How wine affects a person's blood pressure
It is believed that if you drink red wine during a meal, it will normalize metabolism, improve digestion, and raise your tone. But in connection with the spread of arterial hypertension, it is important to understand: does red wine increase or decrease blood pressure? Much depends on the quality of the drink, the dose, the presence of concomitant diseases. Let's try to figure out in which cases a noble drink is useful, and in which it is undesirable.
Aromatic wines of dark scarlet color are made from table red grapes. Crushed berries go into containers: there the resulting mass is infused for several days. During this time, the secreted juice absorbs the flavoring, pigmenting and aromatic components contained in the peel and seeds. In the process of further fermentation, the squeezed juice, with the addition of sugar, gains strength from 9 to 14% (percentage of ethyl alcohol) and turns into dry red wine.
Benefit
If you follow the described technology, a ripe and aged drink acquires a number of properties that are beneficial to the human body.
- Antioxidant action. The role of fighters with free radicals is played by resveratrol passing from seeds and peel (it is almost absent in white wine), quercetins, saponins and catechins. These components inhibit oxidation processes, including cholesterol, preventing the appearance of its deposits on the vascular walls. The most powerful antioxidant is resveratrol. Modern scientific studies have confirmed that it increases the resistance of the immune system, prevents and inhibits the growth of cancers.
- Strengthening blood vessels. Their elasticity and resistance to damage are increased by procyanides and tannin (tannic acid).
- Protection against pathogenic microflora. Anthocyanins, which color wine in a bright color, are natural antibiotics. They infect one of the types of streptococcus that lives in the oral cavity and protect it from many diseases.
Red wines are rich in vitamins and minerals. Among the latter, it is worth noting magnesium, potassium, iodine, phosphorus, rubidium. They have a beneficial effect on the nervous system and brain activity. Vitamins C, group B, PP, organic acids, essential compounds effectively raise the tone of the body. 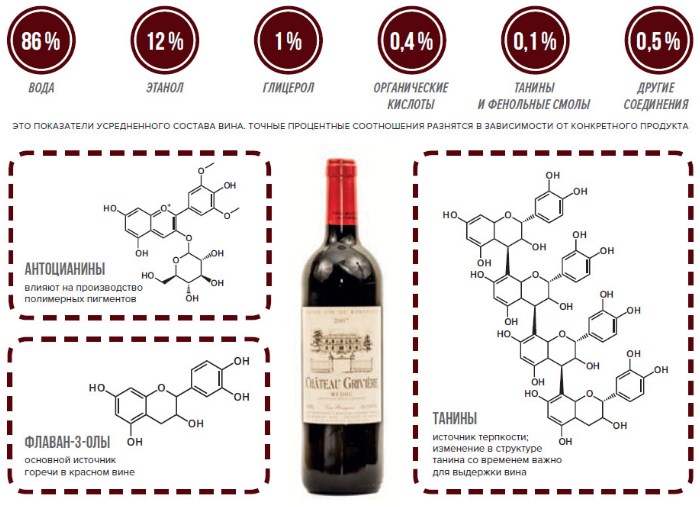
In the course of numerous experiments, it has been established that if you periodically consume high-quality dry wine from red grapes in an amount of not more than 100 ml per day, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of the following pathologies:
- hypertension;
- atherosclerosis;
- strokes;
- tumors;
- diseases of the liver and pancreas;
- endocrine diseases;
- periodontal disease, caries, gingivitis.
Harm
According to doctors, the negative effect of red varieties of dry wine is manifested only with an increased daily rate and systematic use. The constant intake of ethanol in the body causes jumps in blood pressure due to increased contractions of the heart muscle. Regular drinkers develop hypertension, problems with the liver, stomach, and joints. As a result of the immoderate intake of red wine, the following pathological processes may develop:
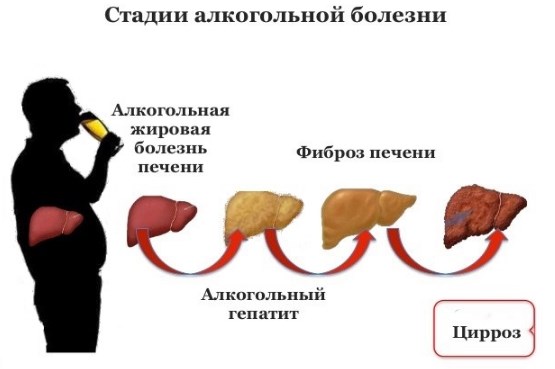
Any alcohol (regardless of the percentage of ethanol) has a bad effect on the nervous system: concentration is lost, the reaction is inhibited, the person becomes irritable. The action of wine depends on individual susceptibility to its components. For example, there are people who suffer from headaches caused by tannin even at small doses.
Please note: A glass of wine contains 160 calories - another strong argument in favor of the reasonable use of an alcoholic beverage.
The effect of wine on blood pressure
Ethyl alcohol, the level of which in red wine is negligible, dilates the vessels: they gradually relax, the lumen increases, and the resistance to blood flow decreases - accordingly, blood pressure decreases for a short time. When the effect of alcohol is over, it will increase again due to vasoconstriction. The persistence and duration of the vasodilating effect depends on the amount and type of wine drunk.
Dose
A smooth decrease in blood pressure is observed after drinking 50-100 ml of the drink. If you drink two glasses, ethanol activates the sympathetic nervous system, which stimulates a rapid heartbeat. At the same time, the heart muscle begins to pump blood in an enhanced mode, the pressure on the walls of blood vessels increases. The risk of negative consequences for the cardiovascular system increases if you consume more than 250 ml of a noble drink every day (for women, the rate is halved). 
Type of drink
Many are interested in: what kind of wine lowers blood pressure for a longer time and then does not increase it too sharply? It is worth mentioning right away: we are talking about grape alcoholic drinks, and not about blends from various fruit and berry wine materials.
White wine and pressure
According to the manufacturing technology, it differs from red: the skin and seeds are immediately removed, the juice is filtered. The molecular size of the finished product is smaller, so the active substances are absorbed faster. Both dry and sweet white wine tend to increase low blood pressure fairly quickly. Mild hypertensive action promotes activation of blood circulation in case of hypotension. Such treatment is permissible only with a daily dose of not more than 100 ml and in agreement with the doctor.
Red dry (vintage) wine
Most varieties contain no more than 11% ethanol, due to which the pressure decreases slightly (by 10-15 units), but for a longer time. A prolonged hypotensive effect is achieved due to the presence of a large amount of fruit acids that prevent vascular spasms after the effect of alcohol has ended. Thanks to this natural antispasmodic, vintage wine constricts blood vessels less intensely than all other alcoholic beverages. 
Finding out how dry red wine can lower rather than increase blood pressure, it is worth noting its ability to increase the concentration of nitric oxide in the blood. In fact, this compound works like nitroglycerin: dilates the coronary arteries, activates blood flow, improves the blood supply to the heart and at the same time reduces the values of systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Magnesium and potassium contained in vintage red varieties strengthen the heart. Procyanides and tannin inhibit the growth of cholesterol plaques, helping to fight atherosclerosis. Thanks to the “bouquet” of useful macro- and microelements, the composition of the blood improves - it liquefies, the percentage of hemoglobin in it increases, and the risk of developing thrombosis and anemia decreases.
Red table wine
Strong sweet and semi-sweet varieties (up to 18% ethanol) only briefly reduce blood pressure. Due to the large amount of sugar, the pressure quickly returns to its previous values. With an increase in the dose of a fortified drink over 150 mg, the heartbeat increases, and hypertension increases. You can reduce the strength of table wine by adding mineral water to it, but hypertensive patients should not drink it.
Warnings and contraindications
Speaking about how red wine affects blood pressure, it is worth noting: people suffering from high blood pressure are at risk. Here are some recommendations for those diagnosed with grade 1 hypertension:

People often ask: is it possible to lower or raise blood pressure with red or white wine, using it instead of medicine? Doctors advise against doing this. If the numbers on the tonometer exceed the norm by 15-20 mm Hg, it is better to drink something from antihypertensive herbal preparations. With hypotension, a cup of strong sweetened coffee will give vivacity and raise the tone.
The use of wine is completely prohibited for expectant mothers, people with hypertension of 2 and 3 degrees, as well as for the following ailments:
- chronic migraine;
- asthma;
- gastritis, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- an allergic reaction to any components of an intoxicating drink (for example, grapes).
Systematically drinking wine is not recommended for both women and men. Under the influence of alcohol in the blood of drinking ladies, an excess of testosterone (male hormone) is formed, and the representatives of the stronger sex produce more estrogen (female hormone). This is fraught with infertility, decreased libido and potency, premature menopause.



















