STD without symptoms: are you sure you are healthy? Asymptomatic diseases are silent killers The disease is asymptomatic and the person
are congenital changes in the number or configuration of the vertebrae. Depending on the type and severity of disorders, they can be asymptomatic or accompanied by a change in the patient's appearance and neurological symptoms: sensory disturbances, paresis, trophic disorders. They are diagnosed according to external examination, radiography, CT and MRI. To assess the severity of damage to the nervous system, a neurological examination is performed. In compensated conditions, treatment is conservative, including massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy. With severe anomalies, the threat of severe complications, surgical correction is indicated.
General information
Anomalies in the development of the spine are congenital conditions accompanied by a change in the number or configuration of the vertebrae. The severity of clinical manifestations can vary significantly, depending on the severity of the defect. According to the observations of specialists in the field of traumatology and orthopedics, any anomaly in the development of the spine reduces the static stability of the spinal column and increases the likelihood of developing acquired diseases of the spine.
Pathoanatomy
The human spine consists of the cervical (7 vertebrae), thoracic (12 vertebrae), lumbar (5 vertebrae), sacral (5 vertebrae) sections and coccyx (1-3 vertebrae). Between the vertebrae are elastic elastic intervertebral discs that act as shock absorbers. The vertebrae have processes that connect with the processes of the vertebrae above and below to form joints. In the center of each vertebra is a hole through which the spinal cord passes. With underdevelopment, changes in shape and other disorders, the normal relationships between the listed structures are violated, which leads to compression of the nerve tissues, deterioration of the depreciation function of the discs and overload of the joints. These disorders cause the appearance of pathological symptoms and provoke the development of other diseases of the spine.
Classification
Anomalies in the development of the spine represent a rather heterogeneous group of pathologies that differ both in the anatomical basis of the disorders and in the severity of manifestations. Taking into account the anatomical features, vertebrologists distinguish the following groups of malformations of the spinal column:
- Change in the number of vertebrae: occipitalization (fusion of the occipital bone and the 1st cervical vertebra), sacralization (fusion of the sacrum and the 5th lumbar vertebra), lumbarization (separation of the 1st sacral vertebra from the sacrum), fusion of several vertebrae.
- Changing the shape of the vertebrae: hemivertebrae or wedge-shaped vertebrae (with a delay in the development of bone structures in the anterior sections), spondylolysis (with a delay in the development of the vertebrae in the posterior sections).
- Underdevelopment of individual parts of the vertebrae: cleft of the arches and vertebral bodies.
Types of anomalies
Klippel-Feil syndrome
Short neck syndrome or Klippel-Feil syndrome is a concretion (fusion) of the cervical vertebrae. Sometimes not only the cervical, but also the upper thoracic vertebrae are fused together. The anomaly is manifested by a pronounced shortening of the neck, a decrease in the hairline, restriction of movement when the head is turned to the side, and a “proud landing of the head” (the head slightly deviates backwards). In some cases, patients with Klippel-Feil syndrome have pronounced skin folds from the ears to the shoulders.
Short neck syndrome is diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and x-ray data of the cervical region, often combined with other anomalies in the development of the spine (cervical ribs, Spina bifida), cardiovascular and nervous systems. Neurological symptoms may be absent. In some cases, compression of the roots is possible, accompanied by a violation of sensitivity, a decrease in hand strength or paresis.
cervical rib syndrome
As a rule, it is asymptomatic, it is detected by chance during an X-ray examination. Sometimes symptoms characteristic of the cervical ribappear after an infection, injury, or hypothermia. Patients may be disturbed by pain, weakness in the muscles of the hands, accompanied by a violation of the normal vascular tone and skin nutrition (sweating, cold, pale, bluish skin).
Spina bifida
The most common anomaly in the development of the spinal column. In most cases, spina bifida (Spina bifida) is caused by non-fusion of the arches of the V lumbar or I sacral vertebrae. Non-fusion of the arches of other vertebrae and splitting of the vertebral body are less common.
The closed variant of the pathology is more common. It may be asymptomatic or be accompanied by moderate pain in the lumbar region and sacrum. With the development of cicatricial changes in the region of the roots, sensitivity disorders and paresis appear along the innervation of the compressed nerve. The regulation of vascular tone and skin nutrition are disturbed, causing the development of edema and the appearance of ulcers.
Open splitting is observed less often. 1 out of 1000-1500 newborns suffers. Pathology belongs to the category of severe anomalies, accompanied by other congenital defects (spinal cord dysplasia, impaired development of roots and membranes of the spinal cord). A particularly unfavorable option is a defect in which not only the vertebrae, but also the spinal cord are split. Through the splitting of the vertebra, the membranes and substance of the spinal cord protrude outward.
In the back of the newborn at the level of splitting there is a hernial protrusion, not covered by muscles and skin. The composition of the hernial sac may include only the membranes of the spinal cord (meningocele) or the membranes and substance of the spinal cord (meningomyelocele). In severe hernias of the spinal cord, sensory disturbances, trophic disorders, disorders of motor and pelvic functions are detected. Vertebral cleavage is diagnosed using a CT scan of the spine. MRI is performed to visualize soft tissue structures (spinal cord, ligaments, intervertebral discs).
Lumbarization and sacralization
Fusion of the sacrum with the 5th lumbar vertebra and separation of the 1st sacral vertebra from the sacrum may be asymptomatic. When the roots are compressed, sensory disturbances, paresis and trophic disorders develop in the region of innervation.
wedge-shaped vertebrae
A common anomaly in the development of the spine. Unlike ordinary vertebrae, wedge-shaped vertebrae (hemivertebrae) consist of a half-body and half-arch with a spinous process. They can be found in all parts of the spine. They are one of the reasons for the development of scoliosis.
Treatment of developmental anomalies of the spine
With mild or moderate radicular syndrome, caused by a change in anatomical relationships and secondary damage to the structures of the spine, conservative treatment of anomalies is carried out. Intensive radicular syndrome, not amenable to conservative therapy, is an indication for surgical intervention. With the cervical ribs, resection of the accessory bone is performed, with other pathologies, operations on the spine are performed. With hernias of the spinal cord, the only treatment is surgical.
You may think that a regular annual visit to the doctor is enough to prevent the risk of cancer, however, there are some types of cancer that are asymptomatic, which means that the examination should be carried out as often as possible. Even if a hereditary predisposition is excluded, you adhere to proper nutrition and lead a healthy lifestyle - this is not an indicator of the absence of risk.
Some types of cancer are difficult to detect. Signs and symptoms of the disease depend on its location, as well as the volume of the tumor. There are those that do not make themselves felt until they grow to a certain size and spread, or the patient experiences symptoms that can be mistaken for another disease (chills, fatigue, sudden weight loss).
The 5 types of cancer considered in the article are precisely those that do not manifest themselves in any way in the early stages. Even if a person does not have a genetic predisposition to the disease, the risk of infection is still present.
Pancreas cancer

The pancreas is a small organ that lies in the abdominal cavity and has several functions, in particular, it is involved in the process of digestion of food and the production of hormones that maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Pancreas cancer is one of the most difficult to diagnose due to the absence of symptoms in the early stages, and if any, they are similar to the symptoms of an ulcer or pancreatitis. There are no tests to detect this type of cancer if there are no symptoms. 
It happens that with a cancerous tumor of the pancreas, symptoms such as pain in the upper abdomen, weakness, chills, weight loss and appetite, nausea and vomiting appear. The tumor causes the pancreas to digest fats incorrectly, so the patient's stool is broken, acquiring an unusual color.
Many of these symptoms can be mistaken for indigestion, poisoning, or the flu. When a person gets cancer, his skin becomes icteric, in particular, this is clearly visible on the skin around the eyes, and fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
Pancreatic cancer - video
prostate cancer

Prostate disease and cancer in particular are becoming more common, with about 1 in 8 men diagnosed with prostate cancer, in 50% of cases the disease manifests itself in men over the age of 50 years.
Doctors state that in most cases the symptoms do not appear in the early stages, and when the disease is detected, the lesion is already transferred to the bone tissue, which is much more difficult to treat.
Anatomically, the prostate gland is located at the base of the bladder, bordering the urethra; it is designed to produce seminal fluid. Since the symptoms of this cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia are similar, many men may not betray them.
Symptoms may also be associated with urinary tract infections, such as scanty urination, blood in the urine, development of erectile dysfunction, back pain.
If there is a hereditary predisposition, then it is necessary to monitor changes in the body, exclude alcohol and drinks containing caffeine, which will warn against the onset of the disease.
bladder cancer

bladder cancer in addition to the fact that it also has no pronounced symptoms, it is still a little-studied disease, which makes it even more dangerous. First of all, men are more subjected to it than women.
: exposure to tobacco, industrial solvents and paints, and especially the elderly.
The most common symptom is blood in the urine, and this " list» manifestations ends. Concomitant factors may be painful and frequent urination, the development of the disease is accompanied by pain in the bladder area. If this type of disease was diagnosed by relatives, and you find one of the symptoms, immediately consult a doctor to make sure that there is no cancerous lesion.
colon cancer

Many men are aware of the fact that blood in the stool is a common symptom. colon cancer, but this does not always appear. Colon cancer arises from a tumor that forms on the inner wall of the colon, and the tumor in turn is caused by polyps or growths on the inner lining of the colon.
If this cancer is detected as early as possible and the polyps are removed, the risk of developing a tumor can be significantly reduced. This type of cancer affects mostly men around the age of 50 and having a genetic predisposition. 
In terms of symptoms, the most common is blood in the stool. It can be dark, closer to black and even tarry. Since the tissue affected by cancer bleeds in a dark color, this indicates that the lesion is located a little higher, namely in the gastrointestinal tract. The presence of blood in the stool does not always mean cancer, it could be an ulcer or ulcerative colitis. Abdominal pain, weight loss and appetite may also be associated with colon cancer.
testicular cancer

While most cancers occur in men over 50, testicular cancer may occur as early as 20-40 years of age. Testicular cancer usually develops in the cells that produce sperm. Simultaneously with the defeat of testicular cells, the spine or lungs can be affected. Despite the fact that testicular cancer sounds daunting, it is treatable if detected at an early stage, but there are chances of studying at later stages.
Some men experience no discomfort in the early stages of testicular cancer, but there are some signs. One of them is a small formation in the form of a lump or an increase in the size of the testicle itself. The formation is the size of a pea and only a doctor can detect it.
Testicular cancer also manifests itself in different sizes of the testicles, aching in the lower abdomen or groin. If you are concerned about any of the signs, see your doctor to rule out other diseases with similar symptoms, such as infections, injuries, cysts.
No one will talk about this topic on a first date. However, even after two months of marriage, not many newlyweds dare to make revelations. Neither partner wants to talk to each other about sexually transmitted diseases. But it's even harder to hear the "verdict" in the doctor's office. According to statistics, several tens of millions of new cases of STDs are registered annually in developed countries. Approximately half of these cases occur in young people between the ages of 15 and 24. Next, we will tell you about STD facts that you might not know.

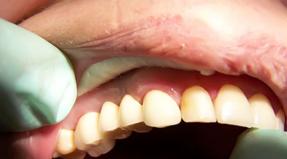
The disease may be asymptomatic
Most sexually transmitted diseases are asymptomatic. However, the infection has already made its way into your body, and it will not leave until you pass the appropriate tests and conduct a course of treatment. Ironically, if you don't know you have a medical condition, you don't worry about safe sex. And that means you endanger all your potential sexual partners. The most common asymptomatic infections are chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis. Sometimes there is swelling in the genital area.

When a person's body encounters an infection, it activates all its forces to fight it. This is a difficult task, given that you are in the dark and are not going to be treated. But your body is forced to work non-stop. It creates more cells to fight off the invader, and this, in turn, causes the lymph nodes to swell. This can be seen during a cold. Your neck becomes covered with lymph nodes, making swallowing even more difficult. By the same principle, the body tries to expel the infection from the genital area. STDs can cause tumors in the groin (in both sexes) and swollen testicles in men, experts warn. Especially dangerous are chlamydia and gonorrhea, which can cause epididymitis and orchitis.


If a sexually transmitted disease causes symptoms, they are often mild (like a cold or the flu, for example). For example, in this way HIV makes itself felt. Before an infected person notices other symptoms, they will go through a fever, sore throat, and rash. If a woman "caught" genital herpes, this may make itself felt with pain in the abdomen. As you can imagine, this symptom is too common to be mistaken for gastritis or gallbladder problems. Chlamydia in men does not cause any symptoms. But gonorrhea, which has entered the body through oral sex, causes sore throats.

STDs can lead to blindness
This complication can surprise even medical professionals. And although most often STIs affect the functions of the reproductive sphere, the eyes can also suffer. For example, chlamydia can cause blindness.

These diseases are transmitted even if there are no symptoms
Of course, symptoms such as genital herpes, sores and blisters should be a red flag for you when it comes to sexual intercourse. But even if your partner has no symptoms at all, you can get the infection through unprotected sex. If we talk about herpes, then infection is also possible through bodily contact, because foci of inflammation can occur not only in the genital area. The only way to know for sure about the presence of an STD is through tests. This is the only way you and your partner can make sure that there are no infections in the body. You should not delay going to the doctor, because when the disease is present in the body for a long time, it can cause various complications.

It can lead to heart disease
Sexually transmitted diseases are very serious and can lead to heart disease. This is another reason why you need to get tested regularly. For example, chlamydia and gonorrhea cause heart valve problems.


STDs can lead to infertility
Sometimes STDs lead to infertility. This is typical for both men and women. Therefore, if you and your partner are planning to have children, you must first be tested. Male infertility in this case is caused by inflammation of the testicles or scars on the testicles. The woman is in even greater danger, since the zones of the small and large pelvis are at risk. For example, infections lead to fibrosis (scar formation in the lining of the uterus).

Sexually transmitted infections are more serious for women
Representatives of the beautiful half of humanity can blame their anatomy for this. The vagina leads to the uterus, then the pelvis is threatened. In fact, the infection has an open path to the abdominal cavity. This is why women may experience vaginal bleeding between periods. This means that the infection has entered the vagina or "settled" in the cervix. If the disease has spread to the pelvic organs, sometimes it causes pain in the abdomen or lower back, or leads to constipation.


STDs can cause random symptoms
If we are talking about obvious symptoms of genital infections, then most often we remember about sores or burning during urination. However, some manifestations may come as a complete surprise to you. For example, syphilis is characterized by the presence of non-painful sores and numbness, while herpes causes a tingling sensation in the problem area. In any case, if you notice something strange, it's best to check your suspicions.

Sex can get painful
Since some infections cause warts and sores in the genital area, this can lead to pain during sex. However, this is not the only problem. Ulcers, blisters or bumps in the penis, vagina, anus or mouth cause burning and itching, which makes it painful not only to have sexual intercourse, but also to urinate or swallow.

This problem is more common than you might think.
We have already said that many STDs occur without any symptoms. And this means that people cannot guess about the existence of a problem. In America alone, 19.7 million new cases are recorded each year. The average age of patients is 25 years. This means that one in two sexually active adults is at risk of infection. According to statistics, more than half of people have experienced sexually transmitted infections during their entire lives. Many of them do not know about it for a long time. Why not take care of your health? Regular check-ups and testing will help prevent infection.

STDs increase the risk of developing HIV
We give you some food for thought. The presence of sexually transmitted infections in the body increases the risk of developing the human immunodeficiency virus. The "black list" includes herpes, gonorrhea, syphilis and chlamydia. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, these ailments increase the chances of HIV infection by 2-5 times.


STD bacteria have different incubation periods
If you allow casual sex but have never been tested for a sexually transmitted disease in the past, exercise extreme caution. First, get tested and stop having sex for a while. Bacteria and viruses that cause STDs have different incubation periods. To guarantee a 100% test result, some time must pass. Don't go to the hospital the day after casual sex. Too little time has passed, and it is quite possible that the antibodies will not yet be detected.
The topic is very prosaic - sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). In recent years, the rates of infection with sexually transmitted diseases have been steadily increasing. Unfortunately, this applies primarily to adolescents, due to the lack of proper sex education in schools and families. Statistics say that every 10 people on our planet suffer from STDs, not excluding children and the elderly.
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a whole group of infectious diseases with a variety of clinical manifestations, united by sexual transmission and high social danger. The term appeared in 1980, and to date, more than 20 types of infections and viruses are classified as STDs: from deadly HIV infection to banal chlamydia, which, by the way, cannot be called trifling either. Moreover, in terms of prevalence in Russia, it is in second place after the flu.
According to the type of causative agent, STDs are divided as follows:
The World Health Organization classifies STDs as follows:
Common sexually transmitted infections
- gonorrhea;
- syphilis;
- lymphogranulomatosis (inguinal form);
- chancroid.
- granuloma of the venereal type.
Other STDs
that affect mainly the organs of the reproductive system:
- urogenital shigellosis (occurs in persons with homosexual sexual intercourse);
- trichomoniasis;
- candidal lesions of the genital organs, manifested by balanoposthitis and vulvovaginitis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- herpes type 2;
- gardnerellosis;
- scabies;
- genital warts;
- chlamydia;
- flatheads (pubic pediculosis);
- molluscum contagiosum.
that affect mainly other organs and systems:
- sepsis of newborns;
- Hepatitis B;
- lamblia;
- cytomegalovirus;
- AIDS;
- amoebiasis (typical for persons with homosexual contacts).
Often, STDs are asymptomatic and are detected only at the stage of development of complications. Therefore, it is very important to pay due attention to their prevention: use contraceptives, avoid casual sexual contact, observe hygiene and take tests twice a year in the direction of a gynecologist or urologist.
Of course, most STDs are curable, but not all. For example, it will never be possible to part with genital herpes - treatment only softens the course of the disease and reduces the frequency and severity of relapses. Only those under 25 have a chance to permanently get rid of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
By the way, it is believed that the human papillomavirus can cause cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva and penis. The genital herpes virus also affects sperm, and if a woman becomes infected with it during pregnancy, it can cause severe congenital diseases of the fetus.
Note: almost all viral and bacterial sexually transmitted diseases penetrate the placental barrier, that is, they are transmitted to the fetus in utero and disrupt its physiological development. Sometimes the consequences of such infection appear only a few years after the birth of a child in the form of dysfunction of the heart, liver, kidneys, developmental disorders.
Treatment will be successful only if it is started without delay and completed. How to spot the very first danger signals?
An alert has been declared!
There are eight main signs, having discovered which, you should not delay a visit to the doctor.
- Itching and burning in the intimate area.
- Redness in the genital area and anus, sometimes - sores, vesicles, pimples.
- Discharge from the genitals, smell.
- Frequent, painful urination.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the groin.
- In women - pain in the lower abdomen, in the vagina.
- Discomfort during intercourse.
- Cloudy urine.
However, for example, syphilis or chlamydia may appear several weeks after infection, and sometimes STDs can generally be hidden for a long time, turning into a chronic form.
Regardless of the presence of discomfort in the genital area, a preventive visit to the doctor is necessary twice a year, as well as after casual sexual contact, sexual violence, in case of infidelity of your regular partner. If you notice any STD symptoms, go to your appointment the same day.
Symptoms of sexually transmitted diseases in women
The presence of certain symptoms of STDs in women is explained by the peculiarities of their physiology.
The following signs should alert a woman and become a reason for an extraordinary visit to the gynecologist:
- pain and dryness during sex;
- single or group enlargement of lymph nodes;
- dysmenorrhea (violations of the normal menstrual cycle);
- pain and discharge from the anus;
- itching in the perineum;
- anus irritation;
- rash on the labia or around the anus, mouth, body;
- atypical vaginal discharge (green, frothy, odorous, bloody);
- frequent painful urge to urinate;
- swelling of the vulva.
Sexually transmitted diseases in men: symptoms
You can suspect an STD in men by the following signs:
- blood in semen;
- frequent and painful urge to urinate;
- low-grade fever (not with all diseases);
- problems with normal ejaculation;
- pain in the scrotum;
- discharge from the urethra (white, purulent, mucous, with a smell);
- rash of various kinds on the head of the penis, the penis itself, around it.
Let's get to know each other better
- Chlamydia
Symptoms. 1-4 weeks after infection, patients develop purulent discharge, painful urination, as well as pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back, bleeding between menstruation in women, in men - pain in the scrotum, perineum.
What is dangerous? In women, it can lead to inflammation of the fallopian tubes, cervix, pathologies of pregnancy and childbirth, diseases of the liver, spleen.
In men - to inflammation of the epididymis, prostate gland, bladder, impaired potency. Newborns may develop conjunctivitis, nasopharyngeal lesions, pneumonia.
- Trichomoniasis
Symptoms. They can appear on the 4-21st day after infection, sometimes later. Women have abundant foamy discharge of white or yellowish-green color with a pungent odor, causing severe itching and irritation of the genital organs, as well as pain, burning during urination, pain during intercourse. In men, there is a burning sensation during urination, mucopurulent discharge from the urethra. However, this disease is often asymptomatic.
What is dangerous? In women, the cervix and inner layer of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and urinary tract are affected. The infection can even cause peritonitis!
In men, the prostate gland, testicles and their appendages, and urinary tract are affected.
- Mycoplasmosis (in men - ureaplasmosis)
Symptoms. It can detect itself 3 days after infection, or maybe even a month later, manifesting itself as itching and discomfort in the genital area, scanty clear discharge, painful urination.
What is dangerous? A frequent complication in women is inflammation of the genital organs, in men - a violation of spermatogenesis.
- Gonorrhea
Symptoms. 3-7 days after infection, women develop yellowish-greenish vaginal discharge, frequent, painful urination, pain in the lower abdomen, and sometimes bloody discharge. However, in most of the fairer sex, the disease goes unnoticed for a long time. Men have pain and burning sensation during urination, yellowish-greenish purulent discharge from the urethra.
What is dangerous? In women, the urethra, vagina, anus, uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes are affected. In men - internal genital organs, chronic inflammation of the epididymis, seminal vesicles, prostate develops, which threatens impotence, infertility.
- Syphilis
Symptoms. The incubation period of the disease is 3 to 6 weeks. The first sign is a rounded sore (hard chancre). In women, it lives on the labia or vaginal mucosa (sometimes in the anus, in the mouth, on the lips), in men - on the penis or scrotum. By itself, it is painless, but a week or two after its appearance, the nearest lymph nodes increase.
This is the time to start treatment! This is the first stage of the disease, when it is still reversible.
2-4 months after infection, the second stage develops - a rash “spreads” all over the body, high fever, headache appear, almost all lymph nodes increase.
In some patients, hair falls out on the head, wide condylomas grow on the genitals and in the anus.
What is dangerous? This disease is called slow death: if not fully cured in time, serious problems arise with the musculoskeletal system, irreversible changes occur in the internal organs, the nervous system - the third stage of the disease begins, in which about a quarter of patients die.
Forget about the Internet!
Did you notice that something is wrong? It is better to play it safe and hurry to the doctor, rather than looking on the Internet for symptoms and treatments.
How is an STD diagnosed? First - an examination by a doctor, then - tests and studies. The most modern method of DNA diagnostics: PCR (polymerase chain reaction). For research, scrapings are taken from the urethra, vagina and cervix.
Doctors also use the ELISA method (blood is taken from a vein or a scraping is done and the presence of antibodies to STDs is determined), bacterioscopy (most often it detects gonococci and Trichomonas) and many other diagnostic methods.
STDs are treated with antibacterial drugs, as well as local procedures (washing the urethra in men, sanitation of the vagina in women and other procedures).
At the end of the course of treatment, it is imperative to undergo a control examination - to pass several tests to make sure that there is no infection in the body.
What is important to know
- Is it possible to get infected in a bath or pool?
In fact, the likelihood of catching STDs in everyday life is very low. Microorganisms that cause venereal diseases are unstable in the external environment. In the pool, for example, it is almost impossible to pick up such an infection (unlike fungal or intestinal). Even if an HIV-infected or syphilis patient swims in the water next to you, chlorinated water will quickly kill pathogens.
However, in public toilets, if surfaces are not monitored there, there is a risk of infection with the papillomavirus or herpes virus. But the classic venereal diseases - syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea and trichomoniasis - require contact with blood or mucous membranes.
The exception is syphilis: it can be transmitted through saliva if you use the same dishes with the patient and do not wash them well. So, in any case, you should not forget about the rules of hygiene.
Keep in mind: for a short time, microorganisms that cause "bad" infections can survive on warm, damp clothes. Therefore, in the bath or pool (and at home too), do not use someone else's wet towel, washcloth or other personal hygiene items.
- Symptoms of sexual disease appear immediately?
Not always. With good immunity, a disease (for example, chlamydia) can proceed for years without symptoms. The person may not even know they are sick. And the only way to detect such a latent infection is through laboratory tests.
The first signs of infection in women are unusual vaginal discharge. In men, urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). Its symptoms are urinary incontinence and purulent discharge. All other symptoms (rashes, swollen lymph nodes, etc.) appear when the infection has already spread in the body.
- Condom - reliable protection against STDs?
Yes. If it is of good quality, has not expired, is properly sized and used correctly, then the risk of contracting most STDs is reduced to zero.
The exception is external warts and severe herpetic infection.
Incidentally, nonoxynol-9 spermicidal lubricant used on condoms does not protect against STDs, according to a 2001 WHO report. By damaging cell membranes, nonoxynol-9 spares neither spermatozoa, nor infections, nor the mucous membranes of the genital organs. By damaging the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, nonoxynol-9 "opens the gate" to infections.
While the condom is not the ideal way to prevent STDs, it is considered the most effective. Therefore, it is necessary to use condoms for all types of sex: vaginal, anal and oral.
In order not to increase the risks, you should buy condoms only in reputable pharmacies. To avoid damaging the condom, do not open the package with a file or fingernails.
It must be remembered: a condom can only be used with special lubricants. Ordinary creams and ointments are not suitable for this.
A common mistake is to use birth control pills, vaginal pills, or spermicidal creams with a condom. Gynecologists warn that these drugs disrupt the microflora of the vagina and provoke the development of candidiasis (thrush). Thus, instead of getting rid of problems, you can acquire them.
If you want to protect yourself as much as possible, it is enough to use a condom correctly and follow personal hygiene measures. A high degree of protection and the almost complete absence of side effects is a definite plus of condoms. However, it should be remembered that the condom can break, in which case you should have emergency prophylaxis on hand.
Emergency drug prophylaxis is also used - a single dose or injection of antibacterial drugs, which can only be prescribed by a dermatovenereologist. The procedure helps to prevent gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, mycoplasmosis, syphilis and trichomoniasis. But this method should not be used frequently.
But you should not count on various gels, suppositories and vaginal tablets in terms of protection against STDs. These products contain spermicidal substances in insufficient quantities to secure at least 80-90%. In addition, the causative agents of many STDs do not live in seminal fluid, but on the genitals and are insensitive to spermicides.
The same applies to douching after intercourse with special gels or chlorine-containing antiseptics.
Remember!
Sexually transmitted diseases are dangerous, first of all, with complications: infertility, impotence, chronic inflammatory processes, lesions of the nervous system and internal organs. Improper treatment, ignoring symptoms, neglecting preventive measures can adversely affect your health.
What can be done in an emergency?
So, what to do after unprotected intercourse if you have no confidence in the health of your partner?
- Urinate profusely.
- Wash hands and external genitalia with soap.
- Treat the genitals, pubis and thighs with an antiseptic (miramistin, chlorhexidine and others). This technique helps to reduce the risk of STDs by 80-90%. But not 100%. So the best prevention is a condom and common sense.
- If it is not possible to visit a doctor in the next 24 hours, take a “shock” dose of antibiotics.
- Seek medical attention as soon as possible.
It makes sense to see a doctor within 5 days of having unprotected sex. There are emergency drug treatments that can prevent the development of syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and other sexually transmitted diseases.
But it will not help against HIV and the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Blood for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV is taken 3 months after contact. It makes no sense to be examined before: antibodies to these diseases do not appear in the blood immediately after infection.
Following these precautions will reduce the likelihood of infection and the severity of its possible consequences.
The sexual freedom that modern man is accustomed to using has its own “pitfalls”: according to WHO, at present, every tenth, including children and the elderly, suffer from one or another STD. Every 15 seconds, someone in the world is diagnosed with a sexually transmitted infection. In order to maintain your health and not endanger your partner, timely prevention and treatment are required.
The constant increase in the number of sexually transmitted diseases does not indicate the complexity of prevention, but the irresponsible attitude of most people to their health and their ignorance in this matter. Often, patients are embarrassed to see a doctor when symptoms occur and try to get by with folk remedies. This is fraught with irreversible consequences for their health.
***
The only effective folk remedy for preventing STDs is complete sexual abstinence :).
Plus: it's free. Minus: does not exclude the possibility of infection by domestic means and in case of violence.
Based on materials

There are situations when a patient, turning to doctors (gynecologist, andrologist, urologist), finds out that in addition to obvious diseases, he also has sexual infections, including chronic ones. The first reaction of the patient is disbelief and surprise, because he did not have any symptoms.
Unfortunately, many sexually transmitted diseases have an unpleasant tendency to not cause specific symptoms of presence. A person does not experience pain, does not complain, while at the same time the pathogen can be in his body for years.
Where does the disease come from and why are there no symptoms
If we talk about people who are adequate in their personal lives, in the sense of respectable, namely, they are usually surprised by the presence of STDs, then it is important to note here that you can “catch an infection” anywhere, for example, in a pool or a public toilet. Some sexual infections can also be in permanent partners, also being in a latent state.
Factors contributing to the course of diseases without pronounced symptoms:
- specificity of the disease;
- inattention;
- neglect of health;
- self-treatment;
- decrease in immunity.
STDs without symptoms
Among the most common problems encountered in more than half of the patients who came for a routine examination, the following can be distinguished:
Chlamydia. This is a disease caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, ie. chlamydia - virulent intracellular bacteria that affects the barrier cells of the body. The main reason for the wide spread of the disease is a course with mild signs or no symptoms at all. Due to the high contagiousness, 80% of the sexual partners of men with this disease are subsequently infected. In other words, when faced with an infection, the body of four out of five women cannot resist it. Men also get the disease easily.
The disease itself is not as dangerous as complications in men's and women's health. Chlamydia can lead to the development of cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, decreased erectile function, gynecological diseases, and infertility.
The cause of inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis) in women is considered to be chlamydia. Chlamydia can occur with clinical signs of arthritis, conjunctivitis, pneumonia, so patients seek treatment instead of a venereologist to the wrong specialists.
Ureaplasmosis. It is caused by small microorganisms belonging to gram-negative microbes. Carriers of this sexual disease are up to 70% of sexual partners of both sexes. In men, mild symptoms of the disease resemble the manifestation of prostatitis. Women may experience mild burning sensations when urinating. Infection can take place, as well as through sexual contact, and through household contact. The danger is that it turns into prostatitis in men, and in women it can provoke infertility.
Its carriers are more than 60% of people. It is transmitted from person to person sexually by anal-genital contact and through oral sex, causing damage to the anogenital tract (anus and genitals) with the formation of warts on them. Some of them are harmless, some can provoke the occurrence of cancerous growths.
Asymptomatic bacteriospermia. Latent infection of the male genital tract. This disease is caused by microorganisms that live in the rectum in women, in rare cases in the vagina. Sex with a woman who carries bacteria can cause infection in a man with a weak antibacterial function of the prostate gland. BBS leads to a decrease in fertility, a decrease in the number of active spermatozoa - to male infertility.
HIV infection. At the beginning of the infection, it is asymptomatic. This infection gradually destroys blood cells and eventually destroys the entire mechanism of the body's immune defense, turning into AIDS - acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. With this disease, with antiviral therapy, people live on average 10 years.
How to know if you have hidden STDs
To do this, it is enough to visit, or, after passing the usual examination, take tests. It is important to understand that any disease is easily treated in the initial stages, but if you start it, you will get a whole bunch of complications.