Excavators - appointment and classification. Excavators. Classification, scope How to classifies excavators
The main in popularity of the machine used in construction sites for the production of earthworks, overloading bulk and lump materials and performing other works, depending on the installed additional equipment, is out of any doubt, is an excavator. Easy, reliability and impressive versatility allow him to play a dominant role almost at any construction site.
The first excavators were built in Russia as early as the early nineties of the 19th century, on the former Putilovsky factory. Until 1917, about 50 cars were issued, of which about 40 railway single-loving excavators and 10 are many-loving. When organizing the serial release of excavators was recognized to establish a number of standards that include classification and machine parameters. The first such standard (on single-loving excavators) appeared in 1933 and after radical processing was approved in the form of the GOST 518-41 standard.
Excavators are called earthmoving machines intended for digging and moving the soil, which are the main type of earthmoving loading and unloading machines.
Multual-list excavators both operations - soil digging and moving it - perform simultaneously; Single-line these operations are performed consistently, interrupting digging at the time of movement of the soil. Thus, the working time of the machine during which the soil is chosen, and the productivity of multi-loving excavators is higher than single-line. Despite this, single-loving excavators are wider as a result of their versatility, i.e. Opportunities to apply them both on earthlings and on loading and unloading works in the most severe, including rocks (with preliminary explosion), soils.
Classification of single-loving excavators
There are three main groups:
construction and universal - with a container buckets up to 3 m3, intended for the production of earthworks;
career - with buckets with a capacity from 2 to 8 m3, designed to work in careers on the development of ore and coal deposits;
running - with latch with a capacity of more than 6 m3, designed to develop upper layers of rocks (opening).
Single-sized excavators are distinguished by using them with various types of work equipment.
Universal excavators are designed to work with various types of interchangeable equipment; Direct and reverse shovel, draglin, crane arrow with a hook suspension or graon, coprom for piles, etc.
Semi-universal excavators except the main work equipment have one or two types of additional interchangeable equipment (direct shovel, reverse shovel, dragline).
Special powerful excavators have only one type of equipment, such as a straight shovel.
Singo-universal excavator is called a cyclic action machine intended for the excavation and movement of soils and other materials using one of the types of working equipment with one bucket, and to perform loading welding and other works by other types of interchangeable work equipment.
The working cycle of this common class of excavators is consisted of:
cutting operations (digging) of soil (with the simultaneous filling of the bucket),
moving the filled bucket to the place of unloading,
unloading the soil from the bucket and return the bucket in the bottom.
The duration of the working cycle depending on the power and type of excavator and the working conditions ranges from 12 to 80 seconds. The performance of the single-circuit excavator per 1 m3 of the bucket capacity, depending on the working conditions, is from 100 to 350 thousand m3 in the year, or 80-180 m3 / h. Single-line excavators are used to develop any, including the strongest and inhomogeneous, soils with large solid inclusions. To work in softer soils, single-line excavators can be supplied with buckets of increased tank. Rock breeds and mourned soils before developing one-dockovy excavator barely (usually explosion)
By the nature of the undercarriage, distinguished tracked, wheezing, walking, on w. - d. Go, floating, wheel-tracked single-loving excavators.
By type of drive - with one engine and with mixed and individual drives of all working mechanisms.
By the nature of the power plant - with the drive from the internal combustion engine (diesel, rarely carburetor and gas generator), electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic and combined.
According to the type of control - with manual, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical and mixed.
According to the type of work equipment, excavators are divided into a single-line with a rigid hinge-sliding bunch of a bucket with an arrow (direct shovel), with a rigid hinge bucket with an arrow (reverse shovel), with a flexible bucket bond with an arrow (draglin, graft, etc.).
The most common equipment direct shovels; They are equipped with excavators of any power with buckets with a capacity of up to 153 m3. Excavators with direct shovel equipment and with unloading to vehicles or dust. It is advisable to apply in the development of mineral deposits and for digging cotlings, mainly in strong, stony and rock rocks and soils, as well as in sustainable soils of Wed. fortress. The reverse shovel equipment is used to dig a narrow trench (width of 0.7 - 1.5 m and a depth of 8 m), especially with vertical walls for laying the sewage networks, oil pipelines, devices of foundations in strong and stony soils, as well as furnaces of small catlings.
Working equipment Excavator-Draglane consists of an arrow and a bucket, suspended to the arrow with the help of lifting and traction ropes. The recess of the soil dragine produces, as a rule, below the installation level of the excavator; The buckets are used in various capacities - in the rocky pre-loose rocks it is allowed to work the dragline with a bucket capacity over 10 m3. The duration of the cycle is usually 10-20 more than when using an excavator with a direct shovel. Up to 40 single-loving excavators operates with draglin equipment. Draglains having t. N. walking stroke, got the name of the stepsing draglines. The equipment of the grafe is used for loading, digging of cotlings with sheer walls, for work under water. Strugg equipment is adapted for planning work, road clothing removal, etc. Separate excavators, designed mainly for construction (with buckets with a capacity of up to 5 m3), supply various interchangeable equipment not only for earthworks, but also for mounting, lifting, loading and unloading, pile and drilling work, rolls of forest and panties etc. Such excavators are usually called universal, because they are applicable in many types of earthy and construction work. If the number of units of replaceable equipment does not exceed three (for example, a shovel, dragline, crane), the excavator is called semi-universal.
Excavators with hydraulic drive, etc. N. are widely distributed. Hydroxcavators, in which all types of working bodies are hingedly connected with a rotary platform and move using hydraulic cylinders, driven by high pressure pumps (10 - 40 MPa). In this case, hydraulic motors are usually used to transmit rotation (rotation drive). This type of single-loving excavators is made with larger ladle (up to 1.8 m3), medium (2-3 m3) and large (3.2-6 m3) containers. Basic work equipment - reverse shovel. The specific power of hydraulic excavators, depending on the working conditions (soft or strong soils) ranges from 133 to 213 kW per 1 m3 of the tank of the bucket.
Depending on the purpose, single-line excavators are divided into construction, career, career and cerpeted, and in addition, tunnel excavators, floating, etc. are distinguished.
Building excavators are the most common type of single-loving excavators: there are about 200 models produced by more than 80th party. and overseas plants. Distinguish: universal low power (bucket capacity 0.05-1.8 m3, crane lifting capacity 0.7-45 t, weight 1.5-65 tons); average power - semi-universal (bucket capacity 2-3 m3, crane load capacity 60-80 t, weight 72-105 t); High power - semi-universal (bucket capacity 3,25-6 m3, crane load capacity 100-150 t, mass 115-210 tons). The specific mass of 1 m3 containers of the bucket for strong soils is for these excavators 33-36 tons. Low power excavators often have a replaceable tracked and pneumatic chassis and a single-engine drive.
In hydraulic excavators, individual or mixed drive. Career excavators are manufactured with shovels, less often with interchangeable equipment of the dragline and crane. They are distinguished by powerful working equipment, high workflow and speeds, a short cycle of work, which causes compared to other excavators of the same sizes a greater performance when loading into vehicles, especially with strong soils. Medium excavators (bucket capacity 2-4 m3) and large (capacity of the bucket 5-20 m3) of power, weighing 76-900 T are designed to work in careers, especially in strong, pre-blown rocks and soils with loading mainly in heavy vehicles. Produced both in the form of semi-universal excavators and specials. Shovel with standard and elongated equipment for the top loading in the means of transportation on the eyebrow (excavation). Running equipment - tracked. Power equipment - electrical with an individual drive mechanisms for the system generator - engine. The specific power of the drive motor 60 is 80 kW per 1 m3 of the bucket capacity, the pressure on the soil 0.15-0.25 MPa, the speed of 0.6-1.5 km / h. Hydraulic career excavators have a bucket capacity up to 8-9 m3, models with buckets with a capacity of 12-20 m3 are being developed.
Construction and career excavators of medium and high power are designed to work mainly on quarries of non-metallic building materials. By their design, they occupy the average position between construction and career. Surveral excavators are usually manufactured with shovel equipment to move into the rear of overlap on quarries. Convered excavators with buckets with a capacity of up to 15 m3 are also used for loading into vehicles located on the rod of the work being developed. Capacity of the excavator bucket from 6 to 153 m3, weight 700-12 700 tons. Running equipment of powerful models - 4 paired caterpillars. Power equipment is the same as the career excavators. The specific mass of 45-90 tons per 1 m3 of the bucket capacity, the speed of 0.3-0.5 km / h. In addition to the mechanical shovels, draglins are used on overlapping work with arrows up to 100 m long, with a capacity of 5 to 168 m3 buckets, weighing up to 14 thousand tons. They are the main equipment for the best transportation systems for developing mineral deposits.
Tunnel and shaft excavator are used in underground conditions in the development of large cross-section when the tunnels arete, the construction of the chambers of underground structures, extrusion of minerals. Bucket capacity 0.75-1 m3, weight 16-30 tons.
Classification of excavators
Excavators are called earthmoving machines designed for digging and moving the soil. All excavators are divided into two large groups: continuous action - multi-loving and periodic (cyclic) action - single-line.
Continuous excavators of both operations - soil digging and its movement is performed simultaneously; Excavators of periodic action perform these operations sequentially, interrupting digging at the time of the movement of the soil. Thus, the working time of the machine during which the soil is chosen, more in continuous excavators and their performance is higher than the performance of periodic excavators. Despite this, single-loving excavators are wider widespread, the advantage of which is their versatility, i.e. the possibilities of application both on earthworks and in loading and unloading works and in any hard, including rocks (with preliminary explosion), soils . Multifungal excavators are used mainly when digging tranches and mining of non-metallic materials in quarries in homogeneous soils that do not have stone inclusions.
Both single-line and multi-loving excavators are land and floating.
Land excavators have a tracked, pneumatic and walking (the latter is used only in single-loving excavators) driving equipment.
Excavator mechanisms are driven by diesel engines, carburetor, steam or electric motors. The overwhelming majority of modern excavators are equipped with diesel engines and electric motors as the most economical. Less frequently apply carburetor engines.
The selection of the engine is determined by the conditions in which the excavator will work. So, on excavators working on the construction of iron and highways, that is, where the car must be relatively often transported from place to place, diesel engines. At excavators that are constantly working in the same place, for example, in careers for non-metallic materials, etc., and so on, it is advantageous to use electric motors, since electricity is the cheapest type of energy. In addition, the service is simplified and the need for permanent supply of the machine with fuel is simplified.
Therefore, diesel engines are often installed on excavators with buckets with a capacity of up to 3 m3, and electric motors are more often installed on excavators.
If all excavator mechanisms are driven from one engine, such a drive is called single-engine. If in the excavator, each mechanism (or some of the mechanisms) is driven by a separate engine (usually electric), such a drive is called multi-motor.
In the USSR, single-wheel drive excavators with a single-engine drive made with buckets with a capacity of up to 2.5-3 m3, abroad - up to 4-4.5 m3. Currently prepare for the production of excavators
with diesel-electric multi-motor drive, on which the buckets with a capacity of 1.6 m3 (E-1602) are installed. In addition, the production of excavators with a multi-intric hydraulic drive, which is used for buckets with a capacity of 0.25 m3 (E-2513 and E-2514), and the production of hydraulic excavatorosis with a bucket of 0.4-0.5 m3 is prepared.
The spread of a multi-motor drive is particularly explained by the fact that the excavator mechanisms are performed as separate units that can easily be installed when assembling machines and replaced during their repair (with an aggregate repair method). In addition, this design allows you to apply the same or almost identical (unified) nodes on different machines, which will make it possible to adjust the large-scale specialized production and reduce the range of spare parts.
To transfer traffic from the engine to work mechanisms, the following types of drive are used:
- mechanical when the movement is transmitted using shafts, gears, worm steam, chain gears;
- hydraulic volumetric, where the role of the drive is performed by hydraulic pump (one or several), oil hydrogen pumps (or 'hydraulic cylinders);
- in oil pipelines circulates fluid transmitting energy from pumps to hydraulic cells (or hydraulic cylinders), leading workers mechanisms in motion; This method is based on the property of the liquid not to compress;
- hydrodynamic, where turfs or turbo-transformers are used for energy transmission; It is usually used in combination with mechanical for smooth operation of mechanisms and automatic control of the movement speed, depending on the load value (with an increase in load, the speed of movement of working mechanisms decreases and vice versa);
- electric used on excavators with multi-motor drive in combination with mechanical; This drive makes it possible to regulate the speed of movement of the excavator mechanisms, automatically change the speed depending on the loads, as well as combine work movements;
- mixed, consisting of two types of drives, such as mechanical and electric.
The mechanical drive is most common, so its presence on the excavator is not specified in the name of the machine, and is usually only the engine type, for example, a diesel single-line excavator with a tank of 0.5 m3. If the drive of another species is used, this is indicated in the name of the excavator, such as a diesel-electric excavator, that is, an excavator with diesel power equipment and electric drive ..
All of the above refers to the excavators of periodic action (SNODOKSHOV), and to continuous excavators (Multi-Volume).
Thus, excavators distinguish:
1) according to the method of moving (floating and land);
2) by type of power equipment (with »diesel, carburetor, electric or steam engine);
3) by the number of engines (single-engine, multi-motor);
4) by type drive (mechanical, hydraulic volumetric, hydrodynamic, electrical, mixed);
5) by type of driving equipment of land excavators (tracked, pneumocoles).
In addition to the listed characteristic classification, each of the groups of excavators is characterized by smaller signs - dimensions, power, appointment.
Single-line excavators are divided into three main groups: - construction, with buckets with a capacity of up to 3 m3, intended for earthy and loading and unloading works in construction;
- careers, with buckets with a capacity of 2 to 8 m3, designed to work in careers on the development of ore and coal deposits, as well as rock rocks;
- Surrounding, with buckets with a capacity of over 6 m3, intended in particular for the development of upper layers of rocks (opening) covering reservoirs of minerals (coal, ore).
Surveral excavators are distinguished by the elongated work equipment, which makes it possible to fall off the ground for a large distance from the placement of production. This group of machines also include powerful walking excavators - draglines used on mining to cover the upper layers of rocks into the developed space, as well as on large hydraulic construction.
Single-sized excavators should be distinguished by using them with various types of work equipment.
Universal excavators are called cars with at least four types of replaceable work equipment. Construction excavators are usually versatile, and one type of work equipment can be replaced by another during operation.
Special call excavators that have only about the rank of work equipment. They are, as a rule, are produced with a container buckets over 6 m3, however, excavators with latter tank buckets (for example, underground) can be special.
In the present book, single-line construction land excavators produced by the domestic industry are described, full-time and incomplete.

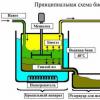
Fig. 1. Single Single Excavator Scheme:
1 - driving equipment, 2 - swivel platform,
The excavator is called a machine that serves for mechanical mining of non-solid or crushed rocks (Fig. 2).
Along with the separation of a part of the rock from the array, the excavator moves the produced breed for a certain distance to the transport, or before the dump if the produced rock is reset into the dump in place (when digging of the kittlers, with clay bille in cone or ridge).
The construction of the first single-sized excavator refers to 1836. Somewhat later, in 1860, a multi-lifted excavator was designed.
In pre-revolutionary Russia, the first single-sized excavator appeared much later - in 1900. A minor number of such excavators was issued to develop sandy quarries of the railway department. The many-loving excavators at that time were completely not manufactured.
In the Soviet Union, the excavator construction received powerful development.
By the method of action and location of the working projectile, excavators are divided into the following basic classes: single-line, cable, multi-loving.
According to the method of movement in working condition, they are divided into excavators with a rail and crawler.
In recent years, heavy engineering industry has become overwhelmed with heavy-duty single-luminous excavators moving in working condition using a walking mechanism.
Multual-line excavators are also built by bonovascular (so-called excavator) for work on the deepening of rivers, canals and other reservoirs. One of the varieties of such excavators are drags used in the gold mining industry.

Fig. 2. Single-sized excavator on a caterpillar.
Excavators are powered by electromotors of direct or alternating current, steam machines or internal combustion engines.
TO Atientary: - Excavator operation
Due to the high performance in the development of soils of various categories, single-line excavators received the greatest distribution. Excavators Classification Excavators are divided into several intended and power groups. Single-line and multi-loving excavators are land and floating. Land excavators have a tracked pneumocole rail and walking chassis.
Share work on social networks
If this job does not come up at the bottom of the page there is a list of similar works. You can also use the Search button.
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution
higher education
"National Research
Tomsk Polytechnic University "
Institute of Natural Resources
Direction of training (specialty) Oil and gas business
Department of Transport and Storage Oil and Gas
ESSAY
under the discipline of the machine and equipment of oil and gas objects
(Discipline name)
on the topic Classification of excavators
(Topic Title)
Performed student c.
(Group number) (signature) (Full name)
Essay Date to the teacher_____ _____________ 20__g.
Checked
(Degree, title, position) (Full name)
Date of verification _____ __________ 20__
Evaluation ___________
Signature ___________
Tomsk 2014
Introduction 3.
1. Classification of excavators 4
2. Classification of single-loving excavators 6
3. Classification of multi-loving excavators 15
4. Specifications of excavators 17
5. Scope 20
Conclusion 22.
References 23.
Introduction
Excavator (from lat. Excavo - hollow out), a landing machine equipped with a hinged working body - a bucket cutting simultaneously with its filling, mainly for the development of soft rocks in an array or rock in a fragmented state. Due to the high performance in the development of soils of various categories, single-line excavators received the greatest distribution.
- Classification of excavators
Excavators are divided into several intended and power groups. If the machine makes all operations in a certain order, repeating them through some time intervals, it relates to a discontinuous (cyclic) action machines if all operations are simultaneously a continuous machine. The excavators of discontinuities include single-line, and to continuous excavators - multi-loving, scraper and milling.
Single-line and multi-loving excavators are land and floating. Land excavators have a tracked, pneumatic, rail and walking chassis.
All excavator mechanisms are driven by diesel engines, carburetor, steam or electric motors. Diesel and electric motors are most economical. The selection of the engine is determined by the conditions in which the excavator will work. Thus, at excavators working in a quarry, it is advantageous to use electric motors, since electricity is the cheapest type of energy, and when working on road construction, where the car is often transported from place to place, it is advisable to use diesel engines.
If all excavator mechanisms are driven from one engine, such a drive is called single-engine. If in the excavator, each mechanism (or group of mechanisms) is driven by a separate engine, such a drive is called multi-motor.
In order to transfer traffic from the engine to work mechanisms, the following types of drives are used:
- mechanical when the movement is transmitted using shafts, gears, worm steam, chain gears;
- hydraulic volume, where the role of the drive is performed by hydraulic pumps, oil hydrogen and hydraulic cylinders (or hydraulic cylinders); In oil harvesters, the liquid circulates the energy transmitting energy from the pumps to hydraulic cells (or hydraulic cylinders), leading work mechanisms into motion;
- hydromechanical, in which a hydrotransformer is used to transmit energy in combination with a mechanical transmission;
- electric used on excavators with multi-motor drive in combination with mechanical;
- Mixed, consisting of two species, for example, mechanical and electric.
Thus, excavators classify:
By type of chassis
- crawler on a normal and broadly elongated chassis;
- walking;
- pneumocoles;
- at the road and in Speetavtoshssassi;
- on the tractor;
- rail and rail (normal. ruts);
- floating (Dzernaryada , excavator shells, excavators);
- on an all-terrain chassis (for example, onpontone with the possibility of "walking" on land);
- on a special (for example, a shark) chassis;
- on a combined chassis (for example, pneumocoles with lowered zhd bears).
According to the principle of work
- cyclic Action Excavators (Single):single excavator(in the direction of the tooth the bucket of the excavator); Work equipment: Draglaline , straight shovel, reverse shovel,graon;
- Continuous Excavators(trench rotary shredrovaand etc.);
- vacuum and vacuum-suction excavators (for example, landfill landfills).
ON OPERATIONAL PURCHASE
- career;
- overlap;
- mine (for underground work);
- construction universal.
According to power equipment
- with an internal combustion engine (usually diesel);
- electrical;
- earlier - steam.
Universal excavators are designed to work with various types of interchangeable equipment; Direct and reverse shovel, draglock, crane arrow with a hook suspension or graon, coprom for a pile hitch, etc.
Semi-universal excavators except the main work equipment have one or two types of additional interchangeable equipment (direct shovel, reverse shovel, dragline).
- Classification of single-loving excavators
Single excavator - Variety of excavator , Cyclic agricultural machine for development (digging), movement and loading of the soil. Working body is movablemiscellaneous bucket cubic volumefixed on arrows, handles or ropes. The bucket is loaded due to the movement relative to the soil developed. In this case, the housing of the excavator relative to the soil remains fixed - the traction force is created by the mechanisms of the excavator. This features an excavator fromscraper and loader Where the traction force when loading the bucket is created by moving the machine housing.
Single-sized excavator is the most common type of earthquakes used in the construction and mining of minerals. According to the type of work, there are two main types of excavator in the direction of the teeth of the bucket - reverseor straight shovel. Excavators with direct shovel apply only incareers when loading the mountain mass in the wagonsdUMMKARA Or for loadingore or other rock career dump trucks. A distinctive feature of such an excavator is the opening bottom of the bucket.
Single-sized excavators are classified by the type of chassis, the type of drive, the type of working equipment, the possibility of rotation of the working equipment relative to the supporting surface.
By the possibility of rotation of the working equipment relative to the reference surface
- Full-turn
Scheme of full-time excavator
Working equipment, drives, machine driver and engine are installed on a rotary platform, which in turn is installed on the chassis by means of a reflux device (OPU), and can be rotated relative to it in any direction to any angle. Parts of the chassis hydraulic system and the turning platform of full-turn excavators are connected to the use of the collector, which allows the unlimited number of complete revolutions in one direction.
- Inbolk-speed
The diagram of the non-fast excavator on the wheel tractor chassis
1 . Excavator frame, fixed on the tractor;2 . Swivel column;3. Arrow; four . Handle; five . Boom drive hydraulic cylinder;6 . Hydraulic cylinder handle drive;7 . Hydraulic cylinder bucket drive;8 . Bucket in the position of the reverse shovel;9 . Embodiment of the bucket in the right shovel position;10 . Replaceable cargo hook;11 . Bulldozer dump;12 . Remote supports.
Working equipment is fixed on the chassis using a rotary speaker. On many machines of this type of type, the rotary column is mounted on transverse guides, which allows you to move it together with the working hardware to the right, with subsequent rigid fixation for a more convenient position of the working equipment. The turn of the work equipment is carried out at an angle of 45-90 degrees from the initial position. Engine, mechanisms, driver cabin placed on a non-turning chassis. Currently, excavators hanging on tractors are executed incoming
By type of chassis
- Hanging on tractors

Excavator hung at the tractor "Belarus "
Tractor Excavator of Foreign Production
As basicchassis used tractor , most often wheeled. Intretable excavator equipment is installed behind (less often from the side) of the tractor, on a special frame. The most common are excavators hanging on class 1.4 tractors. Characteristic volume of the bucket - 0.2-0.5m³. . Used to perform small earthmoving or loading work, most often when repairing engineering networks. The design of the work equipment allows you to quickly rearrangeladle For the work of direct or reverse shovel. Bucket can be replacedgrabie , trucks or hook. The drive uses the engine base tractor. Hydraulic working equipment drive. Due to the relatively high speed, the turn can promptly arrive at the place of work, located at a distance of 20-30 km from the base of the base. The tractor with hung excavator equipment can also be used to perform transport andbulldozer.
- On car chassis

EO-4421 excavator on the chassisKraz-255

UDS excavator on Tatra-141 chassis
As a basic chassis used cargocar most often increased passability. Have a high movement speed. Apply in cases where high mobility is required: inmilitary business ( engineering troops, road troops ), when performing rescue operations, during the construction of roads, cleaning channels. Work equipment - predominantly reverse shovel. Excavators with a telescopic arrow and a rotary bucket are produced, allowing you to quickly move from direct shovel to the reverse. The drive can be used both the engine of the base car and a separate engine installed on the rotary platform.
- Pneumocoles

Modern pneumatic excavator with hydraulic drive
Pneumatic excavator of the 50s - 60s with cable drive
Excavators have their own special chassis based on wheels withpneumatic tires. Most often are fulfilled. To increase the stability and preventing closing when loading the bucket has remote supports. Have speed speeds up to 30 km / h. Can be touched by trucks at a speed of up to 40 km / h. Patency on weak soils limited. Available in a wide range of dimensional groups - frommicreeccavators With the volume of the bucket 0.04 m³ to heavy wheel excavators - with the volume of the bucket to 1.5 m³. Due to the specifics of the work performed: the development of kittlers, trenches, planning work - work equipment - predominantly reverse shovel. Can be used with grab, minimal grip,hydraulic hammer For soil loosening. Wound to be widespread when performing various types of construction and repair work.
The wheel drive chassis can be carried out both from the engine of the working equipment through mechanical or hydraulic transmissions (hydraulic motors) and from a single engine.
- Crawler

Crawler Excavator of the New Holland 2000s weighing 22t.

Excavator Demag Bagger. Execution: Direct shovel. - one of the largest hydraulic excavator in its class
Excavators have their own special chassis with a tracked propulsion. Perfect full-turn. They have high patency and low specific pressure on the ground with a large mass. They can work on weak and overwhelmed soils, including peatpooling. Have speed of 2-15 km / h. The place of work transports tractors on special trailers.
The working range of the bucket volumes is very wide: from the mini-scab with the volume of the bucket 0.04 m³ to the quarry with the volume of the bucket 10 m³. There are also particularly heavy career caterpillar excavators with the volume of the bucket of 26 m³ produced by Demag (Germany).
Work equipment: Direct shovel, reverse shovel,dragline . It can be used with a grab, a jewish grip, hydraulic hammer for soil loosening. They were widespread in construction and during mining. A number of models of caterpillar and pneumatic excavators have a unified turning platform and work equipment.
- Walking
The swivel platform with the equipment of the walking excavator is installed on the support plate. The paws are associated with the rotary platform, which are raised when the excavator is raised (do not touch the soil). With the movement of the excavator, the paws are based on the ground. At the same time, the support plate is removed from the soil. The excavator moves one step forward (for some models it is possible to move back). After that, the paws rise and returned to its original position. On the walking move, large career excavators with a bucket volume of 15 m³ - 40 m³ and an arrow departure up to 65 m - 150 m. Working equipment - Draglain. Running excavators are performed with overwhelming work (clearing of mineral deposits from empty breed), as well as mining and moving them into the dump (up to 40m height). Loading minerals by walking excavators cannot be carried out in vehicles.
- Railway
A railway platform is used as the excavator chassis. Used for repair work on the railway. Have a bucket of up to 4 m³. Rotary platform and equipment is often unified with tracked excavators.
- Floating
Working equipment (draglin or grapple) is installed onpontone . Apply for loading and unloading, sand mining, gravel from water bodies, bottomatic and dredging works. From floating cranes equipped with grabes, floating excavators are characterized by a smaller height and a simplified arrow design.
By type of engine
Works steam excavator
- Steam excavators
Used as an engine usedsteam engine . Were distributed at the beginning of the 20th century. Currently not issued. The moment-speed characteristics of the steam machine and the excessive equipment of the excavator are well coorded (the steam machine can develop the torque even with the inverted shaft), which simplifies mechanical transmissions.
- Excavators with internal combustion engines
The most common type. The excavator has its own engine, most often diesel. This ensures the autonomy of work. The power range of motors installed on modern excavators is very wide (see Dimensional groups).
The moment-speed characteristics of the internal combustion engine and the work equipment of the excavator are not agreed. In particular, the internal combustion engine cannot develop the torque at the crankshaft of the shaft. This requires applying on mechanical excavators of matching gear (clutch couplings, gearboxes, hydrotransformers). Hydraulic excavators appreciation is provided by hydraulic gears.
- Electric excavators
To drive work equipment are usedelectric enginesreceiving energy from the external network or from its own diesel-electric unit. Electric drive with power supply from the external network is used for career excavators. Such excavators are economical and do not contaminate the atmosphere of the career. Electric power drive from its own diesel electrical unit is used in floating excavators. Like a steam machine, the electric motor develops the torque at the inhibited anchor, so the electrical excavator does not need complex mechanical transmissions.
Excavators working in an explosive environment (in mines) of the primary engine do not have. Their hydraulic equipment is powered by high pressure liquid from externalmaslostania.
According to the type of mechanical gear (operating equipment drives)
- With group mechanical cable drive (mechanical)
Swanks of mechanical excavator
swans . The Lebetok drive is carried out from the excavator engine by means of mechanical gear (gear, chain, friction, worm).
The universal excavator with a mechanical drive is equipped with a three-drum winch. The booster boom drum is used to drive (lifting and lowering) arrows. The lifting drum is used for the lifting of the bucket (or return the handle during the operation of the reverse shovel). The traction drum is used to pull up the bucket to the excavator (when the draglock, reverse shovel). When operating a direct shovel, the traction drum is associated with the pressure head mechanism.
Mechanical cable drive was widely used on excavators in the past. In modern models, its use is reduced by the following reasons:
- excavators with mechanical cable drive have a complex design and contain a large number of high-speed products (friction lining, brake tapes, ropes).
- rope drive provides a limited number of independent displacements of work equipment elements;
- rope drive is technically difficult to make automated;
- the rope drive does not fully fix the elements of the working equipment in the specified position.
On modern models, the rope mechanical drive is used only for Draghun or Graper.
Traction effort to the working bodies is transmitted by means of ropes (or chains) movableswans
- With individual electric drive winches (electromechanical)
Traction effort to the working bodies is transmitted by means of ropes (or chains) movableswans . The drive of each winch and auxiliary mechanisms is carried out by an individual electric motor. Such a drive is applied on heavy careers (including walking) and industrial excavators.

Electromechanicalwinch 10-ditch career excavator with direct shovel ECG-10 productionRussia . A well visible system of ropes.
- With hydraulic drive
In hydraulic drive excavators (hydraulic excavators) The effort on the elements of the working equipment is createdhydraulic cylinders and hydrocigning. The excavator engine leads to rotation a hydraulic pump that creates pressureworking fluid In the pressure highway hydraulic system. Through the systemhydraulic distributors cavities of hydraulic cylinders (hydrodal engines) are connected to working or drain highwayshydraulic system What makes the movement of the work equipment. In the neutral position (with locked cavities of the hydraulic cylinders), the position of the working equipment is fixed. To transport the excavator with the help of a tug, the possibility of translating the boom hydraulic cylinder and the hydrometer of the rotation mechanism to neutral transport ("floating") mode.
Currently, hydraulic excavators have predominant distribution.
- Classification of multi-loving excavators
Depending on the direction of movement of the cutting edge of the bucket in relation to the direction of movement of the machine, excavators of longitudinal, transverse and radial digging are distinguished.
- Excavators of longitudinal digging
In the excavators of the longitudinal digging, the direction of movement of the cutting edge of the bucket coincides with the direction of movement of the machine. Used to develop narrow trenches.
- Excavators of transverse digging
Chain transverse digging excavator
In transverse digging excavators, the direction of movement of the cutting edge of the bucket perpendicular to the direction of movement of the machine. Apply to the development of kittlers, digging channels, mining mining.
- Radial Kopania excavators
Moving the working bodies is made by a rotary telescopic arrow. Depending on the method of fixing buckets, chain and rotary excavators distinguish:
Rotary radial digging excavator
- Chain excavators
The buckets are fixed on an infinite chain or chains. Dumping the soil is made directly from the buckets. The shape of the railway chain usually sets the digging profile.
- Rotary excavators
The buckets are fixed on the hard rotor. Dumping the soil can be made both directly from the buckets and through the conveyor.
Rotary trench excavator
According to the design of the working body:
- chains (working elements are placed on an infinite chain or chains);
- bare worker;
- a working organ with a free-saving chain;
- rotary (working elements are placed on circle rotatingrotor);
- working elements are placed on the rotor line;
- working elements are placed on the side surface of the rotor;
- two-rotor, or two-screw (the working body consists of two inclined rotors, the side surface of which works asmill);
- combined:
- plumber-rotor (the working body consists of a rotor andplow);
- snekorotorny (The working body consists of a rotor andscrews);
- bare worker;
By type of working elements:
- bucket organ (multifungal excavators);
- scraper, cutting, plug or mixed worker;
For appointment:
- tranche designed for layingtrenches;
- drainkeepers used to organizedrainage;
- docouplers are used for laying channels (irrigation, drainage) and cuvettes;
- career , Used for overcurrent and mining work.
By type drive:
- with mechanical drive;
- with hydraulic drive;
- with electrical drive;
- with a combined drive;
By type of chassis:
- on a caterpillar;
- on a pneumatic foot;
By the method of connecting work equipment with the chassis:
- mounted (without additional support for the working body);
- semi-trailers (the working body relies on the tractor in front and an additional cart back);
- chairs (the working body has its own running part and towed by tractor)
- Characteristics of excavators
- Frontal Loader ZTM-216

Steering
Hydraulic steering with follow-up feedback, 10MP pressure, power supply from NSh-32 pump. The minimum rotation radius is 5 900 mm.
Brake system
Three-integrated pneumatic brake system. Drum-type working brakes with two inner pads. Parking brake with a pneumatic actuator direct action.
Supplies of the loader are possible: Engines D260.2, Cummins 6BT, DEUTZ TD226, Joystick Manager of the working bodies, ZF gearbox germanium, installation of hydraulic elements.
|
Characteristics |
||
|
Load capacity, T. |
||
|
Capacity bucket, m3 |
1,7-2,0 |
|
|
Performance, m3 / h |
160-200 |
|
|
Duration of the working cycle, with |
||
|
Maximum speed of movement, km / h |
||
|
Operation weight, kg |
10200 |
|
|
Width bucket, mm |
2450 |
|
|
Hydraulics |
||
|
Axial piston pump |
310.3.112.04 |
|
|
Pressure in the working circuit, MPa |
||
|
Engine |
||
|
Model |
60 - 102 |
|
|
A type |
turbocharged diesel |
|
|
Power / speed (hp / rpm) |
130 / 2000 |
|
|
Running |
electrotarter |
|
|
Electrosystem voltage, in |
||
|
Specific fuel consumption, g / hp. |
||
|
Transmission |
||
|
Both bridge leading |
||
|
Number of gears |
forward-4, back-2 |
|
|
Filling tanks |
||
|
Tank working fluid, l |
||
|
Engine tank, fuel, l |
||
|
Tires |
21,3-24,0 |
|
|
Tire pressure, MPa |
0,25 |
|
- Crawler Excavator Hitachi ZX 110-3

Hitachi ZX 110-3 - Specifications
Weight in working condition 11.1 t
Engine manufacturer ISUZU.
Engine model AJ-4JJ1X
Dimensions (length, width, height) 7,28x2,49x2.74 m
Engine power 69 kW
Bucket volume 0.6 m3
Width of tracked tracks 500 mm
Lower SL Trolley
Arrow MB.
The number of revolutions at max. torque 1600 min-1
Mountains 8.24 M.
Digging Depth 5.63 m
Drawing force 60 KN
- Application area
Currently, no construction in the country do without excavators. Their high performance, the ability to work in all conditions, reliability, quality and variety of earthworks performed by them provided with these machines wide use in various fields of the national economy.
What exactly are the work designed excavators? They can be used when digging kittylovanov, channels, trenches, the development of recesses and embankments, the design of dams and clearing areas, at overlooking work and in careers, when overloading bulk building materials and planning work and in many other cases.
The area of \u200b\u200btheir use in construction is practically not limited. Where there is access for this machine, earthworks will be made with a high pace and quality.
Excavators can develop soil as above the site level on which they stand and below this level. They can act in cramped conditions and develop ground under the layer of water, unload the dug in vehicles into vehicles and pour it into a significant distance from the digging site into the blade, can finally separate the bias and surface of the walls of tranches and pita, as well as with sufficient accuracy to plan a horizontal surface. construction site or bottom of tranches and pita.
Obviously, each type of work requires the use of adapted excavators and intended for each specific case of work equipment. Under the working equipment, they are meant those nodes of the machine, with which the excavator directly digs the soil (bucket, arrow, handle with the system of their drive). Playing a certain role in these cases also type of chassis of machines: whether the excavator is equipped with a tracked course, which gives the machine the possibility of access to any place of the construction site in the absence of access roads and with poor ground conditions or has a pneumocole driving part, although it has the worst crossway, but Allows you to quickly move the machine from the object to the object. To perform certain works, the type of driving equipment is important. Thus, the hydraulic drive excavators are more productive, better adapted for planning, finishing operations, but the machines with a rope suspension are more applicable when passing and deepening the channels using a drag-bucket, with earthworks at a considerable distance from the machine.
Thus, the features of the specific types of earthworks that need to perform an excavator - for example, dictate a trench, a canal, plan the surface of the site or overload building materials, as well as the volume of soil, alleged to the excavator, and ground conditions on the object dictate the use of excavators with defined Working equipment, chassis and type of working equipment drive.
Conclusion
The goals and objectives set in the subject of the abstract are made. The classification of excavators was investigated, various types of machines were considered, their scope and destination, as well as during the work, the technical characteristics of individual models of excavators were studied.
Bibliography
- Belletsky B.F. Construction machines and equipment: Tutorial. 3rd ed.: 2008. - 608С.
- Gorelov S.A. Machines and equipment for the construction of gas-pipes: studies. benefit. - M.: RGU oil and gas. I. M. Gubkina, 2000. - 122 p.
- Kretz V.G., Rudachenko A.V., Shmurygin V.A. Machines and equipment of gas-pipeline: studies. Manual: TPU, 2008. - 328 p.
- Internet resources.
Other similar works that may interest you. Ishm\u003e |
|||
| 2724. | Information and logical model of system design of single-line excavators | 77.15 Kb. | |
| The problem solving is often reduced to identifying and examining the preferences of the person's decision maker as well as the construction of an adequate model of choice on this basis in a sense alternative. This feature means that various LPRs in the same situation of decision-making on the basis of the same model can receive a different result. Design Methodology EO | |||
| 8333. | History of development of computing equipment. Classification of computers. Computational system composition. Hardware and software. Classification of service and applied software | 25.49 Kb. | |
| Computational system composition. Computational system composition view hardware and software configuration T. Interfaces of any computing system can be divided into successive and parallel. The system level of transient ensures the interaction of other computer system programs as with the basic level programs and directly with the hardware in particular with the central processor. | |||
| 8841. | EMS classification | 82.43 Kb. | |
| This defines two main directions in the creation of the IC: semiconductor and film. The most common classification according to constructive technological features Since at the same time the designation of the ISS contains information about its design and manufacturing technology. One of the main criteria for assessing the technological level of production and workshop of the design of the ICS is the degree of integration. | |||
| 6891. | Norms of the CRC, their classification | 8.13 Kb. | |
| CPR standards for their classification. Constitutional standards are state-specific community regulations established by the state and components of a homogeneous group expressed in the CRF or received legal consolidation in other legal acts. Some rules are associated with the sphere of social relations in which the foundations of the constitutional system are expressed with the consolidation of the fundamentals of the legal status of a person and a third-party citizen with a federated device fourth with the system of state bodies. Distinguish norms ... | |||
| 8339. | Budget classification | 35.64 KB. | |
| Details Grouping income and expenses make it easier to check the data budget comparison of the estimation of homogeneous departments of territorial budget institutions for several years. Determination of the dynamics of revenues and specific gravity of various income and expenses or the degree of satisfaction of any needs. The classification creates the conditions for the unification of the estimation and budgets in general vaults facilitates their consideration and economic analysis simplifies control over the execution of the budget for the full and timely accumulation of funds and use ... | |||
| 1996. | Classification Steel | 256.31 KB. | |
| The most harmful impurities are sulfur and phosphorus. The sulfur leads to the rollars of steel, i.e. To fragility with hot pressure processing. Manganese, which is introduced into steel when deoxidizing, eliminates the harmful effect of sulfur. Phosphorus causes chlorosity, i.e. embrittlement at low temperatures. | |||
| 8954. | Classification of measurements | 1.58 MB. | |
| Characteristic for such measurements are the assessment of errors and the analysis of sources of their occurrence. According to the method of obtaining measurement: direct - when the physical value is directly associated with its measure; Indirect - when the desired value of the measured value is established according to the results of direct measurements of the values \u200b\u200bthat are associated with the desired value of the known dependence; Cumulative - when systems of equations are used according to the measurement results of several homogeneous values. An example of cumulative measurements can serve ... | |||
| 7926. | Classification of factors in AHD | 32.21 Kb. | |
| Classification of factors in AHD DZ: independently bring the deterministic and stochastic model of the influence of factors to the resultant factor. There is the following classification of factors: by nature ... | |||
| 7482. | Classification and types of ICA | 25.58 Kb. | |
| The basis of the functioning of the ICA is the arbitration agreement of the arbitration parties. Arbitration Agreement Arbitration Agreement This agreement of the parties to transfer to arbitration of all or certain disputes that arose or may arise between them in connection with the same specific legal relationship regardless of whether it was contractual or not. Arbitration Agreement Central Element and the foundation of the entire arbitration production. But despite the fact that the JSC is only part of the contract, it has independent ... | |||
| 9381. | Assets of the enterprise and their classification | 40.49 Kb. | |
| Assets Economic resources Speakers in the form of property values \u200b\u200bthat are used in economic activities in order to make a profit. In the enterprise's balance sheet, all the assets of which it owns are divided into two groups: current all the same means for one organization's operating cycle, that is, from the moment of procurement of raw materials and before the sale of finished products will be transformed into funds. From here it follows that the current assets change rapidly and go into the category of money within 12 months. | |||
Single excavator - A variety of excavator, a slot machine of cyclic action for the development (digging), movement and loading of the soil. The working body is the movable bucket of a different cubic volume, fixed on arrows, handles or ropes. The bucket is loaded due to the movement relative to the soil developed. In this case, the housing of the excavator relative to the soil remains fixed - the traction force is created by the mechanisms of the excavator. This features an excavator from a staple and loader, where the traction force when loading the bucket is created by moving the machine housing.
Single-sized excavator is the most common type of earthquakes used in the construction and mining of minerals. According to the type of work, there are two main types of excavator in the direction of the teeth of the bucket - a reverse or straight shovel. Excavators with a straight shovel are used only in careers when loading the mountain mass into the dumpcar wagons or for loading with ore or other rock career dump trucks. A distinctive feature of such an excavator is the opening bottom of the bucket.
Single-sized excavators are classified by the type of chassis, the type of drive, the type of working equipment, the possibility of rotation of the working equipment relative to the supporting surface.
By the possibility of rotation of the working equipment relative to the reference surface
· Full-turn
Scheme of full-time excavator
Working equipment, drives, machine driver and engine are installed on a rotary platform, which in turn is installed on the chassis by means of a reflux device (OPU), and can be rotated relative to it in any direction to any angle. Parts of the chassis hydraulic system and the turning platform of full-turn excavators are connected to the use of the collector, which allows the unlimited number of complete revolutions in one direction.
· Inbolk-speed
Scheme of an incomplete excavator on the wheel tractor chassis 1. The excavator frame, fixed on the tractor; 2. Rotary column; 3. Arrow; 4. Handle; 5. Board drive hydraulic cylinder; 6. Hydraulic cylinder handle drive; 7. Watercolor hydraulic cylinder; 8. The bucket in the position of the reverse shovel; 9. Option of the bucket in the right shovel position; 10. Replaceable cargo hook; 11. Bulldozer dump; 12. Remote supports
Working equipment is fixed on the chassis using a rotary speaker. On many machines of this type of type, the rotary column is mounted on transverse guides, which allows you to move it together with the working hardware to the right, with subsequent rigid fixation for a more convenient position of the working equipment. The turn of the work equipment is carried out at an angle of 45-90 degrees from the initial position. Engine, mechanisms, driver cabin placed on a non-turning chassis. Currently, excavators hanging on tractors are executed incoming
By type of chassis
· Hanging on tractors
As a basic chassis, a tractor is used, most often the wheels. Intretable excavator equipment is installed behind (less often from the side) of the tractor, on a special frame. The most common are excavators hanging on class 1.4 tractors. The characteristic volume of the bucket is 0.2-0.5 MI. Used to perform small earthmoving or loading work, most often when repairing engineering networks. The design of the working equipment allows you to quickly rearrange the bucket for the work of direct or reverse shovel. The bucket can be replaced by grab, trucks or hook. The drive uses the engine base tractor. Hydraulic working equipment drive. Due to the relatively high speed, the turn can promptly arrive at the place of work, located at a distance of 20-30 km from the base of the base. A tractor with hung excavator equipment can also be used to perform transport and bulldozer.
· On car chassis
As a basic chassis, a truck is used, most often increased passability. Have a high movement speed. Apply in cases where high mobility is required: in military affairs (engineering troops, road troops), when performing rescue operations, during the construction of roads, cleaning channels. Work equipment - predominantly reverse shovel. Excavators with a telescopic arrow and a rotary bucket are produced, allowing you to quickly move from direct shovel to the reverse. The drive can be used both the engine of the base car and a separate engine installed on the rotary platform.
· Pneumocoles
Excavators have their own special chassis based on the wheels with pneumatic tires. Most often are fulfilled. To increase the stability and preventing closing when loading the bucket has remote supports. Have speed speeds up to 30 km / h. Can be touched by trucks at a speed of up to 40 km / h. Patency on weak soils limited. Available in a wide range of dimensional groups - from microexcavators with a bucket volume 0.04 mI to heavy wheel excavators - with a bucket volume up to 1.5 mI. Due to the specifics of the work performed: the development of kittlers, trenches, planning work - work equipment - predominantly reverse shovel. Can be used with grab, mining grip, hydraulic hammer for soil loosening. Wound to be widespread when performing various types of construction and repair work.
The wheel drive chassis can be carried out both from the engine of the working equipment through mechanical or hydraulic transmissions (hydraulic motors) and from a single engine.
· Crawler
Excavator Demag Bagger. Execution: Direct shovel. - one of the largest hydraulic excavator in its class
Excavators have their own special chassis with a tracked propulsion. Perfect full-turn. They have high patency and low specific pressure on the ground with a large mass. They can work on weak and overwhelmed soils, including peatpooling. Have speed of 2-15 km / h. The place of work transports tractors on special trailers.
Work bucket volume range is very wide, from mini-excavator bucket with a volume of 0.04 m³ to dump bucket with a volume of 10 m³. There are also particularly heavy career tracked excavators with the volume of the bucket of 26 MI produced by Demag (Germany).
Work equipment: Direct shovel, reverse shovel, dragine. It can be used with a grab, a jewish grip, hydraulic hammer for soil loosening. They were widespread in construction and during mining. A number of models of caterpillar and pneumatic excavators have a unified turning platform and work equipment.
· Walking
The swivel platform with the equipment of the walking excavator is installed on the support plate. The paws are associated with the rotary platform, which are raised when the excavator is raised (do not touch the soil). With the movement of the excavator, the paws are based on the ground. At the same time, the support plate is removed from the soil. The excavator moves one step forward (for some models it is possible to move back). After that, the paws rise and returned to its original position. In the walking move, large career excavators with a bucket volume of 15 MI - 40 MI and an arrow departure up to 65 m - 150 m. Working equipment - Dragine. Running excavators are performed with overwhelming work (clearing of mineral deposits from empty breed), as well as mining and moving them into the dump (up to 40m height). Loading minerals by walking excavators cannot be carried out in vehicles.
· Railway
A railway platform is used as the excavator chassis. Used for repair work on the railway. Have a bucket of up to 4 mi. Rotary platform and equipment is often unified with tracked excavators.
· Floating
Work equipment (dragline or graon) is installed on the pontoon. Apply for loading and unloading, sand mining, gravel from water bodies, bottomatic and dredging works. From floating cranes equipped with grabes, floating excavators are characterized by a smaller height and a simplified arrow design.
By type of engine
· Steam excavators
A steam machine is used as an engine. Were distributed at the beginning of the 20th century. Currently not issued. The moment-speed characteristics of the steam machine and the excessive equipment of the excavator are well coorded (the steam machine can develop the torque even with the inverted shaft), which simplifies mechanical transmissions.
· Excavators with internal combustion engines
The most common type. The excavator has its own engine, most often diesel. This ensures the autonomy of work. The power range of motors installed on modern excavators is very wide (see Dimensional groups).
The moment-speed characteristics of the internal combustion engine and the work equipment of the excavator are not agreed. In particular, the internal combustion engine cannot develop the torque at the crankshaft of the shaft. This requires applied on mechanical excavators of matching gear (clutch couplings, gearboxes, hydrotransformers). Hydraulic excavators appreciation is provided by hydraulic gears.
· Electric excavators
Electrical engines that receive energy from the external network or from their own diesel-electric unit are used to drive work equipment. Electric drive with power supply from the external network is used for career excavators. Such excavators are economical and do not contaminate the atmosphere of the career. Electric power drive from its own diesel electrical unit is used in floating excavators. Like a steam machine, the electric motor develops the torque at the inhibited anchor, so the electrical excavator does not need complex mechanical transmissions.
Excavators working in an explosive environment (in mines) of the primary engine do not have. Their hydraulic equipment is powered by a high pressure fluid from an external oil plant.
According to the type of mechanical gear (operating equipment drives)
· With group mechanical cable drive (mechanical)
Traction effort to the working bodies is transmitted by means of ropes (or chains) movable swans. The Lebetok drive is carried out from the excavator engine by means of mechanical gear (gear, chain, friction, worm).
The universal excavator with a mechanical drive is equipped with a three-drum winch. The booster boom drum is used to drive (lifting and lowering) arrows. The lifting drum is used for the lifting of the bucket (or return the handle during the operation of the reverse shovel). The traction drum is used to pull up the bucket to the excavator (when the draglock, reverse shovel). When operating a direct shovel, the traction drum is associated with the pressure head mechanism.
Mechanical cable drive was widely used on excavators in the past. In modern models, its use is reduced by the following reasons:
- · Excavators with mechanical cable drive have a complex design and contain a large number of high-speed products (friction lining, brake tapes, ropes).
- · Rope drive provides a limited number of independent displacements of the elements of the working equipment;
- · Rope drive is technically difficult to make automated;
- · Rope drive does not fully fix the elements of the working equipment in the specified position.
On modern models, the rope mechanical drive is used only for Draghun or Graper.
· With individual electric drive winches (electromechanical)
Traction effort to the working bodies is transmitted by means of ropes (or chains) movable swans. The drive of each winch and auxiliary mechanisms is carried out by an individual electric motor. Such a drive is applied on heavy careers (including walking) and industrial excavators.
· With hydraulic drive
In hydraulic drive excavators ( hydraulic excavators) The effort on elements of the working equipment is created by hydraulic cylinders and hydrodic engines. The excavator engine leads to a rotation a hydraulic pump that creates the pressure of the working fluid in the pressure center of the hydraulic system. Through the system of hydraulic distributors of half-cylinders (hydrodal motigaves), they are connected to the working or drain highways of the hydraulic system, which ensures the movement of the work equipment. In the neutral position (with locked cavities of the hydraulic cylinders), the position of the working equipment is fixed. To transport the excavator with the help of a tug, the possibility of translating the boom hydraulic cylinder and the hydrometer of the rotation mechanism to neutral transport ("floating") mode.
Currently, hydraulic excavators have predominant distribution.
Excavators - Purpose and Classification
Excavators (the name comes from the Latin words "EX" and Caveo, "meaning" Food ") differ in high loose abilities. Transporting abilities are small and are determined by the radius of these machines. Excavators are divided into several intended and power groups. If the machine produces all operations in a certain order, repeating them through some spacing gaps, it refers to the interrupted (cyclic) action machines, if performing all operations simultaneously, is a continuous machine. The excavators of discontinuities include single-line, and to continuous excavators - multi-loving, scraper and milling.
Single-line and multi-loving excavators are land and floating. Land excavators have a tracked, pneumatic, rail and walking chassis.
All excavator mechanisms are driven by diesel engines, carburetor, steam or electric motors. Diesel and electric motors are most economical. The selection of the engine is determined by the conditions in which the excavator will work. Thus, at excavators working in a quarry, it is advantageous to use electric motors, since electricity is the cheapest type of energy, and when working on road construction, where the car is often transported from place to place, it is advisable to use diesel engines.
If all excavator mechanisms are driven from one engine, such a drive is called single-engine. If in the excavator, each mechanism (or group of mechanisms) is driven by a separate engine, such a drive is called multi-motor.
In order to transfer movement from the engine to work mechanisms, the following types of drives are used: - mechanical when the movement is transmitted using shafts, gears, worm steam, chain gears; - hydraulic volume, where the role of the drive is performed by hydraulic pumps, oil hydrogen and hydraulic cylinders (or hydraulic cylinders); In oil harvesters, the liquid circulates the energy transmitting energy from the pumps to hydraulic cells (or hydraulic cylinders), leading work mechanisms into motion; - hydromechanical, in which a hydrotransformer is used to transmit energy in combination with a mechanical transmission; - electric used on excavators with multi-motor drive in combination with mechanical; - mixed, consisting of two types of drives, such as mechanical and electric.
Thus, excavators are classified: - according to the method of moving (floating and land); - by type of power equipment (with diesel, carburetor, electric, diesel-electric, etc.); - by the number of engines (single-engine, multi-motor); - by type of drive (mechanical, hydraulic, hydromechanical, electrical); - by type of undercoming device of land excavators (tracked, pneumocoles, rail and with walking chassis).
Each of the groups of excavators is characterized by smaller signs - dimensions, power, appointment.
Single-sized excavators are classified by appointment.
There are three main groups: - Construction and universal - with a container buckets up to 3 m3, intended for the production of earthworks; - careers - with buckets with a capacity from 2 to 8 m3, designed to work in careers on the development of ore and coal deposits; - Convered - with laundry buckets of more than 6 m3, intended for the development of upper layers of rocks (opening).
Single-sized excavators are distinguished by using them with various types of work equipment.
Universal excavators are designed to work with various types of interchangeable equipment; Direct and reverse shovel, draglock, crane arrow with a hook suspension or graon, coprom for a pile hitch, etc.
Semi-universal excavators except the main work equipment have one or two types of additional interchangeable equipment (direct shovel, reverse shovel, dragline).
Special powerful excavators have only one type of equipment, such as a straight shovel.
Single-sized excavators. Singo-universal excavator is called a cyclic action machine intended for the excavation and movement of soils and other materials using one of the types of working equipment with one bucket, and to perform loading welding and other works by other types of interchangeable work equipment.
Single-sized excavators (Fig. 72) consist of the following main nodes: a running device, a turning platform with power equipment and main kinematic links and work equipment.
Tracked driving equipment provides high permeability and good stability when working as an excavator.
In recent years, the release of excavators with a small bucket capacity on a pneumocole trip, which has great mobility and maneuverability when moving the machine from one object to another is significantly increased. When working on weak soils, an extension (or elongated) tracked equipment is used, the presence of which reduces the specific pressure on the ground and improves the passability of the excavator.

Fig. 72. Single Excavator CHEMA

Fig. 74. Scheme of direct shovel
The rotary platform is based on the rollers or special (ball or roller) support-rotary device on the frame of the undercoming device. The platform rotates in the horizontal plane relative to the chassis.
The angle of rotation of the undercarriage equipment in the horizontal plane determines the possibility of an excavator to be a full-turn or incomplete. The rotary part of the full-native excavator can rotate around its axis by 360 °.
These machines on the rotary platform are mounted all the power units, a control panel, working mechanisms and the work equipment is mounted.
Working equipment includes a set of excavator nodes with a working body (bucket, hook, grab, etc.). The soil is developed by the bucket, after which they move to the discharge place in the blade or to the vehicle. Depending on the type of replaceable equipment, use a rigid or flexible suspension of the working body. The nature of the work determines the work equipment: direct shovel, reverse shovel, dragine, crane or grab.
The operating cycle of the excavator is performed in the following sequence: soil digging; Moving the bucket filled with soil to the discharge place; unloading the soil from the bucket into the dump or transporting device; Moving the bucket (rotation of the platform) to the caution; Lowering the bucket to prepare for the next digging operation.
The indexing system of single-line universal excavators. The machine indexing system is called the principle that is laid into the structure of the index (mark), denoting one or another excavator and reflecting its basic characteristic. In 1968, a new system of indexation of single-loving universal excavators was introduced in our country. The excavator index has four main numbers, respectively, indicating: the dimensional group of the machine, the type of undercoming device, the design of the working equipment and the sequence number of the model of this type. Thus, the excavator index contains information about its main characteristic. So, EO-3313 BTV is an excavator of a single-line universal, 3rd dimensional group, on a pneumatic chassis, with a rope suspension of work equipment, the 3rd model that has passed the second modernization, performed for operation in wet tropics.
Direct shovel - equipment designed to develop the soil above the level of the excavator parking. Direct shovel with mechanical drive (Fig. 74) consists of the following main nodes: rope rope, bucket, handle, arrows, saddle bearing. The handle to the arrow is fastened with a saddle bearing, with which the handle rotates in the vertical plane relative to the boom and makes a reciprocating movement along the axis of the handle. When the soil is digging, the ladle needs to pass the position -IV shown in Fig. 74. The bucket rises with a lifting rope envelope head blocks. The pressure of the handle is carried out by a pressure mechanism, which also performs the inverse movement (refund) of the handle. The universal building excavators use rope and gear-roll (pressure mechanisms).
The pressure mechanisms are divided into independent, dependent, the combined, pressure mechanism is called independent if the pressure force can be increased or decreased regardless of the magnitude of the effort in the bucket lifting cable, i.e. when the pressure of the handle with the bucket is made independently of the lifting of the bucket. If the magnitude of the force of the pressure depends on the magnitude of the force in the lifting / broken bucket cable and it is possible only to reduce the pressure, such a pressure mechanism is called dependent.
The pressure mechanism is called combined when the pressure of the pressure depends on the effort in the lifting cable, but when the independent part of the pressure mechanism can be enlarged if desired.
The ladle direct shovel consists of a housing, a folding bottom with a casing and replaceable teeth. The teeth have a shank escaped to the end, which is included in the visor's socket. From the fall out of the teeth are held in the nests with hoptes.
Straight shovels in recent years have been equipped with dipper with a semicircular front wall and with a visor in the form of a scoop without teeth. The bucket of such a design is much easier and has minimal resistance when the soil is digging, which naturally increases the performance of the excavator.
At the excavators with a straight shovel, two types of handles are applied: single-ground (internal type) and two-bit (external type). A single-ground handle passes inside the boom, and two-bit - outside. The handle can perform a reciprocating movement in the guide saddles of the pressure shaft, and also rotate together with the saddle bearing in the vertical plane relative to the pressure shaft. The design of the handle defines the design of the pressure mechanism. In the excavators produced in the USSR, the rope pressure mechanism is used with a single-ground handle, and with a two-bondan - creamers head mechanism.
The straw of direct shovel is made in the form of a welded design of sheet steel. The type of handle defines the arrow design. The arrow is two-ball with a single-ground handle and a single-ground with a two-bit handle.
At the top of the boom, the blocks are mounted on the bearings through which the rope of the bucket lifting and the arright-lifting rope passes. The lower end (fifth) arrow is attached to the rotary platform and can be rotated when it changes its tilt angle. In the middle of the arrows there is a pressure shaft.
The reverse shovel is an equipment designed to develop soils below the level of the excavator parking during the digging of buttons, trenches, recesses.
The reverse shovel (Fig. 75) consists of a bucket, arrows, handles and a two-legged rack. The bucket is fixed rigidly to the handle, hingedly attached to the upper end of the arrows. When pulling up the rope, the handle rotates counterclockwise, the bucket is crashed into the soil (position // position // and /// correspond to the transport position and unloading of the soil from the bucket).

Fig. 75. The work scheme of the reverse shovel:
The process of ground ground bucket. The overall excavation resistance R0 is overcome by the active force W0, aimed at the bucket trajectory, which can be decomposed on the cutting force and the soil shift WVI directional by tangent to the cutting edge of the bucket, and on the WB pushing force, directed normally to the cutting edge of the bucket.
The main parameters of hydraulic single-loving excavators are: Bucket Capacity Q, Mass of the excavator C, engine power N, operations of the excavator, as well as pressure and pump performance.
In the hydraulic drives of excavators, the pumps of permanent performance of gear and blade type (with a pressure of 12-16MPA) and piston with a pressure of up to 30 MP and the pumps of variable performance are used, the prerequisite is an axial-piston.
Pumps with permanent performance are simple on the YCI torture, but do not provide the complete use of the engine power in all modes. Performance variable pumps seminate more rational and stable operation of excavators.
Productivity and technological schemes for the work of single-loving excavators. The productivity of single-line excavators is determined by many factors: the design of the machine, the level of organization of earthworks, the condition and quality of soil and slaughter, the qualification of the machine driver and the technical condition of the machine.
In fig. 77, B is a diagram of the work of the Draghun during the construction of an extract of the earth canvas from the reserve. The excavation of the soil is carried out on two invigays; At one of them, the next layer of soil is pumped and smoothed by a bulldozer, and on the other - freshly added soil is compacted by a bodily removable machine.
Multifungal excavators. Multifungal excavators are earthmoving machines that have a multi-voltage chain or a rotary wheel with buckets, rigidly fixed around the perimeter. They apply: on road construction work; When digging pickles, canals and tranches for laying pipes or for bases Installation, control panel, gearbox, the working body is installed on the stack frame.
Note. EO-1621 excavators (E-153a), EO-1627 (E-1514) are equipped with additional bulldozer equipment: the width of the dust 2000 mm, the height is 680 mm, the cutting depth is 500 mm. EO ZZPB excavators (E-302) are equipped with Draghun equipment with the following parameters: The boom length is 7500 mm, the angle of the boom is 40 °, the depth of cutting 4450 mm, the radius of cutting 6500 and 10 100 mm, the height of the unloading, respectively, 3900 and 6300 mm, happy with Unloading, respectively, 6390 and 8300 mm.