The role of glucose in the body. Biological role of monosaccharides
From the point of view, the monosaccharide biochemistry is carbohydrates that cannot be hydrolyzed to simpler forms of carbohydrates.
Monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose. Read more about the classification of carbohydrates can be viewed in the article. In this article, consider what biological role of monosaccharides.
For biochemistry lovers, we will give a classification of monosaccharides.
Monosaccharides are divided:
On stereoisomers on the conformation of asymmetric carbon atoms - L- and D - forms;
Depending on the conformation of the N-group of the first carbon atom - a. and b.-formes;
Depending on the presence of aldehyde or ketone group - ketosis and aldose.
Monosaccharide derivatives are:
Uranium acids - glucuronic, galacturon, ascorbic acid. Very often they are part of proteoglycans;
Aminosahara is glucosamine, Galactozamine. A number of antibiotics (erythromycin, carbomycin) contain in its composition Aminosahara;
Siletic acids. Included in proteoglycans and glycolipids;
Glycosides - an example serve heart glycosides, antibiotic streptomycin.
Biological role glucose.
Glucose is aldosis and hexose.
1. Glucose is part of the starch, fiber, sucrose.
2. It is the only source of energy for nervous tissue, is actively used by muscles and red blood cells. During the day, a person weighing 70 kg of a brain consumes about 100 g of glucose, cross-striped muscles - 35 g, red blood cells - 30 g.
Oxidation of 1 glucose molecule in anaerobic conditions (without oxygen presence) gives the body 2 ATP molecules, and in aerobic conditions (in the presence of oxygen) - a total of 38 ATP molecules.
That is why, with a decrease in glucose concentration in blood (hypoglycemia), weakness, lethargy, inhibition are noted. With critical hypoglycemia, there is a loss of consciousness, a comatose state develops.
3. With a sufficiently large quantity in the glucose cell is in the form of glycogen.
4. In hepatocytes (liver cells) and adipocytes (adipose tissue cells), glucose is involved in the synthesis of triacyl glycers and in hepatocytes in cholesterol synthesis.
5. The resulting amount of glucose is involved in the formation of riboso-5-phosphate and NAPFN (pentosophosphate path).
6. Glucose is used to synthesize glycosamines and then structural or other heteropolisaccharides.
A constant level of blood glucose concentration is maintained using insulin and glucagon pancreatic hormones.
Glucose enters the body by cleavage in the intestine products containing starch, sucrose, lactose or maltose, honey, fruits, berries and vegetables next, in which it is in free form. A significant amount of glucose contained in apricots, watermelon, eggplant, banana, vinogorade, strawberry, cherry, cabbage, raspberry, sea buckthorn, persimmon, cherry, pumpkin.
Biological role of fructose.
Fructose on the biochemical structure is ketosis and hexose.
1. Fructose has the greatest sweetness of all natural sugars. To achieve the same taste effect, it is 2 times less than glucose or sucrose.
2. Most of the fructose when entering the body is quickly absorbed by tissues without the participation of insulin, the other part turns into glucose. Food containing fructose under certain conditions can be recommended for patients diabetes. They are contraindicated with obesity with obesity, since they contribute to a faster and intense weight gain than products containing glucose. Therefore, people with increased body weight should not be abused by such edible substances.
3. Connecting with iron, fructose forms chelate compounds that are much better absorbed than conventional iron compounds of other products, therefore, anemia is very effectively adding food substances rich in fructose to its diet. In this situation, it can also be used in its pure form.
"CONTENT"
1. Build ............................................................................................................... 2
2. Getting ........................ .. ................................. ................................................ .3
3. Properties .................................................................. …………………………………….....four
4. Biological role ................................................................................................ .6
5. Role in the food industry .............................................................................. 9
6. Literature ......................................................................................................................11
- STRUCTURE.
It is found in the juice of many fruits and berries, including grapes, which there was a name for this type of sugar.
According to the number of carbon atoms in the glucose chain refers to hexosams.
In nature, only D-glucose is found in nature, which is isolated in the form of two anomers: the molar mass of 180 g / Moliai? -Glucopyranose (acc. Frams I and II):
- Getting.
Glucose can be obtained by hydrolysis of natural substances, in which it enters. In industry, it is obtained by hydrolysis of potato and corn starch with acids:
Also in industry glucose is obtained by hydrolysis of cellulose:
In the nature of glucose, along with other carbohydrates is formed as a result of photosynthesis reaction:
- Properties.
White crystalline substance of a sweet taste, well-soluble in water and organic solvents, is soluble in the reagent of Swituer: an ammonary solution of copper hydroxide, in a concentrated zinc chloride solution and a concentrated sulfuric acid solution. Compared to beet sugar, it is less sweet.
Molar weight 180 g / mol; Density of 1.54 g / cm?
Melting point:? -D-glucose: 146 ° C
? -D-glucose: 150 ° C
3.2. Chemical properties.
1) Oxidation
Like all aldehydes, glucose is easily oxidized:
2) Restoration
Glucose can be recovered in six-coat alcohol (sorbitol):
3) Mutarotes
4) fermentation
a) alcohol
b) lactic acid
c) Oily acid
d) lemon-acid
Glucose also forms oximes with hydroxylamine, ozones with hydrazine derivatives.
Easily alkylated and acylated.
4. Biological role.
Glucose is the main product of photosynthesis, formed in Calvin cycle, also a composite unit from which all the most important polysaccharides are built - glycogen, starch, cellulose. It is part of sucrose, lactose, maltose.
In the human body and animal glucose is the main and most universal source of energy to ensure metabolic processes. All cells of animals organism have the ability to absorb glucose. At the same time, the ability to use other energy sources - for example, free fatty acids and glycerin, fructose or milk acid - not all organism cells have, but only some of their types.
Glucose is quickly absorbed into the blood from the gastrointestinal tract, then enters the cells of the organs, where it is involved in the processes of biological oxidation.
Transportation of glucose from the external environment Inside the animal cell is carried out by actively transmembrane transfer using a special protein molecule - the carrier (transporter) hexosis.
Glucose in cells may be subjected to glycolize for the purpose of obtaining energy in the form of adenosyntrifosphoric acid - ATP, which is the source of a unique type of energy. ATP in all living organisms plays the role of a universal battery and energy carrier. In medicine, the drugs of adenosinerphosphate are used in spasms of vessels and muscle dystrophy, and this proves the importance for the body of ATP and glucose.
Glycolizis - (phosphotrious path, or embeden - Mairhefa, or the path of embed-meyergof-Parnassa) - a enzymatic process of sequential glucose cleavage in cells, accompanied by the synthesis of ATP. Glycicoliz in aerobic conditions leads to the formation of peyrogradic acid (pyruvate), glycoliz in anaerobic conditions leads to the formation of lactic acid (lactate). Glycoliz is the main way of catabysses of glucose in the body of animals. The glycolithic path is 10 consecutive reactions, each of which is catalyzed by a separate enzyme.
The first enzyme in the glycolysis chain is hexokinase (cytoplasmic enzyme of transferase class, phosphotransferase subclass). The activity of cell hexochinase is under the control influence of hormones - so, insulin sharply increases hexokinase activity and, consequently, the utilization of glucose by cells, and glucocorticoids (the total collective name of the groovers of the adrenal cortex hormones possessing more strong effect On carbohydrate, than on water-salt exchange) reduce hexokinase activity.
The total glycolysis equation has the form:
Glucose + 2NV + 2ADF + 2FN \u003d 2NPH H + 2PVK + 2ATF + 2H2O + 2N.
Many of the glucose sources of energy can be directly converted to the liver in glucose - for example, lactic acid, many free fatty acids and glycerin, or free amino acids, primarily the simplest of them, such as Alanine. The process of forming glucose in the liver from other compounds is called glukegenesis.
Those energy sources for which there is no way of direct biochemical transformation into glucose can be used by liver cells to generate ATP and subsequent energy supply of glucosegenesis processes, milk-acid residuisa, or energy supply of the gas coating polysaccharide stock process from glucose monomers. From glycogen, by simple splitting, glucose is easily produced.
Gluconeogenesis - the formation in the liver and to some extent in the renal cortex (about 10%) of glucose molecules from molecules other organic compounds - energy sources, e.g. pyruvate, lactate, free amino acids, glycerol.
When fasting in the human body, nutrient reserves (glycogen, fatty acids) are actively used. They are split up to amino acids, ketokyslot and other non-reliable compounds. Most of these compounds are not excreted from the body, and reutence. The substances are transported to the liver from the blood of other tissues and used for the synthesis of gluconeogenesis Glucose - a primary energy source in the body. Thus, in the exhaustion of the organism reserves, gluconeogenesis is the main supplier of energy substrates.
Surmark Gloundogenesis equation:
Due to the exceptional importance of maintaining a stable blood glucose level, a person and many other animals have a complex system of hormonal regulation of parameters. carbohydrate exchange.
When oxidizing 1 gram glucose to carbon dioxide And the water highlighted 17.6 kJ of energy.
The stored maximum "potential energy" in the molecule in the form of glucose oxidation? 4 carbon atoms may decrease in metabolic processes to the extent of 4 (in the CO2 molecule). Its restoration to the previous level can exercise
autoTrophy - living organisms synthesizing organic compounds from inorganic.
During the wake of the body, the energy of glucose replenishes almost half of its energy costs. The remaining unclaimed part of glucose is converted to glycogen - polysaccharide, which is stored in the liver. Due to the difficult-adjustable splitting process of this polysaccharide, a stable blood glucose level is ensured. However, to absorb glucose, insulin is required, and under certain conditions, part of it, sometimes significant, turns into its own fat body. This is primarily due to a violation of hormonal balance and with excessive flow of glucose itself.
The paths of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are directed opposite:
5. Role in the food industry.
The glucose is called "grape sugar", since it is in grapes it is contained in a significant amount in free form, and also part of other fruits and berries, bee honey. Along with the fructose glucose is an integral part of sucrose. Glucose sweetness 0.74.
There are more than 50 specialized enterprises in the development of glucose, 35 of which are located in Europe.
Glucose is applied not only as a sugar substitute, but also as an improver taste and freight type of food. In the confectionery industry, glucose is used for the manufacture of soft candies, pralines, dessert varieties of chocolate, waffles, cakes, dietary and other products.
Since glucose does not mask fragrance and taste, it is widely used in the production of fruit canned food, frozen fruits, ice cream, alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. The use of glucose in bread accumulation improves fermentation conditions, promotes the formation of a beautiful golden-brown crust, uniform porosity and good taste. Crystal glucose is appropriate to use for the nutrition of patients, wounded, recovering and people working with large overloads.
In recent decades, the production of glucose-fructose syrups (GFS) was widely distributed. The resulting glucose is partially converted into fructose, and different glucose and fructose ratio can be achieved. Theoretically, the initial glucose yield is 97 parts per 100 parts of the starch. Technical glucose is produced in small amounts of acid hydrolysis of low-quality potato, corn or other grain starch intended for technical purposes.
If you take a solution containing sucrose and glucose in a ratio of 10: 1, then by thickening it and subsequent rapid cooling, it is possible to obtain a snow-white mass - fondant sugar. When drying this mass, powdered fondant sugar, consisting of small crystals of sucrose and invert sugar, are obtained. When mixing powdered sugar with water, a paste is formed. Feligious sugar is becoming increasingly distributed in the confectionery industry in the production of chocolate, fillings for soft candies and other things.
Glucose prevents crystallization of candy caramel and reduces the hygroscopicity of the final product.
Unmodified and modified starch and glucose are used in the food industry with one or more of the following purposes:
- Directly as a braeshrized starch, kissel, etc.
As a thickener due to viscous properties (in soups, child nuts, sauces, pulls, etc.)
Like a filler that is part of the solid contents of soups, pies
etc.................
TARGET:
Give a classification of carbohydrates.
Consider the physical and chemical properties of glucose.
Examine the structure of the glucose molecule, consider the isomerism of glucose.
Know the finding glucose in nature, in the human body, its biological significance and application field.

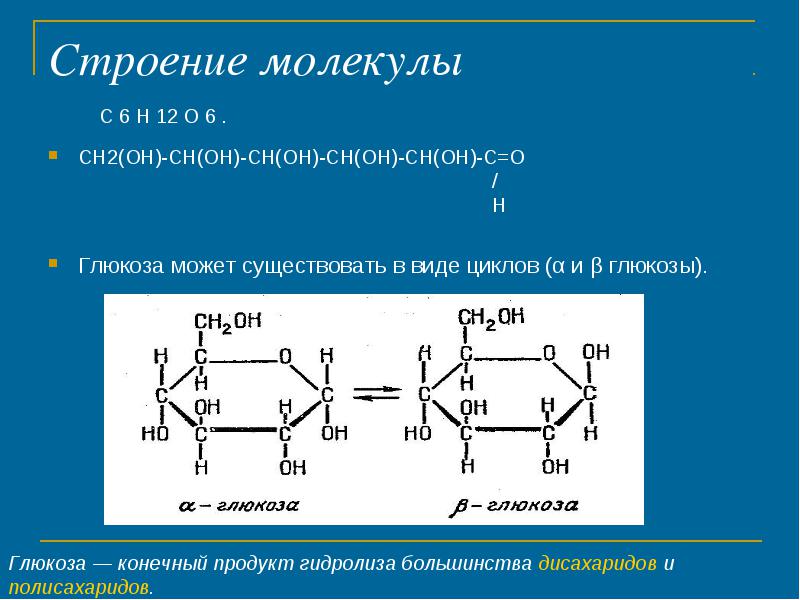
The structure of the molecule
CH2 (OH) -CH (OH) -CH (OH) -CH (OH) -CH (OH) -C \u003d O / H
Glucose can exist in the form of cycles (α and β glucose).
Glucose is a colorless crystalline substance, well soluble in water, sweet taste. It occurs in almost all organs of the plant: in fruits, roots, leaves, colors. Especially a lot of glucose in the juice of grapes and in ripe fruits, berries. Glucose is in animal organisms. In the blood of a person it contains approximately 0.1%.



Biological role:
Glucose is the main product of photosynthesis, is formed in the Calvin cycle. In the human body and animal glucose is the main and most universal source of energy to ensure metabolic processes. All cells of animals organism have the ability to absorb glucose. Glucose in cells may be subjected to glycolize in order to obtain energy in the form of ATP. The first enzyme in the glycolysis chain is hexokinas. Due to the exceptional importance of maintaining a stable blood glucose level, a person and many other animals have a complex system of hormonal regulation of carbohydrate exchange parameters. When oxidizing 1 gram of glucose to carbon dioxide and water, 17.6 kJ of energy is distinguished.

Glucose obtaining:
In industry, glucose is obtained by hydrolysis of starch and cellulose. Glucose can be recovered in six-coat alcohol (sorbitol). Like all aldehydes, glucose is easily oxidized. It restores silver from the ammonia solution of silver oxide and copper (II) to copper (I).

CHEMICAL PROPERTIES:

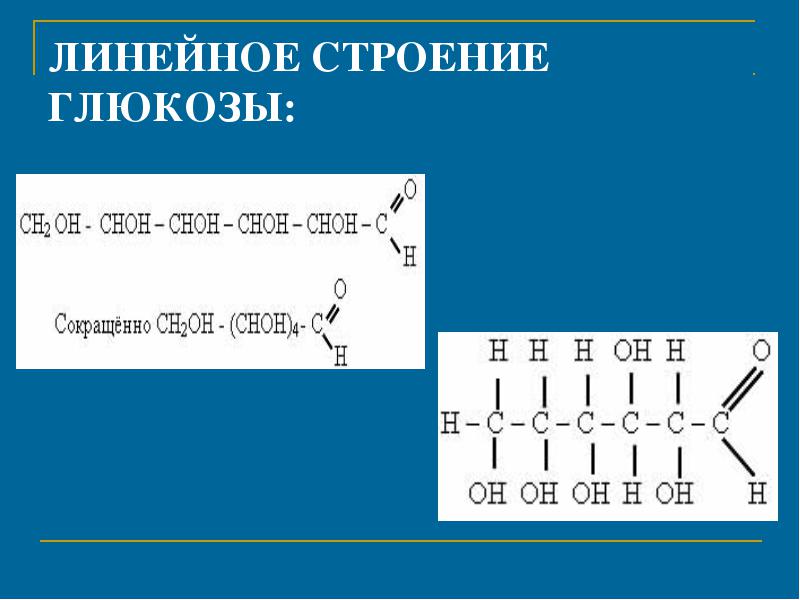
Linear structure of glucose:
Glucose interaction with copper hydroxide (II)

Silver Mirror Reaction:


Esterification reaction

Alcohol fermentation (under the action of yeast)

lactic acid fermentation (under the action of lactic acid bacteria)

oily acid fermentation

- As a polyatomic alcohol, glucose forms esters. - Like aldehyde, it is oxidized. - An important chemical property of glucose is its fermentation under the action of organic catalysts - enzymes produced by microorganisms.

Physical properties:
White crystalline substance of sweet taste, well soluble in water.

Glucose application:
Glucose is a valuable nutrient. As a substance is easily absorbed by the body and gives it energy, glucose finds direct use as a strengthening treatment. Sweet taste led to the application of it in a confectionery case (as part of molasses) in the manufacture of marmalade, caramel, gingerbread, etc.
As a reducing agent, it is used in the manufacture of mirrors and Christmas decorations (silver).
In the textile industry, glucose is used to finish tissue.
Glucose is used for intoxication (for example, with food poisoning or infection), intravenously introduced insertion and drip, because It is a universal antitoxic agent.

Linear structure of glucose:

Glucose is the main source of energy in a living cage, so it is widely used in medicine. In the textile industry, glucose is used to finish tissue. For all these purposes, glucose is obtained from starch, exposing it to hydrolysis in the presence of mineral acids.

Brief readings:
Glucose solution is used with a lack of glucose in the body.

FRUCTOSE:
Fructose - fruit sugar, one of the main sources of carbohydrates. Fructose cannot directly assimilate the human body and in the process of metabolism is converted into glucose.
Doctors traditionally believe that fructose is more useful than glucose and sucrose. However, some researchers suggest that excessive fructose consumption can contribute to the development of obesity.


Photosynthesis scheme

Some interesting facts
Some frogs found the use of glucose in their body - curious, although much less important. In winter, it is sometimes possible to find frogs inserted into ice blocks, but after thawing, amphibians come to life. How do they persuade not to climb death? It turns out that with the onset of cold blood frogs increases 60 times the amount of glucose increases. It interferes with the formation of ice crystals inside the body.

OUTPUT:
Carbohydrates ... These are the hairstyles that we love so much, (fruits, cakes, candy, jam, chocolate, etc., especially many carbohydrates contains grapes). Carbohydrates are vital substances that are needed to each organism. These substances are spent, and the person must constantly replenish their reserves. It is clear that substances included in the body tissues are not similar to those that it uses. The human body processes the foods and in the process of its life is constantly consumed by the energy, which, as we know, is released during oxidation in the tissues of the body, carbohydrates are part of the nucleic acids carrying the protein biosynthesis and the transfer of hereditary signs. And we found out that glucose is aldehydospirt, more precisely - polyatomic aldehydospirt

The work was performed by students of the 11th grade "A" MOU SOSH No. 2 Azarenok Anna Shevtsova Victoria Checkered: Teacher of Chemistry Mososh No. 2. Kupino Garbuzova Vera Evgenievna

Empirical glucose formula FROM 6 N. 12 ABOUT 6 . It can have different spatial forms. In the body of a human glucose, as a rule, is in cyclic form:
Free glucose in the human body is mainly in the blood, where its content is pretty constantly and fluctuated in the range from 3.9 to 6.1 mmol / l.
Glucose main source of energy in the body.
Another carbohydrate typical person is glycogen.It consists of glycogen from highly branched large molecules containing tens of thousands of glucose residues. Empirical Glycogen Formula: (FROM 6 N. 12 ABOUT 5 ) n.where n. The number of glucose residues.
The main glybogen reserves are concentrated in the liver and muscles.
Glycogen is a spare glucose form.
Normally, 400-500 g of carbohydrates comes. It is mainly starch, fiber, sucrose, lactose, glycogen. Digestion of carbohydrate occurs in different parts of the digestive tract, starting with the oral cavity. Carry it out enzymes amylase.The only carbohydrate that does not split in our body is a fiber. All other are split to glucose, fructose, galactose, etc. D. and are involved in catabolic processes, a significant part of glucose turns into a liver in glycogen. Between meals, part of the glycogen in the liver turns into glucose, which enters the blood.
Glucose used for glycogen synthesis is pre-activated. Then after a series of transformations forms glycogen. In this process, the Nucleotide of UTF (uridintrifhosphate) is involved, which in structure resembles ATP. In the course of reactions, an intermediate connection is formed - uridindiphosphatglucose (UDF glucose).It is this compound that forms glycogen molecules, entering into the reaction with the so-called seed.The seed serve the glycogen molecule in the liver.
Glycogen formation reactions are provided by the energy of ATP molecules. Glycogen synthesis is accelerated by hormone insulin.
The decay of glycogen in the liver is carried out in reverse order and ultimately the glucose and phosphoric acid is formed. This process is accelerated by hormones. glucagon and adrenaline.The decay of glycogen in the muscles stimulates the adrenaline hormone, which is released into the blood during muscle work. At the same time, free glucose is not formed in the muscles and the path of glycogen cleavage is somewhat different.
3. Catabolism of carbohydrates. Hexosodiphant glucose splitting path.
Catabolism glucose is carried out in two ways.
The main part of carbohydrates (up to 95%) is subjected to decay by hxozodiphosphate path.It is this way that is the main source of energy for the body.
The rest of the glucose is split through gexosomonophosphate way.
GDF-Path may occur in the absence of oxygen - anaeroboand in the presence of oxygen, that is, in aerobic conditions.This is a very complex chain of consecutive reactions, the end result of which is education. carbon dioxide and water.This process can be divided into three stages that are consistently running each other.
First stage, called glikoliz,it occurs in cytoplasm cells. The final product of this stage is pirogradic acid.
1. Molecule phosphorylation reaction glucose It is that glucose with the participation of a tissue-sophisticated enzyme hexokinase with the cost of energy 1 ATP molecules turns into glucoso-6 phosphate.
Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP
2. Glucose-6-phosphate turns into fructose-6-phosphate
3. Fructose-6-phosphate goes to Frutozo-1.6 phosphate
5. From the phosphoglycerin aldehyde is formed 1.3Difhosphoglycerat
6. 1.3 Diffosphoglycerate passes B3-phosphoglycerat,
7 which goes into 2-phosphoglycerat and then
8 in phospopyruvat, and that
9 in pyruvate (pyruvic acid).
The general equation of glycolysis looks like this:
Glucose + o2 + 8adf + 8 N. 3 RO 4 → 2 Piruvat + 2N2O + 8 ATP
The first stage of the decay of carbohydrates will practically turn. From pyruvate, as well as from lactate (lactic acid), glucose, and from her glycogen can be synthesized.
The second and third phases of the DGF path proceed in mitochondria.These stages require the presence of oxygen. During the second stage, the pirogradic acid is cleaved carbon dioxide and two hydrogen atoms. The decanted hydrogen atoms in the respiratory chain are transmitted to oxygen with simultaneous ATP synthesis. From the pyruvate is formed acetic acid.She joins a special substance, a. ProfimerThis substance is the carrier of acid residues. The result of this process is the formation of a substance acetylcooferment A. This substance has high chemical activity.
The final equation of the second stage of the GDF-NUTI:
C h 4 o z + 1 / 2o 2 + HSKOA + 3 ADF + 3 NZRO4 CH z - with ~ SKOA + CO 2 + H 2 O + 3At
Piruvat Coenzyme A Acetyl CoA
Acetylcoerment A is subjected to further oxidation in tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle)and turns into CO 2 and H 2 O. This is the third stage.Due to the outcomed energy at this stage, the synthesis of ATP is also carried out.
Cycle of tricarboxylic acids (CTC) - This is the final stage of catabolism not only carbohydrates, but also all other classes of organic compounds. This is due to the fact that during the decay of carbohydrates, fats and amino acids, a general intermediate product is formed - acetic acid associated with its carrier - Cophermen A - in the form of acetylcooferment A.
The above can be illustrated by the following scheme:
Proteins carbohydrates fats
Acetyl-Co.
The Krebs cycle proceeds in mitochondria with mandatory oxygen consumption and requires the functioning of tissue respiration.
The first cycle reaction is the interaction of acetylcoperment A with oxhelevo acetic acid(Lump) with education citric acid.
CH + S H 2 1
1 1 + H 2 O but - C - Soam + NS ~ Koa
SKOA 1 s H 2 coenzyme a
Acetyl-CoA lemonic acid
Lemon acid is suitable for three carboxyl groups, i.e. is tricarboxylic acid. What caused the name of this cycle.
Therefore, these reactions are called citric acid cycle. Arriving a series of intermediate tricarboxylic acids, citric acid turns again to the oxhelevo-acetic and cycle repeated. The result of these reactions is the formation of cleaved hydrogen, which, passing along the respiratory chain (see the previous lecture), forms water with oxygen. . The transfer of each pair of hydrogen atoms to oxygen is accompanied by the synthesis of three ATP molecules. In total, during the oxidation of one molecule of acetylcooperment, 12 ATP molecules is synthesized.
The final equalue cycle of Krebs (the third stage of the GDF-NUTU):
CH Z - C ~ SKOA + 2O 2 + H 2 O + 12ADF + 12 H 3 RO NSKOA + 2 CO 2 + H 2 O + 12ATF
Acetyl-Co.
Schematically, Krebs cycle can be represented as follows:
Lemon
Acid (from 6)
NSKOA CO 2
Glucose is the main source of energy for the body. It uses all body cells. It is necessary for us to live like gasoline is needed by a car for movement. But car fuel has a simple composition. We consume "complex" food: in it and proteins, and carbohydrates, and fats. To extract energy, the body must be pulled out carbohydrates and split them to glucose. Of course, you can get the body to extract energy from fats. But at such a "prey", a lot of energy is required. Where to take it from? Again from carbohydrates! More than half of the energy spent a healthy organism, it takes exactly glucose. Interestingly, the brain, muscle cells and erythrocytes (red blood cells), unlike other organs, can only use the energy of carbohydrates. Therefore, when there is not enough glucose in the body, they begin to feel "badly". As a result, a person also feels sluggish, sleepy, dispersed. To do mental or physical labor in this state is simply impossible! To feel better, we usually drink tea with sugar, eat a sandwich or a piece of chocolate. But there will be a lot of time before the body splits this food to glucose. And she, in turn, will get to the brain and muscle cells. To quickly fill the lack of glucose in the body, it is enough to eat a chewing tablet block. It consists of glucose, which will start absorbed into the blood already in the mouth. You almost after 1-2 minutes you will feel the tide of energy. Fatigue as a hand will remove. You can easily focus, remember the necessary facts, re-start mental or physical work. Such an effect when taking glucose inside proven by scientific research. By the way, glucose is also the best and safety tools from stress. That is why in critical situations so much like sweet! But not any "sweetness" can help. For example, honey is hardly able to remove the tension. It contains a lot of fructose, which is difficult to absorb the body. Chewing tablets block, on the contrary, consist of glucose (with the addition of natural fruit juices and vitamins). So stress will be effectively blocked! Also, the chewing tablets block help to cope with the feeling of hunger, because they are saturated with glucose organism. The blocks with some tastes include vitamin C (ascorbic acid). It participates in a number of essential physiological processes. Human body Alone ascorbic acid does not synthesize. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain vitamin C with food. In this you will also help chewing tablets block!



















