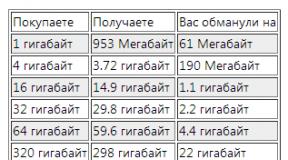
Financial literacy in Russia
The changes that have taken place over the past decades in the economy, as well as in the politics of Russia, left the Russians no choice - in order to live normally in the new conditions, they had, willy-nilly, to master the basics of financial literacy. Today, being financially literate has become a necessity for almost every member of society in order to be able to correctly assess the situation in the market, benefit from it, and make the right decisions.
The financial education of people in Russia today, unfortunately, is at a rather low level. Only a small part of the population is able to navigate the financial sector and its products.
The basics of financial literacy are not studied in schools, they are not taught in universities, except for specialized ones. In some institutions, there are timid attempts to introduce such a subject, however, such a phenomenon has not received mass distribution. Diverse programs in the regions related to improving the financial literacy of the population do not give significant results. Therefore, it makes sense to think about how to solve this problem by doing it yourself.
The Importance of Economic Literacy
Possessing the necessary knowledge in economics and in the field of finance, a person has the opportunity to competently, with benefit for himself, use his own savings and financial resources in general. Financial literacy allows you to fully account for funds, avoid unnecessary spending, as well as debts, teaches you how to plan a budget, which is important for its preservation. The habit of spending more money than you can afford becomes one of the causes of poverty. In addition, knowing the basics of financial literacy, the inhabitants of the country can easily navigate the various monetary intricacies that the economic environment offers today, accumulate and insure their own money.
Also, the general level of education of Russians will be largely influenced by the economic situation of the country. The fight against financial ignorance is important both for each person and for the state as a whole. The implementation of program developments related to the achievement of education of people is becoming a key moment in the position of the state, and not only for the Russian Federation, but also for most developed countries. Education will help reduce the risk of personal debts of the population on consumer loans, as well as the risks associated with fraudulent actions of market participants.

Uncontrolled loans, coupled with consumer loans, undermine the family and personal well-being of citizens, carrying a potential social danger. Therefore, at present, financial literacy is especially relevant in the areas of insurance relations, bank deposits (deposits), money transfers, including Internet banking services, loans (loans), virtual currencies, investment in housing construction, securities, mutual investment funds, as well as the funded part of pensions. What is financial literacy? The concept of financial literacy refers to the ability of the population to:
- effectively manage their own finances;
- keep records of expenses, as well as income and carry out long-term and short-term financial planning;
- be able to optimize the ratio between consumption and savings;
- understand the intricacies of financial products, as well as services (the securities market, collective investments), as well as have up-to-date data on the situation that is developing in the financial markets;
- reasonably make decisions in relation to financial products, as well as services and bear conscious responsibility for them;
- competently plan and implement pension savings.
Read also: Return on investment: what is it, the formula for calculating the balance sheet
There are two key points that are characteristic of a financially literate person.

Ways to improve financial literacy
There are several ways to improve financial literacy. You can use one of the above methods, but it is better to use several at once.
- Do as I do. It is not necessary to study with doctors of economic sciences. There will be much more benefit from master classes by existing professionals who have spent a huge amount of time on a direct study of practical issues. To become a successful entrepreneur, you need to learn from a businessman, a marketer from marketers, a writer from a writer, and so on.
- Selfeducation. If there are no opportunities to contact directly with specialists in the chosen direction, or there is a desire to use several sources of knowledge at once, then you can use a huge number of articles, along with videos, training programs, along with lessons on the Web. In addition, this method is a good opportunity to save money and time. It is only worth remembering that much on the Web is outright nonsense that has nothing to do with reality. However, there are also good materials, sometimes absolutely unique.
- Learning by doing. Financial literacy is a rather unexplored industry, which appeared relatively recently. Therefore, new laws and regulations are constantly being brought to light, so a great way to achieve personal success is to become a pioneer. It will not be possible to go far solely on the knowledge of others, and in any case, you will have to develop the ability to analyze information, supplementing the experience learned from professionals with your own developments, constantly improving.
The relevance of the study is determined by the fact that modern society is in a dynamic state, constantly changing conditions require rapid adaptation to them. The market economy has been in crisis in recent years and requires the population to be literate in their actions.
The purpose of the work is to study theoretical issues on the formation and improvement of the financially literate population of the country.
According to the presidential candidate, Donald Trump:Financial illiteracy is a huge problem. People are constantly entangled in dangerous situations just because they are not properly prepared. » [ 1 ] .
Economists define financial literacy as one of the key concepts of the economy, it is defined as the totality of all knowledge, skills and abilities about the financial market, which will allow a person, being an active subject of a market economy, to correctly assess the current situation in the financial market and make reasonable decisions.
Everyone has to live in the modern world, in which, without knowing the basics of the economy, one can get into a difficult situation.
Therefore, the task of improving financial literacy is the responsibility of the state, business and family. The state, investing in improving financial literacy, is developing an institution for protecting the rights of consumers of financial services. For a large business aimed at long-term presence strategies, raising the level of financial culture of the population through the formation of attitudes, basic knowledge and skills in the financial market is an impetus for its development at a qualitatively new level. In addition, improving financial literacy leads to the development of small businesses: possession of basic financial knowledge helps to rid a person of existing stereotypes and internal phobias, which makes it easier to start your own business and increase its viability and financial success.
Financial literacy is a necessary condition for improving the quality of life, its improvement involves the mastery of financial knowledge by a person throughout his life. Being financially literate means competently managing your money at any age. The fact is that pensioners need to competently manage their savings, not succumbing to the tricks of financial pyramids. And young people are just acquiring the skills of managing a budget, the ability to competently deal with their savings.
The level of financial literacy is manifested in the financial behavior of the population. The components that make up the category "financial literacy" include:
financial knowledge;
Financial skills representing a specific activity;
Financial competencies, which represent the ability of a person to apply knowledge, skills, successfully act on the basis of accumulated practical experience in solving problems in the field of personal finance. An example of financial competence would be the ability to compare existing alternatives when investing and/or applying for a loan and make an informed choice of financial services.
The listed components of financial literacy are of great importance, as they represent a combination of a certain level of financial literacy of citizens with their risk appetite. The propensity of people to take risks is the main problem not only for the population, but contributes to the manifestation of negative effects for the state and society, that is, a low level of financial literacy provokes a high propensity of citizens to take risks. In addition, along with the components of financial literacy and risk appetite, there is a behavioral aspect, that is, attitudes that mean a predisposition to perception and behavior in relation to objects and situations related to personal finance. Behavioral attitudes in the financial sector include:
Trust (or distrust) in financial institutions;
Economic paternalism, which assumes that the population places responsibility for individual financial decisions on the state, or economic individualism;
Economic indifference, that is, the passive and indifferent attitude of citizens to the economic processes in the country, or economic activity;
Priority of profit over compliance with the law, or priority of compliance with the law over profit.
All of the listed components of financial literacy, risk appetite and behavioral attitudes are interrelated with each other and in practice are manifested in the financial behavior of citizens.
Increasing financial literacy along with financial education and protecting the rights of financial consumers has been recognized by the Commission of the European Union and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development as an urgent task of social development.
The financial literacy of the population in countries such as the USA, Canada, Great Britain, Australia, the Czech Republic, and Korea is becoming increasingly acute due to supply and demand factors. In the first case, we are talking about rapid changes in the parameters of the financial services market (growth in the range of financial products, complication of the procedures for their consumption, expansion of the range of organizations providing them and addressees of services). In the second case - about socio-economic and demographic changes (acceleration of the aging process of the population, a decrease in the share of the population of working age, an increase in the heterogeneity of the population, an increase in personal disposable incomes of the population).
In terms of financial literacy of the population, Russia shared 24th place with Belarus, Cameroon, Kenya, Madagascar, Serbia, and the United Arab Emirates. The share of the “financially literate” population, according to S&P, in these states was 38%. At the same time, such countries as Zimbabwe, Turkmenistan and Mongolia (41% each), as well as Kazakhstan, Zambia, Senegal and Ukraine (40% each) outstripped Russia in the ranking.
The issues of studying the financial literacy of the population in the Russian Federation are dealt with by such organizations as: the World Bank, the VISA International Payment System, the National Financial Research Agency (NAFI), the Public Opinion Foundation, the National Fund for the Promotion of Financial Literacy. For the first time, the problem of financial literacy of the population in Russia began to be discussed in 2006 at a meeting in St. Petersburg of finance ministers of the G8 countries, after which measures to develop financial literacy in the country were reflected in a number of documents of the President and Government of the Russian Federation. The main directions for improving the financial literacy of the population in Russia are determined by the order of the Federal Service for Financial Markets of Russia (FFMS) dated September 24, 2009 No. 09-237/pz “On Approval of the Main Directions of Activities Aimed at Increasing the Level of Financial Literacy of the Population” . For the period 2015-2017 in seven regions of Russia: the Republic of Tatarstan, Altai, Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories, Arkhangelsk and Saratov Regions and Moscow, regional programs are being implemented to improve the financial literacy of the population. Regional financial literacy centers have been established in these constituent entities.
According to a survey by the National Financial Research Agency (NAFI), it was revealed that the majority of Russians consider themselves financially illiterate. The survey was conducted as part of a joint project with the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the World Bank in July-December 2015 and covered 5,000 respondents from different cities of our country over the age of 18.
It turned out that only 2% of compatriots consider their knowledge and skills applicable to the concept of "financial literacy" to be excellent. Another 13% note that they have good knowledge and skills, 42% - satisfactory, 25% - unsatisfactory, 16% of respondents indicated that they have no knowledge in this subject at all, 2% found it difficult to answer. Russians are most interested in the problem of protecting the rights of consumers of financial services (31%). The rest of the proposed topics aroused approximately the same interest among the respondents - pensions, long-term purchase planning.
In general, according to NAFI, 21% of the adult population of Russia are not users of banking services. The largest share of people who do not have relations with banks is in rural areas (25%), as well as in the North Caucasus Federal District (27%). The majority (55%) of those who do not use banking services rated their money management skills and knowledge at 1-2 points out of five possible. It is not surprising that financial literacy is directly proportional to the level of education: among the minimum financially literate, 32% have less than a secondary education.
Increasing financial literacy is essential to developing the ability of individuals and their families to manage increased risks. This includes avoiding an excessive increase in personal debt burden, overcoming financial difficulties, reducing the risk of bankruptcy, maintaining savings and ensuring a sufficient level of wealth after retirement. Financially literate consumers are an important prerequisite for the deep development of the financial sector. In addition, improving financial literacy is an important feature of a modern, effective consumer protection regime that includes simple and comparable disclosure to consumers, effective consumer complaint institutions, and the prohibition of unfair market practices.
Financial literacy has a strong impact on the life of a particular person, as it forms his ability to:
Provide for yourself and your family;
Invest in your future and the future of your children;
Develop your creative potential in order to realize your potential and prove yourself a worthy citizen of society.
A low level of financial literacy leads to negative consequences for consumers of financial services, the state, the private sector and society as a whole.
The level of financial literacy indicates the level of development of the country as a whole. There is also a social aspect that should not be forgotten: raising the level of financial education of the working population should be another step towards moving away from “grey” wages. Currently, most Russians acquire theoretical knowledge in the field of finance on their own, through specialized Internet sites, TV shows, literature, news, attending courses and trainings, and gain experience from their own mistakes.
Given the mentality and psychology of the Russian population, it is necessary to concentrate all efforts on creating a state program for the financial education of young people, since the role of an authoritative, independent and reliable provider of information in the field of personal finance, which the state should become, is extremely important in this process. It is from the Government that the younger generation expects "good advice in the field of finance."
Also in modern society, it is necessary to take into account the fact that financial literacy begins with the family, the culture of human financial behavior is associated with the family budget and the strategy for implementing consumer behavior at each stage of the life cycle. The inability to plan a family budget and manage family finances is fraught with negative consequences, both for the family and for society as a whole.
Well-informed and literate consumers place high demands on the quality of goods and services, thereby not only improving their quality, but also stimulating healthy competition among their suppliers, favorably influencing price policy, creating conditions for effective market regulation, the growth of healthy competition among sellers of financial products and services. In the long term, all this leads to lower prices and control over inflation.
It should be noted that the problem of introducing the concept of financial education into existing curricula is relevant for all countries. International experts identify the following main reasons for the need for such integration:
1. This will make it possible to cover all segments of the population with training, regardless of social and financial status, thereby laying the foundations of knowledge and skills for a whole generation;
2. The proportion of students who start making financial decisions at an earlier age (pocket money, spending on a mobile phone, the Internet, etc.) will rapidly increase;
3. It is at an early age that not only the foundations of culture are laid, but also incentives for knowledge and education throughout life.
To address the problem of financial illiteracy among young people, programs aimed at developing the financial literacy of the younger generation are needed, which can have an impact if a number of key conditions are met, which include:
Accessibility and a fascinating form of presentation;
Adaptation to age-related characteristics of perception;
Motivation;
Continuity;
Mass character.
Programs designed to build financial literacy should establish a direct link between the knowledge gained and its practical application, assist in the understanding and use of financial information in the current moment and the long-term future, be guided by the life cycle and life strategies of participants, nurture accountability for financial decisions with taking into account personal safety and well-being.
To have a positive and lasting impact on participants, financial literacy programs for children should be based on up-to-date and understandable real-life examples, developed and presented to students with the participation of representatives of education and the professional community.
Financial literacy is a concept that transcends political, geographic and socio-economic boundaries. The well-being of national economies and the world economic system depends on the contributions that individuals and groups make to them, forming a complex network of interconnected and interdependent relationships.
High financial literacy of the country's population has a positive impact on the economy of the state, on the level of well-being and income of citizens:
Increases the level of use of financial products, transparency of financial markets, market stability;
Promotes an increase in the number of bona fide borrowers, reduces the degree of credit and reputational risks of banks;
Increases the financial well-being of citizens due to the rationalization of family budgets, an increase in the planning horizon, the development of the ability to manage finances throughout the life cycle of the family;
Provides protection against fraud, increases the financial security of citizens.
In the coming years, the need to improve the level of financial education in various countries will increase. In developing countries, improving financial literacy can help reduce poverty. A higher level of financial education provides citizens with an understanding of how the pension and tax systems work, which can contribute to tax collection and the development of small and medium-sized businesses.
The knowledge gained will help not only to better understand how the country's financial system works, but also how the financial life of an individual family is built. Therefore, financial knowledge is as important as the ability to read and write; not only their personal well-being in the future, but also the sustainable economic development of the country will depend on the financial culture of the younger generation. Financial knowledge will help to form a culture of financial behavior and improve the level of financial literacy not only among students and schoolchildren, but also their parents. This knowledge is needed not only by highly educated people who are able to implement high-tech projects, but also by any consumer of financial services.
Improving the financial literacy of the population: international experience and Russian practice Bliskavka Evgenia Aleksandrovna
1.6. Study of the level of financial literacy in Russia
1.6.1. Examples of studies on the level of financial literacy in Russia
Since the problem of financial literacy is relatively new for Russia, it is obvious that the development of programs in the field of increasing FG should be preceded by serious studies of its current level. The results of the study can serve as a basis for determining the most effective directions and methods for bringing financial knowledge to the public.
In order to study the level of FG of the population, studies were carried out by various organizations (the National Agency for Financial Research (NAFI), the Public Opinion Foundation commissioned by the MICEX, etc.). The results indicate the need to increase FG, since:
Up to 40% of respondents believe that the government will compensate them for possible losses associated with personal investments;
Only 9% of adults plan their finances for more than six months and only 0.5% for more than one year;
In the 2007 survey, only 48% of respondents said they were aware of the EIR disclosure requirement;
63.5% of respondents do not trust banks;
60% are not sure that in 20 years the largest companies in the insurance market will not go anywhere. The population has little knowledge of the laws and regulations on financial products.
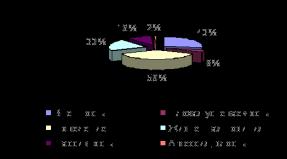
The results of the NAFI sociological study show that financial inclusion rather low – almost half of Russians (44%) do not use financial services (in low-income groups this figure approaches 55%). At the same time, some changes have been noted in recent years. If we talk about the most popular services and products, then the list is headed by bank plastic cards (mainly cards to which wages are transferred) - 21% and consumer loans - 19% (Fig. 1.8).
Rice. 1.8. Use of various financial services by the population, % of respondents
Expectations of state support for individuals carrying out operations in the financial markets are presented in Table. 1.1. The study confirmed that a large number of Russians still expect the government to directly compensate for the losses they have suffered in the financial markets. More than a quarter of the population (28%) believe that the state should compensate their personal financial losses associated with a decrease in the market value of their share in mutual funds, the value of ordinary shares or a fall in real estate prices. There is a high percentage of respondents (32%) who have not formed their own opinion on this issue. Only 9% of respondents believe that in none of the situations listed below, the state should play the role of an insurer.
Table 1.1.
The need to cover financial losses by the state:
Let's provide indicators of the level of financial literacy studied in the survey.
1. Maintaining a personal budget. Less than half of Russians (45%) keep a systematic account of their personal funds (Fig. 1.9).
Maintaining a personal budget; % of respondents
2. Living within your means. Current expenses of 28% of Russians systematically exceed their current income (Fig. 1.10). For the low-income population, this figure is 40%. It was also noted that the poor are more likely to borrow money to make up the difference. In Russia, the ability to borrow money from relatives is still an important factor.
Ratio of income and expenses, % of all respondents*
3. Comparison of alternative financial services (products). 40% of respondents never compare terms offered by different financial service providers (Figure 1.11).
Comparison of financial services of different companies*
4. Planning for the future. Russians are not sure about their income even in the short term (Figure 1.12), and most of the population do not plan their expenses for more than 6 months (Figure 1.13).
Confidence in future income, % of all respondents*
Income planning, % of all respondents*
Concerning basic financial arithmetic skills, then 43% of respondents could not correctly answer any of the six questions that involve calculations (understanding the issue, interest rate, inflation, etc.). Only 11% of respondents answered all questions correctly (Table 1.2).
Table. 1.2.
financial arithmetic skills
1.6.2. Need for financial education and additional information
A large number of NAFI survey respondents say they would like to learn more about personal finance management. The top five topics are: avoiding scams, saving for retirement, managing personal debt, planning for the long term, and the finer points of signing contracts with financial institutions (Figure 1.14).
The study revealed long-term problems of financial literacy of Russians:
Unreasonably high expectations regarding state financial support in cases of financial losses;
Top five topics in financial education, % of all respondents
Low ability of citizens to ensure personal (family) sustainable financial health based on individual financial decisions;
Poor knowledge of the basic principles and instruments of the financial market.
In the latter case, the population, firstly, demonstrates a low ability for long-term planning, people did not respond to the urgent need to independently accumulate funds for their retirement period. While most know that the replacement rate is likely to be very low in the future (projected to be around 24% for 2020) and that pensions alone will not be enough to make ends meet, only 11% of the population have entered into some sort of shaping program. retirement savings. Over 50% of the population knows nothing about private pension funds at all. Only a small number of participants in the funded system of mandatory pension provision independently chose a management company.
Secondly, as noted above, about a third of the respondents systematically go beyond their current income. Low-income strata are more likely to borrow money to cover their financial "holes" (from close and distant relatives).
Thirdly, the majority of the population still places unreasonably high hopes on state assistance in ensuring their personal well-being. These expectations create negative incentives for long-term individual financial planning. As a result, one third of the adult population of Russia does not carry out regular expenditure planning. Those who are engaged in such planning are limited to a short-term period - from a month to six months. Only 9% of the population plans for a period longer than six months. Over half of financial consumers are not aware of their legal rights as financial consumers.
Over 60% of the population is not aware of the obligation of the lender to disclose the annual effective interest rate on the loan. Only 11% of the population knows that the state does not cover all losses resulting from a decrease in the value of investment funds' assets. Only 14% were able to correctly name the amount of insurance coverage for household deposits. 6% of the population believes that state insurance covers all bank deposits in full or up to a million rubles. In addition, it was found that people practically do not know where to look for reliable information regarding the rights of consumers of financial products and services.
Fourth, Russian consumer confidence in the financial sector is generally low. nine % non-saving consumers explained this by their “distrust of financial institutions”. Only 11% of families have insurance policies, while 21% of consumers consider it necessary to insure life, but do not do so because "they do not believe that insurance companies will actually pay out insurance in the event of their death."
Fifth, Russian consumers of financial services have a low level of confidence in the possibility of an easy and fair resolution of problems related to financial transactions. 77% consumers believe that the chances of obtaining a "fast and fair" resolution of disputes with financial institutions are "50:50" or even less. Consumers are also passive in protecting their legal rights. 8% of respondents said that in the last five years they received a financial service (usually some form of consumer credit) that did not meet their needs. And they conclude that they were deceived by the providers of this service. At the same time, over 60% of dissatisfied respondents did not take any action on this issue. Only 4% filed a claim with a financial institution, and 3% filed a complaint with the appropriate government agency.
At sixth, Russian consumers are already taking steps to protect their interests. Over 40% of households responded that they compare the terms of a financial service before purchasing it, although 46% rely on the bank's reputation (and only 37% consider the cost of a loan) as a determining factor when choosing a lending bank. Over 80% receive financial information from newspapers, magazines and specialized television programs. However, when making a financial decision, 51% of respondents turn to family and friends for advice, and 36% turn to “advisers” who accompany the provision of this service.
At the same time, in Russia there is a high demand for financial education and a desire to learn how to protect your interests when interacting with financial institutions, as well as how to recognize and avoid fraudulent financial schemes. 3/4 of families would like to receive financial aid both to protect their financial interests and to plan their future income. 1/3 of respondents want to know about the laws that protect the rights of financial consumers, as well as what should be done if these rights are violated. Over 13% would like to receive information about consumer loans to the population, and another 16% want to get acquainted with the possibilities of obtaining a loan for the purchase of housing. Approximately 26% of the adult population would like to learn how to understand the pension system, as well as learn about ways to save for old age. Another 22% of the population want to learn how to "not get caught up in too much debt when using credit." Young people are particularly interested in planning strategies for large purchases and mortgages. Elderly respondents pay more attention to pension issues. Wealthy households note the need for a clearer understanding of what information a consumer should pay attention to when signing contracts with financial institutions in order not to become a victim of fraud or unfair practices in the future. A quarter of all respondents expressed no interest in financial education of any kind. The population would like PT services to be provided by government regulators, as well as representatives of universities and non-profit organizations (HKOs).
As noted in NAFI studies, a significant part of the economically active population of Russia is not ready to take responsibility for their financial well-being. This largely explains the expectations of citizens to receive “protection” from the state, not so much in the legal aspect of “protection of rights and interests”, but in the paternalistic sense of state “guardianship and guardianship”. And as a consequence of this - low financial literacy and economic inertia of a significant part of the population.
In marketing research on the impact of the 2008–2009 crisis. the financial behavior of citizens shows that Russian citizens do not show an inclination to save (Fig. 1.15).
The period during which a household can live off its savings while maintaining the same level of consumption (%)
The same studies show that those who cannot correctly calculate interest rates on loan products and compare the loan burden with their solvency tend to accumulate credit debt and experience difficulties in repaying debts over a long period. Thus, based on the data presented above, we can conclude that the problem of financial education and increasing FG for Russia is extremely relevant. The level of financial literacy of the population is currently extremely low, and its improvement is an urgent need for everyone.
From the book Rich Dad's Guide to Investing author Kiyosaki Robert ToruChapter 15 Investor Lesson #13: REDUCING RISK THROUGH FINANCIAL LITERACY It was the early spring of 1974. I was only a couple of months away from my discharge from the armed forces. I still did not know what I would do after I left the base gate for the last time. President
From the book Expert No. 11 (2013) author Expert MagazineChapter 16 Investor Lesson #14 JUST ABOUT FINANCIAL LITERACY "Your father is constantly struggling financially because he is literate in words but illiterate in finance," rich dad often told me.
From the book Improving the financial literacy of the population: international experience and Russian practice author Bliskavka Evgenia AlexandrovnaAbout unprecedented financial literacy Alexander Privalov Alexander Privalov The Ministry of Finance proposes to introduce a new subject "Financial Literacy" in schools. The Ministry of Education agrees to recognize discipline as additional. Textbooks are being prepared for schoolchildren of all grades, from the first
From the book It's time to rise! author Kiyosaki Kim2.2. Participation of business in improving the financial literacy of the population A number of leading international banks and financial companies are actively involved in various financial literacy programs that have educational and social goals. The main target audiences
From the book Get Rich! A book for those who dared to earn a lot of money and buy a Ferrari or Lamborghini author DeMarco MJ2.3. Examples of financial literacy programs for schoolchildren A feature of foreign approaches to education in the field of personal finance and financial literacy is that many programs are aimed at school-age children. Necessity and importance
From the author's book2.5. Financial Literacy Programs in the Workplace Financial literacy programs in the workplace are becoming more common. Financial education is useful for both company employees and employers. Research shows that the data
From the author's book2.7. National financial literacy programs: the case of Poland and
From the author's bookChapter 3. Russian practice of improving financial literacy
From the author's book3.1. Overview of the financial literacy and financial consumer protection situation in Russia The financial sector is one of the most dynamically developing in the Russian economy. However, this rapid growth in financial products and services, especially
From the author's book3.2. Financial Literacy Programs for Children and Youth Youth is one of the most vulnerable social groups. The general education system does not include training in personal finance management, and parental experience is often limited or negative.
From the author's book3.6. Increasing financial literacy for start-up entrepreneurs and the self-employed As of 2008, about half of Russia's economically active population did not have access to financial services. A survey dedicated to assessing the accessibility of financial services to Russian
From the author's book3.7. Financial Literacy Training Programs (Train-the-Trainer) The implementation of projects to improve the financial literacy of the population is impossible without the participation of all sectors of society: authorities and state institutions that determine and coordinate
The concept of "financial literacy" means a set of knowledge and practical skills that help a person to effectively manage their funds. A financially literate citizen knows how to plan a personal budget, does not waste money and will not allow scammers to deceive themselves. This quality is so important for life that it needs to be developed constantly, starting from school age.
What is financial literacy
Financial literacy is a set of theoretical knowledge and practical skills related to earning, spending, saving and investing. This is such an important quality for a modern person that it is necessary to lay the foundations of financial literacy at school. The more a person knows about the effective management of money, the richer he will be.
Some people are mistaken in believing that only those who have a lot of them should manage money. Many families live paycheck to paycheck but don't budget for years or keep track of where their finances go. In such conditions, even a salary increase will not help: people will simply start spending more without even understanding what.
On the contrary, competent planning allows you to eliminate unnecessary expenses, create a "safety cushion" and even earn more. Financially literate people choose more favorable terms for deposits and loans in banks, do not borrow from friends, do not overpay in stores, and they are not afraid of scammers. They can quickly calculate which tariff is more profitable and will never invest in a financial pyramid.
This is a skill available to everyone, regardless of gender, education or age. It is only a matter of desire: does a person want to be wealthy or does he like to live without a supply of money? In addition, modern tools and the Internet allow you to learn everything for free.
Only 38% of Russians can be called financially literate, the remaining 62% live under the threat of scammers and overpayments
The level of financial literacy of the population in Russia
Problems with financial literacy among modern Russians grow from the Soviet past. There were no market relations in the USSR, the prices for goods were set by the state for decades, taxes were deducted automatically, and the concepts of "credit" and "mortgage" were absent from the lexicon. The Soviet people trusted the state as much as possible in all monetary matters, and all investments and savings were limited to a savings book.
Adaptation to the market system was difficult and, perhaps, is not over yet. The results of international and domestic studies show the following picture: only 38% of Russians can be considered financially literate. This is an extremely sad conclusion. In fact, monitoring showed that 62% of Russians live under the threat of fraudsters, bad loans and banal overpayments in stores.
For example, in the United States, the ratio of financially literate to illiterate is about 50 to 50, and in advanced countries like Norway, Denmark and Sweden, literates prevail at 71%.
According to officials of the Ministry of Finance, increasing the financial literacy of the population is one of the priorities of the work. Whether the department copes with it is a debatable question. Despite the regular days of financial literacy, many similar projects aimed at teaching how to handle money, there is no positive dynamics yet.
How to check your level
- yourfinance.rf;
- lifehacker.ru
Determining your level in this way will turn out not only accurate, but also interesting. With the help of tests, in just 10 minutes you will receive an objective assessment of your knowledge, and you will also see weaknesses. For example, it often happens that a person as a whole understands how important it is to keep track of money, but cannot compare 2 loans or quickly figure out which deposit rate is more profitable for him.
If the test shows too many errors, you should immediately think about training, for example, take online financial literacy lessons. There are such on the portal yourfinance.rf or dni-fg.ru. Informative videos are easy to find on YouTube. Some of the materials there were prepared jointly with the ICCA and the Higher School of Economics. Even a few good articles can quickly raise the level of literacy, not to mention regular self-education.
Ways to improve financial literacy
So, you realized the importance of the ability to effectively manage money and your lack of knowledge. What to do? First, acknowledging the problem is the first step towards solving it. Practice shows that a person who understands that he still has something to learn in the matter of finance behaves more prudently. It is much worse when it seems to a citizen that he knows everything or, on the contrary, does not know anything and spends money "as it turns out."
Secondly, it is much easier to become financially savvy now than it was in the 1990s. There are many videos, the Financial Literacy project, domestic and foreign books, free courses. From such a range of possibilities, choosing the best way to learn is not a problem.
Thirdly, do not ignore the festival of financial literacy. Such events are regularly held in all regions of Russia: you can listen to lectures for free, get reference books and take tests.

Simple signs of financial literacy
Useful sites
The Internet is the best source of up-to-date information, including financial literacy. You can start from the site yourfinance.rf. This project is working jointly with the Ministry of Finance and the World Bank. Here you can solve the test and also read about:
- family budget planning (as well as find programs for its maintenance in electronic form);
- work and salary;
- contingency insurance;
- debts and loans.
The materials here are divided into categories, so you can both start with the basics and move on to the most interesting questions. Together, this is a complete program. And here you can also ask questions to experts and read instructive personal stories.
Another great source of the most useful information is "T - F", Tinkoff bank blog. The slogan of the magazine "about your money" directly reflects its content: how to save, how to invest, how to save, how to sue and not overpay. The authors of the magazine talk about all the complex problems as simply as possible and with specific examples. Be sure to bookmark "T - F" and read 1-2 times a week.
Another interesting project for financially literate people is the section "Become rich" on the famous site "Lifehacker". There are so many informative and really practical tips about managing money that learning will turn into a pleasant pastime.
Best Books
Of course, books can also be sources of knowledge about finances and savings. But to choose from all the abundance of a really meaningful publication, a full-fledged textbook is not easy. In addition, most books on this topic are foreign, so they are not suitable for Russians. From these, general principles and motivations can be gleaned:
- "The Path to Financial Freedom", B. Schaefer.
- "Think Like a Millionaire" by T. Harv Ecker.
- "The richest man in Babylon", D. Clason.
- “Rich dad, poor dad”, R. Kiyosaki.
- “A million for my daughter. Step by step savings plan. Natural Laws in Business”, V. Savenok.
- "Taste of life", K. Baksht.
- “Global financial crises. Manias, panics and crashes”, C. Kindleberger.
- "Your money", B. Jerry.
- "Personal financial plan", A. Paranic.
- “Save and increase. How to competently and profitably manage savings”, D. Konash.
- Think and Grow Rich, N. Hill.
- “How to teach a child to handle money”, D. Godfrey.
- "Magic ATM", T. Popova (suitable for preschoolers).
- "Economics", M. Goodwin (comics).

The inability to plan a personal budget will lead to poverty, to a life with a constant shortage of money.
For pensioners and students
Online learning and reading books are more suitable for young people and middle-aged people. It is better to develop monetary literacy in childhood. A good way to teach your child how to manage money is school of financial literacy.
Usually these are institutions that work on the principle of circles for additional education: 2-3 classes per week for 1.5 hours. The game format of lessons, communication with peers and practical benefits will help the child manage pocket money more efficiently and be more literate in the future. It is important to make sure that the classes are really meaningful, bring benefits to the child. Otherwise, for parents, they will be nothing more than a waste of money.
Such analogues are also available for pensioners. Something like interest clubs: 1-2 times a week people gather to listen to a lecture and discuss new information. Combining business with pleasure - communication with learning - is favorable for the elderly. By the way, older people are more at risk when handling money: it is easier for fraudsters to deceive them, they may not notice the fine print in a loan agreement, etc. To avoid this, it is worth spending several hours a week on security.
How to understand this expression? Financial literacy of the population is a level of certain knowledge in the monetary sphere that is necessary for every member of society, from a child to an adult. This level is needed in order to be able to correctly assess the market situation and make the right decisions.
Why is it important to be economically literate?
With such knowledge, a person is given the opportunity to competently use his savings and money in general. It helps to fully account for their personal funds, avoiding unnecessary spending and debts, teaches budget planning. Planning spending on needs and desires is very important in maintaining a budget, because spending more money than you can afford is one of the most important.
In addition, knowledge in the financial field helps the inhabitants of the country to navigate the various monetary intricacies offered today in the economic environment. In addition, it gives you the opportunity to accumulate and insure your money.
I must say that much will depend on the general level of education of the inhabitants of Russia and on its economic situation.
Problems of illiteracy of the population
Unfortunately, in Russia it takes place. The fight against ignorance in this area is important both for a particular person and for the state as a whole.
Lack of knowledge can lead to negative consequences that will affect later, not only for users of foreign exchange services, but also for the state and society itself.
Therefore, the implementation of program developments to achieve the education of people has become a key moment for the state position, not only for Russia, but also for most developed countries. The education of people will help reduce the risk of personal debts of people on consumer loans, and will also reduce the risk of fraudulent influences on the part of market participants. And, as you know, loans are widespread among the population, they are taken both for personal needs and for.

In Russia, people's financial education is at a very low level. Only a small part of people are able to orient themselves in the monetary spheres and their products offered by such institutions.
Wrong actions of citizens
Keeping funds at home is observed in half of Russians, but it is obvious that it is much more profitable to do so. The second half does not want to deal with such tools at all.
Insurance of own savings is generally not known to people and few people have come across it. Only a quarter of the population uses bank cards, and then only to withdraw wages from ATMs. The Russians are completely incapable of taking the right steps to regulate their capital, having permanent debt obligations.
The most unacceptable thing is that the population of Russia does not strive to reach the international level of knowledge in the field of money and does not want to accept any specialized advice.
People do not know how to manage their funds and make thoughtless waste. For our citizens, it is a rarity to have. But its absence can lead to serious consequences. It is unacceptable to have just one goal, and not a full-fledged plan that needs to take into account long-term goals, up to retirement.
People do not know what rights they have as a consumer of financial services and how to protect them in case of violations. For example, many do not even realize that banks are required to disclose information about the effectiveness of the interest rate on the required loan.
Only a small part of people know that state protection does not work here, and if they have to face the loss of their funds in investment funds or with, then this will be only their problem. They think that the state will have to compensate them for everything.

Literacy Program
Such data are frightening and point to an urgent need to take up the education of people at a high state level and under its control.
Based on this, a program was adopted to increase the proper level of knowledge for the population, it is designed for five years. The initial stage is already being implemented in many Russian regions. It includes: training teachers and curricula, finalizing and improving the legal framework in the field of monetary services, as well as possible additional consumer rights. About $110 million was allocated to this project by the state, with most of it allocated from the federal budget and only a little from the World Bank.
Main sources of learning
At the present time, the population of Russia receives a huge base of theoretical knowledge. Which are obtained from various sources on their own.
Sources include:
- television programs on important topics for the consumer, teaching the basics of managing funds and capital instruments;
- a large number of specialized Internet sites have been created, which contain all educational information, and there are also forums where specialists in this field can answer questions;
- there are a huge number of open free courses for people to take on financial literacy;
- countless educational literature in printed form;
- showing themed TV shows, and much more.
But as monitoring of the population shows, after all, Russians are used to gaining experience only on their own mistakes.
Therefore, the main attention at the moment was directed to the timely. In the hope that they will be able to achieve success through the knowledge gained at an early age.
“Financial literacy of the population” is the problem of the whole nation and the sooner people understand this, the sooner we will begin to live better.