What foods contain carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds that supply the body with the energy necessary for full functioning. They are part of every tissue and cellular structure. Carbohydrates account for approximately 2.7 percent of total body weight. Without them, internal organs and systems cannot function normally. Maintaining the ratio of carbohydrates in the body becomes possible with a balanced diet, including foods containing these and other beneficial substances.

To understand why these organic compounds are so important, it is necessary to study their functions. Carbohydrates that enter the body with food have the following range of actions:
- They supply energy resources to the human body. This occurs due to the oxidation of the compound. As a result of this process, one gram of carbohydrate produces 17 kilojoules or 4.1 calories. Oxidation is accompanied by the consumption of either glycogen (a reserve reserve of carbohydrates) or glucose.
- They take part in the formation of various structural units. Thanks to carbohydrates, the body builds cell membranes, produces nucleic acids, enzymes, nucleotides, and so on.
- Form energy reserves for the body. Carbohydrates, taking the form of glycogen, are deposited in muscle and other tissues, and the liver.
- They are anticoagulants. These substances thin the blood and also prevent the formation of blood clots.
- They are part of the mucus lining the gastrointestinal tract, the surfaces of the respiratory and genitourinary systems. By covering these internal organs, mucus resists viral and bacterial infections and provides protection from mechanical damage.
- They have a positive effect not on digestion. Carbohydrates stimulate the function of digestive enzymes, and, therefore, improve digestive processes and the quality of absorption of nutrients and valuable substances, and activate gastric motility.
In addition, these organic compounds increase the body’s protective functions, determine blood type, and also reduce the likelihood of developing cancer pathologies.
Types of carbohydrates
Organic substances from the carbon group are divided into two large groups - simple and complex. The former are also called fast or easily digestible, and the latter - slow.

They have a simple composition and are quickly absorbed in the body. This feature of carbohydrate leads to a sharp increase in blood glucose. The body's reaction to the consumption of simple carbohydrates is a large release of insulin, the hormone responsible for the production of pancreas.
The sugar level under the influence of insulin decreases below the standard norm. Thus, a person who has recently eaten foods rich in simple carbohydrates begins to feel hungry quite quickly. In addition, the conversion of sugar molecules into subcutaneous fat occurs in a ratio of one to two.
If you abuse food that is rich in fast carbohydrates, this will lead to the following adverse consequences:
- constant feeling of hunger and desire to snack;
- insulin damage to blood vessels;
- rapid wear of the pancreas;
- increasing the risk of developing diabetes.
These negative effects became the main reason that these carbohydrates began to be called harmful or undesirable.

Slow organic compounds, such as fiber, glycogen, starch, act on the body in a completely different way. The substances included in this group have a complex composition, which means their absorption rate is much lower than that of fast ones. These compounds have high nutritional value and therefore the sugar concentration practically does not increase, and, consequently, a person feels full for a long time.
Since the concentration of sugar is not too high, the liver has time to process it. This means that it is almost completely converted into energy resources, and is not stored as fat. Thus, complex carbohydrates do not cause any harm to the body, that is, they are beneficial.

The daily intake of an organic energy source is determined by age, gender, weight, lifestyle and some other factor. To calculate your daily carbohydrate intake, you can use the following calculation:
- determine your weight norm, that is, subtract 100 centimeters from your height;
- multiply the resulting number by 3.5.
The resulting number will become the daily consumption rate. If your height is 170 cm, then the amount of carbohydrates consumed per day should be 245 grams.
What foods contain simple carbohydrates?

Sources of fast carbohydrates include:
- natural honey, sugar, jam;
- baked goods, confectionery, loaves;
- semolina and white rice flour;
- pasta from white wheat varieties;
- juices and carbonated drinks, as well as syrups;
- dried fruits and sweet types of fruits;
- some varieties of vegetables.
These products are not the most useful.
| Food products | |
|---|---|
| Granulated sugar | 99,6 |
| Caramel | 88,1 |
| Cornflakes | 83,4 |
| Honey | 81,4 |
| Waffles stuffed with fruit jam | 80,7 |
| Semolina | 73,2 |
| Marmalade | 71,1 |
| Jam | 69,9 |
| Bagels | 69,8 |
| Dates | 69,1 |
| Crackers | 67,2 |
| Rye malt | 66,8 |
| Raisin | 64,9 |
| Popcorn | 62,9 |
| Milk chocolate | 60,2 |
| Instant pasta | 56,9 |
| Butter pastries | 55,2 |
| Halva | 54,3 |
| Chocolate candies | 54,1 |
| Viennese waffles with caramel filling | 53,7 |
| Potato chips | 52,8 |
| Shortbread | 49,9 |
| Cookies "Nuts" | 49,3 |
| White bread | 48,9 |
| French bread | 47,4 |
| Cakes | about 46 |
| Coca Cola | 42,3 |
| Prunes | 39,8 |
| Donuts | 38,9 |
| Apple pie | 38,3 |
| Eclair cake with cream filling | 35,9 |
| Alcoholic drinks (wine, vermouth, etc.) | 20–35 |
| Ice cream | 24,9 |
| Boiled white rice | 24,7 |
| Pizza | 24,4 |
| Fried potatoes | 23,2 |
| Canned Sweet Corn | 22,6 |
| White bread croutons | 19,6 |
| Hot Dog | 19,4 |
| Boiled potatoes | 16,8 |
| Grape | 15,2 |
| Mashed potatoes | 14,3 |
| Boiled beets | 10,2 |
| Beer | 9,8 |
| Orange juice | 8,4 |
| Apricot | 7,8 |
| Pumpkin | 7,4 |
| Melon | 5,3 |
| Watermelon | 5,2 |
| Boiled carrots | 4,9 |
What foods contain complex carbohydrates?

Sources of slow carbohydrates include:
- bakery products made from wholemeal flour;
- various types of mushrooms;
- durum wheat pasta;
- cereals and legumes;
- most types of vegetables;
- various greens;
- unsweetened fruits.
These products are healthy.
| Food products | Volume of carbohydrates per 100 g (in grams) |
|---|---|
| Beans | 54,3 |
| Lentils | 53,8 |
| bitter chocolate | 48,3 |
| Wholemeal bread | 46,1 |
| Soybeans | 26,6 |
| Durum wheat pasta | 23,2 |
| Cashew | 22,2 |
| Green pea | 13,2 |
| Olives | 12,8 |
| Pomegranate | 11,9 |
| Apple | 11,4 |
| Pear | 10,8 |
| Root celery | 10,8 |
| Peach | 10,2 |
| Plums | 9,9 |
| Gooseberry | 9,8 |
| Onion | 9,4 |
| Raspberries | 8,9 |
| Mandarin | 8,4 |
| Orange | 8,3 |
| Beans | 8,2 |
| Red Ribes | 8,1 |
| Black currant | 7,9 |
| Kiwi | 7,6 |
| Grapefruit | 7,4 |
| Nuts (except cashews) | 7,1–11,6 |
| Zucchini | 5,8 |
| White cabbage | 5,7 |
| Broccoli | 5,2 |
| Sorrel | 5,2 |
| Brussels sprouts | 5,1 |
| bell pepper | 4,9 |
| Cauliflower | 4,8 |
| Radish | 4,2 |
| Feathered green onions | 4,2 |
| Green beans | 4,2 |
| Lemon | 3,7 |
| Tomatoes | 3,4 |
| Cucumber | 2,4 |
| Spinach | 2,4 |
| Leaf salad | 2,1 |
| Fresh mushrooms (except champignons) | 1,1–3,6 |
| Champignon | 0,6 |
What are the dangers of excess and lack of carbohydrates?
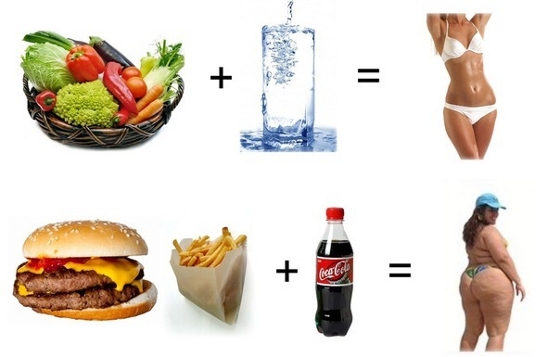
Excess carbohydrates entering the body with food lead to a sharp increase in the concentration of insulin in the blood and rapid formation of fats. In other words, the cause of obesity, diabetes and other health problems associated with excess weight is carbonaceous foods.
The lack of such products in the body is also harmful. If carbohydrates are supplied in limited quantities, glycogen reserves are gradually depleted, fats accumulate in the liver and various dysfunctions of this organ develop. A deficiency of this organic compound leads to increased fatigue, a general feeling of weakness, and decreased physical and intellectual activity.
When there is a lack of carbohydrates, the body receives the energy necessary to maintain vital functions from fatty tissues. The high rate of fat breakdown causes increased production of harmful catenes. This leads to acidification of the body and ketoacidotic coma.
The appearance of the first signs that signal a deficiency or excess of carbohydrates should be carefully reconsidered and the daily diet should be adjusted in the future. A properly composed menu allows you to avoid the negative consequences associated with an overdose or lack of carbon-based food.



















