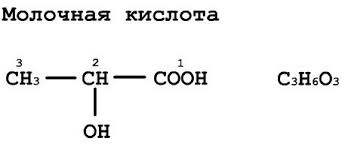
Milk acid from what do. Milk Acid Chemical and Physical Properties Machine Acid Chemical Reference
Milk Acid (lactate) - α-oxypropionic (2-hydroxypropane) acid.
- t pl 25-26 ° C optically active (+) - or (-) - form.
- t pl 18 ° C racemic form.
- Chemical formula: CH 3 CH (OH) COOH
- Racemic formula: C 3 H 6 O 3
Milk acid is formed in the lactic acid fermentation of sugars, in particular, in the black milk, in fermentation of wine and beer. It is used both in the chemical and in the food industry - as a preservative. In the human body, lactic acid (lactate) is formed during glucose decay.
So is there any difference between lactic acid and lactate? Not. In organic chemistry, lactic acid is more often called, in biochemistry - lactate.
Laktat, surrounds probably the largest number of different myths, most of which do not correspond to reality. And although reliable materials about lactate and in Russian, numerous amateur athletes (and some professionals) persistently continue to believe and repeat the myths of the last century.
Let's briefly and thesis repeat the main facts about lactate.
Lactat is always formed in the production of energy in the body.
The main way of energy flow into the cell is a glucose degradation. The glucose molecule is exposed to a series of 10 consecutive reactions to turn out to be pyruvate during the process called Glycoliz. Next, one part of the pyruvate is partially oxidized and turns into carbon dioxide and water. Another part turns into lactate under the control of lactate dehydrogenase enzyme.
This reaction is reversible.
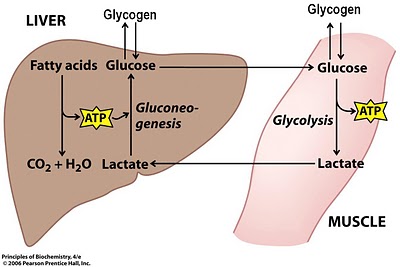
Part of the lactate is used to synthesize energy.
From 15 to 20 percent of the total number of lactate turns into glycogen in the process of gluconeogenesis.
Lactate universal energy carrier.
In terms of high energy production in an anaerobic mode, lactate is a power carrier from those places in which it is impossible to transformation of energy, due to increased acidity, in those places in which it can be transformed into energy (heart, breathing muscles, slowly cut muscle fibers, others muscle groups).
The growth of the level of lactate is not a consequence of the lack of oxygen.
Studies on animals shows that intracellular oxygen deficiency in an isolated muscle does not show any restrictions of the activity of the respiratory chain of mitochondria even during the maximum load. We will always have enough oxygen in the muscles.
Lactate is an indicator of the load of anaerobic glycolysis.
Each time the formation of pyruvate, the final product of glucose metabolism in the process of glycolysis occurs, lactate is based on. Lactate accumulates simply because the speed of energy transformation in anaerobic and aerobic loads differ.
The higher the intensity of work the lactate is made.
The level of blood lactate is closely related to the exercise intensity. Lactate accumulates due to the difference in energy transformation rate in anaerobic and aerobic loads. The rate of energy transformation during an anaerobic energy metabolism is faster than with aerobic.
Laktat does not create acidity, it accompanies it.
By producing energy, we simultaneously produce acidity. Energy reactions in our organism occur with the participation of electrons as energy carriers. Glucolize products are lactate and proton of hydrogen H +. The measure of activity (concentration) of hydrogen ions (H +) in the solution expresses its acidity.
Lactat only takes an acid agent (H +) for a while for the reaction further returning it to a neutral environment.
90% of lactate is disposed of by the body for the first hour after training.
60% of lactate in the body is completely oxidized to CO2 and water. About 20% turns into glycogen during gluconeogenesis, part is used for amino acid neoplasms. Only a small part (less than 5%) lactate is released from then and urine.
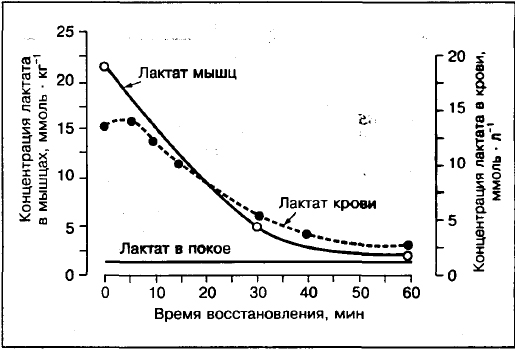
Blood lactate will not systematically reflect the presence of lactate in the muscles.
Comparison of the concentration of lactate in muscles and blood shows that if the force exceeds 75-80% VO2max, the concentration of lactate in the muscles (the biopsy of the muscles of the front of the thigh) is higher than in the blood. Unlike moderate intensity of 30%, 50%, 70% VO2max where lactate concentration in arterial blood higher than in muscles.
Lactat does not cause pain and convulsions in the muscles.
The painful sensations in the muscles the next day after intensive training are caused by muscle damage and inflammation of the tissues that occur after the exercise. Most muscle seizures are caused by nerve muscle receptors, which are overcited with the appearance of fatigue in the muscles.
Based on cmtscience.com (2016).
Oxycycles (alcoholic acids) are derivatives of carboxylic acids containing in a radical connected to carboxyl, one, two or more hydroxyl groups.
Depending on the number of carboxyl groups, oxycycles are divided into monosocondary, two-axis, etc.; Depending on the total number of hydroxyl groups of oxycycles, they are divided into one- or polyatomic.
According to the nature of the radical of oxycycles, there are limiting and unforeseen, acyclic, cyclic or aromatic.
The following types of isomerism are found in oxyc acid:
structural(isomerism of the radical chain, isomerism of the mutual position of carboxyl and hydroxyl);
optical(Mirror), due to the presence of asymmetric carbon atoms.
Names of hydroxy acids are given by the name of the acid with the addition of "Oxy" or "Dioxi", etc. The trivial nomenclature is widely used.
But-sn 2 -son
glycolala (oxyuxus)
dairy (α-oxypropion)
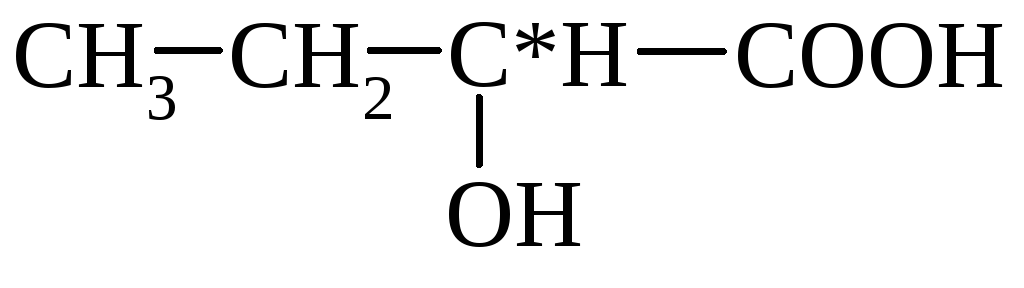
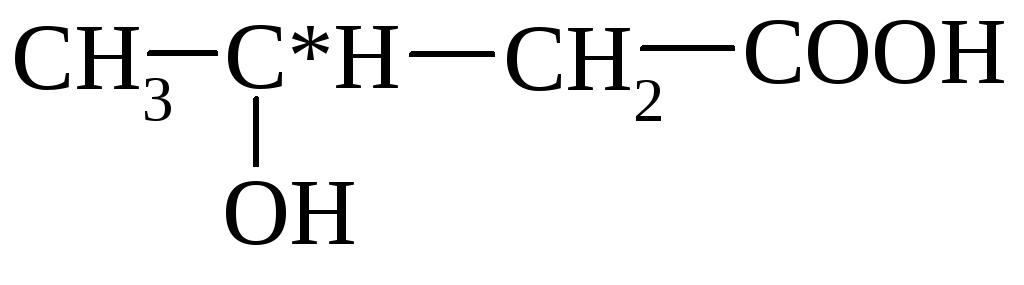
α-hydroxyma β-hydroxymalas
(2-oxibutan) (3-oxibutan)
Physical properties.Lower oxic acids most often are thick, syrupy substances. Oxy acids are mixed with water in any ratios, and solubility decreases with increasing molecular weight.
Chemical properties.
1. Acid properties - hydroxy acids give all reactions characteristic of carboxyla: the formation of salts, esters, amides, halogengidrides, etc. Hydroxy acids are stronger electrolytes than the corresponding carboxylic acids (the effect of the hydroxyl group).
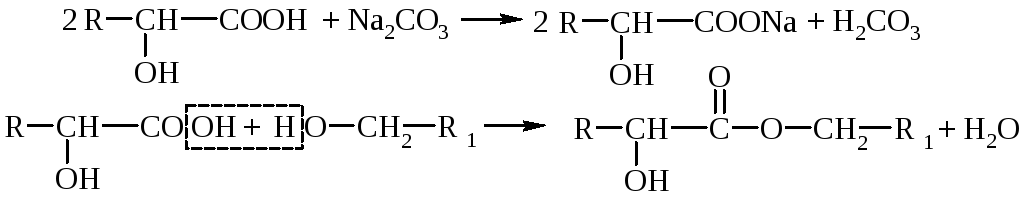
2. Alcohol properties - reactions of hydrogen reaction of hydroxy group, the formation of simple and esters, replacement -On halogen, intramolecular dehydration, oxidation.
chloroaceus glyoxale glyoxale
acid acid acid
a) but-CH 2 -CHON + CH 3 OHNO-CH 2 -CO-O-CH 3 + H 2 O
glycolic acid ester and methyl alcohol
b) but-CH 2 -Oson + 2 ° C 3 ONSN 3 -O-CH 2 -Ost 3 + 2N 2
glycolic methyl methyl ether
acidity of alcohol of methoxyacetic acid
(full ether)
3. The ratio of oxyxlot to heating - when the α-hydroxy acid is heated, water is cleaved by a cyclic ester constructed by the ID of two α-hydoxyclot molecules:
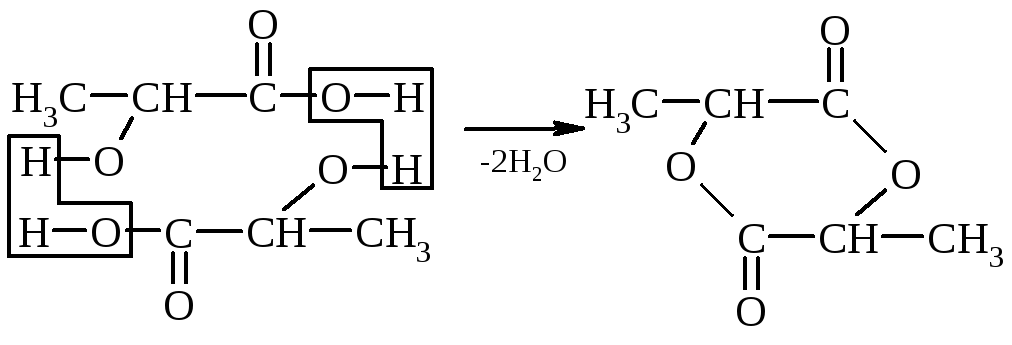
α-oxypropionic acid lactide
β-hydroxy acids in the same conditions easily lose water with the formation of unsaturated acids.
But-CH 2 -CH 2 -Cono  CH 2 \u003d CH-coo
CH 2 \u003d CH-coo
β-hydroxypropionic acrylic acid
γ-hydroxy acids can also lose water molecule with the formation of intramolecular esters - lactones.
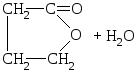
But-CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -Con
γ-oxymalaic acid
γ-butyrolactone
Some oxy acids are obtained from natural products. So, the milk acid is obtained in the milk-acid fermentation of the sugar substances. Synthetic methods of obtaining are based on the following reactions:
1) CL-CH 2 -Son + non  But-sn 2 -son;
But-sn 2 -son;
monochloroaceous glycolic
acid acid
2) CH 2 \u003d CH-coo + non  But-CH 2 -CH 2 -Con.
But-CH 2 -CH 2 -Con.
acrylic acid β-oxypropionic acid
Representatives of Oxycoslot.
Glycolic (hydroxustal) acid - a crystalline substance contained in immature fruits, in beet juice, repex and other plants. Industry is obtained by the reduction of oxalic acid. It is used with dyeing (citrate).
Lactic acid (α-oxypropionic) - a thick liquid or a low-melting crystalline mass. Milk acid is formed in the process of milky-sour fermentation of sugars, under the action of milky-acid bacteria. Contained in fermented milk products, sauerkraut, silo. Used in treasure, in leather production, in medicine.
Measiac acid is contained in the muscular juice of animals and meat extracts.
DiKatomny glycerinic acid participates in the processes of the vital activity of plants and animals.
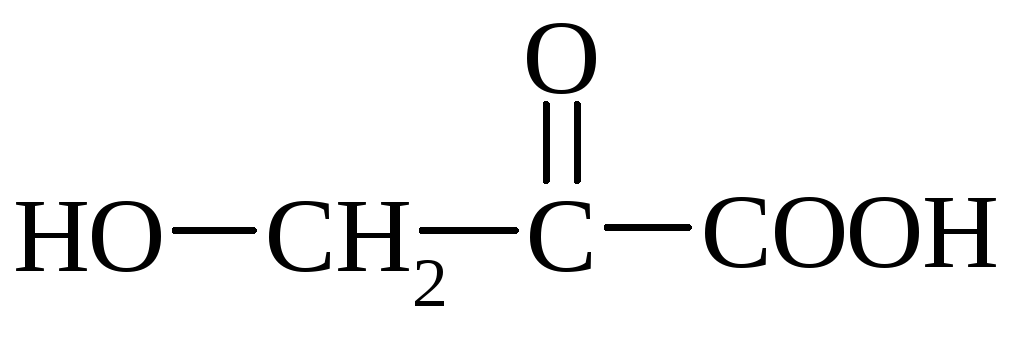
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) - a crystalline substance contained in fresh fruits, lemons, black currant, in fresh vegetables - Cabstone, beans. Synthetically vitamin C is obtained by oxidation of the polyhydric alcohol of sorbitol.
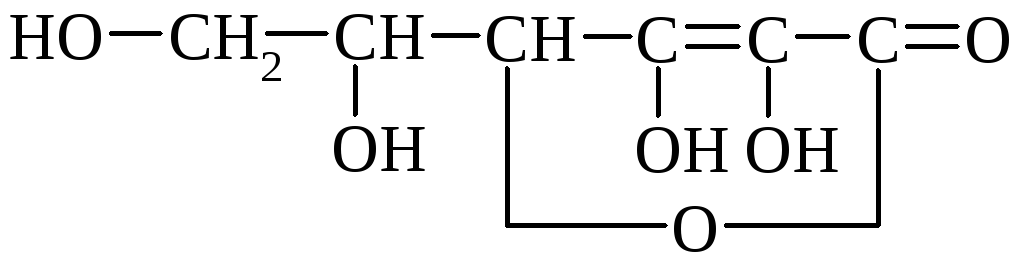 α-ascorbic acid
α-ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is easily decomposed by air oxygen, especially when heated
Acyclic two- And three-axis oxic acids.
Apple (oxicitarian) acid (nos-snon-CH 2 -Con) is a crystalline substance, well soluble in water; It is applied in medicine, contained in the unreliable rowan, barberries, rhubarb, in grape juice, fault.
Wine (Wine-stone, dioxiente) acid (novo-* snon- * Sonya-coxy) has 2 asymmetric carbon atoms and therefore has 4 optical isomers. Forms acidic potassium salts that are poorly dissolved in water and fall into the sediment. Salt crystals can be observed in wine (wine stone). The mixed potassium-sodium salt is called a ferronetic salt. Wine acid salts are called tartrates.
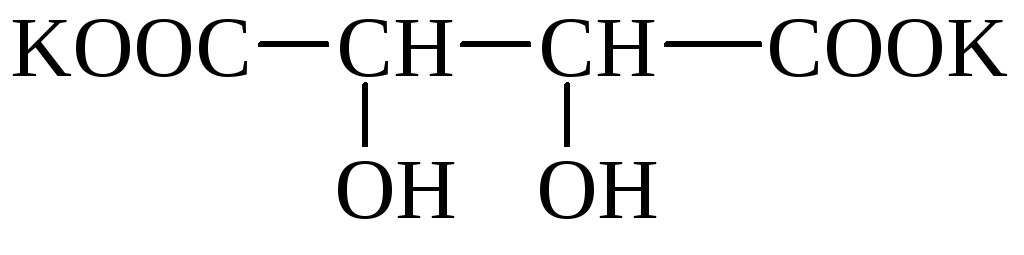
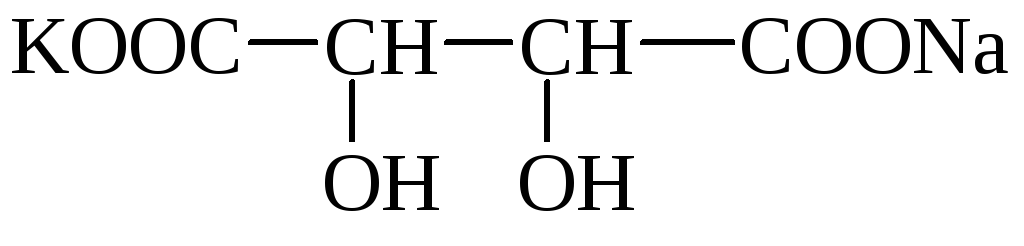
wine Stone Segless Salt
Wine acid is widespread in plants (rowan, grapes, etc.).
Lemon acid
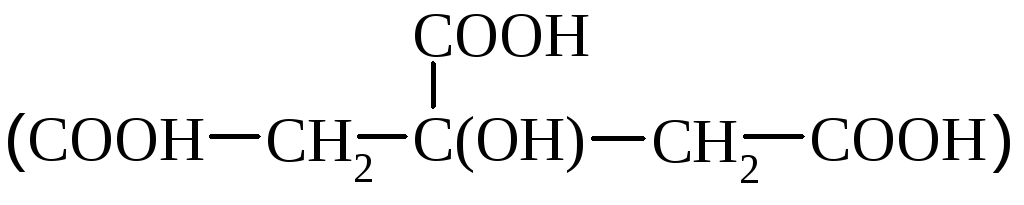 contained in citrus. In industry, it is obtained from lemon fruits, oxidation of sugars with mold fungi, ate with coofing processing.
contained in citrus. In industry, it is obtained from lemon fruits, oxidation of sugars with mold fungi, ate with coofing processing.
Lemon acid is a biologically important compound, takes part in the metabolism. It is used in medicine, food, textile industry as an additive to dyes.
Cyclic monomopic multiatomic oxy acids are part of bile acids and other physiologically important compounds; For example, Auxin enhances plant growth.
Aromatic oxy acidsdivided into phenolocuslots and oily-aromatic acids containing hydroxyl in the side chain.
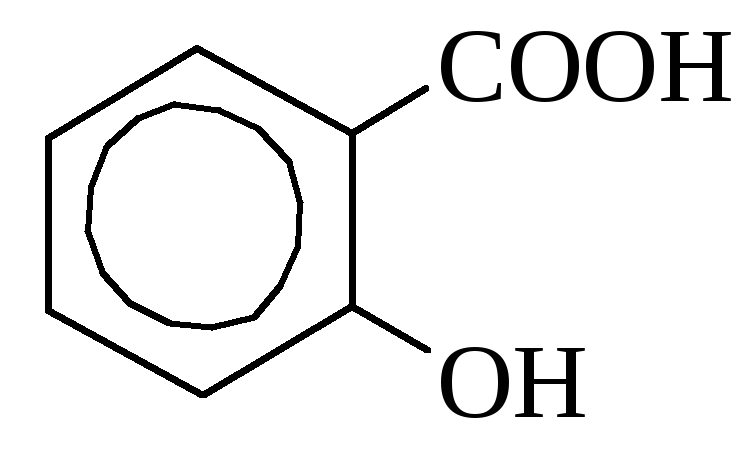
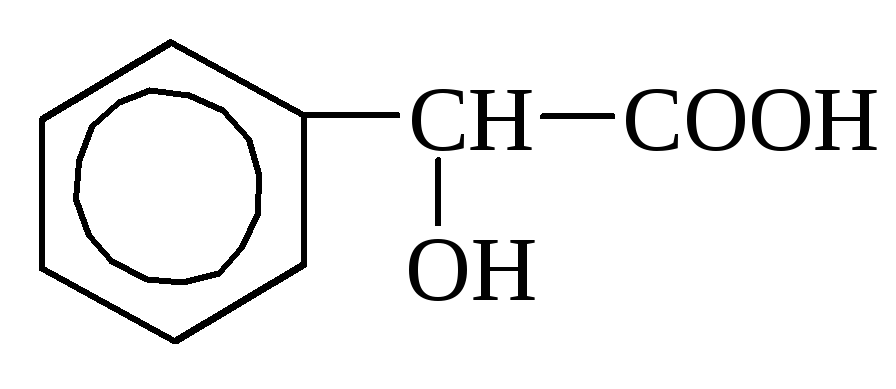
o-oxybenzoic almond acid
(salicylic acid
Salicylic acid it is contained in some plants in free form (calendula), but more often in the form of esters. In industry is obtained by heating sodium phenolate with carbon dioxide. Used as a disinfectant and dyes synthesis. Many salicylic acid derivatives are used as medicines (aspirin, salol).
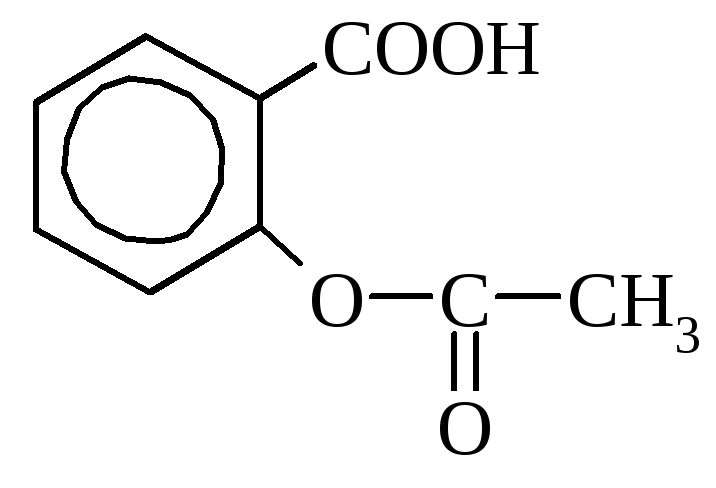
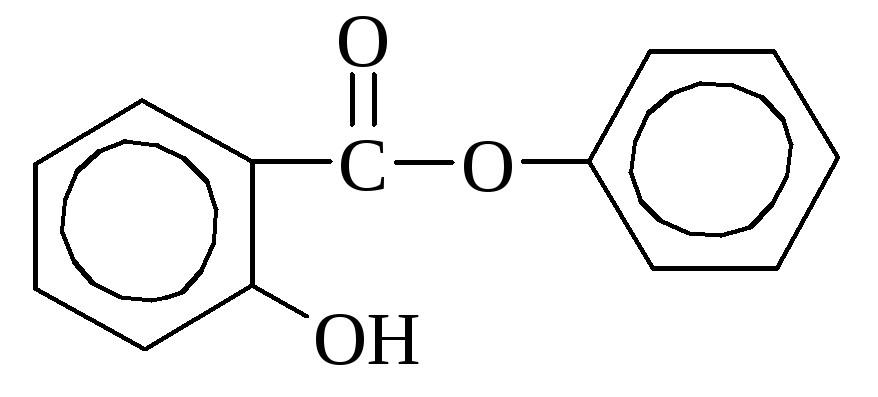
aspirin Salol (phenyl ether
(acetylsalicylic acid) salicylic acid)
Gallic acid (3,4,5-trioxibenzoic).
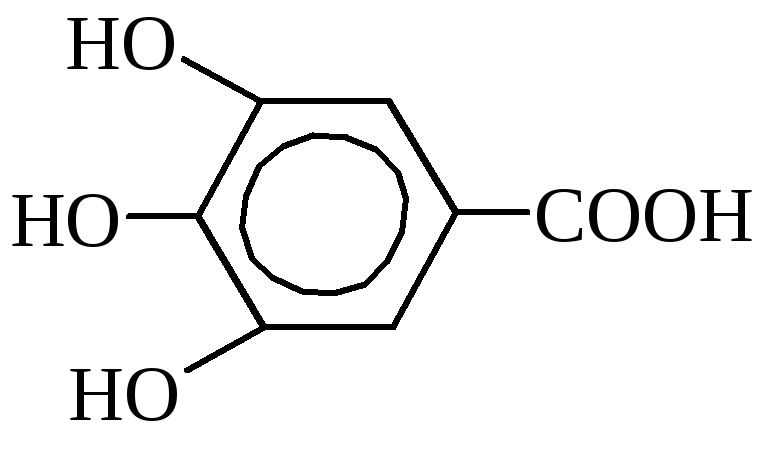
It is contained in the leaves of tea, oak crust, in a pomegranate tree. Industry is obtained from tannin with boiling with diluted acids. It is used for the manufacture of ink, in the photo, in medicine as an antiseptic. Gallic acid and its derivatives are widely used as preservatives for many food products (fats, high-grade soaps, dairy products), has a tanish properties and has a certain value in the skin production and in treasure.
Almond Acid refers to fatty-aromatic acids (from 6 N 5 -CH (OH) -Oson), contains in AmiGdalene, in Mustic, Elder, etc.
Tannins often are derivatives of polyatomic phenols. They are part of plants and are obtained from crust extracts, wood, leaves, roots, fruits or growths (gallins).
Tannins are the most important tanning substances. This is a mixture of different chemical compounds, the main of which are the esters of gallium and digalic acids and glucose or polyatomic alcohols.
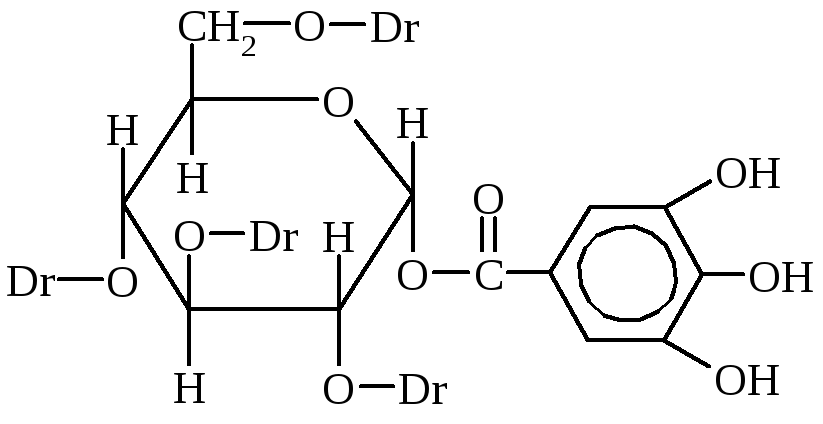
DG-Digal Acid
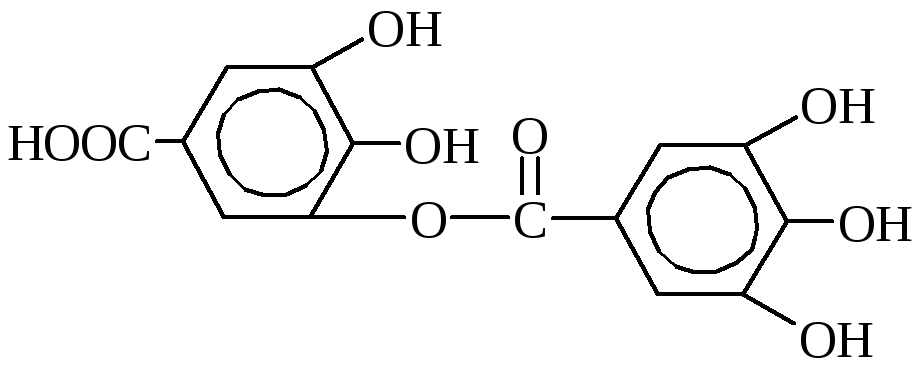
m-Digal Acid
Tannin exhibits the properties of phenols and esters. With a solution of chlorine iron forms a comprehensive compound of black. Tannins are widely used as tubyl extracts, dreashes with a dust of cotton fabrics, like binding substances in medicine (have bactericidal, bloodstand properties) are preservatives.
Lipids include organic substances, many of which are esters of fatty high molecular weights and polyhydric alcohols, are fats, phosphatides, wax, steroids, fatty high molecular weights, etc.
Lipids are mainly in plant seeds, nuclei kernels, and in animal organisms - in fat and nervous tissues, especially in the marines of animals and humans.
Natural fats are mixtures of esters of trothy alcohol of glycerol and higher carboxylic acids, i.e. Mixtures of glycerides of these acids.
ABOUT 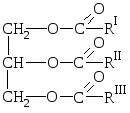 formula fat:
formula fat:
where R i R II R III is hydrocarbon radicals of higher fatty acids of a normal structure with a measurable number of carbon atoms. The composition of fats may include remnants of both saturated and unsaturated acids.
Saturated acids:
With 15 H 31 coh-palmitic;
From 17 H 35 Soon - Stearinovaya;
C 3 H 7 Soam - Oil (contained in butter), etc.
Unsaturated acids:
From 17 H 33 coxy - olein;
From 17 H 31 coh-linoles;
From 17 N 29 Soam - Linolen and others.
Get fats from natural sources of animal and vegetable origin.
Physical propertiesfats are due to acidic composition. Fats containing predominantly saturated acid residues - solid or oil-forming substances (carrying, beef fat, etc.) Fats, which contain mainly the remains of unsaturated acids, have a liquid consistency at room temperature and are called oils. Fats do not dissolve in water, but they are well dissolved in organic solvents: ether, benzene, chloroform, etc.
Chemical properties.Like all the esters, fats are subjected to hydrolysis. Hydrolysis can occur in an acidic, neutral or alkaline medium.
1. Acid hydrolysis.
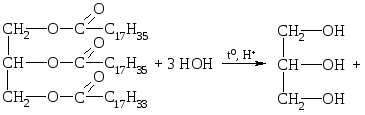
Lactic acid
LACTIC ACID (2-hydroxypropiony K-TA) CH 3 CH (OH) Soam, they say. m. 90.1; Beszvest. crystals. Known d (+) - dairy K-TA, D (-) - dairy (meat-milk) K-Ta and race. Dairy acid milk to-be fermentation. For D, L- and D-lactic acid T.PL acc. 18 ° C and 53 ° C; t. Kip. acc. 85 ° C / 1 mm Hg.st. and 103 ° C / 2mm RT.; For D-lactic acid [A] D 20 -2.26 (concentration of 1.24% in water). For D, L-lactic acid DH 0 arr - 682.45 kJ / mol; DH 0 pl 11.35 kJ / mol; DH is 110.95kJ / mol (25 ° C), 65.73 kJ / mol (150 ° C). For L-lactic acid DH 0 SGR - 1344.8 kJ / mol; DH 0 OP -694,54 kJ / mol; DH 0 pl 16.87 kJ / mol.
Due to the high hygroscopicity of lactic acid, its concentr is usually used. Aquatic Rhine-syrup-shaped Besmene. Fluid odorless. For water ps of lactic acid D 20 4 1.0959 (40%), 1,1883 (80%), 1,2246 (100%); n d 25 1.3718 (37.3%), 1,4244 (88.6%); H 3.09 and 28.5 MPa. C (25 0 s) acc. for 45.48 and 85.32% r-soup; G 46.0. 10 -3 n / m (25 ° C) for 1 m r-ra; E 22 (17 ° C). Milk acid is satisfied. In water, ethanol, bad-in benzene, chloroform, etc. halo originavodors; Рk a 3,862 (25 ° С); pH of aqueous p-mards 1.23 (37.3%), 0.2 (84.0%).
The oxidation of lactic acid is usually accompanied by decomposition. Under the action of HNO 3 or 2 air at the present. Cu or Fe is formed by the NSO, CH 3 coxy, (coxy) 2, CH 3 SNO, CO 2 and pyirograde K-TA. The restoration of the lactic acid Hi leads to propionic k-th, and the restoration of the present. Re-Cherni - to propylene glycol.
Milk acid is dehydrated to acrylic k-you, with nurts. With HBR forms a 2-bromopropione to-one, with the estimates. Case Salts with PCl 5 or SOSL 2 -2-chloropropionyl chloride. In the present Miser. It occurs self-esterification of lactic acid to form a lactone of F-La I, as well as linear polyesters. When completing The lactic acid with alcohols is formed by hydroxy acids RCH 2 CH (OH) Cooh, and with the estimates. milk acid salts withspertametra. Salts and ethers of lactic acid called. lactates (see Table.).
Milk acid is formed as a result laminating fermentation (with milk skiing, sauming cabbage, salting vegetables, ripening cheese, feeding); D-lactic acid is detected in animal tissues, plants, as well as in microorganisms.
In the prom, the milk acid is obtained by hydrolysis of 2-chloropropionic to-you and its salts (100 ° C) or Lactonitrile CH 3 CH (OH) Cn (100 ° C, H 2 SO 4) with the last. The formation of esters, isolation and hydrolysis of the to-ryy leads to a product of high quality. Known others. Methods for producing lactic acid: oxidation of nitrogen oxidizers (15-20 ° C) with the last. Processing H 2 SO 4, Primary. CH 3 SNO with Co (200 ° C, 20 MPa).
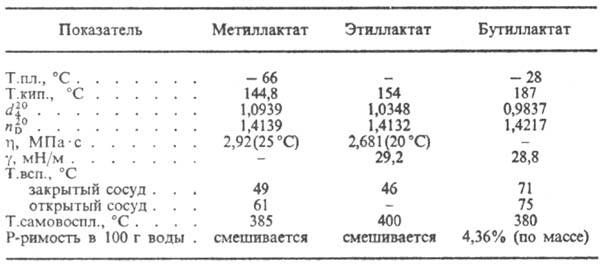
Properties of some lactates
M. oilic acid is used in the Food. Prom-STI, in an etched collapse, in the leather produced, in fermentation shops as a bactericidal CP-Wa, to get lek. CP-B, plasticizers. Ethyl and butyllactates are used as the Esters of Cellulose ethers, Olife, Ramp. oils; Butyl-lactate is also like a rter of some synthetic. polymers.
Lactic acid (2-hydroxypropionic acid) CH 3 CH (O) coxy, molecular weight 90.1; colorless. L (+) is known - lactic acid, D (-) - dairy (meat-milk) acid and racemic milk acid-lactic acid fermentation. For D, L- and D-lactic acid, the melting point corresponds to 18 ° C and 53 ° C; t. Kip. acc. 85 ° C / 1 mm Hg.st. and 103 ° C / 2mm RT.; For D-lactic acid [α] D. 20 -2.26 (concentration of 1.24% century for D, L-lactic acid D H. 0 arr - 682.45 kJ / mol; D. H. 0 pl 11.35 kJ / mol; D. H. PC 110.95 kJ / mol (25 ° C), 65.73 kJ / mol (150 ° C). For L-lactic acid D H. 0 Sgor - 1344.8 kJ / mol; D. H. 0 Opp -694,54 kJ / mol; D. H. 0 pl 16.87 kJ / mol.
Due to the high hygroscopicity of lactic acid, its concentrated aqueous solutions are usually used - syrup-like colorless odorless. For aqueous solutions lactic acid d. 20 4 1,0959 (40%), 1,1883 (80%), 1,2246 (100%); n D. 25 1.3718 (37.3%), 1.4244 (88.6%); H 3.09 and 28.5 MPa. C (25 0 s) acc. for 45.48 and 85.32% solutions; G 46.0. 10 -3 n / m (25 ° C) for 1 m solution; E 22 (17 ° C). Milk acid is soluble in, bad - in, and other halo origoders; R K a. 3.862 (25 ° C); pH of aqueous solutions 1.23 (37.3%), 0.2 (84.0%).
Lactic acid Dehydrates to acrylic acid, when heated with HBR, forms 2-bromopropionic acid, with the interaction of sa-salts with RSl 5 or SOSL 2 -2-chloropropionyl chloride. The presence of mineral acids occurs self-esterification of lactic acid to form formula I, as well as linear polyesters. In the interaction of lactic acid CO, hydroxy acids RCH 2 CH (OH) COOH, A, with the interaction of lactic acid with ethereal alcohols. Milk acid salts and ethers are called lactates (see Table.).
milk acid is formed as a result of a lactic acid (when milk skiing, cabbage sauming, salting of vegetables, ripening cheese, feeding); D-lactic acid is detected in animal tissues, plants, as well as in microorganisms.
In industry, milk acid is obtained 2-chloropropionic acid and its (100 ° C) or CH 3 CH (OH) Cn lactonitrile (100 ° C, H 2 SO 4) followed by the formation of esters, the release and hydrolysis of which leads to a product of high quality. Other methods of producing lactic acid are known: oxidation of nitrogen oxides (15-20 ° C), followed by treating H 2 SO 4, the interaction of CH 3 SO with Co (200 ° C, 20 MPa).
Properties of some lactates

milk acid is used in the food industry, in the treasure, in leather production, in fermentation shops as a bactericidal agent, for obtaining medicinesplasticizers. Ethyl and butyllactates are used as cellulose ethers solvents, oil, vegetable oils; Butyl lactate is also a solvent of some synthetic polymers.
World production of lactic acid 40 thousand tons (1983).
LIT:Holtenc.h., Lactic Acid. Properties and chemistry. Lactic Acid and Derivatives, Weisheim, 1971. Yu. A. TERGER.
Choose the first letter in the title of the article:
Catalog number for lactic acid: CAS 50-21-5
Description of lactic acid:
Almost transparent, slightly yellowish hygroscopic syrup-like liquid with a weakly acidic smell resembling the smell of prokobvashi. Soluble in water, ethanol, bad - in benzene, chloroform and other halo originals. There are various optically active isomers D and L shape. As well as an optically inactive mixture D and L. The latter is obtained with chemical synthesis, and active forms with bacterial. (enzyme method) in the human body, it is the optical form of L fastener in the fastest cycle that is why it is recommended to use as an additive (Lactic ACID, E270), in other industries it does not play a special role.
The global name of the lactanic acid (Lactic ACID) in Russia did not fit, but the name of its lactate salts is found everywhere, much more often than the lactic acid calcium we will slap calcium lactate.
Specification for lactic acid 80%.
Boiling point (100% solution) 122 ° С (115 mm Hg)
Specific weight (20 ° C) 1,22
Solubility in water is completely soluble
Density (at 20 ° C) 1,18-1.20 g / ml
Heavy metals, not more than 0.001%
Iron content, not more than 0.001%
Arsenic content, not more than 0.0001%
Chloride content, not more than 0.002% (by fact.0.0015%)
Sulfate content, not more than 0.01% (by fact.0.004%)
Residue after calcination, not more than 0.1% (by fact.0.06%)
Manufacturer: China
Packing: Barrels 25 kg or Cuba 1200kg
The main physical properties of lactic acid:
Melting temperature: 17 ° C for optically inactive (racematical),
25-26 ° C optically active + or - form
(Differences in melting temperatures allows you to qualitatively and quickly distinguish more expensive optical forms from cheaper inactive !!)
Relative density (water \u003d 1): 1.2
Water solubility: mixed
Molecular weight: 90.08 g / mol
Flash temperature: 110 ° C C.C.
OCTANOL / WATER DISTRIBUTION KOFFORT / WATER LEG POW: -0.6
Explosion and fire hazard:
Supports combustion under normal conditions. Self-burning little likelyDo not allow open fire smoking.
Fire elimination: powder, alcohol-resistant foam, splashing water,
Carbon dioxide.
Chemical stability: Stable for normal temperatures and pressure.
Avoid conditions: dust formation, excessive heating.
Incompatibility with other materials:Strong oxidizers, mineral acids.
Dangerous decomposition products: Nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, couple
Cyanide.
Dangerous polymerization: Not marked.
Danger for man:
Ways of admission to the body:The substance can be absorbed into the body when inhaling the aerosol and through the mouth.
With short-term effects of concentrations exceeding MPC: The substance annoys the skin and airwaysand also has corrosive
Action on the eyes. Corrosive effect when swallowing.
If you get into the eyes: Redness. Pain. Strong deep burns. Protective glasses mask, or
Protective mask. Initially, rinse with plenty of water for several
minutes (take off contact lensesIf it is not difficult), then deliver to the doctor.
Standards of the working area:
TLV (limiting threshold concentration, United States) is not installed.
Carcinogenicity: Not Listed by ACGIH, IARC, NTP, OR CA PROP 65.
Epidemiology: No information.
Tetratogenicity: No information.
Reproductive effects:No information.
Mutagenicity: no information
Neurotoxicity: No information.
Animal experiences showed:
LD50 / LC50:
DRAIZE test, rabbit, eyes: 100 mg severe;
Draize test, rabbit, leather: 500 Mg / 24h Mild;
Inhalation, rat: LC50 \u003d\u003e 26 Mg / m (cubic) / 1H;
Oral, mouse: LD50 \u003d 1940 Mg / kg;
Oral, rat: LD50 \u003d 1700 Mg / kg;
Leather, Rabbit: LD50 \u003d\u003e 10 GM / KG;
Attention. Information is given about the concentrate of a substance, in small quantities and concentrations of lactic acid, according to the currently available data harmless!



















