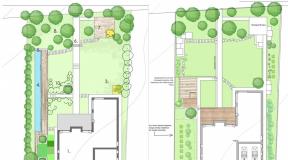
Fight against ground waters. Drainage of the site How to get rid of water in the ditch
Dampness in the cellar is usually caused by the location of groundwater: if they are too close, then it is urgent to solve the problem in order to use the cellar normally at any time of the year. Also, the causes of dampness are increased humidity and lack of ventilation, which leads to the formation of mold. In this article, we will tell you how to get rid of water in the cellar and what means to use to eliminate dampness and mold.
How to get rid of groundwater in the cellar? Build a good drainage system and use waterproofing materials
Water can enter the cellar after a heavy rain in summer or as a result of snow melt in spring, but sometimes dampness annoys regardless of precipitation. In any case, it is possible and necessary to deal with the problem.
How to get rid of groundwater in the cellar
There are several ways to deal with groundwater and dampness:
- perform a good drainage system;
- build a well and lower a pump into it to pump out the incoming water;
- waterproof the cellar with resin, a special gel or using liquid rubber.
The drainage system is equipped inside or outside. External drainage is considered more effective. For him, a trench is first dug 40 cm deep and wide. Further, wells are made to the occurrence of continental sand, usually they go several meters deep. Then plastic pipes wrapped in geotextiles are mounted.
Pipes must be installed so that their top extends beyond the lower edge of the cellar wall. The drainage system is covered with earth in several layers, each of which is carefully compacted.
Through the drainage pipes, water should flow into a specially built well.
It is usually located at the lowest point of the cellar. A pump is lowered into the well, which pumps out water when it reaches a critical level.
A more modern way to get rid of groundwater is waterproofing with liquid rubber, polymer resins and acrylate gels. These products create a seamless, water-impervious coating.
How to get rid of dampness in the cellar
When the water in the cellar is not standing, but still there is increased humidity, leading to the formation of mold, it is worth using effective folk remedies.
They survived the harsh winter and waited for warm spring days, the flood began. The joy of many owners of private houses during the melting snow is overshadowed by the presence of water in the cellar or basement. This problem is repeated in many regions of our country every spring, it can lead to unpleasant consequences for the health of residents, creates a risk of destruction of the foundation, basement and the house as a whole. Let's analyze in detail the causes of water in the basement and how to solve this trouble.
Causes of water in the basement
If measures are not taken to protect the basement from groundwater during construction, then eliminating the consequences of flooding will become a more costly solution.
In the upper layers of the soil, the first aquifer is formed. Moisture gets into it from atmospheric precipitation and melted snow and ice cover, nearby reservoirs. In spring, moisture is abundant, the groundwater level above two meters deep is considered high.
On the way of water penetration into the house, the owners erect two main barriers:
- waterproofing of the foundation, floor and walls of the basement, plinth, which protects the thickness of the concrete and brick layer from gradual seepage of water through microcracks and pores of the material;
- a drainage system under the foundation, around the basement or the entire house, which collects most of the moisture and takes it out of the interior area.
The most common causes of flooding are:
- violations of the technology for arranging external waterproofing of the house;
- clogging, silting of drainage pipes or the volume of effluents exceeding the capacity of the system;
- breakage of water supply or drainage pipes;
- abundant condensation due to poor ventilation of the basement.
Some economical owners build a building without drainage at all, believing that waterproofing will be enough. Often, after several years, water suddenly appears in a dry cellar - this moisture has made its way into the smallest damage to the hydrophobic protection. Calcium carbonate in concrete gradually dissolves, which leads to a loss of the bearing capacity of the walls, mold and fungus grow. The lack of drainage also harms the garden - the root system of fruit trees is eroded, the soil becomes swampy.
It is possible to determine the high level of groundwater occurrence on the site even before the construction of the house with the help of geological expertise, or it is possible according to folk signs: a high water level in the well in nearby areas and the presence of plants such as reeds, willows, alder, horsetail.
What to do if groundwater appears in the basement
If the house has already been built and flooding has been discovered in the basement, then urgent measures must be taken to pump out the incoming moisture in a timely manner and prevent further seepage.

The price of the simplest models of vibration pumps is from 1 to 1.5 thousand rubles
Water pumping methods:
- a vibration (submersible) pump is inexpensive and works efficiently with small volumes of relatively clean water without large debris;
- you can buy a drainage pump yourself or call an emergency team that will do the job professionally and quickly with powerful equipment.
Pumps are divided into submersible and external. The external pump is lowered into the water only by the lower part, and the submersible - completely.
The technology of work on self-removal of the flood with a drainage pump:
- Connect a flexible hose for further discharge outside the house.
- Take a large plastic bucket, drill holes in it, wrap it with a piece of geotextile and place the pump in a makeshift drive. If the water is high, then the entire system with a submersible pump is simply lowered into the water and placed on the floor. For an external pump, pour gravel into the accumulator to the required level so that the lower part is submerged and the upper part remains in the air. The pump with the help of a float determines the water level and turns off after pumping.

The price of drainage pumps starts from 1.5 thousand rubles
To prevent re-flooding after a one-time pumpout, if the water is still slowly coming in, you can make a quick drain, the so-called pit, and create an automatic system that will keep the basement dry until the groundwater level subsides.
Sequencing:

To meet the next flooding season fully armed, you need to equip the internal and external waterproofing, make ring drainage.
To create high-quality internal waterproofing, you will need the following tools and materials:
- composition for penetrating impregnation, bituminous mastic, cement, reinforcing mesh, sand;
- a container for mixing concrete, a drill with a mixer nozzle, a spatula and a brush.
Operating procedure:

For external waterproofing of an already built house, you will have to dig out the foundation as far as possible and coat it with bituminous mastic or wrap it with rolled waterproofing materials 30 cm above the surface level, and then fill the soil back and compact it. Additionally, it can be equipped with a drainage membrane with geotextile.

Drain - an underground artificial watercourse (pipe, cavity) for collecting and draining soil and groundwater
Simultaneously with external waterproofing, it is advisable to make an annular trench drainage, which is placed 50 cm below the level of the foundation heel.
Construction stages:

Drainage will take the brunt of the flood, and high-quality waterproofing will protect against water seepage through the pores of concrete, from dampness and flooding of the basement. Then even in the rainiest spring, the basement of your house will be dry.
The level of groundwater at the site is determined by the results of geodetic surveys.
The high occurrence of underground sources in the upper part of the soil can lead to difficulties in construction work, the appearance of mold on important structural elements, flooding or the destruction of existing buildings.
How to lower the groundwater level on the site to ensure its comfortable and safe operation?
Varieties of water sources
Groundwater is subdivided according to the level of occurrence, the type of soil layers and other characteristics. There are three types of sources:
- surface waters;
- pressure (artesian);
- non-pressure.
Surface waters (perched waters) are aquifers with a depth of up to 2.8 m under the upper layer of soil.
Why can tops rise? This is due to the fact that the level of groundwater directly depends on the amount of precipitation and seasons. However, with the disappearance of the aquifer, the perched water continues to seep into the lower layers of the soil, saturated with limestone and sandy elements. In the hot season, there is a rapid drying of surface sources.
Pressure, or artesian, waters are located at great depths between separate water-resistant soil layers. They are used for arranging drinking water intake points. The location of pressure sources practically does not depend on climatic conditions, therefore, during the operation of the land plot, their removal is not required.
Free-flow groundwater is located above the main aquifer. The level of their occurrence does not change, since the main sources of such waters are atmospheric precipitation penetrating into the soil.
Non-pressure water sources rarely rise to the surface due to the lack of pressure in them, but they can have a negative impact on foundations and underground utilities. Therefore, it is worth determining their presence before the start of construction work.
Negative impact of water sources
Problems associated with high GWL (groundwater level) on the site can lead to an increase in the cost of maintaining land property. Some of them:
- Subsidence of the foundation, deformation of the structure as a result of washing out of the soil. Soils with a high content of clay and sand are affected negatively.
- The formation of floaters and the mobility of the upper layers of the soil.
- Clogging of hydraulic structures, silting of water sources.
- Flooding of technical and utility rooms.
- Increased humidity in residential premises, the formation of mold and fungus.
- Damage to underground utilities.
- Soil erosion under trees and plants, which leads to the need to transfer them to embankments.
If the question of how to deal with groundwater on the site has become relevant, then it is necessary to carefully study the main methods for eliminating such a problem.
The following methods are used to safely lower groundwater levels:
- drainage system device;
- installation of wellpoints;
- use of electric osmosis;
- arrangement of water collection facilities.
Arrangement of the drainage system
Often, a rapid lowering of the groundwater level is carried out as a result of the arrangement of a reliable drainage system. To drain the soil layers, drainages of closed and open type are performed:
- Closed drainage is a system of earthen trenches up to 2 meters deep, filled with perforated plastic pipes, which are used to drain wastewater. The bottom of the trenches is reinforced with sand and gravel cushions and a waterproof layer of geotextile. After installing the pipes, the trenches are covered with gravel and soil.
- Open drainage is represented by a system of narrow ditches, in which special containers equipped with gratings are installed. With their help, an effective lowering of groundwater and the removal of sedimentary runoff from the site are carried out. An open-type drainage system is installed along the perimeter of the foundation crate and is used to drain water from the base of the house or outbuildings.
Installation of light and ejector wellpoints
Effective groundwater control is ensured by the use of modern wellpoints.
- Light wellpoints are used to lower water to a depth of 5 meters. They are represented by steel pipes, at the bottom of which wellpoints are installed. The filter is fixed to the surface pump with a rubber hose and a vacuum type manifold. Installation of the installation is carried out according to the following scheme: the pipe is immersed in the ground along the earthen trench or along the perimeter of the finished pit. Then, under high pressure, fluid is supplied to the wellpoint filter, which contributes to soil erosion and safe immersion of the filter to the required depth.
- Ejector wellpoints are used when soil waters lie at great depths. Such installations are equipped with additional ejector-type lifts, manifolds and centrifugal pumps.
Using Electric Osmosis
The electroosmosis method is used in cases where the lowering of the groundwater level is carried out in areas with a soil filtration coefficient of not more than 0.05 m / day.
This method involves the simultaneous immersion of wellpoints and metal rods into the soil. The wellpoint installation is connected to the negatively charged contact, and the rods to the positively charged contact.
It is important that the electrodes are placed parallel to each other at a distance of 75 to 150 cm. The cathode and anode contacts are installed 2.5 m below the expected level of lowering the water source.
Welding or converting equipment is used as the main current source. When exposed to current, the water contained in the soil rises from the rod to the installation with a wellpoint.
Arrangement of water collection facilities
To safely lower the level of groundwater, it is possible to equip special catchment structures on the land. This method is easy to implement and low financial investment.
To do this, it is necessary to organize a complex of hydraulic structures - ponds with separate pools for collecting water. It is recommended to equip a receiving pool of various configurations near the basement or around the perimeter of the site.
The collection of liquid is carried out through wells of the drainage type with the withdrawal of effluents into the pond.
The bottom of the pond is laid out with reinforced concrete slabs or clay mortar. The bottom thickness is at least 20 cm. The inside of the pool is also strengthened with a clay solution, then it is covered and rammed with rubble, the top layer is fine gravel and sand. Layer thickness - 8 cm.
Pumping equipment is used to divert water.
Lowering the groundwater level prevents possible erosion of the soil on the site, and also protects the finished buildings from deformation and destruction.
The high occurrence of water is quite common among the owners of country houses or cottages. But not everyone knows how to competently get out of the situation, constantly fighting mold and high humidity. It is possible and necessary to fight the root cause, and we know how!
What is groundwater
This is the water that collects in several layers of soil. The occurrence can take place quite far from the surface and not cause any problems to the owner of the site. But when groundwater comes very close, instead of a well-groomed garden, a swamp or a small lake turns out, and constant dampness reigns in the house. Precipitation directly affects the amount of underground reserves, it only seems at first glance that it rained and everything dried up. Moisture tends to accumulate and turn into streams or lakes.
Main types of waters:
- local waters- this means that the depth of their occurrence is approximately 0.5-3 meters. Most often they are located in the depressions between the layers of soil, disappearing in frost or heat. Replenishment of the stock occurs in the rainy season or in the spring, when the snow begins to melt actively.
- Free water- the depth of occurrence is from 1 to 5 meters, they are characterized by a constant nature and are fed from all available sources: springs, wells and other nearby reservoirs. It is non-pressure groundwater that causes the most problems, but they can be removed with a special drainage system.
How to determine the proximity of occurrence
There are several tricks on how to determine the proximity of water.
- Look in and assess the condition of the well and the water level standing there (if there is one, of course). For reliability and accuracy of measurements, the use of twine or tape measure is recommended.
- Reeds and nettles like to settle on moist soil; if they are present, it can be assumed that groundwater is somewhere at the level of 2 meters from the surface.
- A dry area with abundantly green shrubs may also indicate a high water level.
- Partial fogs in the morning.
- Absence of ants.

Peak moments of humidity occur in spring, at its earliest period, and then the necessary measurements are made.
How to get rid of ground water?
Drainage channels and a reservoir come to the rescue.
For this you will need:
- Select a drain location.
- Dig grooves leading to it.
- Cover the bottom with a film so that water does not soak into the ground and replenish underground reserves.

The result directly depends on the choice of a place for an artificial pond and its size. It should be located at the lowest point of the site, and the larger the reservoir, the faster the soil will return to normal. A pond can be used instead of a well or as a supply of irrigation water for garden beds. The depth of the channels must correspond to the level of freezing, and their direction must follow a natural slope.
There is a second disposal option, but it involves pumping water with a pump, which is more difficult to organize from the technical side of the issue.
After solving the problem, you can safely begin construction and installation work, ennoble the territory and bring beauty around the house. Our company "ZemStroy" has been working in the field of earthworks for a long time, we are always ready to make drainage, lay the foundation of a future house or help with finishing!
Excess water in the summer cottage leads to soil leaching, a decrease in the yield of horticultural crops, and deformation of residential and outbuildings. In this case, it is important for everyone who has encountered such a problem to know how to drain the area from water with their own hands.
What influences the choice of dehumidification method
The accumulation of water on the site can occur for many reasons, but the main ones are the following:
- groundwater level rise;
- the site is located in the lowlands, which contributes to the rapid accumulation of precipitation;
- clayey and loamy soils with low moisture absorption coefficient.
The most problematic places on the site are determined in the off-season, when the maximum amount of precipitation falls - in early spring and late autumn. It is recommended to pump water from the site during the dry period - in summer.
Rapid drainage of the land is carried out by several methods. When choosing an appropriate solution to the problem, it is necessary to take into account the main factors:
- type and level of water permeability of the soil;
- size of land;
- optimal level of water drop;
- the period of soil drainage from groundwater;
- finished buildings on the site that require drainage;
- direction of underground sources;
- presence and type of vegetation.
The most popular methods of draining the land on the site are the drainage system, sewage pits and ditches, landscape design elements, moisture-loving shrubs and trees.
Closed and open drainage systems
Modern drainage systems allow you to quickly and effectively get rid of excess fluid in the area. Simple drainage consists of a pipeline and a water receiver. A stream, lake, river, ravine or ditch can be used as a water intake.
The drainage system is equipped from the water intake to the land plot, observing the optimal distance between its main elements. On dense soils with a high content of clay, the distance between individual drains should be 8–10 meters, on loose and heaving soils - up to 18 meters.
open drainage
The open or French drainage system is a shallow ditches, the bottom of which is filled with fine gravel and stones. Such drainage is arranged quite simply: a ditch of small depth is dug out with the discharge of effluents into a drainage well or a deep trench to the level of the sand layer, which is used as a drainage cushion.
A drainage well measuring 1×1 m can have a closed and open design, its bottom is filled with gravel of the middle fraction and brick breakage. Such structures do not clog, but are filled with soil, which is washed out with water. For this reason, draining this type of well is much more difficult than an open gutter.
Closed drainage
A technically sophisticated device that will quickly remove excess water and prevent it from stagnation. The arrangement of closed drainage is carried out using pipes made of clay or asbestos cement with laying in a certain order - in a straight line or herringbone. Closed-type drainage is suitable for areas located on a slight slope, which provides a natural flow of water.
Closed drains are often combined with drainage systems that allow water to be carried away from the base of the house.
Sewage pits and ditches
Many owners choose a fairly simple way to solve the problem of draining areas by digging drains and ditches. The arrangement of a cone-shaped pit is carried out as follows: at the lowest point, you need to dig a pit up to 100 cm deep, up to 200 cm wide at the top and 55 cm at the bottom. The dehumidification system is quite efficient, since excess moisture can be discharged into sewers without the use of additional funds.
The process of arranging sewers is more laborious, but no less effective. Ditches are dug along the entire perimeter of the territory - the depth and width is 45 cm. The walls are made at an angle of 25 degrees. The bottom is laid out with a brick battle or gravel. The main disadvantage of ditches is their gradual shedding, so it is worthwhile to carry out timely cleaning and strengthening the walls with boards or concrete slabs.
Landscape design elements - streams and ponds
We effectively get rid of excess water on the site thanks to the arrangement of artificial ponds and streams. Similar elements of landscape design can be organized in areas located at a slight slope.
Water sources are best arranged in dark places to avoid water blooms. The bottom of the artificial pond is laid out with stone or geotextile.
To enhance the effect, moisture-loving vegetation can be planted next to an artificial reservoir - shrubs, plants, grass.
Such landscape forms are structurally reminiscent of the French drainage system, since they are equipped according to the same principle.
Moisture-loving plantations - shrubs, trees and grass
To drain the soil, moisture-loving trees, shrubs and grasses are used, which are able to pump out excess water.
In order for green spaces to remove moisture, you need to know which varieties are recommended to be planted on the site. Such plantations include: willow, birch, maple, alder and poplar.
Shrubs are no less in demand: hawthorn, wild rose and vesicle. In moist soils, hydrangea, shadberry, spirea, mock orange and Amur lilac develop.
To give the site attractiveness and aesthetics, moisture-loving garden flowers are planted - iris, aquilegia and asters.
Too moist soil is not suitable for growing fruit trees - pears, apples, plums and apricots. Therefore, when choosing trees, it is better to give preference to seedlings with a superficial root system. Planting trees is carried out on hills up to 55 cm high.
To do this, a peg is driven into the soil, the earth around it is dug up to a depth of 25 cm. A prepared seedling is tied to the peg, the roots are sprinkled with earth with the addition of humus. The root neck remains exposed to a height of up to 8 cm above the ground.
After planting is completed, the seedling is watered abundantly with water to get rid of the air gaps between the root system and the soil.
Important! Excessively wet soil has an increased acidity, therefore, when draining, it is recommended to additionally carry out its liming. This will improve the quality of the soil for further gardening and farm work.
During operation, the condition of the soil on the site is carefully checked, since excess moisture can have a negative impact on horticultural crops, residential and outbuildings. The procedure for draining the soil is recommended to be carried out simultaneously with liming.
Now every landowner knows the answer to the question of how to get rid of water on the site and do it right. This will require free time, desire and financial investments.