Treatment for diarrhea in adults. Diarrhea (diarrhea). Causes, risk factors, diagnosis of causes of diarrhea, treatment of diarrhea. Antibiotics for diarrhea in adults - Levomycetin, Tetracycline, Metronidazole: how to take? Furazolidone for diarrhea in adults: how to take
In itself, diarrhea in an adult is not a separate disease, but a symptom that occurs in a wide variety of ailments. Therefore, in order to successfully normalize stool, it is necessary to understand the causes of diarrhea in each specific case and, if possible, eliminate them.
What is diarrhea in adults?
Diarrhea (diarrhea) is a pathological condition when there is an increase in stool in adults more than 3 times a day, as well as a change in its consistency: it becomes watery, maybe with mucus and bloody discharge. Acute diarrhea lasts up to 2 – 3 weeks. Chronic diarrhea lasts more than 21 days.
Classification of diarrhea by mechanism of occurrence
Sodium and chloride ions accumulate in the intestinal lumen, which leads to an increase in osmotic pressure. High osmotic pressure causes additional water intake and a sharp increase in the volume of intestinal contents. Typically, this type of diarrhea is characterized by very large and loose stools, as well as loss of water and electrolytes.
In severe cases, without timely treatment, secretory diarrhea can lead to death due to acute fluid deficiency and the development of hypovolemic coma.
This type of diarrhea is observed with cholera, salmonellosis, viral intestinal infections, and hormonally active tumors. In addition, some laxatives and prostaglandins cause increased stool frequency in this way.
To some extent it is similar to the secretory one, since in this case the increased osmotic pressure also leads to excessive accumulation of water in the intestinal lumen and an increase in the volume of feces. However, here hyperosmolarity does not arise due to increased secretion of sodium and potassium ions, but due to the fact that the intestinal contents initially have high osmotic pressure. This type of diarrhea usually occurs in the case of rotavirus infection, as well as with an overdose of saline laxatives.
Inflammation develops in the lower intestines, which impairs the reabsorption of water. Observed in dysentery and amoebiasis.
Dilution of feces occurs due to additional release of blood, protein exudate, mucus or pus into the intestinal lumen. This type of diarrhea is typical for diseases accompanied by inflammation of the intestinal mucosa - Crohn's disease, intestinal tuberculosis, ulcerative colitis, etc.
Characterized by acceleration of intestinal motility. Typically observed in cases of stress, functional digestive disorders, diabetic enteropathy, amyloidosis, scleroderma.
Main causes of diarrhea in adults
The leading causes of diarrhea in adults are: 
- food poisoning;
- excessive consumption of “heavy” foods;
- diseases of the digestive system, accompanied by inflammation of the intestinal walls (enteritis, enterocolitis);
- food allergies;
- enzyme deficiency;
- taking certain medications (for example, synthetic sweeteners, laxatives);
- sudden change in food style and conditions (travelers' diarrhea);
- intestinal flu and other infections;
- lead and mercury poisoning;
- stress.
When diarrhea is accompanied by a fever up to 380C, vomiting, or diarrhea with blood or water diarrhea, it is important to immediately consult a doctor in order to receive adequate treatment and avoid the development of serious complications.
Why is frequent diarrhea dangerous?
If stools are watery and frequent, you are more likely to develop dehydration and electrolyte loss, which can be fatal. For this reason, you should immediately see a doctor and immediately provide assistance to the sick person if the following symptoms are observed:
- dry mucous membranes;
- increased heart rate;
- chapped lips;
- rare or complete absence of urination;
- decreased blood pressure;
- the appearance of muscle cramps;
- disturbance of consciousness.
Be sure to consult a doctor in the following situations:
- diarrhea does not stop for 3 or more days;
- bowel dysfunction occurs and develops without reason;
- in addition to diarrhea, yellowness of the sclera and skin, intense abdominal pain, sleep disturbance and high fever are observed;
- stools are dark black or green in color, mixed with blood.
First aid for diarrhea
If you experience diarrhea and vomiting or diarrhea and fever, it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since these symptoms may indicate the development of a serious illness, for example, acute intestinal poisoning. First aid until the patient is examined by a doctor is to prevent dehydration and significant loss of minerals. In this regard, experts, in case of diarrhea, recommend the following:
- Drink plenty of minerals. For this purpose, Regidron (and its analogues) is best suited. If it is absent, then you can take lightly salted water or saline solution.
- Stick to a strict diet. When diarrhea begins, it is better to generally abstain from 1 – 2 or more meals, unless the doctor recommends otherwise. To relieve intestinal inflammation, you can drink tea or decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs.
Treatment of diarrhea: diet
Complete treatment for diarrhea includes the following dietary recommendations.
- It is allowed to eat such foods as white crackers, slimy porridges, vegetable purees, steamed and boiled fish, lean meats, rice water, and tea.
- It is prohibited to eat spicy, salty, sour foods, or foods containing large amounts of coarse fiber. In addition, milk, brown bread and anything that can cause increased gas formation and “fermentation” are not recommended.
- In the first days, foods that stimulate the release of bile are excluded from the diet: eggs, fatty meat, butter, etc.

Gradually, the list of permitted products is expanding, and the patient, as stool normalizes, can switch to a normal diet. In situations where diarrhea is caused by enzyme deficiency or any chronic intestinal diseases, systematic diet is one of the most effective means of therapy.
How to treat dehydration with acute or chronic diarrhea
As a rule, glucose-saline solutions are prescribed until stool normalization. They replenish the loss of mineral salts and fluids in the body. The most well-known drugs in this group are Regidron, Gastrolit, Citroglucosan. In the absence of them on hand, you can independently prepare and use the following solution: for 1 liter of water, take ½ teaspoon of baking soda, 1 teaspoon of salt, ¼ teaspoon of potassium chloride, and also add 4 tbsp. l. Sahara. Instead of potassium chloride, you can take a decoction of dried apricots (dried apricots).
How to treat diarrhea with medications
The most common drugs used to treat diarrhea are:
The best prevention of diarrhea is maintaining personal hygiene, eating only high-quality foods and timely treatment of various chronic intestinal diseases.
Find out what are the causes of diarrhea in adults, how to help yourself or a loved one get rid of such an unpleasant condition.
Diarrhea is unpleasant. With such a symptom, it becomes impossible to live a normal life. But discomfort and constant trips to the toilet are just the tip of the iceberg. Diarrhea signals an illness, sometimes quite serious. And sometimes it’s not enough to take one of those “magic pills” that are advertised on TV. In order for diarrhea to go away and not leave health consequences, you need to find out the reason for the change in stool character and fight it.
Diarrhea: disease or symptom?
IMPORTANT: Diarrhea is the popular name for a pathological condition, medically called diarrhea. With it, there is a frequent urge to defecate, the stool becomes watery and may change color. Diarrhea is often accompanied by abdominal pain and flatulence.
Normally, an adult goes to the toilet “mostly” from 2 times a day to 1 time in 2 days. At the same time, he secretes from 150 to 400 g of feces. Defecation occurs without much effort, after which there is a feeling of empty bowel.
The feces of an adult have a soft consistency and are shaped. Its color is brown.
They talk about diarrhea when in an adult:
- Frequent stools – 3 or more times per female
- loose stools – mushy or watery
- It is difficult to hold stool or difficult to hold stool
- stool color is yellow, green or whitish
- there is undigested food, mucus or blood in the stool
- stool foams
- stool has a foul odor
Diarrhea may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting
- a slight increase in temperature, up to 37.5 degrees, and a significant increase, up to 41 degrees
- increased gas formation
- cramps, pulling or cutting pain in the abdomen
- general malaise
Diarrhea, as a symptom, can have a serious consequence in the form of dehydration. We can talk about it if an adult, against a background of general weakness, has an irresistible desire to drink, his mucous membranes and skin become dry, blood pressure drops, tachycardia is observed, spots appear before his eyes, his head hurts and he feels dizzy. An extreme degree of dehydration with diarrhea is fraught with disruption of vital processes in the body and death.
Therefore, if you have diarrhea, it is better not to take symptomatic medications (which, by the way, have a lot of contraindications), but to consult a doctor who can determine the cause of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment.

 Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are a reason to call an ambulance.
Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are a reason to call an ambulance. IMPORTANT: You also need to know the rules of first aid for diarrhea in order to alleviate your condition and prevent dehydration.
The causes of diarrhea can be very different. Diarrhea can begin with:
Changing the nature of the stool (its color and consistency) is often the key to the correct diagnosis. So:
IMPORTANT: Mucus is always present in a certain amount in the stool. It is formed by epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract, mucus swallowed from the respiratory tract and respiratory organs, and blood cells and leukocytes. If a person is healthy, it is almost invisible.
If there are visible mucus inclusions, streaks or lumps in the stool of a liquid consistency, you can suspect:
- intestinal infection
- Crohn's disease
- irritable bowel syndrome
- dysbacteriosis
- cancer
An accurate diagnosis is made based on medical history, other symptoms and laboratory results.
Diarrhea in an adult with fever, vomiting: causes
Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are a classic clinical picture of what is popularly called poisoning, and in official medicine - an intestinal infection. The patient feels very bad, his condition can very quickly become severe or extremely severe. If you suspect a viral or bacterial intestinal infection, you should immediately call an ambulance and be hospitalized.

 Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are symptoms of an intestinal infection.
Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are symptoms of an intestinal infection. IMPORTANT: Vomiting, fever and diarrhea can occur with rotavirus infection in adults. Read about the features of the disease in the article “”.
Diarrhea in an adult with influenza, ARVI, 3 days, a week: causes
Diarrhea with influenza or ARVI in adults is a consequence of intoxication of the body with waste products of viruses. This intoxication can also cause vomiting. To get rid of diarrhea caused by respiratory viruses, it is necessary to take measures to treat the underlying disease and use symptomatic medications for diarrhea. Everything must be done to prevent dehydration of the body.

 Diarrhea can be a complication of ARVI.
Diarrhea can be a complication of ARVI. IMPORTANT: Diarrhea associated with ARVI symptoms is often attributed to “stomach flu”. There is no such diagnosis in medicine. There is not a single influenza virus that directly affects the intestinal mucosa.
Diarrhea in an adult after antibiotics: causes
Antibiotic treatment is very common today. Medicines in this group are designed to kill pathogenic bacteria that attack the human body. Unfortunately, antibiotics act not only on pathogenic microflora, but also on those “good” bacteria that live in the human stomach and intestines and take part in the digestive processes.
Therefore, a couple of days after starting a course of antibiotic treatment, so-called drug-induced diarrhea may begin. They treat it:
- diet
- drugs - prebiotics
- antidiarrheal drugs
IMPORTANT: As a rule, to prevent drug-induced diarrhea, in parallel with antibacterial agents, the patient is immediately prescribed prebiotics.
Diarrhea in an adult after eating or drinking milk: causes
Sometimes one-time or chronically immediately after eating, about half an hour later, an adult begins to have diarrhea. The symptom indicates a functional digestive disorder, in which the food consumed moves too quickly through the gastrointestinal tract, which means it does not have time to be absorbed. This happens when:
- irritable bowel syndrome
- some endocrine diseases
- inflammatory bowel diseases
One-time diarrhea can occur after consuming dairy or too fatty foods, as well as excessive consumption of laxative foods, such as beets or prunes.

 Diarrhea after milk can be one of the symptoms of intolerance to this product.
Diarrhea after milk can be one of the symptoms of intolerance to this product. The protein contained in cow's milk, casein, and milk sugar, lactose, are not tolerated by all adults and children. According to statistics, from 2 to 7 percent of people in the world cannot drink milk. This drink, which is beneficial for others, causes them to have watery, foamy bowel movements. The main way to treat cow's milk intolerance is a diet that minimizes or completely eliminates the consumption of it and dairy products.
Diarrhea in an adult on vacation, at sea: causes
It often happens like this: a long-awaited vacation, a trip to the sea, to some exotic country, a full-time vacation, and then suddenly, diarrhea. Why do both adults and children often experience diarrhea on vacation?
The phenomenon even has a special name - traveler's diarrhea. Do not attribute loose and frequent stools to acclimatization. It’s just that at sea, in any other, especially underdeveloped country, it is more difficult to take personal hygiene measures. Food and water often leave much to be desired. Microorganisms that live where he rests are often alien to the traveler’s body; there is no immunity to them. Hence poisoning with diarrhea, vomiting and fever. If this happens, you need to see a doctor. It will help you heal faster and return to your vacation plans.
VIDEO: 3 tests for diarrhea. Diarrhea as a symptom
First aid for diarrhea in an adult
It is not diarrhea that is treated, but its cause. Even if you influence intestinal motility with any drug, the patient’s condition will only improve temporarily. A diagnosis is necessary and you should consult a doctor.
But immediately and immediately in case of diarrhea, you need to be able to provide first aid to yourself or someone nearby.
- Take an absorbent agent - activated carbon, white carbon, Smecta, Enterol, Atoxil, others.
- Drink water and warm, slightly adjusted tea in small portions, but often.
- Avoid eating for 6-12 hours. Next, follow the diet prescribed by your doctor.
- At the first signs of dehydration, take Regidron or another rehydrating agent.
- Limit physical activity.
- Limit contact with people living with the patient in order to avoid infection if the cause of diarrhea is infection.


Diet, nutrition, products for diarrhea, diarrhea in adults
- normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
- restore intestinal microflora
- restore the intestines' ability to absorb fluids
- suppress fermentation processes in the intestines


IMPORTANT: For acute and chronic intestinal diseases accompanied by diarrhea, a therapeutic diet table No. 4 is prescribed.
The essence of this diet is:
- reducing the calorie content of the daily diet to 2000 kcal
- reducing consumption of fats and simple carbohydrates
- reducing sugar consumption
- eating food that is not too hot, cold, hard, salty, peppery, that is, food that would irritate the gastrointestinal mucosa
- eating 5-6 times a day in small portions
Avoid frying, baking, pickling, and fermenting foods if you have diarrhea. They eat boiled, steamed, pureed. Allowed:
- Meat: veal, beef, lean chicken, turkey.
- Fish: pike perch, perch.
- Eggs: soft-boiled and in the form of a steamed omelet, no more than one per day.
- Cereals: white rice, oatmeal, buckwheat, semolina (porridge with water and without oil).
- Dairy: low-fat cottage cheese, in the form of a casserole, acidophilus.
- Vegetables: boiled, stewed, except cabbage.
- Fruits: unsweetened, in the form of purees or jelly.
- Berries: non-acidic, in the form of jelly.
- Beverages: black, green, herbal tea, uzvar, non-acidic berry compote, natural unsweetened, non-sour juices, diluted in half with water.
- Bread: white, in the form of crackers.
Is it possible and how to eat rice water and kefir for diarrhea in adults?
One of the first dishes introduced into the diet of a person with diarrhea is rice water. It works comprehensively:
- coats the intestinal walls, soothes the mucous membrane
- reduces peristalsis
- nourishes the human body, which due to diarrhea is faced with a deficiency of nutrients and nutrients

 Rice water helps relieve diarrhea.
Rice water helps relieve diarrhea. - The decoction is prepared based on the proportion of 1 teaspoon of rice to 1 liter of water.
- Throw the rice into water that has not yet boiled, and prepare the broth for 40 minutes.
- Take a decoction of 50 g every 2-3 hours, it is not sweetened or salted.
IMPORTANT: Contrary to popular belief, kefir is not recommended for diarrhea. Fresh, it is laxative, and three days old it stimulates fermentation processes in the intestines. Consuming kefir can make the situation even worse.
Effective tablets, medicines, drugs for diarrhea: list. Smecta, Regidron, Enterosgel for diarrhea in adults: how to take? Potassium permanganate, activated carbon, Polysorb: how to use?
Despite the fact that the treatment of diarrhea includes a set of measures, there are very effective medications that can improve the patient’s condition. Among them:
- Energy sorbents: activated carbon, white carbon, Polysorb, Smecta, Gastrolit, Enterosgel, Filtrum STI, others. These drugs can be used either once or according to a regimen prescribed by a doctor. The dosage, frequency and duration of use should be checked with your doctor or in the instructions.
- Probiotics: Linux, Hilak Forte, Bifiform, Bifidobacterin, others. The main purpose of taking them is to normalize the intestinal microflora.
- Oral rehydration products: Regidron, Gastrolit, Hydrolit, others. Needed for dehydration or to prevent it.


Antibiotics for diarrhea in adults - Levomycetin, Tetracycline, Metronidazole: how to take? Furazolidone for diarrhea in adults: how to take?
If diarrhea is caused by an infection, the doctor may prescribe the patient antimicrobial medications and antibiotics, which include:
- Furazolidone. They treat infectious diarrhea, including dysentery and salmonellosis. Adults take it in tablet form for at least 3 days. Pregnant women with infectious diarrhea are rarely treated with Furazolidone.
- Levomycetin. A broad-spectrum antibacterial drug is indicated for various types of infectious and inflammatory diseases, including intestinal diseases, accompanied by diarrhea. It works quickly. Adults drink the drug 300-500 mg three times a day after meals, or according to another regimen prescribed by the doctor.
- Tetracycline. Another strong antibiotic that suppresses pathogenic microflora in the intestines.
- Metronidazole. This antibiotic acts mainly on anaerobic microflora.


IMPORTANT: Antibiotics for diarrhea are prescribed only by a doctor. The specialist is based on test results (if bacteria sensitive to a specific drug are detected in the stool). If the cause of diarrhea is a virus or not an infection at all, the antibacterial drug will be powerless or even worsen the situation by killing beneficial bacteria in the intestines.
VIDEO: Diarrhea. What to do?
Folk remedies for diarrhea: recipes
Treatment of diarrhea is possible with folk remedies:
- having fastening properties
- normalizing intestinal motility
- normalizing intestinal microflora
- reducing symptoms of flatulence
There are several options you can take note of.
RECIPE No. 1. Garlic
Needed:
- garlic – 1 clove
- boiled water at room temperature – 200 ml


- For chronic diarrhea for an established reason, if there are no contraindications, it is recommended to eat 1 clove of garlic.
- It is cut into pieces that can be swallowed, swallowed without chewing, and washed down with water.
- The course of treatment lasts 1 week.
RECIPE No. 2. Cumin infusion.
Needed:
- cumin seeds – 2 tbsp. spoons
- boiling water - 200 ml


- Cumin is poured into a thermos and poured with boiling water.
- Insist for a quarter of an hour.
- Strain and let cool.
- The infusion is divided into equal parts and drunk 3 times a day.
- A fresh infusion is made every day.
Herbs for diarrhea: how to use?
Herbal teas, infusions and decoctions of herbs help with diarrhea.
RECIPE No. 1. Melissa infusion.
Needed:
- dry lemon balm - 3 tbsp. spoons
- boiling water – 250 ml


- The herb is poured into a clay or glass container and poured with boiling water.
- Keep the herbal remedy in a water bath for 20 minutes.
- Then let it cool and brew for 1 hour.
- Drink 1 tbsp three times a day. spoon.
RECIPE No. 2: Infusion of wormwood and dill seeds.
Needed:
- dry wormwood – 1 tbsp. spoon
- dill seeds – 2 teaspoons
- boiling water -200 ml


- Mix wormwood and dill seeds.
- The mixture is poured with boiling water and left for 1 hour.
- Drink 100 ml twice a day 15 minutes before meals.
Pomegranate peels, oak bark for diarrhea in adults: how to use?
Oak bark is a proven folk remedy for diarrhea, as it has astringent, antimicrobial and antiputrefactive properties. Prepare it like this:
- 10 g of oak bark is poured into 0.3 liters of boiling water.
- Boil for 10-15 minutes.
- Cool and filter.
- Drink 100 ml three times a day.


Pomegranate peels, which are usually considered waste, help with diarrhea.
- Pomegranate peels must be prepared in advance - remove from the fruit, wash, separate the white, useless pulp and dry.
- Store dry raw materials in linen bags.
- If you have diarrhea, immediately prepare the following remedy: crush 10 g of dry crusts in a mortar and pour 200 ml of boiling water. After half an hour, strain the broth and drink half of it.
- Drink the second half in two times at equal intervals.


Will vodka help with diarrhea?
Vodka is believed to help with diarrhea. But when using it as a medicine, one should not forget about the harmful effects of alcohol on the body.
Add a third of a teaspoon of salt to 80 g of vodka and drink the resulting product.
VIDEO: Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a condition in which bowel movements occur more frequently than usual. It is characterized by the release of feces of liquid consistency, and in an adult, a single volume of the latter can be up to 300 g. Treatment of the disorder at home can be carried out using both medications and folk remedies.
According to the time of occurrence, diarrhea is divided into 2 types:
- Chronic– can last more than 3 weeks and are interrupted by periods of properly formed stool.
- Acute– passes within a period of 14 to 21 days.
Diarrhea (treatment at home in adults should begin within the first 2 days to prevent dehydration), a specific disease, the course of which differs depending on the causes of its occurrence.
There are several types of digestive disorders:
Causes
There are the following prerequisites for intestinal dysfunction:
- disruption of the processes of breaking down food into simple components and their digestion;
- increased consumption of fatty foods that the body has difficulty digesting;
- low amount of fiber in consumed foods;
- insufficient amounts of enzymes produced by the body necessary to digest food;
- changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora, both quantitatively and qualitatively, which do not allow the correct implementation of physiological processes.
Symptoms of diarrhea
The main symptom indicating diarrhea is repeated, loose stools. It can be repeated 10 to 20 times per day. If the normal amount of water in stool does not exceed 60%, then in case of indigestion this figure increases to 90%.
Symptoms accompanying diarrhea:

When should you take anti-diarrhea medications?
Treatment of diarrhea in adults, carried out at home, most often begins after the first symptoms appear. Not every stomach disorder requires the mandatory use of medications; in some cases, rehydration therapy can be used.
In case of rapid dehydration of the body, medication should be started immediately to reduce possible intoxication and speed up recovery of the body.
Having severe diarrhea can lead to serious health consequences, including possible death. Therefore, therapy should begin in a timely manner, with mandatory (if possible) consultation with a specialist.
Effective medications against diarrhea: table of the best drugs and their prices
To stop diarrhea, a complex of medications should be sequentially used, each of which performs important functions.

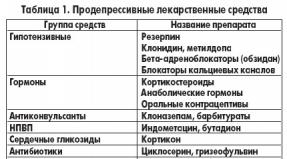
| Name | Functions performed | Price | |
| Adsorbents | Smecta | Adsorb harmful substances that enter the intestines and remove them outside the body | 150 rub. |
| Enterosgel | 390 rub. | ||
| Activated carbon | 34 rub. | ||
| Polysorb | 165 rub. | ||
| Rehydrators | Regidron | Replenish lost fluid, potassium and sodium chlorides | 378 rub. |
| Gastrolit | 250 rub. | ||
| Antibiotics | Nifuroxazide (Enterofuril) | Destroy pathogenic bacteria that cause diarrhea | 380 rub. |
| Rifaximin (Alpha Normix) | 421 rub. | ||
| Intetrix | 471 rub. | ||
| Anti-inflammatory | Galavit | Normalization of the activity of hyperactive macrophages in the intestine. Immunomodulation and inflammation relief | 323 rub. |
| Relieving symptoms | Loperamide | Inhibits intestinal motility, reducing the number of bowel movements | 53 rub. |
| Imodium | 350 rub. | ||
| Probiotics | Bifidumbacterin | Restore damaged microflora, improve metabolic processes | 120 rub. |
| Lactobacterin | 140 rub. | ||
| Linux | 420 rub. | ||
| Hilak forte | 180 rub. | ||
| Enterol | 292 rub. |
Drugs for chronic stool disorder
Diarrhea (treatment at home in adults does not require immediate initiation if it is chronic) is often left without proper attention, which is wrong.
To prescribe medications, a competent diagnosis should be carried out, including:
- Retromanoscopy with bacteriological and microscopic examination of stool: helps determine the nature of the inflammation that has occurred.
- Identifying the type of diarrhea to diagnose the pathogenic mechanism of the problem.
- Studying a person’s eating habits in order to correct an unhealthy diet.
To normalize intestinal function, the following drugs are prescribed:

- anti-inflammatory (Salphasalosin and Diclofenac), which reduce mucus secretion in different parts of the intestine;
- adsorbent (De-Nol, Smecta, Enterosgel), reducing gas formation, bloating and removing harmful bacteria from the body;
- reducing intestinal motility (Loperamide, Octreotide, Imodium);
- enzyme-containing (Festal, Creon, Mezim).
Remedies for viral diarrhea
Digestive disorders of viral etiology require the timely initiation of drug therapy, the purpose of which should be to eliminate its viral component. Timely and high-quality treatment reduces the duration of the disease several times.
The basis of therapy is a set of measures:
- Restoring the disturbed balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. For this, the following drugs are used: Oralit, Regidron or a self-prepared glucose-salt mixture.
- Carrying out infusion therapy (in the presence of severe dehydration) using physiological and colloidal solutions.
- Increasing the optimal level of enzymes (Panzinorm, Mezim, Pancreatin).
- Restoration of disturbed microflora in the intestines (Hilak forte, Laktovit, Lactobacterin).
- Use of antibacterial drugs (in severe cases in the presence of complications in the form of a bacterial infection) - Alpha Normix, Enterofuril.
Medicines for functional diarrhea
More often, the functional type of diarrhea does not require drug intervention and goes away on its own within 2-3 days. It is enough to eliminate the factors that caused the digestive disorder (for example, a stressful situation).
If diarrhea does not go away for more than 3 days, you should consult a physician, who will refer you to specialized specialists (gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist) and prescribe special studies to identify the causes of the disorder (coprogram, bacterial culture of stool, blood test).

To treat a true functional disorder, use:
- sedatives (Valoserdin, motherwort tincture);
- antidiarrheal drugs (Imodium, Loperamide);
- eubiotics to improve microflora in the intestines (Linex, Baktisubtil, Bifiform);
- sorbents (Smecta, Polyphepan, Tannkacomp);
- special diet.
Approved drugs during pregnancy
Diarrhea, treatment at home in adults for which differs from therapy during pregnancy, requires careful attention when choosing medications for a woman. Intestinal dysfunction at this time cannot be treated with conventional medications.
Without consulting a specialist, a woman can only take adsorbents (Polifepan, Smecta, Enterosgel). The main thing is to take a break between taking these medications and vitamins. for pregnant women within 2-3 hours. It is equally important, in case of severe diarrhea, to promptly start using rehydrating compounds that replenish the disturbed water-salt balance (Regidron, Trisol).

Women during pregnancy can get rid of functional intestinal disorders by taking valerian or motherwort in a therapeutic dose.
In the 3rd trimester after 30 weeks, the use of drugs with the active ingredient - loperamide (Imodium, Diara), as well as antibiotics with nifuroxazide (Enterofuril) is allowed. But only after consultation with a specialist. After therapy, it is important to restore the disturbed microflora by taking probiotics (Linex, Bactisubtil).
Treatment at home in adults using traditional methods
Traditional medicine contains many effective recipes to get rid of diarrhea without resorting to the use of medications.
The most popular methods are:
- Unripe walnuts, in the amount of 20 pieces, without peeling, are cut into pieces and poured with 0.5 liters of vodka. After 2 weeks, this tincture is poured into a dark glass container and taken 1 tbsp. three times a day.
- Crushed walnut partitions are poured into a glass of 70% alcohol and after a week of infusion, take 7 drops 3 times a day.
- Strongly brewed black tea is drunk chilled throughout the day.
- Films from chicken stomachs are dried, crushed and taken 1 tbsp. l. with boiled water twice a day.
Oak bark
The beneficial properties inherent in oak bark allow you to quickly get rid of diarrhea, both mild and severe.
Effective recipes:
- Infusion, for the preparation of which 1 tsp. bark is poured with 2 glasses of water and left for 9 hours. You need to drink this mixture within 24 hours.
- Tincture: prepared by filling a 400 ml container with water and 1 tsp. oak bark. It is stored cool, in a dark glass bottle and taken 2 times a day, 15-20 drops.
- Decoction, prepared from half a glass of raw materials mixed with a glass of water. This composition is boiled for half an hour and taken 3 times a day, 2 tbsp. l.

It is important to follow the dosage so as not to cause harm to health.
Pomegranate peel
Pomegranate peel contains a large amount of tannins and antioxidants, which have a beneficial effect on the intestinal mucosa, restoring it and stopping diarrhea.
The decoction is prepared as follows:
- wash the peel;
- remove any remaining white pulp from the inside;
- dry;
- grind to a powder;
- 1 tsp mix the powder with a glass of boiling water;
- boil for a quarter of an hour;
- cool and strain;
- use 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
Congee
If diarrhea goes away without fever, rice decoction can be highly effective.
Prepare it this way:
- rinse a glass of rice in water;
- pour into a container, add 7 glasses of water;
- bring to a boil;
- cook for 40 minutes, covered;
- strain through cheesecloth;
- take 100-150 ml every 3 hours.
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- obesity;
- colitis;
- impurities of mucus and blood in the stool;
- intestinal infections.
Iodine
To get rid of indigestion, it is not pure medical iodine that is used, but its blue variety. The use of traditional iodine can disrupt the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and thyroid gland.
To prepare blue iodine you need:
- dissolve 20 g of starch in 100 ml of cooled boiling water (based on distilled water);
- add 5 g sugar and 1 g citric acid;
- stir until completely dissolved;
- boil 300 ml of boiling water separately;
- add sugar mixture and cook, stirring, 5 minutes;
- cool;
- add 1 tsp. iodine;
- stir until smooth;
- drink 4 times a day, 1 tsp.

This solution should be very thick with a uniform blue tint.
Peppercorns
Black pepper has special properties that make it easy to improve the digestive process. They help cleanse the gastrointestinal tract of toxins and remove them from the body.
Eating peas allows you to synthesize hydrochloric acid, which improves food digestion and the production of special enzymes.
To obtain the desired effect, peppercorns should be swallowed whole before bedtime and washed down with a small amount of water. A single dose is 10 peas; exceeding it can cause intestinal irritation.
Dietary food for diarrhea: basic rules, allowed, prohibited foods
Nutrition has the most direct influence on the process of bowel movements. Some foods (for example, fruits, vegetables and spices) can speed up intestinal motility and cause diarrhea.
In case of digestive disorders, you should eat foods that have fixing properties:
- wheat crackers;
- vegetable puree;
- porridge of liquid consistency;
- meat, fish, steamed or boiled, with a minimum amount of fat;
- blueberry jelly;
- bird cherry decoction;
- rice broth;
- strong tea.
 Diarrhea. Treatment at home can be reduced to the use of products that have a bonding effect.
Diarrhea. Treatment at home can be reduced to the use of products that have a bonding effect. It is important to start a diet from the day of a complete fast, during which you are allowed to drink only strong tea with a sufficient amount of sugar. Then gradually include food in the diet, but in fractional portions, no more than once every 3 hours.
Principles of dietary nutrition:
- exclusion of foods that can irritate the intestines mechanically or chemically (spicy, salty, sour, containing coarse fiber);
- a ban on foods that promote the release of bile (tomatoes, carrots and grape juice);
- avoiding foods that can cause fermentation and increase the formation of gases (cabbage, apples, brown bread).
The following products are prohibited:
- grilled meat;
- offal in any form;
- fatty broths;
- canned fish;
- whole milk;
- cream;
- fatty fish, cooked in any form;
- boiled eggs;
- beets, cucumbers;
- canned vegetables;
- fruits and berries with sour taste;
- flour products;
- cold drink;
- highly carbonated water.
- steam cutlets;
- meat puree;
- boiled fish;
- porridge cooked in water;
- pasta;
- fermented milk products;
- cottage cheese;
- soft-boiled eggs;
- boiled vegetables;
- fruits baked in the oven;
- compotes and tea;
- white bread crackers;
- berry mousses.
Consequences of long-term stool disorder
The most dangerous consequence of prolonged loose stools is dehydration. Moreover, the loss of just a quarter of the amount of water available in the body can be fatal for a person. Very often, dehydration develops after infection with salmonella and cholera.

The risks of dehydration are especially high when:
- frequent stool;
- nausea and vomiting;
- difficulties with fluid intake by a person.
In this case, there is a high risk of blood clots, impaired blood microcirculation and blood contamination with toxins. In such a situation, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
Characteristic signs of dehydration are:
- infrequent urination with a small amount of urine;
- overwork and weakness;
- wrinkling of the skin;
- sunken cheeks and eyes;
- low blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- emaciation;
- thirst.
To prevent dehydration of the body, it is important to promptly replace lost fluid using special dehydration solutions.
For this purpose use:
- strong tea with the addition of fresh lemon;
- blueberry broth;
- tea with rosehip;
- unconcentrated broth;
- jelly;
- still water;
- Regidron and Gastrolit.
Prevention
It is much easier to prevent the occurrence of digestive disorders than to deal with them and their consequences.
Prevention of diarrhea includes:
- maintaining basic hygiene;
- mandatory washing of vegetables and fruits before eating;
- carrying out heat treatment of all products of animal origin;
- use of prescription medications prescribed by a doctor;
- consumption of products in compliance with expiration dates;
- drinking water that has been boiled.

Diarrhea (treatment at home in an adult can be carried out if it is one-time in nature), which has not gone away after 3 days, is a reason to contact a specialist.
Doctors' advice: how to quickly get rid of stool disorder
To quickly get rid of intestinal upset, it is important to follow the following recommendations from specialists:
- Do not allow yourself to overeat, especially fatty foods.
- Do not abuse alcohol.
- Be sure to drink about 2 liters of water a day, but fractionally, in small portions.
- Consume yoghurt (with normal expiration date).
- To soothe the intestines, brew ginger tea and peppermint, and drink chamomile tea with a few drops of lemon juice.
- To get rid of unpleasant symptoms, place a warm heating pad on the abdominal area.
To quickly get rid of diarrhea at home in adults, it is important to undergo a course of therapy to treat the underlying disease, which was the impetus for the intestinal disorder.
Article format: Lozinsky Oleg
Video about treating diarrhea at home
5 ways to get rid of diarrhea at home:
With diarrhea in adults or children, there is a frequent urge to defecate, which is accompanied by liquid stool. This condition is not considered a disease - it is just a symptom of the underlying pathology, which must be identified for treatment to be effective.
Causes
Both diseases and violations of various rules can provoke diarrhea; it is worth considering the main ones:
- After taking antibiotics, antibacterial agents, acting on pathogenic microorganisms, lead to disruption of the intestinal microflora, as a result it reacts with frequent loose stools.
- After eating - can be caused by low-quality, expired products, poorly washed, etc.
- After alcohol, if ethanol regularly enters the body, then over time a person experiences the following gastric changes: the gastric mucosa is damaged, small blood capillaries are destroyed, and food products that enter the digestive system are poorly broken down. The result is an upset stomach and frequent diarrhea.
- Women's problems - against the background of hormonal disorders, for example during pregnancy, approaching menstruation, or menopause, women can often experience diarrhea.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract - chronic diarrhea accompanies all gastric pathologies, including pancreatitis. This condition should not be left to chance; long-term and serious treatment will be required, which, first of all, involves a diet.
- After poisoning - poisoning can be food and drugs, the first thing to do is rinse the stomach.
- Milk – diarrhea from milk can occur due to individual intolerance to the product, as a result of allergic reactions, gastrointestinal diseases. In old age, the human stomach does not digest lactose well or at all.
- Due to nervousness - against the background of excitement, fear, anxiety, hormones are released that weaken the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, diarrhea develops.
The causes of diarrhea are many diseases that develop in the gastrointestinal tract, liver, pancreas, blood vessels, associated with oncology, inflammation or hormonal disorders.
Symptoms
Diarrhea can be accompanied by various symptoms. Everything will depend on the reason that caused it. Diarrhea accompanied by elevated body temperature often present in pregnant women. This can also happen with inflammation of the appendix, pancreas or liver. Fever accompanies diarrhea during infectious diseases, taking antibiotics, poisoning, and taking hormonal medications.
The accompanying symptoms will determine where to administer therapy. For mild cases of the disease, treatment is carried out at home. But if diarrhea is accompanied by the following symptoms, the patient is admitted to a hospital:
- acute abdominal pain;
- temperature;
- Strong smell;
- green or brown stool with blood in it;
- presence of mucus;
- watery stools;
- feces in large quantities.
All these indicators indicate a severe course of the disease and require immediate medical intervention. Otherwise, dehydration will occur and irreversible pathological consequences will occur.
First aid
Start treatment as early as possible. In order to prevent dehydration of the body, especially in the presence of elevated temperature, after each trip to the toilet, the body must be replenished with fluid reserves. For this purpose, a glucose-saline solution is used, which is sold in every pharmacy, its name is Regidron (Citroglucosolan is used less often). They replenish the loss of fluid, electrolytes and other nutrients.
The drug is diluted according to the instructions and taken in small portions, even if diarrhea is accompanied by vomiting. Regidron should be taken in small sips of 150-300 ml. And so on up to 2 liters of solution per hour.
Another important point in the treatment of diarrhea is fasting for 24 hours. It can be shortened in time if the intestinal upset is not so severe. After digestion is restored, a strict diet is indicated for 15-30 days.
Folk remedies
To eliminate signs of intestinal disorder, traditional medicine offers its own recipes that help with mild manifestations, or act as an auxiliary treatment for various poisonings.
- Lemon. Lemon juice mixed with a little water reduces the symptoms of intestinal upset and also prevents the development of the gag reflex.
- Oak bark. This recipe has been used since ancient times, it is capable of... The product is prepared as follows: 1 teaspoon of dry raw materials is poured with a glass of boiling water. The liquid is infused for 24 hours, after which it is taken three times a day, half a glass.
- Rice congee. The most popular and effective remedy for diarrhea. It envelops the gastric mucosa, creating a protective barrier against the negative effects of harmful substances. The product has an astringent effect, retains fluid in the body, limiting its release along with feces.
- The product is prepared like this: Take 2 tbsp. rice per half liter of water. Cook until cooked, after which the liquid is filtered through a sieve. The resulting decoction is drunk. For the next portion, the rice is pre-soaked in cold boiled water, which helps it cook quickly. The next day you are allowed to eat some rice from the broth.
- Starch. The product quickly eliminates the symptoms of mild diarrhea. A teaspoon is diluted in a glass of boiled and cooled water and immediately drunk. Usually a person immediately feels significant relief.
- Onion. For treatment, it is not the vegetable itself that is used, but its husk. A liter of water is poured into a handful of onion peels. The product is placed on the fire and after boiling it simmers for another 7 minutes. After removing from the heat, the product sits for 30 minutes, during which time it cools completely, after which it needs to be strained. You need to drink 500 ml of this decoction per day.
- Pomegranate peel. The pomegranate peel is pre-dried and ground. After this, for the recipe, take 1 teaspoon of powder and add a glass of water. The product is prepared in a water bath for 20 minutes, then infused for 40 minutes. Take 2 tbsp before meals.
- Tea brewing. It doesn’t matter what kind of tea it is – green or black, the main thing is that it is of good quality. The tea is brewed strong and drunk throughout the day until loose stools completely disappear. It is also recommended to chew tea leaves.
- Chicken stomachs. In the treatment of diarrhea, the inner layer lining the stomach of a chicken is used. It needs to be separated, washed well and dried. After which it is ground into powder. For an adult, you will need one chicken gizzard powder per dose. It is poured onto the tongue and washed down with water.
Diarrhea(popular name - diarrhea) - a painful condition of the human body, accompanied by frequent loose (watery) stools and, in most cases, pain in the abdomen, high fever and vomiting.
Diarrhea (diarrhea)- a symptom that causes, and is therefore quite dangerous for children and the elderly, which, if not given proper attention, can lead to serious consequences, even death.
According to statistics for 2009, more than 1.5 million children (under 5 years of age) died from diarrhea in third world countries.
Types of diarrhea
Medicine distinguishes between two types of diarrhea (diarrhea) - acute and chronic, the symptoms of which are generally similar. The main difference is the duration and other accompanying symptoms.
Acute diarrhea
The duration is usually short, 1 – 14 days. The causes of loose stools in acute diarrhea can be: allergic reactions to medications, food poisoning, as well as various infections (viruses, bacteria).
Chronic diarrhea
Chronic diarrhea (diarrhea) is persistent, prolonged diarrhea (diarrhea) with possible periods of remission. Chronic diarrhea (diarrhea) can lead to weakening and dehydration of the body, and can also be a symptom of a hidden disease, so you should definitely see a doctor to prescribe treatment for an intestinal disorder.
Possible causes of chronic diarrhea (diarrhea) as an intestinal disease: ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, IBS (irritable bowel syndrome), drug therapy, endocrine diseases, etc.

Symptoms accompanying diarrhea (diarrhea) are as follows:
- feces with blood;
See a doctor immediately if:
- diarrhea continues in a child for more than 2 days, in an adult for more than 5 days;
- high body temperature;
- stool that is dark, bloody, or contains mucus;
- there is severe and prolonged abdominal pain (more than 2 hours);
- nausea and vomiting appeared;
- diarrhea began after a trip to Africa, Asia and other exotic parts of the planet;
- signs of dehydration appeared.
You should immediately consult a doctor if any of the above symptoms occur in infants or the elderly.

Causes of acute diarrhea:
Causes of chronic diarrhea:


In most cases, diarrhea goes away on its own within 2 days. The main thing these days is to stick to a diet and also prevent dehydration. That is why experts prescribe patients plenty of fluids and other means to prevent the body from losing the necessary amount of fluid for its normal functioning.
If diarrhea does not go away within 2 days in a child or 5 days in an adult, consult a doctor who, based on the examination, can prescribe medications and, if necessary, refer you to the hospital for tests and treatment.
Basically, treatment of diarrhea includes the following set of measures:
— diet;
— maintaining the body’s water balance;
- drug treatment at home;
- treatment in a hospital (if the doctor has concerns or diarrhea does not go away for a long time).

Diet for diarrhea
What to eat for diarrhea? We have selected some useful recommendations:
— For diarrhea, it is necessary to drink plenty of liquid (water, still mineral water, broth), preferably warm or at room temperature.
— If you have no appetite and feel cramps in the abdomen, then it is better to refrain from eating;
— Eat food in small doses;
- If an infant has diarrhea, continue to breastfeed him, but if he is bottle-fed. When bottle feeding, replace cow's milk with clean water.
If you have diarrhea, you should avoid the following foods:
- fatty and fried foods;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- milk and fermented milk products (yogurt, fermented baked milk);
- fruit juices (except apple);
- grapes, plums and most other fresh fruits;
- legumes, beets, radishes, radishes, cucumbers and other green vegetables;
- sweets;
- sauces, ketchups, mayonnaise and spices;
- black bread
What to eat for diarrhea:
- boiled rice, oatmeal and other grains;
- white bread crackers;
- potatoes and other boiled or baked vegetables;
- lean meat, can be in the form of cutlets or meatballs, but always steamed or boiled;
- applesauce;
- bananas.
Medicines for diarrhea
It is better to take medications after seeing a doctor. If there is still such a need, then you can take them, but strictly follow the instructions for use and remember that if over-the-counter antidiarrheal drugs are taken for a long time, diarrhea can become chronic and provoke more serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Antidiarrheal group:“Enterol”, “Eubikor”, “Mezim Forte”, “Smecta”, “Enterosgel”, “Imodium”, “Hilak Forte”, “Loperamide Akri”, “Panzinorm Forte”, “Lopedium”, “”, “Polysorb MP ", "Linex", "Polyphepan", "Diosmectite", "Coapectate", "Enterosorb".
To prevent dehydration:"Regidron", "Hydrovit".
Intestinal antiseptics: Nifuroxazide (Enterofuril, Ersefuril, Stopdiar), Rifaximin (Alfa Normix), Intetrix.
For infectious diarrhea:"Galavit."
Diarrhea due to colitis is treated with drugs that relieve inflammation.
Attention! Products containing salicylate may temporarily darken the tongue or stool.
Antibiotics for diarrhea
Antibiotics for diarrhea are prescribed only by a doctor, and only after diagnosing the body and identifying the “infectious” cause of diarrhea.
Prevention of diarrhea
To prevent diarrhea, the following rules must be followed:
- always wash your hands, especially after going outside, using the toilet, contacting money, before eating, before contact with food for cooking. Hands should be washed with warm water and soap.
— before consumption, fruits and vegetables must be thoroughly washed;
- diarrhea and other gastrointestinal problems can be caused by: unpasteurized dairy products, meat, eggs;
- do not eat food that has expired;
— meat must undergo complete heat treatment before being eaten;
- in the kitchen, including places and objects for preparing food, must be clean (tables, knives, boards, plates, etc.);
- do not leave cooked foods in a warm place for a long time, because... This is an excellent environment for the proliferation of bacteria harmful to the body.
- Try not to drink raw water or any untreated water, especially of unknown origin. To purify water, boil it for 15 minutes and then consume. You can also purify water using special filters, as well as by adding a tablet or drop of iodine and chlorine to it.
- do not eat fruits or vegetables that have not yet reached the ripening season, for example: strawberries, melon, watermelon. Often, unscrupulous producers inject such berries and fruits with “chemicals”, which provokes their rapid ripening and, of course, frequent poisoning of their customers.