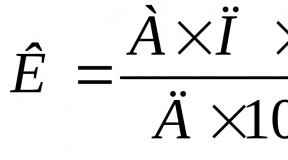The amount of the advance payment. What percentage of the salary is an advance? Is personal income tax charged
Any payment for an employee for his work always brings joy. After all, he will be able to spend money on the realization of his needs.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
What percentage is the advance? How to calculate it? When to expect? Let's consider the issue in more detail.
What it is?
The definition of "advance" means a part of the salary, which is intended to reduce the risk of financial problems for employees.
Advance payments, paid before the full amount of remuneration is accrued, allow you to fully avoid indignation on the part of the hired staff with the amount of your salary.
The legislative framework
Who is supposed to?
The Labor Code does not provide for any restrictions on the hired staff. Based on this, any officially employed resident of the Russian Federation can receive an advance payment.
In addition to those employees who work officially in offices, the advance is due to:
- external partners;
- with low wages.
If, according to the documentation of the internal regulations, a salary is introduced no more than once a month, then such documentation is considered illegal.
Is it required?
The process of accruing advance payments should not be considered as a procedure that is carried out solely at the discretion of the company's management.
It is intended solely for payments that were made for a full calendar month.
For this reason, when issuing advance charges in cash, it is necessary to form a statement according to T-53 or by cash receipts KO-2.
When paying to a card or account
In the process of issuing an advance to the bank account of an employee (including a salary card), the direct employer must display the calculated amount in the payroll or in other primary documentation used exclusively for payroll.
On the basis of the “settlement” primary documentation, the employer generates a payment order (on the basis approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation of June 2012) for each individual transferred advance or payment, accompanied by a register for accruing funds to a bank card, if there is an appropriate agreement with a banking institution .
Issuance in kind
The accrual of an advance payment to employees in kind is accompanied by expenditure cash orders KO-2 or a statement T-53.
Is a note required?
According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, every employee, without exception, must be provided with a payslip after payroll.
If the advance was received by the workers, there is no need for pay slips. In practice, there are often situations when leaflets are issued at the end of the month, although this is not entirely according to the law.
Order formation
Often, the schedule for accruing advance payments and wages is regulated by the Internal Labor Regulations of the company where this or that employee works. To issue an advance, companies can form an appropriate order.
The order is developed on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in particular Article 136.
It must be formed according to the following structure:
- the name of the documentation;
- title;
- main text of the document;
- Date of preparation;
- employer's signature.
Based on the order, further issuance of advance payment is carried out.
The command might look like this:
When is an employee's application required?
If there is an urgent need for a hired worker, he can draw up an application with a request for an advance payment on account of future wages. For example, if you need financial assistance for urgent medical treatment.
Employer's liability for delay and non-payment of funds
Despite the fact that there is no concept of “advance” in the Labor Code, the legislator requires the employer to pay wages several times a month, and if there is a delay, a violation of existing norms is formed, which may entail administrative and criminal penalties.
The verdict on the accrual of penalties or imprisonment directly depends on how much the payment was delayed.
It must be remembered that criminal liability occurs only at the moment when the employer refuses or cannot, for any reason, pay wages for more than 2 months.
In addition, it is mandatory to prove the intentional non-payment of wages by the management of the enterprise.
The employment relationship between the employee and the employer has many features. It is important not only to know about them in advance. All the main points must be reflected in the collective agreement.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
A separate issue is the issue of wages. In addition to the payment of wages at the end of the reporting period, an advance payment is required at least once a month. It is a part expressed as a percentage.
The size of the advance on wages under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2020 is determined by the employer himself. However, it cannot be less than the part specified in the legal documents. It is important to know how much the employer is obliged to transfer each month to the employee.
Concepts and definitions
With official employment, a citizen may demand that their own labor rights be observed. One of the obligations of the employer is the payment of wages for the time actually worked by the citizen. Additional surcharges may also be transferred. These include bonuses, the thirteenth salary. In this case, the latter are considered voluntary contributions under the collective agreement.
The labor legislation notes the right of a person to receive not only a salary after a month. An advance payment is provided for an employee at least once every 30 days.
There are some features that you need to remember when making the calculation. It must be done every half a month.
In addition, the accountant should not forget about the preparation of payment documents. It is also necessary to carefully prepare reports.
Mistakes can lead to serious problems. They relate to the relationship with the tax service. The main rule is the transfer of an advance payment for an already worked period.
Regulatory regulation
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a specific indication of the amount of interest, in accordance with which the advance payment should be calculated. But it is indicated in the Decree of the Council of Ministers of the CCC No. 566, which was issued on May 23, 1957. The normative legal act notes that the amount or the prescribed part is prescribed in the collective agreement.
The minimum amount of the advance must not be lower than the tariff rate provided for the employee during hours worked. Not all employers understand the essence of this phrase.
On February 3, 2016, the Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1/10/B-660 was issued. It reflects that the calculation is based on the time actually worked by the employee for the first half of the month. You can also focus on the fulfillment of the norm of work, if the accounting department highlights this criterion.
It is the responsibility of the employer to pay salaries every half a month. The amount can be fixed or a percentage of salary. The final decision is made by the employer. It must necessarily be reflected in the collective agreement or the Regulation on remuneration.
Most often, half of the salary is paid. But in practice, employers decide to give a smaller part in the form of an advance. This is due to the fact that allowances and bonuses are transferred along with the main payment. In addition, the amount of the advance is already underestimated from the outset. Therefore, organizations usually focus on indicators of 25-30%.
What should be the amount of the advance?
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation prescribes only the established terms for the payment of an advance. At the same time, its size is silent at the legislative level.
Usually the advance is calculated as half of the amount that is the salary. In this case, information about wages must be included in the employment contract concluded with the employee.
Due to the fact that tax is levied on the transferred amount, the advance payment is 42 and a half percent. This is provided if personal income tax is 13%.
For example, the total monthly income is 50 thousand rubles. To calculate the advance, it is necessary to determine the amount of tax: 50 thousand - 13% \u003d 43 thousand 500 rubles. The final value is then divided by two. As a result, the advance will amount to 21 thousand 750 rubles.
Another option for transferring an advance payment is also possible. The time actually worked by the citizen is taken as the basis. This option is considered more difficult for an accountant in terms of calculations.
It is important to focus on two factors. One is the salary of the employee for the month, which contains the employment contract. You also need to know the number of days worked by an employee for the first half of the month.
It is worth remembering one important nuance.
In accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to notify the employee in writing about:
- payments included in the salary (for the billing period);
- material payment due to the employee by law;
- compensation of wages, which is transferred in case of violation of the terms of payment of wages;
- the amount of vacation allowance;
- transfers as part of the sick leave;
- funds deducted from the salary with a detailed reason;
- the amount of money that is ultimately transferred to the employee.
These data are reflected in the payslip. The form of the document is developed by the administration of the institution together with the trade union organization. When preparing the form, you can focus on the sample provided by other accountants.
Determining the number of days worked
A mandatory step is to determine the number of days worked by the employee. After all, the advance is charged in proportion to the period during which the citizen worked in the first half of the month.
Employers are guided by this value. How many people have worked for days, for how much he will receive an advance. If during this period the employee was on vacation or on sick leave, then the time will not be included in the calculated time.
What fees are included
The Ministry of Finance has allocated some accruals that should be used in the calculation of the advance.
The main among them is the salary or tariff rate provided for an employee in a particular position.
The second part of the calculations are allowances and surcharges.
Their size is not affected by:
- the results of the citizen's work for the month;
- fulfillment of the monthly labor norm;
- compliance with the requirements of the labor schedule.
This article includes, for example, an additional payment for going to work at night, a special length of service, part-time work in several positions.
If, when calculating, you are guided only by the tariff rate or salary, then the controlling authorities may consider this a violation of the rights of the employee. The organization may be fined. The institution will have to pay an amount of up to fifty thousand rubles.
Calculations
To understand how the advance payment is calculated, you need to consider an example. Worker S. has a salary of 26,500 rubles. A tax in the amount of 26 thousand 500 rubles * 13% = 3 thousand 445 rubles is charged from this value. Thus, the advance payment is determined only from the amount of 26 thousand 500 rubles - 3 thousand 445 rubles = 23 thousand 55 rubles.
Since the advance is paid based on the actual hours worked, you need to calculate the number of workdays in October 2020. For example, with a full working out of half a month, an advance payment of 23 thousand 55 rubles / 22 * 10 \u003d 10 thousand 479 rubles is paid.
Payment terms
The terms for payment of wages and advances are reflected in the Letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1 / V-725, which was issued on August 10, 2017. In accordance with it, the Labor Code does not determine how long payments are made. Also, the amount of payment for half a month is not established.
Each organization has the opportunity to independently determine when it will make transfers. Usually, the terms are prescribed in local regulatory documents: regulations, rules, agreements and a collective agreement.
Allocate an important criterion, which should be guided by the employer. It is forbidden to transfer funds later than 15 days after the end of the period for which the salary is accrued. The exact date is written in the internal documentation of the institution.
Employer's liability for violation
Some unscrupulous employers violate the procedure for paying wages. They may be subject to penalties. Their size is determined by the circumstances identified by the labor inspectorate.
The amount that you have to pay is prescribed in the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. It will be from 10 to 20 thousand rubles for managers who have committed a violation. The organization will have to contribute from 30 to 50 thousand rubles.
If a repeated violation is found, the fines increase. Management will have to contribute from 20 to 30 thousand rubles. Legal entities are punished in the form of a payment of 50 to 100 thousand rubles.
Is there a tax
Hello.
The legislation does not define the percentage ratio of the advance to wages.
But there are legal acts, according to which the size of the advance and wages should be approximately the same, but cannot be lower than the tariff rate for the period worked, but nothing is said that the advance cannot exceed half of the wages.
For example:
Letter of Rostrud dated 08.09.2006 N 1557-6 "Accounting advances on wages"
In accordance with Article 136 of the Labor Code, wages are paid at least every half a month on the day established by the internal labor regulations of the organization, the collective agreement, the labor contract.
The Labor Code does not regulate the specific terms for the payment of wages, as well as the size of the advance.
At the same time, it should be borne in mind that, according to Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR of May 23, 1957 N 566 "On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month is determined by an agreement between the administration of the enterprise (organization) and the trade union organization at the conclusion of the collective agreement, however, the minimum amount of the specified advance must not be lower than the wage rate of the worker for the hours worked.
Thus, with regard to the specific terms of payment of wages, including the advance (specific dates of the calendar month), as well as the amount of the advance, they are determined by the internal labor regulations, the collective agreement, the labor contract.
Thus, in addition to the formal fulfillment of the requirements of Article 136 of the Labor Code on the payment of wages at least 2 times a month by the employer, when determining the amount of the advance payment, the time actually worked by the employee (actual work performed) should be taken into account.
Letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of February 25, 2009 No. 22-2-709 "On the timing and procedure for paying wages"
Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the payment of wages at least every half a month on the day established by the internal labor regulations of the organization, the collective agreement, the employment contract.
This means that with the advance method of calculating wages for each half of the month, wages should be accrued in approximately equal amounts (excluding bonus payments).Since your work is hourly, then, accordingly, the calculation of the advance payment and wages should be made based on the period worked. If you think that your rights are being violated, you can contact the Labor Disputes Inspectorate in order to conduct an audit at your enterprise on the correct application of labor legislation when calculating advance payments and wages.
Back to Advance 2018
An employee has the right to receive wages twice a month in certain installments, one of which is usually called an advance payment. Such requirements are regulated by the legislation of the Russian Federation. If they are ignored, a fine is imposed. Therefore, the accountant must know exactly how many percent of the salary in 2018 is an advance.
All employers are required to pay salaries at least every half month. The part of the salary that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation obliges to pay to employees after the expiration of the crescent cannot be less than the tariff rate or salary for the time actually worked (actual work performed).
This conclusion is in the letter of Rostrud No. 1557-6. Salary must be paid no later than the 15th day after the end of the period for which it is accrued. That is, the deadline for issuing an advance is the 30th of the current month, and the salary itself is the 15th of the next month (part 6 of article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
An advance is a part of the salary that is accrued to staff for the performance of labor duties. The date of its issuance must be specified in internal regulations: internal rules, collective or labor agreement.
Officials of Rostrud and the Ministry of Health and Social Development recommend setting the day for issuing an advance payment in the middle of the month: the 15th or 16th.
In practice, companies can make payments on the 25th. But then, when a new employee is hired in the first days of the month, the salary will be delayed for a period of more than 15 days. And in such cases, employees have the right to temporarily stop performing their labor functions and even go to court.
For the lack of an advance on wages, employers are recognized as violators of the requirements of Art. 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The penalty will be:
For the head of the company, a merchant: 1000 - 5000 rubles;
For a company - up to 50,000 rubles.
Additional costs can be avoided by timely provision of staff remuneration for labor. The accountant also needs to know what percentage of the salary is the advance in 2018.
When applying for a job, the applicant must be familiarized with the internal regulation, which indicates the date of the advance payment. The approximate time interval is 15 days. But it is not forbidden to transfer funds more often.
The amount and timing of the advance payment should be fixed in the organization's local documents (part 6 of article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), for example:
Labor regulations;
Collective or labor agreements;
Regulations on wages.
The Labor Code does not provide an answer to this question. But the resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR No. 566 says: the amount must be determined by an internal document of the organization, and the amount cannot be lower than the tariff rate.
In practice, different calculation methods are used:
1. By the amount of time actually worked (letter of the Ministry of Labor No. 14-1 / 10 / V-660). The use of this method is possible only if it is mentioned in the local rules on salary advances.
2. Fixed percentage of advance payment from salary. With this calculation option, its amount is unchanged throughout the entire working period. The most optimal bar is 50% of the salary (excluding personal income tax). Some pay only 40 percent. The formula for this calculation of the advance is given below: Advance = (SALARY + Allowances)x 50% Advance = (SALARY + Allowances)x 40%
When deciding how many percent of the salary in 2018 the advance will be, it is necessary to take into account other factors that affect the amount of wages:
The situation and complexity of the work;
Supplements for high qualifications;
Overfulfillment of the norm;
Payment for combining (substituting) positions.
Labor legislation does not prohibit in 2018 to establish a percentage of the advance payment from the salary, equal to half of the employee's allowance. Whatever its value and method of calculation, the company must necessarily issue funds in the first half of the month. And the frequency of payments is indicated in the internal regulatory documents for the organization.
Wages must be paid to the employee at least every half a month on the day established by the internal labor regulations, collective agreement, labor contract. This is a requirement of the law (part 6 of article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). This means that the employer cannot do without the division of wages into at least 2 parts. After all, if he decides to ignore the payment of the advance part of the salary (salary for the first half of the month), then he can be fined 30,000 - 50,000 rubles for violation of labor laws, and the head or individual entrepreneur - 1,000 - 5,000 rubles (Article 5.27 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
When paying an advance in cash, make the entry:
Debit 70 Credit 50 - advance payment from the cash register.
The transfer of the advance to the employee’s bank account is reflected in the following postings:
Debit 76 Credit 51 - money was transferred to pay an advance on wages;
Debit 70 Credit 76 - the bank transferred money to the salary cards of employees.
What percentage of the salary is an advance in 2017?
When transferring an advance to an individual employee account, make the following entry:
Debit 70 Credit 51 - the advance payment was transferred to the employee by a separate payment order.
When issuing an advance payment for finished products or goods, make the following entries:
Debit 70 Credit 90-1 - reflected the proceeds from the transfer of finished products (goods, works, services) on account of the salary advance;
Debit 90-2 Credit 43 (41, 20, 23) - the cost of finished products (goods, works, services) transferred as an advance on wages has been written off.
Record the transfer of other property (materials, fixed assets) against the advance payment as follows:
Debit 70 Credit 91-1 - reflected the proceeds from the transfer of other property as an advance payment;
Debit 91-2 Credit 01 (08, 10, 21 ...) - the cost of other property transferred as a salary advance was written off;
Debit 02 Credit 01 - depreciation was written off for retired property (when transferred as an advance payment of fixed assets).
1. With what frequency and in what terms it is necessary to pay wages to employees.
2. How to determine the amount of advance due to employees.
3. In what order are insurance premiums and personal income tax calculated and paid from wages and advance payments.
“The main thing in paying employees on wages is to correctly calculate the amounts due to them.” This statement is only half true: it is important not only to correctly calculate the salary of employees, but also to pay it correctly. At the same time, the stumbling block for many is the advance payment to employees. Is it necessary to split the salary into an advance payment and a final payment, if its amount is already small? Is there an advance payment for external part-time workers? How to calculate the advance amount? We will look into these and other issues related to the payment of wages to employees in this article.
Periodicity of payment of wages
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation of the employer to pay wages to employees at least every half month(Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). It should be noted that the Labor Code does not contain such a thing as an “advance” at all: according to its wording, this is wages for the first half of the month. And the widely used concept of “advance” came from a Soviet-era document, Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 23, 1957 No. 566 “On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month,” which is still in force in the part that does not contradict the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, to facilitate perception in this article, advance means wages for the first half of the month.
So, for wages, the frequency of payment is set at least every half a month. At the same time, for other payments to employees, their own deadlines are set:
- holiday pay must be paid no later than 3 days before the start of the holiday;
- The termination settlement must be paid on the day the employee leaves.
But the payment of sick leaves is just tied to the payment of wages: benefits must be paid on the next day after the assignment of benefits, set for the payment of wages. If the next day is the advance payment date, the benefits must be paid with it.
! Note: the requirement of the Labor Code to pay wages at least twice a month does not contain any exceptions and is mandatory for all employers in relation to all employees (Letter of Rostrud dated November 30, 2009 No. 3528-6-1). That is advance must be paid, including:
- if the employee is an external part-time worker;
- if the employee voluntarily wrote an application for the payment of wages once a month;
- if local regulations of the employer, employment contracts, etc. wages are paid once a month. Such a provision is void and not enforceable, as it violates the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- regardless of the amount of earnings and the accepted system of remuneration.
If the employer nevertheless neglected the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on the payment of wages to employees at least every half a month, then in the event of an inspection by the labor inspectorate, he faces liability in the form of a fine(Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for officials - from 1,000 rubles. up to 5,000 rubles
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 1,000 rubles. up to 5,000 rubles
- for legal entities - from 30,000 rubles. up to 50,000 rubles
Terms of payment of wages
Currently, labor legislation does not contain specific terms for the payment of wages, that is, the employer has the right to establish them independently, fixing them in the internal labor regulations, the collective agreement, labor contracts with employees (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In doing so, the following must be taken into account:
- The time interval between wage payments should not exceed half a month. At the same time, payments do not have to fall within one calendar month (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242). For example, if wages for the first half of the month are paid on the 15th, then for the second - on the 30th (31st) of the current month, if for the first half of the month on the 25th, then for the second - on the 10th of the next month, etc. . In addition, the employer can establish the frequency of payment of wages more often than once every half a month, for example, every week - this approach is acceptable, since it does not worsen the position of employees and does not contradict the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Terms of payment of wages should be indicated in the form of specific days, and not time periods (Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242). For example: 10th and 25th of each month. Such a wording as “from the 10th to the 13th and from the 25th to the 28th” is unacceptable, since in fact the requirement of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation to pay wages at least every half a month can be violated: the employee will receive a salary on the 10th, and the next payment will be on the 28th, that is, the interval between payments will exceed half a month.
- If the established payment day falls on a weekend or non-working holiday, then wages must be paid on the eve of this day (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
! Note: The employer bears (including advance payments and other payments in favor of employees): material, administrative, and in some cases even criminal.
Advance payment
The Labor Code does not contain requirements regarding the proportions (amounts) in which parts of wages should be paid. However, Decree No. 566, which was already mentioned above, provides that the amount of the advance must not be lower than the wage rate of the worker for the hours worked. Despite the fact that the specified resolution refers to the wages of workers, with respect to other workers, a similar approach can be used.
The amount of the advance payable to an employee can be calculated in one of the following ways:
- in proportion to hours worked;
- in the form of a fixed amount, for example, calculated as a percentage of salary.
Using the second option, paying an advance in a fixed amount, has one significant drawback - the likelihood that the employee will not work off the advance received. For example, in cases where an employee spent most of the month on sick leave, on leave without pay, etc., and at the same time he was paid an advance, at the end of the month, the accrued wages may not be enough to cover the advance. In this case, the employee has a problem, the retention of which for the employer is associated with certain difficulties.
The use of the first option, the payment of an advance in proportion to the hours actually worked, is more preferable, although more laborious for the accountant. In this case, the calculation of the advance payment amount is calculated based on the employee’s salary and the days actually worked by him for the first half of the month (based on the time sheet), so the probability of “transferring” the advance payment is practically excluded. In Letter No. 1557-6 dated September 8, 2006, Rostrud specialists also recommended that, when determining the amount of the advance payment, take into account the time actually worked by the employee (actual work performed).
! Note: The Labor Code obliges the employer with each payment of wages (including advance payments) notify the employee in writing(Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- on the constituent parts of the wages due to him for the relevant period;
- on the amounts of other amounts accrued to the employee, including monetary compensation for violation by the employer of the established deadline, respectively, payment of wages, vacation pay, payments upon dismissal and (or) other payments due to the employee;
- on the amount and grounds for the deductions made;
- about the total amount of money to be paid.
The specified information is contained in the pay slip, the form of which is approved by the employer himself, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
Ways to pay wages
Wages are paid to employees either in cash from the employer's cash desk or by bank transfer. In addition, labor legislation does not prohibit paying part of the salary (no more than 20%) in kind, for example, finished products (part 2 of article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the specific method of paying wages must be specified in the employment contract with the employee. Let us dwell in more detail on the monetary forms of payment of wages.
- Payment of wages in cash
Payment of wages to employees from the cash desk is made out by the following documents:
- payment (form T-53) or payroll (form T-49);
- expenditure cash warrant (KO-2).
If the number of employees is small, then the payment of wages to each employee can be drawn up by a separate cash receipt. However, with a large staff, it is more convenient to draw up a settlement (settlement and payment) statement for all employees and make one expense note for the entire amount paid according to the statement.
- Transfer of salary to a bank card
The conditions for the payment of wages in a non-cash form must be prescribed in a collective agreement or an employment contract with an employee. For the convenience of transferring wages, many employers enter into appropriate agreements with banks for the issuance and maintenance of salary cards for employees. This allows you to transfer the entire amount of wages in one payment order with a register attached, which specifies the amounts to be credited to the card account of each employee.
! Note: it is possible to transfer wages in non-cash form only with the consent of the employee and only according to the details specified in his application. In addition, the employer cannot “tie” his employees to a specific bank: labor legislation gives the employee the right to change the bank at any time to which his salary should be transferred. In this case, it is enough for the employee to notify the employer in writing about the change in payment details for the payment of wages no later than five working days before the day of payment of wages (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for calculating and paying personal income tax and insurance premiums from wages
We found out that wages to employees should be paid at least twice a month. In this regard, many people have a question: is it necessary to charge insurance premiums and personal income tax from an advance? Let's figure it out. According to the legislation, insurance premiums must be accrued based on the results of the month for which wages are accrued (clause 3, article 15 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ). As for personal income tax, in accordance with the Tax Code, the date of receipt of income in the form of wages is recognized as the last day of the month for which income for the performed labor duties is accrued (clause 2 of article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this way, no insurance premiums or personal income tax should be charged from the advance.
The terms for paying insurance premiums from wages for all employers are the same and do not depend on the date of payment of wages. At present, contributions to off-budget funds must be paid before the 15th day of the month following the month of payroll (clause 5, article 15 of Law No. 212-FZ). The exception is insurance contributions to the FSS of the Russian Federation against accidents and occupational diseases - they must be paid on the day set for receiving funds from the bank to pay salaries for the past month (clause 4, article 22 of Law No. 125-FZ).
Unlike insurance premiums, the deadline for paying personal income tax depends on the date and method of payment of wages:
Payroll Accounting
In accounting, payroll, as well as personal income tax and insurance premiums, is reflected on the last day of the month worked. This generates the following entries:
the date
Account debit Account credit Date set for the payment of wages for the first half of the month 70 50(51) Wages paid for the first half of the month from the cash desk (transferred to employee cards) Last day of the month 20(23, 26, 44) 70 Wages accrued Last day of the month 70 68 Withheld personal income tax from wages Last day of the month 20(23, 26, 44) 69 Payroll insurance premiums Date set for the payment of wages for the second half of the month (final settlement) 70 50(51) Wages paid from the cash desk (transferred to employees' cards) The last day of the deadline set for the payment of wages according to the statement from the cash desk 70 76 Amount of lost wages deposited The next day after the end of the period established for the payment of wages according to the statement from the cash desk 51 50 The amount of the deposited salary is credited to the current account 50 51 Received money from the current account for the issuance of deposited salaries When an employee applies for unpaid wages 76 50 Deposited wages issued Do you find this article useful and interesting? share with colleagues on social networks!
Remaining questions - ask them in the comments to the article!
Yandex_partner_id = 143121; yandex_site_bg_color = "FFFFFF"; yandex_stat_id = 2; yandex_ad_format = "direct"; yandex_font_size = 1; yandex_direct_type = "vertical"; yandex_direct_border_type = "block"; yandex_direct_limit = 2; yandex_direct_title_font_size = 3; yandex_direct_links_underline = false; yandex_direct_border_color = "CCCCCC"; yandex_direct_title_color = "000080"; yandex_direct_url_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_text_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_hover_color = "000000"; yandex_direct_favicon = true; yandex_no_sitelinks = true; document.write(" ");
Normative base
- Labor Code of the Russian Federation
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law No. 212-FZ dated July 24, 2009 “On insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation, the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund”
- Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n “On Approval of the Chart of Accounts for Accounting for the Financial and Economic Activities of Organizations and Instructions for its Application”
- Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR of May 23, 1957 No. 566 “On the procedure for paying wages to workers for the first half of the month”
- Rostrud Letter No. 3528-6-1 dated November 30, 2009
- Letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242
How to get acquainted with the official texts of these documents, find out in the section
Payroll advance paymentis carried out in accordance with the current labor legislation and the decision of the employer. You will learn how advances are correctly calculated and when to pay them to employees from our article.
When is it necessary (and whether it is necessary at all) to pay an advance on wages?
Before deciding whether it is necessary to pay salaries in advance, let's figure out what an advance payment is. In fact, an advance payment is nothing more than a salary paid to an employee for the first half of the month of work. However, in the Labor Code of Russia (hereinafter - the Code) there is no such thing as "advance payment", although this term is often used by federal authorities when providing clarifications. In particular, Rostrud, in its letter “Accrual of advances ...” dated 08.09.2006 No. 1557-6, mentioned advances and explained that only a certain period for paying an advance (and not a period of several days) and its amount should be established in a collective agreement, internal labor regulations (hereinafter - PVTR) and labor contracts.
In part 6 of Art. 136 of the Code states that the employer must pay wages at least twice a month. At the same time, even the desire of an employee expressed in writing to receive payment for his work only once a month does not relieve the employer of responsibility for non-compliance with labor laws (Rostrud letter “On Administrative Responsibility ...” dated March 1, 2007 No. 472-6-0).
The deadline for paying wages for the month worked is the 15th day after it is accrued. Thus, the salary advance must be paid for at least half a month of work, and the specific date of payment is determined by the employer himself, taking into account the rules established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: the impossibility of payment later than 15 days after the advance payment, as well as the need to pay the advance monthly at least once and the final payment - at least once.
Is it necessary to pay twice a month or can it be done three times?
Since in Part 6 of Art. 136 of the Code only states that wages should be paid to employees at least every half a month, then each employer can establish in the relevant local acts a regime that provides for more frequent payments. That is, the salary at the enterprise can be paid, for example, three times a month (that is, every 10 days).
When establishing its own wage payment regime for employees, the employer should only take into account the recommendations of the Ministry of Labor, set out in paragraph 3 of the letter “On the application of labor legislation” dated November 28, 2013 No. 14-2-242, regarding the approval of specific dates for payments. It is also important to remember that the terms and amounts of wage payments are prescribed in the PWTR, the collective agreement and the employment contract of each employee.
How to correctly calculate the amount of the advance?
There are no rules for calculating the amount of the advance, there are only certain restrictions established by regulations and official explanatory letters from departments. Each enterprise establishes its own methodology for calculating the advance, which should be fixed in the regulation on the payment of salaries and other local regulations.
What is the minimum advance payment?
According to the Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 23, 1957 No. 566, the norms of which, according to Art. 423 of the Code, are applied to the extent that they do not contradict the current labor legislation, the amount of the advance paid for the first half of the month cannot be less than the employee's tariff rate for the time worked by him. That is, this normative act specifies the minimum allowable advance payment. It is important to consider this before accruing an advance on wages.
What is taken into account when calculating the advance?
When calculating the amount of the advance, it should be taken into account that this is the salary paid to the employee for the working hours already worked in the first half of the month.
Accordingly, the advance payment includes:
- part of the salary (in proportion to the hours worked);
- allowances established for harmful or dangerous working conditions;
- surcharges for performing above-standard/additional volume of work;
- allowances for temporary replacement of an employee absent from the workplace.
At the same time, the amount of expected bonuses or other stimulating remuneration cannot be included in the calculation of the advance. This is due to the fact that the results of the work for which the bonus will be awarded become known only at the end of the month when summing up - this is exactly what the Ministry of Health and Social Development says in its letter “On the timing and procedure for paying wages ...” dated February 25, 2009 No. 22- 2-709.
The same restriction on inclusion in the advance payment applies to adding a percentage of salary, which, as a rule, depends on the volume of sales or cash flow in the unit where the employee is employed. When calculating the advance, material assistance or other payments that are of a social nature cannot be taken into account, since they cannot be attributed directly to wages.
Don't know your rights?
Days off when calculating the advance
Depending on the choice made at the enterprise, an advance payment for the time worked by employees can be calculated both with and without weekends.
If the employer decides not to take weekends/holidays into account when calculating the advance salary payment, then it is only necessary to divide the monthly salary previously calculated by 2 (if the salary is paid at the enterprise twice a month).
In formula form, it would look like this:
A \u003d (Ok + D / N) / 2,
where A is an advance payment, OK is the salary in rubles, D / N is the amount (in rubles) of additional payments and allowances for working conditions and the amount of work.
In the same case, if the employer decides to take into account only working days for the first half of the month when calculating the advance (which is especially important for the rich on holidays in January and May), the formula will look different:
A \u003d (Ok + D / N) / HPBm × HPVp / m,
where НРВм is the standard of working time (in days) established for the month of work; НРВп / m - the standard of working hours (in days) established for the first half of the month of work.
Fixed advance payment
Although this is not prohibited by law, the employer should not set a fixed advance payment in absolute terms (rubles), since it is calculated for hours worked, and the amount of earnings for different months may differ due to possible additional payments (or if a piecework payment system is established). It is especially unacceptable to set the same size for all employees. For example, it is not recommended for all employees in an enterprise to set an advance in the amount of 2,000 rubles if the salary is different for everyone.
What is the percentage of salary advance in 2017-2018?
According to the aforementioned resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR, an advance payment is a payment for hours worked. Consequently, its size should be approximately half of the salary, excluding bonuses, incentives and social payments (letter of the Ministry of Health and Social Development No. 22-2-709).
Another thing is if the employer sets a fixed amount of the advance, expressed in relative terms (as a percentage of the total monthly salary). As a rule, based on the fact that the advance is about half of the salary remaining after withholding income tax, a value equal to 40% is taken to establish a fixed amount of such a payment.
This calculation is based on the fact that, excluding personal income tax (excluding insurance premiums and due tax deductions), the employee is supposed to pay 87% (100% - 13%) of the salary for this period at the end of the month. When rounding to ten, the value calculated by dividing by 2 received 87%, the advance payment in relative terms will be 40%. Since the personal income tax rate did not change in 2017-2018, employers continue to use this value to calculate the advance.
Advance payment calculator - what rules to use in the algorithm?
When writing a program that will automatically determine the amount of the advance, you must use 2 algorithms that describe the following calculation options:
- Based on the norm prescribed in the above-mentioned resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR that an advance payment is a payment for half a month worked. When choosing this option, the entered value of the accrued salary for the month will simply be divided by 2, although the algorithm can be complicated by subtracting weekends and holidays from the number of days in the first half.
- Calculated as 40% of wages. Here the calculation is simple: you need to enter the salary, from which 40% will be calculated.
Application for advance payment, sample application
An application for an advance payment is submitted by an employee if he wants to receive wages before the deadline set by the employer.
The main part of the application may contain the following justification:
“I ask you to issue an advance on wages on December 20, 2017 instead of the date set at the enterprise for issuing advance payments (on the 26th). I ask you to pay ahead of time due to family circumstances that forced me to take a vacation at my own expense for 5 days from December 22.
You can download a complete application form (with all the necessary details) on our website.
So, following the recommendations of the federal authorities, the employer needs to establish for the calculation of such an advance payment that would be no less than the established tariff rate for the first half of the month. In addition, some employers simply calculate 40% of the salary for the month of work to calculate the advance.