Innovations in the treatment of type 1 diabetes
Every year, new treatments for type 1 diabetes appear in medicine. This is due to the fact that pathology is getting younger from year to year, and medicine does not stand still.
Type 1 diabetes mostly affects young people. But in the modern world, medicine does not stand still. Patients often wonder if there is anything new in the treatment of type 1 diabetes? What innovations will soon overcome the disease?
Vaccination
News in the fight against type 1 diabetes in 2016 came from the American Association, which introduced a vaccine against the disease. The developed vaccine is completely innovative action. It does not produce antibodies against the disease like other vaccines do. The vaccine blocks the production of a specific immune response to pancreatic cells.
The new vaccine recognizes blood cells that attack the pancreas without affecting other elements. For three months, 80 volunteers participated in the study.
In the control group, it was found that pancreatic cells are able to self-repair. This increases the secretion of your own insulin.
Prolonged use of the vaccine leads to a gradual decrease in insulin dosage. It should be noted that no complications were observed during the clinical trials.
However, vaccination is ineffective in patients with a long history of diabetes. But it has a good therapeutic effect during the manifestation of the disease, when an infectious factor becomes the cause.
BCG vaccine
The Massachusetts Science Laboratory has conducted clinical trials of the well-known BCG vaccine, which is used to prevent tuberculosis. Scientists have concluded that after vaccination, the production of leukocytes, which can affect the pancreas, decreases. Along with this, the release of T cells is stimulated, which protect beta cells from autoimmune attack.
Observing patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, a gradual increase in the population of T-cells has been noted, which has a protective effect. Over time, the secretion of their own insulin came to normal levels.
After two vaccinations with an interval of 4 weeks, patients showed a significant improvement in their condition. The disease has passed into the stage of stable compensation. Vaccination allows you to forget about insulin injections.
Encapsulation of pancreatic beta cells
A good result for the treatment of diabetes is the latest biological material that can deceive one's own immune system. The material became popular thanks to scientists from Massachusetts and Harvard University. The technique has been successfully tested on laboratory animals and had no side effects.
For the experiment, pancreatic islet cells were grown in advance. The substrate for them was stem cells, which, under the influence of the enzyme, were transformed into beta cells.
After obtaining a sufficient amount of material, the islet cells were encapsulated with a special gel. The gel-coated cells had good nutrient permeability. The resulting substance was administered to experimental laboratory animals suffering from diabetes mellitus by intraperitoneal injection. The prepared islets were inserted into the pancreas.
Over time, the pancreatic islets produce their own insulin, limiting themselves from the influence of the immune system. However, the lifespan of the implanted cells is six months. Then a new replanting of protected islets is required.
Regular injection of islet cells wrapped in a polymer shell makes it possible to forget about insulin therapy forever. Scientists plan to develop new capsules for islet cells with a prolonged lifespan. The success of clinical trials will be the impetus for maintaining long-term normoglycemia.
Brown fat transplant
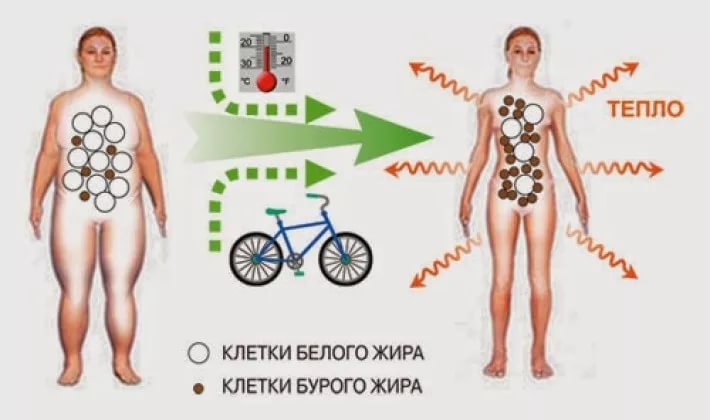
Brown fat is well developed in newborns and hibernating animals. In adults, it is present in small quantities. Functions of brown adipose tissue:
- thermoregulation;
- acceleration of metabolism;
- normalization of blood sugar levels;
- reduced need for insulin.
Brown fat does not affect the occurrence of obesity. The reason for the development of obesity is only white adipose tissue, and this is the basis of the mechanism of transplantation of brown fat.
The first news in the treatment of type 1 diabetes with brown fat grafting was provided by scientists at Vanderbilt University. They transplanted fatty tissue from healthy laboratory mice into experimental specimens. The result of transplantation showed that 16 out of 30 sick laboratory mice got rid of type 1 diabetes.
Developments are underway to allow the use of brown fat in humans. Given the undeniable positive results, this direction is very promising. Perhaps this particular transplant technique will be a breakthrough in the treatment of type 1 diabetes.
Pancreas transplant
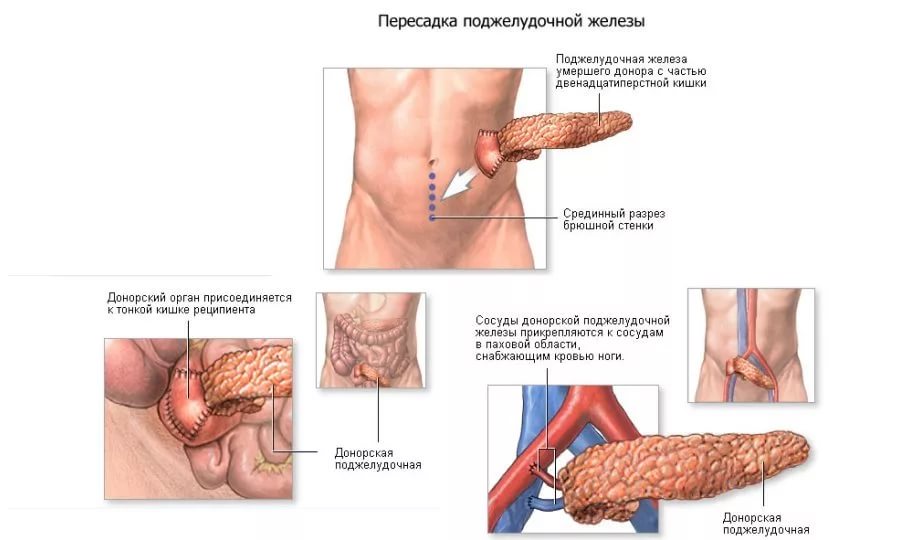
The first news about a pancreas transplant from a healthy donor to a person with diabetes mellitus began to spread as early as 1966. The operation allowed the patient to achieve stabilization of sugars. However, the patient died 2 months later from autoimmune pancreatic rejection.
At the present stage of life, the latest technologies have made it possible to return to clinical research. Two types of surgical interventions for diabetes mellitus have been developed:
- replacement of the islets of Langerhans;
- complete transplantation of the gland.
Islet transplantation requires material obtained from one or more donors. The material is injected into the portal vein of the liver. They get their nutrients from the blood by producing insulin. Until the end, the function of the pancreas is not restored. However, patients achieve stable compensation of the disease.
The donor pancreas is surgically placed to the right of the bladder. Your own pancreas is not removed. Partially, she still takes part in digestion.
Anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants are used to treat postoperative complications. Suppressive therapy stops the aggression of one's own body to the donor material of the gland. It is thanks to postoperative treatment that most surgical interventions end in success.
When transplanting a donor pancreas, there is a high risk of postoperative complications associated with autoimmune rejection. A successful operation permanently relieves the patient of insulin dependence.
insulin pump
The device is a syringe pen. The insulin pump does not save the patient from injecting insulin. However, the frequency of reception is significantly reduced. This is of great convenience to the patient. The diabetic independently programs the device, setting the parameters of the required insulin therapy.
The pump consists of a reservoir for the drug and a catheter, which is inserted into the subcutaneous fatty tissue. The medicinal substance is received by the body continuously. The device independently controls blood sugar.
In 2016, the well-known company Medtronik released a pump for mass consumption. The new system is easy to use, has the ability to self-clean the catheter. Soon the insulin pump will be available to a wide range of consumers.
Conclusion
New treatments will soon replace insulin injections. Every day, scientists publish news in clinical advances. In the future, modern technologies will make it possible to defeat the disease forever.



















