.
Rehabilitation of the disabled
For a citizen recognized as a disabled person, the specialists of the bureau who carried out medical and social expertise are developing individual rehabilitation program (IPR), which is a list of rehabilitation measures aimed at restoring the abilities of a disabled person to household, social and professional activity in accordance with the structure of his needs, the range of interests, the level of aspirations, taking into account the predicted level of his somatic state, psychophysiological endurance, social status and real capabilities of the social and environmental infrastructure. The IPR defines the types, forms of recommended rehabilitation measures, their
volume, timing and performers.
Rehabilitation of the disabled- the process and system of medical, psychological, pedagogical, socio-economic measures aimed at eliminating or possibly more fully compensating for disabilities caused by health disorders with persistent disorder of body functions.
There are the following main types of rehabilitation of disabled people:
Medical rehabilitation - a type of rehabilitation aimed at restoring impaired functions or at carrying out various therapeutic and corrective measures that adapt a disabled person to life and socially useful activities.
Psychological rehabilitation- a type of rehabilitation aimed at developing an active life position and a positive work attitude in a disabled person, mainly through psychotherapy.
Vocational rehabilitation includes a set of measures for vocational guidance, vocational training and retraining, selection of an appropriate profession, provision of working conditions that meet the state of health, adaptation of the workplace to an existing defect, etc.
Social rehabilitation- the process of restoring the individual's abilities for independent social and family activities. It includes social and environmental orientation and social adaptation. Social and environmental orientation is an individual selection of available types of social and family and household activities, and social and household adaptation determines the optimal modes of social and family and household activities in specific social and environmental conditions and the adaptation of a disabled person to them.
To register cases of disability in the bureau of medical and social expertise, a 7-social security form is maintained. This form contains data on the number, composition of persons over 18 years old, first recognized as disabled, the results of re-examination of disabled people for this year, as well as indicators of medical, professional and social rehabilitation of disabled people. Similar data on children with disabilities under the age of 18 are contained in the 7-d (social security) form.
Based on the development of statistical documents, the following main ones are calculated indicators of disability of the population:
Primary disability rate;
Indicator of the structure of primary disability (by disability group);
Indicator of complete medical and vocational rehabilitation of disabled people;
The total indicator of partial medical and vocational rehabilitation of disabled people.
Primary disability rate characterizes
prevalence of cases of disability among people of working age
installed for the first time this year. The indicator is calculated by the formula:
*Note: the indicator can be calculated for individual age and sex groups, classes of diseases, nosological forms.
In the structure of primary disability of the adult population, 1st place is taken by diseases of the circulatory system (51%), 2nd - malignant neoplasms (13%), 3rd - diseases musculoskeletal system and connective tissue(eight%). These reasons account for more than 70% in the structure of all causes of primary disability in the population.

Indicator of the structure of primary disability (by disability groups) characterizes the distribution of the primary disability indicator by groups. The indicator is calculated by the formula:

In the structure of primary disability of the population of the Russian Federation in 2013, the share of disabled people of group I accounted for 9.4%, group II - 54.7%, and group III - 35.9%.
Examination of working capacity - this is a type of examination, which consists in determining the reasons, duration, degree of temporary or permanent disability of a person due to illness, injury or other reason, as well as determining the patient's need for types of medical care and social protection measures.
Naturally, the question arises, what should be understood by a person's ability to work?
Work capacity - this is a state of the human body in which the combination of physical and spiritual capabilities allows you to perform work of a certain volume and quality. A medical worker, based on the data of a comprehensive medical examination, must establish the presence or absence of a disease in a particular person. The ability to work has medical and social criteria.
Medical criteria for work ability include a timely clinical diagnosis, taking into account the severity of morphological changes, the severity and nature of the course of the disease, the presence of decompensation and its stage, complications, determination of the immediate and long-term prognosis of the development of the disease.
However, a sick person is not always disabled. For example, two people suffer from the same disease - panaritium. One of them is a teacher, the other is a cook. A teacher with a panaritium can fulfill his professional duties - he is able to work, but the cook is not, that is, he is disabled. In addition, the cause of disability does not always lie in the patient's own illness. For example, the same cook himself may be healthy, but in his family someone has contracted viral hepatitis, as a result of which the cook cannot fulfill his professional duties, that is, cook food, since he has contact with a sick viral hepatitis. Hence the disease
and disability are not identical concepts. In the presence of a disease, a person can be able to work, if the disease does not interfere with the performance of professional duties, and disabled, if their implementation is difficult or impossible.
Social criteria for work ability determine the labor prognosis for a specific disease and the conditions of his work, reflect everything that is associated with the patient's professional activity: the characteristics of the prevailing stress (physical or neuropsychic), the frequency and rhythm of work, the load on individual systems and organs, the presence of unfavorable working conditions and professional harmfulness.
Using medical and social criteria for work ability, a medical worker conducts an examination, during which the fact of a patient's disability can be established. Under incapacity for work should be understood as a condition caused by illness, injury, its consequences or other reasons, when the performance of professional work is impossible in whole or in part for a limited time or permanently. Disability can be temporary and permanent.
13.2. Examination of temporary
DISABILITY
If changes in the patient's health status are temporary, reversible, and recovery or improvement is expected in the near future, as well as restoration of working capacity, then this type of disability is considered temporary. Temporary disability (VN)- this is a state of the human body caused by illness, injury and other reasons in which functional disorders are accompanied by the impossibility of performing professional work in normal production conditions for a certain period of time, that is, they are reversible.
Distinguish between full and partial temporary disability.
Total temporary disability - this is the impossibility of performing any work for a certain period, accompanied by the need to create a special regimen and conduct treatment.
Partial temporary disability occurs in a person in relation to his usual professional activities when
maintaining the ability to perform other work with a different light duty or reduced volume.
The establishment of the fact of temporary incapacity for work is carried out on the basis of an examination and has an important legal and economic significance, since it guarantees a citizen to be released from work and receive benefits at the expense of state social insurance funds. Timely release of sick people from work is one of the most effective preventive measures to prevent complications of diseases and their chronicity.
In this way, examination of temporary disability is one of the types of medical expertise, the main purpose of which is to assess the patient's health status, the quality and effectiveness of the treatment, the ability to carry out professional activities, as well as to determine the degree and timing of temporary disability.
The examination of temporary disability is carried out in state, municipal and private health organizations.
The morbidity with temporary disability reflects the morbidity of the working population, therefore, in addition to medical and social, it also has great economic importance.
A document certifying the temporary disability of citizens and confirming their temporary release from work is certificate of incapacity for work, which is issued:
With diseases;
In case of injuries, poisoning and other conditions associated with temporary disability;
For the period of aftercare in sanatoriums;
If necessary, caring for a sick family member;
For the quarantine period;
At the time of prosthetics in a hospital;
For the period of maternity leave;
When adopting a child.
There are two ways to issue certificates of incapacity for work: centralized and decentralized. Centralized way it is more often used in large clinics, where sick leave certificates are issued at the registry or in specialized offices for the centralized issuance of sick leave certificates.
The nurse working in this office must be able to correctly fill out the passport part of the certificate of incapacity for work and the items related to exemption from work. At decentralized way a certificate of incapacity for work is drawn up and issued by the attending physician himself; a nurse helps him in filling out the passport part.
A certificate of incapacity for work, in addition to the attending physician, can be issued by paramedics and dentists medical organizations by decision of the health management body of the subject Russian Federation agreed with the regional department of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
Medical workers of the following health care institutions do not issue certificates of incapacity for work:
Ambulance institutions;
Blood transfusion facilities;
Reception departments of hospitals;
Medical and physical dispensaries;
Balneological hospitals and mud baths;
Health care institutions of a special type (centers for medical prevention, disaster medicine, forensic medical examination bureaus);
Health care institutions overseeing consumer protection and human well-being.
The issuance of certificates of incapacity for work is carried out upon presentation of a passport or a document replacing it. If a citizen works for several employers, several certificates of incapacity for work are issued for each place of work.
Control over the observance of the procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work by medical workers is carried out by the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare and social development jointly with the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
Permanent disability or disability is a permanent or long-term, complete or partial disability.
A disabled person (Latin invalidus is powerless, weak) is a person who has permanently or for a long time lost the ability to work partially or completely as a result of illness or injury.
A comprehensive study of the causes of disability, prevention of early disability, restoration and use of the residual working capacity of the population are important in relation to both assessing the health of the population and preserving labor resources.
Recognition of a person as a disabled person is carried out during a medical and social examination (MSE) based on a comprehensive assessment of his health and the degree of limitation of his life activity in accordance with the classifications and criteria approved by the Ministry of Social Protection of the Population of the Russian Federation (RF) and the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Depending on the degree of impairment of body functions and limitation of vital functions, a person recognized as a disabled person is assigned I, II or III disability group, and a person under the age of 16 is assigned a category “disabled child”.
The first group of disability is established for patients who cannot serve themselves and need constant help, care or supervision. These include not only persons with complete disability, but also those who can be adapted to certain types of work in specially created individual conditions. For example, the blind, blind-deaf, etc.
The second group of disability is established with pronounced disorders of the body's functions, which, however, do not cause complete helplessness. This group includes persons who have permanent or long-term complete disability, but who do not need constant care, as well as persons whose dysfunctions at the time of examination are not so severe, but nevertheless all types of work are contraindicated for them for a long period. due to the possibility of worsening the course of the disease under the influence of work.
The third group of disability is established with a significant decrease in working capacity, when:
* for health reasons, it is necessary to transfer to another job in another profession of lower qualifications;
* significant changes are required in working conditions in their profession, leading to a significant reduction in the volume of production activities;
* significantly limited employment opportunities due to pronounced functional disorders for persons with low qualifications or previously not employed.
In addition to the listed cases, the third and second disability groups are established regardless of the work performed if patients have defects and deformities that entail functional impairment, which are listed in a special list attached to the Instructions for determining disability groups.
The medical and social examination of a citizen is carried out at the bureau of medical and social examination (BMSE) at his place of residence or at the place of attachment to a state or municipal medical and preventive institution (LPI) of health care. If, in accordance with the conclusion of the healthcare facility, a person cannot appear at the BMSE for health reasons, the medical and social examination can be carried out at home, in the hospital where the citizen is being treated, or in absentia, on the basis of the submitted documents with his consent, or with the consent of his legal representative.
According to the Regulation on recognizing a person as a disabled person (Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 13.08.96 No. 965), the head of the BMSE appoints the composition of specialists who conduct a medical and social examination of a person and make an expert decision on recognizing a person as disabled.
A citizen, or his legal representative, has the right to involve any specialist at his own expense to participate in the medical and social examination with an advisory vote.
BMSE is obliged to familiarize a citizen in a form accessible to him with the procedure and conditions for conducting a medical and social examination ...
1. Federal Law of 24.11.1995 No. 181-FZ "On social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation" (as amended in 2015)
2. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 20.02.2006 No. 95 "On the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as a disabled person" (as amended in 2016).
3. Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated January 31, 2007 No. 77 "On approval of the form of Referral for medical and social examination by an organization providing medical and preventive care" (as revised in 2009).
4. Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated 25.12.2006 No. 874 "On approval of the form of the Referral for medical and social examination issued by the body providing pension provision, or the body of social protection of the population" (as amended in 2009).
5. The list of diseases, defects, irreversible morphological changes, dysfunctions of organs and systems of the body, in which a disability group without specifying a re-examination period (category "disabled child" until a citizen reaches the age of 18) is established for citizens no later than 2 years after the initial recognition as a disabled person (establishing the category "disabled child"). Appendix to the “Rules for recognizing a person as a disabled person” (as amended by the RF Government Decree of 07.04.2008 No. 247).
6. ORDER of December 17, 2015 N 1024n "ON CLASSIFICATIONS AND CRITERIA USED IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MEDICAL AND SOCIAL EXAMINATION OF CITIZENS BY FEDERAL STATE INSTITUTIONS OF THE MEDICAL AND SOCIAL INSTITUTIONS.
7. Clarifications of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated April 15, 2003 No. 1 "On the determination of federal government agencies medical and social examination of the causes of disability ", approved by the decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated April 15, 2003 No. 17 (as amended by the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated April 29, 2005 No. 317).
8. The order from July 31, 2015 N 528n On approval of the development and implementation of individual programs of rehabilitation or habilitation disabled, individual programs of rehabilitation or habilitation of disabled child GRANTED federal government agencies Health Social Examination, and their shape (in the red. 2016 G)
Didactic material
DISABLED RECOGNITION
1. These Rules are determined in accordance with Federal law"On social protection of disabled people in the Russian Federation" the procedure and conditions for recognizing a person as disabled. Recognition of a person (hereinafter referred to as a citizen) as a disabled person is carried out by federal state institutions of medical and social expertise: the Federal Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise (hereinafter referred to as the Federal Bureau), the main bureaus of medical and social expertise (hereinafter referred to as the main bureaus), as well as the bureau of medical and social expertise in cities and regions (hereinafter referred to as bureaus), which are branches of the main bureaus.
2. Recognition of a citizen as a disabled person is carried out during a medical and social examination based on a comprehensive assessment of the state of the citizen's body on the basis of an analysis of his clinical and functional, social, household, professional, labor and psychological data using classifications and criteria approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation. Federation.
3. Medical and social expertise is carried out to establish the structure and degree of restriction of the life of a citizen (including the degree of restriction of the ability to work) and his rehabilitation potential.
4. The specialists of the bureau (main bureau, Federal Bureau) are obliged to familiarize the citizen (his legal representative) with the procedure and conditions for recognizing a citizen as a disabled person, as well as provide explanations to citizens on issues related to the establishment of disability.
II. Conditions for recognizing a citizen as a disabled person
5. The conditions for recognizing a citizen as a disabled person are:
a) health disorder with persistent disorder of body functions caused by diseases, consequences of trauma or defects;
b) limitation of life activity (complete or partial loss by a citizen of the ability or ability to carry out self-service, independently move, navigate, communicate, control his behavior, study or engage in labor activity);
c) the need for social protection measures, including rehabilitation.
6. The presence of one of the conditions specified in paragraph 5 of these Rules is not a sufficient basis for recognizing a citizen as a disabled person.
7. Depending on the degree of disability due to persistent disorder of body functions resulting from diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects, a citizen recognized as a disabled person is assigned I, II or III disability group, and a citizen under the age of 18 - the category "child -disabled person".
8. When establishing a disability group for a citizen, it is simultaneously determined in accordance with the classifications and criteria provided for in paragraph 2 of these Rules, the degree of restriction of his ability to work (III, II or I degree of restriction) or the disability group is established without restricting the ability to work.
9. Disability of the I group is established for 2 years, for the II and III groups - for 1 year.
The degree of limitation of the ability to work (no limitation of the ability to work) is established for the same period as the disability group.
11. In the event that a citizen is recognized as a disabled person, the date of the establishment of disability shall be the day when the citizen's application for a medical and social examination is received by the bureau.
12. Disability is established before the 1st day of the month following the month for which the next medical and social examination of the citizen (re-examination) is scheduled.
13. Citizens are assigned a disability group without specifying the period of re-examination, and citizens under 18 years old - the category "disabled child" until a citizen reaches the age of 18:
no later than 2 years after the initial recognition of a disabled person (establishment of the category "disabled child") of a citizen with diseases, defects, irreversible morphological changes, dysfunctions of organs and body systems according to the list according to the appendix;
no later than 4 years after the initial recognition of a citizen as a disabled person (establishment of the category of "disabled child") in the event of the impossibility of eliminating or reducing the degree of limitation of the citizen's life during the implementation of rehabilitation measures, caused by persistent irreversible morphological changes, defects and dysfunctions of organs and systems of the body ( except for those specified in the appendix to these Rules).
Establishment of a disability group without specifying a re-examination period (category "disabled child" until a citizen reaches the age of 18) can be carried out upon initial recognition of a citizen as a disabled person (establishment of the category "disabled child") on the grounds specified in paragraphs two and three of this paragraph, in the absence of positive results of rehabilitation measures carried out to a citizen before he is sent for a medical and social examination. At the same time, it is necessary that in the direction for a medical and social examination issued to a citizen by an organization that provides him with medical and preventive care and sent him for a medical and social examination, or in medical documents in the case of sending a citizen for a medical and social examination in accordance with paragraph 17 of these Rules contained data on the absence of positive results of such rehabilitation measures.
Citizens who have applied to the bureau on their own in accordance with paragraph 19 of these Rules, a disability group without specifying a re-examination period (category "disabled child" until a citizen reaches the age of 18) can be established upon initial recognition of a citizen as a disabled person (establishing the category "disabled child" ) in the absence of positive results of the rehabilitation measures assigned to him in accordance with the specified paragraph.
(Clause 13 as amended by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 07.04.2008 N 247)
13.1. Citizens who have been assigned the category "disabled child", upon reaching the age of 18, are subject to re-certification in the manner prescribed by these Rules. In this case, the calculation of the terms provided for in paragraphs two and three of clause 13 of these Rules is carried out from the date of establishing a disability group for the first time after reaching the age of 18 years.
(Clause 13.1 was introduced by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 07.04.2008 N 247)
14. If a citizen is recognized as a disabled person, a general illness, work injury, occupational disease, childhood disability, childhood disability due to injury (concussion, injury) associated with hostilities during the Great Patriotic War, military injury, illness received during military service, disability associated with the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, the consequences of radiation exposure and direct participation in the activities of special risk units, as well as other reasons established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In the absence of documents confirming the fact of an occupational disease, work injury, military injury or other circumstances stipulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation that are the cause of disability, a general disease is indicated as the cause of disability. In this case, the citizen is assisted in obtaining these documents. Upon submission of the relevant documents to the bureau, the reason for the disability changes from the date of submission of these documents without additional examination of the disabled person.
III. The procedure for sending a citizen
for medical and social expertise
15. A citizen is sent for a medical and social examination by an organization that provides treatment and prophylactic assistance, regardless of its organizational and legal form, a body that provides pensions, or a body for social protection of the population.
16. An organization providing medical and preventive care sends a citizen for a medical and social examination after carrying out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures in the presence of data confirming persistent dysfunction of the body caused by diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects.
At the same time, in the direction of a medical and social examination, the form of which is approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation, data on the state of the citizen's health are indicated, reflecting the degree of dysfunction of organs and systems, the state of the body's compensatory capabilities, as well as the results of the rehabilitation measures taken.
17. The body carrying out pensions, as well as the body of social protection of the population, has the right to send for a medical and social examination of a citizen who has signs of limitation of life and needs social protection, if he has medical documents, confirming dysfunctions of the body due to diseases, the consequences of injuries or defects.
The form of the corresponding referral for medical and social expertise, issued by the body providing pension provision, or the body of social protection of the population, is approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
18. Organizations providing medical and preventive care, bodies providing pension provision, as well as bodies of social protection of the population are responsible for the accuracy and completeness of the information specified in the direction for medical and social expertise, in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
19. If the organization providing medical and preventive care, the body providing pension provision, or the body of social protection of the population refused to send a citizen for a medical and social examination, he is issued a certificate, on the basis of which the citizen (his legal representative) has the right to apply in the office yourself.
The bureau's specialists conduct an examination of a citizen and, based on its results, draw up a program for an additional examination of a citizen and conduct rehabilitation measures, after which they consider the question of whether he has disabilities.
IV. The procedure for conducting medical and social
citizen examination
20. Medical and social examination of a citizen is carried out at the office at the place of residence (at the place of stay, at the location of the pension file of a disabled person who has left for permanent residence outside the Russian Federation).
21. In the main bureau, a medico-social examination of a citizen is carried out in case of an appeal against the decision of the bureau, as well as in the direction of the bureau in cases requiring special types of examination.
22. In the Federal Bureau, a medico-social examination of a citizen is carried out in case of an appeal against the decision of the main bureau, as well as in the direction of the head bureau in cases requiring particularly complex special types of examination.
23. Medical and social examination can be carried out at home if a citizen cannot appear at the bureau (main bureau, Federal Bureau) for health reasons, which is confirmed by the conclusion of the organization providing medical and preventive care, or in the hospital where the citizen is at treatment, or in absentia by decision of the relevant bureau.
24. Medical and social examination is carried out at the request of a citizen (his legal representative).
The application is submitted to the office in writing with the attachment of a referral for a medical and social examination issued by an organization providing treatment and prophylactic assistance (a body that provides pensions, a body for social protection of the population), and medical documents confirming a health disorder.
25. Medical and social examination is carried out by specialists of the bureau (main bureau, Federal bureau) by examining a citizen, studying the documents submitted by him, analyzing social, everyday, professional, labor, psychological and other data of a citizen.
26. When carrying out a medical and social examination of a citizen, a protocol is kept.
27. Representatives of state extra-budgetary funds, the Federal Service for Labor and Employment, as well as specialists of the relevant profile (hereinafter referred to as consultants) can participate in the medical and social examination of a citizen at the invitation of the head of the bureau (main bureau, Federal Bureau).
28. The decision to recognize a citizen as a disabled person or to refuse to recognize him as a disabled person is taken by a simple majority of votes of specialists who have carried out a medical and social examination, on the basis of a discussion of the results of his medical and social examination.
The decision is announced to a citizen who has undergone a medical and social examination (his legal representative), in the presence of all specialists who have conducted a medical and social examination, who, if necessary, provide explanations on it.
29. Based on the results of a medical and social examination of a citizen, an act is drawn up, which is signed by the head of the relevant bureau (main bureau, Federal Bureau) and the specialists who made the decision, and then certified by the seal.
The conclusions of the consultants involved in the medical and social examination, the list of documents and the basic information that served as the basis for the decision, are entered into the act of the medical and social examination of the citizen or attached to it.
The procedure for drawing up and the form of an act of medical and social examination of a citizen is approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
The shelf life of the certificate of medical and social examination of a citizen is 10 years.
30. When conducting a medico-social examination of a citizen in the main bureau, an act of a medico-social examination of a citizen with the attachment of all available documents is sent to the main bureau within 3 days from the date of the medical and social examination in the bureau.
When conducting a medico-social examination of a citizen in the Federal Bureau, an act of a medico-social examination of a citizen with the attachment of all available documents is sent to the Federal Bureau within 3 days from the date of the medical and social examination in the main bureau.
31. In cases requiring special types of examination of a citizen in order to establish the structure and degree of limitation of life activity (including the degree of limitation of the ability to work), rehabilitation potential, as well as obtaining other additional information, an additional examination program may be drawn up, which is approved by the head of the relevant bureau (main bureau, federal bureau). This program is brought to the attention of a citizen undergoing a medical and social examination in a form accessible to him.
The additional examination program may provide for the conduct of the necessary additional examination in a medical, rehabilitation organization, obtaining an opinion from the main bureau or the Federal Bureau, requesting the necessary information, conducting an examination of the conditions and nature of professional activity, the social and living situation of a citizen and other measures.
32. After receiving the data provided for by the program of additional examination, the specialists of the relevant bureau (main bureau, Federal bureau) make a decision on recognizing a citizen as a disabled person or on refusing to recognize him as a disabled person.
33. In case of refusal of a citizen (his legal representative) from additional examination and submission of the required documents, the decision to recognize the citizen as a disabled person or to refuse to recognize him as disabled is made on the basis of the available data, about which a corresponding entry is made in the act of medical and social examination of the citizen.
34. For a citizen recognized as a disabled person, the specialists of the bureau (main bureau, federal bureau) who performed medical and social expertise develop an individual rehabilitation program, which is approved by the head of the relevant bureau.
35. An extract from the act of medical and social examination of a citizen recognized as a disabled person is sent by the relevant bureau (main bureau, Federal Bureau) to the body that provides his pension provision, within 3 days from the date of the decision on recognizing the citizen as a disabled person.
The procedure for drawing up and the form of discharge are approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
Information about all cases of recognition as disabled persons liable for military service or citizens of conscription age is submitted to the bureau (main bureau, federal bureau) to the corresponding military commissariats.
36. A citizen recognized as a disabled person is issued a certificate confirming the fact of establishing a disability, indicating the disability group and the degree of limitation of the ability to work, or indicating the group of disability without limiting the ability to work, as well as an individual rehabilitation program.
The procedure for the preparation and form of the certificate and individual program rehabilitation is approved by the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
A citizen who is not recognized as a disabled person, at his request, is issued a certificate of the results of a medical and social examination.
37. A citizen who has a document on temporary disability and is recognized as a disabled person, the group of disability and the date of its establishment shall be entered in the specified document.
V. Procedure for re-examination of a disabled person
38. Re-examination of a disabled person is carried out in the manner prescribed by Sections I - IV of these Rules.
39. Re-examination of disabled persons of group I is carried out once every 2 years, disabled persons of groups II and III - once a year, and disabled children - 1 time during the period for which the child is assigned the category of "disabled child".
Re-examination of a citizen whose disability has been established without specifying the period of re-examination can be carried out at his personal application (application of his legal representative), either by the direction of an organization providing medical and preventive care in connection with a change in his state of health, or by the main bureau, the Federal Bureau control over the decisions taken by the bureau, respectively, by the main bureau.
40. Re-examination of a disabled person may be carried out in advance, but not more than 2 months before the expiration of the established period of disability.
41. Re-examination of a disabled person before the established deadline is carried out at his personal application (application of his legal representative), or by the direction of the organization providing medical and preventive care in connection with a change in the state of health, or when the main bureau, the Federal Bureau of Control over the decisions made respectively bureau, main bureau.
Vi. Procedure for appealing against decisions of the bureau,
Head Office, Federal Bureau
42. A citizen (his legal representative) can appeal against the decision of the bureau to the main bureau within a month on the basis of a written application submitted to the bureau that conducted the medical and social examination, or to the main bureau.
The bureau that carried out the medical and social examination of the citizen, within 3 days from the date of receipt of the application, sends it with all the available documents to the main bureau.
43. The main bureau, no later than 1 month from the date of receipt of the citizen's application, conducts his medical and social examination and, on the basis of the results obtained, makes an appropriate decision.
44. In the event that a citizen appeals against the decision of the main bureau, the chief expert on medical and social expertise for the relevant constituent entity of the Russian Federation, with the consent of the citizen, may instruct another staff of specialists from the main bureau to conduct his medical and social expertise.
45. The decision of the main bureau can be appealed against within a month to the Federal Bureau on the basis of an application submitted by the citizen (his legal representative) to the main bureau that carried out the medical and social examination, or to the Federal Bureau.
The Federal Bureau, no later than 1 month from the date of receipt of the citizen's application, conducts his medical and social examination and, based on the results obtained, makes an appropriate decision.
46. Decisions of the bureau, the main bureau, the Federal Bureau may be appealed in court by a citizen (his legal representative) in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.