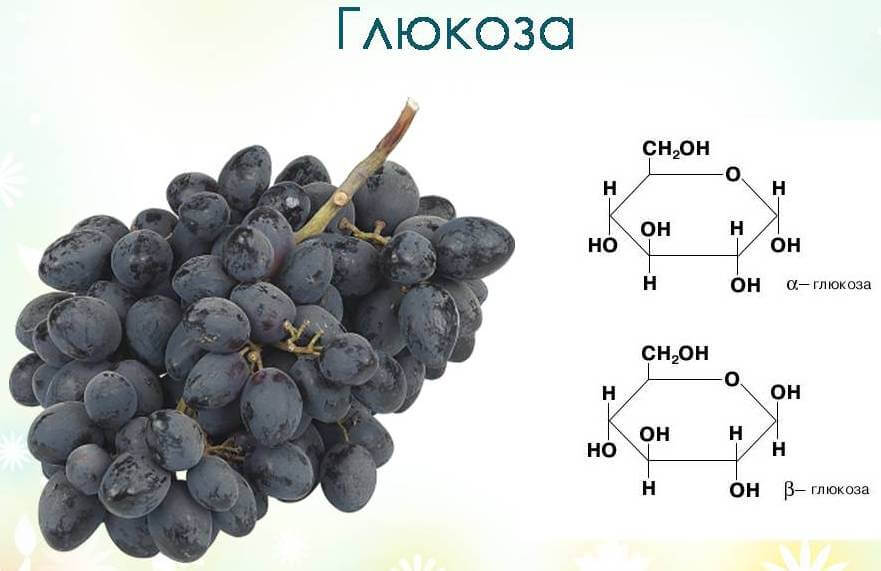
Glucose
Glucose (dextrose) is a monosaccharide that is a universal source of energy for humans. It is the end product of the hydrolysis of di- and polysaccharides. The compound was discovered by the English physician William Prout in 1802.
 Glucose or grape sugar is an essential nutrient for the human central nervous system. It ensures the normal functioning of the body with strong physical, emotional, intellectual stress and a quick response of the brain to force majeure situations. In other words, glucose is a jet fuel that supports all life processes at the cellular level.
Glucose or grape sugar is an essential nutrient for the human central nervous system. It ensures the normal functioning of the body with strong physical, emotional, intellectual stress and a quick response of the brain to force majeure situations. In other words, glucose is a jet fuel that supports all life processes at the cellular level.
The structural formula of the compound is C6H12O6.
Glucose is a crystalline substance of sweet taste, odorless, highly soluble in water, concentrated solutions of sulfuric acid, zinc chloride, Schweitzer's reagent. In nature, it is formed as a result of plant photosynthesis, in industry - by hydrolysis of cellulose,.
The molar mass of the compound is 180.16 grams per mole.
The sweetness of glucose is half that of sucrose.
Used in cooking, medical industry. Preparations based on it are used to relieve intoxication and determine the presence, type of diabetes mellitus.
Consider hyperglycemia / hypoglycemia - what it is, the benefits and harms of glucose, where it is contained, and its use in medicine.
Daily rate
To nourish brain cells, red blood cells, striated muscles and provide the body with energy, a person needs to eat “his” individual norm. To calculate it, multiply the actual body weight by a factor of 2.6. The resulting value is the daily requirement of your body for a monosaccharide.
 At the same time, knowledge workers (office employees) performing computational planning operations, athletes and people experiencing heavy physical exertion should increase the daily norm. Since these operations require more energy expended.
At the same time, knowledge workers (office employees) performing computational planning operations, athletes and people experiencing heavy physical exertion should increase the daily norm. Since these operations require more energy expended.
The need for glucose decreases with a sedentary lifestyle, a tendency to diabetes, and overweight. In this case, for energy production, the body will use not easily digestible saccharide, but fat reserves.
Remember, glucose in moderate doses is a medicine and “fuel” for internal organs and systems. At the same time, excessive consumption of sweetness turns it into poison, turning beneficial properties into harm.
Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia
In a healthy person, the fasting blood glucose level is 3.3 - 5.5 millimoles per liter, after eating it rises to 7.8.
If this indicator is below the norm, hypoglycemia develops, if it is higher, hyperglycemia develops. Any deviation from the permissible value causes disturbances in the body, often irreversible disorders.
Elevated blood glucose increases the production of insulin, which leads to intensive work of the pancreas "for wear and tear." As a result, the body begins to deplete, there is a risk of developing diabetes, immunity suffers. When the concentration of glucose in the blood reaches 10 millimoles per liter, the liver ceases to cope with its functions, the work of the circulatory system is disrupted. An excess of sugar is converted into triglycerides (fat cells), which provoke the appearance of coronary disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart attack, cerebral hemorrhage.
The main reason for the development of hyperglycemia is a violation of the functioning of the pancreas.
 Foods that lower blood sugar:
Foods that lower blood sugar:
- oatmeal;
- lobsters, lobsters, crabs;
- blueberry juice;
- tomatoes, Jerusalem artichoke, blackcurrant;
- soy cheese;
- lettuce leaves, pumpkin;
- green tea;
- avocado;
- meat, fish, chicken;
- lemon, grapefruit;
- almonds, cashews, peanuts;
- legumes;
- watermelon;
- garlic and onion.
A drop in blood glucose leads to malnutrition of the brain, a weakening of the body, which sooner or later leads to fainting. A person loses strength, muscle weakness, apathy appears, physical activity is difficult, coordination deteriorates, there is a feeling of anxiety, clouding of consciousness. Cells are in a state of starvation, their division and regeneration slows down, and the risk of tissue death increases.
Causes of hypoglycemia: alcohol poisoning, lack of sugary foods in the diet, cancer, thyroid dysfunction.
To maintain blood glucose within normal limits, pay attention to the work of the insular apparatus, enrich the daily menu with healthy natural sweets containing monosaccharide. Remember, a low level of insulin prevents the full absorption of the compound, as a result, hypoglycemia develops. At the same time, adrenaline, on the contrary, will help to increase it.
Benefit and harm
The main functions of glucose are nutritional and energy. Thanks to them, it supports the heartbeat, breathing, muscle contraction, brain function, nervous system and regulates body temperature.
 The value of glucose in the human body:
The value of glucose in the human body:
- Participates in metabolic processes, acts as the most digestible energy resource.
- Supports the body's performance.
- Nourishes brain cells, improves memory, learning.
- Stimulates the work of the heart.
- Quickly satisfies the feeling of hunger.
- Relieves stress, corrects mental state.
- Accelerates the recovery of muscle tissue.
- Helps the liver to neutralize toxic substances.
How many years have glucose been used to intoxicate the body, with hypoglycemia. Monosaccharide is part of blood substitutes, anti-shock drugs used to treat diseases of the liver and central nervous system.
In addition to the positive effect, glucose can harm the body of people in old age, patients with impaired metabolism and lead to the following consequences:
- obesity
- the development of thrombophlebitis;
- overload of the pancreas;
- the occurrence of allergic reactions;
- an increase in cholesterol;
- the appearance of inflammatory, heart diseases, coronary circulation disorder;
- arterial hypertension;
- damage to the retina;
- endothelial dysfunction.
Remember, the delivery of a monosaccharide to the body must be fully compensated by the consumption of calories for energy needs.
Sources
The monosaccharide is found in animal muscle glycogen, starch, berries and fruits. 50% of the energy needed for the body, a person receives from glycogen (deposited in the liver, muscle tissue) and the use of glucose-containing foods.
The main natural source of the compound is honey (80%), it also contains another useful carbohydrate - fructose.
| Product name | Monosaccharide content in 100 grams, grams |
|---|---|
| Rafinated sugar | 99,7 |
| Bee Honey | 80,1 |
| Marmalade | 79,2 |
| Gingerbread | 77,6 |
| Pasta | 70,5 |
| sweet straw | 69,1 |
| Dates | 69,0 |
| Pearl barley | 66,8 |
| Dried apricots | 66,1 |
| Raisin | 65,6 |
| apple jam | 65,0 |
| Chocolate | 63,2 |
| Rice | 62,2 |
| Oatmeal | 61,7 |
| Corn | 61,3 |
| Buckwheat | 60,3 |
| White bread | 52,8 |
| Rye bread | 44,2 |
| Ice cream | 21,2 |
| Potato | 8,0 |
| Apples | 7,8 |
| Grape | 7,7 |
| Beet | 6,6 |
| Carrot | 5,6 |
| Cherry | 5,4 |
| Cherries | 5,4 |
| Milk | 4,4 |
| Gooseberry | 4,3 |
| Pumpkin | 4,1 |
| Legumes | 4,1 |
| Cabbage | 4,0 |
| Raspberries | 3,8 |
| Tomatoes | 3,3 |
| Cottage cheese | 3,2 |
| Sour cream | 3,0 |
| plums | 3,0 |
| Liver | 2,7 |
| Strawberry | 2,6 |
| Cranberry | 2,4 |
| Watermelon | 2,3 |
| oranges | 2,3 |
| 2,1 | |
| tangerines | 2,0 |
| Cheese | 2,0 |
| Peaches | 2,0 |
| Pear | 1,7 |
| Black currant | 1,4 |
| cucumbers | 1,2 |
| Oil | 0,4 |
| Eggs | 0,3 |
Glucose in medicine: release form
Glucose preparations are classified as detoxification and metabolic agents. Their spectrum of action is aimed at improving metabolic and redox processes in the body. The active substance of these medicines is dextrose monohydrate (sublimated glucose in combination with excipients).
 Forms of release and pharmacological properties of the monosaccharide:
Forms of release and pharmacological properties of the monosaccharide:
- Tablets containing 0.5 grams of dry dextrose. When taken orally, glucose has a vasodilating and sedative effect (moderately pronounced). In addition, the drug replenishes energy reserves, increasing intellectual and physical productivity.
- Solution for infusion. In a liter of 5% glucose, there are 50 grams of anhydrous dextrose, in a 10% composition - 100 grams of the substance, in a 20% mixture - 200 grams, in a 40% concentrate - 400 grams of saccharide. Given that a 5% saccharide solution is isotonic with respect to blood plasma, the introduction of the drug into the bloodstream helps to normalize the acid-base and water-electrolyte balance in the body.
- Solution for intravenous injection. A milliliter of 5% concentrate contains 50 milligrams of dried dextrose, 10% contains 100 milligrams, 25% contains 250 milligrams, and 40% contains 400 milligrams. When administered intravenously, glucose increases osmotic blood pressure, dilates blood vessels, increases urination, enhances the outflow of fluid from tissues, activates metabolic processes in the liver, and normalizes myocardial contractile function.
In addition, the saccharide is used for artificial therapeutic nutrition, including enteral and parenteral.
In what cases and in what dosage is "medical" glucose prescribed?
 Indications for use:
Indications for use:
- hypoglycemia (low blood sugar);
- lack of carbohydrate nutrition (with mental and physical overload);
- rehabilitation period after protracted diseases, including infectious ones (as additional nutrition);
- decompensation of cardiac activity, intestinal infectious pathologies, liver diseases, hemorrhagic diathesis (in complex therapy);
- collapse (sudden drop in blood pressure);
- dehydration caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or surgery;
- intoxication or poisoning (including drugs, arsenic, acids, carbon monoxide, phosgene);
- to increase the size of the fetus during pregnancy (in case of suspected low weight).
In addition, "liquid" glucose is used to dilute drugs administered parenterally.
Isotonic glucose solution (5%) is administered in the following ways:
- subcutaneously (single serving - 300 - 500 milliliters);
- intravenous drip (maximum injection rate - 400 milliliters per hour, daily rate for adults - 500 - 3000 milliliters, daily dose for children - 100 - 170 milliliters of solution per kilogram of the child's weight, for newborns this figure is reduced to 60);
- in the form of enemas (a single portion of the substance varies from 300 to 2000 milliliters, depending on the age and condition of the patient).
Hypertonic glucose concentrates (10%, 25% and 40%) are used only for intravenous injections. And at one time, no more than 20 - 50 milliliters of the solution are injected. However, with large blood loss, hypoglycemia, hypertonic fluid is used for infusion infusions (100 - 300 milliliters per day).
Remember, the pharmacological properties of glucose enhance (1%), insulin, methylene blue (1%).
Glucose tablets are taken orally, 1 to 2 pieces per day (if necessary, increase the daily dose to 10 tablets).
Contraindications to taking glucose:
- diabetes;
- pathologies accompanied by an increase in the concentration of sugar in the blood;
- individual glucose intolerance.
Side effects:
- hyperhydration (due to the introduction of volumetric portions of isotonic solution);
- loss of appetite;
- necrosis of the subcutaneous tissue (if a hypertonic solution gets under the skin);
- acute heart failure;
- inflammation of the veins, thrombosis (due to the rapid introduction of the solution);
- dysfunction of the insular apparatus.
Remember, too rapid administration of glucose is fraught with hyperglycemia, osmotic diuresis, hypervolemia, hyperglucosuria.
Conclusion
Glucose is an important nutrient for the human body.
 Monosaccharide intake should be reasonable. Excessive or insufficient intake undermines the immune system, disrupts metabolism, causes health problems (leads to an imbalance in the work of the heart, endocrine, nervous systems, reduces brain activity).
Monosaccharide intake should be reasonable. Excessive or insufficient intake undermines the immune system, disrupts metabolism, causes health problems (leads to an imbalance in the work of the heart, endocrine, nervous systems, reduces brain activity).
In order for the body to be at a high level of efficiency and get enough energy, avoid exhausting physical exertion, stress, monitor the functioning of the liver, pancreas, eat healthy carbohydrates (cereals, fruits, vegetables, dried fruits, honey). At the same time, refuse to take "empty" calories, represented by cakes, pastries, sweets, cookies, waffles.