How to cure ovaries at home. Inflammation of the ovaries in women: signs and treatment at home How to cure inflammatory
Positive results in the treatment of adnexitis (salpingoophoritis, inflammation of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, appendages) can be achieved by allopathic methods in combination with the use of the experience of traditional medicine, which has proven recipes for how to treat inflammation of the ovaries in women (appendages) at home so that the disease goes away without a trace.
Herbs can heal: relieve pain, inflammation and muscle spasms, destroy microbes, stimulate local and general immune defense. Plants serve as raw materials for preparing water-based decoctions (tinctures) or alcohol-based tinctures.
Rules for preparation and treatment with herbal solutions
 To prepare medicinal solutions, utensils made of glass, porcelain, clay or enameled metal are used. It is advisable to purchase herbs at a pharmacy, and not at spontaneous markets.
To prepare medicinal solutions, utensils made of glass, porcelain, clay or enameled metal are used. It is advisable to purchase herbs at a pharmacy, and not at spontaneous markets.
The medicinal raw material is poured with boiling water, then the decoction/infusion must be infused for 2 hours in a warm place or kept in a water bath for 20-30 minutes to draw out the extractive substances from the plant and make the drink rich. Then it is filtered and used.
The shelf life of water-based medicines in the refrigerator is no more than 2 days, but it is preferable to prepare them immediately before use. Alcohol tinctures retain their properties in a cool place protected from light for up to six months.
You cannot heat prepared solutions in the microwave. If the recipe states “take warm,” then the solution should be diluted with boiling water to the desired temperature.
The dosage for internal use should not exceed the recommended one: increasing the dose does not speed up the healing process, but leads to poisoning.
The course of herbal treatment lasts at least 4 weeks; complete recovery may require six months or more.
 Herbal treatment is carried out against the background of a gentle diet (it is necessary to exclude fatty, smoked, spicy foods, alcohol and sweets) and abstinence from sexual intercourse.
Herbal treatment is carried out against the background of a gentle diet (it is necessary to exclude fatty, smoked, spicy foods, alcohol and sweets) and abstinence from sexual intercourse.
During the treatment process, short breaks should be taken: a month of treatment, then a 5-7 day break.
For longer breaks, the course has to be started again.
It is advisable to change herbs from month to month, selecting ones that are similar in action, in order to prevent the body from becoming addicted.
A general contraindication for the use of herbal infusions is an acute period of illness and a partial allergic reaction to a medicinal plant.
Recipes

- Hog queen(ramishia one-sided, orthinia one-sided). It is used for many diseases of the reproductive system; each of them has its own dosage regimen, which is prescribed by the doctor. Basic recipe: 2 tablespoons of raw materials per half liter of water. Take a quarter glass 4 times a day before meals. Contraindicated in acute gastritis, decreased blood clotting, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, taking hormonal drugs and contraceptives, pregnancy and breastfeeding. Take a break on the days when your period expires.
- Wintergreen round-leaved. 8 teaspoons of raw materials per 1 liter of boiling water. Take 3 times a day, a quarter glass. Should not be used if you are prone to blood clots, high blood pressure, or varicose veins.
- White acacia. 8 teaspoons of raw material per 1 glass of water. Drink as tea 4-6 times a day. Should not be used for gastritis with reduced secretion.
- St. John's wort. Pour 1 tablespoon of raw material into 1 glass of boiling water and simmer for 15-20 minutes in a water bath. Take a quarter glass 3 times a day. Should not be used if you have high blood pressure or pregnancy. Significantly weakens the effect of contraceptives, cardiac and antibacterial drugs.
- Mixture No. 1 from yellow sweet clover flowers, centaury grass and coltsfoot flowers, mixed in equal parts. 5 tablespoons of the mixture per 1 liter of boiling water. Take a third of a glass 4-6 times a day. The mixture should not be used if there is reduced blood clotting, a tendency to bleeding, pregnancy and breastfeeding, gastritis with increased secretion, stomach and duodenal ulcers, liver diseases.
- Mixture No. 2 from knotweed, cinquefoil, horsetail and centaury, mixed in equal parts. 1 tablespoon per 1 glass of water. After straining, add boiled water to 250 ml and take a quarter glass 4 times a day. The mixture should not be used if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, if you are prone to thrombosis, urolithiasis, unstable hypertension, atonic constipation, or diseases of the stomach and intestines.
There are many options for medicinal preparations. The same recipe for the same disease affects different people in completely different ways. Therefore, you should look for the plant that is right for you.
Dry heating
The dry heating method is used only for the chronic course of the disease, in the stage of subsiding of acute manifestations.
Local thermal effects increase blood flow and lymph movement in the diseased organ, help eliminate microbial waste products, suppress their growth, eliminate swelling and congestive inflammation.
It is prohibited to use dry heating in case of any acute inflammatory processes in the body, elevated body temperature, threat of appendicitis or internal bleeding, during menstruation.
Paraffin applications
You can buy paraffin for applications at the pharmacy; it can be used several times; you will need approximately 250-350 g. Melt the substance in a water bath, heating to approximately 70 ВВ°С, then pour it into a container covered with film in a layer 2.5-3 cm thick. After After 15 minutes, remove the paraffin in the film and wrap it in cotton cloth and apply it to the stomach. Keep the application until the paraffin cake cools.
To enhance the effect of dry heating, before poultice or application, a paste of fresh wormwood minced in a meat grinder is applied to the projection of the ovaries, covered with a film, and a source of dry heat is placed on it, which can also be a regular or electric heating pad.
Read what symptoms you can use to identify ovarian inflammation.
Dry salt poultices
 It is better to take sea salt or table salt, coarsely ground and without additives; you will need 2.5-3 kg of it.
It is better to take sea salt or table salt, coarsely ground and without additives; you will need 2.5-3 kg of it.
Prepare two canvas bags, pour salt heated to approximately 70 ° C into one, and lightly moistened hops into the other in a layer of 2-3 cm.
Lie on a sack of salt with your stomach down, placing a bag of hops on your lower back directly opposite it, pressing it down and wrapping yourself in a blanket. The duration of the procedure is 1.5-2 hours. The course is 7 days, then a pause for 3 days, then repeat the course.
Ointment and tampons
You can use medicinal ointments, oils and thick herbal decoctions intravaginally.
 When mixing ointments, all ingredients must be at the same temperature.
When mixing ointments, all ingredients must be at the same temperature.
They should be rubbed thoroughly, until smooth, with a wooden or glass spatula, in one direction, so that the ointment does not separate.
Then the ointment is applied to a gauze swab and inserted into the vagina as deeply as possible.
Do the procedure at night. Course 10-14 days.
To administer the medicine into the vagina, use tampons: twist a cylinder from cotton wool and a bandage like a hygienic tampon, leaving a tail of 8-10 cm at one end.
There is an alternative option for administering the ointment: take the ointment into a two-gram syringe, insert it into the vagina without a needle (!) and smoothly squeeze the contents inside, and then insert a tampon. Take a new syringe for each procedure. This method helps with very dirty ointments.
It is forbidden to use ointment tampons if you have an individual intolerance to the ingredients and menstruation.
During treatment, sexual contact must be excluded. If local disturbing sensations appear, treatment with this drug should be discontinued.
Recipes

- Ointment with iodine. Mix one tablespoon each of glycerin and ichthyol ointment, one teaspoon each of camphor oil and iodine.
- Ointment with propolis. Mix lanolin 50 g, petroleum jelly 40 g, propolis tincture 5 ml.
- Mix honey and aloe equally and soak the tampon. Course 15-21 days.
- Healing oil. Sea buckthorn oil, propolis and honey in equal parts should be thoroughly ground.
Douching
They involve irrigation and washing of the vagina with medicinal herbal solutions - decoctions and infusions, which are prepared immediately before use. The solution should be at body temperature, about 35-37 ВВ°С.
 The technology for preparing infusions for douching is similar to the recipe for preparing them for internal use.
The technology for preparing infusions for douching is similar to the recipe for preparing them for internal use.
The difference is in concentration: for ablutions, take 1 tablespoon of raw material (herbs or a mixture of herbs) per 1 glass of water.
The procedure is performed using a syringe (rubber bulb). Before carrying out the manipulation, the syringe is treated in boiling water.
You should lie in the bathtub on your back, with your feet on its edges. Insert the bulb cannula into the vagina and slowly, smoothly squeeze out the medicine. Remove the cannula and lie down, relaxing, for 5-7 minutes.
In the first three days, the procedure is repeated approximately 12 hours later: in the morning and before bedtime. In subsequent days only at night. The course of treatment is 7-21 days.
It is prohibited to douche in the acute period of illness, during pregnancy, in the postpartum period for 8 weeks, after an abortion for 2 weeks, during menstruation, for women over 45 years of age.
Recipes

- Herbs. Upland uterus, white acacia, chamomile, calendula, celandine, sage - each herb is used individually and in multicomponent collections.
- Collection No. 1. Chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula in equal parts.
- Collection No. 2. Yarrow, sage, rosemary 1 part each and oak bark - 2 parts.
Dry heating performed 1.5-2 hours after douching enhances the effect of intravaginal irrigation.
Pharmacy products
Drug treatment of inflammation of the appendages includes several groups of drugs. Everything is prescribed by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the severity of the disease.
 Candles. The group is represented by suppositories with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects: Voltaren, Movalis, Indomethacin, Diclofenac, suppositories with belladonna.
Candles. The group is represented by suppositories with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects: Voltaren, Movalis, Indomethacin, Diclofenac, suppositories with belladonna.
The following have an antibacterial effect: Polygynax, Hexicon, Metronidazole, Cefibuten, Zomax, Cedex.
Douching with the use of pharmaceutical drugs also require the preparation of a solution. It should be borne in mind that they will not be subjected to heat treatment, so the preparations must be diluted with clean boiled water.
Use 3 percent hydrogen peroxide (1 tablespoon per half liter of water), 1 percent chlorophyllipt tincture (half a tablespoon per half liter of water), calendula tincture.
Ointments. Levomekol, which has activity against bacteria and inflammation, is used for treatment from pharmaceutical ointments. Vishnevsky's ointment has proven itself well.
Prevention
A primary role in the prevention of inflammation of the appendages is played by the prevention of primary and secondary infections of the genital tract. This is achieved subject to the following conditions:
- maintain proper intimate hygiene, teach girls from childhood to take care of the organs of their reproductive system;
- do not use other people's personal items;
- change underwear and pads in a timely manner, and refuse to use sanitary tampons;
- show disgust towards casual sexual relationships, use barrier contraceptives;
- sanitize foci of dormant infection (carious teeth, tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- do not get cold in your legs and pelvic organs: do not sit on stone, metal, or earth; wear loose, non-squeezing clothing made from natural fabrics.
The principles of a healthy lifestyle - a balanced diet, physical activity, an optimal work and rest regime, giving up bad habits, increasing the body's immune forces - have acquired great importance in the prevention of adnexitis and its relapses in the chronic course of the disease.
Video on the topic
When considering ways to cure ovarian inflammation at home, you should remember that only therapy that was started on time can provide the desired result. In alternative medicine, there are many ways to eliminate the inflammatory process that develops in the ovaries, so you should select the appropriate recipe and not delay the start of treatment.
Phytotherapy
Treatment of ovarian inflammation at home can be carried out using the beneficial properties of medicinal plants. An infusion made from blueberry leaves will help with this. Young leaves must be washed well under running water and chopped. To prepare the product, pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water. The medicine should sit for half an hour in a closed container, after which you need to strain it.
Note! This infusion is only suitable for douching.
Many people treat the symptoms of this disease with the help of linden infusion. During the flowering period of linden, you need to collect its inflorescences and rinse well under running water. Take a few tablespoons of raw materials (2-3), pour in 0.5 liters of boiling water, cover the container with a lid and leave for at least half an hour, then strain. The resulting medicine should be drunk 3 times a day, half a glass.
Note! You can also prepare a douching solution from small-leaved linden inflorescences by brewing 5 tbsp. l. in 2 glasses of boiling water. You need to leave it for at least 3 hours, tightly wrapping the container with a warm scarf or towel.

Chamomile is widely used for inflammation of the ovaries. By combining it with lemon balm, you can prepare an effective remedy that helps get rid of the disease in a short time. Dry ingredients need to be taken in equal quantities, mixed, pour a tablespoon of herbs with a glass of boiling water. The infusion should stand in a closed container for at least 4 hours, after which you can strain it and take it orally 3 times a day before meals, a glass.

When considering how to treat ovarian inflammation at home, you need to pay attention to rosehip decoction. To prepare, you need to cut several young branches of the plant, wash them, chop them, and add water. Calculating the proportions in this recipe is simple - for 200 ml of liquid you will need 2 tbsp. l. chopped rosehip branches. Place the container on the fire, bring everything to a boil, boil for 15 minutes, turn off the heat and leave in a closed container for another half hour, then filter. For treatment of oophoritis with a folk remedy to be successful, it should be taken 3 times a day, half a glass, pre-heated in a steam bath.
Advice. You can store the prepared rosehip decoction in the refrigerator for 2-3 days.
In order to cure inflammation of the ovaries with folk remedies, you can also use rose hips, adding a little healthy black currant to them. You will need to take the components in equal proportions. For one serving of the medicine, you need to pour 20 g of berries with a glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour under the lid, then filter. Add sugar to the resulting drink to taste, or better yet, honey. You need to take 1 glass 4 times a day.

A drink made from acacia flowers is very effective. This remedy is perfect for restoring a woman’s reproductive health. For the product 1 tsp. dried acacia flowers should be poured with a glass of boiling water, leave for 30-40 minutes, strain, drink instead of the usual tea, adding honey to taste.
Healing ointment
Treatment of symptoms of ovarian inflammation at home can be carried out with healing ointments. To prepare you need to take:
- Glycerin - 1 tbsp. l.
- Ichthyol ointment - 1 tbsp. l.
- Camphor oil.
First you need to mix glycerin and ichthyol ointment, then add 4-5 drops of iodine and a little camphor oil, mix everything thoroughly. The finished consistency should not be very thick. Thoroughly soak the tampon with the resulting medicine, insert it into the vagina before bed and leave it overnight.
Advice. To obtain the maximum therapeutic effect, a tampon soaked in ointment must be inserted deep into the vagina.

Douching using onions
There is another simple method of therapy. For this you will need regular onions. Pour 1 liter of clean water into a saucepan, put a medium-sized peeled onion in it, cook everything under a closed lid for 1 hour over low heat. After an hour, turn off the heat, let the broth brew and cool, strain and use for douching before bed.

Note! Treatment lasts until complete recovery. You can douche not only before going to bed, but also immediately after waking up.
When choosing a way to treat ovarian inflammation at home, it is necessary to take into account possible side effects and allergic reactions to drug components. It is necessary to strictly follow the preparation recipe and the rules for using each product.
The materials are published for informational purposes only and are not a prescription for treatment! We recommend that you consult an endocrinologist at your medical institution!
Inflammation of the ovaries requires immediate and effective treatment. The advantage of folk remedies is their natural composition and ability to have a beneficial effect on the condition of the entire body. Effective recipes allow you not only to cure ovarian inflammation at home, but also restore the full functioning of the entire reproductive system.
- Phytotherapy
- Healing ointment
When considering ways to cure ovarian inflammation at home, you should remember that only therapy that was started on time can provide the desired result. In alternative medicine, there are many ways to eliminate the inflammatory process that develops in the ovaries, so you should select the appropriate recipe and not delay the start of treatment.
Phytotherapy
Treatment of ovarian inflammation at home can be carried out using the beneficial properties of medicinal plants. An infusion made from blueberry leaves will help with this. Young leaves must be washed well under running water and chopped. To prepare the product, pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water. The medicine should sit for half an hour in a closed container, after which you need to strain it.
Note! This infusion is only suitable for douching.
It is best to douche with an infusion of blueberry leaves 2 times a day.
Many people treat the symptoms of this disease with the help of linden infusion. During the flowering period of linden, you need to collect its inflorescences and rinse well under running water. Take a few tablespoons of raw materials (2-3), pour in 0.5 liters of boiling water, cover the container with a lid and leave for at least half an hour, then strain. The resulting medicine should be drunk 3 times a day, half a glass.
Note! You can also prepare a douching solution from small-leaved linden inflorescences by brewing 5 tbsp. l. in 2 glasses of boiling water. You need to leave it for at least 3 hours, tightly wrapping the container with a warm scarf or towel.

Simultaneous douching and ingestion of linden infusion will speed up recovery
Chamomile is widely used for inflammation of the ovaries. By combining it with lemon balm, you can prepare an effective remedy that helps get rid of the disease in a short time. Dry ingredients need to be taken in equal quantities, mixed, pour a tablespoon of herbs with a glass of boiling water. The infusion should stand in a closed container for at least 4 hours, after which you can strain it and take it orally 3 times a day before meals, a glass.

Melissa and chamomile tea is best drunk hot, so the drink should be prepared in small quantities so that it is always fresh
When considering how to treat ovarian inflammation at home, you need to pay attention to rosehip decoction. To prepare, you need to cut several young branches of the plant, wash them, chop them, and add water. Calculating the proportions in this recipe is simple - for 200 ml of liquid you will need 2 tbsp. l. chopped rosehip branches. Place the container on the fire, bring everything to a boil, boil for 15 minutes, turn off the heat and leave in a closed container for another half hour, then filter. For treatment of oophoritis with a folk remedy to be successful, it should be taken 3 times a day, half a glass, pre-heated in a steam bath.
Advice. You can store the prepared rosehip decoction in the refrigerator for 2-3 days.
In order to cure inflammation of the ovaries with folk remedies, you can also use rose hips, adding a little healthy black currant to them. You will need to take the components in equal proportions. For one serving of the medicine, you need to pour 20 g of berries with a glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour under the lid, then filter. Add sugar to the resulting drink to taste, or better yet, honey. You need to take 1 glass 4 times a day.

The combination of rose hips and black currants will saturate the body with beneficial vitamins and help reduce the inflammatory process in the ovaries
A drink made from acacia flowers is very effective. This remedy is perfect for restoring a woman’s reproductive health. For the product 1 tsp. dried acacia flowers should be poured with a glass of boiling water, leave for 30-40 minutes, strain, drink instead of the usual tea, adding honey to taste.

You can drink a drink made from acacia flowers throughout the entire course of treatment; it will complement other remedies and speed up the healing process.
Healing ointment
Treatment of symptoms of ovarian inflammation at home can be carried out with healing ointments. To prepare you need to take:
- Glycerin - 1 tbsp. l.
- Ichthyol ointment - 1 tbsp. l.
- Camphor oil.
First you need to mix glycerin and ichthyol ointment, then add 4-5 drops of iodine and a little camphor oil, mix everything thoroughly. The finished consistency should not be very thick. Thoroughly soak the tampon with the resulting medicine, insert it into the vagina before bed and leave it overnight.
Advice. To obtain the maximum therapeutic effect, a tampon soaked in ointment must be inserted deep into the vagina.

You need to use any folk remedy for ovarian inflammation until the symptoms of the disease disappear completely.
Douching using onions
There is another simple method of therapy. For this you will need regular onions. Pour 1 liter of clean water into a saucepan, put a medium-sized peeled onion in it, cook everything under a closed lid for 1 hour over low heat. After an hour, turn off the heat, let the broth brew and cool, strain and use for douching before bed.

After just a few douching procedures, you can feel a significant relief in your general condition.
Note! Treatment lasts until complete recovery. You can douche not only before going to bed, but also immediately after waking up.
When choosing a way to treat ovarian inflammation at home, it is necessary to take into account possible side effects and allergic reactions to drug components. It is necessary to strictly follow the preparation recipe and the rules for using each product.
pozhelezam.ru
How to treat ovarian inflammation at home
Inflammation of the ovaries is a fairly serious disease that leads to female infertility. The cause of the disease may be:
- banal hypothermia;
- stress;
- frequent abortions;
- venereal diseases.
This problem can be easily resolved if you properly treat it in natural home conditions. To prevent exacerbations, experts strongly recommend conducting a course of injections with vitreous or aloe juice every six months, calculating it for 10 days.
Herbal treatment

Among the folk remedies often used for such ailments as inflammation of the ovaries, as well as when there is pain associated with this process, the following are recommended:
- St. John's wort;
- chamomile;
- sweet clover;
- yarrow;
- oregano
The latter herb, by the way, is considered a strong natural antibiotic, which also has analgesic properties.
Chamomile helps normalize estrogen levels in the blood, as well as improve digestion. St. John's wort and sweet clover protect against uterine bleeding. Brew the herbal mixture with a glass of boiling water and you can consume it.
In a complex of herbal decoctions, additional dry heating is done. An infusion of the above-mentioned medicinal plants helps treat as follows. Take 80 g of carefully chopped herbs and pour boiling water over them in an enamel pan. Then let it simmer, remembering to stir over low heat. Afterwards, cool the composition slightly and leave for two hours. After the specified time, strain and douche in the evening. Three hours after this, perform dry heating at home.
Dry heating
In order to treat emerging inflammation of the ovaries by heating, you should heat table salt (about three kilograms) to a temperature of 70-80 degrees.
Then place it inside a canvas bag. Also take a similar bag and pour moistened hops inside (the layer thickness should be a couple of centimeters). Place the heated salt on the bed, lie on your stomach, and place the hops on your lower back, pressing it tightly.

Important: the bags must be on the same line.
Cover yourself with a blanket while performing the treatment for a couple of hours. It is advisable to treat yourself this way for a week, then take a short break. Positive dynamics are already observed after several procedures. Treatment is carried out until recovery occurs.
If there is chronic, frequently recurring inflammation of the ovaries, mud baths and potassium iodide, which should be taken orally 0.1 g three times a day, are more effective at home. For women, in addition, it is useful to completely abstain from intimacy, so as not to provoke pain and other complications.
Ointment and infusion
A fairly popular treatment for this disease is ointment. To prepare it you will need the following components:
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of pharmaceutical glycerin;
- pharmaceutical iodine;
- camphor oil;
- 1 tbsp. spoon of ichthyol ointment.
Combine all ingredients and mix thoroughly until smooth. Then make a cotton swab, soak it in the prepared ointment and insert it as deep as possible into the vagina. Carry out treatment until even very small signs of inflammation disappear.
Important: if the form is advanced, it will take at least two weeks to treat ovarian inflammation in this way.
There is nothing more effective than treating such a female problem as inflammation of the ovaries with acacia decoction. This remedy has many advantages and is used for treatment:
- erosions on the cervix;
- genitourinary system;
- many other diseases.

If you experience reproductive problems, you should definitely take a decoction of acacia orally and douche with it. The infusion is quite easy to make:
- dry acacia flowers (about a teaspoon) are poured with boiling water;
- close the container;
- leave for half an hour to infuse.
Use the liquid as a treatment all day long. It tastes very good. You can add honey to it.
Douching
To treat ovarian inflammation with douching, you need to take a tablespoon of raw material per liter of boiling water, boil for about five minutes and let it brew. Carry out the procedure in the morning and evening. Treatment should be carried out for at least two weeks. It is advisable to treat yourself in combination with internal intake of acacia decoction.
An excellent treatment is provided by using onions for douching. For a liter of water you need to take a large onion and cook it in a container under a closed lid. After the decoction, let it brew and douche.
Important: it is enough to treat ovarian inflammation with douching just a couple of times to feel an improvement.

Prevention
It is very important for every woman to carry out preventive measures in a timely manner to prevent the occurrence of problems in the intimate sphere. To do this you need:
- use high-quality contraception to avoid unwanted pregnancy;
- protect yourself from infections transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- Avoid hypothermia, extreme fatigue and stress.
If problems arise in the intimate sphere, you should contact a gynecologist.
Conclusion
Every woman is simply obliged to undergo ultrasound monitoring of the condition of her own ovaries in order to preserve her and her future offspring’s health. Periodically use medications that promote improved blood circulation and regulate hormonal levels.
uchidoma.ru
Inflammation of the appendages in women: symptoms and treatment with folk remedies
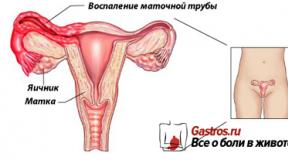
Every caring mother teaches her daughter from a very early age to take care of her women's health: dress warmly for the weather, do not sit in the cold. In adulthood, childhood neglect of health can turn into illness. This article will discuss inflammation of the appendages in women: symptoms and treatment. Doctors interpret the concept of inflammation of the appendages as inflammation of the tube, ligaments and ovarian tissue and call it adnexitis (salpingo-orophitis). Learn about the forms of the disease, symptoms and treatment methods.
Causes of adnexitis
The main cause of inflammation of the appendages are microorganisms that have entered the cavity of the pipe. An infection that is only sexually transmitted: pathogens gonococci, chlamydia, trichomanas, and E. coli provoke the female body to develop the disease, especially if a woman has a weakened immune system, she suffers from frequent fatigue and nervous strain. Often inflammation of the appendages occurs after childbirth or abortion as a complication.

Often the symptoms of adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages) are similar to signs of appendicitis; only an experienced doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis. Nagging, sharp or muted pain in the lower abdomen directly indicates that you urgently need to be examined by a gynecologist. With different forms of inflammation of the appendages, body temperature can range from normal to 39 C. How do the symptoms of inflammation of the ovaries and appendages differ at different stages of the disease?
An acute form of adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages) occurs when an infection enters the woman’s pelvic organs against the background of severe hypothermia. Often, with a diagnosis of “acute inflammation of the appendages,” inpatient treatment is recommended. During the acute form of adnexitis the following is observed:
- sharp pain on one side of the abdomen or on both sides at once, which radiates to the lower back and legs;
- high body temperature, reaching 39 C, chills, fever;
- severe sharp pain during intimate intercourse;
- copious uncharacteristic purulent discharge, sometimes foamy;
- frequent painful urination, as with cystitis;
- painful menstruation, cycle disruption.

For chronic
Untreated acute salpingo-orophitis (inflammation of the appendages) threatens to develop into a chronic one, which will often “remind” itself, especially in the off-season. Chronic inflammation of the appendages during an exacerbation is characterized by:
- frequent dull aching pain in the groin, vagina;
- severe pain before and during menstruation;
- cycle disruption;
- constant, albeit scanty, discharge;
- long-term temperature 37.0 -37.6 C;
- decreased libido, pain during intercourse;
- violation of patency in the pipes, the appearance of adhesions;
- inability to have a desired pregnancy with regular sexual activity;

With latent
Sluggish inflammation of the uterine appendages without obvious symptoms is called latent. This is the most dangerous form, since the disease can progress asymptomatically, causing only mild malaise, insomnia, and lethargy. In the absence of severe pain, women rarely seek help at the hospital. In this case, gynecology is considered even less often as a cause. Against the background of latent adnexitis (inflammation of the appendages), processes begin in the appendages, which lead to adhesions and then to complete infertility.
Diagnostic methods
When a woman contacts a gynecologist with relevant complaints, an examination should be prescribed, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made. After analyzing the nature of the complaints, the presence of concomitant colds or gynecological diseases, the doctor examines the patient. Bimanual examination simultaneously through the vagina and abdominal wall helps determine whether the uterus and appendages are enlarged. Particular attention is paid to painful points.
An ultrasound examination is prescribed to clarify the size of possible enlargements of the fallopian tubes and ovaries and confirm the presumed diagnosis of inflammation of the appendages. A photo is taken so that it is possible to track the dynamics after treatment. Ultrasound diagnostics helps to detect foci of inflammation and possible abscesses in the pelvis. Using bacteriological culture, the doctor will select the necessary antibiotics for treatment for inflammation of the appendages.

To find out about the presence of microorganisms that cause inflammation of the appendages in women: the main symptoms and treatment of which are determined by the doctor, secretions are collected from the vagina or cervical canal and sent to the laboratory. When a certain infectious group is sown in the microflora, the doctor recommends that the sexual partner also undergo a thorough examination. Full recovery cannot occur with treatment of only one partner.
How to treat inflammation of the appendages in women
Like any disease, inflammation of the appendages in women: symptoms and proper treatment should be determined by a qualified doctor. A timely diagnosis of adnexitis and correctly prescribed medications and procedures will quickly relieve the painful symptoms of inflammation of the appendages. Fully followed instructions from a gynecologist will eliminate negative consequences such as infertility and surgery.
Medications
The main treatment for inflammation of the appendages, prescribed by a gynecologist, is based on the complex use of medications. Based on their effects and method of application, they are divided into several categories. Treatment of inflammation of the appendages can be with the help of intramuscular, intravenous injections, tablets, suppositories and a course of physiotherapeutic procedures.
Antibiotics
The choice of medicine depends on which microorganism is the causative agent. The prescribed dose of an antimicrobial drug should create such a concentration at the site of inflammation that it is enough to destroy cocci and bacteria. Apply:
- "Doxycycline." Has proven itself well as an antibiotic. It has a minimum of side effects and is eliminated from the body in a short time.
- "Klacid", "Sumamed". They are not destroyed in gastric juice, they have a long half-life, due to which the concentration in the body quickly accumulates and leads to a speedy recovery.
- "Ofloxacin", "Norfloxacin", "Lomefloxacin". These antibiotics are not addictive. On the recommendation of a doctor, Ceftributen capsules, Erythromycin injections, and Tsiprolet tablets can be prescribed.
Immunomodulators
To increase the body's resistance during treatment and recovery, immunomodulatory drugs are prescribed. By having an antioxidant effect on the body, they thereby increase a woman’s immunity. Dosages and duration of use are prescribed by the doctor individually to each patient. Apply:
- "Imunofan";
- "Gropsinosin";
- "Polyoxidonium".
Antihistamines
To prevent the body from reacting in the form of an allergy to any medicine used against inflammation of the appendages, antihistamines are prescribed in parallel. Most tablets in this series are taken once a day. These include:
- "Cetrin";
- "Suprastin";
- "Pipolfen."
Local treatment: vaginal suppositories and douching
In combination with tablets and injections, vaginal and rectal suppositories, which have an anti-inflammatory effect, are necessarily prescribed. Using suppositories for inflammation of the female organs, there is rapid local anesthesia, relief of pain symptoms, and the microflora is restored. Every night, douching with decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and a weak solution of manganese before inserting the suppository has a calming effect on inflamed tissues. Use candles with:
- "Metronidazole";
- "Nystatin";
- "Hexicon";
- "Betadine";
- "Movalis";
- "Polygynax".
Physiotherapy
Using an integrated approach to treatment, the doctor prescribes electrophoresis with absorbable medications such as aloe. The use of ultrasound and laser devices to treat inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes helps the body recover faster. Treatment with mud and mineral baths at a certain temperature, according to reviews, gives a very good positive effect.
Surgical intervention
In complex advanced cases, when the disease of inflammation of the appendages progresses quickly, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. The operation is prescribed when examination reveals purulent formations in the fallopian tubes. Laparoscopy is less traumatic and has a short recovery period after surgery. If there is a large amount of pus, multiple adhesions in the abdominal cavity, or peritonitis, which can lead to death, a classic operation is prescribed by cutting the abdominal wall (laparotomy).

Treatment with folk remedies at home
Some methods have come down from our ancestors on how to treat inflammation of the appendages at home using herbal decoctions and other improvised means. These methods cannot be the main treatment; the doctor offers them as accompanying ones when the cause of the disease is identified and a diagnosis of adnexitis is made. Here are some ways:
- Yarrow. Tea will help with an acute attack of pain. Dried yarrow (1 tablespoon) pour 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 10 minutes.
- Oat infusion. 1.5 tablespoons of oats, 2 tablespoons of peppermint, 3 tablespoons of dried birch leaves, pour half a liter of boiling water. Leave for an hour. Add honey, lemon juice. Drink 80-90 ml every 3 hours.
- Honey tampon. Soak a gauze swab with honey and place it in the vagina overnight.
Possible complications and prevention of the disease
With improper or untimely treatment, infertility develops. In some advanced cases, female organs are surgically removed. To avoid this, you need to be examined by a gynecologist regularly, maintain the body’s immunity, and avoid abortions. Maintaining personal hygiene and constancy of the partner will help to avoid infection with infectious diseases.
Video: how to treat inflammation of the appendages in women
The common, but no less dangerous disease of adnexitis in women has a number of symptoms, which are discussed in the proposed video. What are the dangers of adhesions in pipes and ligaments and why do they appear? How to protect yourself from ectopic pregnancy? What is the main source of inflammation of the appendages and what should be the treatment? You will learn all this from the video.
I didn’t know what adnexitis was for many years, until one day, a sharp nagging pain literally put me to bed in broad daylight. I knew how to treat ovarian inflammation in women from books on traditional medicine - I repeatedly recommended recipes to friends and acquaintances, but I never imagined that I would have to use them myself. However, who even thinks about this?
The disease overtook me in the winter cold, when the thermometer showed minus 25°C, and traveling to work on public transport was real torture: the minibuses were bitterly cold. After traveling in such conditions for several days, I learned with horror what kind of torment it is - inflammation of the ovaries in women, the treatment of which must be started immediately (otherwise the disease may become chronic).
From the available arsenal of methods for treating inflammation of the appendages, I chose the simplest and most effective one - it cured several female employees, one even from advanced adnexitis, which had been haunting her for years. In addition to this recipe, I also publish a number of others, tested repeatedly on many people.

How to treat ovarian inflammation in women: quick home methods
First of all, I will describe the recipe that cured myself, and then the other methods. After all, each person’s body is individual, and what helps one will not necessarily be effective for another. Try, if there are no results, use another method. One of them will definitely help.
Effective ointment - a proven recipe for the treatment of adnexitis in women
For medicinal ointment you should take: 
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of pharmaceutical glycerin
- 1 tbsp. spoon of ichthyol ointment
- 1 teaspoon iodine
- 1 teaspoon of camphor oil. Total of four ingredients.
Mix all components until smooth, make a gauze swab and insert it as deep as possible. Do this until the slightest signs of inflammation completely disappear.
I needed 3 treatments to relieve the pain, but I continued treatment for at least a week. The ointment warms up the painful area well and relieves pain perfectly. In case of advanced inflammation, treatment should be carried out for 2-3 weeks, and the course should be continued during exacerbation of the disease.
Salt bath
Much has been said about the healing properties of ordinary rock salt, but I never cease to be amazed at its wide spectrum of action. Salt treats sinusitis, mastitis, urological diseases, dislocations, bruises, abscesses, bronchopulmonary diseases and inflammatory processes.
 Salt mines
Salt mines A salt bath is one of the quick ways to relieve pain before the main procedures. My grandmother told me about it: according to her, in the villages this was the only way women could escape after hard work in the fields.
So, you need to fill a basin, bathtub or large bowl with hot water, dilute salt in it (10 liters - a third of a pack), and sit in the saline solution for at least 15 minutes. Naturally, the room should be warm and draft-free. Then quickly dry yourself, put on dry underwear and immediately go to bed. Do this every evening until complete healing (until the pain disappears). This method is best used in combination with other methods of treating ovarian inflammation.
White acacia is the best healer of female ailments
There is nothing better than treating ovarian inflammation in women with acacia decoction. This method helps cure the most stubborn adnexitis and has a number of other advantages: it treats the genitourinary system, cervical erosion and many other diseases.
I want to tell all the ladies: if you have problems with the female part, drink acacia and douche with its decoction. This is a very effective remedy! Tested on myself and many women. Personally, with the help of acacia tea, I cured chronic inflammation of the bladder, but my neighbor cured inflammation of the appendages.

Infusion:
The infusion is very simple to make: pour a teaspoon of dried white acacia flowers into a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for at least 20 minutes. You need to drink this tea at least 4 times a day. The drink turns out very tasty - with a pleasant sourness and aroma. Can be consumed with honey.
Douching:
Per liter of boiling water 1 tbsp. spoon of dry raw materials, boil for 5 minutes, leave until warm. Douche every evening and in the morning. Course – 2-3 weeks. It is advisable to combine it with acacia infusion.
Recipe for treating inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis) and adnexitis in women
Grind the anise seeds into powder in a coffee grinder (you should get about 100 g) and mix with 0.5 liters of liquid honey. Should be consumed 3 times a day before meals. You can drink it with water.
How to treat ovarian inflammation in women with steam baths
There is another way, at home. To do this, you need to prepare a clean basin and an old warm blanket or blanket. Prepare a decoction of various herbs (chamomile, yarrow, rue, wormwood, etc.), pour it hot into a basin and stand over it, legs apart and covered with a blanket. You need to steam exclusively at night, and then immediately go to bed. In total, do at least 5 procedures. By the way, the site has a detailed article about its use for infants, for children and adults in the treatment of a variety of diseases.
Treatment with tincture of elecampane roots
No wonder it has such an eloquent name. I respect this medicinal herb, or rather its roots, very much, as it cures many, many diseases. So she can handle inflammation of the ovaries. The tincture is very simple to make (you can’t buy it at the pharmacy):
Pour vodka or moonshine into the dry roots in a 1:2 ratio. For example, for a glass of roots you need two glasses of “combustible mixture”)). Leave in a dark place for two weeks. It would be a good idea to shake it occasionally during this period for better penetration of the liquid into the plant tissue.
Adnexitis in women is treated as follows: soak a gauze swab with elecampane tincture, moisten the top with a mixture of aloe juice and honey and leave it overnight for at least 14 days.
 Elecampane
Elecampane There are many more different ways to treat inflammation of the appendages in women, but I wrote only those with which I was treated myself and my friends were cured. Perhaps I will decide to write those recipes that are in my piggy bank, but have not been tested by anyone around me. Let's see.
In the meantime, relax)). Let great music set you in a positive mood - everything will be fine with us))
With wishes of health, Irina Lirnetskaya
Inflammation of the female genital organs is an extensive and very common group of diseases in gynecology. It includes a whole range of pathologies that affect all parts of the female reproductive system. They are divided into inflammation of the external and internal genital organs.
Thus, the vulva, labia majora and minora, vagina and cervix are usually classified as external. And the internal ones include the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, as well as their ligaments, which are an integral part of the female reproductive system.
Most often, women of reproductive age face the problem of inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system.
Since unprotected sexual intercourse has been considered the main method of transmission for a long time, inflammation occurs mainly in the sexually active part of the female population. The average age is 20 - 40 years.
It should be noted that the risk group for inflammation is occupied by girls and women with more than 3 sexual partners, in which case the frequency of development of pathology increases several times. The most common inflammations include vaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, cervical erosion and, less commonly, adnexitis.
Inflammatory processes such as bartholinitis are quite rare. Very often, inflammation is associated with the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. Therefore, when diagnosing and the presence of pathology, one should not forget about this type of lesion. Among sexually transmitted infections, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and gonorrhea are currently leading.
Causes of inflammation of the female genital organs
As for diseases such as vaginitis, cervicitis, these are quite a lot of pathogens. These are not always specific microorganisms.
When the body's defenses decrease, opportunistic microorganisms that are normally found in the female body can also show their pathogenicity, but immune forces do not allow them to manifest their effects.
These include mainly staphylococcus, streptococcus, fungi of the genus Candida, and some viral particles. Of the pathogenic ones, gonococci and others have their negative effects.
Factors contributing to inflammation
They will depend on the form of the process:

Symptoms of the disease
They can be completely different:

Forms of the disease
Firstly, I share all inflammation of the female genital organs for the reason that contributes to its formation:
- Bacterial
- Fungal
- Viral.
These are also the stages of inflammation development:
- Acute
- Subacute
- Chronic
- Latent.
Types of inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs
Vulvitis
This is an inflammation of the outer part of the vulva. It occurs in females; girls are most susceptible to this inflammatory process.
Moreover, the frequency of this inflammation is due to the fact that the vulva has an anatomically accessible location for the penetration of an infectious factor.
Currently, several options for the development of inflammation have been identified, including infectious nonspecific causes, as well as specific inflammation and strophic lesions associated with hormonal deficiency.
Symptoms of vulvitis:

This is an inflammatory lesion of the external genital tract. Normally, they perform very important functions, aimed at producing mucus in the vaginal area, as well as lubrication to ensure full-fledged intercourse.
Let's take a closer look at this disease:
- The mechanism of infection is associated with the anatomical features of the location of the gland. This is due to the fact that the excretory duct is located in the vestibule of the vagina, so there is wide access for microorganisms to enter.
- There may be pathogens from the vaginal environment or from the surrounding space, due to the close anatomical connection with the rectum.
- In addition, in order for the pathogen to exhibit its pathogenic properties, it is necessary to act on provoking factors that contribute to a decrease in immunity, mainly local. These include shaving with someone else's tools or old blades, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, and wearing tight underwear, especially made of synthetic materials.
- Inflammation is quite rare, mainly occurs at the age of 25 - 35 years, very often it can be combined with other inflammatory pathologies of the genital organs. It begins initially, usually acutely.
The woman notes:
- The appearance of severe painful irritation in the area of the vaginal opening.
- She cannot work normally, has difficulty sitting down and sexual intercourse is impossible.
- A formation can be palpated on the labia; the dimensions can vary, from 2-3 cm to 10 cm; the consistency at the initial stage is soft.
- The skin has an increased temperature compared to other areas.
If inflammation is not cured at this stage, then it later becomes chronic or develops complications such as cysts or abscesses.
When the disease turns into an abscess, the tumor has a dense consistency, the size is large in most cases, the shape is round or oval, and in some cases fluctuation appears. The general condition is disturbed, the temperature rises, signs of intoxication appear, sometimes it develops into fever. Inflammation of the Bartholin gland requires mandatory treatment.

This is inflammation of the cervix. It is an intermediate area between the internal and external genitalia. In this case, the mucous membrane is involved in the pathological process. Since the cervix is divided into two main sections - the exocervix and the endocervix.
The outer parts are predominantly stratified by squamous epithelium, while the inside is lined with cylindrical epithelium. It is the inflammation of the cylindrical epithelium that is most dangerous, since it increases the risk of its transfer to the uterus.
Cervicitis can be caused by various factors, including bacteria, viruses or fungi. The presence of provoking factors contributing to the development of inflammation is of great importance.
For cervicitis it is:

In most cases, cervical inflammation is asymptomatic. Therefore, it is often detected only when a woman is examined by a specialist.
Only in some cases is the presence of discharge from the genital tract. During a vaginal examination, redness of the mucous membrane, the presence of an enhanced vascular pattern, as well as focal defects of the mucous membrane are revealed. A predominantly pathological discharge appears from the external pharynx, ranging from creamy to purulent.
 This is a pathological process that occurs on the outer part of the cervix. It is characterized by the presence of a defect in the mucous membrane.
This is a pathological process that occurs on the outer part of the cervix. It is characterized by the presence of a defect in the mucous membrane.
This process can occur in women at any age, but the frequency increases in sexually active women.
The average age of this group is 18 - 35 years. This is due to frequent changes of sexual partners.
This pathology is especially dangerous when a human papillomavirus infection is combined with a defect in the mucous membrane.
Types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous; they can contribute to the development of cancer. In most cases, it is combined with inflammation in the cervix and vagina, and may become a consequence of this process.
It is usually asymptomatic. A woman will not feel pain due to the fact that the cervix is devoid of pain receptors, which means inflammation will only manifest itself morphologically. It can only be manifested by the appearance of bloody or brown discharge, especially after sexual intercourse.
It is detected mainly when examined in the speculum by a gynecologist. You can see defects on the mucous membrane of the exocervix of the cervix; in this case, the cervix will not be uniformly smooth and pink. It appears hyperemia, hemorrhages, defects in the mucous membrane, as well as signs of an old inflammatory process.
Endometritis
This is an inflammatory process that is characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity.
The pathological condition affects functional cells that are rejected during menstruation.
The process can have a different course, it is either acute or chronic.
The acute process has a clear clinical picture:

In case of chronic course of the process symptoms are usually erased. The pain syndrome in this case has a gradual course, the aching pain is slightly pronounced. It intensifies with physical activity, sexual intercourse, etc.
In the autumn-spring period, an aggravation of the process may occur. The temperature during the chronic process usually does not rise, and only in rare cases is it low-grade.
It may also be noted latent, in which the clinical picture can be very blurred, but it is usually the most insidious, since there is a violation in the organ, and complications very often develop, and treatment, as a rule, is not prescribed.
This is a common inflammation of the ovaries in women. It is a very dangerous pathology, since an untreated process leads to the development of complications. The risk group for inflammation of the appendages consists of young women, 20 - 30 years old.
The acute process usually begins to develop quickly:

Inflammation of the ovaries can spread to nearby tissues, which in some cases is complicated by salpingoophoritis, pelivioperitonitis, and diffuse peritonitis.
During the transition of an acute process to a chronic one, the pain syndrome becomes less pronounced. It begins to bother a woman when inflammation worsens or in the autumn-spring period. This course of inflammation can lead to adhesions in the pelvic organs.
The menstrual cycle may be disrupted, it is prone to delays and absence of ovulation. The latent course of inflammation leads to infertility.
This is an inflammatory disease of the reproductive system. It can occur at any stage of the external genitalia. The cause of this inflammation is fungus of the genus Candida .
This is an opportunistic pathogen that is normally found on the skin and mucous membranes and in a normal state of immunity no inflammation occurs.
Characteristics of candidiasis:
- For the development of a pathological process, exposure to provoking factors is necessary. These include severe endocrine and somatic diseases, violations of lifestyle, hygiene and nutrition, as well as sexual transmission.
- Candida inflammation is characterized by the appearance of severe itching and burning, which contributes to irritation of the mucous membranes and skin. At the site of the lesion, swelling appears in varying degrees of severity, which is also accompanied by redness of the mucous membrane.
- For a woman, such a symptom contributes to a violation of the general condition, there is a deterioration in well-being, the quality of sleep changes, and also increases nervousness and tolerance to stress. Urination is manifested by urgency, cramping and, in some cases, severe pain.
- Body temperature, as a rule, remains normal. It usually increases after the addition of a bacterial or viral infection.
- The main manifestation of genital candidiasis is abundant cheesy discharge from the genital tract. Usually their color is white or slightly yellowish. The consistency is thick, with dense inclusions. It is due to this that they are called curdled, and the disease is called thrush.

Infectious inflammations
- this is an inflammatory lesion belonging to the class of specific. It is caused by a specific microorganism belonging to the gram-negative group.
Characteristics of the disease:
- This pathogen is specific and primarily affects the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract. The result is an inflammatory process that can affect all parts of the reproductive system.
- The pathogen is sensitive, so it quickly dies in the environment.
Inflammation is caused to a greater extent among females.
Symptoms:

Chlamydia
This is one of the specific inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract. Currently, this pathology is very common. This is due to the fact that the causative agent is chlamydia - an intracellular microorganism that is tropic to the organs of the genitourinary system.
It is resistant to environmental factors, easily transmitted by contact, and is also slightly susceptible to drugs. That is why this inflammatory disease leads to the development of complications in many women. Among them, the most common is the adhesive process.
Chlamydia is most often detected in women aged 25 - 40 years. Moreover, these characteristics are associated with the fact that women are at risk for inflammatory diseases due to high sexual activity, planning pregnancy, and frequent visits to specialists for possible diagnostic testing.
Symptoms:
- Very often, chlamydia does not manifest itself at all or the symptoms are mild. In most cases, this inflammation is detected only during a random examination for periodic pelvic pain or infertility.
- Sometimes a woman is bothered by itching and discharge from the genital tract. A discharge of a pathological nature appears, it becomes liquid, almost transparent, sometimes accompanied by itching. Separation usually occurs in the morning, 20 - 30 minutes after waking up.
- With prolonged course, pain syndrome is detected, which has a mild course, intensifies with physical activity or sexual intercourse. Subsequently leads to complications such as ectopic pregnancy or infertility associated with chronic inflammation in the uterine cavity.
 This is a viral infection of the reproductive system. The disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus.
This is a viral infection of the reproductive system. The disease is caused by the herpes simplex virus.
There are several varieties of it, each of which causes damage to one or another part of the body.
In this case, there is a predominant damage to the organs of the reproductive system, in particular the external parts.
It occurs in both men and women, but the fair sex is more susceptible to this pathology.
The age groups that have inflammation of the genital organs caused by herpes are also different, but most are 20 - 40 years old. This corridor is due to the fact that it is during this period that a person can have the largest number of partners and sexual life is very diverse.
Symptoms:
- The disease is characterized by the involvement of the mucous membranes of the genital organs, as well as the skin, in the pathological process.
- In this case, the appearance of bubbles is noted, which are filled with liquid contents and have a slightly yellowish color. The sizes of these formations vary, from several millimeters to centimeters, this is due to the fact that they can merge. In this case, severe pain, constant itching, and, if the integrity is violated, a burning sensation is manifested.
- Subsequently, elements deprived of a protective film are covered with crusts and a bacterial process can join them. The general condition changes, body temperature may rise and intoxication may increase.
Consequences of inflammatory diseases
- One of the most common complications is the transition of inflammation to a chronic course.
- In addition, relapses of the process may develop.
- With inflammation of the cervix, a chronic process can develop with the further formation of a malignant process.
- The upper genital organs are prone to the development of infertility in women of reproductive age, as well as miscarriage and spontaneous miscarriages.
- In women, against the background of inflammatory processes, the menstrual cycle may be disrupted and menstruation becomes more painful and prolonged.
- With massive inflammation, a purulent focus may occur, which requires surgical treatment.
- When inflammation spreads to neighboring organs, there is a risk of life threatening.
Treatment
Vulvitis
- In girls, as well as in case of nonspecific lesions, you can use the appointment of washings. These include good solutions with an anti-inflammatory effect, such as Furacilin, Chlorhexidine and or calendula.
- In case of severe inflammation, antibacterial or antiviral, as well as antifungal agents in the form of creams and gels can be used.
This type of inflammation usually requires complex treatment.
- In the development of the process, it is necessary to exclude viral infection of the cervix. Tablets and local forms of medications are used.
- When the cause of inflammation is precisely clarified, remedies are selected taking into account sensitivity, and in the case of a nonspecific process, this inflammation is usually eliminated with properly selected treatment without problems.
- The woman does not require hospitalization in a hospital, or interruption of the work process.
Endometritis and adnexitis
These inflammations require mandatory and timely treatment due to the high risk of complications.
The mode will be selected based on the stage of the process:
- In severe conditions, hospitalization in a hospital is required. Antibacterial or antiviral treatment is considered etiopathogenetic therapy. The route of administration is selected exclusively parenteral; only after completion of treatment can you choose medications in tablet form.
- In addition, detoxification therapy must be carried out. For this purpose, blood replacement and isotonic solutions are used in combination with vitamins.
- After the main course, anti-relapse courses are required aimed at preventing the development of complications or recurrent inflammation.
- When a mass formation forms or inflammation spreads to other organs with the development of a purulent process, surgical intervention is required with possible washing, removal of formations and drainage with the introduction of antibacterial agents.
Tactics in this case will depend on the stage of the inflammatory process:
- At the initial stages, this may include the prescription of anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics, as well as local antiseptics.
- With the development of a purulent process and the development of a limited formation or transition to an abscess, surgical intervention is necessary, followed by drainage of the inflamed cavity.
- Prescribing thermal or physiotherapy procedures before opening the cavity is strictly contraindicated, as this can lead to generalization of the process.
Inflammation of the genital organs requires etiotropic therapy, these are antifungal agents. The form of drugs is selected based on the level of damage:
- For vulvitis these can be creams or solutions that have antifungal activity. These include a solution of baking soda, which is applied to the skin and relieves inflammation.
- For inflammation of the vaginal cavity You can use not only the form of cream and ointment, but the most effective and common are vaginal suppositories or tablets. These can be drugs with only an antifungal mechanism or a complex effect (inexpensive or). In addition, systemic tablet forms are prescribed in combination with local therapy.
Very often, candidiasis tends to recur. In this case, even in the absence of signs of inflammation, systematic prescription of drugs is required.
Other diseases
- Treatment of inflammation caused by is required after exact confirmation of the cause. To do this, it is necessary to select funds after determining sensitivity. After treatment, additional monitoring of treatment is necessary.
- This is a special group of diseases of the female genital organs. When combined with a viral infection, mandatory treatment of inflammation with the prescription of antiviral drugs is required. Surgical treatment of the inflammatory process is very popular. Among them is diathermocoagulation or cryodestruction.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is traditional therapy that is widely used to cure diseases of the genital organs:

Prevention
This is a fairly broad concept that concerns gynecological pathology.
To prevent inflammation, several rules should be followed: