Can we make Mars habitable? A natural anomaly created a new Mars on Earth: video Connection with Earth
For many years, Mars existed as a sort of "Planet B" - a fallback option if Earth became no longer habitable. From science fiction stories to scientific exploration, people have long dreamed of the possibility of living on Mars. A core element of many Mars colonization concepts is terraforming—the hypothetical process of changing conditions on the planet to make it suitable for life that exists on Earth, including humans, without the need for life support systems.
Unfortunately, according to a new paper, terraforming Mars is simply not possible with current technology. According to its authors, Bruce Jakoski, a planetary scientist and principal investigator for NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN missions studying the atmosphere of Mars, and Christopher Edwards, an assistant professor of planetary science at Northern Arizona University, it is simply not possible to terraform the Red Planet with current technology.
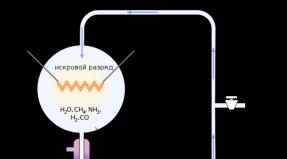
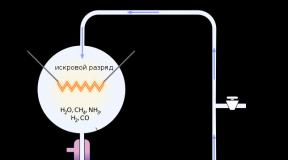
To successfully make Mars into Earth, we need to increase the temperature to have stable liquid water and a dense atmosphere. In the paper, Jakoski and Edwards explained that by using greenhouse gases already present on Mars, we could theoretically raise the temperature and change the atmosphere enough to make the Red Planet Earth-like. They noted that the only greenhouse gas on Mars sufficient to cause significant warming is carbon dioxide (CO2). Unfortunately, they found that there was not enough of it on the planet to make it like Earth.
On Mars, CO 2 is present in rocks and polar ice caps. Jakoski and Edwards used data from the various rovers and spacecraft that have observed and studied Mars over the past 20 years to essentially take an "inventory" of the planet's CO 2 .

What terraforming Mars might look like.
They documented all the surface and subsurface carbon dioxide reservoirs on Mars, and what percentage of existing volumes could be put into the atmosphere to change it. However, although there is a significant amount of CO 2 on Mars, using all the available volume of gas would only triple the atmospheric pressure. To successfully terraform Mars, the atmosphere must be thick enough for people to walk around without wearing spacesuits. Alas, although tripling the atmospheric pressure on the Red Planet seems like a significant figure, it is still 50 times less than what is needed for people to live comfortably on it.
Additionally, the amount of available CO 2 found by the researchers would increase the planet's temperature by less than 10 degrees Celsius. And since the average is minus 60 degrees Celsius, and winter temperatures drop so low that carbon dioxide from the atmosphere condenses into ice on the surface, this increase in temperature does not play any significant role.
Moreover, even if there was more CO 2 on Mars, most of it would be difficult to access, and it would take a lot of effort to release it into the planet's atmosphere, according to the paper's authors. For example, carbon dioxide could be extracted from the polar ice caps by blowing them up with explosives, a solution favored by SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, or explosives could be used to increase the amount of dust in the atmosphere so that it would settle on the polar ice caps and increase the amount of solar energy. which they absorb, which will again lead to their melting and release of CO 2 into the atmosphere.
There are a number of proposed and theorized methods to allow humans to access and release CO 2 into the Martian atmosphere. But many of them would be very difficult to implement, and as Jakoski and Edwards found, existing CO 2 reserves are still not enough to terraform the planet. Both Jakoski and Edwards said it's possible future technology will find an alternative solution and make terraforming the Red Planet possible. However, "with current technology, we simply don't see viable options," says Edwards.

Artist's depiction of "spring" on Mars, when heating causes frozen CO 2 to turn into gas and escape from the rock into the atmosphere.
Mars has been the "obvious" choice for terraforming for years. This is due to a number of reasons, including the fact that Mars is (relatively) close to Earth - “the most easily accessible planet, and the only one on the surface of which Earth-based spacecraft can land and function properly there for a long time,” says Jakoski. The allure of a terraformed Mars is perhaps “part of the mythology. A lot of science fiction has been written about Mars,” adds Edwards.
However, while future technologies may allow humanity to change Mars in ways that are not possible today, instead of focusing our energies on turning Mars into Earth 2.0, "I think our efforts would be better spent on ensuring that Earth retains its benevolent climate for us,” Jakoski says.
In Crete (Greece), the sandstorm that raged on the peninsula for three days in a row has finally ended. Red dust was brought from the coast of North Africa. Locals say that now the entire area resembles the Red Planet, such significant consequences:
“Everything is fine now, but yesterday it was like being on Mars,” said Tez Tour Greece managing director Dimitris Charitidis.
In mid-April, African winds often blow here, so flights are postponed, because it is extremely dangerous on an airplane.
“But what happened yesterday probably happened for the first time. Almost everyone says that they have never seen anything like this before. Yesterday it was even difficult to breathe: 17 people were hospitalized - mostly elderly people,” he added.
Watch: natural anomaly in Greece
Some people are already accustomed to such anomalies. They happen annually and do not last longer than 4-5 days. The last time there was rain with sand was in the central part of mainland Greece in the city of Volos, which is almost 400 kilometers from southern Crete.

Tourists don’t come here either, so the season opens after Easter to wait out natural disasters. But the network was filled with amateur footage - all of Crete in crimson colors, something you won’t see on TV, real “Martian photo shoots”.

Only German pensioners were not afraid of the storm; they are relaxing on the island as if nothing had happened and observing the phenomenon quite calmly.
The infinity of the Universe has always worried scientists and travelers. Colonization of planets is one of the most interesting options for the progressive development of society. This is not only about organizing a reserve bridgehead for humanity. The initiators of such projects also expect to receive commercial and political benefits.

Why should humanity colonize Mars?
The gradual relocation of people to hitherto unexplored spaces should serve for the benefit of humanity. The development of deposits of valuable metals will pay for the costs of overcoming ultra-long distances and surviving outside the usual environment. The exploration of Mars will prove our ability to exist autonomously outside our native civilization.
Why Mars
The presence of the atmosphere, glaciers, and geological structure make it possible for man-made habitats to be closer to those on Earth. Colonization of Mars looks more realistic than attempts to conquer the lifeless Moon or hot Venus with its acid rain. The length of a day there is slightly more than 24 hours. The year lasts 687 days, but the seasons change in the manner familiar to earthlings. This will help the settlers adapt to their new habitat and join the natural cycle.
List of Mars colonization goals
Due to the complexity of life support, stationary bases are more effective than the deployment of individual units. In some situations, their existence is simply invaluable:
- In the event of a global catastrophe on Earth, we will survive as a species, maintaining our cultural potential.
- Growing populated areas will help solve the demographic problem.
- Construction and mining in an aggressive environment will give impetus to the formation of new technologies.
- There will be a base for scientific research, a testing ground for experiments dangerous to our biosphere.
- The developed territories will become a launching pad for long-distance expeditions.
To achieve a common goal, the strongest states and commercial structures will join forces. Fundamentally new social relations will be formed.
Problems of colonization of Mars
Important and complex tasks include transporting living organisms and materials, providing food, and protecting against radiation. There are many questions, but not all have been resolved yet. Therefore, only a few optimists are confident that the imminent appearance of extraterrestrial cities is even possible.

Delivering people to Mars
The first issue that will need to be resolved when moving in is how to get the first residents to the site. With current technology, a flight to Mars will take about 8 months. A convenient moment for launch appears once every two years, when the distance between celestial bodies is minimal. This means that in the event of an emergency, pioneers will not be able to get quick help.
The ship's hull blocks only 5% of cosmic rays. During the flight, expedition members will receive potentially dangerous doses of radiation. We can only hope that when people go to Mars, safe hull protection will be invented.
Harsh conditions of the planet
The inhabitants of the colony will face a harsh, cold and dry climate. The average is -55°C and fluctuates sharply throughout the day. Besides:
- The gravity force is only 1.8 g, which leads to muscle atrophy and osteoporosis.
- It has a low density and is 95% carbon dioxide.
- There is almost no magnetic field, resulting in strong ionizing radiation.
- Atmospheric pressure is less than 1% of what is required for life, which makes existence unrealistic without a spacesuit.
- An additional danger is the constant threat of falling meteorites.
 Living conditions on Mars: storms, radiation, meteorites, life in a spacesuit, low temperature.
Living conditions on Mars: storms, radiation, meteorites, life in a spacesuit, low temperature. But this does not mean that the obstacles are insurmountable. Although it is unknown how the body will adapt to a long stay in such a harsh environment.
Where to start - main tasks
At the preliminary stage of preparation for the colonization of Mars, a detailed study of the landscape and available resources is necessary. The determination of specific landing points, the choice of equipment and technology depends on this.
Possible locations for founding a colony
It is likely that the exploration of a distant world will begin from beneath its surface. According to reports, there are deep caves there that can protect against dangerous radiation. If they can be connected by tunnels and sealed, this will eliminate the need for oxygen tanks.
It is better to set up settlements near the equator, where the air temperature is highest, for example, in the Marineris Valley. The maximum air pressure is noted at the bottom of the Hellas depression. There is an idea to build shelters in craters, which are covered from the inside with a layer of ice, which means there will be a source of moisture at hand.
Colonists' housing
At the beginning of the colonization of Mars, buildings can be shielded with local soil - regolith. Later, a thick layer of ceramic bricks produced there will become a material for the walls and an obstacle to radiation.
Recently, scientists discovered large diameter lava tubes on the red planet. They appear under the surface after volcanic eruptions and stretch for hundreds of meters. Such an underground system could become the basis for creating an entire Martian city.
 On Earth, lava tubes reach a width of 30 meters; on Mars, this figure is much more than 250 meters.
On Earth, lava tubes reach a width of 30 meters; on Mars, this figure is much more than 250 meters. Energy sources
The emergence of industrial civilization is difficult to imagine without energy resources. The sun's rays cannot be counted on due to dust storms that continue for months. Hopes are pinned on nuclear energy. Deposits of uranium and lithium, as well as the high deuterium content of ice, will make energy supply from nuclear reactors cost-effective.
Oxygen production
The atmosphere and soil are saturated with carbon dioxide, reserves of which in the form of dry ice are also found at the south pole. By direct decomposition of CO2, it will be possible to synthesize the oxygen necessary for breathing. To do this, settlers will bring with them photosynthetic plants: blue-green algae and plankton. There is, for example, the use of low-temperature plasma.
Water extraction
Water reserves, according to information from probes, are quite large. Glaciers have formed at the cold poles, and in the depths of the earth, experts hope to find underground rivers. Scans of the probes showed that under the surface of the southern polar cap at a depth of 1.5 kilometers there is a width of 20 kilometers. The soil itself contains up to 6% moisture at a depth of about a meter. Everything suggests that there is water on Mars, but not in liquid form, but in the form of ice. The reason we don't see it on the surface is because the low pressure at the surface causes the water to evaporate immediately. But there is a good chance of still extracting the ice and cleaning it to drinkable quality. Melting ice in special seals will become the main way for colonists to obtain water.
Farm buildings
To replenish food supplies, it is planned to build complexes with functions similar to earthly farms. As an option for protection from harmful radiation, the greenhouses will be hidden under the top layer of soil.
 Growing fruit in Martian soil
Growing fruit in Martian soil In theory, plants can be grown in local soil. But most likely it will be either too acidic or very alkaline, so serious pre-treatment will be required. With an established water supply, vegetables and herbs can be cultivated using hydroponics.
Connection with the Earth
The new Martians will not be completely cut off from the rest of human society. The exchange of information () is technically feasible, but will occur with a delay of 5 to 45 minutes. To do this, a relay satellite will be launched into orbit around the Sun. Later, the number of orbiting satellites will even make it possible to connect settlers to the global Internet network.
 A project to provide stable communications when the Sun is between the planets
A project to provide stable communications when the Sun is between the planets Proposed colonization plans
Various projects for the colonization of Mars are actively discussed in academic and business circles. The most realistic of them accurately indicate the time when people will already live on Mars. But in practice, these dates are constantly shifting, no matter how well thought out the colonization strategies are.
Mars One Plan
A group of entrepreneurs from the Netherlands announced the beginning of the creation of a habitable base. The Dutch are going to compensate for the costs through television broadcasts covering the preparation process and all further events. In 2024, it is planned to launch a communications satellite into orbit, followed by an automatic Mars rover and cargo ships. In 2031, a crew of 4 people will be sent, but only in one direction; technically, they will have no chance of returning back. Then the number of pioneers will increase.
 Project Mars One
Project Mars One Elon Musk's plan
According to SpaceX, led by Elon Musk, the first hundred colonists will appear on Mars in 2022.
SpaceX is developing reusable rocket engines to transport goods and people in both directions. The interplanetary transport system will ensure the life of the established colony. As a businessman, Elon Musk hopes to profit from the sale of rare metals and precious stones, real estate trading and the results of unique experiments.

NASA plan
In 2017, NASA published a report on support for the long-range manned flight program. It provides detailed research on the ISS, including studying the effects of long stays in space on living beings. Then an interplanetary station will be installed in low-Earth orbit. The last phase will include the actual construction of structures and the establishment of communications via satellite. The mission is planned for the 2030s.
The concept of moving to alien worlds also has its opponents. In their opinion, nothing particularly valuable has been discovered there yet, and there are plenty of free territories on Earth. Many fear the unpredictable consequences of encountering unknown life forms. But despite this, more and more people want to go into the unknown and leave a mark on history.