Academy Department “Public health and health care. Criteria for determining the ability to work Head of health care facility
Chapter 10 Fundamentals of Expertise of Work Ability
The concept of working capacity
Work capacity- a set of physical and spiritual capabilities of a person (depending on the state of his health), allowing him to engage in labor activities. The medical criterion for work capacity is the presence of a disease, its complications and prognosis.
Medical and social criteria should always be clearly defined and reflected in the patient's outpatient card.
Medical criterion is leading in establishing the fact of incapacity for work. However, it is not always the disease that is a sign of disability.
Examination of working capacity
The main task of the examination of the ability to work is to determine the ability of a given person to fulfill his professional duties, with the obligatory consideration of medical and social criteria. Besides, the tasks of the medical examination of the ability to work include:
determining the treatment and regimen that are necessary to restore and improve human health;
determination of the degree and duration of incapacity for work due to illness, accident or other reasons;
identification of long-term or permanent disability and referral of such patients to the medical and social expert commission.
By type, temporary work ability can be:
pregnancy and childbirth
adoption from a maternity hospital
Spa treatment
for the period of medical rehabilitation
quarantine
for prosthetics
caring for a sick family member
when switching to light work
disease
Temporary disability by nature is divided into: full and partial.
Complete incapacity for work- this is the impossibility of performing any work by a person due to illness and the need for a special treatment regimen.
Partial incapacity for work- this is incapacity for work in one's profession while maintaining the ability to perform other work. If a person can work in lighter conditions or perform a smaller amount of work, then he is considered partially disabled.
When examining a disability, a doctor sometimes has to meet with manifestations of aggravation and simulation.
Aggravation- patient exaggeration of the symptoms of a really existing disease. With active aggravation, the patient takes measures to deteriorate his health or prolong the disease.
At passive aggravation it is limited to exaggerating individual symptoms, but does not accompany them with actions that interfere with the treatment.
Pathological aggravation typical for mental patients (hysteria, psychopathy, etc.), being one of the manifestations of these diseases.
Simulation- a person's imitation of the symptoms of a disease that he does not have.
The concept of a certificate of incapacity for work
Documents certifying temporary disability and confirming temporary release from work (study) are certificate of incapacity for work(sick leave) and, in some cases, reference, fixed or freeform.
Functions of the certificate of incapacity for work:
legal - certifies the right to be released from work for a certain period
statistical - is an accounting document for reporting and analyzing the incidence of temporary disability
financial is a document that gives the right to receive social insurance benefits in accordance with current legislation
Functions of the certificate of incapacity for work:
legal
statistical
Forms of certificates of incapacity for work are documents of strict accountability. They should be stored in fireproof cabinets in rooms that should be sealed outside of working hours. All health authorities and treatment-and-prophylactic institutions are required to keep accurate quantitative records of the availability, receipt and consumption of forms of sick leave. If a patient loses a certificate of incapacity for work, a duplicate is issued by the institution that issued the certificate of incapacity for work, upon presentation of a certificate from the place of work stating that this time has not been paid for with benefits. Disability certificates are issued to patients and patients upon presentation of their identity document.
Features of issuing a certificate of incapacity for work
There are two ways to issue certificates of incapacity for work:
centralized
decentralized.
Centralized The way of issuing a certificate of incapacity for work is more common in large polyclinics, where a nurse is located in the registry or in a separate office to issue a certificate of incapacity for work, who, on the basis of a doctor's certificate (coupon), writes out a certificate of incapacity for work and registers its issuance in the "Book of registration of certificates of incapacity for work."
With a decentralized system the issuance of a certificate of incapacity for work, the document is written out by the doctor himself, who receives the forms of the certificate of incapacity for work on receipt from the persons appointed by the chief doctor and responsible for keeping them.
Doctors are required to report on the expenditure of sick leave by handing over the stubs of previously received forms. Doctors are personally responsible for the safety of the received forms of sick leave.
The issuance and extension of a document certifying temporary disability is carried out by a doctor after a personal examination and is confirmed by an entry justifying the temporary release from work in the medical documentation.
All columns of the certificate of incapacity for work are filled in in clear handwriting, without errors and corrections, in ink or paste in accordance with the instructions.
The diagnosis of the disease, in order to observe medical confidentiality, is made with the consent of the patient, and in case of his disagreement, only the reason for the disability is indicated (illness, caring for a child, etc.).
Exception in the sheets of incapacity for work is put down a code in the following cases of incapacity for work:
exemption from work in connection with quarantine and bacterial carriers
injuries and poisoning in accidents at work
injuries and poisoning on the way to and from work in the performance of public duties, the duty of a citizen of the Russian Federation
trauma and poisoning in everyday life
free, which is assigned in two cases - with additional leave for tuberculosis patients or with maternity leave (prenatal and postnatal)
sick leave is prescribed for treatment in a hospital
bed - if it is impossible to visit the clinic
bed with a visit to the clinic - with this regime, the patient should mainly be in bed, but on certain days and hours he can visit the clinic
sanatorium - during treatment in sanatoriums, dispensaries, boarding houses
outpatient
nursing
Disability certificates are issued:
Russian citizens, foreign citizens, including citizens of the CIS member states, stateless persons, refugees and internally displaced persons working in enterprises, organizations and institutions of Russia, regardless of their form of ownership;
in accordance with the Agreement "On the procedure for providing medical care to citizens of the member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States";
foreign citizens of other states are issued an extract from the medical history indicating the timing of temporary disability;
citizens who have a disability or maternity leave within a month after dismissal from work for valid reasons;
citizens recognized as unemployed and registered with the territorial bodies of labor and employment;
former servicemen dismissed from military service from the Armed Forces of Russia upon the onset of disability within a month after dismissal;
when providing medical care under contracts with citizens or organizations (on a paid basis), a certificate of incapacity for work is issued on a general basis in accordance with the established procedure.
Disability certificates are not issued:
not working;
upon the onset of incapacity for work during the leave without pay;
for prosthetics in an outpatient setting;
caring for a sick family member during the next vacation;
for the period of periodic medical examinations in the occupational pathology departments of hospitals and clinics of the Research Institute of Occupational Hygiene and Occupational Diseases.
Features of the examination of temporary incapacity for work
The examination of temporary disability is organized in polyclinics if there are at least 15 doctors in their staff. The expertise includes the chairman - chief physician or (in large medical institutions) his deputy for medical and labor expertise, the head of the relevant department and the attending physician. If necessary, the heads of specialized offices can be involved in consulting patients. The specific composition of the commission is appointed by the head of the medical institution.
Doctors on the commission decide the following issues:
resolves complex and conflicting issues of medical and labor expertise;
authorizes the extension of the certificate of incapacity for work for more than 30 days and carries out systematic control over the validity and correctness of their issuance;
issues an opinion on the need to transfer to another job, release from work on the night shift, etc.;
issues extra pay certificates of incapacity for work in case of temporary transfer to another job for patients with tuberculosis and occupational diseases;
issues certificates of incapacity for work for spa treatment, as well as for special treatment in another city;
directs patients to medical and social expertise.
Functions of the attending physician during the examination of temporary disability:
establishes the fact of temporary incapacity for work of the sick person, taking into account the nature of his work and working conditions;
identifies possible cases of simulation and aggravation;
issues a certificate of incapacity for work individually and at a time for up to 10 calendar days and extends it individually for up to 30 calendar days;
registers in the relevant documents anamnestic and objective data that served as the basis for issuing a certificate of incapacity for work;
controls the exact implementation of medical appointments by the patient and the prescribed regimen;
identifies signs of disability;
promptly directs the patient for consultation to the head of the department and to the clinical expert commission to resolve the issue of further treatment and extension of the certificate of incapacity for work or referral of the patient to a medical and social examination.
Duties of the head of the department during temporary examination of incapacity for work:
The head of the department during the examination of temporary disability is responsible:
for the setting and quality of the examination in the department;
provides consultations to treating doctors on diagnostics, treatment and employment of patients;
authorizes the extension of sick leave beyond 30 days;
carries out selective control over the initially issued certificates of incapacity for work;
controls the timeliness and completeness of examination, diagnosis and treatment of patients;
controls the correctness of the issuance, execution, extension and closing of certificates of incapacity for work;
carries out organizational and methodological guidance and control over the work of attending physicians in the study and prevention of morbidity with temporary disability and disability;
together with the attending physician, issues a certificate of incapacity for work for the entire period of stay in the inpatient department upon discharge from it.
The position of the deputy chief physician for the examination of temporary disability is established when the number of posts of outpatient doctors due to the polyclinic is at least 25.
Duties of the deputy chief physician for examination of incapacity for work:
organizes and supervises the activities of attending physicians and heads of departments on issues of medical labor expertise;
examines complaints from the public on expert examination and takes the necessary measures;
is the chairman of the commission;
quarterly organizes medical conferences on morbidity and errors in the examination of temporary work ability;
If in medical institution there is no position of the deputy chief physician for the examination of temporary disability, then his functional duties are performed by the chief physician of this medical institution.
Issuance of a certificate of incapacity for work in case of illness,
trauma or abortion
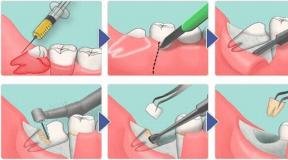
A certificate of incapacity for work is issued to a patient at work for a period from the onset of the disease to the restoration of working capacity or the onset of permanent incapacity for work (disability). In case of abortion surgery, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued from the first day for the entire period of incapacity for work, but not less than 3 days, including with a mini-abortion.
In case of diseases and injuries, the attending physician issues a certificate of incapacity for work at a time for up to 10 calendar days and extends it individually for up to 30 calendar days, taking into account the approximate terms of temporary incapacity for work for various diseases and injuries approved by the Ministry of Health of Russia.
Features of drawing up a certificate of incapacity for work
Citizens outside permanent place residence (business trip, vacation, etc.), a certificate of incapacity for work is issued (extended) by the attending physician who has established the fact of incapacity for work, with the permission of the administration of the medical and prophylactic institution, taking into account the days required to travel to the place of residence. Such a certificate of incapacity for work is stamped with a stamp (round) stamp of a medical institution.
When a temporarily disabled person who has a certificate of incapacity for work leaves the place of permanent residence, its extension in another place is allowed only if there is a conclusion of the attending and chief physician or the clinical expert commission on the possibility of leaving.
Documents confirming the temporary disability of Russian citizens during their stay abroad, upon their return, must be replaced with a certificate of incapacity for work by the attending physician with the approval of the administration of the medical institution.
In the event that a disease or injury that caused temporary disability was the result of alcoholic, narcotic, non-narcotic intoxication, the certificate of incapacity for work is issued with a corresponding note about the fact of intoxication in the medical history (outpatient card) and in the certificate of incapacity for work.
In case of temporary incapacity for work of women on parental leave, or persons caring for a child who work part-time or at home, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued on a general basis.
Citizens sent by a court decision for a forensic medical or forensic psychiatric examination, recognized as incapable of work, are issued a certificate of incapacity for work from the date of admission for examination.
For outpatient treatment of patients for the period of invasive methods of examination and treatment (endoscopic studies with biopsy, chemotherapy using the intermittent method, hemodialysis, etc.), a certificate of incapacity for work, by the decision of the clinical expert commission, may be issued intermittently, on the days of arrival at a medical institution ... In these cases, the days are indicated on the certificate of incapacity for work procedures, and release from work is made only for these days.
In the event of temporary disability during the period of unpaid leave, maternity leave, partially paid parental leave, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued from the date of the end of the said leave in case of continuing disability.
In case of temporary incapacity for work that has arisen during the period of the next annual leave, including during sanatorium treatment, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued in the manner prescribed by the Instruction.
Citizens who independently apply for advice, undergo research in outpatient and inpatient institutions in the direction of military commissariats, investigative bodies, prosecutors and the court, are issued certificates of arbitrary form.
In case of illness of students and pupils of secondary and higher educational institutions, a certificate of the established form is issued to release them from studies.
Terms of issuance of a certificate of incapacity for work for pregnancy and childbirth
For pregnancy and childbirth, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued by an obstetrician-gynecologist, and in its absence - by a doctor conducting a general appointment for the following periods:
in the absence of complications from 30 weeks of pregnancy lasting 140 calendar days (70 days before delivery and 70 days after delivery)
with multiple pregnancies - from 28 weeks of gestation to 180 days
in case of complicated childbirth, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued for an additional 16 calendar days. In these cases, the total duration of prenatal and postnatal leave is 156 calendar days (70 + 16 + 70)
Features of issuing a certificate of incapacity for work for pregnancy and childbirth:
For childbirth that occurs before 30 weeks of pregnancy and the birth of a live child, a certificate of incapacity for work for pregnancy and childbirth is issued by a medical and preventive institution where the birth took place for 156 calendar days, and in the case of a stillbirth or his death within the first 7 days after birth - for 86 calendar days (70 + 16).
When pregnancy occurs while a woman is on partially paid leave or additional leave without retention wages for child care, a certificate of incapacity for work is issued on a general basis.
If a pregnant woman is registered with a medical institution when the pregnancy is up to 12 weeks, she is issued a certificate that is attached to the certificate of incapacity for work for pregnancy and childbirth and is paid at the rate of 50% of the minimum wage along with a certificate of incapacity for work (one-time childbirth allowance) ...
In the event that a woman, for some reason, did not use her right to timely registration of maternity leave or in the event of premature birth, a certificate of incapacity for work for the entire period of maternity leave is issued by an antenatal clinic or a maternity hospital. At the same time, the maternity clinic and the maternity hospital do not issue a certificate of incapacity for work.
For a woman who has adopted newborn baby, the certificate of incapacity for work is issued by the hospital at the place of his birth for 70 calendar days from the date of birth.
During the operation "embryo replanting" a certificate of incapacity for work is issued by the operating doctor for the period from the moment of hospitalization until the fact of pregnancy is established.
Features of issuing a certificate of incapacity for work in case of complicated childbirth:
Currently under the term "Complicated labor" means the following conditions:
multiple births
childbirth that was accompanied or immediately preceded by severe nephropathy (kidney disease), preeclampsia, eclampsia
childbirth accompanied by the following obstetric operations ( caesarean section and other gluttony during childbirth, classical or combined rotation of the fetus on the pedicle, the imposition of obstetric forceps, extraction of the fetus using a vacuum extractor, fruit-destroying operations, manual separation of the placenta, manual or instrumental examination of the uterine cavity)
childbirth accompanied by significant blood loss, causing secondary anemia
childbirth accompanied by a rupture of the cervix of the III degree, rupture of the perineum of the III degree, divergence of the bottom articulation
childbirth complicated by postpartum diseases: endometritis, thrombophlebitis, inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum and cellulose, sepsis, purulent mastitis
childbirth in women suffering from diseases of the heart and blood vessels
childbirth in women with other chronic diseases (eg, chronic lung disease, amyloidosis, hepatitis)
premature birth and childbirth with an immature fetus, regardless of the gestational age, if the postpartum woman was discharged with a living child (fetal immaturity is determined by a commission-related act with a record in the history of the development of the newborn)
childbirth in women after in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer into the uterine cavity (ECOiPE)
The provision of postnatal leave for an additional 16 days (for the birth of two or more children - for 40 days) is formalized by the doctor of the antenatal clinic, polyclinic, rural medical outpatient clinic on the recommendation of the medical institution in which the birth took place. In this case, in the "exchange card of the maternity hospital, the maternity ward of the hospital" in the section "information of the maternity hospital, the maternity ward of the hospital about the postpartum woman", clause 15 "special remarks" is written: "86 (110) days postpartum leave" or "additional postnatal leave for 16 (40) days ".
In cases where a woman has temporarily left her place of permanent residence during the period of prenatal leave, a certificate of incapacity for work for an additional period of postnatal leave must be issued by the medical institution in which the birth took place, regardless of the woman's place of permanent residence.
If a complicated delivery took place outside a medical institution, then when granting postnatal leave for 86 (110) days, the attending physician may, if necessary, consult with the medical worker who took the delivery.
Ability to work - a set of physical and spiritual capabilities of a person, allowing him to engage in labor activities.
Distinguish between general (ability to work unskilled) and professional (ability to work in their own, or adequate to her, profession) working capacity.
Each of them can be complete or partial.
Disability - the inability to carry out the usual profession due to medical or social contraindications. Establishing the fact of incapacity for work has legal significance, since, according to Art. 39 and 41 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and Art. 20 Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the protection of the health of citizens, guarantees the employee the right to be released from work, free treatment under the compulsory medical insurance program and payment of benefits at the expense of social insurance funds.
Distinguish between temporary and permanent disability.
Temporary incapacity for work (TM) - temporary inability to carry out work duties due to medical reasons (illness, injury, spa treatment, prenatal and postnatal leave, prosthetics in a hospital), when health changes are reversible and recovery is expected in the near future, or significant improvement with the restoration of working capacity, as well as social factors provided for by law (caring for a sick family member, for healthy child up to 3 years old and a disabled child, quarantine, adoption from the hospital).
VN can be complete and partial.
Full VL is determined when a person, due to a disease, cannot and should not perform any work and needs a special treatment regimen. The documents confirming the temporary release from work (study) are: for employees - a certificate of incapacity for work (l / n), which serves as the basis for the appointment and payment of benefits for HI; for students - help f. 095 / y. In some cases, VN is confirmed by certificates of free form.
Partial VN - VN in their profession, while maintaining the ability to perform other work, with a different mode and volume, without disrupting the treatment process, damage to health and production. Rational employment of an employee in this case is carried out on the basis of a certificate issued by the clinical expert commission of a healthcare facility.
Persistent disability - permanent or long-term disability, when the impairment of body functions caused by a disease or injury has become irreversible (partially reversible), has led to a significant decrease in the volume of work (reduced qualifications, termination of work in normal working conditions, loss of profession), persistent social failure a person requiring measures of social assistance and protection, determined by institutions of medical and social expertise (establishing a group of disability, determining the percentage of loss of professional ability to work in accidents at work and occupational diseases, etc.).
The main criterion that differentiates VL from persistent is a favorable clinical and work prognosis, the potential reversibility of the disease process with the possibility of restoring the impaired body functions, working capacity and social activity of the patient.
Examination of the ability to work is a kind of medical examination, the main task of which is to assess the patient's health with a decision on the possibility of continuing it labor activity.
The main principles of organizing the examination of working capacity are its state nature, preventive focus and collegiality in solving all issues.
The state nature of the examination of the ability to work lies in the fact that for its implementation, the legislation defines unified bodies - health care facilities that carry out the examination of VN (if there is a license for this type of medical activity), and social protection bodies (bureau of medical and social examination) that carry out an examination of persistent loss work capacity and disability.
The preventive focus of the examination of the ability to work is the most effective implementation of medical, labor and social rehabilitation of the disabled, the main goal of which is fastest recovery work capacity and prevention of disability.
Tasks of the examination of the ability to work:
Determination of a person's ability to perform their professional duties depending on medical and social criteria;
Determination of the degree and duration of disability due to illness, accident or other reasons, timely referral of patients with signs of persistent disability (disability) to MSU;
Determination of the treatment and regimen necessary to restore and improve human health;
Determination and implementation of a plan for medical, labor and social rehabilitation of disabled people (treatment and regime necessary to restore health; rational employment of temporarily disabled people who need to ease working conditions in their profession; determination of labor recommendations for disabled people in order to use their residual working capacity);
Study of the levels, structure and causes of morbidity with temporary disability and disability, in order to reduce these indicators among the population.
Examination of VN is a type of medical examination, the main tasks of which are: assessing the patient's health with a solution to the question of whether he can continue to work, determining the timing of VN, identifying signs of persistent disability (disability) in a timely manner and referring the patient to MSU.
Medical and social examination (MSE) is a type of medical examination, the main tasks of which are: assessment of the patient's health, determination of signs of persistent limitation of life activity, establishment (if indicated) of the corresponding groups of disability and the degree of limitation of the ability to work, their reasons and timing; determination of the degree of loss of professional working capacity in case of accidents at work and occupational diseases in percentage; development individual program rehabilitation of a disabled person, as well as determining the need for a disabled person in measures of social assistance or protection.
Chapter 13. Examination of working capacity
Chapter 13. Examination of working capacity
13.1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
Examination of working capacity is a type of examination, which consists in determining the reasons, duration, degree of temporary or permanent disability of a person due to illness, injury or other reason, as well as determining the patient's need for types of medical care and social protection measures.
Naturally, the question arises, what should be understood by a person's ability to work?
Work capacity - this is a state of the human body, in which the combination of physical and spiritual capabilities allows you to perform work of a certain volume and quality. A medical worker, based on the data of a comprehensive medical examination, must establish the presence or absence of a disease in a particular person. The ability to work has medical and social criteria.
Medical criteria for work ability include timely delivered clinical diagnosis taking into account the severity of morphological changes, the severity and nature of the course of the disease, the presence of decompensation and its stage, complications, determination of the immediate and distant prognosis of the development of the disease.
However, a sick person is not always disabled. For example, two people suffer from the same disease - panaritium. One of them is a teacher, the other is a cook. A teacher with a panaritium can fulfill his professional duties - he is able to work, but the cook is not, that is, he is disabled. In addition, the cause of disability does not always lie in the patient's own illness. For example, the same chef himself may be healthy, but in his family someone has contracted viral hepatitis, as a result of which the chef cannot fulfill his professional duties, that is, engage in cooking, since he has contact with the patient viral hepatitis... Hence the disease
and disability are not identical concepts. In the presence of a disease, a person can be able to work, if the disease does not interfere with the performance of professional duties, and disabled, if their implementation is difficult or impossible.
Social criteria for work ability determine the labor prognosis for a specific disease and the conditions of his work, reflect everything that is associated with the patient's professional activity: the characteristics of the prevailing stress (physical or neuropsychic), the frequency and rhythm of work, the load on individual systems and organs, the presence of unfavorable working conditions and professional harmfulness.
Using medical and social criteria for work ability, a medical worker conducts an examination, during which the fact of a patient's disability can be established. Under incapacity for work should be understood as a condition caused by illness, injury, its consequences or other reasons, when the performance of professional work is impossible in whole or in part for a limited time or permanently. Disability can be temporary and permanent.
13.2. EXPERTISE OF THE TEMPORARY
DISABILITY
If changes in the patient's health status are temporary, reversible, and recovery or improvement is expected in the near future, as well as restoration of working capacity, then this type of disability is considered temporary. Temporary disability(VN)- this is a state of the human body caused by disease, injury and other reasons in which functional disorders are accompanied by the impossibility of performing professional work in normal production conditions for a certain period of time, that is, they are reversible.
Distinguish between full and partial temporary disability.
Total temporary disability - this is the impossibility of performing any work for a certain period, accompanied by the need to create a special regimen and conduct treatment
Partial temporary disability occurs in a person in relation to his usual professional activities when
maintaining the ability to perform other work with a different light duty or reduced volume.
The establishment of the fact of temporary incapacity for work is carried out on the basis of an examination and has an important legal and economic significance, since it guarantees a citizen to be released from work and receive benefits at the expense of state social insurance funds. Timely release of sick people from work is one of the most effective preventive measures to prevent complications of diseases, their chronicity.
Thus, examination of temporary disability is one of the types of medical expertise, the main purpose of which is to assess the patient's health status, the quality and effectiveness of the treatment, the ability to carry out professional activity, as well as determining the degree and timing of temporary disability.
The examination of temporary disability is carried out in state, municipal and private health organizations.
The incidence with temporary disability reflects the incidence of the working population, therefore, in addition to medical and social, it also has great economic importance.
A document certifying the temporary disability of citizens and confirming their temporary release from work is certificate of incapacity for work, which is issued:
With diseases;
In case of injuries, poisoning and other conditions associated with temporary disability;
For the period of aftercare in sanatoriums;
If necessary, caring for a sick family member;
For the quarantine period;
At the time of prosthetics in a hospital;
For the period of maternity leave;
When adopting a child.
There are two ways to issue certificates of incapacity for work: centralized and decentralized. Centralized way it is more often used in large clinics, where sick leave certificates are issued at the registry or in specialized offices for the centralized issuance of sick leave certificates.
The nurse working in this office must be able to correctly fill out the passport part of the certificate of incapacity for work and the items related to exemption from work. At decentralized way a certificate of incapacity for work is drawn up and issued by the attending physician himself; a nurse helps him in filling out the passport part.
A certificate of incapacity for work, in addition to the attending physician, can be issued by paramedics and dentists medical organizations by the decision of the healthcare management body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, agreed with the regional department of the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
Medical workers of the following health care institutions do not issue certificates of incapacity for work:
Ambulance institutions;
Blood transfusion facilities;
Reception departments of hospitals;
Medical and physical dispensaries;
Balneological hospitals and mud baths;
Health care institutions of a special type (centers for medical prevention, disaster medicine, forensic medical examination bureaus);
Health care institutions overseeing consumer protection and human well-being.
The issuance of certificates of incapacity for work is carried out upon presentation of a passport or a document replacing it. If a citizen works for several employers, several certificates of incapacity for work are issued for each place of work.
Control over compliance with the procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work by medical workers is carried out by the Federal Service for Supervision of Healthcare and Social Development in conjunction with the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation.
13.3. RACK EXPERTISE
DISABILITY
Permanent disability is a long-term or permanent loss of ability to work or its significant limitation caused by chronic disease(trauma, anatomical defect), leading to a pronounced dysfunction of the body. Depending on the degree of persistent disability, disability is established by conducting a medical and social examination.
Medical and Social Expertise (ITU)- This is the determination of the needs of the examined person in measures of social protection based on an assessment of the disabilities caused by a persistent disorder of the body's function. In Russia, a three-stage system of federal government agencies ITU, which includes: the Federal Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise, the main bureaus of medical and social expertise, as well as bureaus of medical and social expertise in municipalities, which are branches of the main bureaus.
Citizens with persistent disabilities and disabilities are sent to ITU and in need of social protection, according to the conclusion of the medical commission when:
Obvious unfavorable clinical and labor prognosis, regardless of the timing of temporary disability, but no later than 4 months from the date of its onset;
Favorable clinical and labor prognosis with temporary disability lasting more than 10 months (in some cases: conditions after injuries and reconstructive operations, in the treatment of tuberculosis - more than 12 months);
The need to change the vocational rehabilitation program for working disabled people in the event of a worsening clinical and work prognosis, regardless of the group of disability and the timing of temporary disability.
A citizen is sent for a medical and social examination by an organization that provides him with treatment and prophylactic assistance (a body that provides pensions, a body for social protection of the population), after carrying out the necessary diagnostic, therapeutic and rehabilitation measures in the presence of data confirming persistent dysfunction of the body due to diseases, the consequences of injury or defect-
mi. At the same time, in the "Direction for medical and social expertise" (f. 088 / y-06), data on the state of the citizen's health are indicated, reflecting the degree of dysfunction of organs and systems, the state of the body's compensatory capabilities, as well as the results of the rehabilitation measures taken.
If an organization providing medical and preventive care has refused a citizen to be sent to the ITU, he will be issued a certificate, on the basis of which he has the right to apply to the bureau on his own. The bureau's specialists conduct an examination of a citizen and, based on its results, draw up a program of additional examination (and rehabilitation measures), after which they consider the question of whether he has disabilities.
Medical and social examination is carried out at the office at the place of residence. In the main bureau, a medical and social examination is carried out in case of an appeal by a citizen of the bureau's decision, as well as in the direction of the bureau in cases requiring special types of examination. In the Federal Bureau, a medical and social examination is carried out in case of an appeal by a citizen of the decision of the main bureau, as well as in the direction of the head bureau in cases requiring particularly complex special types of examination. Medical and social examination can be carried out at home if a citizen cannot appear at the bureau for health reasons, which is confirmed by the conclusion of the organization providing medical and preventive care, or in the hospital where the citizen is being treated, or in absentia by decision of the relevant bureau. The examination is carried out at the request of the citizen, which is submitted to the bureau in writing with the attachment "Directions for medical and social examination" issued by the organization providing medical and preventive care (the body that provides pensions, the body of social protection of the population) and medical documents confirming the violation health. Medical and social examination is carried out by the bureau's specialists by examining the citizen, studying the documents submitted to him, analyzing the social, everyday, professional, labor, psychological and other data of the citizen. The decision to recognize a citizen as a disabled person or to refuse to recognize him as a disabled person is made by a simple majority of votes of specialists who have conducted a medical and social examination, on the basis of discussion
the results of his medical and social examination. The decision is announced to a citizen who has undergone a medical and social examination, in the presence of all specialists who have conducted a medical and social examination, who, if necessary, give explanations on it. Based on the results of the medical and social examination of a citizen, an act is drawn up. In cases requiring special types of examination of a citizen in order to establish the degree of limitation of life activity (including the degree of limitation of the ability to work), rehabilitation potential, as well as obtaining other additional information, an additional examination program may be drawn up, which is approved by the head of the relevant bureau. This program is brought to the attention of a citizen undergoing a medical and social examination in a form accessible to him.
After receiving the data provided for by the additional examination program, the specialists of the relevant bureau make a decision on recognizing a citizen as a disabled person or on refusing to recognize him as a disabled person. In case of refusal of a citizen from additional examination, such a decision is made by specialists on the basis of the available data, about which a corresponding entry is made in the act of medical and social examination of the citizen.
The patient's working capacity is determined by two groups of factors: medical and social.
Medical factors include correct and timely diagnosis, which is based on a comprehensive examination of the patient.
The need for a thorough all-round examination may also arise in cases where there is no correspondence between the patient's subjective feelings and the data of an objective examination. Various expert situations are possible, for example, there is a lot of subjective and little objective (such an expert situation occurs quite often). But a situation may arise when the patient (for various reasons) wants to hide the existing disease. In such cases, no complaints are made, and objective research reveals significant changes.
Clinical expert diagnosis should reflect the following components:
- the nosological form of the disease;
- its etiology;
- predominant syndromes;
- the nature of the pathological process;
- stage (if the disease has a staged course, the frequency and duration of exacerbations, if the disease has a relapsing course);
- the presence and severity of functional disorders;
- the presence and nature of complications;
- accompanying illnesses.
In determining the state of ability to work, along with medical, acquire social factors: profession and specialty of the patient, the level of qualifications, the nature and conditions of the work performed, the presence of harmful production factors, work experience, age, sex, education, place of residence, marital status, attitude to continue working, etc.
However, when conducting an examination of temporary disability, the attending physician, when assessing social factors, first of all, clarifies the nature and conditions of the work performed, determining the prevailing factor (hard or stressful or hard and stressful work), then establishes the severity of the prevailing factor. In this case, the Guidelines for the hygienic assessment of the factors of the working environment and the labor process, the criteria and classification of working conditions R 2.2.2006-05, approved by Rospotrebnadzor on July 29, 05 and put into effect on November 1, 05, are used.
Thus, a substantiated expert opinion on the state of working capacity and a correct assessment of the clinical and labor prognosis are possible only taking into account medical and social factors, the combination of which determines the practice of two main components of medical examination: examination of temporary disability and medical and social.
Most patients seeking medical help, when assessing the prognosis, medical factors prevail. Social factors prevail much less often, as a rule, with mild functional disorders... Therefore, the concepts of temporary and permanent (permanent) disability are medical and social.
Questions on the topic
1. The history of the development of social insurance in the Russian Federation. Social insurance fund, its functions.
2. The concept of working capacity, disability, classification.
3. Clinical and labor prognosis.
4. Factors affecting the ability to work. The main reasons for temporary disability.
5. Statistical form 16-VN, methods of analysis
6. Solving problems 114-117, preparing an abstract and making a presentation.
Abstract topics
1. Social protection and social Security population.
2. The state nature of social insurance and social protection of the population.
3. Legislation on social insurance and social protection of the population.
4. Interaction of bodies and institutions of health care with institutions of social insurance and social protection.
Basic
1. Lisitsyn, Yu. P. Public health and health care [Text]: textbook / Yu. P. Lisitsyn. - M .: Medicine, 2007. - S. 402–442.
2. Zakharova, E. V. Collection of tasks and independent works [Text] / E. V. Zakharova, I. L. Sizikova. - Abakan: Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Khakass State University named after N. F. Katanova ", 2014. - S. 61, 62.
Electronic media
1. Educational portal KSU named after N.F.Katanova. - URL: http://edu.khsu.ru
2. EBS "Student's Consultant" / Publishing house GEOTAR-Media. - URL: http://studmedlib.ru/
Practical lesson 19.
Organization and procedure for the examination of temporary
disability. Documents certifying VN,
the order of their registration
Relevance of the topic
Medical examination issues are encountered daily in the practice of the attending physician. Expertise is the study of special issues, for the solution of which special knowledge is required, with the making of a certain judgment. A medical examination is understood as a study conducted in accordance with the established procedure, aimed at establishing the state of health of a citizen, in order to determine his ability to carry out labor or other activities, as well as to establish a causal relationship between the impact of any events, factors and the state of health of a citizen. Thus, to resolve the issues of medical expertise, a fairly extensive amount of knowledge is required.
Lesson objectives:
- to study the procedure for organizing EVN in a medical institution;
- to learn the basic concepts and terms of the examination of temporary disability;
- to apply the acquired knowledge in practice and complete independent individual tasks.
The initial level of knowledge and skills necessary to achieve the goals: fundamentals of healthcare organization, medical statistics and informatics, computer skills at the user level
32. Definition of the concepts of "work ability" and "disability". Medical and social criteria for incapacity for work.
Work capacity - this is a state of the body in which the combination of physical and spiritual capabilities allows a person to perform work of a certain volume and quality. There are two types of its violation: temporary and permanent disability. Their differentiation is based on clinical and labor prognosis, i.e. medical and social criteria.
Medical criterion - accurate diagnosis in accordance with the accepted classification, reflecting the stage of development, clinical variant and severity of the course of the disease, phase of the disease, in case of exacerbation - the severity of the exacerbation, the degree of functional disorders, complications; accompanying illnesses.
Social criterion - the nature and working conditions of the patient, which determine the labor prognosis for a specific disease. The attending physician needs to find out and record in the medical documentation the nature and working conditions of the patient: the presence of unfavorable working conditions and occupational hazards, the organization, frequency and rhythm of work, the load on individual organs and systems, body position during work, job responsibilities and skills, qualifications.
Temporary disability - the inability of the employee to perform his work duties due to medical reasons, as well as social factors provided for by the current legislation, which are temporary, reversible, when recovery or improvement of his condition and restoration of working capacity is expected in the near future. VN can be complete and partial.
Total VN - the inability of the employee to work for a certain period and the need for treatment and compliance with the regime.
Partial VN - such a state of the body when an employee, due to illness (injury), cannot perform his usual professional activities, but without harm to health can perform another, with a different volume and mode.
Temporary disability may result from
Diseases and injuries, poisoning (other consequences of external causes);
Aftercare in sanatoriums;
Caring for a sick family member;
Quarantine;
Pregnancy and childbirth;
Child adoption;
Prosthetics in a hospital.
33. Persons with and without the right to receive a certificate of incapacity for work.
LN is issued insured disabled citizens of the Russian Federation, as well as foreign citizens permanently or temporarily residing in the territory of the Russian Federation, stateless persons, including persons whose illness or injury occurred within 30 calendar days from the date of termination of work under an employment contract, performance of official or other activities or in the period from the date of the conclusion of the employment contract until the day of its cancellation;
to citizens recognized as unemployed and registered with the territorial bodies of the Federal Service for Labor and Employment, in case of illness, injury, pregnancy and childbirth.
LN is not issued citizens not subject to social insurance:
Military personnel;
Police officers;
Employees of the FSB, FSO, UFSIN, drug control;
Pupils, students, graduate students, doctoral students;
Individual entrepreneurs, notaries, lawyers who have not entered into a voluntary social insurance agreement;
Persons under arrest and in the course of a forensic medical examination,
Able-bodied workers sent from periodic medical examinations to inpatient and outpatient examinations to find out the cause of the disease and establish its connection with occupational hazards;
Draftees sent by military registration and enlistment offices for examination to clarify fitness for military service;
Able to work for the period of examination and consultation;
While on unpaid leave, maternity leave, parental leave up to 3 years old. With the remaining VN, the LN is issued from the date of the end of the specified holidays.